Page 1
TL/F/11109
DP8420V/21V/22V-33, DP84T22-25 microCMOS Programmable
256k/1M/4M Dynamic RAM Controller/Drivers
May 1992
DP8420V/21V/22V-33, DP84T22-25 microCMOS
Programmable 256k/1M/4M Dynamic RAM
Controller/Drivers
General Description
The DP8420V/21V/22V-33, DP84T22-25 dynamic RAM
controllers provide a low cost, single chip interface between
dynamic RAM and all 8-, 16- and 32-bit systems. The
DP8420V/21V/22V-33, DP84T22-25 generate all the required access control signal timing for DRAMs. An on-chip
refresh request clock is used to automatically refresh the
DRAM array. Refreshes and accesses are arbitrated on
chip. If necessary, a WAIT
or DTACK output inserts wait
states into system access cycles, including burst mode accesses. RAS
low time during refreshes and RAS precharge
time after refreshes and back to back accesses are guaranteed through the insertion of wait states. Separate on-chip
precharge counters for each RAS
output can be used for
memory interleaving to avoid delayed back to back accesses because of precharge. An additional feature of the
DP8422V, DP84T22 is two access ports to simplify dual accessing. Arbitration among these ports and refresh is done
on chip. To make board level circuit testing easier the
DP84T22 incorporates TRI-STATE
É
output buffers.
Features
Y
On chip high precision delay line to guarantee critical
DRAM access timing parameters
Y
microCMOS process for low power
Y
High capacitance drivers for RAS, CAS,WEand DRAM
address on chip
Y
On chip support for nibble, page and static column
DRAMs
Y
TRI-STATE outputs (DP84T22 only)
Y
Byte enable signals on chip allow byte writing in a word
size up to 32 bits with no external logic
Y
Selection of controller speeds: 25 MHz and 33 MHz
Y
On board Port A/Port B (DP8422V, DP84T22 only)/refresh arbitration logic
Y
Direct interface to all major microprocessors (application notes available)
Y
4 RAS and 4 CAS drivers (the RAS and CAS configuration is programmable)
Ý
of Pins
Ý
of Address
Largest Direct Drive Access
Control
(PLCC) Outputs
DRAM Memory Ports
Possible Capacity Available
DP8420V 68 9 256 kbit 4 Mbytes Single Access Port
DP8421V 68 10 1 Mbit 16 Mbytes Single Access Port
DP8422V 84 11 4 Mbit 64 Mbytes Dual Access Ports (A and B)
DP84T22 84 11 4 Mbit 64 Mbytes Dual Access and TRI-STATE
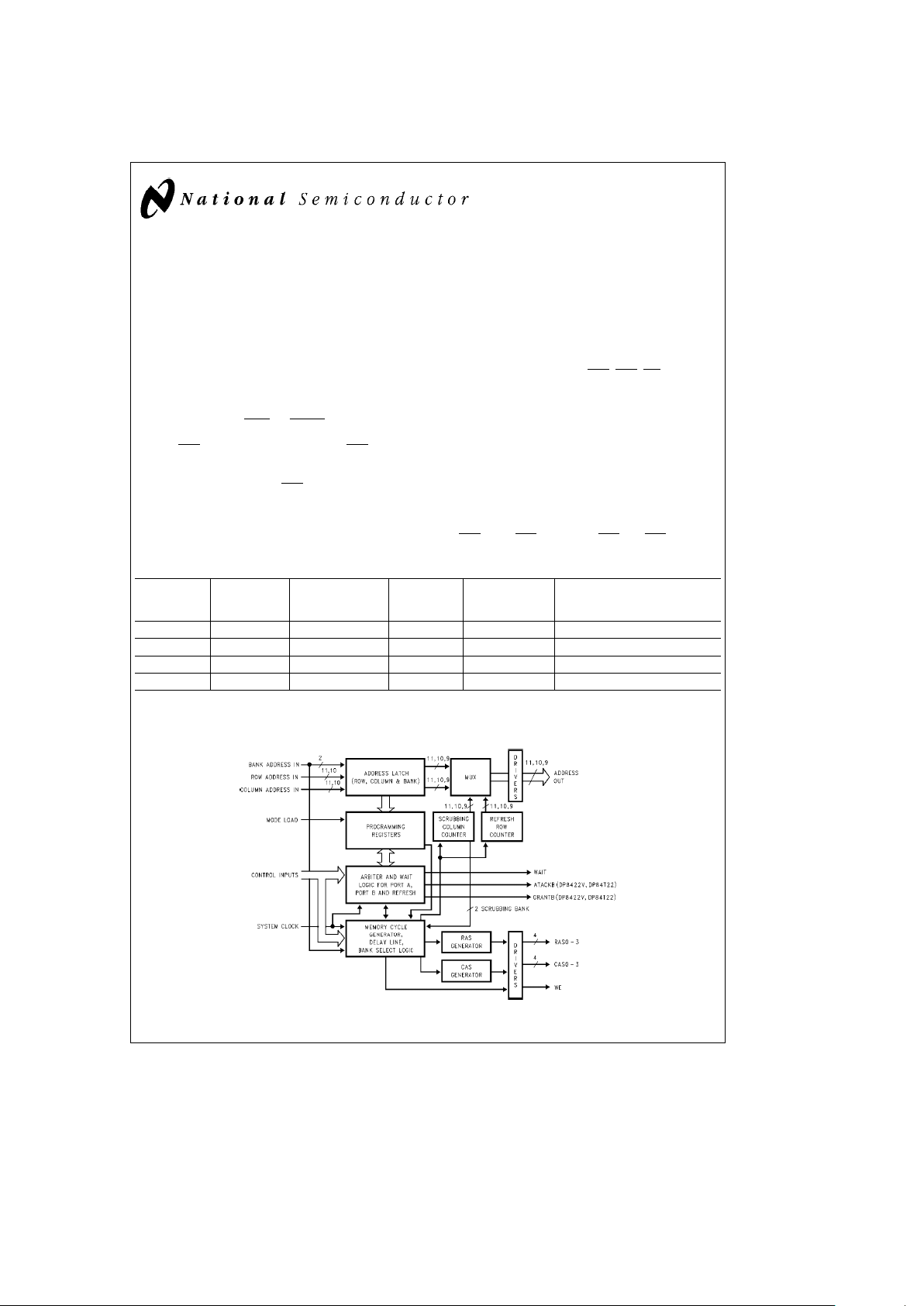
Block Diagram
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP74T22 DRAM Controller
TL/F/11109– 1
FIGURE 1
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
Staggered Refresh
TM
is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M105/Printed in U. S. A.
Page 2

Table of Contents
1.0 INTRODUCTION
2.0 SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
2.1 Address, R/W and Programming Signals
2.2 DRAM Control Signals
2.3 Refresh Signals
2.4 Port A Access Signals
2.5 Port B Access Signals (DP8422V, DP84T22)
2.6 Common Dual Port Signals (DP8422V, DP84T22)
2.7 Power Signals and Capacitor Input
2.8 Clock Inputs
3.0 PROGRAMMING AND RESETTING
3.1 External Reset
3.2 Programming Methods
3.2.1 Mode Load Only Programming
3.2.2 Chip Selected Access Programming
3.3 Internal Programming Modes
4.0 PORT A ACCESS MODES
4.1 Access Mode 0
4.2 Access Mode 1
4.3 Extending CAS with Either Access Mode
4.4 Read-Modify-Write Cycles with Either Access Mode
4.5 Additional Access Support Features
4.5.1 Address Latches and Column Increment
4.5.2 Address Pipelining
4.5.3 Delay CAS
during Write Accesses
5.0 REFRESH OPTIONS
5.1 Refresh Control Modes
5.1.1 Automatic Internal Refresh
5.1.2 Externally Controlled/Burst Refresh
5.1.3 Refresh Request/Acknowledge
5.2 Refresh Cycle Types
5.2.1 Conventional Refresh
5.2.2 Staggered Refresh
TM
5.2.3 Error Scrubbing Refresh
5.3 Extending Refresh
5.4 Clearing the Refresh Address Counter
5.5 Clearing the Refresh Request Clock
6.0 PORT A WAIT STATE SUPPORT
6.1 WAIT
Type Output
6.2 DTACK
Type Output
6.3 Dynamically Increasing the Number of Wait States
6.4 Guaranteeing RAS
Low Time and RAS Precharge
Time
7.0 RAS
AND CAS CONFIGURATION MODES
7.1 Byte Writing
7.2 Memory Interleaving
7.3 Address Pipelining
7.4 Error Scrubbing
7.5 Page/Burst Mode
8.0 TEST MODE
9.0 DRAM CRITICAL TIMING PARAMETERS
9.1 Programmable Values of t
RAH
and t
ASC
9.2 Calculation of t
RAH
and t
ASC
10.0 DUAL ACCESSING (DP8422V and DP84T22V)
10.1 Port B Access Mode
10.2 Port B Wait State Support
10.3 Common Port A and Port B Dual Port Functions
10.3.1 GRANTB Output
10.3.2 LOCK
Input
10.4 TRI-STATE Outputs (DP84T22 Only)
11.0 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
12.0 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
13.0 AC TIMING PARAMETERS
14.0 FUNCTIONAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 AND THE
DP8420/21/22
15.0 DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 USER HINTS
2
Page 3

1.0 Introduction
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 are CMOS Dynamic
RAM controllers that incorporate many advanced features
which include address latches, refresh counter, refresh
clock, row, column and refresh address multiplexer, delay
line, refresh/access arbitration logic and high capacitive
drivers. The programmable system interface allows any
manufacturer’s microprocessor or bus to directly interface
via the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 to DRAM arrays up to
64 Mbytes in size.
After power up, the user must first reset and program the
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 before accessing the DRAM.
The chip is programmed through the address bus.
Reset:
Due to the differences in power supplies, an External (hardware) Reset must be performed before programming the
chip.
Programming:
After resetting the chip, the user can program the controller
by either one of two methods: Mode Load Only Programming or Chip Select Access Programming.
Initialization Period:
Once the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 has been programmed for the first time, a 60 ms initialization period is
entered. During this time the DRC performs refreshes to the
DRAM array so further warm up cycles are unnecessary.
The initialization period is entered only after the first programming after a reset.
Accessing Modes:
After resetting and programming the chip, the
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 is ready to access the
DRAM. There are two modes of accessing with these controllers. Mode 0, which indicates RAS
synchronously and
Mode 1, which indicates RAS
asynchronously.
Refresh Modes:
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have expanded refresh
capabilities compared to previous DRAM controllers. There
are three modes of refreshing available: Internal Automatic
Refreshing, Externally Controlled/Burst Refreshing and Refresh Request/Acknowledge Refreshing. Any of these
modes can be used together or separately to achieve the
desired results.
Refresh Types:
These controllers have three types of refreshing available:
Conventional, Staggered and Error Scrubbing. Any refresh
control mode can be used with any type of refresh.
Wait Support:
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have wait support available as DTACK
or WAIT. Both are programmable. DTACK,
Data Transfer ACKnowledge, is useful for processors
whose wait signal is active high. WAIT
is useful for those
processors whose wait signal is active low. The user can
choose either at programming. These signals are used by
the on chip arbiter to insert wait states to guarantee the
arbitration between accesses, refreshes and precharge.
Both signals are independent of the access mode chosen
and both signals can be dynamically delayed further through
the WAITIN
signal to the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22.
Sequential Accesses (Static Column/Page Mode):
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have address latches,
used to latch the bank, row and column address inputs.
Once the address is latched, a COLumn INCrement (COLINC) feature can be used to increment the column address.
The address latches can also be programmed to be fall
through. COLINC can be used for Sequential Accesses of
Static Column DRAMs. Also, COLINC in conjunction with
ECAS
inputs can be used for Sequential Accesses to Page
Mode DRAMs.
RAS
and CAS Configuration (Byte Writing):
The RAS and CAS drivers can be configured to drive a one,
two or four bank memory array up to 32 bits in width. The
ECAS
signals can then be used to select one of four CAS
drivers for Byte Writing with no extra logic.
Memory Interleaving:
When configuring the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 for
more than one bank, Memory Interleaving can be used. By
tying the low order address bits to the bank select lines B0
and B1, sequential back to back accesses will not be delayed since these controllers have separate precharge
counters per bank.
Address Pipelining:
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 are capable of performing Address Pipelining. In address pipelining, the DRC will
guarantee the column address hold time and switch the internal multiplexor to place the row address on the address
bus. At this time, another memory access to another bank
can be initiated.
Dual Accessing:
The DP8422V, DP84T22 have all the features previously
mentioned and unlike the DP8420V/21V, the DP8422V,
DP84T22 have a second port to allow a second CPU to
access the same memory array. The DP8422V, DP84T22
have four signals to support Dual Accessing, these signals
are AREQB
, ATACKB, LOCK and GRANTB. All arbitration
for the two ports and refresh is done on chip by the controller through the insertion of wait states. Since the DP8422V,
DP84T22 have only one input address bus, the address
lines must be multiplexed externally. The signal GRANTB
can be used for this purpose.
TRI-STATE Outputs:
The DP84T22 implements TRI-STATE outputs. When the
input OE
is asserted the output buffers are enabled, when
OE
is negated, logic 1, the output buffers at TRI-STATE
(high Z).
Terminology:
The following explains the terminology used in this data
sheet. The terms negated and asserted are used. Asserted
refers to a ‘‘true’’ signal. Thus, ‘‘ECAS0
asserted’’ means
the ECAS0
input is at a logic 0. The term ‘‘COLINC asserted’’ means the COLINC input is at a logic 1. The term negated refers to a ‘‘false’’ signal. Thus, ‘‘ECAS0
negated’’
means the ECAS0
input is at a logic 1. The term ‘‘COLINC
negated’’ means the input COLINC is at a logic 0. The table
shown below clarifies this terminology.
Signal Action Logic Level
Active High Asserted High
Active High Negated Low
Active Low Asserted Low
Active Low Negated High
3
Page 4
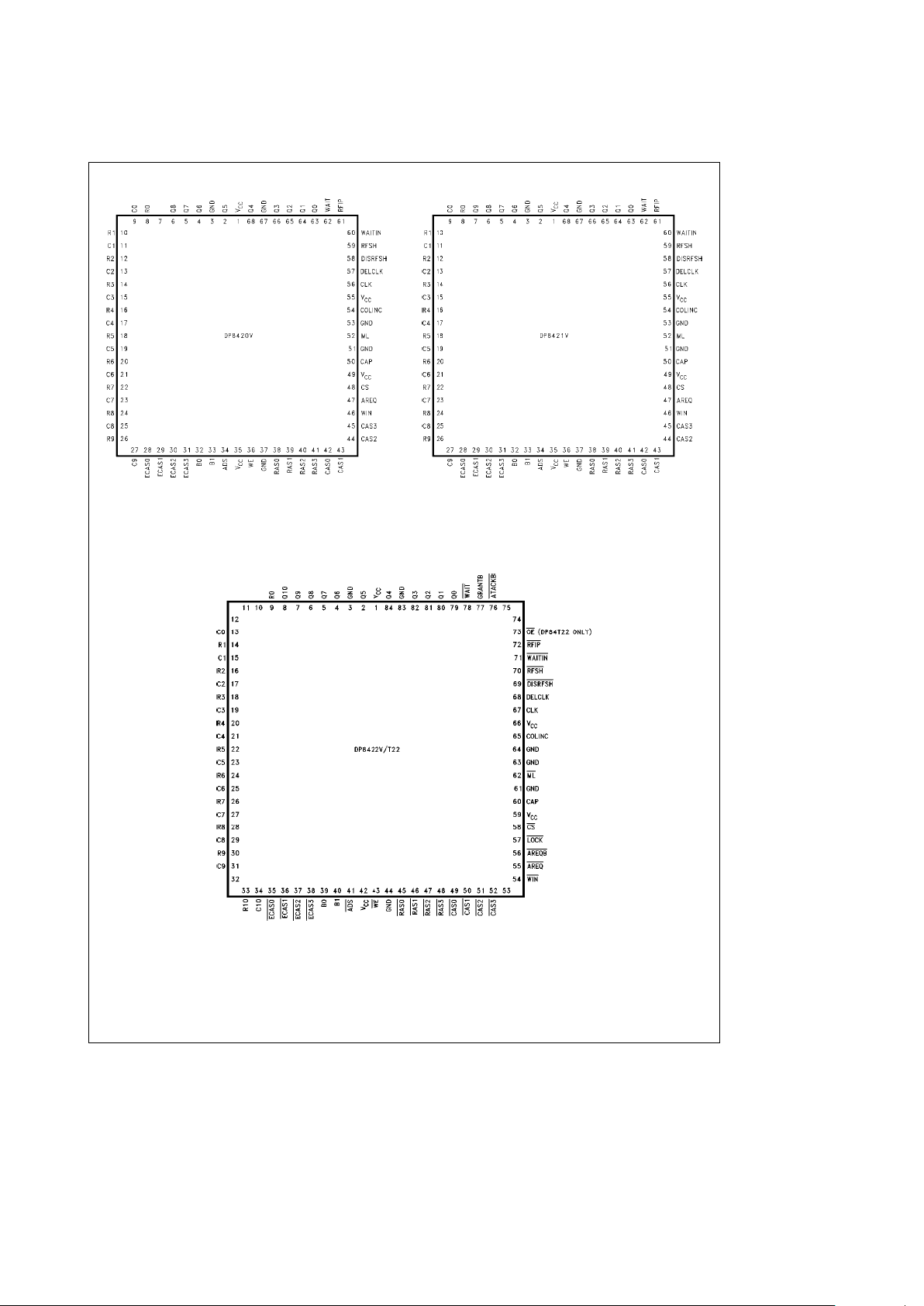
Connection Diagrams
TL/F/11109– 2
Top View
FIGURE 2
Order Number DP8420V-33
See NS Package Number V68A
TL/F/11109– 3
Top View
FIGURE 3
Order Number DP8421V-33
See NS Package Number V68A
TL/F/11109– 4
Top View
FIGURE 4
Order Number DP8422V-33 or DP84T22-25
See NS Package Number V84A
4
Page 5
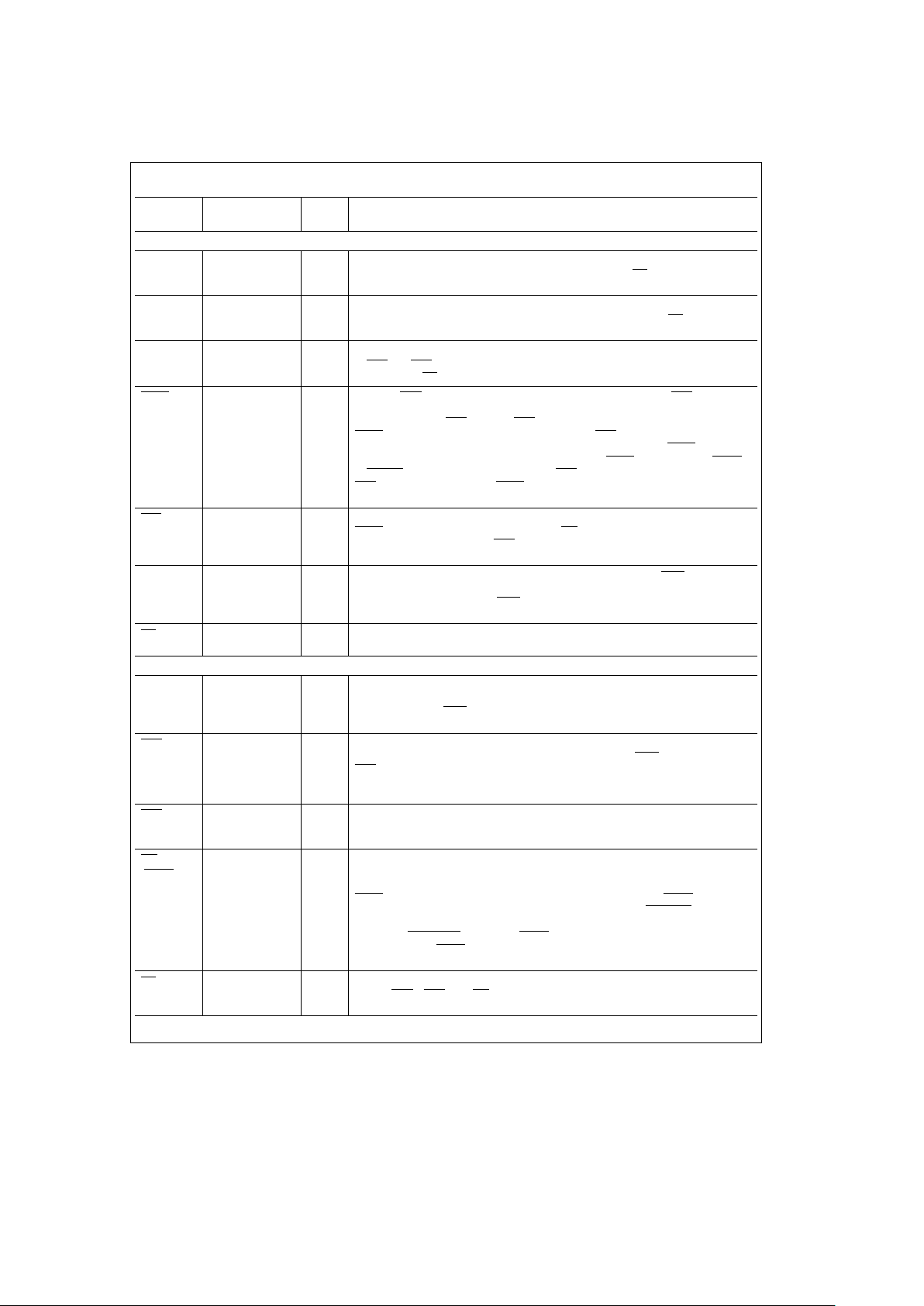
2.0 Signal Descriptions
Pin Device (If Not Input/
Description
Name Applicable to All) Output
2.1 ADDRESS, R/W AND PROGRAMMING SIGNALS
R0–10 DP8422V/T22 I ROW ADDRESS: These inputs are used to specify the row address during an access
to the DRAM. They are also used to program the chip when ML
is asserted (except
R0–9 DP8420V/21V I
R10).
C0–10 DP8422V/T22 I COLUMN ADDRESS: These inputs are used to specify the column address during an
access to the DRAM. They are also used to program the chip when ML
is asserted
C0–9 DP8420V/21V I
(except C10).
B0, B1 I BANK SELECT: Depending on programming, these inputs are used to select a group
of RAS and CAS outputs to assert during an access. They are also used to program
the chip when ML
is asserted.
ECAS0–3 I ENABLE CAS: These inputs are used to enable a single or group of CAS outputs
when asserted. In combination with the B0, B1 and the programming bits, these
inputs select which CAS
output or CAS outputs will assert during an access. The
ECAS
signals can also be used to toggle a group of CAS outputs for page/nibble
mode accesses. They also can be used for byte write operations. If ECAS
0is
negated during programming, continuing to assert the ECAS
0 while negating AREQ
or AREQB during an access, will cause the CAS outputs to be extended while the
RAS
outputs are negated (the ECASn inputs have no effect during scrubbing
refreshes).
WIN I WRITE ENABLE IN: This input is used to signify a write operation to the DRAM. If
ECAS
0 is asserted during programming, the WE output will follow this input. This
input asserted will also cause CAS
to delay to the next positive clock edge if address
bit C9 is asserted during programming.
COLINC I COLUMN INCREMENT: When the address latches are used, and RFIP is negated,
this input functions as COLINC. Asserting this signal causes the column address to
(EXTNDRF) I
be incremented by one. When RFIP
is asserted, this signal is used to extend the
refresh cycle by any number of periods of CLK until it is negated.
ML I MODE LOAD: This input signal, when low, enables the internal programming register
that stores the programming information.
2.2 DRAM CONTROL SIGNALS
Q0–10 DP8422V/T22 O DRAM ADDRESS: These outputs are the multiplexed output of the R0 – 9, 10 and
C0–9, 10 and form the DRAM address bus. These outputs contain the refresh
Q0–9 DP8421V O
address whenever RFIP
is asserted. They contain high capacitive drivers with 20X
Q0–8 DP8421V O
series damping resistors.
RAS0–3 O ROW ADDRESS STROBES: These outputs are asserted to latch the row address
contained on the outputs Q0–8, 9, 10 into the DRAM. When RFIP
is asserted, the
RAS
outputs are used to latch the refresh row address contained on the Q0–8, 9, 10
outputs in the DRAM. These outputs contain high capacitive drivers with 20X series
damping resistors.
CAS0–3 O COLUMN ADDRESS STROBES: These outputs are asserted to latch the column
address contained on the outputs Q0–8, 9, 10 into the DRAM. These outputs have
high capacitive drivers with 20X series damping resistors.
WE O WRITE ENABLE or REFRESH REQUEST: This output asserted specifies a write
operation to the DRAM. When negated, this output specifies a read operation to the
(RFRQ
)O
DRAM. When the controller is programmed in address pipelining mode or when
ECAS0 is negated during programming, this output will function as RFRQ. When
asserted, this pin specifies that 13 msor15ms have passed. If DISRFSH
is negated,
the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will perform an internal refresh as soon as
possible. If DISRFRSH
is asserted, RFRQ can be used to externally request a refresh
through the input RFSH
. This output has a high capacitive driver and a 20X series
damping resistor.
OE DP84T22 I OUTPUT ENABLE: This input asserted, enables the output buffers for the row,
column RASs, CASs and WE. If this input is disabled, logic 1, the output buffers are at
(Only)
TRI-STATE facilitating the board level circuit testing.
5
Page 6
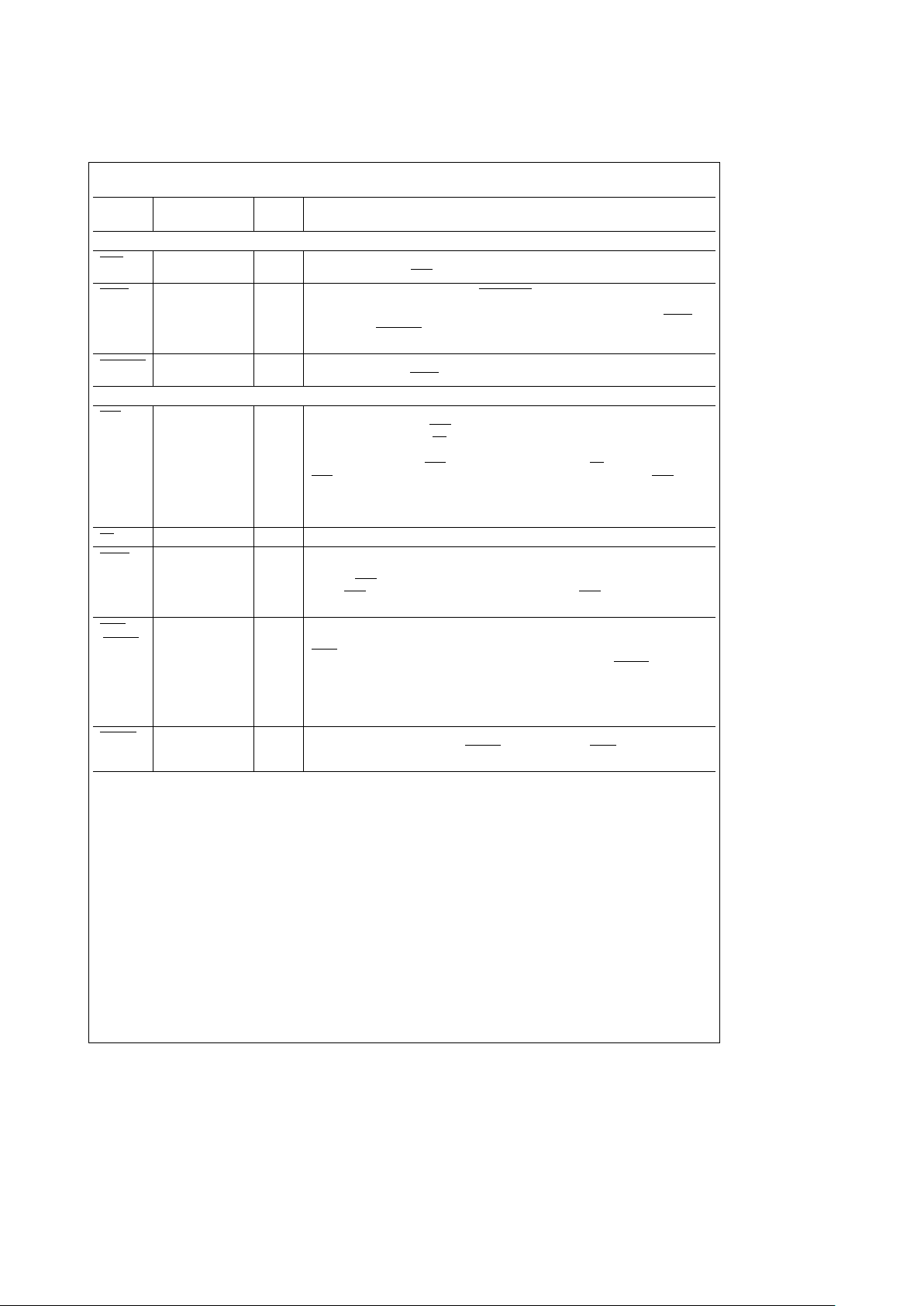
2.0 Signal Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Device (If Not Input/
Description
Name Applicable to All) Output
2.3 REFRESH SIGNALS
RFIP O REFRESH IN PROGRESS: This output is asserted prior to a refresh cycle and is
negated when all the RAS
outputs are negated for that refresh.
RFSH I REFRESH: This input asserted with DISRFRSH already asserted will request a
refresh. If this input is continually asserted, the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will
perform refresh cycles in a burst refresh fashion until the input is negated. If RFSH
is
asserted with DISRFSH
negated, the internal refresh address counter is cleared
(useful for burst refreshes).
DISRFSH I DISABLE REFRESH: This input is used to disable internal refreshes and must be
asserted when using RFSH
for externally requested refreshes.
2.4 PORT A ACCESS SIGNALS
ADS I ADDRESS STROBE or ADDRESS LATCH ENABLE: Depending on programming,
this input can function as ADS
or ALE. In mode 0, the input functions as ALE and
(ALE) I
when asserted along with CS
causes an internal latch to be set. Once this latch is set
an access will start from the positive clock edge of CLK as soon as possible. In Mode
1, the input functions as ADS
and when asserted along with CS, causes the access
RAS
to assert if no other event is taking place. If an event is taking place, RAS will be
asserted from the positive edge of CLK as soon as possible. In both cases, the low
going edge of this signal latches the bank, row and column address if programmed to
do so.
CS I CHIP SELECT: This input signal must be asserted to enable a Port A access.
AREQ I ACCESS REQUEST: This input signal in Mode 0 must be asserted some time after
the first positive clock edge after ALE has been asserted. When this signal is
negated, RAS
is negated for the access. In Mode 1, this signal must be asserted
before ADS
can be negated. When this signal is negated, RAS is negated for the
access.
WAIT O WAIT or DTACK: This output can be programmed to insert wait states into a CPU
access cycle. With R7 negated during programming, the output will function as a
(DTACK
)O
WAIT
type output. In this case, the output will be active low to signal a wait condition.
With R7 asserted during programming, the output will function as DTACK
. In this
case, the output will be negated to signify a wait condition and will be asserted to
signify the access has taken place. Each of these signals can be delayed by a
number of positive clock edges or negative clock levels of CLK to increase the
microprocessor’s access cycle through the insertion of wait states.
WAITIN I WAIT INCREASE: This input can be used to dynamically increase the number of
positive clock edges of CLK until DTACK
will be asserted or WAIT will be negated
during a DRAM access.
6
Page 7
2.0 Signal Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Device (If Not Input/
Description
Name Applicable to All) Output
2.5 PORT B ACCESS SIGNALS
AREQB DP8422V/T22 I PORT B ACCESS REQUEST: This input asserted will latch the row, column and bank
address if programmed, and requests an access to take place for Port B. If the
only
access can take place, RAS
will assert immediately. If the access has to be delayed,
RAS
will assert as soon as possible from a positive edge of CLK.
ATACKB DP8422V/T22 O ADVANCED TRANSFER ACKNOWLEDGE PORT B: This output is asserted when
the access RAS
is asserted for a Port B access. This signal can be used to generate
only
the appropriate DTACK
or WAIT type signal for Port B’s CPU or bus.
2.6 COMMON DUAL PORT SIGNALS
GRANTB DP8422V/T22 O GRANT B: This output indicates which port is currently granted access to the DRAM
array. When GRANTB is asserted, Port B has access to the array. When GRANTB is
only
negated, Port A has access to the DRAM array. This signal is used to multiplex the
signals R0–8, 9, 10; C0 –8, 9, 10; B0 – 1; WIN
; LOCK and ECAS0 – 3 to the DP8422V
when using dual accessing.
LOCK DP8422V/T22 I LOCK: This input can be used by the currently granted port to ‘‘lock out’’ the other
port from the DRAM array by inserting wait states into the locked out port’s access
only
cycle until LOCK is negated.
2.7 POWER SIGNALS AND CAPACITOR INPUT
V
CC
I POWER: Supply Voltage.
GND I GROUND: Supply Voltage Reference.
CAP I CAPACITOR: This input is used by the internal PLL for stabilization. The value of the
ceramic capacitor should be 0.1 mF and should be connected between this input and
ground.
2.8 CLOCK INPUTS
There are two clock inputs to the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 CLK and DELCLK. These two clocks may both be tied to the
same clock input, or they may be two separate clocks, running at different frequencies, asynchronous to each other.
CLK I SYSTEM CLOCK: This input may be in the range of 0 Hz up to 33 MHz (up to 25 MHz
in the DP84T22V). This input is generally a constant frequency but it may be
controlled externally to change frequencies or perhaps be stopped for some arbitrary
period of time.
This input provides the clock to the internal state machine that arbitrates between
accesses and refreshes. This clock’s positive edges and negative levels are used to
extend the WAIT
(DTACK) signals. This clock is also used as the reference for the
RAS
precharge time and RAS low time during refresh.
All Port A and Port B accesses are assumed to be synchronous to the system clock
CLK.
DELCLK I DELAY LINE CLOCK: The clock input DELCLK, may be in the range of 6 MHz to
20 MHz and should be a multiple of 2 (i.e., 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 MHz) to have
the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 switching characteristics hold. If DELCLK is not
one of the above frequencies the accuracy of the internal delay line will suffer. This is
because the phase locked loop that generates the delay line assumes an input clock
frequency of a multiple of 2 MHz.
For example, if the DELCLK input is at 7 MHz and we choose a divide by 3 (program
bits C0–2) this will produce 2.333 MHz which is 16.667% off of 2 MHz. Therefore, the
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 delay line would produce delays that are shorter
(faster delays) than what is intended. If divide by 4 was chosen the delay line would
be longer (slower delays) than intended (1.75 MHz instead of 2 MHz). (See Section 9
for more information.)
This clock is also divided to create the internal refresh clock.
7
Page 8

3.0 Programming and Resetting
Due to the variety in power supplies power-up times, an
EXTERNAL RESET must be performed before the DRAM
controller can be programmed and used.
After going through the reset procedure, the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22 can be programmed by either of two
methods; Mode Load Only Programming or Chip Select Access Programming. After programming the DRC for the first
time after reset, the chip enters a 60 ms initialization period,
during this period the controller performs refreshes every
13 msor15ms, this makes further DRAM warm up cycles
unnecessary. After this stage the chip can be reprogrammed as many times as the user wishes and the 60 ms
period will not be entered into unless the chip is reset and
programmed again.
During the 60 ms initialization period, RFIP
is asserted low
and RAS
toggles every 13 msor15ms depending on the
programming bit for refresh (C3). CAS
will be inactive (logic
1) and the ‘‘Q’’ outputs will count from 0 to 2047 refreshing
the entire DRAM array. The actual initialization time period
is given by the following formula. T
e
4096* (Clock Divisor
Select)* (Refresh Clock Fine Tune)/(DELCLK Frq.)
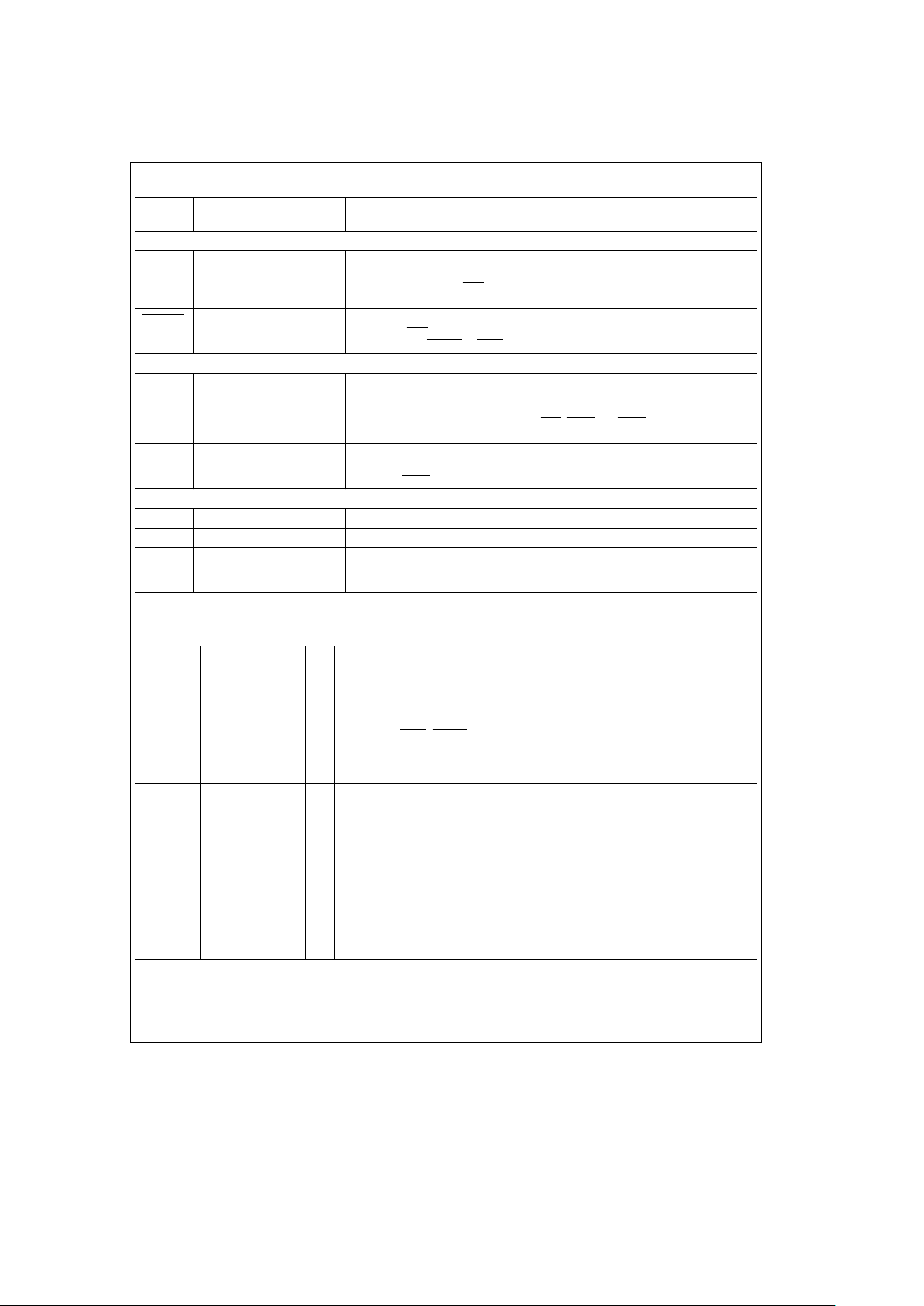
3.1 EXTERNAL RESET
At power up, if the internal power up reset worked, all internal latches and flip-flops are cleared and the part is ready to
be programmed. The power up state can also be achieved
by performing an External Reset, which is required to insure
proper operation. External Reset is achieved by asserting
ML
and DISRFSH for at least 16 positive clock edges. In
order to perform simply a Reset, the ML
signal must be
negated before DISRFSH
is negated as shown in
Figure 5a
.
This procedure will only reset the controller which now is
ready for programming.
While performing an External Reset, if the user negates
DISRFSH
at least one clock period before negating ML,as
shown in
Figure 5b
,MLnegated will program the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22 with the values in R0 –9, C0–9, B0– 1
and ECAS0. The 60 ms initialization period will be entered
since it is the first programming after reset. This is a good
way of resetting and programming the part at the same time.
Make sure the right programming bits are on the address
bus before ML
is negated.
The DRC may be programmed any time on the fly, but the
user must make sure that No Access or Refresh is in progress. Reset is asynchronous.
TL/F/11109– 5
FIGURE 5a. Chip Reset but Not Programmed
TL/F/11109– 6
FIGURE 5b. Chip Reset and Programmed
8
Page 9
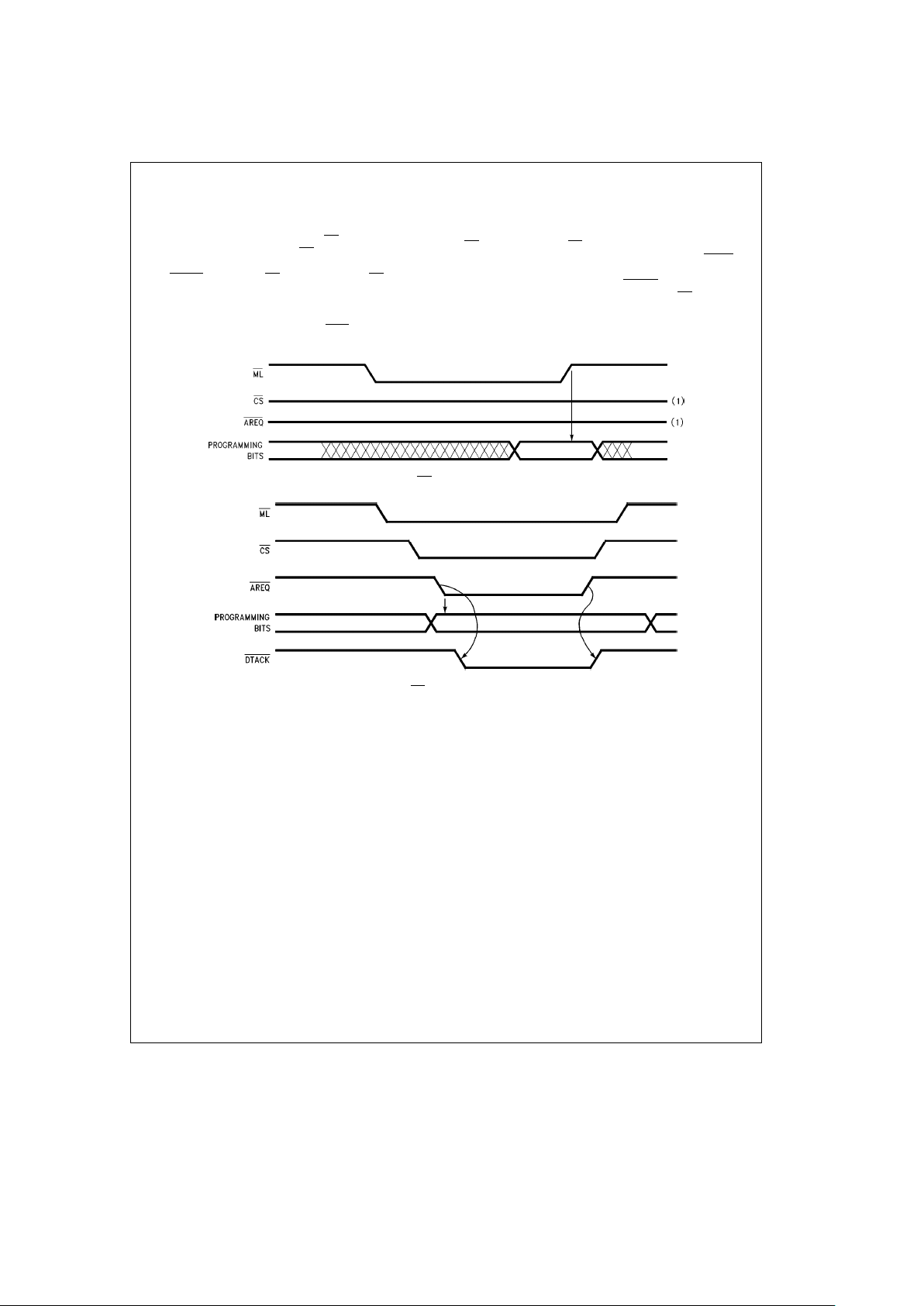
3.0 Programming and Resetting (Continued)
3.2 PROGRAMMING METHODS
3.2.1 Mode Load Only Programming
To use this method the user asserts ML
enabling the inter-
nal programming register. After ML
is asserted, a valid programming selection is placed on the address bus, B0, B1
and ECAS0
inputs, then ML is negated. When ML is negated the programming bits are latched into the internal programming register and the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 is
programmed, see
Figure 6
. When programming the chip,
the controller must not be refreshing, RFIP
must be high (1)
to have a successful programming.
3.2.2 Chip Selected Access Programming
The chip can also be programmed by performing a chip
selected access. To program the chip using this method,
ML
is asserted, then CS is asserted and a valid program-
ming selection is placed on the address bus. When AREQ
is
asserted, the programming bits affecting the wait logic become effective immediately, then DTACK
is asserted allow-
ing the access to terminate. After the access, ML
is negated
and the rest of the programming bits take effect.
TL/F/11109– 7
FIGURE 6. ML Only Programming
TL/F/11109– 8
FIGURE 7. CS Access Programming
9
Page 10

3.0 Programming and Resetting (Continued)
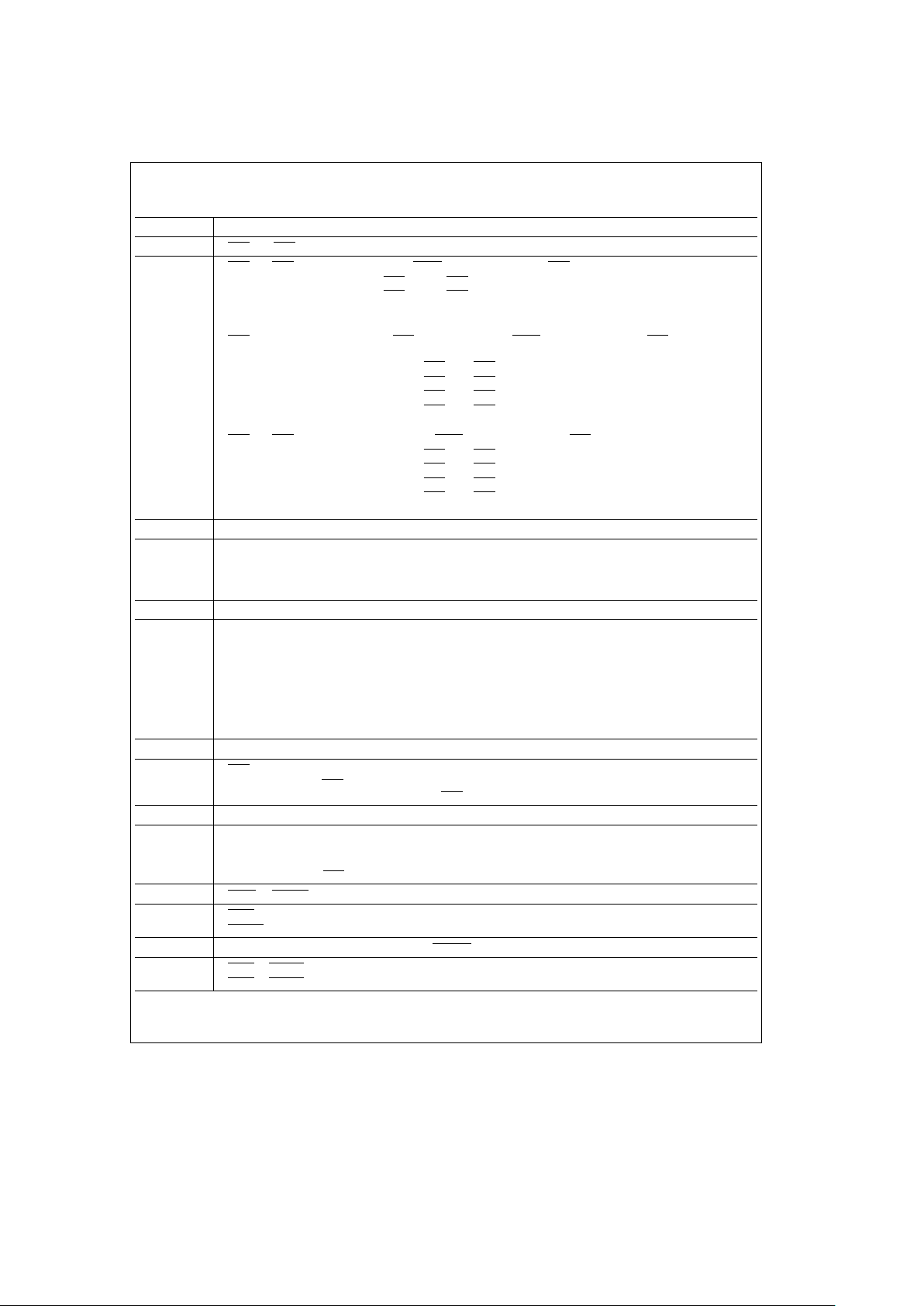
3.3 PROGRAMMING BIT DEFINITIONS
Symbol Description
ECAS0 Extend CAS/Refresh Request Select
0 The CASn outputs will be negated with the RASn outputs when AREQ (or AREQB, DP8422V, DP84T22 only) is
negated. The WE
output pin will function as write enable.
1 The CASn outputs will be negated, during an acccess (Port A (or Port B, DP8422V, DP84T22 only)) when their
corresponding ECAS
n inputs are negated. This feature allows the CAS outputs to be extended beyond the RAS
outputs negating. Scrubbing refreshes are NOT affected. During scrubbing refreshes the CAS outputs will negate
along with the RAS
outputs regardless of the state of the ECAS inputs.
The WE output will function as ReFresh ReQuest (RFRQ) when this mode is programmed.
B1 Access Mode Select
0 ACCESS MODE 0: ALE pulsing high sets an internal latch. On the next positive edge of CLK, the access (RAS)
will start. AREQ
will terminate the access.
1 ACCESS MODE 1: ADS asserted starts the access (RAS) immediately. AREQ will terminate the access.
B0 Address Latch Mode
0 ADS or ALE asserted for Port A or AREQB asserted for Port B with the appropriate GRANT latch the input row,
column and bank address.
1 The row, column and bank latches are fall through.
C9 Delay CAS during WRITE Accesses
0 CAS is treated the same for both READ and WRITE accesses.
1 During WRITE accesses, CAS will be asserted by the event that occurs last: CAS asserted by the internal delay
line or CAS
asserted on the positive edge of CLK after RAS is asserted.
C8 Row Address Hold Time
0 Row Address Hold Timee25 ns minimum
1 Row Address Hold Time
e
15 ns minimum
C7 Column Address Setup Time
0 Column Address Setup Timee10 ns miniumum
1 Column Address Setup Timee0 ns minimum
C6, C5, C4 RAS
and CAS Configuration Modes/Error Scrubbing during Refresh
0, 0, 0 RAS0– 3 and CAS0 –3 are all selected during an access. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B0 and B1 are not used during an access. Error scrubbing during refresh.
0, 0, 1 RAS
and CAS pairs are selected during an access by B1. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1
e
0 during an access selects RAS0– 1 and CAS0–1.
B1e1 during an access selects RAS2– 3 and CAS2–3.
B0 is not used during an Access.
Error scrubbing during refresh.
0, 1, 0 RAS and CAS singles are selected during an access by B0 – 1. ECAS
n must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1
e
0, B0e0 during an access selects RAS0 and CAS0.
B1
e
0, B0e1 during an access selects RAS1 and CAS1.
B1
e
1, B0e0 during an access selects RAS2 and CAS2.
B1e1, B0e1 during an access selects RAS3 and CAS3.
Error scrubbing during refresh.
0, 1, 1 RAS
0–3 and CAS0 –3 are all selected during an access. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1, B0 are not used during an access.
No error scrubbing. (RAS
only refreshing)
1, 0, 0 RAS pairs are selected by B1. CAS0 – 3 are all selected. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1
e
0 during an access selects RAS0– 1 and CAS0–3.
B1e1 during an access selects RAS2– 3 and CAS0–3.
B0 is not used during an access.
No error scrubbing.
10
Page 11
3.0 Programming and Resetting (Continued)
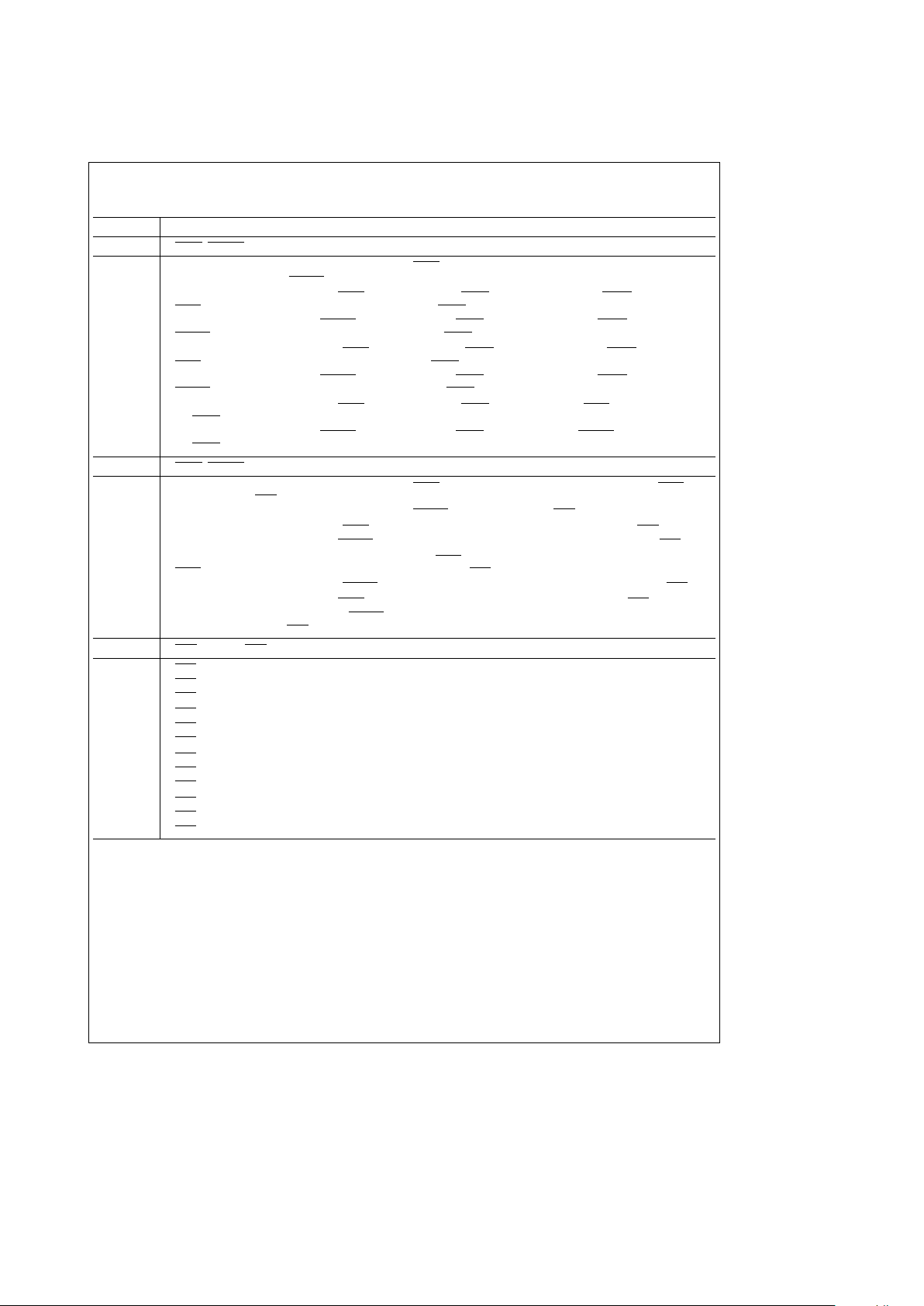
3.3 PROGRAMMING BIT DEFINITIONS (Continued)
Symbol Description
C6, C5, C4 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes (Continued)
1, 0, 1 RAS and CAS pairs are selected by B1. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1
e
0 during an access selects RAS0– 1 and CAS0–1.
B1
e
1 during an access selects RAS2– 3 and CAS2–3.
B0 is not used during an access.
No error scrubbing.
1, 1, 0 RAS singles are selected by B0 – 1. CAS0–3 are all selected. ECASn must be asserted for CASntobe
asserted.
B1
e
0, B0e0 during an access selects RAS0 and CAS0–3.
B1
e
0, B0e1 during an access selects RAS1 and CAS0–3.
B1
e
1, B0e0 during an access selects RAS2 and CAS0–3.
B1
e
1, B0e1 during an access selects RAS3 and CAS0–3.
No error scrubbing.
1, 1, 1 RAS and CAS singles are selected by B0, 1. ECASn must be asserted for CASn to be asserted.
B1
e
0, B0e0 during an access selects RAS0 and CAS0.
B1
e
0, B0e1 during an access selects RAS1 and CAS1.
B1
e
1, B0e0 during an access selects RAS2 and CAS2.
B1
e
1, B0e1 during an access selects RAS3 and CAS3.
No error scrubbing.
C3 Refresh Clock Fine Tune Divisor
0 Divide delay line/refresh clock further by 30 (If DELCLK/Refresh Clock Clock Divisore2 MHze15 ms
refresh period).
1 Divide delay line/refresh clock further by 26 (If DELCLK/Refresh Clock Clock Divisor
e
2 MHze13 ms
refresh period).
C2, C1, C0 Delay Line/Refresh Clock Divisor Select
0, 0, 0 Divide DELCLK by 10 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
0, 0, 1 Divide DELCLK by 9 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
0, 1, 0 Divide DELCLK by 8 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
0, 1, 1 Divide DELCLK by 7 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
1, 0, 0 Divide DELCLK by 6 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
1, 0, 1 Divide DELCLK by 5 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
1, 1, 0 Divide DELCLK by 4 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
1, 1, 1 Divide DELCLK by 3 to get as close to 2 MHz as possible.
R9 Refresh Mode Select
0 RAS0–3 will all assert and negate at the same time during a refresh.
1 Staggered Refresh. RAS
outputs during refresh are separated by one positive clock edge. Depending on the
configuration mode chosen, either one or two RAS
s will be asserted.
R8 Address Pipelining Select
0 Address pipelining is selected. The DRAM controller will switch the DRAM column address back to the row
address after guaranteeing the column address hold time.
1 Non-address pipelining is selected. The DRAM controller will hold the column address on the DRAM address
bus until the access RAS
s are negated.
R7 WAIT or DTACK Select
0 WAIT type output is selected.
1 DTACK
(Data Transfer ACKnowledge) type output is selected.
R6 Add Wait States to the Current Access if WAITIN is Low
0 WAIT or DTACK will be delayed by one additional positive edge of CLK.
1 WAIT
or DTACK will be delayed by two additional positive edges of CLK.
11
Page 12
3.0 Programming and Resetting (Continued)
3.3 PROGRAMMING BIT DEFINITIONS (Continued)
Symbol Description
R5, R4 WAIT/DTACK during Burst (See Section 5.1.2 or 5.2.2)
0, 0 NO WAIT STATES; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will remain negated during burst portion of access.
If R7
e
1 programming, DTACK will remain asserted during burst portion of access.
0, 1 1T; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will assert when the ECAS inputs are negated with AREQ asserted.
WAIT
will negate from the positive edge of CLK after the ECASs have been asserted.
If R7e1 during programming, DTACK will negate when the ECAS inputs are negated with AREQ asserted.
DTACK
will assert from the positive edge of CLK after the ECASs have been asserted.
1, 0 (/2T; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will assert when the ECAS inputs are negated with AREQ asserted.
WAIT
will negate on the negative level of CLK after the ECASs have been asserted.
If R7
e
1 during programming, DTACK will negate when the ECAS inputs are negated with AREQ asserted.
DTACK
will assert from the negative level of CLK after the ECASs have been asserted.
1, 1 0T; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will assert when the ECAS inputs are negated. WAIT will negate when
the ECAS
inputs are asserted.
If R7e1 during programming, DTACK will negate when the ECAS inputs are negated. DTACK will assert when
the ECAS
inputs are asserted.
R3, R2 WAIT/DTACK Delay Times (See Section 5.1.1 or 5.2.1)
0, 0 NO WAIT STATES; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will remain high during non-delayed accesses. WAIT
will negate when RAS is negated during delayed accesses.
NO WAIT STATES; If R7
e
1 during programming, DTACK will be asserted when RAS is asserted.
0, 1 (/2T; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will negate on the negative level of CLK, after the access RAS.
1T; If R7e1 during programming, DTACK will be asserted on the positive edge of CLK after the access RAS.
1, 0 NO WAIT STATES, (/2T; If R7
e
0 during programming, WAIT will remain high during non-delayed accesses.
WAIT
will negate on the negative level of CLK, after the access RAS, during delayed accesses.
(/2T; If R7
e
1 during programming, DTACK will be asserted on the negative level of CLK after the access RAS.
1, 1 1T; If R7e0 during programming, WAIT will negate on the positive edge of CLK after the access RAS.
1(/2T; If R7
e
1 during programming, DTACK will be asserted on the negative level of CLK after the positive edge
of CLK after the access RAS
.
R1, R0 RAS Low and RAS Precharge Time
0, 0 RAS asserted during refreshe2 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
precharge timee1 positive edge of CLK.
RAS
will start from the first positive edge of CLK after GRANTB transitions (DP8422V, DP84T22).
0, 1 RAS
asserted during refreshe3 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
precharge timee2 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
will start from the second positive edge of CLK after GRANTB transitions (DP8422V, DP84T22).
1, 0 RAS asserted during refreshe2 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
precharge timee2 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
will start from the first positive edge of CLK after GRANTB transitions (DP8422V, DP84T22).
1, 1 RAS asserted during refreshe4 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
precharge timee3 positive edges of CLK.
RAS
will start from the second positive edge of CLK after GRANTB transitions (DP8422V, DP84T22).
12
Page 13

4.0 Port A Access Modes
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have two general purpose access modes. Mode 0 RAS
synchronous and Mode 1
RAS
asynchronous. One of these modes is selected at pro-
gramming through the B1 input. A Port A access to DRAM is
initiated by two input signals: ADS
(ALE) and CS. The ac-
cess is always terminated by one signal: AREQ
. These input
signals should be synchronous to the input clock.
4.1 ACCESS MODE 0
Mode 0, synchronous access, is selected by negating the
input B1 during programming (B1
e
0). To initiate a Mode 0
access, ALE is pulse high and CS
is asserted. If precharge
time was met, a refresh of DRAM or a Port B access was
not in progress, the RAS
(RASs) would be asserted on the
first rising edge of clock. If a refresh or a Port B access is in
progress or precharge time is required, the controller will
wait until these events have taken place and assert RAS
(RASs) on the next positive edge of clock.
Sometime after the first positive edge of clock after ALE and
CS
have been asserted, the input AREQ must be asserted.
In single port applications, once AREQ
is asserted, CS can
be negated. On the other hand, ALE can stay asserted several periods of clock; however, ALE must be negated before
or during the period of CLK in which AREQ
is negated.
The controller samples AREQ on the every rising edge of
clock after DTACK
is asserted. The access will end when
AREQ
is sampled negated.
TL/F/11109– 9
FIGURE 8a. Access Mode 0
13
Page 14

4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.2 ACCESS MODE 1
Mode 1, asynchronous access, is selected by asserting the
input B1 during programming (B1
e
1). This mode allows accesses to start immediately from the access request input,
ADS
. To initiate a Mode 1 access, CS is asserted followed
by ADS
asserted. If precharge time was met, a refresh of
the DRAM or a Port B access was not in progress, the RAS
(RASs) would be asserted from ADS being asserted. If a
refresh or Port B access is in progress or precharge time is
required, the controller will wait until these events have tak-
en place and assert RAS
(RASs) from the next rising edge
of clock.
When ADS
is asserted or sometime after, AREQ must be
asserted. At this time, ADS
can be negated and AREQ will
continue the access. Also, ADS
can continue to be asserted
after AREQ
has been asserted and negated; however, a
new access will not start until ADS
is negated and asserted
again. When address pipelining is not implemented, ADS
and AREQ can be tied together.
The access will end when AREQ is negated.
TL/F/11109– 10
FIGURE 8b. Access Mode 1
14
Page 15
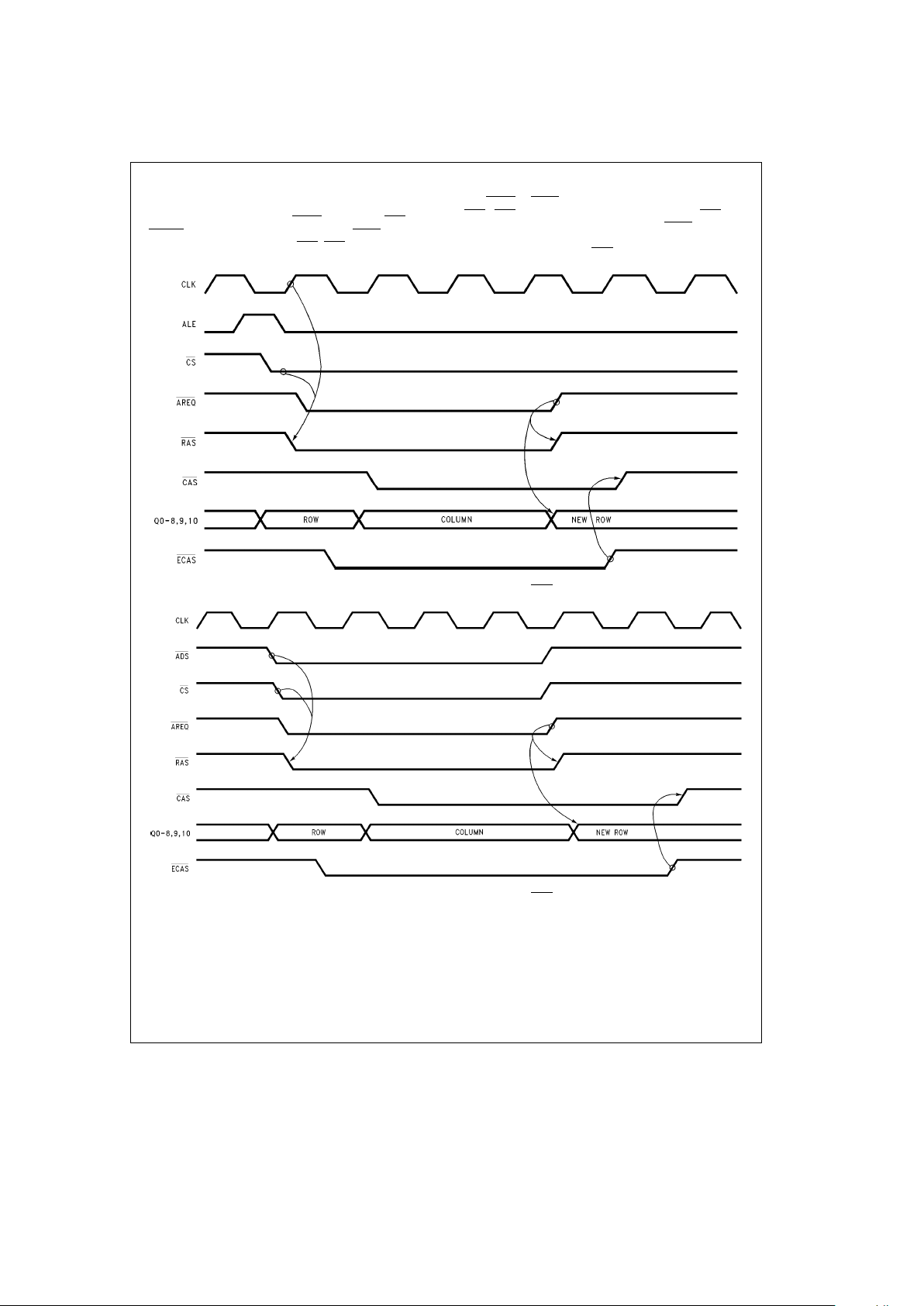
4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.3 EXTENDING CAS WITH EITHER ACCESS MODE
In both access modes, once AREQ
is negated, RAS and
DTACK
if programmed will be negated. If ECAS0 was as-
serted (0) during programming, CAS
(CASs) will be negated
with AREQ
. If ECAS0 was negated (1) during programming,
CAS
(CASs) will continue to be asserted after RAS has
been negated, given that the appropriate ECAS
inputs are
asserted. This allows a DRAM to have data present on the
data out bus while gaining RAS
precharge time.
TL/F/11109– 11
FIGURE 9a. Access Mode 0 Extending CAS
TL/F/11109– 12
FIGURE 9b. Access Mode 1 Extending CAS
15
Page 16
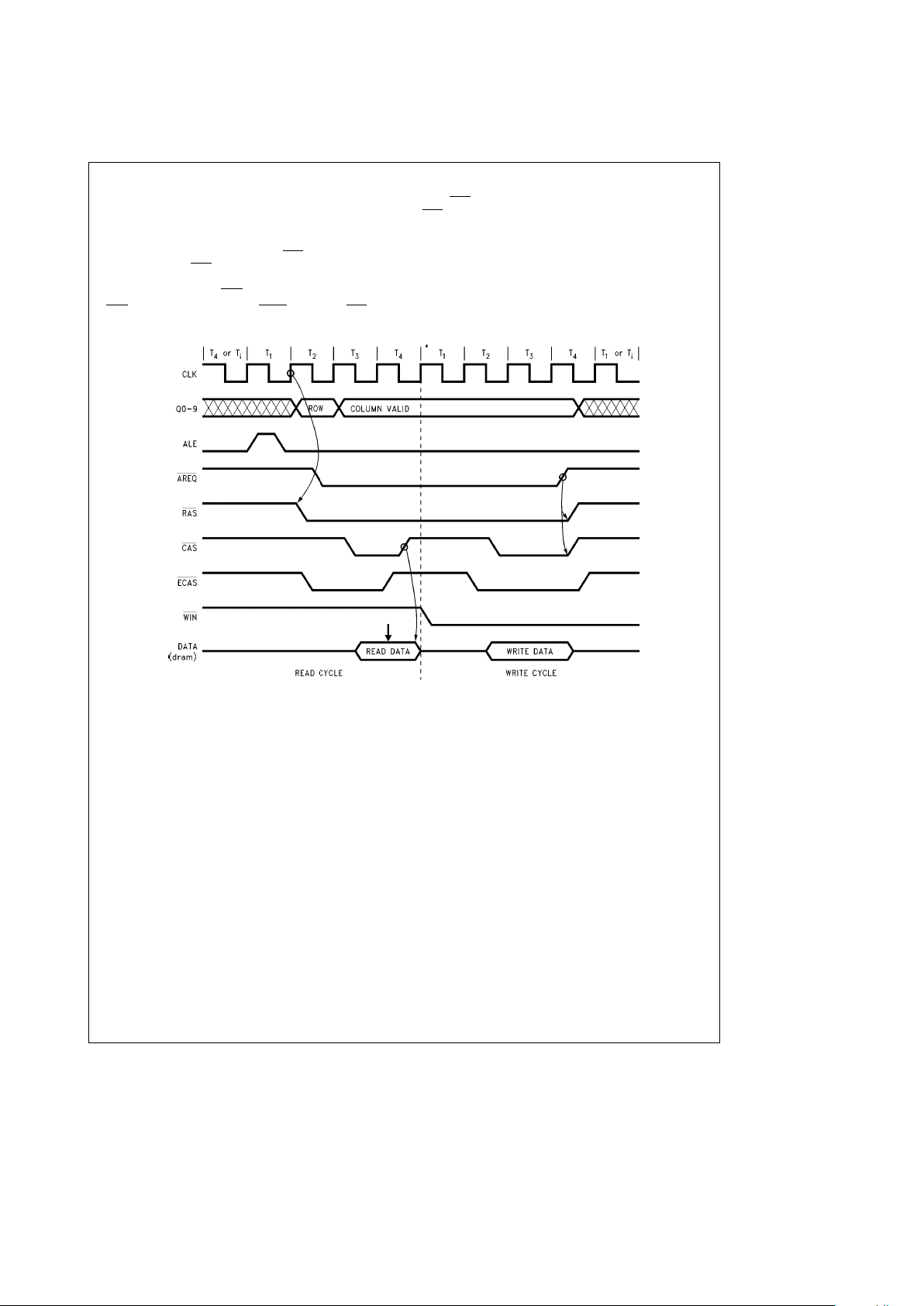
4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.4 READ-MODIFY-WRITE CYCLES
WITH EITHER ACCESS MODE
There are 2 methods by which this chip can be used to do
read-modify-write access cycles. The first method involves
doing a late write access where the WIN
input is asserted
some delay after CAS
is asserted. The second method involves doing a page mode read access followed by a page
mode write access with RAS
held low (see
Figure 9c
).
CASn must be toggled using the ECASn inputs and WIN has
to be changed from negated to asserted (read to write)
while CAS
is negated. This method is better than changing
WIN
from negated to asserted in a late write access because here a problem may arise with DATA IN and DATA
OUT being valid at the same time. This may result in a data
line trying to drive two different levels simultaneously. The
page mode method of a read-modify-write access allows
the user to have transceivers in the system because the
data in (read data) is guaranteed to be high impedance during the time the data out (write data) is valid.
TL/F/11109– 13
*There may be idle states inserted here by the CPU.
FIGURE 9c. Read-Modify-Write Access Cycle
16
Page 17

4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.5 ADDITIONAL ACCESS SUPPORT FEATURES
To support the different modes of accessing, the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22 offer other access features. These additional features include: Address Latches and Column Increment (for page/burst mode support), Address Pipelining,
and Delay CAS
(to allow the user with a multiplexed bus to
ensure valid data is present before CAS
is asserted).
4.5.1 Address Latches and Column Increment
The Address Latches can be programmed, through programming bit B0. They can be programmed to either latch
the address or remain in a fall-through mode. If the address
latches are used to latch the address, the controller will
function as follows:
In Mode 0, the rising edge of ALE places the latches in fallthrough, once ALE is negated, the address present in the
row, column and bank input is latched.
In Mode 1, the address latches are in fall through mode until
ADS
is asserted. ADS asserted latches the address.
Once the address is latched, the column address can be
incremented with the input COLINC. COLINC can be used
for sequential accesses of static column DRAMs. COLINC
can also be used with the ECAS
inputs to support sequen-
tial accesses to page mode DRAMs as shown in
Figure 10
.
COLINC should only be asserted when the signal RFIP
is
negated during an access since this input functions as extended refresh when RFIP
is asserted. COLINC must be
negated (0) when the address is being latched (ADS
falling
edge in Mode 1). If COLINC is asserted with all of the bits of
the column address asserted (ones), the column address
will return to zero.
TL/F/11109– 14
FIGURE 10. Column Increment
The address latches function differently with the DP8422V,
DP84T22. The DP8422V, DP84T22 will latch the address of
the currently granted port. If Port A is currently granted, the
address will be latched as described in Section 4.5.1. If Port
A is not granted, and requests an access, the address will
be latched on the first or second positive edge of CLK after
GRANTB has been negated depending on the programming
bits R0, R1.
For Port B, if GRANTB is asserted, the address will be
latched with AREQB
asserted. If GRANTB is negated, the
address will latch on the first or second positive edge of
CLK after GRANTB is asserted depending on the programming bits R0, R1.
17
Page 18

4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.5.2 Address Pipelining
Address pipelining is the overlapping of accesses to different banks of DRAM. If the majority of successive accesses
are to a different bank, the accesses can be overlapped.
Because of this overlapping, the cycle time of the DRAM
accesses are greatly reduced. The DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22 can be programmed to allow a new row address
to be placed on the DRAM address bus after the column
address hold time has been met. At this time, a new access
can be initiated with ADS
or ALE, depending on the access
mode, while AREQ
is used to sustain the current access.
The DP8422V and DP84T22 support address pipelining for
Port A only. This mode cannot be used with page, static
column or nibble modes of operations because the DRAM
column address is switched back to the row address after
CAS
is asserted. This mode is programmed through ad-
dress bit R8 (see
Figures 11a
and
11b
). In this mode, the
output WE
always functions as RFRQ.
During address pipelining in Mode 0, shown in
Figure 11c
,
ALE cannot be pulsed high to start another access until
AREQ
has been asserted for the previous access for at
least one period of CLK. DTACK
, if programmed, will be
negated once AREQ
is negated. WAIT, if programmed to
insert wait states, will be asserted once ALE and CS
are
asserted.
In Mode 1, shown in
Figure 11d
, ADS can be negated once
AREQ
is asserted. After meeting the minimum negated
pulse width for ADS
, ADS can again be asserted to start a
new access. DTACK
, if programmed, will be negated once
AREQ
is negated. WAIT, if programmed, will be asserted
once ADS
is asserted.
In either mode with either type of wait programmed, the
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will still delay the access for
precharge if sequential accesses are to the same bank or if
a refresh takes place.
TL/F/11109– 15
FIGURE 11a. Non-Address Pipelined Mode
TL/F/11109– 16
FIGURE 11b. Address Pipelined Mode
18
Page 19

4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 17
FIGURE 11c. Mode 0 Address Pipelining (WAIT of 0, (/2T Has Been Programmed.
WAIT
is Sampled at the ‘‘T3’’ Falling Clock Edge)
TL/F/11109– 18
FIGURE 11d. Mode 1 Address Pipelining (DTACK 1(/2T Programmed, DTACK is Sampled at the ‘‘T3’’ Falling Clock Edge)
19
Page 20

4.0 Port A Access Modes (Continued)
4.5.3 Delay CAS
during Write Accesses
Address bit C9 asserted during programming will cause CAS
to be delayed until the first positive edge of CLK after RAS
is asserted when the input WIN is asserted. Delaying CAS
during write accesses ensures that the data to be written to
DRAM will be setup to CAS
asserting as shown in
Figures
12a
and
12b.
If the possibility exists that data still may not
be present after the first positive edge of CLK, CAS
can be
delayed further with the ECAS
inputs. If address bit C9 is
negated during programming, read and write accesses will
be treated the same (with regard to CAS
).
TL/F/11109– 19
FIGURE 12a. Mode 0 Delay CAS
TL/F/11109– 20
FIGURE 12b. Mode 1 Delay CAS
20
Page 21

5.0 Refresh Options
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 support three refresh
control mode options:
1. Automatic Internally Controlled Refresh.
2. Externally Controlled/Burst Refresh.
3. Refresh Request/Acknowledge.
With each of the control modes above, three types of refresh can be performed.
1. All RAS
Refresh.
2. Staggered Refresh.
3. Error Scrubbing During All RAS
Refresh.
There are three inputs, EXTNDRF, RFSH and DISRFSH,
and two outputs, RFIP
and RFRQ, associated with refresh.
There are also ten programming bits: R0–1, R9, C0 –6 and
ECAS0 used to program the various types of refreshing.
Asserting the input EXTNDRF, extends the refresh cycle for
a single or multiple integral periods of CLK.
The output RFIP
is asserted one period of CLK before the
first refresh RAS
is asserted. If an access is currently in
progress, RFIP
will be asserted up to one period of CLK
before the first refresh RAS
, after AREQ or AREQB is nega-
ted for the access (see
Figure 13
).
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will increment the refresh address counter automatically, independent of the refresh mode used. The refresh address counter will be incremented once all the refresh RAS
s have been negated.
In every combination of refresh control mode and refresh
type, the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 is programmed to
keep RAS
asserted a number of CLK periods. The time val-
ues of RAS
low during refresh are programmed through pro-
gramming bits R0 and R1.
5.1 REFRESH CONTROL MODES
5.1.1. Automatic Internal Refresh
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have an internal refresh
clock. The period of the refresh clock is generated from the
programming bits C0 –3. Every period of the refresh clock,
an internal refresh request is generated. As long as a DRAM
access is not currently in progress and precharge time has
been met, the internal refresh request will generate an automatic internal refresh. If a DRAM access is in progress, the
DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 on-chip arbitration logic will
wait until the access is finished before performing the refresh. The refresh/access arbitration logic can insert a refresh cycle between two address pipelined accesses. However, the refresh arbitration logic can not interrupt an access cycle to perform a refresh. To enable automatic internally controlled refreshes, the input DISRFSH
must be neg-
ated.
TL/F/11109– 21
Explanation of Terms
RFRQeReFresh ReQuest internal to the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22. RFRQ has the ability to hold off a pending access.
RFSH
e
Externally requested ReFreSH
RFIP
e
ReFresh in Progress
ACIP
e
Port A or Port B (DP8422V and DP84T22 only) ACcess in Progress. This means that either RAS is low for an access or is in the
process of transitioning low for an access.
FIGURE 13. DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 Access/Refresh Arbitration State Program
21
Page 22

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.1.2 Externally Controlled/Burst Refresh
To use externally controlled/burst refresh, the user must
disable the automatic internally controlled refreshes by asserting the input DISRFSH
. The user is responsible for gen-
erating the refresh request by asserting the input RFSH
.
Pulsing RFSH
low, sets an internal latch, that is used to
produce the internal refresh request. The refresh cycle will
take place on the next positive edge of CLK as shown in
Figure 14a
. If an access to DRAM is in progress or precharge time for the last access has not been met, the refresh will be delayed. Since pulsing RFSH
low sets a latch,
the user does not have to keep RFSH
low until the refresh
starts. When the last refresh RAS
negates, the internal re-
fresh request latch is cleared.
TL/F/11109– 22
FIGURE 14a. Single External Refreshes (2 Periods of RAS Low during Refresh Programmed)
By keeping RFSH
asserted past the positive edge of CLK
which ends the refresh cycle as shown in
Figure 14b
, the
user will perform another refresh cycle. Using this technique, the user can perform a burst refresh consisting of any
number of refresh cycles. Each refresh cycle during a burst
refresh will meet the refresh RAS
low time and the RAS
precharge time (programming bits R0 –1).
If the user desires to burst refresh the entire DRAM (all row
addresses) he could generate an end of count signal (burst
refresh finished) by looking at one of the DP8420V/21V/
22V, DP84T22 high address outputs (Q7, Q8, Q9 or Q10)
and the RFIP
output. The Qn outputs function as a decode
of how many row addresses have been refreshed (Q7
e
128 refreshes, Q8e256 refreshes, Q9e512 refreshes,
Q10
e
1024 refreshes).
TL/F/11109– 23
FIGURE 14b. External Burst Refresh (2 Periods of RAS Precharge,
2 Periods of Refresh RAS
Low during Refresh Programmed)
22
Page 23

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.1.3 Refresh Request/Acknowledge
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 can be programmed to
output internal refresh requests. When the user programs
ECAS
0 negated (1) and/or address pipelining mode is se-
lected, the WE
output functions as RFRQ. RFRQ (WE) will
be asserted by one of two events:
First, when the external circuitry pulses low the input RFSH
which will request an external refresh.
Second, when the internal refresh clock has expired, which
signals that another refresh is needed.
An example of the first case, where an external refresh is
requested while RFRQ
is negated (1), is shown in
Figure
15a
. Notice that RFRQ will be asserted from a positive edge
of clock.
On the second case, when the RFRQ
is asserted from the
expiration of the internal refresh clock, the user has two
options:
First, if DISRFSH
is negated, an automatic internal refresh
will take place. See
Figure 15b
.
Second, with DISRFSH asserted, RFRQ will stay asserted
until RFSH
is pulsed low . This option will cause an external-
ly requested/burst refresh to take place. See
Figure 15c
.
RFRQ will go high and then assert (toggle) if additional periods of the internal refresh clock have expired and neither an
externally controlled refresh nor an automatically controlled
internal refresh have taken place, see
Figure 15d
. If a time
critical event, or long accesses like page/static column
mode can not be interrupted, RFRQ
pulsing high can be
used to increment a counter. This counter can be used to
perform a burst refresh of the number of refreshes missed
(through the RFSH
input).
TL/F/11109– 24
FIGURE 15a. Externally Controlled Single and Burst Refresh with Refresh Request
(RFRQ
) Output (2 Periods of RAS Low during Refresh Programmed)
TL/F/11109– 25
FIGURE 15b. Automatic Internal Refresh with Refresh Request (3T of RAS Low during Refresh Programmed)
23
Page 24

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 26
FIGURE 15c. External Burst Refresh (2 Periods of RAS Precharge,
2 Periods of Refresh RAS
Low during Refresh Programmed)
TL/F/11109– 27
FIGURE 15d. Refresh Request Timing
24
Page 25

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.2 REFRESH CYCLE TYPES
Three different types of refresh cycles are available for use.
The three different types are mutually exclusive and can be
used with any of the three modes of refresh control. The
three different refresh cycle types are: all RAS
refresh, stag-
gered RAS
refresh and error scrubbing during all RAS re-
fresh. In all refresh cycle types, the RAS
precharge time is
guaranteed: between the previous access RAS
ending and
the refresh RAS
0 starting; between refresh RAS3 ending
and access RAS
beginning; between burst refresh RASs.
5.2.1 Conventional RAS
Refresh
A conventional refresh cycle causes RAS
0–3 to all assert
from the first positive edge of CLK after RFIP
is asserted as
shown in
Figure 16
. RAS0 –3 will stay asserted until the
number of positive edges of CLK programmed have passed.
On the last positive edge, RAS
0–3, and RFIP will be negated. This type of refresh cycle is programmed by negating
address bit R9 during programming.
TL/F/11109– 28
FIGURE 16. Conventional RAS Refresh
5.2.2 Staggered RAS
Refresh
A staggered refresh staggers each RAS or group of RASs
by a positive edge of CLK as shown in
Figure 17
. The num-
ber of RAS
s, which will be asserted on each positive edge
of CLK, is determined by the RAS
, CAS configuration mode
programming bits C4 – C6. If single RAS
outputs are select-
ed during programming, then each RAS
will assert on suc-
cessive positive edges of CLK. If two RAS
outputs are se-
lected during programming then RAS
0 and RAS1 will assert
on the first positive edge of CLK after RFIP
is asserted.
RAS
2 and RAS3 will assert on the second positive edge of
CLK after RFIP
is asserted. If all RAS outputs were selected
during programming, all RAS
outputs would assert on the
first positive edge of CLK after RFIP
is asserted. Each RAS
or group of RASs will meet the programmed RAS low time
and then negate.
TL/F/11109– 29
FIGURE 17. Staggered RAS Refresh
25
Page 26

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.2.3 Error Scrubbing during Refresh
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 support error scrubbing
during all RAS
DRAM refreshes. Error scrubbing during refresh is selected through bits C4 –C6 with bit R9 negated
during programming. Error scrubbing can not be used with
staggered refresh (see Section 8.0). Error scrubbing during
refresh allows a CAS
or group of CASs to assert during the
all RAS
refresh as shown in
Figure 18
. This allows data to
be read from the DRAM array and passed through an Error
Detection And Correction Chip, EDAC. If the EDAC determines that the data contains a single bit error and corrects
that error, the refresh cycle can be extended with the input
extend refresh, EXTNDRF, and a read-modify-write operation can be performed by asserting WE
. It is the responsibili-
ty of the designer to ensure that WE
is negated. The
DP8422V, DP84T22 have a 24-bit internal refresh address
counter that contains the 11 row, 11 column and 2 bank
addresses. The DP8420V/21V have a 22-bit internal refresh
address counter that contains the 10 row, 10 column and 2
bank addresses. These counters are configured as bank,
column, row with the row address as the least significant
bits. The bank counter bits are then used with the programming selection to determine which CAS
or group of CASs
will assert during a refresh.
TL/F/11109– 30
FIGURE 18. Error Scrubbing during Refresh
26
Page 27

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.3 EXTENDING REFRESH
The programmed number of periods of CLK that refresh
RAS
s are asserted can be extended by one or multiple peri-
ods of CLK. Only the all RAS
(with or without error scrubbing) type of refresh can be extended. To extend a refresh
cycle, the input extend refresh, EXTNDRF, must be asserted before the positive edge of CLK that would have negated
all the RAS
outputs during the refresh cycle and after the
positive edge of CLK which starts all RAS
outputs during the
refresh as shown in
Figure 19
. This will extend the refresh to
the next positive edge of CLK and EXTNDRF will be sampled again. The refresh cycle will continue until EXTNDRF is
sampled low on a positive edge of CLK.
5.4 CLEARING THE REFRESH ADDRESS COUNTER
The refresh address counter can be cleared by asserting
RFSH
while DISRFSH is negated as shown in
Figure 20a
.
This can be used prior to a burst refresh of the entire memory array. By asserting RFSH
one period of CLK before
DISRFSH
is asserted and then keeping both inputs asserted, the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will clear the refresh
address counter and then perform refresh cycles separated
by the programmed value of precharge as shown in
Figure
20b
. An end-of-count signal can be generated from the Q
DRAM address outputs of the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22 and used to negate RFSH
.
TL/F/11109– 31
FIGURE 19. Extending Refresh with the Extend Refresh (EXTNDRF) Input
TL/F/11109– 32
FIGURE 20a. Clearing the Refresh Address Counter
TL/F/11109– 33
FIGURE 20b. Clearing the Refresh Counter during Burst
27
Page 28

5.0 Refresh Options (Continued)
5.5 CLEARING THE REFRESH REQUEST CLOCK
The refresh request clock can be cleared by negating
DISRFSH
and asserting RFSH for 500 ns, one period of the
internal 2 MHz clock as shown in
Figure 21
. By clearing the
refresh request clock, the user is guaranteed that an internal refresh request will not be generated for approximately
15 ms, one refresh clock period, from the time RFSH
is neg-
ated. This action will also clear the refresh address counter.
TL/F/11109– 34
FIGURE 21. Clearing the Refresh Request Clock Counter
6.0 Port A Wait State Support
Wait states allow a CPU’s access cycle to be increased by
one or multiple CPU clock periods. The wait or ready input is
named differently by CPU manufacturers. However, any
CPU’s wait or ready input is compatible with either the WAIT
or DTACK output of the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22. The
user determines whether to program WAIT
or DTACK (R7)
and which value to select for WAIT
or DTACK (R2, R3) depending upon the CPU used and where the CPU samples its
wait input during an access cycle.
The decision to terminate the CPU access cycle is directly
affected by the speed of the DRAMs used. The system designer must ensure that the data from the DRAMs will be
present for the CPU to sample or that the data has been
written to the DRAM before allowing the CPU access cycle
to terminate.
The insertion of wait states also allows a CPU’s access cycle to be extended until the DRAM access has taken place.
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 insert wait states into
CPU access cycles due to; guaranteeing precharge time,
refresh currently in progress, user programmed wait states,
the WAITIN
signal being asserted and GRANTB not being
valid (DP8422V, DP84T22 only). If one of these events is
taking place and the CPU starts an access, the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22 will insert wait states into the access
cycle, thereby increasing the length of the CPU’s access.
Once the event has been completed, the DP8420V/21V/
22V, DP84T22 will allow the access to take place and stop
inserting wait states.
There are six programming bits, R2–R7; an input, WAITIN
;
and an output that functions as WAIT
or DTACK.
6.1 WAIT
TYPE OUTPUT
With the R7 address bit negated during programming, the
user selects the WAIT
output. As long as WAIT is sampled
asserted by the CPU, wait states (extra clock periods) are
inserted into the current access cycle as shown in
Figure
22
. Once WAIT is sampled negated, the access cycle is
completed by the CPU. WAIT
is asserted at the beginning of
a chip selected access and is programmed to negate a
number of positive edges and/or negative levels of CLK
from the event that starts the access. WAIT
can also be
programmed to function in page/burst mode applications.
Once WAIT
is negated during an access, and the ECAS
inputs are negated with AREQ asserted, WAIT can be programmed to toggle, following the ECAS
inputs. Once AREQ
is negated, ending the access, WAIT will stay negated until
the next chip selected access. For more details about WAIT
Type Output, see Application Note AN-773.
TL/F/11109– 35
FIGURE 22. WAIT Type Output
28
Page 29

6.0 Port A Wait State Support (Continued)
6.2 DTACK
TYPE OUTPUT
With the R7 address bit asserted during programming, the
user selects the DTACK
type output. As long as DTACK is
sampled negated by the CPU, wait states are inserted into
the current access cycle as shown in
Figure 23.
Once
DTACK
is sampled asserted, the access cycle is completed
by the CPU. DTACK
, which is normally negated, is programmed to assert a number of positive edges and/or negative levels from the event that starts RAS
for the access.
DTACK
can also be programmed to function during page/
burst mode accesses. Once DTACK
is asserted and the
ECAS
inputs are negated with AREQ asserted, DTACK can
be programmed to negate and assert from the ECAS
inputs
toggling to perform a page/burst mode operation. Once
AREQ
is negated, ending the access, DTACK will be negated and stays negated until the next chip selected access.
For more details about DTACK
type output, see Application
Note AN-773.
6.3 DYNAMICALLY INCREASING THE
NUMBER OF WAIT STATES
The user can increase the number of positive edges of CLK
before DTACK
is asserted or WAIT is negated. With the
input WAITIN
asserted, the user can delay DTACK asserting
or WAIT
negating either one or two more positive edges of
CLK. The number of edges is programmed through address
bit R6. If the user is increasing the number of positive edges
in a delay that contains a negative level, the positive edges
will be met before the negative level. For example if the user
programmed DTACK
of (/2T, asserting WAITIN, programmed as 2T, would increase the number of positive edges resulting in DTACK
of 2(/2T as shown in
Figure 24a
. Simi-
larly, WAITIN
can increase the number of positive edges in
a page/burst access. WAITIN
can be permanently asserted
in systems requiring an increased number of wait states.
WAITIN
can also be asserted and negated, depending on
the type of access. As an example, a user could invert the
WRITE
line from the CPU and connect the output to
WAITIN
. This could be used to perform write accesses with
1 wait state and read accesses with 2 wait states as shown
in
Figure 24b
.
TL/F/11109– 36
FIGURE 23. DTACK Type Output
TL/F/11109– 37
FIGURE 24a. WAITIN Example (DTACK is Sampled at the ‘‘T3’’ Falling Clock Edge)
29
Page 30

6.0 Port A Wait State Support (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 38
FIGURE 24b. WAITIN Example (WAIT is Sampled at the End of ‘‘T2’’).
6.4 GUARANTEEING RAS
LOW TIME
AND RAS
PRECHARGE TIME
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 will guarantee RAS
precharge time between accesses; between refreshes; and between access and refreshes. The programming bits R0 and
R1 are used to program combinations of RAS
precharge
time and RAS
low time referenced by positive edges of
CLK. RAS
low time is programmed for refreshes only. During an access, the system designer guarantees the time
RAS
is asserted through the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22
wait logic. Since inserting wait states into an access increases the length of the CPU signals which are used to
create ADS
or ALE and AREQ, the time that RAS is assert-
ed can be guaranteed.
The precharge time is also guaranteed by the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22. Each RAS
output has a separate posi-
tive edge of CLK counter. AREQ
is negated setup to a positive edge of CLK to terminate the access. That positive
edge is 1T. The next positive edge is 2T. RAS
will not be
asserted until the programmed number of positive edges of
CLK have passed as shown in
Figure 25
. Once the pro-
grammed precharge time has been met, RAS
will be asserted from the positive edge of CLK. However, since there is a
precharge counter per RAS
, an access using another RAS
will not be delayed. Precharge time before a refresh is always referenced from the access RAS
negating before
RAS
0 for the refresh asserting. After a refresh, precharge
time is referenced from RAS
3 negating, for the refresh, to
the access RAS
asserting.
TL/F/11109– 39
FIGURE 25. Guaranteeing RAS Precharge (DTACK is Sampled at the ‘‘T2’’ Falling Clock Edge)
30
Page 31

7.0 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 allow the user to configure the DRAM array to contain one, two or four banks of
DRAM. Depending on the functions used, certain considerations must be used when determining how to set up the
DRAM array. Programming address bits C4, C5 and C6
along with bank selects, B0 –1, and CAS
enables, ECAS0–
3, determine which RAS
or group of RASs and which CAS
or group of CASs will be asserted during an access. Different memory schemes are described. The DP8420V/21V/
22V, DP84T22 is specified driving a heavy load of 72
DRAMs, representing four banks of DRAM with 16-bit words
and 2 parity bits. The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 can
drive more than 72 DRAMs, but the AC timing must be increased. Since the RAS
and CAS outputs are configurable,
all RAS
and CAS outputs should be used for the maximum
amount of drive.
7.1 BYTE WRITING
By selecting a configuration in which all CAS
outputs are
selected during an access, the ECAS
inputs enable a single
or group of CAS
outputs to select a byte (or bytes) in a word
size of up to 32 bits. In this case, the RAS
outputs are used
to select which of up to 4 banks is to be used as shown in
Figures 26a
and
26b
. In systems with a word size of 16 bits,
the byte enables can be gated with a high order address bit
to produce four byte enables which gives an equivalent to 8
banks of 16-bit words as shown in
Figure 26d
. If less memo-
ry is required, each CAS
should be used to drive each nibble
in the 16-bit word as shown in
Figure 26c
.
TL/F/11109– 40
FIGURE 26a. DRAM Array Setup for 32-Bit System (C6, C5, C4e1, 1, 0 during Programming)
TL/F/11109– 41
FIGURE 26b. DRAM Array Setup for 32-Bit, 1 Bank System (C6, C5, C4e0, 0, 0 Allowing Error Scrubbing
or C6, C5, C4
e
0, 1, 1 No Error Scrubbing during Programming)
31
Page 32

7.0 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 42
FIGURE 26c. DRAM Array Setup for 16-Bit System (C6, C5, C4e1, 1, 0 during Programming)
TL/F/11109– 43
FIGURE 26d. 8 Bank DRAM Array for 16-Bit System (C6, C5, C4e1, 1, 0 during Programming)
32
Page 33

7.0 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes (Continued)
7.2 MEMORY INTERLEAVING
Memory interleaving allows the cycle time of DRAMs to be
reduced by having sequential accesses to different memory
banks. Since the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 have separate precharge counters per bank, sequential accesses will
not be delayed if the accessed banks use different RAS
outputs. To ensure different RAS outputs will be used, a
mode is selected where either one or two RAS
outputs will
be asserted during an access. The bank select or selects,
B0 and B1, are then tied to the least significant address bits,
causing a different group of RAS
s to assert during each
sequential access as shown in
Figure 27
. In this figure there
should be at least one clock period of all RAS
’s negated
between different RAS
’s being asserted to avoid the condi-
tion of a CAS
before RAS refresh cycle.
7.3 ADDRESS PIPELINING
Address pipelining allows several access RAS
stobeas-
serted at once. Because RAS
s can overlap, each bank re-
quires either a mode where one RAS
and one CAS are used
per bank as shown in
Figure 28a
or where two RASs and
two CAS
s are used per bank as shown in
Figure 28b
. Byte
writing can be accomplished in a 16-bit word system if two
RAS
s and two CASs are used per bank. In other systems,
WE
s (or external gating on the CAS outputs) must be used
to perform byte writing. If WE
s are used separate data in
and data out buffers must be used. If the array is not layed
out this way, a CAS
to a bank can be low before RAS, which
will cause a refresh of the DRAM, not an access. To take
full advantage of address pipelining, memory interleaving is
used. To memory interleave, the least significant address
bits should be tied to the bank select inputs to ensure that
all ‘‘back to back’’ sequential accesses are not delayed,
since different memory banks are accessed.
TL/F/11109– 44
FIGURE 27. Memory Interleaving (C6, C5, C4e1, 1, 0 during Programming)
33
Page 34

7.0 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 45
FIGURE 28a. DRAM Array Setup for 4 Banks Using Address Pipelining (C6, C5, C4e1, 1, 1
or C6, C5, C4
e
0, 1, 0 (Also Allowing Error Scrubbing) during Programming)
TL/F/11109– 46
FIGURE 28b. DRAM Array Setup for Address Pipelining with 2 Banks (C6, C5, C4e1, 0, 1
or C6, C5, C4
e
0, 0, 1 (Also Allowing Error Scrubbing) during Programming)
7.4 ERROR SCRUBBING
In error scrubbing during refresh, the user selects one, two
or four RAS
and CAS outputs per bank. When performing
error detection and correction, memory is always accessed
as words. Since the CAS
signals are not used to select
individual bytes, the ECAS
inputs can be tied low as shown
in
Figures 29a
and
29b
.
TL/F/11109– 47
FIGURE 29a. DRAM Array Setup for 4 Banks Using Error Scrubbing (C6, C5, C4e0, 1, 0 during Programming)
TL/F/11109– 48
FIGURE 29b. DRAM Array Setup for Error Scrubbing with 2 Banks (C6, C5, C4e0, 0, 1 during Programming)
34
Page 35

7.0 RAS and CAS Configuration Modes (Continued)
7.5 PAGE/BURST MODE
In a static column, page or burst mode system, the least
significant bits must be tied to the column address in order
to ensure that the page/burst accesses are to sequential
memory addresses, as shown in
Figure 30.
In a nibble
mode system, the least significant bits must be tied to the
highest column and row address bits in order to ensure that
sequential address bits are the ‘‘nibble’’ bits for nibble mode
accesses
(Figure 30)
. The ECAS inputs may then be tog-
gled with the DP8420V/21V/22V’s, DP84T22’s address
latches in fall-through mode, while AREQ
is asserted. The
ECAS
inputs can also be used to select individual bytes.
When using nibble mode DRAMS, the third and fourth address bits can be tied to the bank select inputs to perform
memory interleaving. In page or static column modes, the
two address bits after the page size can be tied to the bank
select inputs to select a new bank if the page size is exceeded.
TL/F/11109– 49
*See table below for row, column & bank address bit map. A0, A1 are used for byte addressing in this example.
Addresses Nibble Mode*
Page Mode/Static Column Mode Page Size
256 Bits/Page 512 Bits/Page 1024 Bits/Page 2048 Bits/Page
Column C9,R9eA2,A3 C0– 7eA2–9 C0–8eA2–10 C0–9eA2–11
C0–10
e
A2–12
Address C0 –8
e
X C8–10eX C9,10eX C10eX
Row
XXX X X
Address
B0 A4 A10 A11 A12 A13
B1 A5 A11 A12 A13 A14
Assume that the least significant address bits are used for byte addressing. Given a 32-bit system A0,A1 would be
used for byte addressing.
X
e
DON’T CARE, the user can do as he pleases.
*Nibble mode values for R and C assume a system using 1 Mbit DRAMs.
FIGURE 30. Page, Static Column, Nibble Mode System
35
Page 36

8.0 Test Mode
Staggered refresh in combination with the error scrubbing
mode places the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 in test
mode. In this mode, the 24-bit refresh counter is divided into
a 13-bit and 11-bit counter. During refreshes both counters
are incremented to reduce test time.
9.0 DRAM Critical Timing
Parameters
The two critical timing parameters, shown in
Figure 31
, that
must be met when controlling the access timing to a DRAM
are the row address hold time, t
RAH
, and the column ad-
dress setup time, t
ASC
. Since the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22 contain a precise internal delay line, the values of
these parameters can be selected at programming time.
These values will also increase and decrease if DELCLK
varies from 2 MHz.
9.1 PROGRAMMABLE VALUES OF t
RAH
AND t
ASC
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 allow the values of t
RAH
and t
ASC
to be selected at programming time. For each pa-
rameter, two choices can be selected. t
RAH
, the row ad-
dress hold time, is measured from RAS
asserted to the row
address starting to change to the column address. The two
choices for t
RAH
are 15 ns and 25 ns, programmable
through address bit C8.
t
ASC
, the column address setup time, is measured from the
column address valid to CAS
asserted. The two choices for
t
ASC
are 0 ns and 10 ns, programmable through address bit
C7.
9.2 CALCULATION OF t
RAH
AND t
ASC
There are two clock inputs to the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22. These two clocks, DELCLK and CLK can either
be tied together to the same clock or be tied to different
clocks running asynchronously at different frequencies.
The clock input, DELCLK, controls the internal delay line
and refresh request clock. DELCLK should be a multiple of
2 MHz. If DELCLK is not a multiple of 2 MHz, t
RAH
and t
ASC
will change. The new values of t
RAH
and t
ASC
can be calcu-
lated by the following formulas:
If t
RAH
was programmed to equal 15 ns then t
RAH
e
15*(((DELCLK Divisor)* 2 MHz/(DELCLK Frequency))b1)
a
15 ns.
If t
RAH
was programmed to equal 25 ns then t
RAH
e
25*(((DELCLK Divisor)* 2 MHz/(DELCLK Frequency))b1)
a
25 ns.
If t
ASC
was programmed to equal 0 ns then t
ASC
e
12.5* ((DELCLK Divisor)* 2 MHz/(DELCLK Frequency))
b
12.5 ns.
If t
ASC
was programmed to equal 10 ns then t
ASC
e
22.5* ((DELCLK Divisor)* 2 MHz/(DELCLK Frequency))
b
22.5 ns.
Since the values of t
RAH
and t
ASC
are increased or de-
creased, the time to CAS
asserted will also increase or decrease. These parameters can be adjusted by the following
formula:
Delay to CAS
e
Actual Spec.aActual t
RAH
b
Programmed t
RAH
a
Actual t
ASC
b
Programmed t
ASC
.
TL/F/11109– 50
FIGURE 31. t
RAH
and t
ASC
36
Page 37

10.0 Dual Accessing (DP8422V, DP84T22)
The DP8422V, DP84T22 has all the functions previously described. In addition to those features, the DP8422V,
DP84T22 also has the capabilities to arbitrate among refresh, Port A and a second port, Port B. This allows two
CPUs to access a common DRAM array. DRAM refresh has
the highest priority followed by the currently granted port.
The ungranted port has the lowest priority. The last granted
port will continue to stay granted even after the access has
terminated, until an access request is received from the ungranted port (see
Figure 32a
). The dual access configuration assumes that both Port A and Port B are synchronous
to the system clock. If they are not synchronous to the system clock they should be externally synchronized (Ex. By
running the access requests through several Flip-Flops, see
Figure 34a
).
10.1 PORT B ACCESS MODE
Port B accesses are initiated from a single input, AREQB
.
When AREQB
is asserted, an access request is generated.
If GRANTB is asserted and a refresh is not taking place or
precharge time is not required, RAS
will be asserted when
AREQB
is asserted. Once AREQB is asserted, it must stay
asserted until the access is over. AREQB
negated, negates
RAS
as shown in
Figure 32b
. Note that if ECAS0e1 during
programming the CAS
outputs may be held asserted (be-
yond RAS
n negating) by continuing to assert the appropri-
ate ECAS
n inputs (the same as Port A accesses). If Port B
is not granted, the access will begin on the first or second
positive edge of CLK after GRANTB is asserted (See R0,
R1 programming bit definitions) as shown in
Figure 32c
, as-
suming that Port A is not accessing the DRAM (CS
, ADS/
ALE and AREQ
) and RAS precharge for the particular bank
has completed. It is important to note that for GRANTB to
transition to Port B, Port A must not be requesting an access at a rising clock edge (or locked) and Port B must be
requesting an access at that rising clock edge. Port A can
request an access through CS
and ADS/ALE or CS and
AREQ
. Therefore during an interleaved access where CS
and ADS/ALE become asserted before AREQ from the previous access is negated, Port A will retain GRANTB
e
0
whether AREQB
is asserted or not.
Since there is no chip select for Port B, AREQB must incorporate this signal. This mode of accessing is similar to Mode
1 accessing for Port A.
TL/F/11109– 51
Explanation of Terms
AREQA
e
Chip Selected access request from Port A
AREQB
e
Chip Selected access request from Port B
LOCK
e
Externally controlled LOCKing of the Port
that is currently GRANTed.
FIGURE 32a. DP8422V, DP84T22 Port A/Port B
Arbitration State Diagram. This arbitration
may take place during the ‘‘ACCESS’’ or
‘‘REFRESH’’ state (see
Figure 13
).
TL/F/11109– 52
FIGURE 32b. Access Request for Port B
TL/F/11109– 53
FIGURE 32c. Delayed Port B Access
37
Page 38
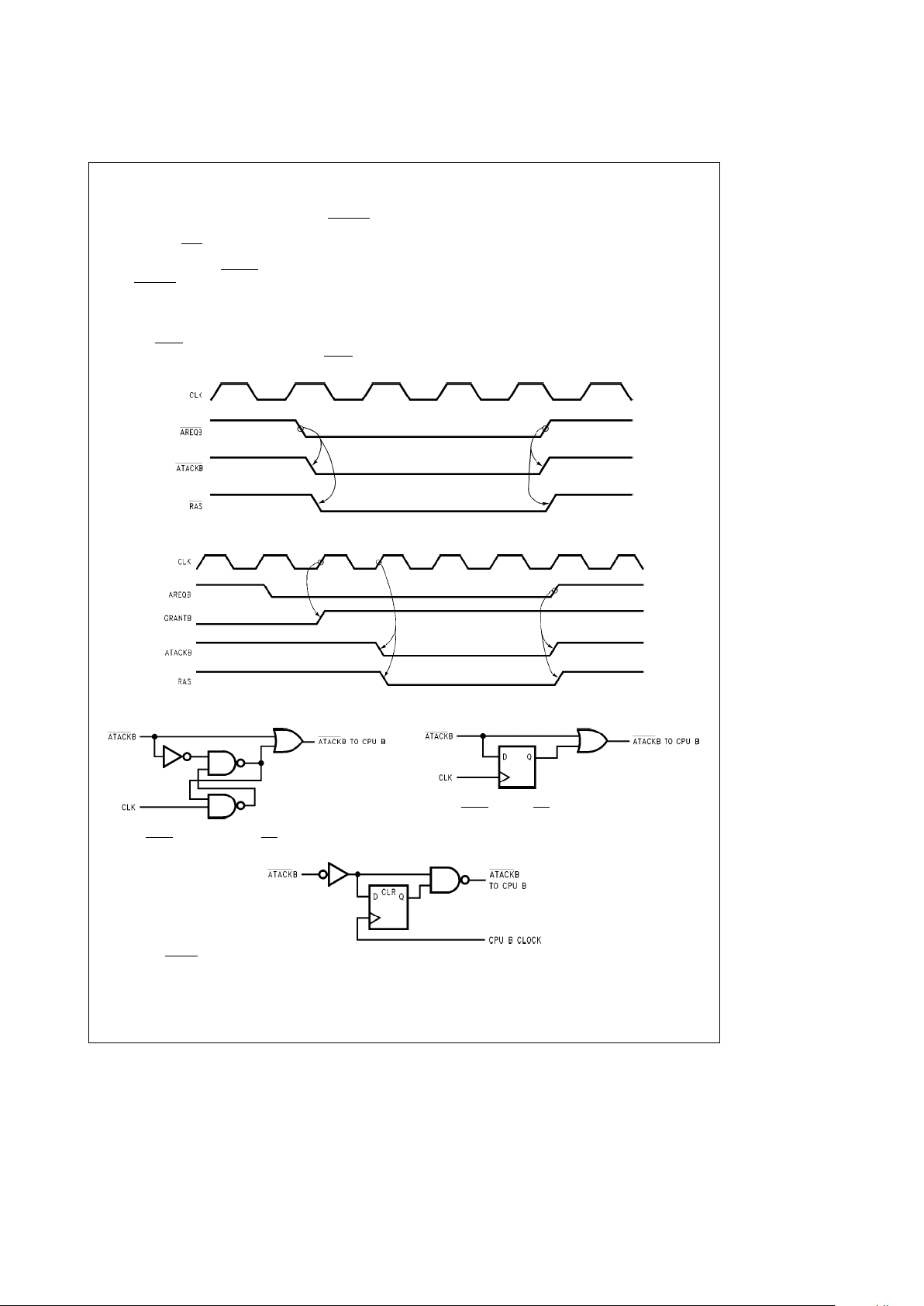
10.0 Dual Accessing (DP8422V, DP84T22) (Continued)
10.2 PORT B WAIT STATE SUPPORT
Advanced transfer acknowledge for Port B, ATACKB
,is
used for wait state support for Port B. This output will be
asserted when RAS
for the Port B access is asserted, as
shown in
Figures 33a
and
33b
. Once asserted, this output
will stay asserted until AREQB
is negated. With external
logic, ATACKB
can be made to interface to any CPU’s wait
input as shown in
Figure 33c
.
10.3 COMMON PORT A AND PORT B DUAL PORT
FUNCTIONS
An input, LOCK
, and an output, GRANTB, add additional
functionality to the dual port arbitration logic. LOCK
allows
Port A or Port B to lock out the other port from the DRAM.
When a Port is locked out of the DRAM, wait states will be
inserted into its access cycle until it is allowed to access
memory. GRANTB is used to multiplex the input control signals and addresses to the DP8422V, DP84T22.
10.3.1 GRANTB Output
The output GRANTB determines which port has current access to the DRAM array. GRANTB asserted signifies Port B
has access. GRANTB negated signifies Port A has access
to the DRAM array.
TL/F/11109– 54
FIGURE 33a. Non-Delayed Port B Access
TL/F/11109– 55
FIGURE 33b. Delayed Port B Access
TL/F/11109– 56
A. Extend ATACK to (/2T((/2 Clock) after RAS goes low.
TL/F/11109– 57
B. Extend ATACK to 1T after RAS goes low.
TL/F/11109– 58
C. Synchronize ATACKB to CPU B Clock. This is useful if CPU B runs asynchronous to the DP8422V, DP84T22.
FIGURE 33c. Modifying Wait Logic for Port B
38
Page 39

10.0 Dual Accessing (DP8422V, DP84T22) (Continued)
Since the DP8422V, DP84T22 has only one set of address
inputs, the signal is used, with the addition of buffers, to
allow the currently granted port’s addresses to reach the
DP8422V, DP84T22. The signals which need to be bufferred are R0 – 10, C0– 10, B0 –1, ECAS
0–3, WE, and
LOCK
. All other inputs are not common and do not have to
be buffered as shown in
Figure 34a.
If a Port, which is not
currently granted, tries to access the DRAM array, the
GRANTB output will transition from a rising clock edge from
AREQ
or AREQB negating and will precede the RAS for the
access by one or two clock periods. GRANTB will then stay
in this state until the other port requests an access and the
currently granted port is not accessing the DRAM as shown
in
Figure 34b
.
TL/F/11109– 59
*If Port B is synchronous the Request Synchronizing logic will not be required.
FIGURE 34a. Dual Accessing with the DP8422V, DP84T22 (System Block Diagram)
39
Page 40

10.0 Dual Accessing (DP8422V, DP84T22) (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 60
FIGURE 34b. Wait States during a Port B Access
40
Page 41
10.0 Dual Accessing (DP8422V, DP84T22) (Continued)
10.3.2 LOCK
Input
When the LOCK input is asserted, the currently granted port
can ‘‘lock out’’ the other port through the insertion of wait
states to that port’s access cycle. LOCK
does not disable
refreshes, it only keeps GRANTB in the same state even if
the other port requests an access, as shown in
Figure 35
.
LOCK
can be used by either port.
TL/F/11109– 61
FIGURE 35. LOCK Function
10.4 TRI-STATE OUTPUTS (DP84T22V Only)
This version is a metal option on the DP8420V/21V/22V-33
DRAM controllers. It comes in a 84-pin PLCC and implements TRI-STATE output capabilities. It has only one extra
pin OE
. When OE is asserted the output buffers are enabled
allowing the DRAM controller to interface to the DRAM array.
If OE
is negated, the output buffers are at TRI-STATE (highZ) making the board level circuit testing easier. The time
penalty for the TRI-STATE option has been minimized making this option attractive to high performance designs. This
part is functionally compatible to the DP8422A-20, -25.
TRI-STATE Output Drivers
TL/F/11109– 62
41
Page 42

11.0 Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Temperature under Bias 0
§
Ctoa70§C
Storage Temperature
b
65§Ctoa150§C
All Input or Output Voltage
with Respect to GND
b
0.5V toa7V
Power Dissipation@20 MHz 0.5W
ESD Rating 2000V
Temp Cycle 3000 of 0/125§C
12.0 DC Electrical Characteristics T
A
e
0§Ctoa70§C, V
CC
e
5Vg10%, GNDe0V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
IH
Logical 1 Input Voltage Tested with a Limited
2.0 V
CC
a
0.5 V
Functional Pattern
V
IL
Logical 0 Input Voltage Tested with a Limited
b
0.5 0.8 V
Functional Pattern
V
OH1
Q and WE Outputs I
OH
eb
10 mA V
CC
b
1.0 V
V
OL1
Q and WE Outputs I
OL
e
10 mA 0.5 V
V
OH2
All Outputs except Qs, WE I
OH
eb
3mA V
CC
b
1.0 V
V
OL2
All Outputs except Qs, WE I
OL
e
3 mA 0.5 V
I
IN
Input Leakage Current V
IN
e
VCCor GND
b
10 10 mA
I
IL ML
ML Input Current (Low) V
IN
e
GND 200 mA
I
CC1
Standby Current CLK at 8 MHz (V
IN
e
VCCor GND) 6 15 mA
I
CC1
Standby Current CLK at 20 MHz (V
IN
e
VCCor GND) 8 17 mA
I
CC1
Standby Current CLK at 33 MHz (V
IN
e
VCCor GND) 10 20 mA
I
CC2
Supply Current CLK at 8 MHz (Inputs Active)
25 45 mA
(I
LOAD
e
25 pF) (V
IN
e
VCCor GND)
I
CC2
Supply Current CLK at 20 MHz (Inputs Active)
65 90 mA
(I
LOAD
e
25 pF) (V
IN
e
VCCor GND)
I
CC2
Supply Current CLK at 33 MHz (Inputs Active)
115 150 mA
(I
LOAD
e
25 pF) (V
IN
e
VCCor GND)
I
OZH
Leakage Current V
CC
e
Max
10 mA
V
O
e
V
CC
b
1.0V
I
OZL
Leakage Current V
CC
e
Max
b
10 mA
V
O
e
0.5V
CIN* Input Capacitance fINat 1 MHz 10 pF
*CINis not 100% tested.
Note 1: ‘‘Absolute Maximum Ratings’’ are the values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the device
should be operated at these limits. The table of ‘‘Electrical Characteristics’’ provides conditions for actual device operation.
Note 2: Input pulse 0V to 3V; tR
etFe
2.5 ns. Input reference point on AC measurements is 1.5V. Output reference point is 1.5V.
Note 3: AC Production testing is done at 50 pF.
42
Page 43

13.0 AC Timing Parameters
Two speed selections are given, the DP8420V/21V/22V-33
and the DP84T22-25. The differences between the two
parts are the maximum operating frequencies of the input
CLKs and the maximum delay specifications. Low frequency
applications may use the ‘‘-33’’ part to gain improved timing.
The AC timing parameters are grouped into sectional numbers as shown below. These numbers also refer to the timing diagrams.
1–36 Common parameters to all modes of operation
50–56 Difference parameters used to calculate;
RAS
low time,
RAS
precharge time,
CAS
high time and
CAS
low time
100–121 Common dual access parameters used for Port
B accesses and inputs and outputs used only in
dual accessing
200–212 Refresh parameters
300–315 Mode 0 access parameters used in both single
and dual access applications
400–416 Mode 1 access parameters used in both single
and dual access applications
450–455 Special Mode 1 access parameters which super-
sede the 400 –416 parameters when dual accessing
500–506 Programming parameters
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0kT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of
18 DRAMs per bank, including trace capacitance (see Note
2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
TL/F/11109– 63
FIGURE 36. Clock, DELCLK Timing
43
Page 44

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Common Parameter
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
1f
CLK
CLK Frequency 0 33 0 33
2 tCLKP CLK Period 30 30
3, 4 tCLKPW CLK Pulse Width 12 12
5 fDCLK DELCLK Frequency 6 20 6 20
6 tDCLKP DELCLK Period 50 166 50 166
7, 8 tDCLKPW DELCLK Pulse Width 12 12
9a tPRASCAS0 RAS Asserted to CAS
Asserted
30 30
(tRAH
e
15 ns, tASCe0 ns)
9b tPRASCAS1 RAS Asserted to CAS Asserted
40 40
(tRAHe15 ns, tASCe10 ns)
9c tPRASCAS2 (RAS Asserted to CAS Asserted
40 40
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe0 ns)
9d tPRASCAS3 (RAS Asserted to CAS Asserted
50 50
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe10 ns)
10a tRAH Row Address Hold Time (tRAHe15) 15 15
10b tRAH Row Address Hold Time (tRAHe25) 25 25
11a tASC Column Address Setup Time (tASCe0) 0 0
11b tASC Column Address Setup Time (tASCe10) 10 10
12 tPCKRAS CLK High to RAS Asserted
18 22
following Precharge
13 tPARQRAS AREQ Negated to RAS Negated 25 29
14 tPENCL ECAS0 – 3 Asserted to CAS Asserted 15 22
15 tPENCH ECAS0– 3 Negated to CAS Negated 14 21
16 tPARQCAS AREQ Negated to CAS Negated 36 43
17 tPCLKWH CLK to WAIT Negated 25 25
18 tPCLKDL0 CLK to DTACK Asserted
(Programmed as DTACK of 1/2, 1, 1(/2 23 23
or if WAITIN is Asserted)
19 tPEWL ECAS Negated to WAIT Asserted
29 29
during a Burst Access
20 tSECK ECAS Asserted Setup to CLK High to
Recognize the Rising Edge of CLK 13 13
during a Burst Access
44
Page 45

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Common Parameter
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
21 tPEDL ECAS Asserted to DTACK
Asserted during a Burst Access 29 29
(Programmed as DTACK
0)
22 tPEDH ECAS Negated to DTACK
30 30
Negated during a Burst Access
23 tSWCK WAITIN Asserted Setup to CLK 5 5
24 tPWINWEH WIN Asserted to WE Asserted 18 28
25 tPWINWEL WIN Negated to WE Negated 18 28
26 tPAQ Row, Column Address Valid to
20 29
Q0–8, 9, 10 Valid
27 tPCINCQ COLINC Asserted to Q0 – 8, 9, 10
24 33
Incremented
28 tSCINEN COLINC Asserted Setup to ECAS
14 16
Asserted to Ensure tASC
e
0ns
29a tSARQCK1 AREQ, AREQB Negated Setup to CLK
25 25
High with 1 Period of Precharge
29b tSARQCK2 AREQ, AREQB Negated Setup to CLK High
11 11
withl1 Period of Precharge Programmed
30 tPAREQDH AREQ Negated to DTACK Negated 20 20
31 tPCKCAS CLK High to CAS Asserted
21 28
when Delayed by WIN
32 tSCADEN Column Address Setup to ECAS
10 11
Asserted to Guarantee tASCe0
33 tWCINC COLINC Pulse Width 10 10
34a tPCKCL0 CLK High to CAS Asserted following
65 73
Precharge (tRAH
e
15 ns, tASCe0 ns)
34b tPCKCL1 CLK High to CAS Asserted following
75 83
Precharge (tRAHe15 ns, tASCe10 ns)
34c tPCKCL2 CLK High to CAS Asserted following
75 83
Precharge (tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe0 ns)
34d tPCKCL3 CLK High to CAS Asserted following
85 93
Precharge (tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe10 ns)
35 tCAH Column Address Hold Time
25 25
(Interleave Mode Only)
36 tPCQR CAS Asserted to Row Address
70 70
Valid (Interleave Mode Only)
45
Page 46

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Difference
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
50 tD1 (AREQ or AREQB Negated to RAS
Negated) Minus (CLK High to RAS 99
Asserted)
51 tD2 (CLK High to Refresh RAS Negated)
77
Minus (CLK High to RAS Asserted)
52 tD3a (ADS Asserted to RAS Asserted
(Mode 1)) Minus (AREQ
Negated 4 4
to RAS
Negated)
53 tD3b (CLK High to RAS Asserted (Mode 0))
22
Minus (AREQ Negated to RAS Negated)
54 tD4 (ECAS Asserted to CAS Asserted)
b
55
b
55
Minus (ECAS
Negated to CAS Negated)
55 tD5 (CLK to Refresh RAS Asserted) Minus
44
(CLK to Refresh RAS
Negated)
52 tD6 (AREQ Negated to RAS Negated)
Minus (ADS
Asserted to RAS 55
Asserted (Mode 1))
TRI-STATE
DP8420V/21V/22V-33 DP84T22-25
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
80 t
PZL
Delay from TRI-STATE
15 22
to Low Level
81 t
PZH
Delay from TRI-STATE
18 25
to High Level
82 t
PLZ
Delay from TRI-STATE
18 25
to TRI-STATE
83 t
PHZ
Delay from TRI-STATE
18 25
to TRI-STATE
46
Page 47
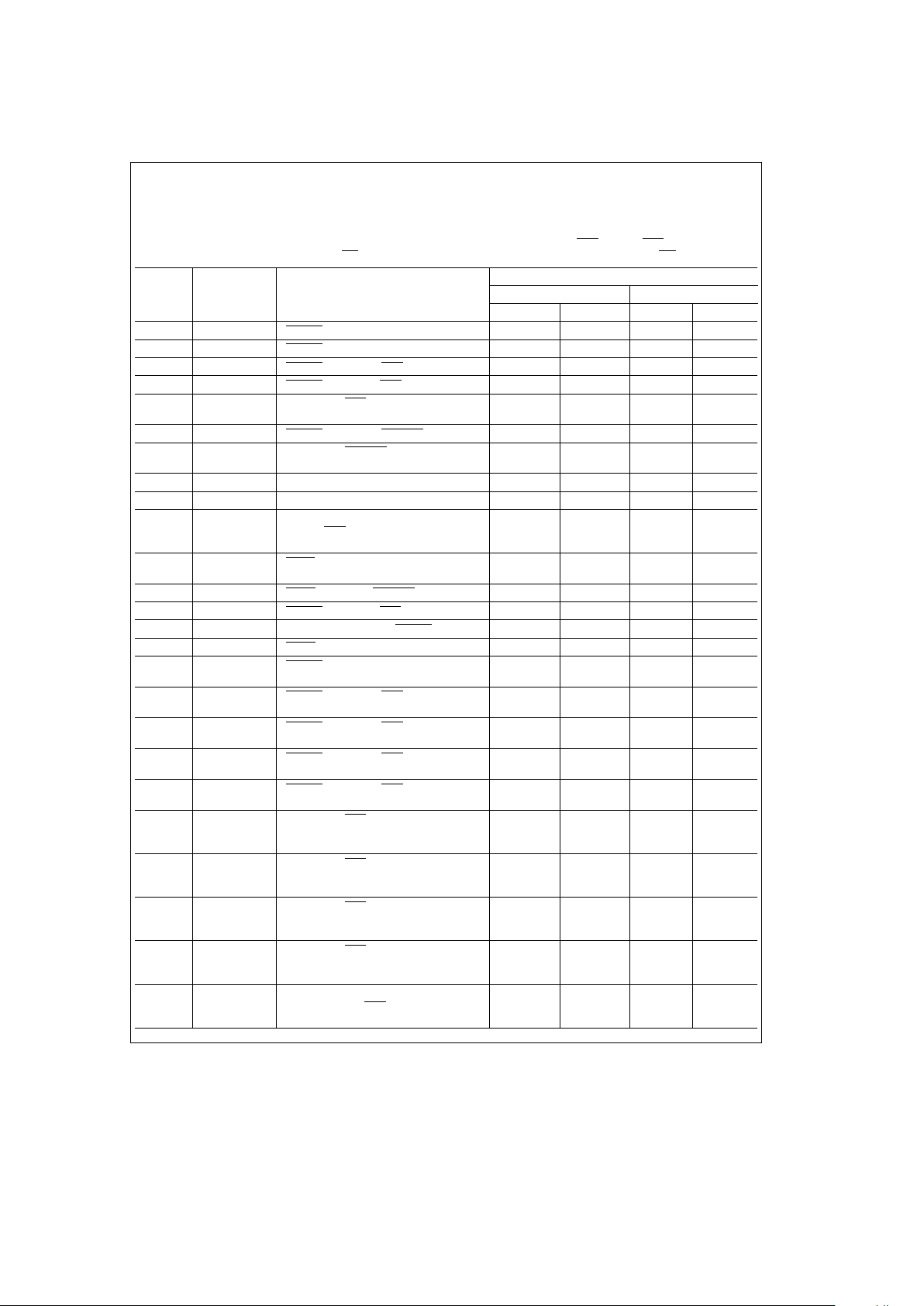
13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Common Dual Access
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
100 tHCKARQB AREQB Negated Held from CLK High 2 2
101 tSARQBCK AREQB Asserted Setup to CLK High 5 5
102 tPAQBRASL AREQB Asserted to RAS Asserted 29 33
103 tPAQBRASH AREQB Negated to RAS Negated 24 28
105 tPCKRASG CLK High to RAS Asserted for
37 41
Pending Port B Access
106 tPAQBATKBL AREQB Asserted to ATACKB Asserted 37 37
107 tPCKATKB CLK High to ATACKB Asserted
45 45
for Pending Access
108 tPCKGH CLK High to GRANTB Asserted 28 28
109 tPCKGL CLK High to GRANTB Negated 26 26
110 tSADDCKG Row Address Setup to CLK High That
Asserts RAS
following a GRANTB 7 11
Change to Ensure tASR
e
0 ns for Port B
111 tSLOCKCK LOCK
Asserted Setup to CLK Low
44
to Lock Current Port
112 tPAQATKBH AREQ Negated to ATACKB Negated 16 16
113 tPAQBCASH AREQB Negated to CAS Negated 38 45
114 tSADAQB Address Valid Setup to AREQB Asserted 6 10
116 tHCKARQG AREQ Negated Held from CLK High 5 5
117 tWAQB AREQB High Pulse Width
17 19
to Guarantee tASR
e
0ns
118a tPAQBCAS0 AREQB Asserted to CAS Asserted
79 86
(tRAH
e
15 ns, tASCe0 ns)
118b tPAQBCAS1 AREQB Asserted to CAS Asserted
89 96
(tRAHe15 ns, tASCe10 ns)
118c tPAQBCAS2 AREQB Asserted to CAS Asserted
89 96
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe0 ns)
118d tPAQBCAS3 AREQB Asserted to CAS Asserted
99 106
(tRAHe25 ns, tASCe10 ns)
120a tPCKCASG0 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Port B Access 84 91
(tRAHe15 ns, tASCe0 ns)
120b tPCKCASG1 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Port B Access 94 101
(tRAH
e
15 ns, tASCe10 ns)
120c tPCKCASG2 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Port B Access 94 101
(tRAHe25 ns, tASCe0 ns)
120d tPCKCASG3 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Port B Access 104 111
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe10 ns)
121 tSBADDCKG Bank Address Valid Setup to CLK
High That Starts RAS
55
for Pending Port B Access
47
Page 48
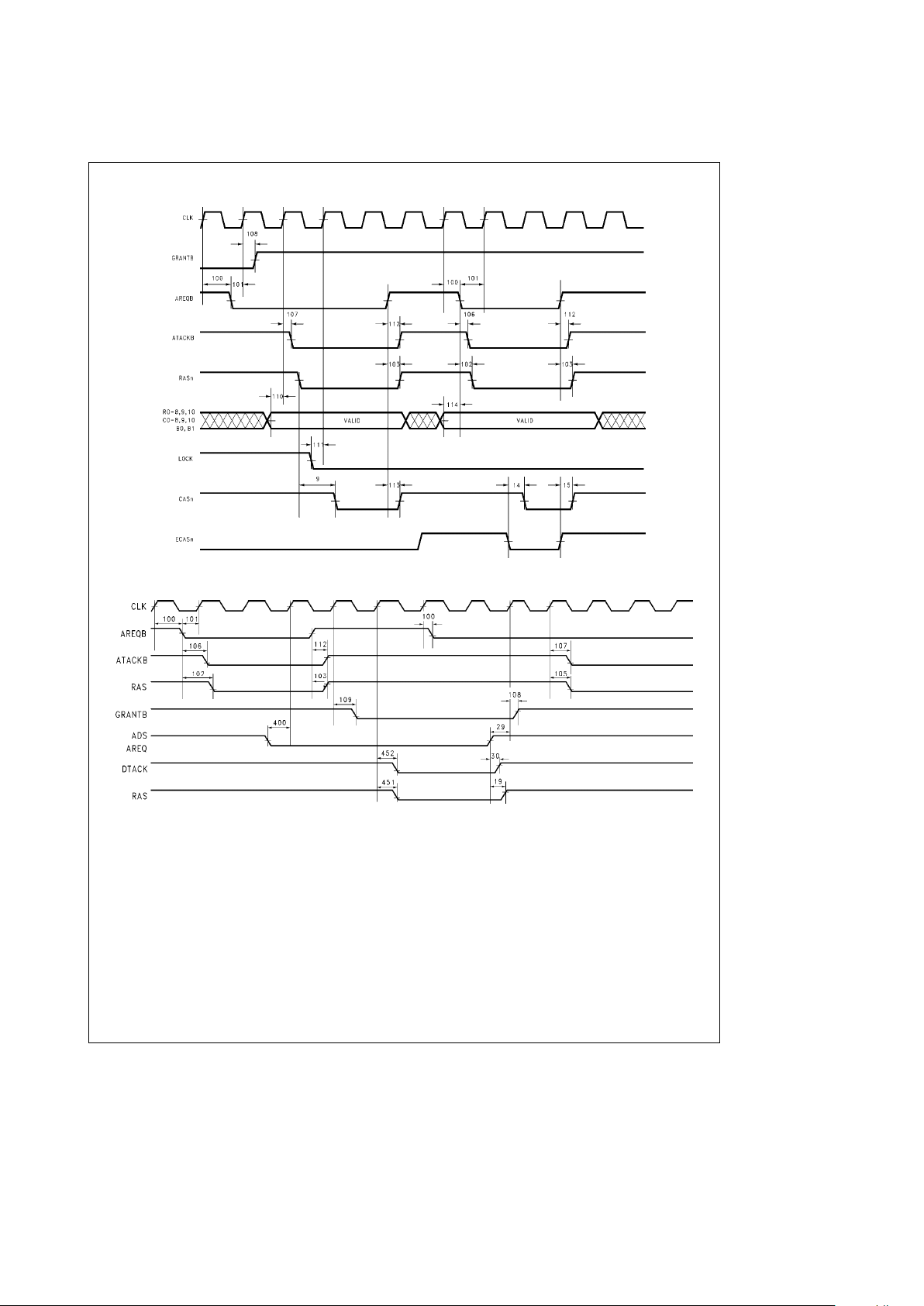
13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 64
FIGURE 37. 100: Dual Access Port B
TL/F/11109– 65
FIGURE 38. 100: Port A and Port B Dual Access
48
Page 49

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Refresh Parameter
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
200 tSRFCK RFSH Asserted Setup to CLK High 16 16
201 tSDRFCK DISRFSH Asserted Setup to CLK High 16 16
202 tSXRFCK EXTENDRF Setup to CLK High 8 8
204 tPCKRFL CLK High to RFIP Asserted 26 26
205 tPARQRF AREQ Negated to RFIP Asserted 38 38
206 tPCKRFH CLK High to RFIP Negated 41 41
207 tPCKRFRASH CLK High to Refresh RAS Negated 26 30
208 tPCKRFRASL CLK High to Refresh RAS Asserted 20 24
209a tPCKCL0 CLK High to CAS Asserted
during Error Scrubbing 64 73
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
209b tPCKCL1 CLK High to CAS Asserted
during Error Scrubbing 74 83
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
209c tPCKCL2 CLK High to CAS Asserted
during Error Scrubbing 74 83
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
209d tPCKCL3 CLK High to CAS Asserted
during Error Scrubbing 85 94
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
210 tWRFSH RFSH Pulse Width 9 9
211 tPCKRQL CLK High to RFRQ Asserted 22 22
212 tPCKRQH CLK High to RFRQ Negated 22 22
TL/F/11109– 66
FIGURE 39. 200: Refresh Timing
49
Page 50

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Mode 0 Access
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
300 tSCSCK CS Asserted to CLK High 8 8
301a tSALECKNL ALE Asserted Setup to CLK High
Not Using On-Chip Latches or
11 11
if Using On-Chip Latches and
B0, B1, Are Constant, Only 1 Bank
301b tSALECKL ALE Asserted Setup to CLK High,
if Using On-Chip Latches if B0, B1 20 20
Can Change, More Than One Bank
302 tWALE ALE Pulse Width 10 10
303 tSBADDCK Bank Address Valid Setup to CLK High 10 10
304 tSADDCK Row, Column Valid Setup to
CLK High to Guarantee 6 10
tASR
e
0ns
305 tHASRCB Row, Column, Bank Address
Held from ALE Negated 6 6
(Using On-Chip Latches)
306 tSRCBAS Row, Column, Bank Address
Setup to ALE Negated 1 1
(Using On-Chip Latches)
307 tPCKRL CLK High to RAS Asserted 19 23
308a tPCKCL0 CLK High to CAS Asserted
65 72
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
308b tPCKCL1 CLK High to CAS Asserted
75 82
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
308c tPCKCL2 CLK High to CAS Asserted
75 82
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
308d tPCKCL3 CLK High to CAS Asserted
85 92
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
309 tHCKALE ALE Negated Hold from CLK High 0 0
310 tSWINCK WIN Asserted Setup to CLK High
b
16
b
16
to Guarantee CAS
is Delayed
311 tPCSWL CS Asserted to WAIT Asserted 20 20
312 tPCSWH CS Negated to WAIT Negated 20 20
313 tPCLKDL1 CLK High to DTACK Asserted
27 27
(Programmed as DTACK0
)
314 tPALEWL ALE Asserted to WAIT Asserted
21 21
(CS
is Already Asserted)
315 AREQ Negated to CLK High That Starts
Access RAS to Guarantee tASRe0ns 27 31
(Non-Interleaved Mode Only)
316 tPCKCV0 CLK High to Column
Address Valid 58 67
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
317 tPCKCV1 CLK High to Column
Address Valid 68 75
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
50
Page 51

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 67
FIGURE 40. 300: Mode 0 Timing
51
Page 52

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 68
(Programmed as C4e1, C5e1, C6e1)
FIGURE 41. 300: Mode 0 Interleaving
52
Page 53

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Mode 1 Access
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
400a tSADSCK1 ADS Asserted Setup to CLK High 9 9
400b tSADSCKW ADS Asserted Setup to CLK
(to Guarantee Correct WAIT
19 19
or DTACK Output; Doesn’t Apply for DTACK0)
401 tSCSADS CS Setup to ADS Asserted 4 4
402 tPADSRL ADS Asserted to RAS Asserted 20 24
403a tPADSCL0 ADS Asserted to CAS Asserted
70 77
(tRAH
e
15 ns, tASCe0 ns)
403b tPADSCL1 ADS Asserted to CAS Asserted
80 87
(tRAHe15 ns, tASCe10 ns)
403c tPADSCL2 ADS Asserted to CAS Asserted
80 87
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe0 ns)
403d tPADSCL3 ADS Asserted to CAS Asserted
90 97
(tRAH
e
25 ns, tASCe10 ns)
404 tSADDADS Row Address Valid Setup to ADS
611
Asserted to Guarantee tASR
e
0ns
405 tHCKADS ADS Negated Held from CLK High 0 0
406 tSWADS WAITIN Asserted Setup to ADS
Asserted to Guarantee DTACK00 0
Is Delayed
407 tSBADAS Bank Address Setup to ADS Asserted 6 6
408 tHASRCB Row, Column, Bank Address Held from
66
ADS Asserted (Using On-Chip Latches)
409 tSRCBAS Row, Column, Bank Address Setup to
11
ADS
Asserted (Using On-Chip Latches)
410 tWADSH ADS Negated Pulse Width 12 17
411 tPADSD ADS Asserted to DTACK Asserted
29 29
(Programmed as DTACK0
)
412 tSWINADS WIN Asserted Setup to ADS Asserted
(to Guarantee CAS Delayed during
b
10
b
10
Writes Accesses)
413 tPADSWL0 ADS Asserted to WAIT Asserted
19 19
(Programmed as WAIT
0, Delayed Access)
414 tPADSWL1 ADS Asserted to WAIT Asserted
22 22
(Programmed WAIT
1/2 or 1)
415 tPCLKDL1 CLK High to DTACK Asserted
(Programmed as DTACK0, 27 27
Delayed Access)
416 AREQ Negated to ADS Asserted
to Guarantee tASR
e
0ns 27 29
(Non Interleaved Mode Only)
417 tPADSCV0 ADS Asserted to Column
Address Valid 51 60
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
53
Page 54

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 69
FIGURE 42. 400: Mode 1 Timing
54
Page 55

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
TL/F/11109– 70
FIGURE 43. 400: COLINC Page/Static Column Access Timing
55
Page 56

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Mode 1 Dual Access
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
450 tSADDCKG Row Address Setup to CLK High That
Asserts RAS
following a GRANTB 10 12
Port Change to Ensure tASR
e
0ns
451 tPCKRASG CLK High to RAS Asserted
30 34
for Pending Access
452 tPCLKDL2 CLK to DTACK Asserted for Delayed
37 37
Accesses (Programmed as DTACK
0)
453a tPCKCASG0 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Access 81 88
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
453b tPCKCASG1 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Access 91 98
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
453c tPCKCASG2 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Access 91 98
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
453d tPCKCASG3 CLK High to CAS Asserted
for Pending Access 101 108
(t
RAH
e
25 ns, t
ASC
e
10 ns)
454 tSBADDCKG Bank Address Valid Setup to CLK High
33
that Asserts RAS
for Pending Access
455 tSADSCK0 ADS Asserted Setup to CLK High 8 8
56
Page 57

13.0 AC Timing Parameters (Continued)
Unless otherwise stated V
CC
e
5.0Vg10%, 0§CkT
A
k
70§C, the output load capacitance is typical for 4 banks of 18 DRAMs
per bank, including trace capacitance (Note 2).
Two different loads are specified:
C
L
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
L
e
150 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE;or
C
H
e
50 pF loads on all outputs except
C
H
e
125 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3 and
C
H
e
380 pF loads on Q0 –8, 9, 10 and WE.
Programming
DP8420V/21V/22V and DP84T22V
Number Symbol
Parameter Description
C
L
C
H
Min Max Min Max
500 tHMLADD Mode Address Held from ML Negated 6 6
501 tSADDML Mode Address Setup to ML Negated 6 6
502 tWML ML Pulse Width 12 12
503 tSADAQML Mode Address Setup to AREQ Asserted 0 0
504 tHADAQML Mode Address Held from AREQ Asserted 30 30
505 tSCSARQ CS Asserted Setup to
66
AREQ
Asserted
506 tSMLARQ ML Asserted Setup to AREQ Asserted 6 6
TL/F/11109– 71
FIGURE 44. 500: Programming
57
Page 58

14.0 Functional Differences
between the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22 and the DP8420/21/22
1. Extending the Column Address Strobe (CAS) after
AREQ
Transitions High
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 allows CAS to be asserted for an indefinite period of time beyond AREQ
(or
AREQB
, DP8422V, DP84T22 only. Scrubbing refreshes
are not affected.) being negated by continuing to assert
the appropriate ECAS
inputs. This feature is allowed as
long as the ECAS
0 input was negated during program-
ming. The DP8420/21/22 does not allow this feature.
2. Dual Accessing
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 asserts RAS
either
one or two clock periods after GRANTB has been asserted or negated depending upon how the R0 bit was programmed during the mode load operation. The
DP8420/21/22 will always start RAS
one clock period
after GRANTB is asserted or negated. The above statements assume that RAS
precharge has been completed
by the time GRANTB is asserted or negated.
3. Refresh Request Output (RFRQ
)
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 allows RFRQ
(refresh
request) to be output on the WE
output pin given that
ECAS
0 was negated during programming or the controller was programmed to function in the address pipelining
(memory interleaving) mode. The DP8420/21/22 only allows RFRQ
to be output during the address pipelining
mode.
4. Clearing the Refresh Request Clock Counter
The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 allows the internal refresh request clock counter to be cleared by negating
DISRFSH
and asserting RFSH for at least 500 ns. The
DP8420/21/22 clears the internal refresh request clock
counter if DISRFSH
remains low for at least 500 ns. Once
the internal refresh request clock counter is cleared the
user is guaranteed that an internally generated RFRQ
will
not be generated for at least 13 ms–15 ms (depending
upon how programming bits C0, 1, 2, 3 were programmed).
15.0 DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22
User Hints
1. All inputs to the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 should be
tied high, low or the output of some other device.
Note: One signal is active high. COLINC (EXTNDRF) should be tied low
to disable.
2. Each ground on the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 must
be decoupled to the closest on-chip supply (V
CC
) with
0.1 mF ceramic capacitor. This is necessary because
these grounds are kept separate inside the DP8420V/
21V/22V, DP84T22. The decoupling capacitors should
be placed as close as possible with short leads to the
ground and supply pins of the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22.
3. The output called ‘‘CAP’’ should have a 0.1 mF capacitor
to ground.
4. The DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 has 20X series
damping resistors built into the output drivers of RAS
,
CAS
, address and WE/RFRQ. Space should be provided
for external damping resistors on the printed circuit board
(or wire-wrap board) because they may be needed. The
value of these damping resistors (if needed) will vary depending upon the output, the capacitance of the load,
and the characteristics of the trace as well as the routing
of the trace. The value of the damping resistor also may
vary between the wire-wrap board and the printed circuit
board. To determine the value of the series damping resistor it is recommended to use an oscilloscope and look
at the furthest DRAM from the DP8420V/21V/22V,
DP84T22. The undershoot of RAS
, CAS,WEand the addresses should be kept to less than 0.5V below ground
by varying the value of the damping resistor. The damping resistors should be placed as close as possible with
short leads to the driver outputs of the DP8420V/21V/
22V, DP84T22.
5. The circuit board must have a good V
CC
and ground
plane connection. If the board is wire-wrapped, the V
CC
and ground pins of the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22,
the DRAM associated logic and buffer circuitry must be
soldered to the V
CC
and ground planes.
6. The traces from the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 to the
DRAM should be as short as possible.
7. ECAS
0 should be held low during programming if the user
wishes that the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 be compatible with a DP8420/21/22 design.
8. Parameter Changes due to Loading
All A.C. parameters are specified with the equivalent load
capacitances, including traces, of 64 DRAMs organized
as 4 banks of 18 DRAMs each. Maximums are based on
worst-case conditions. If an output load changes then the
A.C. timing parameters associated with that particular
output must be changed. For example, if we changed our
output load to
C
e
250 pF loads on RAS0 –3 and CAS0–3
C
e
760 pF loads on Q0 –9 and WE
we would have to modify some parameters (not all calculated here)
$308a clock to CAS
asserted
(t
RAH
e
15 ns, t
ASC
e
0 ns)
A ratio can be used to figure out the timing change per
change in capacitance for a particular parameter by using
the specifications and capacitances from heavy and light
load timing.
Ratio
e
$308a w/Heavy Loadb$308a w/Light Load
CH(CAS)bCL(CAS)
e
79 nsb72 ns
125 pFb50 pF
e
7ns
75 pF
$308a (actual)
e
(capacitance difference
c
ratio)a$308a (specified)
e
(250 pFb125 pF)
7ns
75 pF
a
79 ns
e
11.7 nsa79 ns
e
90.7 ns@250 pF load
9. It is required that the user perform a hardware reset to
the DP8420V/21V/22V, DP84T22 before programming
and using the chip. A hardware reset consists of asserting both ML
and DISRFSH for a minimum of 16 positive
edges of CLK, see Section 3.1.
58
Page 59

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters)
Plastic Chip Carrier (V)
Order Number DP8420V-33 or DP8421V-33
NS Package Number V68A
59
Page 60

DP8420V/21V/22V-33, DP84T22-25 microCMOS Programmable
256k/1M/4M Dynamic RAM Controller/Drivers
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) (Continued)
Plastic Chip Carrier (V)
Order Number DP8422V-33 or DP84T22-25
NS Package Number V84A
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant support device or system whose failure to perform can
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life
failure to perform, when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can effectiveness.
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 86 13th Floor, Straight Block, Tel: 81-043-299-2309
Arlington, TX 76017 Email: cnjwge@tevm2.nsc.com Ocean Centre, 5 Canton Rd. Fax: 81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
Fax: 1(800) 737-7018 English Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
Fran3ais Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
Italiano Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...