Page 1
8-Bit, High Speed, Multiplying D/A Converter
a
FEATURES
Fast Settling Output Current: 85 ns
Full-Scale Current Prematched to 61 LSB
Direct Interface to TTL, CMOS, ECL, HTL, PMOS
Nonlinearity to 0.1% Maximum Over
Temperature Range
High Output Impedance and Compliance:
–10 V to +18 V
Complementary Current Outputs
Wide Range Multiplying Capability: 1 MHz Bandwidth
Low FS Current Drift: 610 ppm/8C
Wide Power Supply Range: 64.5 V to 618 V
Low Power Consumption: 33 mW @ 65 V
Low Cost
Available in Die Form
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DAC08 series of 8-bit monolithic digital-to-analog converters provide very high-speed performance coupled with low cost
and outstanding applications flexibility.
Advanced circuit design achieves 85 ns settling times with very
low “glitch” energy and at low power consumption. Monotonic
multiplying performance is attained over a wide 20 to 1 reference current range. Matching to within 1 LSB between refer-
(Universal Digital Logic Interface)
DAC08
ence and full-scale currents eliminates the need for full-scale
trimming in most applications. Direct interface to all popular
logic families with full noise immunity is provided by the high
swing, adjustable threshold logic input.
High voltage compliance complementary current outputs are
provided, increasing versatility and enabling differential operation to effectively double the peak-to-peak output swing. In
many applications, the outputs can be directly converted to voltage without the need for an external op amp.
All DAC08 series models guarantee full 8-bit monotonicity, and
nonlinearities as tight as ±0.1% over the entire operating temperature range are available. Device performance is essentially
unchanged over the ±4.5 V to ±18 V power supply range, with
33 mW power consumption attainable at ± 5 V supplies.
The compact size and low power consumption make the
DAC08 attractive for portable and military/aerospace applications; devices processed to MIL-STD-883, Level B are
available.
DAC08 applications include 8-bit, 1 µs A/D converters, servo
motor and pen drivers, waveform generators, audio encoders
and attenuators, analog meter drivers, programmable power
supplies, CRT display drivers, high-speed modems and other
applications where low cost, high speed and complete input/output versatility are required.
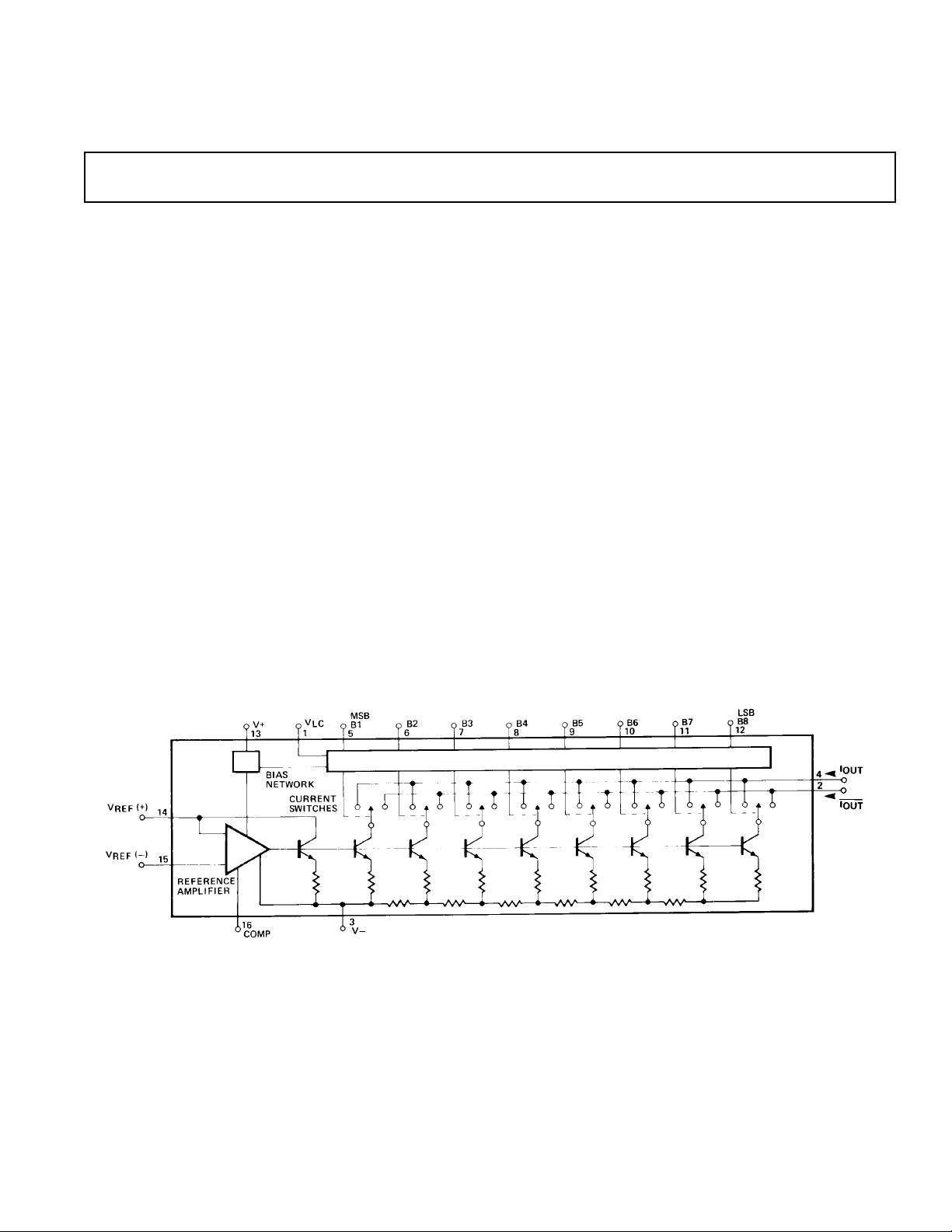
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
Page 2
DAC08–SPECIFICA TIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DAC08C, E & H unless otherwise noted. Output characteristics refer to both I
(@ VS = 615 V, I
= 2.0 mA, –558C ≤ TA ≤ +1258C for DAC08/08A, 08C ≤ TA ≤ +708C for
REF
I
OUT
and
.)
OUT
DAC08A/H DAC08E DAC08C
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
Resolution 8 8 8 Bits
Monotonicity 8 8 8 Bits
Nonlinearity NL ±0.1 ±0.19 ±0.39 % FS
Settling Time t
Propagation Delay
Each Bit t
All Bits Switched t
Full-Scale Tempco
1
S
PLH
PHL
TCI
To ±1/2 LSB, 85 135 85 150 85 150 ns
All Bits Switched ON
or OFF, T
TA = 25°C
= 25°C
A
1
1
35 60 35 60 35 60 ns
35 60 35 60 35 60 ns
FS
±10 ±50 ±10 ±80 ± 10 ±80 ppm/°C
DAC08E ±50
Output Voltage
Compliance V
Full-Scale Current
OC
(True Compliance) Change <1/2 LSB, –10 +18 –10 +18 –10 +18 V
> 20 MΩ typ
R
Full Range Current I
FR4
OUT
V
= 10.000 V 1.984 1.992 2.000 1.94 1.99 2.04 1.94 1.99 2.04 mA
REF
R14, R15 = 5.000 kΩ
= +25°C
T
Full Range Symmetry I
Zero-Scale Current I
Output Current Range I
I
FRS
ZS
OR1
OR2
A
I
FR4
– I
FR2
±0.5 ±4 ±1 ±8 ±2 ±16 µA
0.1 1 0.2 2 0.2 4 µA
R14, R15 = 5.000 kΩ 2.1 2.1 2.1 mA
V
= +15.0 V,
REF
V– = –10 V
= +25.0 V, 4.2 4.2 4.2 mA
V
REF
V– = –12 V
Output Current Noise I
= 2 mA 25 25 25 nA
REF
Logic Input Levels
Logic “0” V
Logic Input “1” V
Logic Input Current V
Logic “0” I
Logic Input “1” I
IL
IH
Logic Input Swing V
Logic Threshold Range V
Reference Bias Current I
15
Reference Input dI/dt R
Slew Rate R
Power Supply Sensitivity PSSI
PSSI
Power Supply Current I+ V
VLC = 0 V 0.8 0.8 0.8 V
IL
IL
= 0 V
LC
22 2 V
VIN = –10 V to +0.8 V –2 –10 –2 –10 –2 –10 µA
VIN = 2.0 V to 18 V 0.002 10 0.002 10 0.002 10 µA
V– = –15 V –10 +18 –10 +18 –10 +18 V
IS
THR
VS = ±15 V
1
–10 +13.5 –10 +13.5 –10 +13.5 V
–1 –3 –1 –3 –1 –3 µA
= 200 Ω 4 8 4 8 4 8 mA/µs
EQ
= 100 Ω
L
= 0 pF See Fast Pulsed Ref. Info Following.
C
C
V+ = 4.5 V to 18 V ±0.0003 ±0.01 ±0.0003 ±0.01 ±0.0003 ±0.01 %∆IO/%∆V+
FS+
V– = –4.5 V to –18 V ± 0.002 ±0.01 ±0.002 ±0.01 ±0.002 ±0.01 %∆IO/%∆V–
FS–
I
= 1.0 mA
REF
= ±5 V, I
S
= 1.0 mA 2.3 3.8 2.3 3.8 2.3 3.8 mA
REF
1
I– –4.3 –5.8 –4.3 –5.8 –4.3 –5.8 mA
I+ V
I– I
I+ V
= +5 V, –15 V, 2.4 3.8 2.4 3.8 2.4 3.8 mA
S
= 2.0 mA –6.4 –7.8 –6.4 –7.8 –6.4 –7.8 mA
REF
= ±15 V, I
S
= 2.5 3.8 2.5 3.8 2.5 3.8 mA
REF
I– 2.0 mA –6.5 –7.8 –6.5 –7.8 –6.5 –7.8 mA
Power Dissipation P
±5 V, I
d
+5 V, –15 V, I
2.0 mA 108 136 103 136 108 136 mW
±15 V, I
NOTES
1
Guaranteed by design.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= 1.0 mA 33 48 33 48 33 48 mW
REF
=
REF
= 2.0 mA 135 174 135 174 135 174 mW
REF
–2–
REV. A
Page 3
DAC08
TYPICAL ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
characteristics apply to both I
OUT
and
I
.)
OUT
(@ VS = 615 V, and I
= 2.0 mA, unless otherwise noted. Output
REF
All Grades
Parameter Symbol Conditions Typical Units
Reference Input Slew Rate dI/dt 8 mA/µs
Propagation Delay t
Settling Time t
PLH
S
, t
PHL
TA = 25°C, Any Bit 35 ns
To +1/2 LSB, All Bits
Switched ON or OFF, 85 ns
TA = 25°C
NOTES
For DAC08NT & GT 25°C characteristics, see DAC08N & G characteristics respectively.
Specifications subject to change without notice
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Operating Temperature
DAC08AQ, Q . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–55°C to +125°C
DAC08HQ, EQ, CQ, HP, EP, CP, CS . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
Junction Temperature (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–65°C to +150°C
J
1
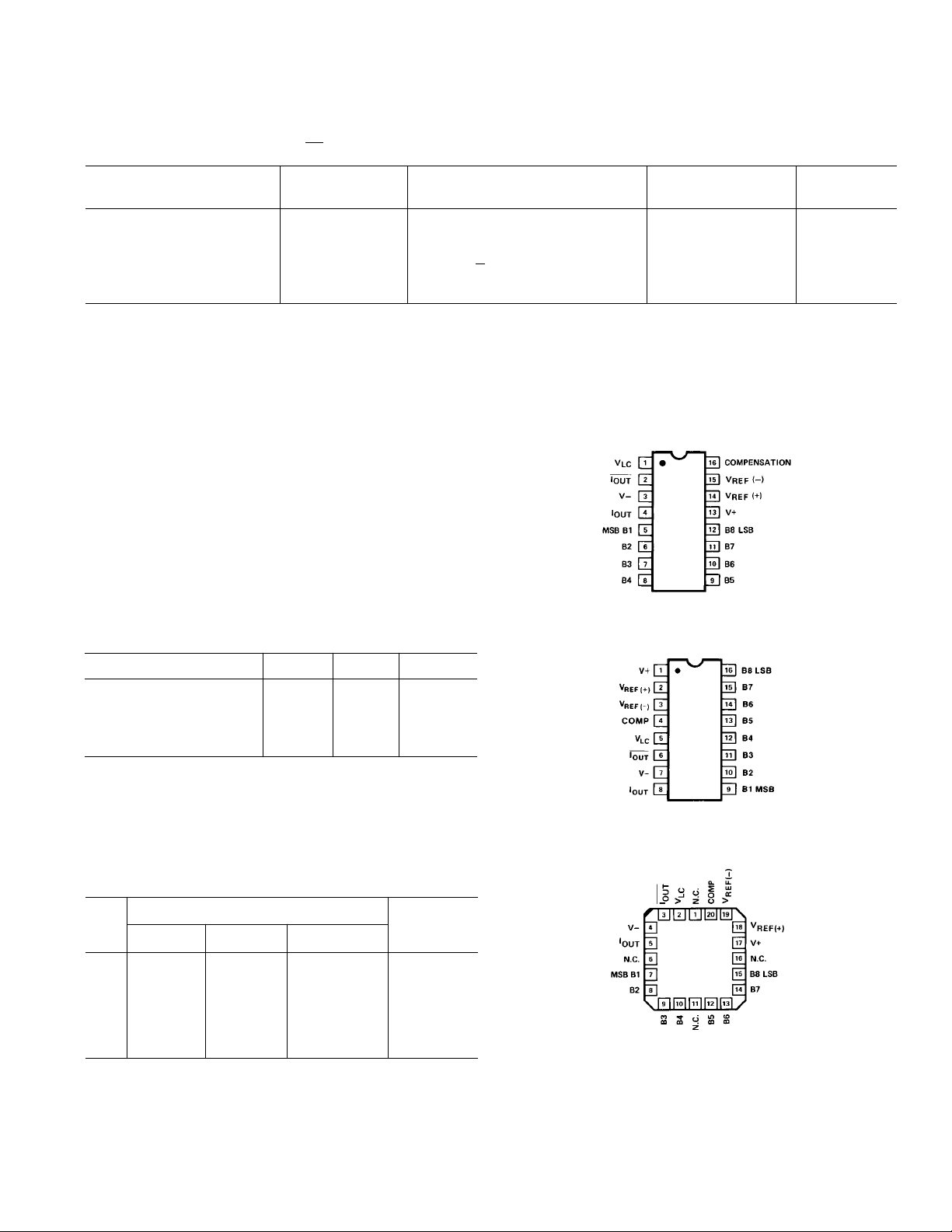
PIN CONNECTIONS
16-Pin Dual-In-Line Package
(Q Suffix)
Storage Temperature Q Package . . . . . . . . . .–65°C to +150°C
Storage Temperature P Package . . . . . . . . . .–65°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300°C
V+ Supply to V– Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36 V
Logic Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .V– to V– plus 36 V
V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V– to V+
LC
Analog Current Outputs (at V
Reference Input (V
to V15) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V– to V+
14
– = 15 V) . . . . . . . . . . 4.25 mA
S
Reference Input Differential Voltage
(V
to V15) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
14
Reference Input Current (I
Package Type u
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.0 mA
14
2
JA
u
JC
Units
16-Lead SO
(S Suffix)
16-Pin Hermetic DIP (Q) 100 16 °C/W
16-Pin Plastic DIP (P) 82 39 °C/W
20-Contact LCC (RC) 76 36 °C/W
16-Pin SO (S) 111 35 °C/W
NOTES
1
Absolute maximum ratings apply to both DICE and packaged parts, unless
otherwise noted.
2
θJA is specified for worst case mounting conditions, i.e., θJA is specified for device
in socket for cerdip, P-DIP, and LCC packages; θJA is specified for device soldered
to printed circuit board for SO package.
DAC08RC/883 20-Lead LCC
(RC Suffix)
ORDERING GUIDE
16-Pin Dual-In-Line Package Operating
NL Hermetic Plastic LCC Range
0.1% DAC08AQ
DAC08HQ DAC08HP COM
0.19% DAC08Q
DAC08EQ DAC08EP COM
0.39% DAC08CQ DAC08CP COM
NOTES
1
Burn-in is available on commercial and industrial temperature range parts in
cerdip, plastic DIP, and TO-can packages.
2
For devices processed in total compliance to MIL-STD-883, add /883 after
part number. Consult factory for 883 data sheet.
3
For availability and burn-in information on SO and PLCC packages, contact
your local sales office.
2
2
DAC08CS
DAC08RC/883 MIL
3
1
Temperature
MIL
COM
REV. A
NC = NO CONNECT
–3–
Page 4
DAC08
WAFER TEST LIMITS
(@ VS = 615 V, I
DAC08G and DAC08GR devices, unless otherwise noted. Output characteristics apply to both I
= 2.0 mA, TA = 1258C for DAC08NT, DAC08GT devices; TA = 258C for DAC08N,
REF
I
OUT
and
.)
OUT
DAC08NT DAC08N DAC08GT DAC08G DAC08GR
Parameter Symbol Conditions Limit Limit Limit Limit Limit Units
Resolution 8 8 8 8 8 Bits min
Monotonicity 8 8 8 8 8 Bits min
Nonlinearity NL ±0.1 ±0.1 ±0.19 ±0.19 ±0.39 % FS max
Output Voltage V
OC
Full-Scale Current +18 +18 +18 +18 +18 V max
Compliance Change < 1/2 LSB –10 –10 –10 –10 –10 V min
Full-Scale Current I
Full-Scale Symmetry I
Zero-Scale Current I
Output Current Range I
or V
FS4
I
FS2
FSS
ZS
FS1
= 10.000 V 2.04 2.04 2.04 2.04 2.04 mA max
REF
R14, R15 = 5.000 kΩ 1.94 1.94 1.94 1.94 1.94 mA min
±8 ±8 ±8 ±8 ±16 µA max
22444µA max
V– = –10 V,
= +15 V 2.1 2.1 2.1 2.1 2.1 mA min
V
REF
V– = –12 V,
V
I
FS2
Logic Input “0” V
Logic Input “1” V
IL
IH
Logic Input Current V
Logic “0” I
Logic “1” I
Logic Input Swing V
IL
IH
IS
= +25 V 4.2 4.2 4.2 4.2 4.2 mA min
REF
, R15 = 5.000 kΩ
R
14
0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 V max
2 2 2 2 2 V min
= 0 V
LC
VIN = –10 V to +0.8 V ±10 ±10 ±10 ±10 ±10 µA max
VIN = 2.0 V to 18 V ±10 ±10 ±10 ±10 ±10 µA max
V– = –15 V +18 +18 +18 +18 +18 V max
–10 –10 –10 –10 –10 V min
Reference Bias Current I
Power Supply PSSI
Sensitivity PSSI
Power Supply Current I+ V
Power Dissipation P
NOTE
Electrical tests are performed at wafer probe to the limits shown. Due to variations in assembly methods and normal yield loss, yield after packaging is not guaranteed
for standard product dice. Consult factory to negotiate specifications based on dice lot qualification through sample lot assembly and testing.
15
d
V+ = 4.5 V to 18 V 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 % FS/% V max
FS+
V– = –4.5 V to –18 V
FS–
= 1.0 mA
I
REF
= ±15 V 3.8 3.8 3.8 3.8 3.8 mA max
S
≤ 2.0 mA –7.8 –7.8 –7.8 –7.8 –7.8 µA max
I
REF
VS = ±15 V 174 174 174 174 174 mW max
I
≤ 2.0 mA
REF
–3 –3 –3 –3 –3 µA max
DICE CHARACTERISTICS
(+125°C Tested Dice Available)
–4–
REV. A
Page 5

Figure 1. Pulsed Reference Operation
DAC08
Figure 2. Burn-in Circuit
Figure 3. Fast Pulsed Reference
Operation
Figure 4. True and Complimentary
Output Operation
Figure 5. LSB Switching
Figure 6. Full-Scale Settling Time
REV. A
–5–
Page 6

DAC08
–Typical Performance Characteristics
Figure 7. Full-Scale Current
vs. Reference Current
Figure 10. Reference Amp
Common-Mode Range
Figure 8. LSB Propagation
Delay vs. I
Figure 11. Logic Input Current vs.
Input Voltage
FS
Figure 9. Reference Input
Frequency Response
Figure 12. VTH–VLC vs. Temperature
Figure 13. Output Current vs.
Output Voltage (Output
Voltage Compliance)
Figure 14. Output Voltage
Compliance vs. Temperature
–6–
Figure 15. Bit Transfer Characteristics
REV. A
Page 7

DAC08
Figure 16. Power Supply
Current vs. V+
Figure 19. Accomodating Bipolar References Figure 20. Basic Positive Reference Operation
Figure 17. Power Supply
Current vs. V–
BASIC CONNECTIONS
Figure 18. Power Supply
Current vs. Temperature
REV. A
Figure 21. Basic Unipolar Negative Operation
–7–
Page 8

DAC08
Figure 22. Basic Bipolar Output Operation
Figure 23. Recommended Full-Scale Adjustment Circuit
Figure 25. Offset Binary Operation
Figure 24. Basic Negative Reference Operation
–8–
REV. A
Page 9

DAC08
Figure 26. Positive Low Impedance
Output Operation
Figure 28. Interfacing With Various Logic Families
Figure 27. Negative Low Impedance
Output Operation
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
REFERENCE AMPLIFIER SET-UP
The DAC08 is a multiplying D/A converter in which the output
current is the product of a digital number and the input reference current. The reference current may be fixed or may vary
from nearly zero to +4.0 mA. The full-scale output current is a
linear function of the reference current and is given by:
255
I
=
× I
FR
256
, where I
REF
REF
= I14.
In positive reference applications, an external positive reference
voltage forces current through R14 into the V
REF(+)
terminal
(pin 14) of the reference amplifier. Alternatively, a negative reference may be applied to V
flows from ground through R14 into V
at pin 15; reference current
REF(–)
as in the positive
REF(+)
reference case. This negative reference connection has the advantage of a very high impedance presented at pin 15. The voltage at pin 14 is equal to and tracks the voltage at pin 15 due to
the high gain of the internal reference amplifier. R15 (nominally
equal to R14) is used to cancel bias current errors; R15 may be
eliminated with only a minor increase in error.
REV. A
–9–
Bipolar references may be accommodated by offsetting V
REF
or
pin 15. The negative common-mode range of the reference amplifier is given by: V
– = V– plus (I
CM
× 1 kΩ) plus 2.5 V. The
REF
positive common-mode range is V+ less 1.5 V.
When a dc reference is used, a reference bypass capacitor is rec-
ommended. A 5.0 V TTL logic supply is not recommended as a
reference. If a regulated power supply is used as a reference, R14
should be split into two resistors with the junction bypassed to
ground with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
For most applications the tight relationship between I
I
will eliminate the need for trimming I
FS
. If required,
REF
REF
and
full-scale trimming may be accomplished by adjusting the value
of R14, or by using a potentiometer for R14. An improved
method of full-scale trimming which eliminates potentiometer
T.C. effects is shown in the recommended full-scale adjustment
circuit.
Using lower values of reference current reduces negative power
supply current and increases reference amplifier negative commonmode range. The recommended range for operation with a dc
reference current is +0.2 mA to +4.0 mA.
Page 10

DAC08
REFERENCE AMPLIFIER COMPENSATION FOR
MULTIPLYING APPLICATIONS
AC reference applications will require the reference amplifier to
be compensated using a capacitor from pin 16 to V–. The value
of this capacitor depends on the impedance presented to pin 14:
for R14 values of 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 kΩ, minimum values of C
C
are 15, 37, and 75 pF. Larger values of R14 require proportionately increased values of C
the ratio of C
(pF) to R14 (kΩ) = 15.
C
for proper phase margin, such that
C
For fastest response to a pulse, low values of R14 enabling small
C
values should be used. If pin 14 is driven by a high imped-
C
ance such as a transistor current source, none of the above values will suffice and the amplifier must be heavily compensated
which will decrease overall bandwidth and slew rate. For R14 =
1 kΩ and C
enabling a transition from I
= 15 pF, the reference amplifier slews at 4 mA/µs
C
= 0 to I
REF
= 2 mA in 500 ns.
REF
Operation with pulse inputs to the reference amplifier may be
accommodated by an alternate compensation scheme. This
technique provides lowest full-scale transition times. An internal
clamp allows quick recovery of the reference amplifier from a
cutoff (I
= 0) condition. Full-scale transition (0 mA to 2 mA)
REF
occurs in 120 ns when the equivalent impedance at pin 14 is
200 Ω and C
which is relatively independent of R
LOGIC INPUTS
= 0. This yields a reference slew rate of 16 mA/µs
C
and VIN values.
IN
The DAC08 design incorporates a unique logic input circuit
which enables direct interface to all popular logic families and
provides maximum noise immunity. This feature is made possible by the large input swing capability, 2 µA logic input cur-
rent and completely adjustable logic threshold voltage. For V– =
–15 V, the logic inputs may swing between –10 V and +18 V.
This enables direct interface with +15 V CMOS logic, even
when the DAC08 is powered from a +5 V supply. Minimum input logic swing and minimum logic threshold voltage are given
by: V– plus ( I
× 1 kΩ) plus 2.5 V. The logic threshold may
REF
be adjusted over a wide range by placing an appropriate voltage
at the logic threshold control pin (pin 1, V
graph shows the relationship between V
temperature range, with V
nominally 1.4 above VLC. For
TH
). The appropriate
LC
and VTH over the
LC
TTL and DTL interface, simply ground pin 1. When interfacing
ECL, an I
= 1 mA is recommended. For interfacing other
REF
logic families, see preceding page. For general set-up of the logic
control circuit, it should be noted that pin 1 will source 100 µA
typical; external circuitry should be designed to accommodate
this current.
Fastest settling times are obtained when pin 1 sees a low impedance. If pin 1 is connected to a 1 kΩ divider, for example, it
should be bypassed to ground by a 0.01 µF capacitor.
ANALOG OUTPUT CURRENTS
Both true and complemented output sink currents are provided
where I
+
= IFS. Current appears at the “true” (IO) output
O
I
O
when a “1” (logic high) is applied to each logic input. As the binary count increases, the sink current at pin 4 increases proportionally, in the fashion of a “positive logic” D/A converter. When a
“0” is applied to any input bit, that current is turned off at pin 4
and turned on at pin 2. A decreasing logic count increases
as
I
O
in a negative or inverted logic D/A converter. Both outputs may
be used simultaneously. If one of the outputs is not required it
must be connected to ground or to a point capable of sourcing
I
; do not leave an unused output pin open.
FS
Both outputs have an extremely wide voltage compliance enabling fast direct current-to-voltage conversion through a resistor tied to ground or other voltage source. Positive compliance
is 36 V above V– and is independent of the positive supply.
Negative compliance is given by V– plus (I
× 1 kΩ) plus 2.5 V.
REF
The dual outputs enable double the usual peak-to-peak load
swing when driving loads in quasi-differential fashion. This feature is especially useful in cable driving, CRT deflection and in
other balanced applications such as driving center-tapped coils
and transformers.
POWER SUPPLIES
The DAC08 operates over a wide range of power supply voltages from a total supply of 9 V to 36 V. When operating at supplies of ±5 V or less, I
≤ 1 mA is recommended. Low
REF
reference current operation decreases power consumption and
increases negative compliance, reference amplifier negative
common-mode range, negative logic input range, and negative
logic threshold range; consult the various figures for guidance.
For example, operation at –4.5 V with I
= 2 mA is not rec-
REF
ommended because negative output compliance would be reduced to near zero. Operation from lower supplies is possible,
however at least 8 V total must be applied to insure turn-on of
the internal bias network.
Symmetrical supplies are not required, as the DAC08 is quite
insensitive to variations in supply voltage. Battery operation is
feasible as no ground connection is required: however, an artificial ground may be used to insure logic swings, etc. remain between acceptable limits.
Power consumption may be calculated as follows:
Pd = (I+) (V+) + (I–) (V–). A useful feature of the DAC08 design
is that supply current is constant and independent of input logic
states; this is useful in cryptographic applications and further
serves to reduce the size of the power supply bypass capacitors.
TEMPERATURE PERFORMANCE
The nonlinearity and monotonicity specifications of the DAC08
are guaranteed to apply over the entire rated operating temperature range. Full-scale output current drift is low, typically
±10 ppm/°C, with zero-scale output current and drift essentially
negligible compared to 1/2 LSB.
The temperature coefficient of the reference resistor R14 should
match and track that of the output resistor for minimum overall
full-scale drift. Settling times of the DAC08 decrease approximately 10% at –55°C; at +125°C an increase of about 15%
is typical.
The reference amplifier must be compensated by using a capacitor from pin 16 to V–. For fixed reference operation, a 0.01 µF
capacitor is recommended. For variable reference applications,
see previous section entitled “Reference Amplifier Compensation for Multiplying Applications”.
–10–
REV. A
Page 11

DAC08
MULTIPLYING OPERATION
The DAC08 provides excellent multiplying performance with an
extremely linear relationship between I
and I
FS
over a range
REF
of 4 mA to 4 mA. Monotonic operation is maintained over a
typical range of I
SETTLING TIME
from 100 µA to 4.0 mA.
REF
The DAC08 is capable of extremely fast settling times, typically
85 ns at I
= 2.0 mA. Judicious circuit design and careful
REF
board layout must be employed to obtain full performance potential during testing and application. The logic switch design
enables propagation delays of only 35 ns for each of the 8 bits.
Settling time to within 1/2 LSB of the LSB is therefore 35 ns,
with each progressively larger bit taking successively longer. The
MSB settles in 85 ns, thus determining the overall settling time
of 85 ns. Settling to 6-bit accuracy requires about 65 ns to 70 ns.
The output capacitance of the DAC08 including the package is
approximately 15 pF, therefore the output RC time constant
dominates settling time if R
> 500 Ω.
L
Settling time and propagation delay are relatively insensitive to
logic input amplitude and rise and fall times, due to the high
gain of the logic switches. Settling time also remains essentially
constant for I
values. The principal advantage of higher I
REF
REF
values lies in the ability to attain a given output level with lower
load resistors, thus reducing the output RC time constant.
Measurement of settling time requires the ability to accurately
resolve ±4 µA, therefore a 1 kΩ load is needed to provide ad-
equate drive for most oscilloscopes. The settling time fixture
shown in schematic labelled “Settling Time Measurement” uses
a cascode design to permit driving a 1 kΩ load with less than
5 pF of parasitic capacitance at the measurement node. At I
REF
values of less than 1.0 mA, excessive RC damping of the output
is difficult to prevent while maintaining adequate sensitivity.
However, the major carry from 01111111 to 10000000 provides
an accurate indicator of settling time. This code change does
not require the normal 6.2 time constants to settle to within
±0.2% of the final value, and thus settling times may be observed at lower values of I
REF
.
DAC08 switching transients or “glitches” are very low and may
be further reduced by small capacitive loads at the output at a
minor sacrifice in settling time.
Fastest operation can be obtained by using short leads, minimizing output capacitance and load resistor values, and by adequate
bypassing at the supply, reference and V
terminals. Supplies
LC
do not require large electrolytic bypass capacitors as the supply
current drain is independent of input logic states; 0.1 µF capaci-
tors at the supply pins provide full transient protection.
REV. A
Figure 30. Settling Time Measurement
–11–
Page 12

DAC08
0.210 (5.33)
MAX
0.160 (4.06)
0.115 (2.93)
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
N-16
0.840 (21.33)
0.745 (18.93)
16
18
PIN 1
0.022 (0.558)
0.014 (0.356)
0.100
(2.54)
BSC
9
0.280 (7.11)
0.240 (6.10)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.070 (1.77)
0.045 (1.15)
SEATING
PLANE
Q-16
0.130
(3.30)
MIN
0.325 (8.25)
0.300 (7.62)
0.015 (0.381)
0.008 (0.204)
0.195 (4.95)
0.115 (2.93)
000000000
0.005 (0.13) MIN
0.200 (5.08)
MAX
0.200 (5.08)
0.125 (3.18)
0.1574 (4.00)
0.1497 (5.80)
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0040 (0.10)
SEATING
16
0.023 (0.58)
0.014 (0.36)
PLANE
1
0.0500
(1.27)
0.080 (2.03) MAX
PIN 1
0.840 (21.34) MAX
0.100
0.070 (1.78)
(2.54)
0.030 (0.76)
BSC
SO-16
0.3937 (10.00)
0.3859 (9.80)
16 9
PIN 1
BSC
0.0688 (1.75)
0.0532 (1.35)
0.0192 (0.49)
0.0138 (0.35)
9
0.310 (7.87)
0.220 (5.59)
8
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.2550 (6.20)
81
0.2284 (5.80)
0.150
(3.81)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
0.0099 (0.25)
0.0075 (0.19)
0.320 (8.13)
0.290 (7.37)
15°
0°
0.0196 (0.50)
0.0099 (0.25)
8°
0°
0.0500 (1.27)
0.0160 (0.41)
0.015 (0.38)
0.008 (0.20)
x 45°
0.358 (9.09)
0.342 (8.69)
SQ
TOP
VIEW
0.100 (2.54)
0.064 (1.63)
0.358
(9.09)
MAX
SQ
0.088 (2.24)
0.054 (1.37)
E-20
0.095 (2.41)
0.075 (1.90)
0.011 (0.28)
0.007 (0.18)
R TYP
0.075 (1.91)
REF
–12–
0.075
(1.91)
REF
19
13
0.055 (1.40)
0.045 (1.14)
0.200 (5.08)
BSC
20
18
1
BOTTOM
VIEW
14
0.150 (3.81)
0.100 (2.54) BSC
3
4
8
9
45° TYP
BSC
0.015 (0.38)
MIN
0.028 (0.71)
0.022 (0.56)
0.050 (1.27)
BSC
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...