Page 1
1
Features
■ Direct Sensor Input
■ High Output Torque
■ Wide Output Voltage
Range
■ High Impedance Inputs
■ Accurate down to 10V V
CC
■ Fault Protection
Overvoltage
Short Circuit
■ Low Voltage Operation
Package Options
16 Lead PDIP
(internally fused leads)
CS8191
Precision Air-Core Tach/Speedo Driver
with Short Circuit Protection
20 Lead SOIC
(internally fused leads)
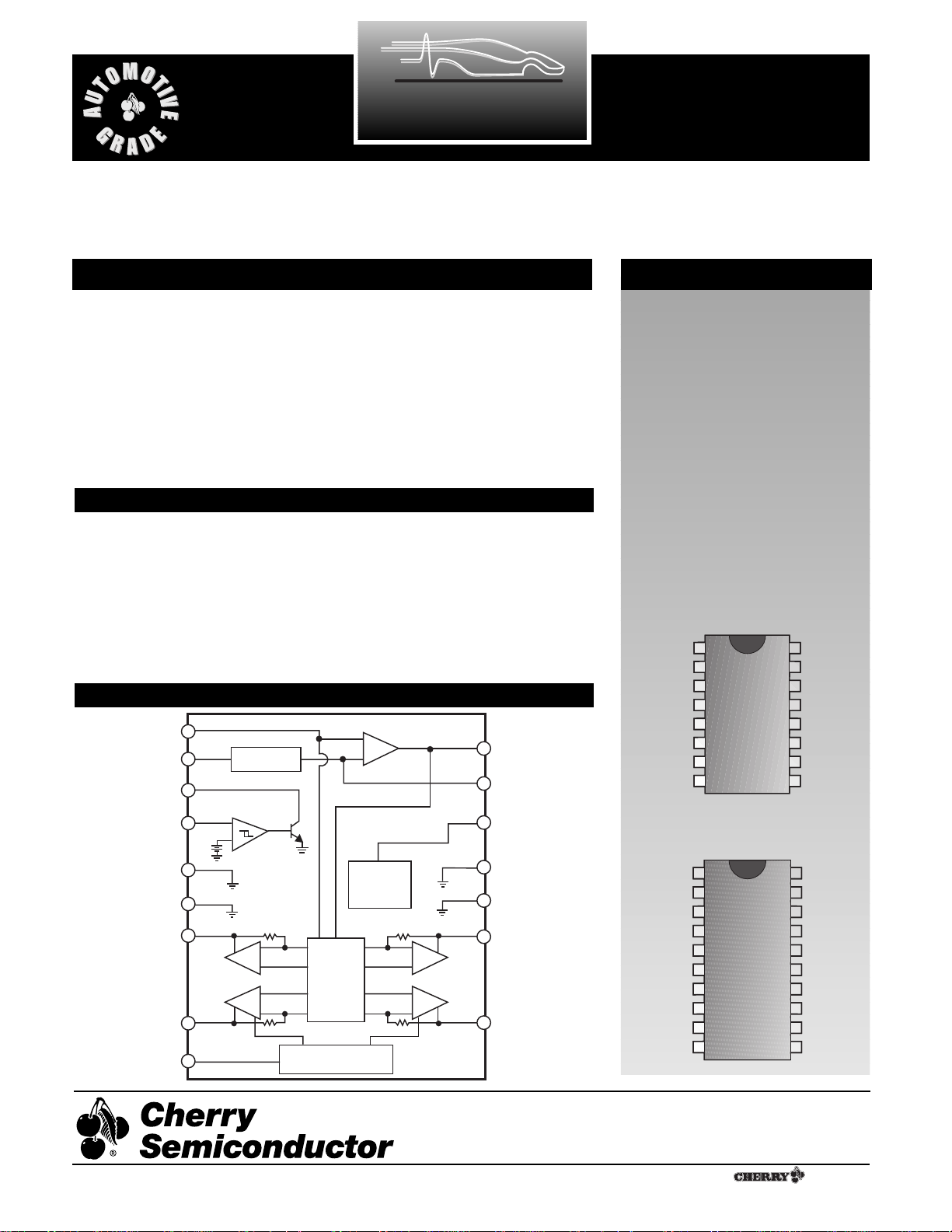
1
CP+
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SQ
OUT
FREQ
IN
NC
Gnd
Gnd
NC
COS+
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
CP-
F/V
OUT
V
REG
NC
Gnd
Gnd
NC
SIN+
9
COS-
SIN-
17
18
V
CC
BIAS
19
20
Description
Block Diagram
Absolute Maximum Ratings
The CS8191 is specifically designed
for use with 4 quadrant air-core
meter movements. The IC includes
an input comparator for sensing
input frequency such as vehicle
speed or engine RPM, a charge
pump for frequency to voltage conversion, a bandgap reference for
stable operation and a function
generator with sine and cosine
amplifiers that differentially drive
the motor coils.
The CS8191 has a higher torque
output and better output signal
symmetry than other competitive
parts (CS289, and LM1819). It is
protected against short circuit and
overvoltage (60V) fault conditions.
Enhanced circuitry permits functional operation down to 8V.
CS8191
Supply Voltage ( ² 100ms pulse transient) ...........................................V
CC
= 60V
(continuous)..................................................................V
CC
= 24V
Operating Temperature Range ........................................................-40¡C to +105¡C
Junction Temperature Range ...........................................................-40¡C to +150¡C
Storage Temperature Range.............................................................-55¡C to +165¡C
Electrostatic Discharge (Human Body Model)...................................................4kV
Lead Temperature Soldering
Wave Solder (through hole styles only)..................10 sec. max, 260¡C peak
Reflow (SMD styles only)...................60 sec. max above 183¡C, 230¡C peak
Rev 3/9/99
Cherry Semiconductor Corporation
2000 South County Trail, East Greenwich, RI 02818
Tel: (401)885-3600 Fax: (401)885-5786
Email: info@cherry-semi.com
Web Site: www.cherry-semi.com
A Company
¨
BIAS
SQ
FREQ
CP+
OUT
IN
Charge Pump
Input
Comp.
+
Ð
+
Ð
Voltage
Regulator
F/V
CP-
V
OUT
REG
V
1
CC
V
2
REG
BIAS
3
4
Gnd
5
Gnd
COS-
6
SINE-
7
FREQ
8
IN
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
F/V
CP+
CP-
Gnd
Gnd
COS+
SINE+
SQ
OUT
OUT
Gnd
Gnd
COS
COS
V
V
REG
7.0V
+
COS
Output
-
CC
Ð
+
+
Ð
High Voltage, Short
Circuit Protection
Function
Generator
Ð
+
SINE
Output
+
Ð
Gnd
Gnd
SINE+
SINE-
Page 2
2
Electrical Characteristics: -40¡C ² TA² 105¡C, 8V ² VCC² 16V unless otherwise specified.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
CS8191
■ Supply Voltage Section
ICCSupply Current VCC= 16V, -40¡C, No Load 70 125 mA
VCCNormal Operation Range
8.0 13.1 16.0 V
■ Input Comparator Section
Positive Input Threshold 2.4 2.7 3.0 V
Negative Input Threshold 2.0 2.3 V
Input Hysteresis 200 400 1000 mV
Input Bias Current * 0V ² VIN² 8V -2 ±10 µA
Input Frequency Range 0 20 kHz
Input Voltage Range in series with 1k½ -1 V
CC
V
Output V
SAT
ICC= 10mA 0.15 0.40 V
Output Leakage V
CC
= 7V 10 µA
Logic 0 Input Voltage 2.0 V
*Note: Input is clamped by an internal 12V Zener.
■ Voltage Regulator Section
Output Voltage 6.50 7.00 7.50 V
Output Load Current 10 mA
Output Load Regulation 0 to 10 mA 10 50 mV
Output Line Regulation 8.0V ² VCC² 16V 20 150 mV
Power Supply Rejection VCC= 13.1V, 1VP/P1kHz 34 46 dB
■ Charge Pump Section
Inverting Input Voltage 1.5 2.0 2.5 V
Input Bias Current 40 150 nA
V
BIAS
Input Voltage 1.5 2.0 2.5 V
Non Invert. Input Voltage IIN= 1mA 0.7 1.1 V
Linearity* @ 0, 87.5, 175, 262.5, + 350Hz -0.10 0.28 +0.70 %
F/V
OUT
Gain @ 350Hz, CT= 0.0033µF, RT= 243k½ 7 10 13 mV/Hz
Norton Gain, Positive IIN= 15µA 0.9 1.0 1.1 I/I
Norton Gain, Negative IIN= -15µA 0.9 1.0 1.1 I/I
*Note: Applies to % of full scale (270¡).
■ Function Generator Section: -40¡ ² T
A
² 85¡C, VCC= 13.1V unless otherwise noted.
Differential Drive Voltage 10V ² VCC² 16V 7.5 8.0 8.5 V
(V
COS
+ - V
COS
-) Q = 0¡
Differential Drive Voltage 10V ² VCC² 16V 7.5 8.0 8.5 V
(V
SIN
+ - V
SIN
-) Q = 90¡
Differential Drive Voltage 10V ² VCC² 16V -8.5 -8.0 -7.5 V
(V
COS
+ - V
COS
-) Q = 180¡
Differential Drive Voltage 10V ² VCC² 16V -8.5 -8.0 -7.5 V
(V
SIN
+ - V
SIN
-) Q = 270¡
Differential Drive Load 10V ² VCC² 16V, -40¡C 178 ½
25¡C 239 ½
105¡C 314 ½
Zero Hertz Output Voltage -0.08 0.0 +0.08 V
Page 3

3
PACKAGE LEAD # LEAD SYMBOL FUNCTION
CS8191
Electrical Characteristics:
continued
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Package Lead Description
Typical Performance Characteristics
0 45 90 135 180 225 270 315
Output Voltage (V)
Degrees of Deflection (°)
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
COS
SIN
045
90
135 180 225 270 315
F/V Output (V)
Frequency/Output Angle (°)
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Figure 2: Charge Pump Output Voltage vs Output Angle
Figure 1: Function Generator Output Voltage
vs Degrees of Deflection
F/V
OUT
= 2.0V + 2 FREQ ´ CT´ RT´ (V
REG
- 0.7)
■ Function Generator Section: continued
Function Generator Error * Q = 0¡ to 225¡ -2 0 +2 deg
Reference Figures 1 - 4 Q = 226¡ to 305¡ -3 0 +3 deg
Function Generator Error 13.1V ² V
CC
² 16V -1 0 +1 deg
Function Generator Error 13.1V ² V
CC
² 10V -1 0 +1 deg
Function Generator Error 13.1V ² V
CC
² 8.0V -7 0 +7 deg
Function Generator Error 25¡C ² T
A
² 80¡C -2 0 +2 deg
Function Generator Error 25¡C ² T
A
² 105¡C -4 0 +4 deg
Function Generator Error Ð40¡C ² T
A
² 25¡C -2 0 +2 deg
Function Generator Gain T
A
= 25¡C, Q vs F/V
OUT
60 77 95 ¡/V
*Note: Deviation from nominal per Table 1 after calibration at 0¡ and 270¡.
16L PDIP 20L SO
11VCCIgnition or battery supply voltage.
22V
REG
Voltage regulator output.
3 3 BIAS Test point or zero adjustment.
4, 5, 12, 13 5, 6, 15, 16 Gnd Ground Connections.
6 8 COS- Negative cosine output signal.
7 9 SIN- Negative sine output signal.
8 10 FREQ
IN
Speed or rpm input signal.
911SQ
OUT
Buffered square wave output signal.
10 12 SIN+ Positive sine output signal.
11 13 COS+ Positive cosine output signal.
14 18 CP- Negative input to charge pump.
15 19 CP+ Positive input to charge pump.
16 20 F/V
OUT
Output voltage proportional to input signal frequency.
4, 7, 14, 17 NC No connection.
Page 4

4
CS8191
Nominal Angle vs. Ideal Angle (After calibrating at 180¡)
+7V
Ð7V
(V
COS+
) - (V
COS-
)
7V
Angle
-7V
Q
(V
SINE+
) - (V
SINE-
)
]
V
SIN+
Ð V
SIN-
V
COS+
Ð V
COS-
Q = ARCTAN
[
-1.50
Deviation (°)
0 45 90 135 180 225 270 315
-1.25
-1.00
-0.75
-0.50
-0.25
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
1.50
Theoretical Angle (°)
Figure 4: Nominal Output Deviation
Figure 3: Output Angle in Polar Form
Ideal Angle (Degrees)
Nominal Angle (Degrees)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
1 5 9 13 17 21 25 29 33 37 41 45
Ideal Degrees
Nominal Degrees
Typical Performance Characteristics: continued
00
1 1.09
2 2.19
3 3.29
4 4.38
5 5.47
6 6.56
7 7.64
8 8.72
9 9.78
10 10.84
11 11.90
12 12.94
13 13.97
14 14.99
15 16.00
16 17.00
17 17.98
18 18.96
19 19.92
20 20.86
21 21.79
22 22.71
23 23.61
24 24.50
25 25.37
26 26.23
27 27.07
28 27.79
29 28.73
30 29.56
31 30.39
32 31.24
33 32.12
34 33.04
35 34.00
36 35.00
37 36.04
38 37.11
39 38.21
40 39.32
41 40.45
42 41.59
43 42.73
44 43.88
45 45.00
50 50.68
55 56.00
60 60.44
65 64.63
70 69.14
75 74.00
80 79.16
85 84.53
90 90.00
95 95.47
100 100.84
105 106.00
110 110.86
115 115.37
120 119.56
125 124.00
130 129.32
135 135.00
140 140.68
145 146.00
150 150.44
155 154.63
160 159.14
165 164.00
170 169.16
175 174.33
180 180.00
185 185.47
190 190.84
195 196.00
200 200.86
205 205.37
210 209.56
215 214.00
220 219.32
225 225.00
230 230.58
235 236.00
240 240.44
245 244.63
250 249.14
255 254.00
260 259.16
265 264.53
270 270.00
275 275.47
280 280.84
285 286.00
290 290.86
295 295.37
300 299.21
305 303.02
Ideal Q Nominal Ideal Q Nominal Ideal Q Nominal Ideal Q Nominal Ideal Q Nominal Ideal Q Nominal
Degrees Q Degrees Degrees Q Degrees Degrees Q Degrees Degrees Q Degrees Degrees Q Degrees Degrees Q Degrees
Table 1: Function Generator Output Nominal Angle vs. Ideal Angle (After calibrating at 270¡)
Note: Temperature, voltage and nonlinearity not included.
Note: Temperature, voltage and nonlinearity not included.
Page 5

5
The CS8191 is specifically designed for use with air-core
meter movements. It includes an input comparator for
sensing an input signal from an ignition pulse or speed
sensor, a charge pump for frequency to voltage conversion, a bandgap voltage regulator for stable operation,
and a function generator with sine and cosine amplifiers
to differentially drive the motor coils.
From the simplified block diagram of Figure 5A, the
input signal is applied to the FREQINlead, this is the
input to a high impedance comparator with a typical positive input threshold of 2.7V and typical hysteresis of
0.4V. The output of the comparator, SQ
OUT
, is applied to
the charge pump input CP+ through an external capacitor
CT. When the input signal changes state, CTis charged
or discharged through R3 and R4. The charge accumulated on CTis mirrored to C4 by the Norton Amplifier circuit comprising of Q1, Q2 and Q3. The charge pump output voltage, F/V
OUT
, ranges from 2V to 6.3V depending
on the input signal frequency and the gain of the charge
pump according to the formula:
F/V
OUT
= 2.0V + 2 ´ FREQ ´ CT´ RT´ (V
REG
Ð 0.7V)
RTis a potentiometer used to adjust the gain of the F/V
output stage and give the correct meter deflection. The
F/V output voltage is applied to the function generator
which generates the sine and cosine output voltages. The
output voltage of the sine and cosine amplifiers are
derived from the on-chip amplifier and function generator circuitry. The various trip points for the circuit (i.e., 0¡,
90¡, 180¡, 270¡) are determined by an internal resistor
divider and the bandgap voltage reference. The coils are
differentially driven, allowing bidirectional current flow
in the outputs, thus providing up to 305¡ range of meter
deflection. Driving the coils differentially offers faster
response time, higher current capability, higher output
voltage swings, and reduced external component count.
The key advantage is a higher torque output for the
pointer.
The output angle, Q, is equal to the F/V gain multiplied
by the function generator gain:
Q = A
F/V
´ AFG,
where:
A
FG
= 77¡/V (typ)
The relationship between input frequency and output
angle is:
Q = AFG´ 2 ´ FREQ ´ CT´ RT´ (V
REG
Ð 0.7V)
or, Q = 970 ´ FREQ ´ C
T
´ R
T
The ripple voltage at the F/V converterÕs output is determined by the ratio of CTand C4 in the formula:
ÆV =
Ripple voltage on the F/V output causes pointer or needle flutter especially at low input frequencies.
The response time of the F/V is determined by the time
constant formed by RTand C4. Increasing the value of C4
will reduce the ripple on the F/V output but will also
increase the response time. An increase in response time
causes a very slow meter movement and may be unacceptable for many applications.
Design Example
Maximum meter Deflection = 270¡
Maximum Input Frequency = 350Hz
1. Select RTand C
T
Q = A
GEN
´ Æ
F/V
Æ
F/V
= 2 ´ FREQ ´ CT´ RT´ (V
REG
Ð 0.7V)
Q = 970 ´ FREQ ´ CT´ R
T
Let CT= 0.0033µF, Find R
T
RT=
RT= 243k½
RTshould be a 250k½ potentiometer to trim out any inaccuracies due to IC tolerances or meter movement pointer
placement.
2. Select R3 and R4
Resistor R3 sets the output current from the voltage regulator. The maximum output current from the voltage regulator is 10mA, R3 must ensure that the current does not
exceed this limit.
Choose R3 = 3.3k½
The charge current for C
T
is:
= 1.90mA
C1 must charge and discharge fully during each cycle of
the input signal. Time for one cycle at maximum frequency is 2.85ms. To ensure that CTis discharged, assume that
the (R3 + R4) CTtime constant is less than 10% of the
minimum input frequency pulse width.
T = 285µs
Choose R4 = 1k½.
Charge time: T = R3 ´ C
T
= 3.3k½ ´ 0.0033µF = 10.9µs
Discharge time:T = (R3 + R4)C
T
= 4.3k½ ´ 0.0033µF = 14.2µs
3. Determine C4
C4 is selected to satisfy both the maximum allowable ripple voltage and response time of the meter movement.
C4 =
With C4 = 0.47µF, the F/V ripple voltage is 44mV.
Figure 7 shows how the CS8191 and the CS8441 are used
to produce a Speedometer and Odometer circuit.
CT(V
REG
Ð 0.7V)
V
RIPPLE(MAX)
V
REG
Ð 0.7V
3.3k½
270¡
970 ´ 350Hz ´ 0.0033µF
C
T(VREG
Ð 0.7V)
C4
Circuit Description and Application Notes
CS8191
Page 6

+
Ð
R
T
C4
CPÐ
+
Ð
F/V
OUT
F to V
2.5V
Q2
Q1
Q3
0.25V
CP+
R4C
T
VC(t)
+Ð
R3
V
REG
SQ
OUT
Q
SQUARE
2.7V
FREQ
IN
T
PW T-PW
FREQ
IN
I
CP+
SQ
OUT
V
CC
V
REG
0
0
0
V
CP+
Figure 5A: Partial Schematic of Input and Charge Pump
Figure 5B: Timing Diagram of FREQINand I
C
P
6
CS8191
Circuit Description and Application Notes: continued
Page 7

7
CS8191
Speedometer/Odometer or Tachometer Application
In some cases a designer may wish to use the CS8191 only
as a driver for an air-core meter having performed the F/V
conversion elsewhere in the circuit.
Figure 8 shows how to drive the CS8191 with a DC voltage
ranging from 2V to 6V. This is accomplished by forcing a
voltage on the F/V
OUT
lead. The alternative scheme shown
in figure 9 uses an external op amp as a buffer and operates
over an input voltage range of 0V to 4V.
Figure 8. Driving the CS8191 from an external DC voltage.
An alternative solution is to use the CS4101 which has a
separate function generator input lead and can be driven
directly from a DC source. Figure 8 and 9 are not temperature compensated.
Figure 9. Driving the CS8191 from an external DC voltage using an Op
Amp Buffer.
Figure 6
R1 - 3.9, 500mW
R2 - 10k½
R3 - 3k½
R4 - 1k½
R
T
- Trim Resistor +/- 20 PPM/DEG. C
C1 - 0.1µF
C2 - With CS-8441 application, 10µF
C3 - 0.1µF
C4 - 0.47µF
C
T
- 0.0033µF, +/- 30 PPM/¡C
D1 - 1A, 600 PIV
D2 - 50V, 500mW Zener
Note 1: The product of C
T
and RThave a direct effect on gain and
therefore directly effect temperature compensation.
Note 2: C4 Range; 20pF to .2µF.
Note 3: R4 Range; 100k½ to 500k½.
Figure 7
Note 4: The IC must be protected from transients above 60V and reverse
battery conditions.
Note 5: Additional filtering on the FREQ
IN
lead may be required.
Ground
Battery
D1
R2
Typical Speedometer
Input
CP+
V
CC
V
REG
BIAS
Gnd
Gnd
COS-
SINE-
FREQ
CS8191
IN
SINE
COSINE
COS+
SINE+
SQ
F/V
CP+
CP-
Gnd
Gnd
OUT
16
OUT
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C4
Air Core
Gauge
Speedometer
R
+
T
R4
R3
C
T
Battery
R1
D1
Ground
R2
Typical Speedometer
Input
1
CC
2
V
C1
D2
C3
C2
REG
BIAS
3
Gnd
4
Gnd
5
COS-
6
SINE-
7
8
FREQ
1
IN
SINE
COSINE
OUT
CP+
CP-
Gnd
Gnd
CS8191
COS+
SINE+
SQ
OUT
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
Speedometer
Air Core
Gauge
C4
R
+
T
R4
R3
C
T
F/V
V
CP+
CS8441
R1
C1
D2
C3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VREG
V
IN
2V to 6V DC
100kW
10kW
N/C
F/VOUT
CP
-
BIAS
CS8191
-
+
Air Core
Stepper Motor
200W
Odometer
BIAS
CP
CS8191
+
-
-
V
IN
0V to 4V DC
100kW
100kW
+
-
100kW
100kW
10kW
F/VOUT
Page 8

D
Lead Count Metric English
Max Min Max Min
16L PDIP (internally fused leads) 19.69 18.67 .775 .735
20L SOIC (internally fused leads) 13.00 12.60 .512 .496
8
Rev. 3/9/99
CS8191
Thermal Data 16L PDIP* 20L SOIC*
R
QJC
typ
15 9 ûC/W
R
QJA
typ 50 55 ûC/W
Package Specification
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS IN mm (INCHES)
PACKAGE THERMAL DATA
Part Number Description
CS8191XNF16 16L PDIP (internally fused leads)
CS8191XDWF20 20L SOIC (internally fused leads)
CS8191XDWFR20 20L SOIC (internally fused leads)
(tape & reel)
Ordering Information
© 1999 Cherry Semiconductor Corporation
Cherry Semiconductor Corporation reserves the
right to make changes to the specifications without
notice. Please contact Cherry Semiconductor
Corporation for the latest available information.
Plastic DIP (N); 300 mil wide
0.39 (.015)
MIN.
2.54 (.100) BSC
1.77 (.070)
1.14 (.045)
D
Some 8 and 16 lead
packages may have
1/2 lead at the end
of the package.
All specs are the same.
.203 (.008)
.356 (.014)
REF: JEDEC MS-001
3.68 (.145)
2.92 (.115)
8.26 (.325)
7.62 (.300)
7.11 (.280)
6.10 (.240)
.356 (.014)
.558 (.022)
1.27 (.050) BSC
7.60 (.299)
7.40 (.291)
10.65 (.419)
10.00 (.394)
D
0.32 (.013)
0.23 (.009)
1.27 (.050)
0.40 (.016)
REF: JEDEC MS-013
2.49 (.098)
2.24 (.088)
0.51 (.020)
0.33 (.013)
2.65 (.104)
2.35 (.093)
0.30 (.012)
0.10 (.004)
Surface Mount Wide Body (DW); 300 mil wide
*Internally Fused Leads
 Loading...
Loading...