Datasheet CLC452MDC, CLC452AJP, CLC452AJM5X, CLC452AJM5, CLC452AJE-TR13 Datasheet (NSC)
...Page 1
Features
■
100mA output current
■
3.0mA supply current
■
130MHz bandwidth (Av= +2)
■
-78/-85dBc HD2/HD3 (1MHz)
■
25ns settling to 0.05%
■
400V/µs slew rate
■
Stable for capacitive loads up to 1000pF
■
Single 5V to ±5V supplies
■
Available in Tiny SOT23-5 package
Applications
■
Coaxial cable driver
■
Twisted pair driver
■
Transformer/Coil Driver
■
High capacitive load driver
■
Video line driver
■
Portable/battery-powered applications
■
A/D driver
V
EE
+
-
CLC452
1kΩ
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
+5V
3
2
4
7
6
+
1kΩ
5kΩ
5kΩ
0.1µF
10m of 75Ω
Coaxial Cable
75Ω
0.1µF
75Ω
0.1µF
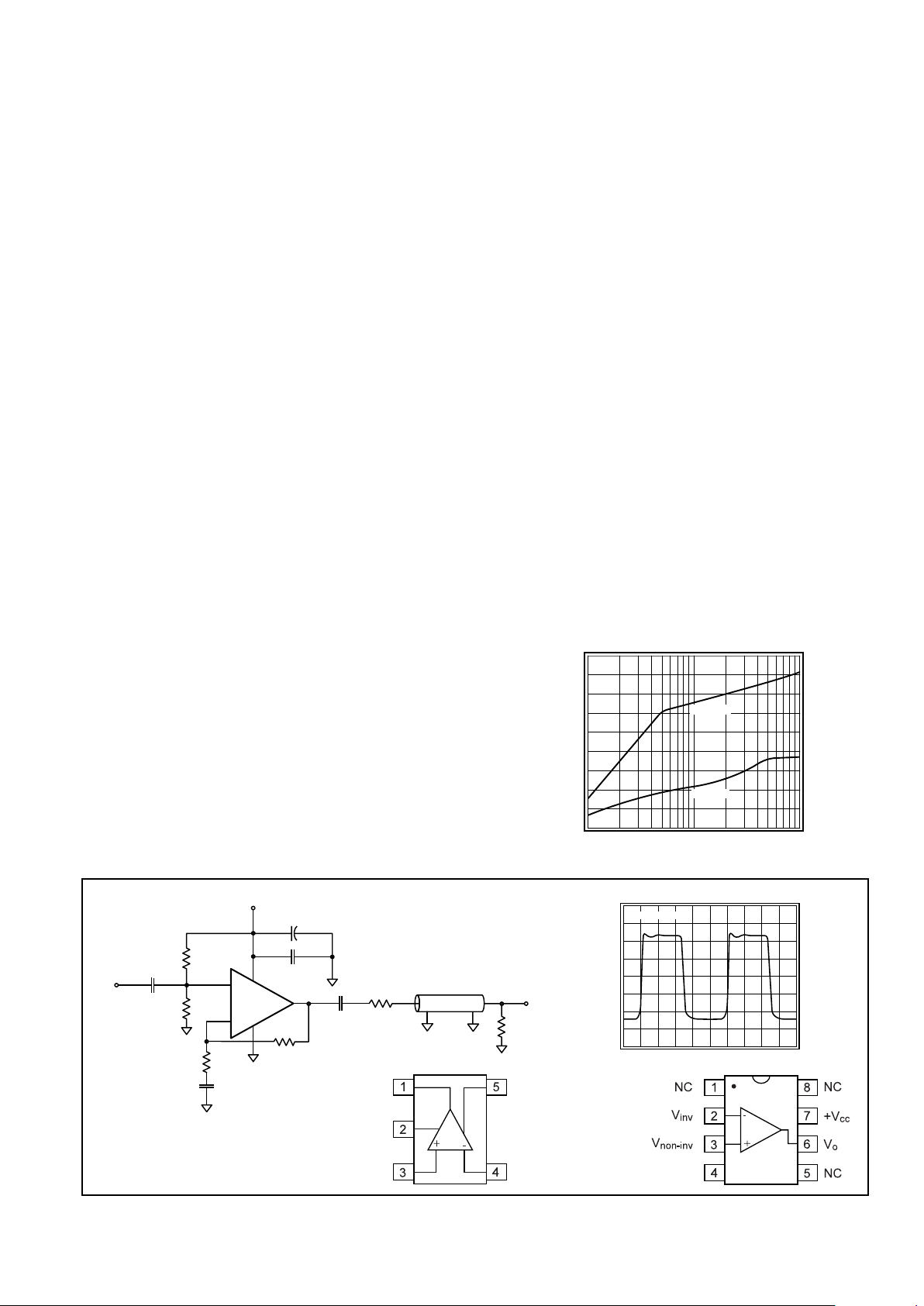
Typical Application
Single Supply Cable Driver
Pinout
DIP & SOIC
General Description
The CLC452 has a new output stage that delivers high output
drive current (100mA), but consumes minimal quiescent supply
current (3.0mA) from a single 5V supply. Its current feedback
architecture, fabricated in an advanced complementary bipolar
process, maintains consistent performance over a wide range of
gains and signal levels, and has a linear-phase response up to
one half of the -3dB frequency.
The CLC452 offers superior dynamic performance with a
130MHz small-signal bandwidth, 400V/µs slew rate and 4.5ns
rise/fall times (2V
step
). The combination of low quiescent power,
high output current drive, and high-speed performance make
the CLC452 well suited for many battery-powered personal
communication/computing systems.
The ability to drive low-impedance, highly capacitive loads,
makes the CLC452 ideal for single ended cable applications. It
also drives low impedance loads with minimum distortion. The
CLC452 will drive a 100Ω load with only -75/-74dBc second/third
harmonic distortion (Av= +2, V
out
= 2Vpp, f = 1MHz). With a 25Ω
load, and the same conditions, it produces only -65/-77dBc second/third harmonic distortion. It is also optimized for driving high
currents into single-ended transformers and coils.
When driving the input of high-resolution A/D converters, the
CLC452 provides excellent -78/-85dBc second/third harmonic
distortion (Av= +2, V
out
= 2Vpp, f = 1MHz, RL= 1kΩ) and fast
settling time.
Available in SOT23-5, the CLC452 is ideal for applications where
space is critical.
Maximum Output Voltage vs. R
L
Output Voltage (V
pp
)
RL (Ω)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
10
100
1000
Vs = +5V
VCC = ±5V
CLC452
Single Supply, Low-Power, High Output,
Current Feedback Amplifier
N
June 1999
CLC452
Single Supply, Low-Power, High Output, Current Feedback Amp
Response After 10m of Cable
100mV/div
20ns/div
Vin = 10MHz, 0.5V
pp
V
inv
V
CC
V
EE
V
o
V
non-inv
Pinout
SOT23-5
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation http://www.national.com
Printed in the U.S.A.
Page 2
http://www.national.com 2
PARAMETERS CONDITIONS TYP MIN/MAX RATINGS UNITS NOTES
Ambient T emper ature CLC452AJ +25°C +25°C 0 to 70°C -40 to 85°C
FREQUENCY DOMAIN RESPONSE
-3dB bandwidth V
o
= 0.5V
pp
130 95 90 85 MHz
V
o
= 2.0V
pp
95 80 77 75 MHz
-
0.1dB bandwidth Vo= 0.5V
pp
30 25 20 20 MHz
gain peaking <200MHz, V
o
= 0.5V
pp
0 0.5 0.9 1.0 dB
gain rolloff <30MHz, V
o
= 0.5V
pp
0.1 0.3 0.3 0.3 dB
linear phase deviation <30MHz, V
o
= 0.5V
pp
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.3 deg
TIME DOMAIN RESPONSE
rise and fall time 2V step 4.5 6.0 6.4 6.8 ns
settling time to 0.05% 1V step 25 – – – ns
overshoot 2V step 11 15 18 18 %
slew rate 2V step 400 300 275 260 V/µs
DISTORTION AND NOISE RESPONSE
2
nd
harmonic distortion 2Vpp, 1MHz -75 -69 -67 -67 dBc
2V
pp
, 1MHz; RL= 1kΩ -78 -70 -68 -68 dBc
2V
pp
, 5MHz -65 -58 -56 -56 dBc
3
rd
harmonic distortion 2Vpp, 1MHz -74 -70 -68 -68 dBc
2V
pp
, 1MHz; RL= 1kΩ -85 -75 -73 -73 dBc
2V
pp
, 5MHz -60 -55 -53 -53 dBc
equivalent input noise
voltage (e
ni
) >1MHz 2.8 3.5 3.8 3.8 nV/√Hz
non-inverting current (i
bn
) >1MHz 7.5 10 11 11 pA/√Hz
inverting current (i
bi
) >1MHz 10.5 14 15 15 pA/√Hz
STATIC DC PERFORMANCE
input offset voltage 1 4 6 6 mV A
average drift 8 – – – µV/˚C
input bias current (non-inverting) 6 18 22 24 µAA
average drift 40 – – – nA/˚C
input bias current (inverting) 6 14 16 17 µAA
average drift 25 – – – nA/˚C
power supply rejection ratio DC 48 45 43 43 dB
common-mode rejection ratio DC 51 48 46 46 dB
supply current R
L
= ∞ 3.0 3.4 3.6 3.6 mA A
MISCELLANEOUS PERFORMANCE
input resistance (non-inverting) 0.39 0.28 0.25 0.25 MΩ
input capacitance (non-inverting) 1.5 2.3 2.3 2.3 pF
input voltage range, High 4.2 4.1 4.0 4.0 V
input voltage range, Low 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.0 V
output voltage range, High R
L
= 100Ω 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.8 V
output voltage range, Low R
L
= 100Ω 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.2 V
output voltage range, High R
L
= ∞ 4.1 4.0 4.0 3.9 V
output voltage range, Low R
L
= ∞ 0.9 1.0 1.0 1.1 V
output current 100 80 65 40 mA B
output resistance, closed loop DC 70 105 105 140 mΩ
Min/max ratings are based on product characterization and simulation. Individual parameters are tested as noted. Outgoing quality levels are
determined from tested parameters.
+5V Electrical Characteristics
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,Vs= +5V1,Vcm= VEE+ (Vs/2), RLtied to Vcm, unless specified)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
supply voltage (VCC- VEE)
+
14V
output current (see note C) 140mA
common-mode input voltage
VEEto
V
CC
maximum junction temperature +150°C
storage temperature range -65°C to +150°C
lead temperature (soldering 10 sec) +300°C
ESD rating (human body model) 500V
Notes
A) J-level:spec is 100% tested at +25°C.
B)The short circuit current can exceed the maximum safe
output current.
1) V
s
= VCC- V
EE
Reliability Information
Transistor Count 49
MTBF (based on limited test data) 31Mhr
Page 3
3 http://www.national.com
PARAMETERS CONDITIONS TYP GUARANTEED MIN/MAX UNITS NOTES
Ambient T emper ature CLC452AJ +25°C +25°C 0 to 70°C -40 to 85°C
FREQUENCY DOMAIN RESPONSE
-3dB bandwidth V
o
= 1.0V
pp
160 135 120 115 MHz
V
o
= 4.0V
pp
75 60 57 55 MHz
-
0.1dB bandwidth Vo= 1.0V
pp
30 25 25 20 MHz
gain peaking <200MHz, V
o
= 1.0V
pp
0 0.5 0.9 1.0 dB
gain rolloff <30MHz, V
o
= 1.0V
pp
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.3 dB
linear phase deviation <30MHz, V
o
= 1.0V
pp
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.3 deg
differential gain NTSC, R
L
=150Ω 0.05 – – – %
differential phase NTSC, R
L
=150Ω 0.08 – – – deg
TIME DOMAIN RESPONSE
rise and fall time 2V step 3.2 4.2 4.5 5.0 ns
settling time to 0.05% 2V step 20 – – – ns
overshoot 2V step 8 12 15 15 %
slew rate 2V step 540 400 370 350 V/µs
DISTORTION AND NOISE RESPONSE
2
nd
harmonic distortion 2Vpp, 1MHz -77 -71 -69 -69 dBc
2V
pp
, 1MHz; RL= 1kΩ -78 -72 -70 -70 dBc
2V
pp
, 5MHz -69 -63 -61 -61 dBc
3
rd
harmonic distortion 2Vpp, 1MHz -72 -68 -66 -66 dBc
2V
pp
, 1MHz; RL= 1kΩ -90 -80 -78 -78 dBc
2V
pp
, 5MHz -58 -54 -52 -52 dBc
equivalent input noise
voltage (e
ni
) >1MHz 2.8 3.5 3.8 3.8 nV/√Hz
non-inverting current (i
bn
) >1MHz 7.5 10 11 11 pA/√Hz
inverting current (i
bi
) >1MHz 10.5 14 15 15 pA/√Hz
STATIC DC PERFORMANCE
input offset voltage 1 6 8 8 mV
average drift 10 – – – µV/˚C
input bias current (non-inverting) 3 18 23 25 µA
average drift 40 – – – nA/˚C
input bias current (inverting) 13 24 31 31 µA
average drift 30 – – – nA/˚C
power supply rejection ratio DC 48 45 43 43 dB
common-mode rejection ratio DC 53 50 48 48 dB
supply current R
L
= ∞ 3.2 3.8 4.0 4.0 mA
MISCELLANEOUS PERFORMANCE
input resistance (non-inverting) 0.52 0.35 0.30 0.30 MΩ
input capacitance (non-inverting) 1.2 1.8 1.8 1.8 pF
common-mode input range
±
4.2
±
4.1
±
4.1
±
4.0 V
output voltage range R
L
= 100Ω
±
3.8
±
3.6
±
3.6
±
3.5 V
output voltage range R
L
= ∞
±
4.0
±
3.8
±
3.8
±
3.7 V
output current 130 100 80 50 mA B
output resistance, closed loop DC 60 90 90 120 mΩ
±5V Electrical Characteristics
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,VCC= ±5V, unless specified)
Notes
B)The short circuit current can exceed the maximum safe
output current.
Ordering Information
Model Temperature Range Description
CLC452AJP -40°C to +85°C 8-pin PDIP
CLC452AJE -40°C to +85°C 8-pin SOIC
CLC452AJM5 -40°C to +85°C 5-pin SOT
CLC452ALC -40°C to +85°C dice
CLC452A8B -55°C to +175°C 8-pin CerDIP,
MIL-STD-883
CLC452ALC -55°C to +175°C dice, MIL-STD-883
Pac kage Thermal Resistance
Package
θθ
JC
θθ
JA
Plastic (AJP) 105°C/W 155°C/W
Surface Mount (AJE) 95°C/W 175°C/W
Surface Mount (AJM5) 140°C/W 210°C/W
Dice (ALC) 25°C/W –
CerDIP (A8B) 70°C/W 215°C/W
Page 4
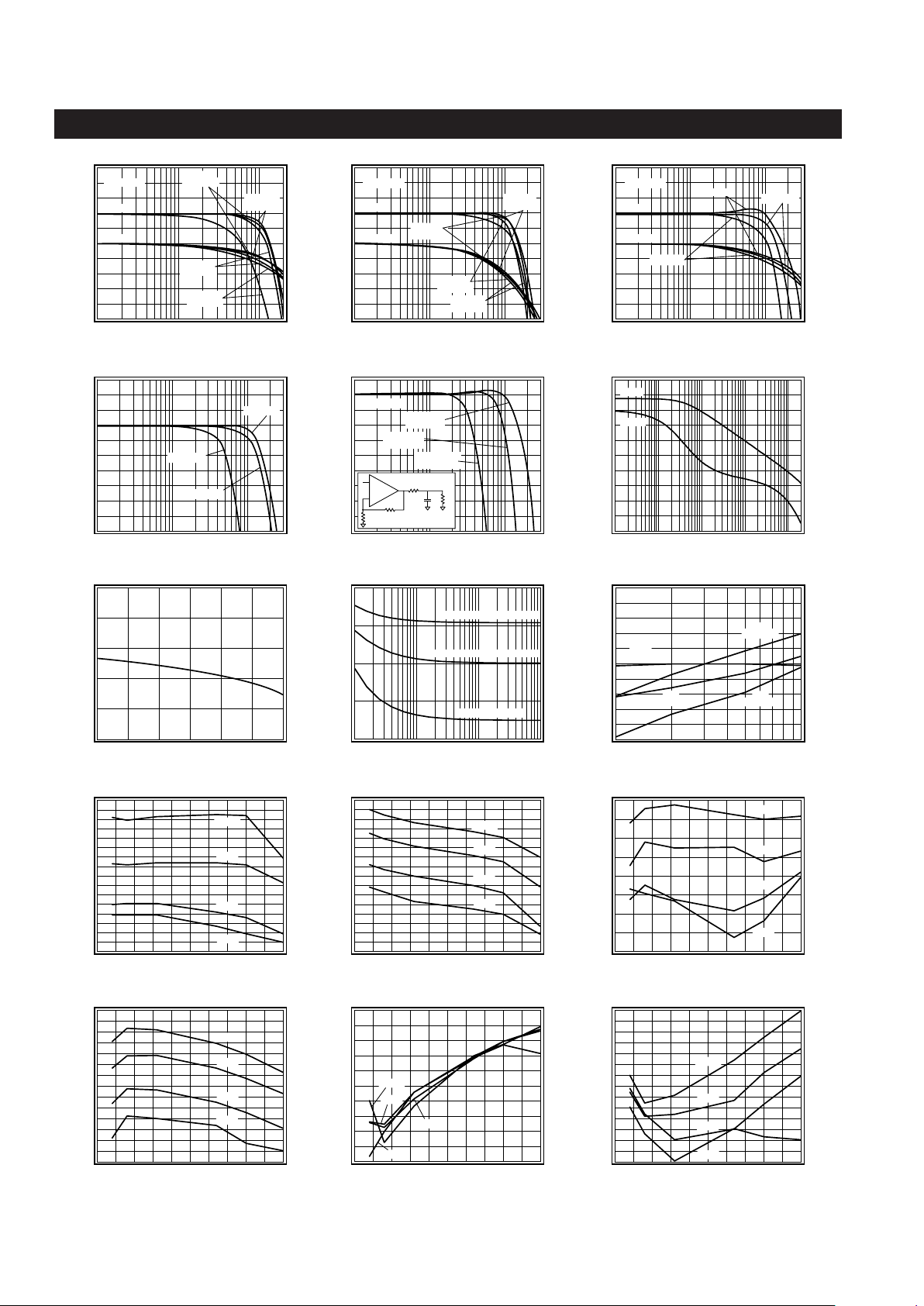
http://www.national.com 4
+5V T ypical P erformance
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,Vs= +5V1,Vcm= VEE+ (Vs/2), RLtied to Vcm, unless specified)
Non-Inverting Frequency Response
Normalized Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-90
0
-180
-450
-270
-360
Gain
Phase
Vo = 0.5V
pp
Av = 2
R
f
= 750Ω
Av = 1
Rf = 1kΩ
Av = 5
Rf = 402Ω
Av = 10
Rf = 249Ω
Inverting Frequency Response
Normalized Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-225
-180
-270
-405
-315
-360
Gain
Phase
Vo = 0.5V
pp
Av = -2
Rf = 604Ω
Av = -1
Rf = 681Ω
Av = -5
Rf = 453Ω
Av = -10
Rf = 402Ω
Frequency Response vs. R
L
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-90
0
-180
-450
-270
-360
Gain
Phase
Vo = 0.5V
pp
RL = 25Ω
RL = 100Ω
RL = 1kΩ
Frequency Response vs. V
o
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Vo = 0.1V
pp
Vo = 1V
pp
Vo = 2.5V
pp
Frequency Response vs. C
L
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Vo = 0.5V
pp
CL = 10pF
Rs = 46.4Ω
CL = 100pF
Rs = 20Ω
CL = 1000pF
Rs = 6.7Ω
C
L
1k
R
s
+
-
1k
1k
Open Loop Transimpedance Gain, Z(s)
Magnitude (dBΩ)
Frequency (Hz)
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
Gain
Phase (deg)
20
60
100
140
180
220
20
40
60
80
100
120
Phase
Gain Flatness
Magnitude (0.05dB/div)
Frequency (MHz)
10
20
30
Equivalent Input Noise
Noise Voltage (nV/√Hz)
Frequency (Hz)
3.2
3.1
1k 100k 1M 10M
3
2.8
2.9
Non-Inverting Current 7.5pA/√Hz
Inverting Current 10.5pA/√Hz
Voltage 2.85nV/√Hz
Noise Current (pA/√Hz)
10
12.5
7.5
2.5
5
2nd & 3rd Harmonic Distortion
Distortion (dBc)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
Vo = 2V
pp
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
2nd
RL = 1kΩ
2nd
RL = 100Ω
3rd
RL = 1kΩ
3rd
RL = 100Ω
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 25Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-44
-46
-48
-50
-52
-54
-56
-58
-60
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 25Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-35
-40
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 100Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 100Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 1kΩ
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 1kΩ
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
Page 5

5 http://www.national.com
+5V T ypical P erformance
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,Vs= + 5V1,Vcm= VEE+ (Vs/2), RLtied to Vcm, unless specified)
Closed Loop Output Resistance
Output Resistance (Ω)
Frequency (Hz)
10k 100k 1M 10M
100M
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
Recommended Rs vs. C
L
R
s
(Ω)
CL (pF)
10 100 1000
0
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
C
L
1k
R
s
+
-
1k
1k
Large & Small Signal Pulse Response
Output Voltage (0.5V/div)
Time (10ns/div)
Large Signal
Small Signal
PSRR & CMRR
PSRR & CMRR (dB)
Frequency (Hz)
1k 10k 100M
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
100k 1M 10M
PSRR
CMRR
IBN, Vos vs. Temperature
Offset Voltage V
os
(mV)
Temperature (°C)
-100 -50 0 50 100 150
-1.1
I
BN
(µA)
1
-1 2
-0.9 3
-0.8 4
-0.7 5
-0.6 6
I
BN
V
os
Maximum Output Voltage vs. R
L
Output Voltage (V
pp
)
RL (Ω)
10 100 1000
1.6
2
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4
4.8
4.4
±5V T ypical P erformance
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,VCC= ± 5V,unless specified)
Non-Inverting Frequency Response
Normalized Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-45
0
-90
-225
-135
-180
Gain
Phase
Vo = 1V
pp
Av = +1
Rf = 1kΩ
Av = +2
Rf = 750Ω
Av = +5
Rf = 402
Av = +10
Rf = 249Ω
Inverting Frequency Response
Normalized Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-225
-180
-270
-425
-315
-360
Gain
Phase
Vo = 1V
pp
Av = -1
Rf = 681Ω
Av = -2
Rf = 604Ω
Av = -5
Rf = 453Ω
Av = -10
Rf = 402Ω
Frequency Response vs. R
L
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Phase (deg)
-90
0
-180
-450
-270
-360
Gain
Phase
Vo = 1V
pp
RL = 25Ω
RL = 100Ω
RL = 1kΩ
Frequency Response vs. V
o
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Vo = 2V
pp
Vo = 1V
pp
Vo = 0.1V
pp
Vo = 5V
pp
Frequency Response vs. C
L
Magnitude (1dB/div)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
100M
Vo = 1V
pp
CL = 10pF
Rs = 68.1Ω
CL = 100pF
Rs = 17.4Ω
CL = 1000pF
Rs = 6.7Ω
C
L
1k
R
s
+
-
1k
1k
Gain Flatness
Magnitude (0.05dB/div)
Frequency (MHz)
5
15
30
0102025
Page 6

http://www.national.com 6
±5V T ypical P erformance
(Av= +2, Rf= 1kΩ,RL= 100Ω,VCC= ± 5V,unless specified)
Small Signal Pulse Response
Output Voltage (200mV/div)
Time (10ns/div)
Av = +2
Av = -2
Large Signal Pulse Response
Output Voltage (1V/div)
Time (10ns/div)
Av = +2
Av = -2
2nd & 3rd Harmonic Distortion
Distortion (dBc)
Frequency (Hz)
1M
10M
Vo = 2V
pp
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
2nd
RL = 1kΩ
2nd
RL = 100Ω
3rd
RL = 100Ω
3rd
RL = 1kΩ
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 25Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-40
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 25Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 100Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 100Ω
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
2nd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 1kΩ
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
3rd Harmonic Distortion, RL = 1kΩ
Distortion (dBc)
Output Amplitude (Vpp)
012345
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
2MHz
5MHz
10MHz
1MHz
Recommended Rs vs. C
L
R
s
(Ω)
CL (pF)
10 100 1000
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
C
L
R
L
R
s
+
-
1k
1k
Maximum Output Voltage vs. R
L
Output Voltage (V
pp
)
RL (Ω)
10 100 1000
2
4
6
8
10
Differential Gain & Phase
Gain (%)
Number of 150Ω Loads
1234
-0.035
-0.03
-0.025
-0.02
-0.015
-0.01
Phase (deg)
-0.7
-0.6
-0.5
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
f = 3.58MHz
Gain Positive Sync
Phase Negative Sync
Phase Positive Sync
Gain Negative Sync
IBN, Vos vs. Temperature
Offset Voltage V
os
(mV)
Temperature (°C)
-100 -50 0 50 100 150
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
I
BN
(µA)
-4
0
4
8
12
I
BN
V
os
Short Term Settling Time
V
o
(% Output Step)
Time (ns)
1 10 100 1000
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
Vo = 2Vstep
Long Term Settling Time
V
o
(% Output Step)
Time (s)
1µ10µ100µ1m 10m 100m 1
-0.2
-0.15
-0.1
-0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
Vo = 2Vstep
Page 7

7 http://www.national.com
CLC452 Operation
The CLC452 is a current feedback amplifier built in an
advanced complementary bipolar process. The CLC452
operates from a single 5V supply or dual ±5V supplies.
Operating from a single supply, the CLC452 has the
following features:
■
Provides 100mA of output current while
consuming 15mW of power
■
Offers low -78/-85dB 2nd and 3rd harmonic
distortion
■
Provides BW > 80MHz and 1MHz distortion
< -70dBc at Vo = 2.0V
pp
The CLC452 performance is further enhanced in ±5V
supply applications as indicated in the
±5V Electrical
Characteristics
table and
±5V Typical Performance
plots.
Current Feedback Amplifiers
Some of the key features of current feedback technology
are:
■
Independence of AC bandwidth and voltage gain
■
Inherently stable at unity gain
■
Adjustable frequency response with feedbac k resistor
■
High slew rate
■
Fast settling
Current feedback operation can be described using a simple
equation. The voltage gain for a non-inverting or inverting
current feedback amplifier is approximated by Equation 1.
Equation 1
where:
■
Avis the closed loop DC voltage gain
■
Rfis the feedback resistor
■
Z(jω) is the CLC452’s open loop transimpedance
gain
■
is the loop gain
The denominator of Equation 1 is approximately equal to
1 at low frequencies. Near the -3dB corner frequency, the
interaction between Rfand Z(jω) dominates the circuit
performance. The value of the feedback resistor has a
large affect on the circuits performance. Increasing R
f
has the following affects:
■
Decreases loop gain
■
Decreases bandwidth
■
Reduces gain peaking
■
Lowers pulse response overshoot
■
Affects frequency response phase linearity
Refer to the
Feedback Resistor Selection
section for
more details on selecting a feedback resistor value.
V
V
A
1
R
Z(j )
o
in
v
f
=
+
ω
ZjRω
()
CLC452 Design Information
Single Supply Operation (VCC= +5V, VEE= GND)
The specifications given in the
+5V Electrical Character-
istics
table for single supply operation are measured with
a common mode voltage (Vcm) of 2.5V. Vcmis the voltage around which the inputs are applied and the
output voltages are specified.
Operating from a single +5V supply, the Common Mode
Input Range (CMIR) of the CLC452 is typically +0.8V to
+4.2V. The typical output range with RL=100Ω is +1.0V
to +4.0V.
For single supply DC coupled operation, keep input
signal levels above 0.8V DC. For input signals that drop
below 0.8V DC, AC coupling and level shifting the signal
are recommended. The non-inverting and inverting
configurations for both input conditions are illustrated in
the following 2 sections.
DC Coupled Single Supply Operation
Figures 1 and 2 show the recommended non-inverting
and inverting configurations for input signals that remain
above 0.8V DC.
+
-
CLC452
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
R
g
R
t
3
2
4
7
6
V
V
A1
R
R
o
in
v
f
g
==+
+
V
cm
V
CC
R
L
V
cm
Note: Rt, RL and Rg are tied
to Vcm for minimum power
consumption and maximum
output swing.
V
cm
+
-
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
R
b
4
7
6
R
g
V
V
A
R
R
o
in
v
f
g
==−
+
CLC452
R
t
3
2
V
cm
V
CC
R
L
V
cm
Note: Rb, provides DC bias
for non-inverting input.
Rb, RL and Rt are tied
to Vcm for minimum power
consumption and maximum
output swing.
V
cm
Select Rt to yield
desired Rin = Rt || R
g
+
-
Figure 1: Non-Inverting Configuration
Figure 2: Inverting Configuration
Page 8

http://www.national.com 8
AC Coupled Single Supply Operation
Figures 3 and 4 show possible non-inverting and inverting configurations for input signals that go below 0.8V
DC. The input is AC coupled to prevent the need for
level shifting the input signal at the source. The resistive
voltage divider biases the non-inverting input to VCC÷2
= 2.5V (For VCC= +5V).
Figure 3: AC Coupled Non-Inverting Configuration
Figure 4: AC Coupled Inverting Configuration
Dual Supply Operation
The CLC452 operates on dual supplies as well as single
supplies. The non-inverting and inverting configurations
are shown in Figures 5 and 6.
Figure 5: Dual Supply Non-Inverting Configuration
Figure 6: Dual Supply Inverting Configuration
Feedback Resistor Selection
The feedback resistor, Rf, affects the loop gain and
frequency response of a current feedback amplifier.
Optimum performance of the CLC452, at a gain of +2V/V,
is achieved with Rfequal to 1kΩ.The frequency response
plots in the
Typical Performance
sections
illustrate the recommended Rffor several gains. These
recommended values of Rfprovide the maximum bandwidth with minimal peaking. Within limits, Rfcan be
adjusted to optimize the frequency response.
■
Decrease Rfto peak frequency response and
extend bandwidth
■
Increase Rfto roll off frequency response and
compress bandwidth
As a rule of thumb, if the recommended Rfis doubled,
then the bandwidth will be cut in half.
Unity Gain Operation
The recommended Rffor unity gain (+1V/V) operation
is 1kΩ.Rgis left open. Parasitic capacitance at the
inverting node may require a slight increase in Rfto
maintain a flat frequency response.
Bandwidth vs. Output Amplitude
The bandwidth of the CLC452 is at a maximum for
output voltages near 1Vpp. The bandwidth decreases
for smaller and larger output amplitudes. Refer to the
Frequency Response vs.V
o
plots.
Load Termination
The CLC452 can source and sink near equal amounts of
current. For optimum performance, the load should be
tied to V
cm
.
Driving Cables and Capacitive Loads
When driving cables, double termination is used to
prevent reflections. For capacitive load applications, a
small series resistor at the output of the CLC452 will
improve stability and settling performance. The
Frequency Response vs. C
L
and
Recommended R
s
vs. C
L
plots, in the typical performance section, give the
recommended series resistance value for optimum
flatness at various capacitive loads.
+
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
R
g
R
4
7
6
C
C
c
R
+
VV1
R
R
2.5
o
in
f
g
=+
+
low frequency cutoff
1
2RC
,where: R
R
2
in
c
in
==
π
RR
source
>>
CLC452
3
2
V
CC
V
CC
2
+
-
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
R
4
7
6
C
c
R
+
VV
R
R
2.5
o
in
f
g
=−
+
low frequency cutoff
1
2RC
gc
=
π
R
g
CLC452
3
2
V
CC
V
CC
2
+
-
CLC452
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
V
CC
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
EE
3
2
4
7
6
+
+
R
g
R
t
V
V
A1
R
R
o
in
v
f
g
==+
+
-
CLC452
R
f
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
o
V
in
V
CC
0.1µF
6.8µF
V
EE
R
g
R
b
3
2
4
7
6
+
+
R
t
Note: Rb provides DC bias
for the non-inverting input.
Select R
t
to yield desired
Rin = Rt || Rg.
V
V
A
R
R
o
in
v
f
g
==−
Page 9

9 http://www.national.com
Transmission Line Matching
One method for matching the characteristic impedance
(Zo) of a transmission line or cable is to place the
appropriate resistor at the input or output of the amplifier.
Figure 7 shows typical inverting and non-inverting circuit
configurations for matching transmission lines.
Figure 7:Transmission Line Matching
Non-inverting gain applications:
■
Connect Rgdirectly to ground.
■
Make R1, R2, R6, and R7equal to Zo.
■
Use R3to isolate the amplifier from reactive
loading caused by the transmission line,
or by parasitics.
Inverting gain applications:
■
Connect R3directly to ground.
■
Make the resistors R4, R6, and R7equal to Zo.
■
Make R5II Rg= Zo.
The input and output matching resistors attenuate the
signal by a factor of 2, therefore additional gain is needed.
Use C6to match the output transmission line over a
greater frequency range. C6compensates for the increase
of the amplifier’s output impedance with frequency.
Power Dissipation
Follow these steps to determine the power consumption
of the CLC452:
1. Calculate the quiescent (no-load) power:
P
amp
= ICC(VCC- VEE)
2. Calculate the RMS power at the output stage:
Po= (VCC- V
load
) (I
load
), where V
load
and I
load
are the RMS voltage and current across the
external load.
3. Calculate the total RMS power:
Pt= P
amp
+ P
o
The maximum power that the DIP, SOIC, and SOT
packages can dissipate at a given temperature is
illustrated in Figure 8. The power derating curve for
any CLC452 package can be derived by utilizing the
following equation:
where
T
amb
= Ambient temperature (°C)
θJA= Thermal resistance, from junction to ambient,
for a given package (°C/W)
Figure 8: Power Derating Curves
Layout Considerations
A proper printed circuit layout is essential for achieving
high frequency performance. Comlinear provides
evaluation boards for the CLC452 (730013-DIP, 730027SOIC, 730068-SOT) and suggests their use as a guide
for high frequency layout and as an aid for device testing
and characterization.
General layout and supply bypassing play major roles in
high frequency performance. Follow the steps below as
a basis for high frequency layout:
■
Include 6.8µF tantalum and 0.1µF ceramic
capacitors on both supplies.
■
Place the 6.8µF capacitors within 0.75 inches
of the power pins.
■
Place the 0.1µF capacitors less than 0.1 inches
from the power pins.
■
Remove the ground plane under and around the
part, especially near the input and output pins to
reduce parasitic capacitance.
■
Minimize all trace lengths to reduce series
inductances.
■
Use flush-mount printed circuit board pins for
prototyping, never use high profile DIP sockets.
Evaluation Board Information
Data sheets are available for the CLC730013/
CLC730027 and CLC730068 evaluation boards. The
evaluation board data sheets provide:
■
Evaluation board schematics
■
Evaluation board lay outs
■
General information about the boards
The CLC730013/CLC730027 data sheet also contains
tables of recommended components to evaluate several
of Comlinear’s high speed amplifiers. This table for the
CLC452 is illustrated below. Refer to the evaluation
board data sheet for schematics and further information.
Components Needed to Evaluate the
CLC452 on the Evaluation Board:
■
Rf, Rg- Use this product data sheet to select values
■
Rin, R
out
- Typically 50Ω (Refer to the
Basic
Operation
section of the evaluation board data
sheet for details)
(175 T
amb
JA
°− )
θ
Power (W)
Ambient Temperature (°C)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 180
AJP
AJE
SOT
140 160
CLC452
+
-
R
3
Z
0
R
6
V
o
Z
0
R
1
R
2
+
R
g
Z
0
R
4
R
5
V
1
V
2
+
-
R
f
C
6
R
7
Page 10

http://www.national.com 10
■
Rt- Optional resistor for inverting gain configurations (Select Rtto yield desired input impedance
= Rg || Rt)
■
C1, C2- 0.1µF ceramic capacitors
■
C3, C4- 6.8µF tantalum capacitors
Components not used:
■
C5, C6, C7, C
8
■
R1thru R
8
The evaluation boards are designed to accommodate
dual supplies. The boards can be modified to provide
single supply operation. For best performance; 1) do
not connect the unused supply, 2) ground the unused
supply pin.
SPICE Models
SPICE models provide a means to evaluate amplifier
designs. Free SPICE models are available for
Comlinear’s monolithic amplifiers that:
■
Support Berkeley SPICE 2G and its many derivatives
■
Reproduce typical DC, AC, Transient, and Noise
performance
■
Support room temperature simulations
The
readme
file that accompanies the diskette lists
released models, and provides a list of modeled parameters. The application note OA-18, Simulation SPICE
Models for Comlinear’s Op Amps, contains schematics
and a reproduction of the readme file.
Single Supply Cable Driver
The typical application shown on the front page shows
the CLC452 driving 10m of 75Ω coaxial cable. The
CLC452 is set for a gain of +2V/V to compensate for the
divide-by-two voltage drop at Vo.
Single Supply Lowpass Filter
Figures 9 and 10 illustrate a lowpass filter and design
equations. The circuit operates from a single supply of
+5V. The voltage divider biases the non-inv erting input to
2.5V. And the input is AC coupled to prevent the need for
level shifting the input signal at the source. Use the
design equations to determine R1, R2, C1, and C2based
on the desired Q and corner frequency.
Figure 9: Lowpass Filter Topology
Figure 10: Design Equations
This example illustrates a lowpass filter with Q = 0.707
and corner frequency fc= 10MHz. A Q of 0.707 was chosen to achieve a maximally flat, Butterworth response.
Figure 11 indicates the filter response.
Figure 11: Lowpass Response
Twisted Pair Driver
The high output current and low distortion, of the
CLC452, make it well suited for driving transformers.
Figure 12 illustrates a typical twisted pair driver utilizing
the CLC452 and a transformer. The transformer
provides the signal and its inversion for the twisted pair.
Figure 12:Twisted Pair Driver
To match the line’s characteristic impedance (Zo) set:
■
RL= Z
o
■
Rm= R
eq
Application Circuits
+
R
f
1kΩ
0.1µF
C
1
V
o
V
in
R
g
5kΩ
4
7
6
0.1µF
0.1µF
5kΩ
CLC452
3
2
+5V
0.1µF
100Ω
1.698kΩ
R
1
158Ω
R
2
158Ω
C
2
100pF
Gain K 1
R
R
Corner frequency
1
RR CC
Q
1
RC
RC
RC
RC
(1 K)
RC
RC
For R R R and C C C
1
RC
Q
1
(3 K)
f
g
c
1212
22
11
12
21
11
22
12 12
c
==+
==
=
++−
== ==
=
=
−
ω
ω
Magnitude (dB)
Frequency (Hz)
3
0
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
-18
-21
-24
-27
-30
1M 10M 100M
+
-
+
V
o
-
R
m
R
f
R
g
V
in
R
t
R
L
Z
o
UTP
I
L
R
eq
1:n
V = Av V
in
CLC452
3
2
6
A1
R
R
v
f
g
=+
V
n
4
AV
v
in
=
V
-n
4
AV
v
in
=
V
1n
2
AV
ov
in
=
Page 11

11 http://www.national.com
Where Reqis the transformed value of the load impedance, (RL), and is approximated by:
Select the transformer so that it loads the line with a
value close to Zo, over the desired frequency range. The
output impedance, Ro, of the CLC452 varies with
frequency and can also affect the return loss.The return
loss, shown below, takes into account an ideal
transformer and the value of Ro.
The load current (IL) and voltage (Vo) are related to the
CLC452’s maximum output voltage and current by:
From the above current relationship, it is obvious that an
amplifier with high output drive capability is required.
R
R
n
eq
L
2
=
Return Loss(dB) 20log n
R
Z
10
2
o
o
≈− ⋅
VnV
I
I
n
o max
L
max
≤⋅
≤
Page 12

CLC452, Single Supply, Low-Power,
High Output, Current Feedback Amp
http://www.national.com 12
Customer Design Applications Support
National Semiconductor is committed to design excellence. For sales, literature and technical support, call the
National Semiconductor Customer Response Group at 1-800-272-9959 or fax 1-800-737-7018.
Life Support Policy
National’s products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without the express written approval of
the president of National Semiconductor Corporation. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or b) support or
sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to
cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax: (+49) 0-180-530 85 86 2501 Miramar Tower Tel: 81-043-299-2309
Arlington, TX 76017 E-mail: europe.support.nsc.com 1-23 Kimberley Road Fax:81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel: (+49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
Fax:1(800) 737-7018 English Tel: (+49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
Francais Tel: (+49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
Italiano Tel: (+49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said
circuitry and specifications.
N
 Loading...
Loading...