Page 1
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
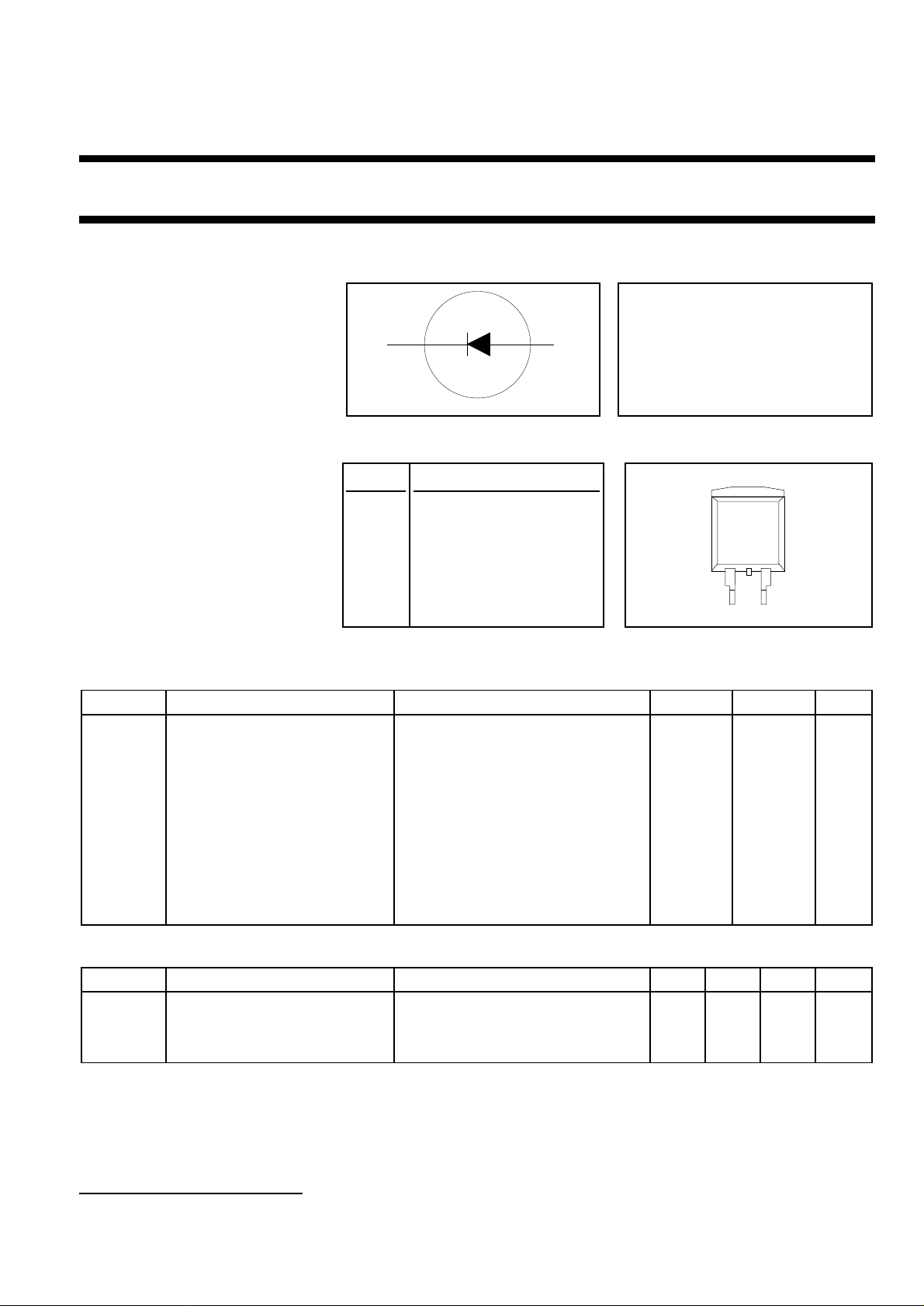
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
FEATURES SYMBOL QUICK REFERENCE DATA
• Extremely fast switching VR = 600 V
• Low reverse recovery current
• Low thermal resistance VF ≤ 1.85 V
• Reduces switching losses in
associated MOSFET I
APPLICATIONS PINNING SOT404
k a
tab 3
= 8 A
F(AV)
trr = 19 ns (typ)
• Active power factor correction PIN DESCRIPTION
tab
• Half-bridge lighting ballasts
• Half-bridge/ full-bridge switched 1 no connection
mode power supplies.
2 cathode
1
The BYC8B-600 is supplied in the
SOT404 surface mounting 3 anode
package.
2
tab cathode
13
LIMITING VALUES
Limiting values in accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
I
F(AV)
I
FRM
I
FSM
T
T
RRM
RWM
R
stg
j
Peak repetitive reverse voltage - 600 V
Crest working reverse voltage - 600 V
Continuous reverse voltage Tmb ≤ 110 ˚C - 500 V
Average forward current δ = 0.5; with reapplied V
Tmb ≤ 82 ˚C
Repetitive peak forward current δ = 0.5; with reapplied V
Tmb ≤ 82 ˚C
1
1
;-8A
RRM(max)
; - 16 A
RRM(max)
Non-repetitive peak forward t = 10 ms - 55 A
current. t = 8.3 ms - 60 A
sinusoidal; Tj = 150˚C prior to surge
Storage temperature -40 150 ˚C
with reapplied V
RWM(max)
Operating junction temperature - 150 ˚C
THERMAL RESISTANCES
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
R
th j-mb
R
th j-a
1 it is not possible to make connection to pin 2 of the SOT404 package
October 1998 1 Rev 1.200
Thermal resistance junction to - - 2.2 K/W
mounting base
Thermal resistance junction to minimum footprint, FR4 board - 50 - K/W
ambient
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Tj = 25 ˚C unless otherwise stated
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
F
I
R
t
rr
t
rr
I
rrm
V
fr
Forward voltage IF = 8 A; Tj = 150˚C - 1.4 1.85 V
IF = 16 A; Tj = 150˚C - 1.7 2.3 V
IF = 8 A; - 2.0 2.8 V
Reverse current VR = 600 V - 9 150 µA
VR = 500 V; Tj = 100 ˚C - 1.1 3.0 mA
Reverse recovery time IF = 8 A to VR = 400 V; - 19 - ns
dIF/dt = 500 A/µs
Reverse recovery time IF = 8 A to VR = 400 V; - 32 40 ns
dIF/dt = 500 A/µs; Tj = 125˚C
Peak reverse recovery current IF = 8 A to VR = 400 V; - 9.5 12 A
dIF/dt = 500 A/µs; Tj = 125˚C
Forward recovery voltage IF = 10 A; dIF/dt = 100 A/µs-810V
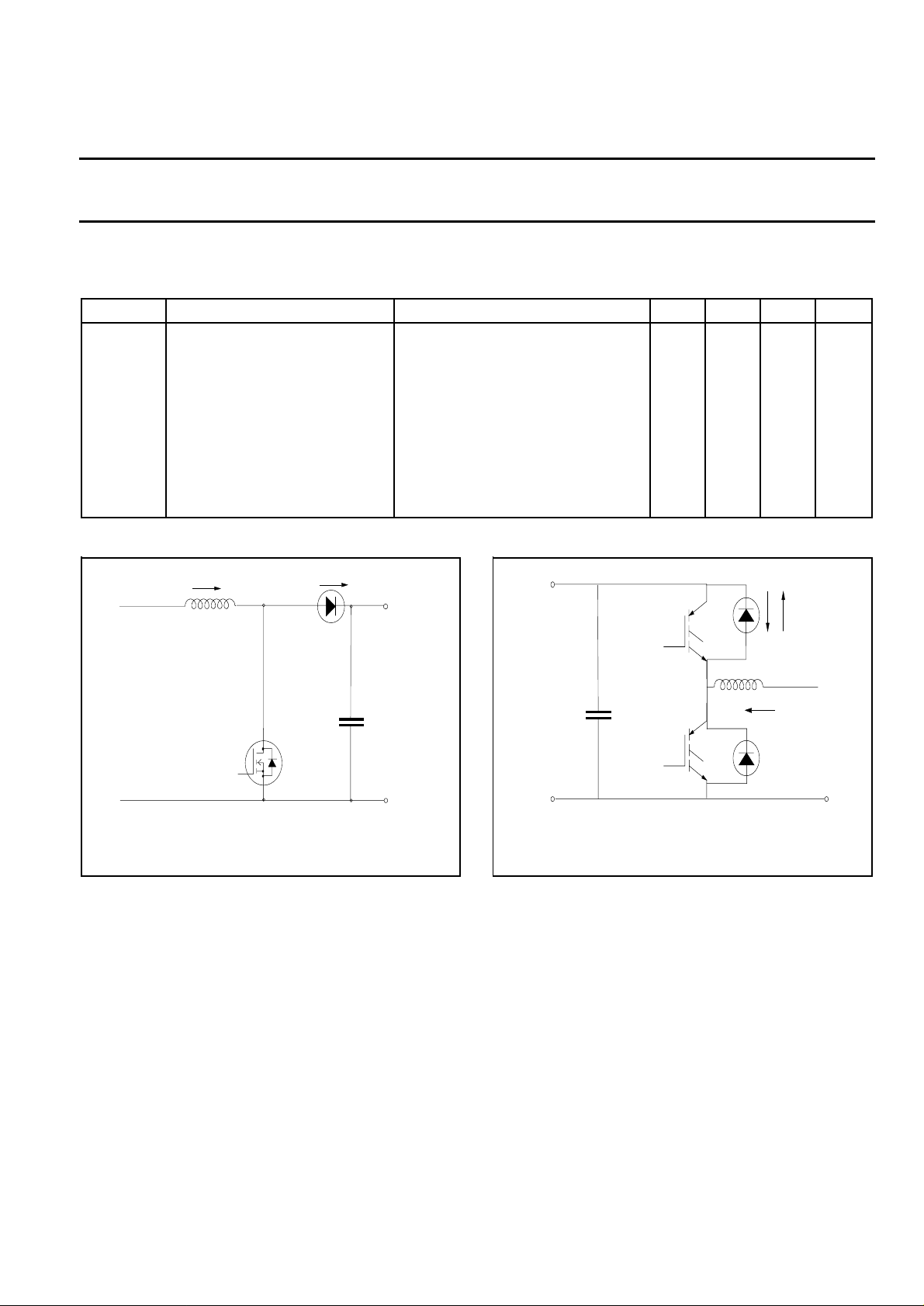
IL
Vin
150 uH
typ
500 V MOSFET
ID
Vo = 400 V d.c.
OUTPUT DIODE
Fig.1. Typical application, output rectifier in boost
converter power factor correction circuit. Continuous
conduction, mode where the transistor turns on whilst
forward current is still flowing in the diode.
Vin = 400 V d.c.
Vin
IFIR
inductive load
IL
Fig.2. Typical application, freewheeling diode in half
bridge converter. Continuous conduction mode, where
each transistor turns on whilst forward current is still
flowing in the other bridge leg diode.
October 1998 2 Rev 1.200
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
0.2
BYC8-600
I
0.5
95
D = 1.0
106
117
128
p
D =
t
T
139
t
150
t
p
T
Forward dissipation, PF (W) Tmb(max) C
25
Vo = 1.4 V
Rs = 0.05625 Ohms
20
15
10
5
0
024681012
0.1
Average forward current, IF(AV) (A)
Fig.3. Maximum forward dissipation as a function of
average forward current; rectangular current
waveform where I
Diode reverse recovery switching losses, Pdsw (W)
0.25
f = 20 kHz
Tj = 125 C
0.2
VR = 400 V
0.15
16 A
0.1
IF = 8 A
0.05
BYC8-600
0
100 1000
Rate of change of current, dIF/dt (A/us)
F(AV)
12 A
=I
F(RMS)
x √D.
Fig.4. Typical reverse recovery switching losses in
diode, as a function of rate of change of current dIF/dt.
ID
dIF/dt
VD
Irrm
ID = IL
losses due to
diode reverse recovery
time
Fig.6. Origin of switching losses in transistor due to
diode reverse recovery.
Reverse recovery time, trr (ns)
100
16 A
IF = 5 A
Tj = 125 C
VR = 400 V
10
100 1000
Rate of change of current, dIF/dt (A/us)
12 A
8 A
BYC8-600
Fig.7. Typical reverse recovery time trr, as a function
of rate of change of current dIF/dt.
Transistor losses due to diode reverse recovery, Ptsw (W)
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
100 1000
16 A
12 A
8 A
IF = 5 A
BYC8-600
Rate of change of current, dIF/dt (A/us)
f = 20 kHz
Tj = 125 C
VR = 400 V
Fig.5. Typical switching losses in transistor due to
reverse recovery of diode, as a function of of change
Peak reverse recovery current, Irrm (A)
100
10
Tj = 125 C
VR = 400 V
1
100 1000
Rate of change of current, dIF/dt (A/us)
16 A
IF = 5 A
Fig.8. Typical peak reverse recovery current, I
function of rate of change of current dIF/dt.
BYC8-600
rrm
as a
of current dIF/dt.
October 1998 3 Rev 1.200
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
I
F
dI
F
dt
t
rr
time
Q
s
I
R
I
rrm
10%
100%
Fig.9. Definition of reverse recovery parameters trr, I
Peak forward recovery voltage, Vfr (V)
20
Tj = 25 C
IF = 10 A
15
10
5
BYC8-600
typ
rrm
Forward current, IF (A)
20
Tj = 25 C
Tj = 150 C
15
10
5
0
01234
Forward voltage, VF (V)
maxtyp
BYC8-600
Fig.12. Typical and maximum forward characteristic
IF = f(VF); Tj = 25˚C and 150˚C.
Reverse leakage current (A)
100mA
10mA
1mA
100uA
10uA
Tj = 125 C
BYC8-600
100 C
75 C
50 C
25 C
0
0 50 100 150 200
Rate of change of current, dIF/dt (A/ s)
Fig.10. Typical forward recovery voltage, Vfr as a
function of rate of change of current dIF/dt.
I
F
time
V
F
V
V
F
time
Fig.11. Definition of forward recovery voltage V
1uA
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Reverse voltage (V)
Fig.13. Typical reverse leakage current as a function
of reverse voltage. IR = f(VR); parameter T
Transient thermal impedance, Zth j-mb (K/W)
10
1
0.1
p
t
0.01
fr
0.001
1us 10us 100us 1ms 10ms 100ms 1s 10s
fr
Fig.14. Maximum thermal impedance Z
function of pulse width.
P
D
pulse width, tp (s)
D =
T
BYC8
p
t
T
t
th j-mb
j
as a
October 1998 4 Rev 1.200
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
MECHANICAL DATA
Dimensions in mm
Net Mass: 1.4 g
2.54 (x2)
MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS
Dimensions in mm
10.3 max
11 max
15.4
0.85 max
(x2)
4.5 max
1.4 max
0.5
Fig.15. SOT404 : centre pin connected to mounting base.
11.5
2.5
Notes
1. Epoxy meets UL94 V0 at 1/8".
9.0
17.5
2.0
3.8
5.08
Fig.16. SOT404 : soldering pattern for surface mounting
.
October 1998 5 Rev 1.200
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Rectifier diode BYC8B-600
ultrafast, low switching loss
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values are given in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one
or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and
operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Philips Electronics N.V. 1998
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the
copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, it is believed to be
accurate and reliable and may be changed without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any
consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license under patent or other
industrial or intellectual property rights.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of these
products can be reasonably expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting
from such improper use or sale.
October 1998 6 Rev 1.200
 Loading...
Loading...