Page 1

DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
BLF542
UHF power MOS transistor
Product specification
October 1992
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
FEATURES
• High power gain
• Easy power control
• Gold metallization
• Good thermal stability
• Withstands full load mismatch
• Designed for broadband operation.
DESCRIPTION
Silicon N-channel enhancement
mode vertical D-MOS transistor
designed for large signal amplifier
applications in the UHF frequency
range.
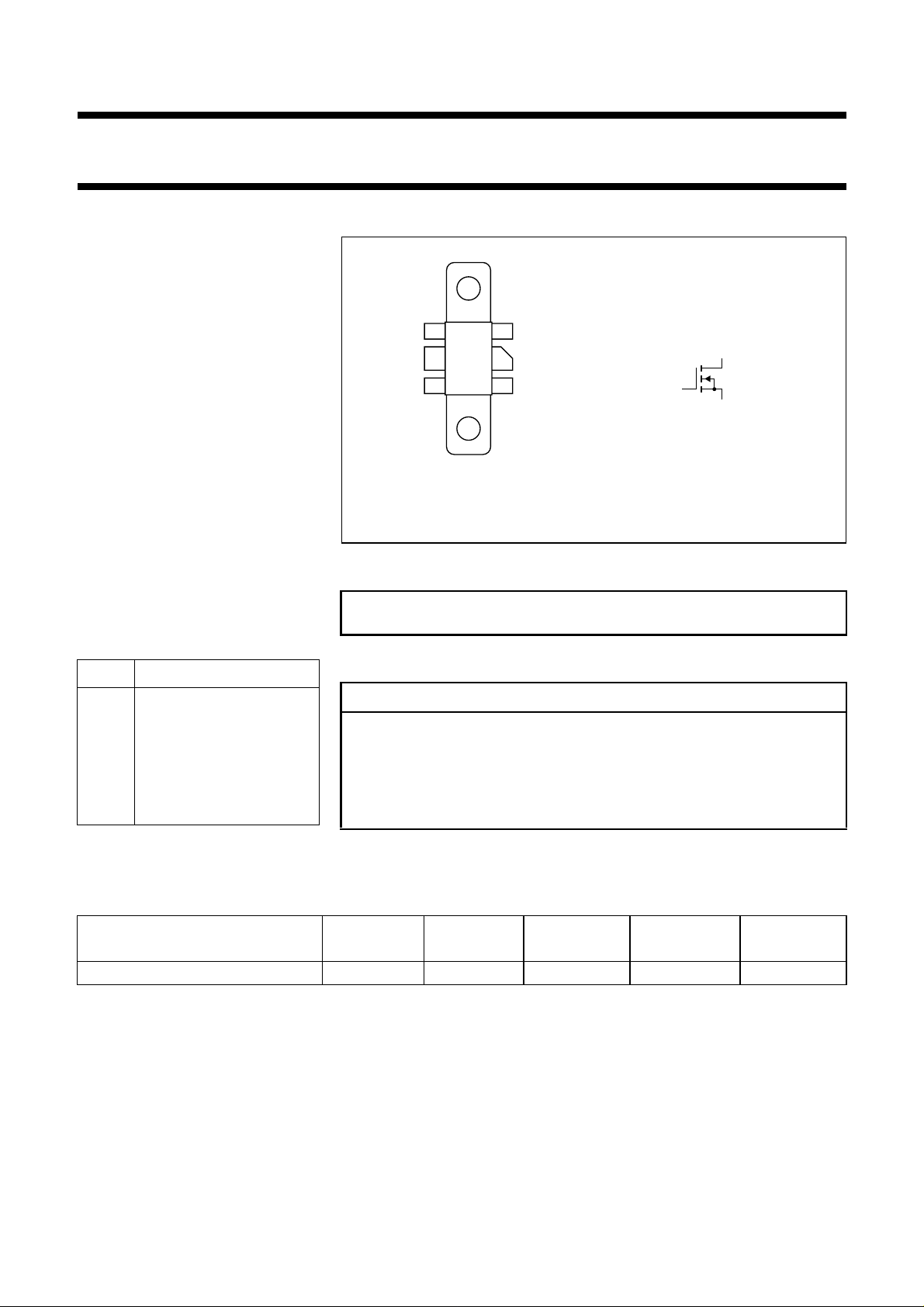
The transistor is encapsulated in a
6-lead, SOT171 flange envelope, with
a ceramic cap. All leads are isolated
from the flange.
PINNING - SOT171
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 source
2 source
3 gate
4 drain
5 source
6 source
PIN CONFIGURATION
alfpage
1
3
5
Top view
2
4
6
MBA931 - 1
g
MBB072
d
s
Fig.1 Simplified outline and symbol.
CAUTION
The device is supplied in an antistatic package. The gate-source input must
be protected against static charge during transport and handling.
WARNING
Product and environmental safety - toxic materials
This product contains beryllium oxide. The product is entirely safe provided
that the BeO disc is not damaged. All persons who handle, use or dispose of
this product should be aware of its nature and of the necessary safety
precautions. After use, dispose of as chemical or special waste according to
the regulations applying at the location of the user. It must never be thrown
out with the general or domestic waste.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
RF performance at T
MODE OF OPERATION
= 25 °C in a common source test circuit.
mb
f
(MHz)
V
(V)
DS
P
(W)
L
G
P
(dB)
(%)
CW, class-B 500 28 5 > 13 > 50
October 1992 2
η
D
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DS
±V
GS
I
D
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
THERMAL RESISTANCE
SYMBOL PARAMETER THERMAL RESISTANCE
R
th j-mb
R
th mb-h
drain-source voltage − 65 V
gate-source voltage − 20 V
DC drain current − 1.5 A
total power dissipation Tmb=25°C − 20 W
storage temperature −65 150 °C
junction temperature − 200 °C
thermal resistance from junction to mounting base 8.8 K/W
thermal resistance from mounting base to heatsink 0.4 K/W
10
handbook, halfpage
I
D
(A)
1
−1
10
−2
10
(1) Current in this area may be limited by R
(2) Tmb=25°C.
(1)
101
Fig.2 DC SOAR.
V
DS
DS(on)
(2)
(V)
MRA735
2
10
.
35
handbook, halfpage
P
tot
(W)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 30 50 70 90 110 130
(1) Continuous operation.
(2) Short time operation during mismatch.
(2)
(1)
MRA734
Th (
o
C)
Fig.3 Power derating curves.
October 1992 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
CHARACTERISTICS
T
= 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
(BR)DSS
I
DSS
I
GSS
V
GS(th)
g
fs
R
DS(on)
I
DSX
C
is
C
os
C
rs
drain-source breakdown voltage ID= 0.1 mA; VGS=0 65 −−V
drain-source leakage current VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V −−10 µA
gate-source leakage current ±VGS= 20 V; VDS=0 −−1µA
gate-source threshold voltage ID= 10 mA; VDS= 10 V 2 − 4.5 V
forward transconductance ID= 0.3 A; VDS= 10 V 160 240 − mS
drain-source on-resistance ID= 0.3 A; VGS= 15 V − 3.3 5 Ω
on-state drain current VGS= 15 V; VDS= 10 V − 1.4 − A
input capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 14 − pF
output capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 9.4 − pF
feedback capacitance VGS= 0; VDS= 28 V; f = 1 MHz − 1.7 − pF
handbook, halfpage
4
T.C.
(mV/K)
2
0
–2
–4
0 100 200 300
VDS= 10 V.
ID (mA)
Fig.4 Temperature coefficient of gate-source
voltage as a function of drain current, typical
values.
MBB777
1.5
handbook, halfpage
I
D
(A)
1
0.5
0
0
VDS= 10 V; Tj= 25 °C.
51015
MBB759
VGS (V)
Fig.5 Drain current as a function of gate-source
voltage, typical values.
October 1992 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
handbook, halfpage
6
R
DS (on)
(Ω)
4
2
0
0
ID= 0.3 A; VGS= 15 V
50 100 150
MBB778
Tj (oC)
Fig.6 Drain-source on-resistance as a function of
junction temperature, typical values.
30
handbook, halfpage
C
(pF)
20
10
0
0
VGS= 0; f = 1 MHz.
C
is
C
os
10 20 30
MBB776
VDS (V)
Fig.7 Input and output capacitance as functions
of drain-source voltage, typical values.
handbook, halfpage
6
C
rs
(pF)
4
2
0
0
VGS= 0; f = 1 MHz.
10 20 30
VDS (V)
Fig.8 Feedback capacitance as a function of
drain-source voltage, typical values.
MBB775
October 1992 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
APPLICATION INFORMATION FOR CLASS-B OPERATION
T
= 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
mb
RF performance in CW operation in a common source class-B test circuit.
MODE OF OPERATION
f
(MHz)
V
(V)
DS
I
DQ
(mA)
P
(W)
L
G
(dB)
CW, class-B 500 28 50 5 > 13
typ. 16.5
Ruggedness in class-B operation
The BLF542 is capable of withstanding a full load
mismatch corresponding to VSWR = 50:1 through all
phases under the following conditions: VDS= 28 V;
f = 500 MHz at rated output power.
20
handbook, halfpage
G
p
(dB)
15
10
G
p
η
MRA969
80
60
40
(%)
10
η
handbook, halfpage
P
L
(W)
8
6
4
P
η
D
(%)
> 50
typ. 59
MRA970
P
(W)
L
20
0
5
0
Class-B operation; VDS= 28 V; IDQ= 10 mA;
= 9.7+ j24.5 Ω; f = 500 MHz.
Z
L
2468100
Fig.9 Power gain and efficiency as functions of
load power, typical values.
October 1992 6
2
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Class-B operation; VDS= 28 V; IDQ= 10 mA;
= 9.7+ j24.5Ω; f = 500 MHz.
Z
L
PIN (W)
Fig.10 Load power as a function of input power,
typical values.
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
,,
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
handbook, full pagewidth
input
50 Ω
C1 L1 L2
C3
L3 L4
C9
DUT
R1C4C2
C5
R4
L6L5 L7
C10 C12
L8
C6
L9
C7
C11
C13
output
50 Ω
MBB760
f =500 MHz.
R2
R3
C8
VDD = + 28 V
Fig.11 Test circuit for class-B operation.
October 1992 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
List of components (see test circuit)
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION VALUE DIMENSIONS CATALOGUE NO.
C1, C5, C13 multilayer ceramic chip capacitor
(note 1)
C2, C4, C10, C12 film dielectric trimmer 2 to 18 pF 222 809 05217
C3, C9 multilayer ceramic chip capacitor
(note 1)
C6 multilayer ceramic chip capacitor
(note 2)
C7 multilayer ceramic chip capacitor 100 nF 2222 852 47104
C8 electrolytic capacitor 63 V, 10 µF 2222 030 28109
C11 multilayer ceramic chip capacitor
(note 1)
L1 stripline (note 3) 50 Ω 11 mm × 2.5 mm
L2 stripline (note 3) 50 Ω 37 mm × 2.5 mm
L3 stripline (note 3) 50 Ω 13 mm × 2.5 mm
L4, L5 stripline (note 3) 42 Ω 3mm×3 mm
L6 stripline (note 3) 50 Ω 39 mm × 2.5 mm
L7 stripline (note 3) 50 Ω 22 mm × 2.5 mm
L8 8 turns 0.8 mm enamelled copper
wire
L9 grade 3B Ferroxcube wideband
RF choke
R1 metal film resistor 10 kΩ, 0.4 W 2322 151 71003
R2 10 turn potentiometer 50 kΩ
R3 metal film resistor 205 kΩ, 0.4 W 2322 151 72054
R4 metal film resistor 10 Ω, 0.4 W 2322 151 71009
390 pF
39 pF
220 pF
10 pF
250 nH length 9 mm
int. dia. 6 mm
leads 2 × 5 mm
4312 020 36640
Notes
1. American Technical Ceramics (ATC) capacitor, type 100A or other capacitor of the same quality.
2. American Technical Ceramics (ATC) capacitor, type 100B or other capacitor of the same quality.
3. The striplines are on a double copper-clad printed circuit board with PTFE fibre-glass dielectric (ε
thickness1⁄32inch.
October 1992 8
= 2.2);
r
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
h
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
handbook, full pagewidth
C1
L1
C2
andbook, full pagewidth
strap
(8x)
L2
rivet
(12x)
C3
C4
R1
V
G
L9
C5
L3
L4
C6
L5 L6
150 mm
R4
L8
C7
V
D
C8
C9
C11
L7
C13
C12C10
MBB762
70 mm
mounting
screws
(12x)
The components are mounted on one side of a copper-clad printed circuit board; the other side is unetched and
serves as a ground plane. Earth connections from the component side to the ground plane are made by means
of fixing screws, hollow rivets and copper foil straps, as shown.
Fig.12 Component layout for 500 MHz test circuit.
October 1992 9
MBB761
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
10
handbook, halfpage
Z
i
(Ω)
0
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
100 200 300 400 500
Class-B operation; VDS= 28 V; IDQ= 10 mA;
= 5 W.
P
L
r
i
x
i
Fig.13 Input impedance as a function of
frequency (series components), typical
values.
MRA732
f (MHz)
70
handbook, halfpage
Z
L
(Ω)
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
100 200 300 400 500
Class-B operation; VDS= 28 V; IDQ= 10 mA;
= 5 W.
P
L
X
L
R
L
Fig.14 Load impedance as a function of
frequency (series components), typical
values.
MRA733
f (MHz)
handbook, halfpage
Z
i
Z
MBA379
L
Fig.15 Definition of MOS impedance.
October 1992 10
35
handbook, halfpage
gain
(dB)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
100 200 300 400 500
Class-B operation; VDS= 28 V; IDQ= 10 mA;
= 5 W.
P
L
f MHz)
Fig.16 Power gain as a function of frequency,
typical values.
MRA971
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
PACKAGE OUTLINE
Flanged ceramic package; 2 mounting holes; 6 leads SOT171A
D
A
F
D
1
U
1
q
H
1
b
1
2
H
U
2
Db
9.25
9.04
0.364
0.356
1
D
1
9.30
8.99
0.366
0.354
E
5.95
5.74
0.234
0.226
A
DIMENSIONS (millimetre dimensions are derived from the original inch dimensions)
UNIT
mm
inches
A
6.81
6.07
0.268
0.239
2.15
1.85
0.085
0.073
b
1
3.20
2.89
0.126
0.114
c
0.16
0.07
0.006
0.003
6
345
b
e
0 5 10 mm
scale
e
E
1
6.00
3.58
5.70
0.236
0.140
0.224
C
w
M
C
2
p
w
M
3
F
H
11.31
3.05
10.54
2.54
0.445
0.120
0.415
0.100
w
H
9.27
9.01
0.365
0.355
B
1
c
E
1
M
AB
1
Q
qw
18.42
U
1
24.90
24.63
0.980
0.970
6.00
5.70
0.236
0.224
p
3.43
3.17
0.135
0.125
Q
4.32
4.11
0.170
0.162
E
w
U
2
2
1
w
3
0.260.51 1.02
0.010.02 0.040.725
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT171A 97-06-28
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
October 1992 11
ISSUE DATE
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
UHF power MOS transistor BLF542
DEFINITIONS
Data Sheet Status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
October 1992 12
 Loading...
Loading...