Page 1
BA6438S
Motor driver ICs
3-phase motor driver
BA6438S
The BA6438S is a 3-phase, full-wave, pseudo-linear motor driver suited for VCR capstan motors. The IC has a torque
ripple cancellation circuit to reduce wow and flutter, and an output transistor saturation prevention circuit that provides
superb motor control over a wide range of current. The built-in motor power switching regulator allows applications with
low power consumption
Applications
!
3-phase VCR capstan motors
Features
!
1) 3-phase, full-wave, pseudo-linear drive system.
2) Torque ripple cancellation circuit.
3) Reversal brake based on the detection of motor
direction.
4) Output transistor (high-and low-sides) saturation
prevention circuit
5) Motor power switching regulator with oscillation circuit.
6) Output-to-GND short-circuit detection.
7) Available in SDIP 24-pin power package (with radiation
fins).
Absolute maximum ratings
!
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
Applied voltage
Applied voltage
Power dissipation
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Allowable output current
1 Reduced by 16mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
∗
2 Should not exceed the ASO value.
∗
Recommended operating conditions
!
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Operating power supply voltage
Operating power supply voltage
(Ta = 25°C)
V
CC
M
V
Pd
Topr −10 ∼ +75
Tstg −40 ∼ +150
I
Opeak
(Ta = 25°C)
V
V
7V
24 V
1
∗
2000
2
∗
1.7
CC
M
456 V
31223 V
mW
°C
°C
A
Page 2
Motor driver ICs
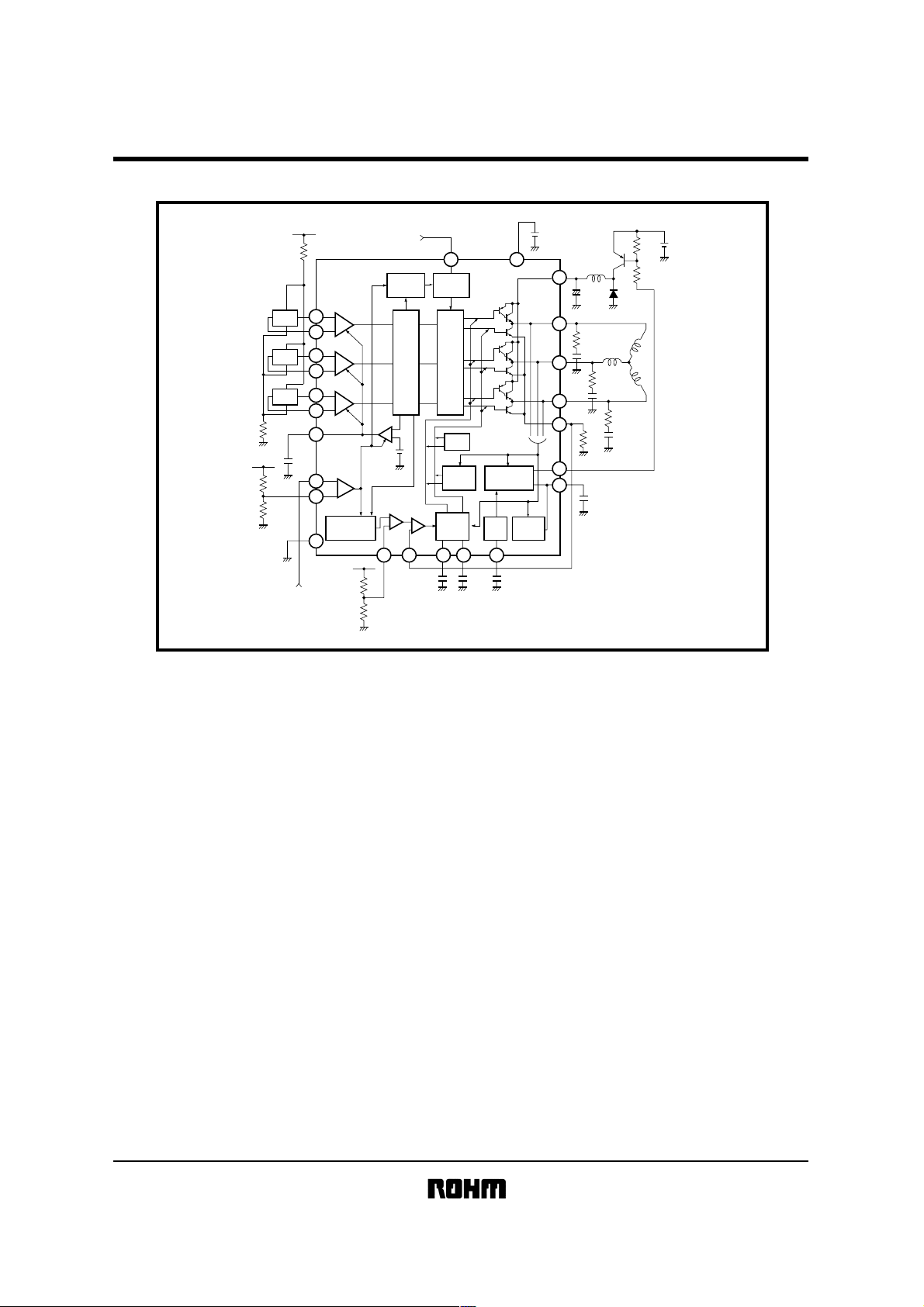
Block diagram
!
CC
V
Hall
Hall
Hall
TORQUE
COMMAND
H1+Hall
10
9
−
H1
+
H2
8
7
−
H2
+
H3
6
5
−
H3
4
C
H
P
E
C
17
16
E
CR
RIPPLE
CANCELLATION
12
GND
V
CC
Amp.
CONTROL
SIGNAL
DIRECTION
AGC
TL CS
20 22
11
MOTOR
MOTOR
DIRECTION
DET
SETTING
P SIGNAL COMBINER
TSD
SHORT
CIRCUIT
OUTPUT
SATURATION
P
PCV
18
SIGNAL V
19
V
CC
ED / S
MOTOR DIRECTION SWITCHING
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
DET.
OSC
C
I
21
15
OUTPUT
SATURATION
OSC
M
V
24
A1
23
A2
3
A3
1
ATC
2
13
14
CC
REG
VS
MOTOR V
BA6438S
CC
Page 3
Motor driver ICs
Pin descriptions
!
BA6438S
Pin No.
Pin name Function
1A3
2 ATC
3A2
4 PCH
5H3
6H3
7H2
8H2
9H1
10 H1
11
−
+
−
+
−
+
ED / S
12 GND
13 REG
14 V
S
15 OSC
16 ECR
17 EC
18 PCV
19 V
CC
20 TL
21 PCI
22 CS
23 A1
24 V
M
Motor output
Driver ground
Motor output
Hall amplifier AGC phase compensation
Hall signal input
Hall signal input
Hall signal input
Hall signal input
Hall signal input
Hall signal input
Forward when LOW; stop when MEDIUM; reverse when HIGH
Signal ground
Switching regulator output (sink output)
High-side saturation detection output
Oscillator capacitor connection
Torque control reference voltage input
Torque control signal input
Phase compensation for preventing driver high-side saturation
Signal power supply
Torque limiter
Phase compensation for preventing driver low-side saturation
Current sensing input
Motor output
Motor power supply
Electrical characteristics
!
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
Torque control input / output gain
Ripple cancel ratio
Output high level voltage
Output low level voltage
Oscillator frequency
Saturation detection output gain
Regulator current capacity
Not designed for radiation resistance.
(unless otherwise noted, Ta = 25°C, VCC = 5V, VM = 12V)
G
io
0.25 0.31 0.36 −
V
V
V
f
OSC
G
REGO
I
RCC
OH
OL
us
4.6 6.4 7.2 %
1.1 1.5 1.9 V I
0.95 1.3 1.65 V I
100 135 160 kHz C = 470pF
5.0 6.5 8.0 −−
30 −−mA
C =
2.2→2.1V,
E
=
L, L, H
Input
=
L, L, H→L, M, H
Input
O =
0.8A
O =
0.8A
V
O =
5V
Page 4

Motor driver ICs
Circuit operation
!
(1) Pseudo-linear output and torque ripple cancellation
The IC generates a trapezoidal (pseudo-linear) output
current, whose waveform phase is 30 degrees ahead of
that of the Hall input voltage (Fig. 1).
.
30°
Hall input
Output current
Fig. 1
The trapezoidal waveform of output current would create
intermittence in the magnetic field generated by the 3phase motor, and would result in an irregular rotation of
the motor. To prevent this, the output waveform is obtained by superimposing a triangular wave on the trapezoidal wave (Fig. 2). This process is called torque ripple
cancellation.
BA6438S
A brake is applied to the motor as described in the
following.When the motor is running, pin 17 is given a
negative potential with respect to the reference potential. If
the pin 17 potential becomes positive, the IC detects the
rise of pin 17 potential above the reference potential and
activates the motor direction detecting circuit.
The motor direction detecting circuit sends a signal to the
motor direction setting circuit to reverse the motor direction. This causes a braking torque that depends on the
pin 17 potential, so that the motor quickly reduces its
speed. At the same time, the positive pin 17 potential is
shifted to the reference potential, so that the motor stops
smoothly.
(3) Output current sensing and torque limitation
Pin 2 is the ground pin for the output stage. To sense the
output current, a resistor (0.5Ω recommended) is connected between pin 2 and the ground. The output current
is sensed by applying the voltage developed across this
resistor to pin 22 as a feedback.
The output current can be limited by adjusting the voltage
applied to pin 20. The current is limited when pin 20
reaches the same potential as pin 22. The output current
MAX
(I
. ) under this condition is given by:
Fig. 2
(2) Torque control and reversal brake
The output current can be controlled by adjusting the
voltage applied to the torque control pins (pins 16 and 17).
These pins are the inputs to a differential amplifier. A reference voltage between 2.3 ~ 3.0V (2.5V recommended)
is applied to pin 16.
Output current
0
Pin 16
reference voltage (2.5 V)
Offset
Dead zone (100 mV typically)
Fig. 3
Pin 17 voltage
20P(
TL−CS
ofs
I
MAX
V
.=
R
2P
)
where R2P is the value of the resistor connected between
pin 2 and the ground, V
and (TL–CS
ofs
) is the offset between the TL and CS pins.
ATC
2pin
20P
is the voltage applied to pin 20,
V
M
24pin
1pin 3pin 23pin
Fig.4 Output circuit
Page 5

Motor driver ICs
BA6438S
(4) Motor direction control (pin 11)
The motor mode is :
Forward when the pin 11 voltage is less than 0.9V,
Stop when the voltage is between 1.3
~
3.0V,
Reverse when the voltage is above 3.5V.
In the stop mode, high-and low-side output transistors
are turned off, resulting in a high impedance state.
(5) Output transistor saturation prevention circuit
This circuit monitors the output voltage and maintain the
operation of the output transistors below their saturation
levels. Operating the transistors in the linear characteristic
range provides good control over a wide range of current
and good torque characteristics even during overloading.
0
1.5V
HIGH level voltage
HIGH level output voltage
800mA
Fig.5 High level output voltage vs.
output current (reference curves)
LOW level voltage
1.3V
LOW level output voltage
0
Fig.6 Low level output voltage vs. output
current (reference curves)
800mA
Output current
Output
saturation
voltage
Output saturation voltage
ATC-pin voltage
Output current
(6) Switching regulator
The BA6438S has a switching regulator output pin. The
IC outputs a PWM signal by comparing the output of the
internal oscillator with the HIGH level output voltage
monitored.
24
V
M
+
Driver
voltage monitor
Oscillator
15
OSC
HIGH level
14
V
S
13
REG
Fig. 7
As shown in Fig. 7, the switch regulator circuit reduces the
power consumed by the IC by reducing the collector-toemitter (C-E) voltage of the driver transistors.
Nearly all the power dissipated by the IC is dissipated between the collectors and emitters of the output transistors.
More power is consumed as the C-E voltage increases and
as the output current increases.
The output transistor C-E voltage is equal to the difference
between the supply voltage and the voltage applied to the
motor. Because the voltage across the motor decreases with
decreasing drive current, the C-E voltage must increase if the
supply voltage is fixed.
Therefore, to improve the efficiency of the driver and to
prevent the power rating of the IC being exceeded, the supply
voltage must be varied in response to changes in the output
current. The supply voltage is decreased at low current and
increased at high current so that no excessive voltage is
applied between the transistor collectors and emitters .
(7) Output-to-ground short-circuit detection
The motor output pins of the IC may be short-circuited to the
ground by some fault conditions. A short-circuited output can
destroy the output transistors because of excessive current,
excessive voltage, or both. Even when a short-circuit
condition does not completely destroy the device, it can still
cause extreme overheating. To prevent this, the BA6438S
contains a short-circuit detection circuit that turns off the motor
drive current if the output-to-ground potential becomes
abnormally low.
Page 6

Motor driver ICs
Application example
!
Hall
Hall
Hall
0.033
V
CC
µF
Torque control
signal
H1
10
9
H1
H2
8
7
6
5
H3
4
PCH
EC
17
16
ECR
12
+
Hall amp
−
+
−
H2
+
H3
−
Ripple
cancellation
GND
VCC
Motor direction
control signal
Motor
direction
detection
AGC
TL CS P
20 22 18 21
Motor direction
P signal combiner
saturation
prevention
PCV
0.033
µF
V
Switching
Oscil-
lator
15
CC
regulator
OSC
470PF
ED / S
setting
Motor direction switching
TSD
Short-circuit
detection
Output
C
I
0.1µF
1911
Output
saturation
detector
Signal power
supply
V
M
24
A1
23
A2
3
A3
1
ATC
2
REG
13
14
BA6438S
Motor power supply
0.5Ω
VS
0.1µF
Operation notes
!
The BA6438S has two thermal shutdown circuits (TSD1
and TSD2) to protect the IC. The typical shutdown temperatures are 175°C for TSD1 and 215°C for TSD 2.
When the TSD1 is activated at an elevated chip temperature, the output pins (pins 1, 3, and 23) are set to the open
state. TSD1 is functional against excessive power dissipation, output short-circuiting, and other irregularities in
the output current, but does not work against overheating
caused by high internal currents due to externally caused
IC damage or pin-to-pin short-circuiting.
When TSD2 is activated at a higher chip temperature, the
high-and low-side output transistors are turned on, and
the internal resistance between the motor power supply
pin (pin 24) and the output ground pin (pin 2) drops to less
Fig. 8
than 3Ω. The motor power supply current (I
M
en by
R
M+R2P
VM[V]
+3
[
Ω]
I
M
=
where
M
I
is the motor supply current,
M
V
is the motor supply voltage,
M
R
is the motor power supply output resistance,
2P
R
is the pin-2 resistance.
In your application, make sure to connect between the
motor power supply and pin 24 a circuit breaker that
operates at currents less than I
M
.
) is then giv-
Page 7

Motor driver ICs
Electrical characteristic curves
!
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
ATC VOLTAGE : ATC (V)
0.1
V
CC
=
5V, V
M
=
12V, R
ATC
=
0.5Ω
+
+
+
, H
3
) = (LMH)
, H
2
(H
1
0
0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
TORQUE CONTROL : E
C
Fig.9 Output current vs. torque
control voltage
(Ι)
BA6438S
160
140
120
100
+
+
, H3
80
(H1+, H2
=
60
40
ATC VOLTAGE : ATC (mV)
20
0
(V)
−800 −600 −400 −200
)
(LLH)
TORQUE CONTROL : E
(H1+, H2+, H3
=
(LMH)
0
VCC=5V
M
=12V
V
R
ATC
+
(mV)
C
=0.5Ω
)
200 400
Fig.10 Output current vs. torque
control voltage (ΙΙ)
30
25
20
15
10
ATC VOLTAGE : ATC (mV)
−120 −80 −40
VCC=5V,VM=12V,RATC=0.5Ω
+
1
(H
5
0
TORQUE CONTROL : EC
+
+
) =
(LMH)
, H
3
, H
2
E
CR
(2.5V)
Fig.11 Output current vs. torque
control voltage (ΙΙΙ)
+40 +80
(mV)
1.8
1.6
(V)
1.4
OH
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE : V
00200 400 600 800 1000
OUTPUT CURRENT : I
HIGH level output voltage
(1, 3, 23pin)
(mA)
OH
Fig.12 Output high level voltage
vs. output current
VCC=5V
1M
500k
300k
200k
100k
OSCILLATION FREQUENCY(Hz)
50k
50 100 200 300 500 1000
OSC PIN CAPACITANCE(PF)
Fig.15 Capacitance of the capacitor
connected to the OSC pin vs.
oscillation frequency
1.8
1.6
(V)
LOW level output voltage
OL
1.4
(1, 3, 23pin)
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE : V
0
0
400 800 1200
OUTPUT CURRENT : I
Fig.13 Output low level voltage
vs. output current
5
4
3
2
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
S
1
V
0
0
Ec=2.3V
0.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
1.0 1.5
V
M
-
V
OH
Fig.16 High-side saturation detection
output voltage (pin 14) vs.
output voltage
ATC(2pin)
Pin voltage
(R
OL
2V
1.5V
(V)
ATC
1.0V
= 0.5Ω)
(mA)
0.5V
70
VCC=5V, VM=12V, R
C
=OV, ECR=2.5V
E
60
50
40
30
S OFFSET (mV)
C
20
TL -
10
0
0
TORQUE LIMIT VOLTAGE : TL(V)
ATC
=0.5Ω
0.2 0.4 0.6
Fig.14 TL-CS offset vs. torque
limit voltage
6
5
4
3
2
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1
10 20 30 40 50 60
0
SINK CURRENT(13pin) (mA)
Fig.17 Switching regulator sink
current vs. output voltage
VCC=5V
Page 8

Motor driver ICs
3.0
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
POWER DISSIPATION : Pd (W)
0
0 40 80 120 160
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE : Ta(°C)
Fig.18 Thermal derating curve
External dimensions
!
24
(Units : mm)
23.8±0.3
18.8
BA6438S
R1.8
13
12.0±0.3
1
0.51Min.
1.778 0.55±0.1
3.2±0.2 5.3±0.3
12
SDIP-M24
13.8
0.4±0.1
0°∼15°
 Loading...
Loading...