Page 1
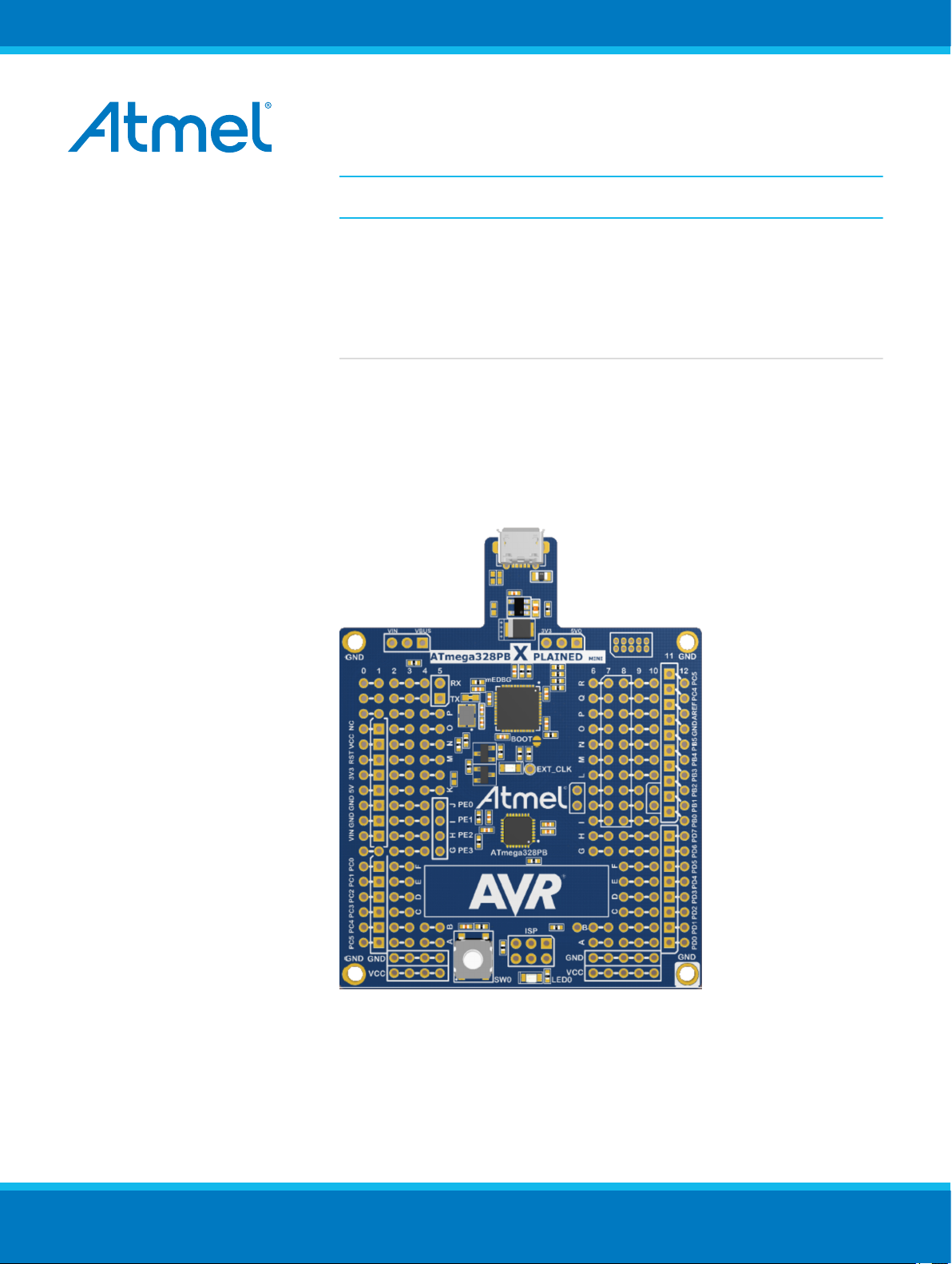
AVR 8-bit Microcontrollers
ATmega328PB Xplained Mini
USER GUIDE
Introduction
This user guide describes how to get started with the Atmel® ATmega328PB
Xplained Mini board. The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini evaluation kit is a
hardware platform to evaluate the Atmel ATmega328PB microcontroller. The
evaluation kit comes with a fully integrated debugger that provides seamless
integration with Atmel Studio 6.2 (and later version). The kit provides access
to the features of the ATmega328PB enabling easy integration of the device
in a custom design.
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction......................................................................................................................1
1. Getting Started...........................................................................................................3
1.1. Features....................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2. Design Documentation and Related Links................................................................................... 3
1.3. Xplained Mini Quick Start............................................................................................................. 3
1.3.1. Connect to Atmel Studio................................................................................................ 3
1.3.2. Connect to the COM Port.............................................................................................. 4
1.4. Programming and Debugging...................................................................................................... 4
1.4.1. Programming the Target using mEDBG........................................................................ 4
1.4.2. Debugging the Target using mEDBG.............................................................................5
1.4.3. Programming the Target using an External Programmer.............................................. 6
1.4.4. Programming the ATmega32U4 using an External Programmer...................................6
1.4.5. Programming the ATmega32U4 using a Bootloader..................................................... 7
1.5. Board Assembly........................................................................................................................... 8
1.5.1. Custom Assembly..........................................................................................................8
1.5.2. Standalone Node........................................................................................................... 8
1.5.3. Connecting an Arduino Shield....................................................................................... 8
1.6. mEDBG Command Line Interface................................................................................................8
1.6.1. mEDBG Low Power Modes........................................................................................... 8
1.6.2. mEDBG Fuse Filter........................................................................................................8
1.6.3. How to Issue Commands...............................................................................................8
2. Hardware User Guide.............................................................................................. 11
2.1. Board Overview.......................................................................................................................... 11
2.2. Target Headers and Connectors.................................................................................................11
2.2.1. Target Digital I/O.......................................................................................................... 11
2.2.2. Board Power Header................................................................................................... 12
2.2.3. Target Analogue I/O.....................................................................................................12
2.2.4. Target Programming.................................................................................................... 13
2.2.5. Target Additional I/O.................................................................................................... 13
2.3. Target GUI.................................................................................................................................. 13
2.3.1. Push Button................................................................................................................. 14
2.3.2. User LED..................................................................................................................... 14
2.3.3. QTouch buttons............................................................................................................15
2.4. On-board Power Supply............................................................................................................. 16
2.5. mEDBG...................................................................................................................................... 16
2.5.1. mEDBG Status LED.................................................................................................... 16
2.5.2. mEDBG External Clock............................................................................................... 17
2.5.3. mEDBG COM Port Connection................................................................................... 17
2.5.4. mEDBG JTAG Interface...............................................................................................17
2.5.5. mEDBG USB Interface................................................................................................ 18
2.6. Extension Header Area.............................................................................................................. 18
2.7. Factory Programmed..................................................................................................................19
2.8. Document Revision History........................................................................................................ 20
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
2
Page 3

1. Getting Started
1.1. Features
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini evaluation board provides a development platform for the Atmel
ATmega328PB.
Key Features
• On-board debugger with full source-level debugging support in Atmel Studio
• Auto-ID for board identification in Atmel Studio
• Access to all signals on target MCU
• One green mEDBG status LED
• One yellow user LED
• One mechanical user push button
• QTouch® user area
• Virtual COM port (CDC)
• External target CLK 16MHz at 5V, 8MHz at 3.3V
• USB powered
• 3V3 regulator
• Arduino shield compatible foot prints
• Target SPI bus header foot print
• Xplained Pro extension headers can easily be strapped in
1.2. Design Documentation and Related Links
The most relevant documents and software for the evaluation board are available here:
Design Documentation - ZIP file containing CAD source, schematics, BOM, assembly drawings, 3D plots,
layer plots, etc.
Atmel Studio - Free Atmel IDE for development of C/C++ and assembler code for Atmel microcontrollers.
Xplained - Atmel Xplained prototyping and evaluation platform.
Atmel Spaces - Open Source projects for Xplained Mini.
1.3. Xplained Mini Quick Start
How to connect the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board embedded debugger to Atmel Studio and how to
connect the ATmega328PB UART to a COM port.
1.3.1. Connect to Atmel Studio
How to connect the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board embedded debugger to Atmel Studio to get
started with SW development.
1. Download and install Atmel Studio version 6.2 or later versions.
2. Launch Atmel Studio.
3. Connect the board to the USB port and it will be visible in Atmel Studio.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
3
Page 4
1.3.2. Connect to the COM Port
How to connect the ATmega328PB UART to a COM port.
All Xplained Mini boards have an embedded debugger (mEBDG) with a number of features, among them
a CDC/COM port, which enables the user to connect the ATmega328PB UART to the PC.
1. Connect the Xplained Mini USB to the PC.
2. A COM port named "mEDBG Virtual COM Port" will be available.
3. Start a terminal emulator or other applications using the COM port, typical COM port settings are
9600 baud N81.
1.4. Programming and Debugging
Programming and debugging the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini.
The target micro-controller is the ATmega328PB.
The mEDBG FW is running on the ATmega32U4.
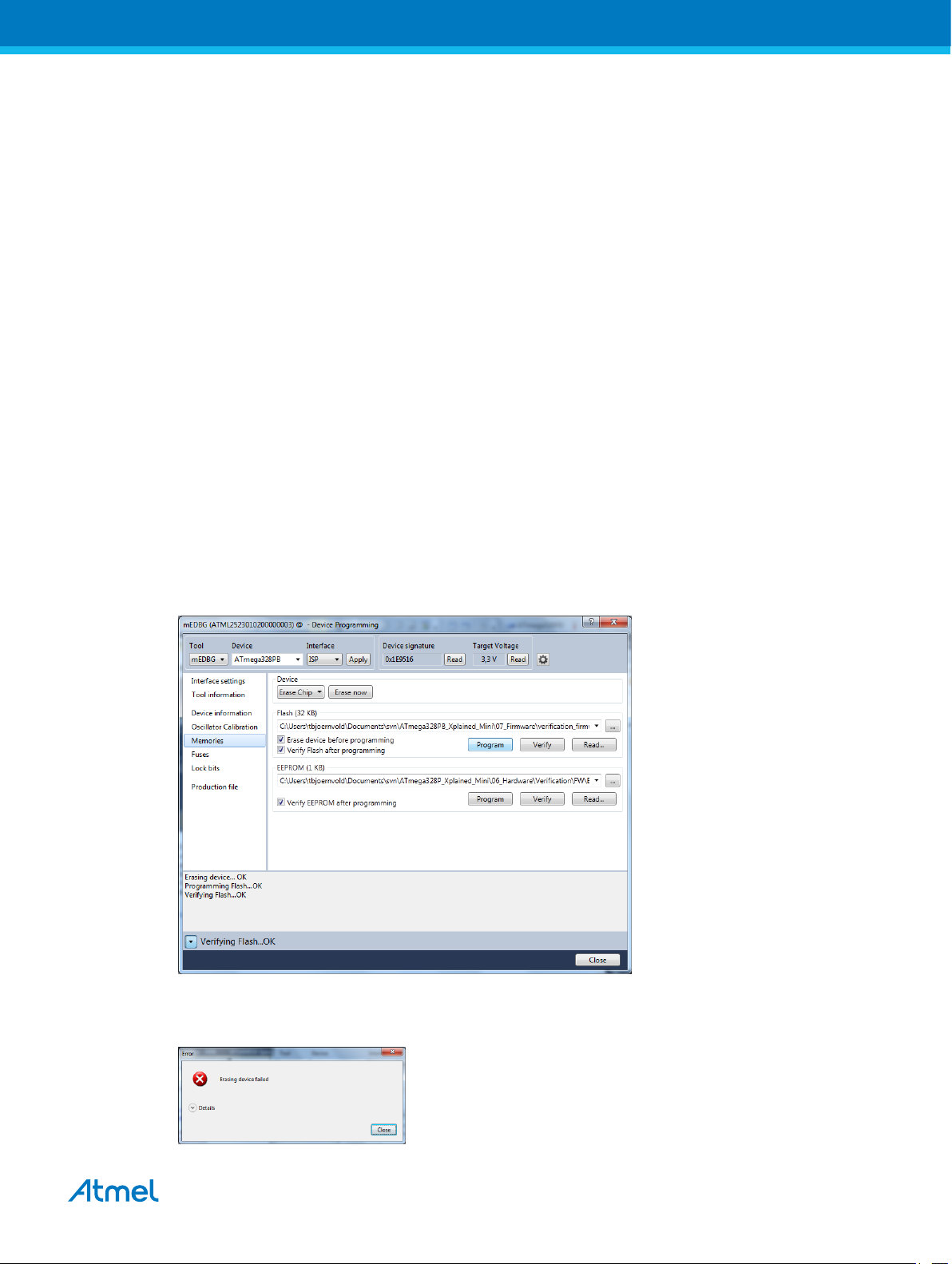
1.4.1. Programming the Target using mEDBG
Using the Embedded Debugger on the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board to program the
ATmega328PB and setting the fuses.
1. Connect the Xplained Mini USB to the PC.
2. Go to Atmel Studio: click the Tools tab, select Device Programming, and select the connected
mEDBG as Tool with Device as ATmega328PB and Interface to SPI, click Apply.
3. Select "Memories" and locate the source .hex or .elf file and click Program.
4. NOTE: If a previous debug session was not closed by selecting "Disable debugWIRE and Close" in
the Debug menu, the DWEN fuse will be enabled and the target will still be in debug mode, i.e. it
will not be possible to program the target using the SPI.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
4
Page 5
5. If the source file contains fuse settings, select "Production file" and upload the .elf file to program
the fuses.
6. Select "Fuses" to program the fuses manually. Set the fuse(s) and click "Program". Recommended
fuse settings:
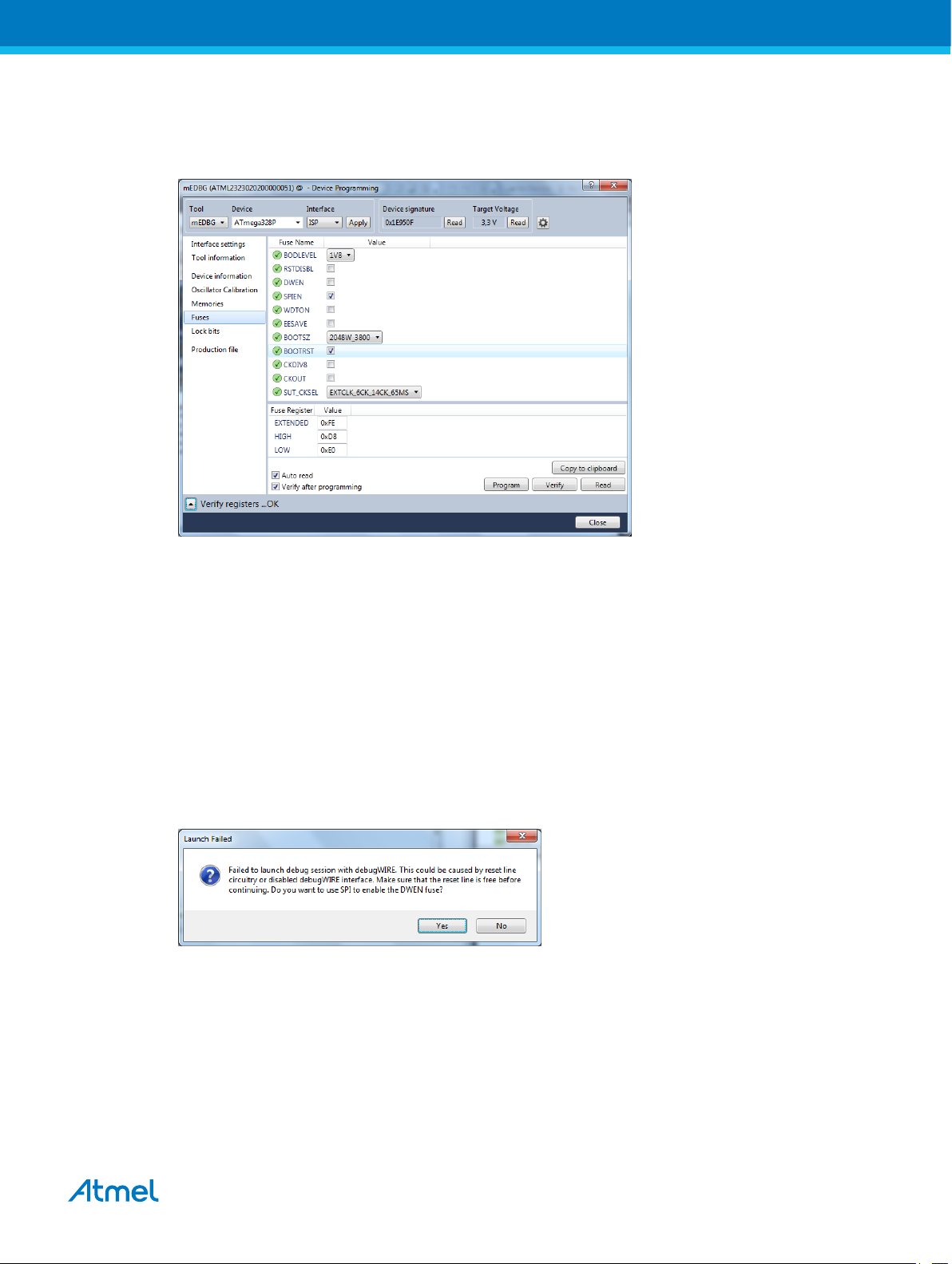
1.4.2. Debugging the Target using mEDBG
Using the Embedded Debugger on the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board to debug the ATmega328PB
via debugWIRE.
1. Start Atmel Studio.
2. Connect the Xplained Mini USB to the PC.
3. Open your project.
4. Click the "Project" tab and select the project "properties", click the "Tools" tab and select mEDBG
as debugger and debugWIRE as interface.
5. Click the "Debug" tab and select "Start Debugging and Break".
6. Atmel Studio will display an error message if the DWEN fuse in the ATmega328PB is not enabled,
click YES to make Studio set the fuse using the SPI interface.
7. A debug session is started with a break in main, debugging can start.
8. When exiting debug mode select "Disable debugWIRE and Close" in the Debug tab, this will
disable the DWEN fuse.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
5
Page 6
Important: If not exiting debug mode by selecting "Disable debugWIRE and Close" in the
Debug menu, the DWEN fuse will be enabled and the target will still be in debug mode, i.e. it
will not be possible to program the target using the SPI.
Important: If any other CPU CLK than the external CLK supplied by the mEDBG is used the
debugWIRE is not guaranteed to work.
Important: Applying a signal to J202/RESET (the RESET_SENSE signal) while debugging
may result in unexpected behaviour. This signal is NOT available during a debugging session
because the RESET line is actively used by the debugWIRE interface
1.4.3. Programming the Target using an External Programmer
How to program the target ATmega328PB using the AVR® JTAGICE mkII, JTAGICE3, Atmel-ICE, or
other Atmel Programmers.
1. Connect the External Programmer USB to the PC.
2. Connect the External Programmer to the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board SPI connector.
3. Go to Atmel Studio: click the Tools tab, select Device Programming, and select the External
Programmer connected as Tool with Device as ATmega328PB and Interface to SPI, click Apply.
4. Select "Memories" and locate the source .hex or .elf file and click Program.
1.4.4. Programming the ATmega32U4 using an External Programmer
How to program the ATmega32U4 using the AVR® JTAGICE mkII, JTAGICE3, Atmel-ICE, or other Atmel
Programmers.
1. Connect the External Programmer USB to the PC.
2. Connect the External Programmer to the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board JTAG connector.
3. Go to Atmel Studio: click the Tools tab, select Device Programming, and select the connected
mEDBG as Tool with Device as ATmega32U4 and Interface to JTAG, click Apply.
4. Select "Memories" and locate the source .hex or .elf file and click Program.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
6
Page 7
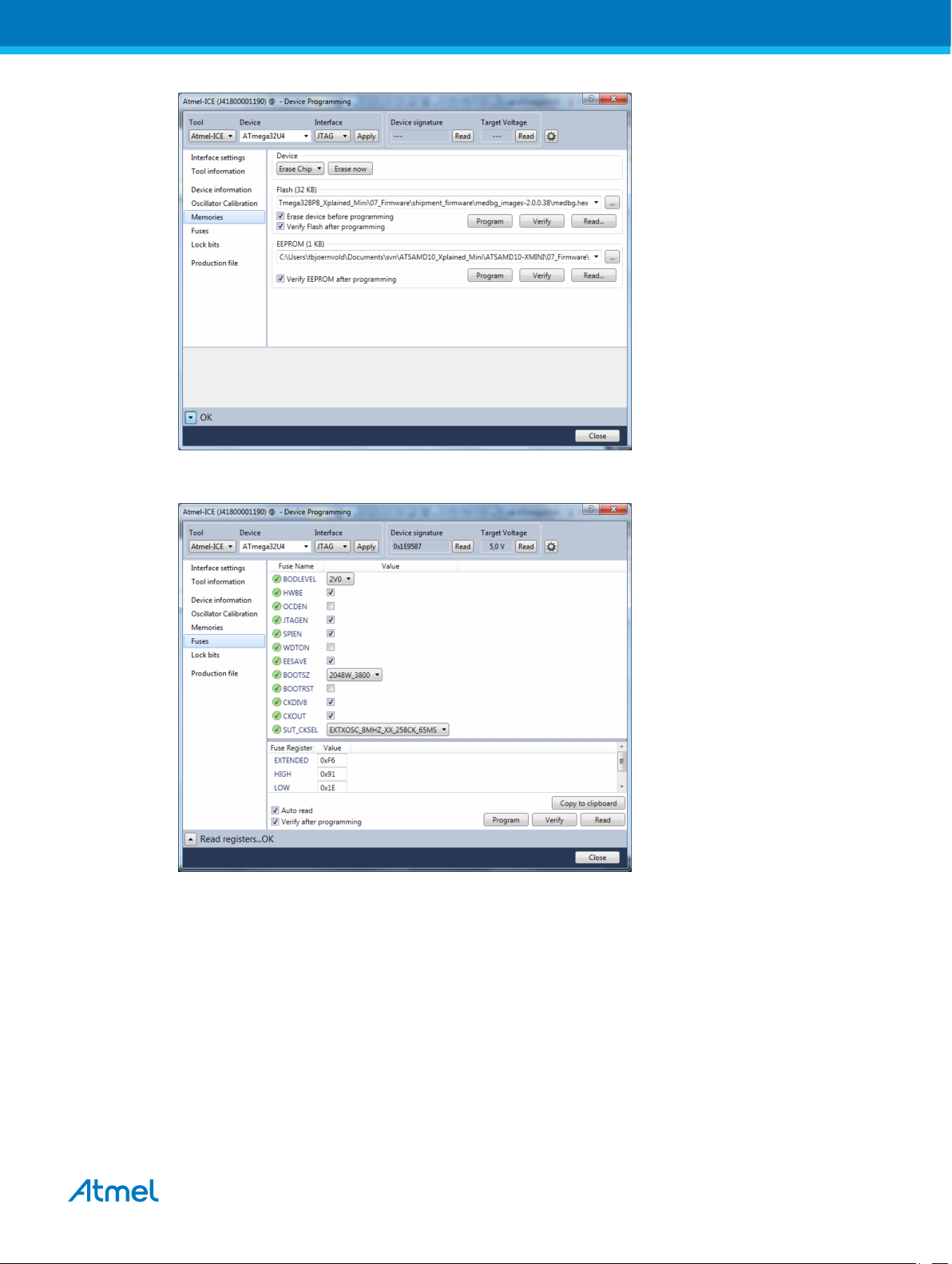
5. Select "Fuses" to program the fuses manually. Set the fuse(s) and click "Program". Recommended
fuse settings:
1.4.5. Programming the ATmega32U4 using a Bootloader
This section describes how to use the bootloader to program the ATmega32U4.
1. Install the Bootloader interface on the PC, download the installer from FLIP.
2. Start the Bootloader PC GUI "FLIP".
3. Short strap J102.
4. Connect the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board USB connector to the PC.
5. Select Device = ATmega32U4 (Device - Select).
6. Select USB communication (Ctrl+U).
7. Select memory area to program (use the toggle memory button bellow the Atmel logo).
8. Select Load Hex file (Ctrl+L).
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
7
Page 8

9. Select Programming Options.
10. Click "Run", observe status in status field.
1.5. Board Assembly
The Xplained Mini board can easily be assembled into a product prototype for software development and
hardware verification.
1.5.1. Custom Assembly
All signals of the ATmega328PB are available in the Xplained Mini board connector grid, enabling easy
connection of external sensors and output devices in order to prototype the customer specific application.
1.5.2. Standalone Node
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board can be used as a standalone node with an external power
source, e.g. the 4xAAA or 2xAAA battery pack available from Atmel.
1.5.3. Connecting an Arduino Shield
Arduino® shields can be mounted in the marked positions (J200, J201, J202, and J203) .
1.6. mEDBG Command Line Interface
The mEDBG has a command line interface enabling configuration of the mEDBG.
1.6.1. mEDBG Low Power Modes
There are two modes enabling the Xplained Mini to save power when connected to an external power
source other than an USB connection.
Sleep Mode where the mEDBG is disabled. When enabled the ATmega32U4 will enter sleep mode if not
enumerated within about 5sec. In this mode the external clock is not available to the target MCU.
1MHz Mode where the mEDBG/ATmega32U4 is set to run at 1MHz, saving power while maintaining the
USB connection for the COM port. The external clock will be 1MHz.
Table 1-1 Available Commands
Mode Command External CLK COM port mEDBG program mEDBG debug
Sleep 0xFB (bit2=0) disabled disabled disabled disabled
1MHz 0xFD (bit1=0) 1MHz enabled useless useless
Factory settings 0xFF 16MHz (@5V)
1.6.2. mEDBG Fuse Filter
The mEDBG does not initially allow users to program the CLK related fuses in the target. This is done to
avoid problems with the debugger when the target and mEDBG is not in CLK sync. This filter can be
disabled by issuing the command 0xFE ( bit0 = 0) enabling configuration of all ATmega328PB fuses.
enabled enabled enabled
8MHz (@3V3)
1.6.3. How to Issue Commands
The command line interface is supported by mEDBG version 1.6 or later.
The mEDBG command line interface can be accessed with the Python script found on Atmel Spaces
Releases (mEDBG_script.zip).
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
8
Page 9

If you have Studio 7.0 (and later versions), the mEDBG included supports the command line interface, if
not, the mEDBG can be downloaded from Atmel Spaces Releases (medbg_fw.zip).
Basic Python is required to run the script, Python can be downloaded from Python.
How to issue commands
1. Install Python.
2. Download the file "mEDBG_script.zip" from Atmel Spaces Releases.
3. Unzip the file "mEDBG_script.zip".
4. Edit "stuff.py" to issue the selected command "c.set_suffer(0xXX)".
5. Open a command window in the directory where "stuff.py" is located. (Browse to the, folder rightclick on folder with shift pressed and select “Open command window here”.)
6. Connect the Xplained Mini.
7. Run "stuff.py" (c:\Python27\python stuff.py).
8. The script will print the selected tool and display SUFFER setting.
9. Recycle power (disconnect/connect the board) for the change to take effect.
10. Edit "stuff.py" to issue the command c.set_suffer(0xFF) to reset to factory setting.
How to upgrade the Xplained Mini mEDBG
1. Start Atmel Studio.
2. Connect the Xplained Mini to the computer.
3. In Atmel Studio, select Tools – Device programming (Ctrl – Shift – P)
4. In the Device Programming window, select Tool to mEDBG and click Apply. If there is a new
mEDBG version available, the Atmel Studio will ask if you want to upgrade.
5. To verify mEDBG version, click "Tool Information" when mEDBG is selected as Tool.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
9
Page 10

Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
10
Page 11

2. Hardware User Guide
Enter a short description of your concept here (optional).
This is the start of your concept.
2.1. Board Overview
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini headers overview.
.
2.2. Target Headers and Connectors
The ATmega328PB related headers.
2.2.1. Target Digital I/O
The J200 and J201 headers provide access to the ATmega328PB digital I/O pins.
Table 2-1 J200 Digital I/O High Byte Header
J200 pin ATmega328PB pin Function
1 PB0
2 PB1
3 PB2 SS, SPI Bus Master Slave select
4 PB3 MOSI, SPI Bus Master Output/Slave Input
5 PB4 MISO, SPI Bus Master Input/Slave Output
6 PB5 SCK, SPI Bus Master clock Input
7 GND
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
11
Page 12

J200 pin ATmega328PB pin Function
8 AREF
9 PC4 SDA, 2-wire Serial Bus Data Input/Output Line. Shared with
ADC4
10 PC5 SCL, 2-wire Serial Bus Clock Line. Shared with ADC5
Table 2-2 J201 Digital I/O High Low Header
J201 pin ATmega328PB pin Function
1 PD0 TXD (ATmega328PB USART Output Pin)
2 PD1 RXD (ATmega328PB USART Input Pin)
3 PD2
4 PD3
5 PD4
6 PD5
7 PD6
8 PD7
2.2.2. Board Power Header
The J202 header enables connection to the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini power system.
Table 2-3 J202 Power Header
J202 pin Signal Description
1 NC
2 VCC_TARGET The power source selected for the target. (Select by J301)
3 RESET_SENSE This is a RESET signal monitored by the mEDBG, if pulled low the
4 VCC_P3V3 The 3.3V regulator output
5 VCC_P5V0 The selected power source. (VIN or VBUS selected by J300)
6 GND
7 GND
8 VCC_VIN The external power source connection.
.
2.2.3. Target Analogue I/O
The ATmega328PB ADC input pins are available in the J203 header.
target RESET line will be pulled low by the mEDBG. The ATmega32U4
internal pull-up is enabled. This signal is not available during debugging.
AREF is available in J200 pin 8.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
12
Page 13

Table 2-4 J203 Analogue Header
J203 pin ATmega328PB pin Function
1 PC0 ADC Input Channel 0
2 PC1 ADC Input Channel 1
3 PC2 ADC Input Channel 2
4 PC3 ADC Input Channel 3
5 PC4 ADC Input Channel 4
6 PC5 ADC Input Channel 5
2.2.4. Target Programming
The J204 header enable direct connection to the SPI bus with an external programmer for programming
of the ATmega328PB.
Table 2-5 SPI Header
J204 pin ATmega328PB pin Function
1 PB4 MISO
2 VCC target
3 PB5 SCK
4 PB3 MOSI
5 PC6 RESET
6 GND
2.2.5. Target Additional I/O
Signals not available in any of the headers or connectors, are available in column 5 of the grid.
Table 2-6 Additional I/O
ATmega328PB pin Grid position
2.3. Target GUI
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini has One LED, one push button, and a QTouch area.
PE0 J5
PE1 I5
PE2 H5
PE3 G5
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
13
Page 14

2.3.1. Push Button
A general purpose push button, SW200, is connected to PB7.
2.3.2. User LED
There is one yellow LED, D200, available for use by the application SW.
The LED is connected to ATmega328PB pin 17 - PB5 and to the SPI bus SCK signal for, SCK is in 3state when not used by the mEDBG.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
14
Page 15

2.3.3. QTouch buttons
Up to 4 QTouch buttons are available on the ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board. The QTouch area can
be configured as buttons or as a limited slider. For a typical button or slider reference design use the QT1
Xplained Pro extension.
Tip: There is a range of QTouch reference designs demonstrated with the QT Xplained Pro
extensions located at
Xplained - Atmel Xplained prototyping and evaluation platform.
Table 2-7 QTouch Buttons Wiring
Button ATmega328PB PTC
A PE2 via 100k. Y6
V PE3 via 100k. Y7
R PC3 via 100k. Y3
S Connected via 0Ω to A enabling slider
configuration.
In the default HW configuration the QTouch area can be configured in SW as 3 buttons or as a limited
slider.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
15
Page 16

To get 4 buttons the S touch area can be connected to e.g. PC2 by removing the 0Ω resistor R214 and
adding a wire or a 100k resistor from PC2 (D1) to the test point in B5.5.
.
2.4. On-board Power Supply
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board has an on-board 3.3V regulator (150mA) which can be used to
power the ATmega328PB.
The J300 and J301 headers configure the ATmega328PB power supply and the board power source.
The default configuration is set by R300 and R301 0Ω resistors which can be easily removed to change
the default configuration.
Table 2-8 Board Power Options
Mode J301 connection,
target
J300 connection,
board
Function
5V (Default) pin2 connected to pin1 pin2 connected to pin1 Board and target powered by VBUS
3.3V USB pin2 connected to
pin3, remove R301
VIN pin2 connected to pin1 pin2 connected to pin3,
3.3V VIN pin2 connected to
pin3, remove R301
pin2 connected to pin1 Target powered by 3.3V and USB
interface powered by VBUS
Board and target powered by VIN,
remove R300
pin2 connected to pin3,
remove R300
J202.8. 1.8V < VIN < 5.5V
Target powered by 3.3V. VIN as
regulator input. 4V < VIN < 16V
Tip: Use the BOD LEVEL fuse to avoid the following challenges:
For the CPU to successfully decode and execute instructions, the supplied voltage must always
stay above the minimum voltage level set by the chosen operating frequency.
When supplied voltage drops below this level, the CPU may start to execute some instructions
incorrectly. The result is unexpected activity on the internal data and control lines.
This activity may cause CPU Registers, I/O Registers and Data Memories to get corrupted.
To avoid these problems, the CPU should be prevented from executing code during periods of
insufficient supply voltage.
2.5. mEDBG
The ATmega328PB Xplained Mini board has an embedded debugger/programmer enabling debugging
and programming of the ATmega328PB without any additional external equipment.
2.5.1. mEDBG Status LED
The mEDBG has a green status LED connected to ATmega32U4 PC6 to signal the embedded debugger
state.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
16
Page 17

Table 2-9 mEDBG Green Status LED Function
mEDBG state LED Function
Enumeration ON During the initial USB connection process the LED is on until enumerated
Programming ON The LED is on during programming
Debugging ON The LED is on when the debugger is running
2.5.2. mEDBG External Clock
The mEDBG (ATmega32U4) clock out signal (PC7) is connected to the ATmega328PB external clock
input signal and can be used as the system clock source. The External Clock frequency is 16MHz when
the target is running at 5V and 8MHz when running at 3V3.
Tip: The External Clock can be set to 1MHz to save power using the mEDBG command line
interface.
Tip: There is a test point marked EXT.CLK enabling easy measuring and/or connection to the
CLK signal.
or if not enumerated it is turned off within about 5 seconds
2.5.3. mEDBG COM Port Connection
The mEDBG provide a CDC COM port connection when connected to a USB host device.
The mEDBG (ATmega32U4) USART is used for communication with the CDC COM port. The USART
TX/RX signals are available on the J104 header and are also connected to the ATmega328PB via 0Ω
resistors enabling easy disconnect from the ATmega328PB if needed.
Table 2-10 J104 USART Header
J104 pin ATmega32U4 ATmega328PB Function
1 - USART TxD PD3 PD1 TxD out from ATmega32U4
2 - USART RxD PD2 PD0 RxD in to ATmega32U4
2.5.4. mEDBG JTAG Interface
The mEDBG (ATmega32U4) JTAG interface is available for programming and debugging of the
ATmega32U4.
Table 2-11 J100 JTAG Header
J100 pin Signal name Description
1 TCK
2 GND
3 TDO
4 VCC_BOARD ATmega32U4 V
CC
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
17
Page 18

J100 pin Signal name Description
5 TMS
6 RESET Connected to ATmega32U4 only
7 NC
8 NC
9 TDI
10 GND
2.5.5. mEDBG USB Interface
J101 is a Micro-B USB connector connected to the embedded debugger (ATmega32U4).
Table 2-12 J101 USB Header
J101 pin Signal name
1 VBUS
2 D-
3 D+
4 NC
5 GND
The VBUS has a resettable PTC fuse (F100), with a hold current of 0.5A and a trip current of 1.0A to
protect the USB host device.
2.6. Extension Header Area
The marked area on the grid I7 to R8 can be used for strapping in an Xplained Pro extension header or a
10-pin Xplained/RZ600 header.
The SPI bus signals are made available close to the header at row J and K, enabling easy connection to
header pin 15 to 18.
Using Pin 11 to 20 enables connection of the 10-pin connector used on the RZ600 wireless modules and
the 10-pin Xplained sensor modules.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
18
Page 19

The general bus connections for an Xplained PRO Extension board is indicated in the table below,
detailed wiring can be found in the selected extension board documentation.
Table 2-13 Extension Header Typical Signals
Pin Signal name Signal description
1 ID Communication line to the ID chip on the Xplained extension board
2 GND Ground
3 ADC(+) Analog to digital converter, alternatively positive part of differential ADC
4 ADC(-) Analog to digital converter, alternatively negative part of differential ADC
5 GPIO1 General purpose I/O
6 GPIO2 General purpose I/O
7 PWM(+) Pulse width modulation, alternatively positive part of differential PWM
8 PWM(-) Pulse width modulation, alternatively negative part of differential PWM
9 IRQ/GPIO Interrupt request line and/or general purpose I/O
10 SPI_SS_B/
GPIO
11 I2C_SDA Data line for I2C interface
12 I2C_SCL Clock line for I2C interface
13 UART_RX Receiver line of ATmega328PB USART
14 UART_TX Transmitter line of ATmega328PB USART
15 SPI_SS_A Slave A select for SPI
16 SPI_MOSI Master out slave in line of serial peripheral interface
17 SPI_MISO Master in slave out line of serial peripheral interface
18 SPI_SCK Clock for serial peripheral interface
19 GND Ground
20 VCC Power for extension board
2.7. Factory Programmed
The ATmega328PB is preprogrammed with a demo program, ReMorse.
Source code is available in Atmel Spaces.
Slave B select for SPI and/or general purpose I/O
When the CDC COM port is connected to a terminal window (9600 N81), the text you write will be
transmitted via the LED in Morse code. Any Morse code transmitted by using the switch will be displayed
as text in the terminal window.
The ATmega32U4 is preprogrammed with the mEDBG.
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
19
Page 20

2.8. Document Revision History
Document revision Date Comment
42469A 07/2015 Initial document release
Atmel ATmega328PB Xplained Mini [USER GUIDE]
Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
20
Page 21

Atmel Corporation 1600 Technology Drive, San Jose, CA 95110 USA T: (+1)(408) 441.0311 F: (+1)(408) 436.4200 | www.atmel.com
©
2015 Atmel Corporation. / Rev.: Atmel-42469A-ATmega328PB-Xplained-Mini_User Guide-07/2015
Atmel®, Atmel logo and combinations thereof, Enabling Unlimited Possibilities®, AVR®, QTouch®, and others are registered trademarks or trademarks of Atmel
Corporation in U.S. and other countries. Other terms and product names may be trademarks of others.
DISCLAIMER: The information in this document is provided in connection with Atmel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any
intellectual property right is granted by this document or in connection with the sale of Atmel products. EXCEPT AS SET FORTH IN THE ATMEL TERMS AND
CONDITIONS OF SALES LOCATED ON THE ATMEL WEBSITE, ATMEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER AND DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS, IMPLIED
OR STATUTORY WARRANTY RELATING TO ITS PRODUCTS INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL ATMEL BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE, SPECIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS AND PROFITS, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION, OR LOSS OF INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF ATMEL HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Atmel makes no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this
document and reserves the right to make changes to specifications and products descriptions at any time without notice. Atmel does not make any commitment to
update the information contained herein. Unless specifically provided otherwise, Atmel products are not suitable for, and shall not be used in, automotive
applications. Atmel products are not intended, authorized, or warranted for use as components in applications intended to support or sustain life.
SAFETY-CRITICAL, MILITARY, AND AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS DISCLAIMER: Atmel products are not designed for and will not be used in connection with any
applications where the failure of such products would reasonably be expected to result in significant personal injury or death (“Safety-Critical Applications”) without
an Atmel officer's specific written consent. Safety-Critical Applications include, without limitation, life support devices and systems, equipment or systems for the
operation of nuclear facilities and weapons systems. Atmel products are not designed nor intended for use in military or aerospace applications or environments
unless specifically designated by Atmel as military-grade. Atmel products are not designed nor intended for use in automotive applications unless specifically
designated by Atmel as automotive-grade.
 Loading...
Loading...