Page 1

BDTIC www.bdtic.com/Semiconductor
Migrating from ATV750B/BL PLD to ATF750C/CL
1. Introduction
The ATF750C/CL is a PLD from Atmel® in a 24- or 28-pin package with 24D or T-type
flip-flops, and it is an enhanced version of the well-known ATF750B/BL PLD. The
ATF750C/CL is reprogrammable using Atmel’s proven EEPROM-based technology
and is pin-to-pin, functionally, and JEDEC fuse-map wise compatible with the UV
EPROM-based ATV750B/BL.
In addition to all the features available in the ATV750B/BL, the ATF750C/CL also has
programmable pin-keeper circuits on all of its input and I/O pins, and the ATF750CL
has a much lower standby current (approximately 1 mA) than the ATV750BL. Moreover, package options offered for the ATF750C/CL are broader including RoHS
compliant (fully Green) packaging and TSSOP package type in addition to the traditional DIP, SOIC, PLCC, and LCC packages. For the ATF750C/CL in the LCC and
PLCC package types, there are also more V
ATV750B/BL in the same package types, which could help improve noise immunity of
the PLD.
The ATF750C is offered in Commercial, Industrial and Military temperature grades
while the ATF750CL is offered in Commercial and Industrial temperature grades.
Hence, only the ATF750C is offered in Military temperature grade but not the
ATF750CL. The ATF750C in Military temperature grade is also MIL-STD-883
compliant.
With the obsolescence of the ATV750B/BL family of devices, they are to be replaced
by the ATF750C/CL devices. This application note will provide details of the
ATV750B/BL-to-ATF750C/CL migration.
and GND pins available than the
CC
Migrating from
ATV750B/BL PLD
to ATF750C/CL
Application
Note
The datasheet for the ATF750C/CL can be viewed on-line at:
http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc0776.pdf
2. Cross Reference Tables
Table 2-1 lists the ATV750B/BL devices that are obsolete and the corresponding rec-
ommended ATF750C/CL replacements. For commercial and industrial applications, it
is recommended to use the ATF750C/CL in fully Green (RoHS) package types even
though some leaded packages are still available.
Rev. 3697A–PLD–9/08
Page 2
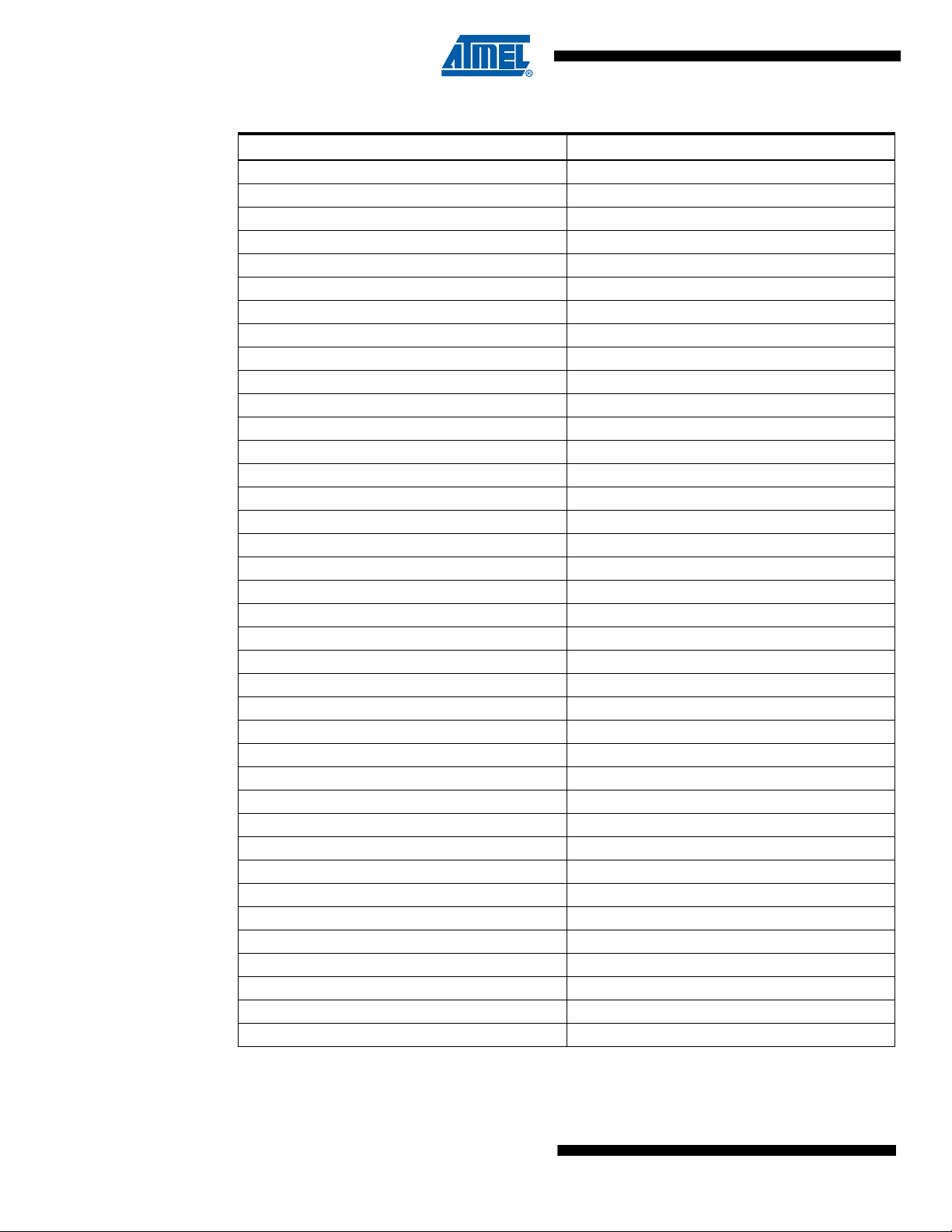
Table 2-1. Obsolete Devices and Recommended Replacements
Obsolete Part Number Replaced with Part Number
ATV750B-7JC ATF750C-10JU
ATV750B-7PC ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-10JC ATF750C-10JU
ATV750B-10PC ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-10SC ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-10SI ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-10PI ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-10JI ATF750C-10JU
ATV750B-15JC ATF750C-10JU
ATV750B-15PC ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-15SC ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-15SI ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-15PI ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-15JI ATF750C-10JI
ATV750B-25JC ATF750C-10JU
ATV750B-25PC ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-25SC ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-25SI ATF750C-10SU
ATV750B-25PI ATF750C-10PU
ATV750B-25JI ATF750C-10JU
ATV750BL-15JC ATF750CL-15JU
ATV750BL-15PC ATF750CL-15PU
ATV750BL-15SC ATF750CL-15SU
ATV750BL-15SI ATF750CL-15SU
ATV750BL-15PI ATF750CL-15PU
ATV750BL-15JI ATF750CL-15JU
ATV750BL-25JC ATF750CL-15JU
ATV750BL-25PC ATF750CL-15PU
ATV750BL-25SC ATF750CL-15SU
ATV750BL-25SI ATF750CL-15SU
ATV750BL-25PI ATF750CL-15PU
ATV750BL-25JI ATF750CL-15JU
ATV750B-10DM/883 or 5962-8872608LA ATF750C-10GM/883 or 5962-0720101MLA
ATV750B-10LM/883 or 5962-88726083X ATF750C-10NM/883 or 5962-0720101M3A
ATV750B-15DM/883 or 5962-88726083X ATF750C-15GM/883 or 5962-0720102MLA
ATV750B-15LM/883 or 5962-88726093X ATF750C-15NM/883 or 5962-0720102M3A
ATV750BL-15DM/883 or 5962-8872611LA ATF750C-15GM/883 or 5962-0720102MLA
ATV750BL-15LM/883 or 5962-88726113X ATF750C-15NM/883 or 5962-0720102M3A
Notes: 1. The speed grade of the recommended replacement device is not the same as the speed grade
of the device being replaced.
2. The recommended replacement device is a Standard-Power device while the device being
replaced is a Low-Power (L) device.
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
2
Migrating from ATV750B/BL PLD to ATF750C/CL
3697A–PLD–9/08
Page 3

Atmel strongly recommends customers who are using the ATV750BL-15DM/883 or ATV750BL-
SUPPLY CURRENT VS. FREQUENCY
LOW-POWER ("L") VERSION (T
A
= 25°C)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0 5 10 25 50 75 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
I
CC
(mA)
15LM/883 devices to replace them with the ATF750C-15GM/883 or ATF750C-15NM/883,
respectively, if lower power consumption is not an important consideration for their application
since the ATF750CL is not offered in the Military temperature grade. More information is provided in the following section.
3. Power Consumption Considerations
When migrating from the ATV750BL Military temperature grade device to the ATF750C, designers should consider power consumption requirements for their applications. For applications that
are using the Low-Power devices (ATV750BL-15DM/883 or ATV750BL-15LM/883), designers
must first determine whether the Low-Power feature is required or not when considering the
migration to the ATF750C. As shown in the Supply Current vs. Frequency Curve (Figure 3-1),
the Low-Power feature only takes effect at operating frequencies below 20 MHz. At frequencies
above 20 MHz, the Low-Power feature in the CPLD is effectively disabled and the power consumption of the CPLD will be the same as a Standard-Power device. Hence, the applications will
not benefit from the Low-Power feature. Please refer to the ATF750C(L) datasheet on Atmel’s
website for the latest ICC data.
Figure 3-1. Supply Current vs. Frequency Curve
Migrating from ATV750B/BL PLD to ATF750C/CL
For Commercial and Industrial applications where the PLD stays idle for long periods of time,
migrating from the ATV750BL to ATF750CL will provide more power savings to these systems
since the ATF750CL has a much lower ICC (standby) than the ATV750BL (1 mA vs. 30 mA max,
and 0.15 mA vs. 15 mA typical). For more information on the Low-Power feature, please refer to
the “Saving Power with Atmel PLDs” application note available on-line at:
http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/DOC0457.PDF
3697A–PLD–9/08
3
Page 4

4. New Features in ATF750C/CL
The following list summarizes the enhanced feature of the ATF750C/CL:
•
Programmable Pin-keeper circuits on input and I/O pins
• Very low standby current consumption for the ATF750CL
• Additional VCC and GND pins for the PLCC and LCC package types
• Electrically erasable
• Improved testability
• Improved programming yields
The sections below contain details on these enhanced features.
4.1 Pin-keeper (Programmable Option)
The ATF750C/CL has programmable Pin-keeper circuits on its input and I/O pins but the
ATV750B/BL does not. This means that any un-driven input or I/O pin (e.g. unused pin or tristated output) on the ATV750B/BL may float between “high” and “Low” logic levels, which can
lead to higher power consumption since more current flows during transitions to each level. To
prevent input and I/O pins from floating, the Pin-keeper circuits in the ATF750C/CL can be
enabled by specifying the appropriate device mnemonic in the CUPL design as described in
Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. WinCUPL Device Mnemonic
Device WinCUPL Device Mnemonic Pin-keeper
ATF750C/CL-DIP
ATF750C/CL-PLCC
V750C
V750CPPK
V750CLCC
V750CPPKLCC
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
When cross-programming an ATV750B/BL JEDEC file into the ATF750C/CL, the Pin-keeper
option will be disabled automatically during programming since the ATV750B/BL does not support this feature.
4.2 Low Standby Current
The ATF750CL features a low standby current of 1 mA (max) in Commercial temperature range,
compared to 30 mA of the ATV750BL. This can be extremely beneficial in designs where the
PLD implements logic functions that operate only for a short time and then stays idle until the
next operation is executed (for example, a data acquisition system which takes measurements
in certain periods of time and then goes idle).
4.3 Electrically Erasable
The ATF750C/CL is a EEPROM based PLD while the ATV750B/BL is UV EPROM based.
Therefore, the ATF750C/CL can be electrically erased but the ATV750B/BL cannot. This gives
users the capability to easily erase and re-program the ATF750C/CL using a device
programmer.
Furthermore, EEPROM-based PLD allows the part to be better tested with improved programming, quality, and overall yields to customers and hence lower the overall cost.
4
Migrating from ATV750B/BL PLD to ATF750C/CL
3697A–PLD–9/08
Page 5

Migrating from ATV750B/BL PLD to ATF750C/CL
4.4 Additional VCC and GND Pins
The ATF750C/CL devices in the PLCC and LCC package types have 1 more VCC pin (pin #1)
and 3 more GND pins (pin #8, 15, and 22) than the ATV750B/BL in the same package types.
These additional power pins can be used to improve the noise immunity of the ATF750C/CL.
Connections to these pins are not required but are highly recommended for enhanced noise
immunity.
5. Programming (How do I program the ATF750C/CL?)
Cross-programming is the fastest way to port an ATV750B/BL design to the ATF750C/CL. ThirdParty Programmer support for ATF750C/CL (including cross-programming capability) is available from major vendors such as Data I/O, BPM Microsystems and HI-LO Systems. Some ThirdParty Programmers such as Data I/O [UniSite/3900 models] have a device listing specifically for
Atmel cross-programming (ATMEL-XPGM). In simplistic terms, cross-programming implies that
existing ATV750B/BL JEDEC fuse-map files can be programmed into the ATF750C/CL without
the need to recompile designs specifically for the ATF750C/CL. Table 5-1 lists examples of
device menu types that are used by some of the Third-Party programmer vendors.
For example:
Use device type “TF750C-PLCC as ATV750B-PLCC” to cross-program an ATV750B
JEDEC file into an ATF750C in the PLCC package type.
Table 5-1. Cross-programming Device Type Examples
Programmer Cross-programming Device Type Example
BPM Microsystems Atmel ATF750C as v750B
Data I/O 750C-PLCC as 750B-PLCC
HI-LO Systems ATF750C/CL (V750B)
Note: 1. Under the ATMEL-XPGM manufacturer list.
6. Design Tools
Customers who need to recompile their designs to target the ATF750C/CL must use Atmel WinCUPL. This is free to download from the Tools & Software section of the PLD home page at
http://www.atmlel.com/products/pld. Customers who are using DOS ABEL or ATMEL SYNARIO
(with ABEL 6.x) can continue to target designs to an ATV750B device and then use cross programming to program the ATF750C/CL device.
7. Technical Support
URL: http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/support.asp
E-mail: pld@atmel.com
Hotline: (408) 436-4333
(1)
3697A–PLD–9/08
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/Semiconductor
5
 Loading...
Loading...