Page 1
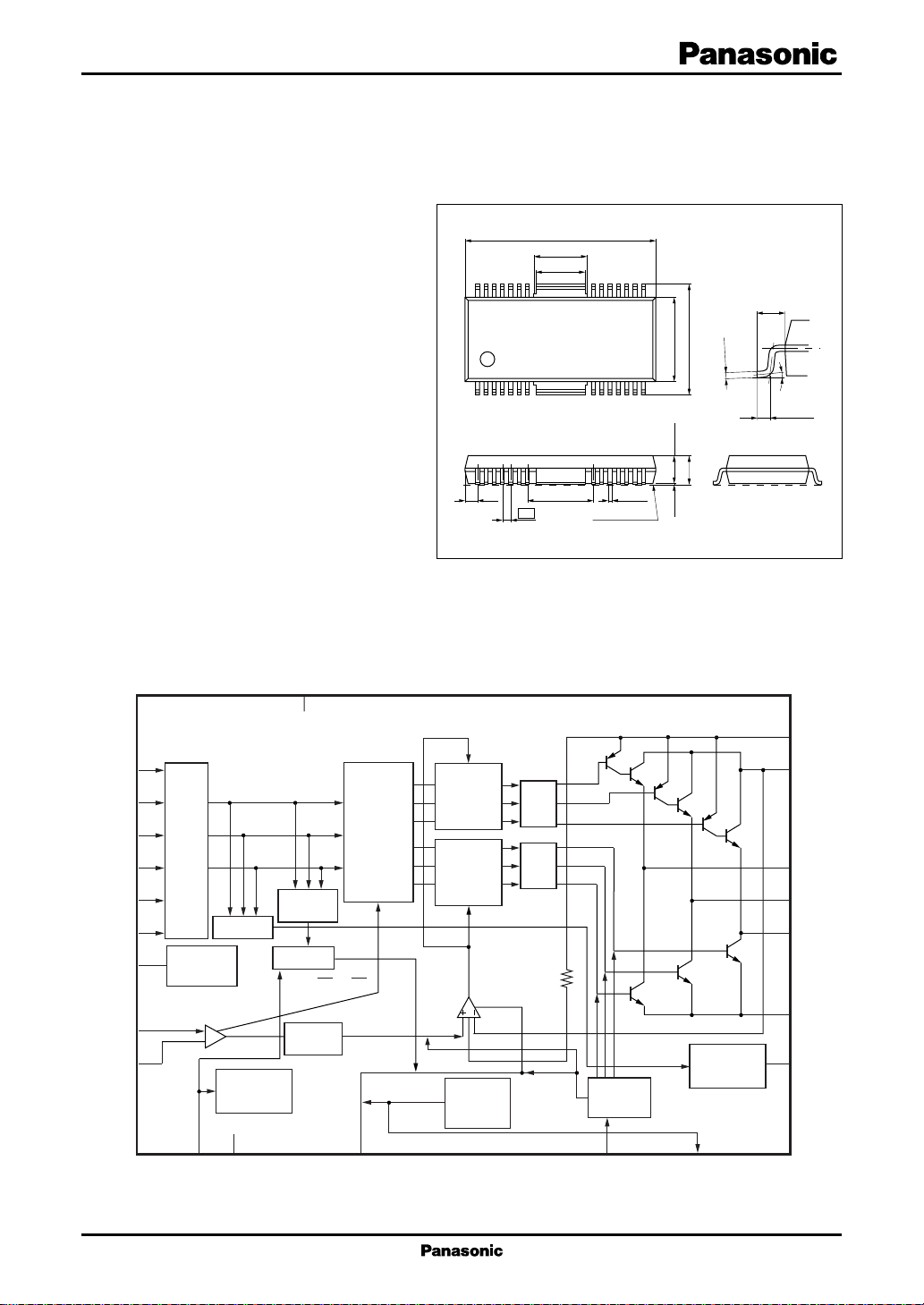
ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player
AN8480NSB
3-phase full-wave motor driver IC
■ Overview
The AN8480NSB is a 3-phase full-wave motor
driver IC with a reverse rotation brake/short brake
changeover function, incorporating a thermal protection circuit with its protection monitor pin.
■ Features
• 3-phase full-wave and snubberless
• FG output
• Current limit
• Reverse rotation prevention
• Thermal protection circuit built-in (with thermal
protection monitor pin)
■ Applications
• Various types of optical disk drive
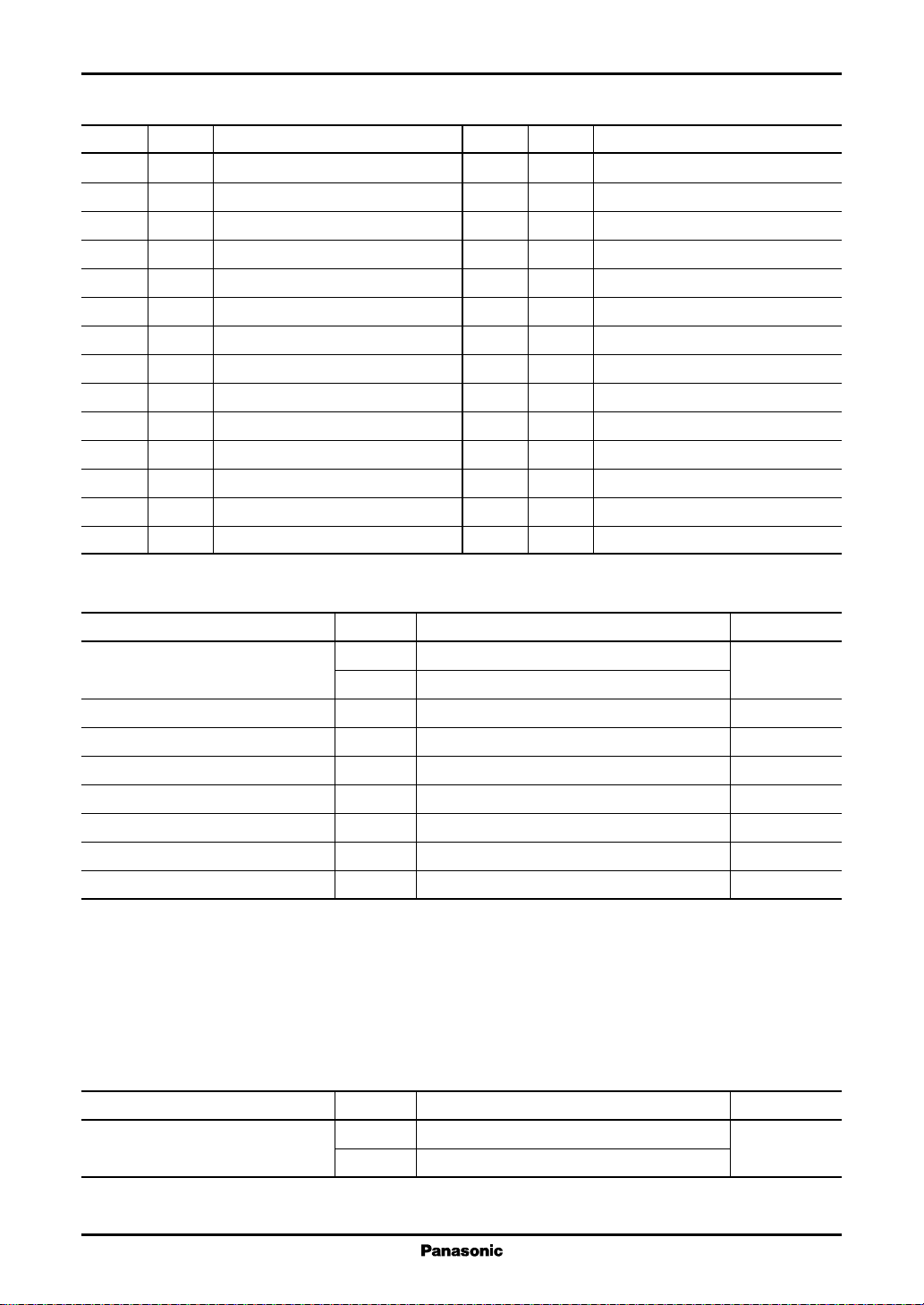
■ Block Diagram
SG
15
2
H1+
3
H1−
H2+
H2−
H3+
H3−
VH
EC
ECR
5
6
8
9
7
18
17
Hall
amp.
matrix
Hall
bias
10
S/S
Detection
EA
Start/stop
16
CC
V
Direction
detection
ER
Logic
EP = ER × ΕΑ
Absolute
value
Direction
changeover
20
PCI
28 22 21
17 814
(1.2)
Upper side
distribution
Lower side
distribution
VTL
Thermal
protection
circuit
0.8
Amp.
Amp.
18.4±0.2
(5.15)
(4.8)
(6.4)
HSOP042-P-0400
+0.10
0.35
–0.05
Seating plane
Brake
circuit
13
BRK
Unit: mm
15
(1.315)
–0.05
+0.10
8.3±0.22.7±0.20.1±0.1
10.93±0.30
0.30
FG
comparator
0° to 10°
0.65±0.20
21
VM
22
CS1
28
A1
27
A2
26
A3
1
PG
12
FG
11
TSDF
1
Page 2
AN8480NSB ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player
■ Pin Descriptions
Pin No. Symbol Description
1 PG Power GND pin
2H1+ Hall element-1 positive input pin
3H1− Hall element-1 negative input pin
4 N.C. N.C.
5H2+ Hall element-2 positive input pin
6H2− Hall element-2 negative input pin
7 VH Hall bias pin
8H3+ Hall element-3 positive input pin
9H3− Hall element-3 negative input pin
10 SS Start/stop changeover pin
11 TFLG Thermal protection monitor pin
12 FG FG signal output pin
13 BRK Brake mode setting pin
14 N.C. N.C.
Pin No. Symbol Description
15 SG Signal GND pin
16 V
Supply voltage pin
CC
17 ECR Torque command reference input pin
18 EC Torque command input pin
19 N.C. N.C.
20 PCI
Current feedback phase compensation pin
21 VM Motor supply voltage pin
22 CS Current det. pin 1
23 N.C. N.C.
24 N.C. N.C.
25 N.C. N.C.
26 A3 Drive output 3
27 A2 Drive output 2
28 A1 Drive output 1
■ Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Supply voltage V
4
Control signal input voltage
*
Supply current I
3
Output current
*
Hall bias current I
2
Power dissipation
Operating ambient temperature
Storage temperature
Note) Do not apply external currents or voltages to any pins not specifically mentioned.
For circuit currents, '+' denotes current flowing into the IC, and '−' denotes current flowing out of the IC.
1: Except for the operating ambient temperature and storage temperature, all ratings are for Ta = 25°C.
*
2: For 70°C and IC alone.
*
3: n = 1, 22, 26, 27, 28
*
4: n = 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 13, 17, 18
*
*
1
*
1
*
V
V
I
T
T
CC
O(n)
HB
P
CC
M
(n)
D
opr
stg
7.0 V
14.4
0 to V
CC
30 mA
±1 200 mA
50 mA
667 mW
−20 to +70 °C
−55 to +150 °C
■ Recommended Operating Range
Parameter Symbol Range Unit
Supply voltage V
CC
V
M
4.25 to 5.5 V
4.5 to 14
V
2
Page 3

ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player AN8480NSB
■ Electrical Characteristics at Ta = 25°C
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Overall
Circuit current 1 I
Circuit current 2 I
Start/stop
Start voltage V
START
Stop voltage V
Medium voltage V
Hall bias
Hall bias voltage V
Hall amplifier
Input bias current I
In-phase input voltage range V
Minimum input level V
Torque command
In-phase input voltage range EC VCC = 5 V 0.5 3.9 V
Offset voltage EC
Dead zone EC
Input current EC
Input/output gain A
Output
High-level output saturation voltage V
Low-level output saturation voltage V
Torque limit current I
FG
FG output high-level FG
FG output low-level FG
In-phase input voltage range V
FG hysteresis width H
Brake cirrcuit
Short brake model level V
Reverse rotation brake mode level V
Short brake start level V
Short brake current I
VCC = 5 V in power save mode 00.1mA
CC1
VCC = 5 V, IO = 0 mA 1 8 16 mA
CC2
Voltage with which a circuit operates 2.7 V
at VCC = 5 V and L → H
Voltage with which a circuit becomes 0.7 V
STOP
off at VCC = 5 V and H → L
Voltage with which V
MED
becomes 1.55 1.75 V
PC1
low at VCC = 5 V and EC = 0 V
VCC = 5 V, IHB = 20 mA 0.7 1.2 1.6 V
HB
VCC = 5 V 15µA
BH
VCC = 5 V 1.5 4.0 V
HBR
VCC = 5 V 60 mV[p-p]
INH
VCC = 5 V −100 0 100 mV
OF
VCC = 5 V 25 75 125 mV
DZ
VCC = 5 V, EC = ECR = 1.65 V −5 −1 µA
IN
VCC = 5 V, RCS = 0.5 Ω 0.75 1.0 1.25 A/V
CS
VCC = 5 V, IO = −300 mA 0.9 1.6 V
OH
VCC = 5 V, IO = 300 mA 0.2 0.6 V
OL
VCC = 5 V, RCS = 0.5 Ω 400 500 600 mA
TL
VCC = 5 V, IFG = − 0.01 mA 3.0 V
H
VCC = 5 V, IFG = 0.01 mA 0.5 V
L
VCC = 5 V, 1.5 3.0 V
FGR
Input D-range at H2+, H2−
VCC = 5 V 1 10 20 mV
FG
V
SBR
RBR
SBRLVCC
SBR
= 5 V 1.0 V
CC
V
= 5 V 3 .5 V
CC
= 5 V, ECR = 1.65 V 1.65 1.74 V
V
= 5 V 12 35 mA
CC
CC
V
3
Page 4

AN8480NSB ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player
■ Electrical Characteristics at Ta = 25°C (continued)
• Design reference data
Note) The characteristics listed below are theoretical values based on the IC design and are not guaranteed.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Thermal protection
Thermal protection operating T
SDONVCC
temperature
Thermal protection hysteresis width ∆T
SD
Thermal protection flag
Level at thermal protection = on V
Level at thermal protection = off V
TSDONVCC
TSDOFFVCC
■ Usage Notes
Prevent this IC from being line-to-ground fault. (To be concrete, do not short-circuit any of A1 (pin 28), A2 (pin 27)
and A3 (pin 26) with VM pin (pin 21).)
■ Application Notes
• PD Ta curves of HSOP042-P-0400
2.500
2.240
= 5 V, ∆EC = 100 mV 160 °C
VCC = 5 V, ∆EC = 100 mV 45 °C
= 5 V 0.5 V
= 5 V 3.0 V
P
T
D
a
2.000
(W)
D
1.500
1.042
1.000
Power dissipation P
0.500
0.000
Independent IC
without a heat sink
= 119.9°C/W
R
th(j-a)
025
50 12575 100 150
Ambient temperature Ta (°C)
Mounted on standard board
(glass epoxy: 75 × 75 × t1.6 mm
R
= 55.8°C/W
th(j-a)
3
)
4
Page 5

ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player AN8480NSB
■ Application Notes (continued)
• Phase conditions between Hall input and output current
Phase of Hall pin
H1+ H3+H2+
A
HML
B
HML
C
MLH
D
LMH
E
LMH
F
MLH
H1
H3
H2
H2H1
H3
ECR
EC
0
A3 A3A2 A1 A2 A1
Emit
Output current
Sink
ABCDE
F
• Power consumption calculation method
You can find a rough value of electric power to be consumed in the IC in the following method and the use of EXCEL
(computer soft ware) will enable you to put it on a graph.
Calculating formula:
1. Let an induced voltage generated in each phase as below:
(Reference to a motor center point)
E
= EO × sin (X) · · · (1) EA2 = EO × sin (X+120) · · · (2)
A1
E
= EO × sin (X+240) · · · (3) X: Phase angle
A3
2. Let a current flowing in each phase as below:
IA1 = IO × sin (X) · · · (4) IA2 = IO × sin (X+120) · · · (5)
I
= IO × sin (X+240) · · · (6)
A3
3. The voltages generated by a wire-wound resistance of a motor are:
= IA1 × R · · · (7) VR2 = IA2 × R · · · (8) VR3 = IA3 × R · · · (9)
V
R1
4. In each phase, add the voltage generated by an induced voltage and that by a wire-wound resistance.
' = (1) + (4) VA2' = (2) + (5) VA3' = (3) + (6)
V
A1
5. As the lowest voltage in each phase angle must be 0 V, you can get the voltage to be generated in each phase by
means of subtracting the lowest voltage from the voltage of the remaining two phases.
V
= VA1' − MIN (VA1', VA2', VA3') · · · (10)
A1
V
= VA2' − MIN (VA1', VA2', VA3') · · · (11)
A2
V
= VA3' − MIN (VA1', VA2', VA3') · · · (12)
A3
6. Subtract the supply voltage from each phase's voltage found in item 5 and then multiply it by each phase's current,
so that you can get the power consumption.
3
P = Σ (12 − VAn ) × I
n=1
An
0
0
5
Page 6

AN8480NSB ICs for Compact Disc/CD-ROM Player
■ Application Notes (continued)
• Theory of thermal resistance
A chip temperature or the fin temperature can be understood in the same way as Ohm's Law.
T
j
R
j-c
R
f
R
c-a
T
a
Make sure that T
P
= Ta + P × (R
T
j
does not exceed 150°C.
j
: Chip temperature
T
j
T
: Ambient temperature
a
P : Electric power generated by IC
R
: Thermal resistance between a chip and a package
j-c
R
: Thermal resistance between a package and a surface of a heat sink or free air
c-a
R
: Thermal resistance between a package and surface of a heat sink
f
+ R
// Rf)
j-c
c-a
If it exceeds 150°C, you can suppress the rise of a chip temperature by adding a heat sink which is equivalent to
R
in the above figure.
f
Tj = Ta + P × (R
j-c
+ R
c-a
// Rf)
A package surface and the fin are available for a temperature measurement. But the fin part is recommendable for
measurement because a package surface measurement does not always promise you a consistent measuring result.
■ Application Circuit Example
FG
Low: TSD on
TSDF
High: TSD off
VM = 12 V
VM
21
CS1
22
A1
28
27
A2
A3
26
PG
1
FG
12
RCS = 0.5 Ω
H1+
H1−
H2+
H2−
H3+
H3−
VH
Servo
EC
torque
command
ECR
High: Start
Medium: FG is on.
Low: Stop
SG
15
2
3
5
Hall
amp.
6
matrix
8
9
7
18
17
Detection
Hall
bias
EA
10
S/S
Start/stop
16
CC
V
Direction
detection
ER
Logic
EP = ER × EA
Absolute
value
Direction
changeover
20
PCI
0.1 µF
Upper side
distribution
Lower side
distribution
VTL
protection
Thermal
circuit
Amp.
Amp.
Brake
circuit
13
BRK
Low: Short brake
High: Reverce rotation brake
comparator
11
FG signal
= 5 V
V
CC
6
 Loading...
Loading...