Datasheet AM29LV800BT90WCIB, AM29LV800BT90WCI, AM29LV800BT90WCEB, AM29LV800BT90WCE, AM29LV800BT90WCCB Datasheet (AMD Advanced Micro Devices)
...Page 1

PRELIMINARY
This document contains information on a product under development at Advanced Micro Devices. The information
is intended to help you ev aluate this product. AMD reserves the right to change or dis continue work on thi s proposed
product without notice.
Publication# 21490 Rev: E Amendment/+1
Issue Date: March 1998
Refer to AMD’s Website (www.amd.com) for the latest information.
Am29LV800B
8 Megabit (1 M x 8-Bit/512 K x 16-Bit)
CMOS 3.0 Volt-onl y Boot Sector Flash Memory
DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS
■ Single power supply operation
— Full voltage range: 2.7 to 3. 6 volt read and write
operations for battery-powered applications
— Regulated voltage range: 3.0 to 3.6 volt read
and write operations and for compatibility with
high performance 3.3 volt microprocessors
■ Manufactured on 0.35 µm process technology
— Compatible with 0.5 µm Am29LV800 device
■ High performance
— Full voltage range: access times as fast as 80 ns
— Regulated voltage range: access times as fast
as 70 ns
■ Ultra low power consumption (typical values at
5 MHz)
— 200 nA Automatic Sleep mode current
— 200 nA standby mode current
— 7 mA read current
— 15 mA program/erase current
■ Flexible sector architecture
— O ne 16 Kbyte, two 8 Kbyte, one 32 Kbyte, and
fifteen 64 Kbyte sectors (byte mode)
— One 8 Kword, two 4 Kword, one 16 Kword, and
fifteen 32 Kword sectors (word mode)
— Supports full chip erase
— Sector Protection features:
A hardware method of locking a sector to
prevent any program or erase operations within
that sector
Sectors can be locked in-system or via
programming equipment
T emporary Sector Unprotect feat ure allows code
changes in previously locked sectors
■ Unlock Bypass Program Command
— Reduces overall programming time when
issuing multiple program command sequences
■ Top or bottom boot block configurations
available
■ Embedded Al gorithms
— Embedded Erase algorithm automatically
preprograms and erases the entire chip or any
combination of designated sectors
— Embedded Program algorithm automatically
writes and verifies data at specified addresses
■ Minimum 1,000,000 write cycle guarantee per
sector
■ Package option
— 48-ball FBGA
— 48-pin TSOP
— 44-pin SO
■ Compatibility with JEDEC standards
— Pinout and software compatible with single-
power supply Flash
— Superior inadvertent write protection
■ Data# Polling and toggle bits
— P rovides a software method of detecting
program or erase operation completion
■ Ready/Busy# pin (RY/BY#)
— Provides a hardware method of detecting
program or erase cycle completion
■ Erase Suspend/Erase Resume
— Suspends an erase oper ation to read data from,
or program data to, a sector that is not being
erased, then resumes the erase operation
■ Hardware reset pin (RESET#)
— Hardware method to reset the device to reading
array data
Page 2

2 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Am29LV800B is an 8 Mbit, 3.0 volt-only Flash
memory organized as 1,048,576 bytes or 524,288
words. The device i s offered in 48-ba ll FBGA, 44-pin
SO, and 48-pin TSOP packages. The word-wide data
(x16) appears on DQ15–DQ0; the byte-wide (x8) data
appears on DQ7–DQ0. This device requires only a
single, 3.0 volt V
CC
supply to perform read, program,
and erase operations. A stand ard EPROM programmer can also be used to program and erase the
device.
This device is manufactured using AMD’s 0.35 µm
process technology, and offers all the features and
benefits of the Am29LV800, which was manufactured
using 0.5 µm process technology. In addition, the
Am29LV800B features unlock bypass programming
and in-system sector protection/unprotection.
The standard device offers access times of 70, 80, 90
and 120 ns, allowing high speed microprocessors to
operate without wait s tates. To el iminate bus contention the device has separate chip enable (CE#), write
enable (WE#) and output enable (OE#) controls.
The device requires only a single 3. 0 v o lt po wer sup-
ply for both read and write functions. Internally generated and regulated voltages are provided for the
program and erase operations.
The device is entirely command set compatible with the
JEDEC single-power-supply Flash standard. Commands are written to the command regis ter using
standard micropr ocessor wri te timings. Register co ntents serve as input to an internal state-machine that
controls the erase and programming circuitry. Write
cycles also internally latch addresses and data needed
for the programming and erase operations. Reading
data out of the device is similar to reading from other
Flash or EPROM devices.
Device programming occurs by executing the program
command sequence. This initiates the Embedded
Program algorithm—an internal algorithm that automatically times the program pulse widths and verifies
proper cell margin. The Unlock Bypass mode facilitates faster programming times by requir ing only two
write cycles to program data instead of four.
Device erasure occurs by ex ecuting the erase command
sequence. This initiates the Embedded Erase algorithm—an i nternal algorithm that autom atically prepro -
grams the array (if it is not already programmed) before
executing the erase operation. During erase, the device
automatically times the erase pulse widths and verifies
proper cell margin.
The host system can detect whether a program or
erase operation is complete by observing the RY/BY#
pin, or by reading the DQ7 (Data# Polling) and DQ6
(toggle) status bits. After a program or erase cycle
has been completed, the device is ready to read array
data or accept another command.
The sector erase ar chitecture allo ws memo ry secto rs
to be erased and reprogrammed without affecting the
data contents of other sectors. The device is fully
erased when shipped from the factory.
Hardware data protection meas ures include a low
V
CC
detector that automatically in hibits write operations during power transitions. The hardware sector
protection feature disables both program and erase
operations in any combination of the sectors of memory. This can be achieved in-system or via programming equipment.
The Erase Suspend feature enables the user to put
erase on hold for any period of time to read data from,
or program data to, any sector that is not selected for
erasure. True background erase can thus be achieved.
The hardware RESET# pi n terminates any operation
in progress and resets the internal state machine to
reading array dat a. The RESET# pin ma y be tied to the
system reset circuitry. A system reset would thus also
reset the device, enabling the system microprocessor
to read the boot-up firmware from the Flash memory.
The device offers two power-saving features. When
addresses have been stable for a specified amount of
time, the device enters the automatic sleep m ode.
The system can also place the de vice into the standby
mode. Power consumption is greatly reduced in both
these modes.
AMD’s Flash technology combines years of Flash
memory manufacturing experience to produce the
highest levels of quality, reliability and cost effectiveness. The device electrically erases all bi ts with in
a sector simultaneously via Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. The data is programmed using hot electron
injection.
Page 3
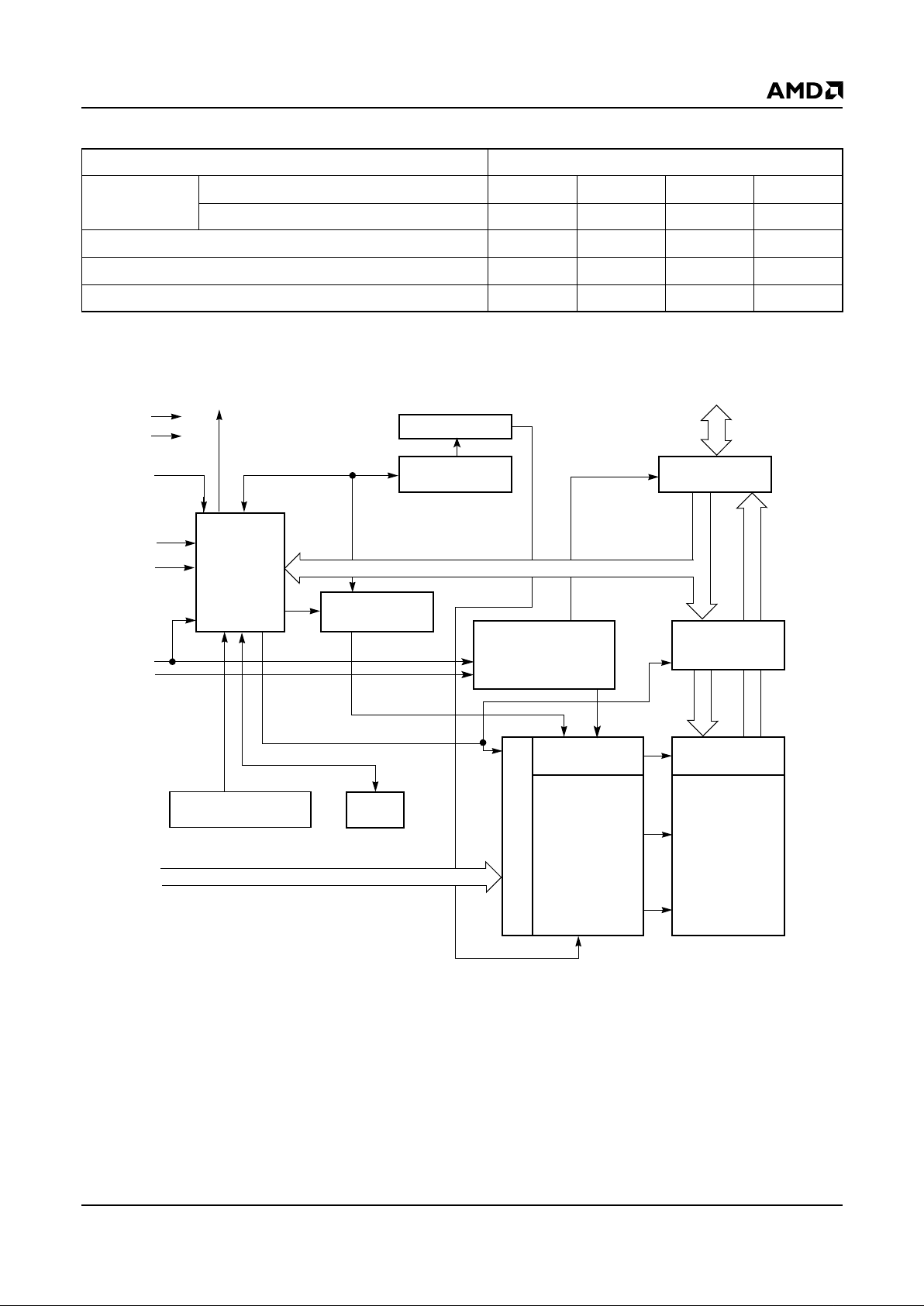
Am29LV800B 3
PRELIMINARY
PRODUCT SELECTOR GUIDE
Note: See “AC Characteristics” for full specifications.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Family Part Number Am29LV800B
Speed Options
Regulated Voltage Range: VCC =3.0–3.6 V 70R
Full Voltage Range: VCC = 2.7–3.6 V 80 90 120
Max access time, ns (t
ACC
) 70 80 90 120
Max CE# access time, ns (tCE) 70 80 90 120
Max OE# access time, ns (tOE) 30 30 35 50
Input/Output
Buffers
X-Decoder
Y-Decoder
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Logic
Erase Voltage
Generator
PGM Voltage
Generator
Timer
VCC Detector
State
Control
Command
Register
V
CC
V
SS
WE#
BYTE#
CE#
OE#
STB
STB
DQ0
–
DQ15 (A-1)
Sector Switches
RY/BY#
RESET#
Data
Latch
Y-Gating
Cell Matrix
Address Latch
A0–A18
21490E-1
Page 4
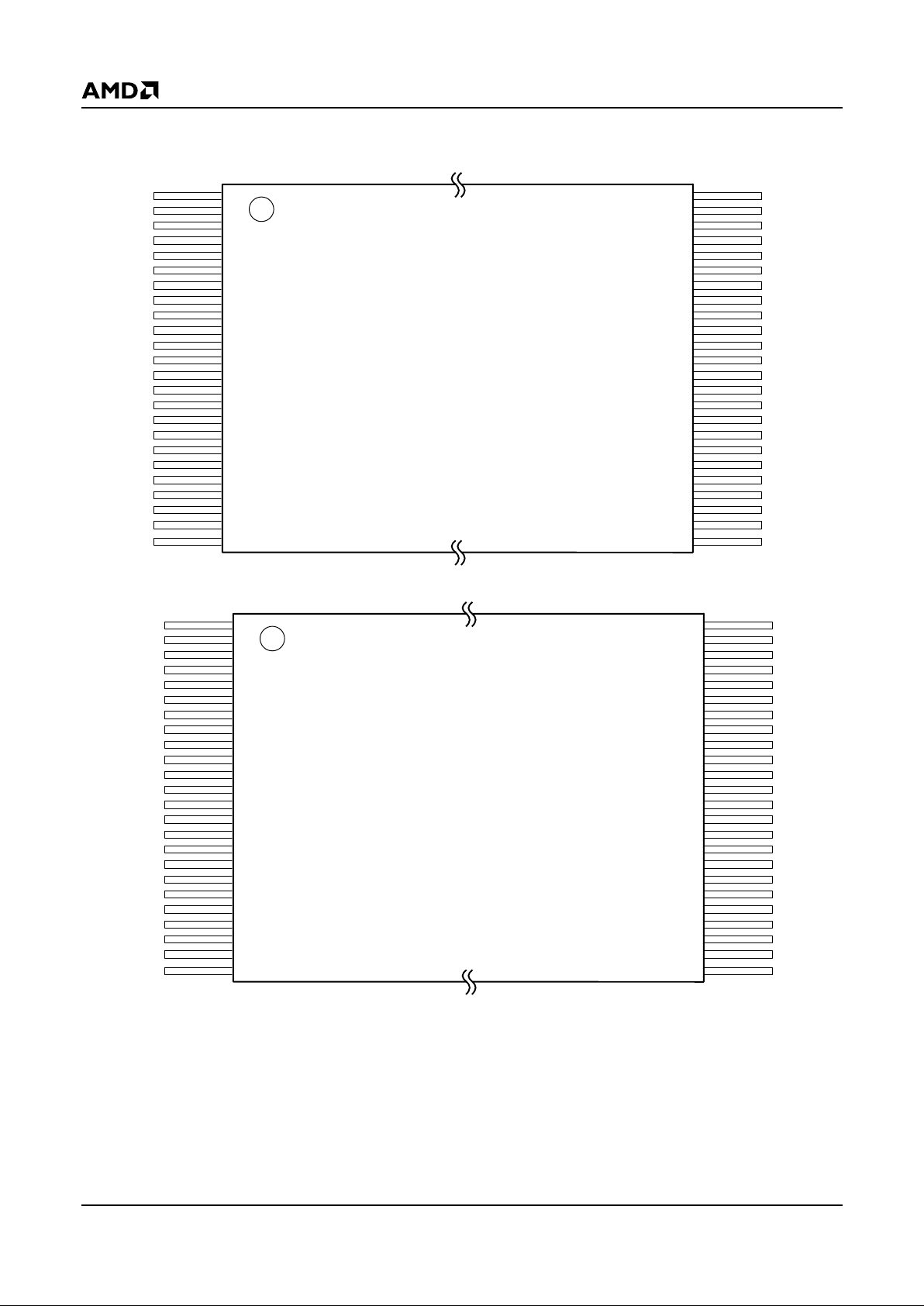
4 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
A1
A15
A18
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
NC
NC
WE#
RESET#
NC
NC
RY/BY#
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
1
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
A16
DQ2
BYTE#
V
SS
DQ15/A-1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE#
V
SS
CE#
A0
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
48
33
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
25
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
A1
A15
A18
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
NC
NC
WE#
RESET#
NC
NC
RY/BY#
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
1
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
A16
DQ2
BYTE#
V
SS
DQ15/A-1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE#
V
SS
CE#
A0
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
48
33
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
25
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
21490E-2
Reverse TSOP
Standard TSOP
Page 5
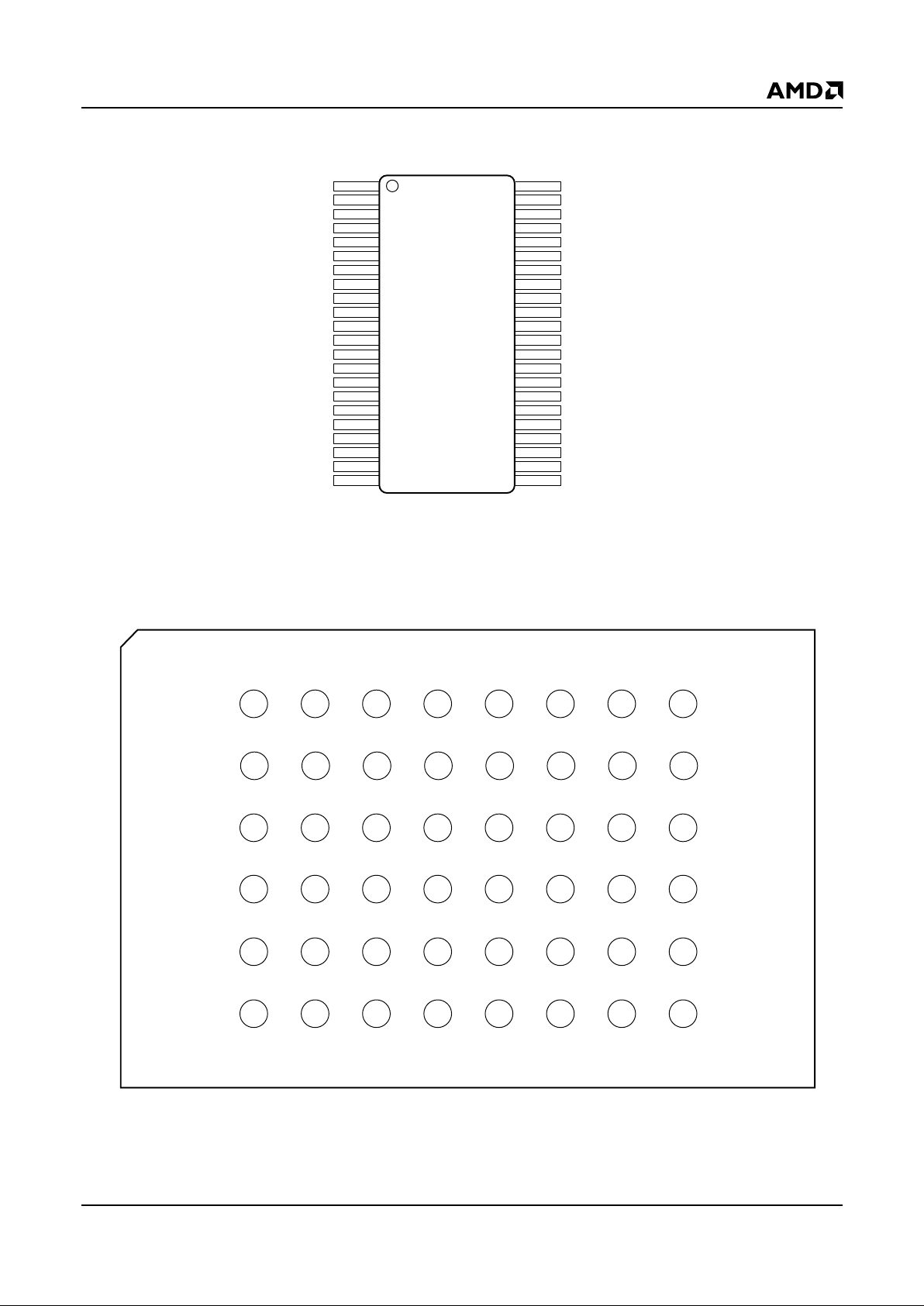
Am29LV800B 5
PRELIMINARY
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
RY/BY#
A18
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
CE#
V
SS
OE#
DQ0
DQ8
DQ1
DQ9
DQ2
DQ10
DQ3
DQ11
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
RESET#
WE#
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE#
V
SS
DQ15/A-1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
A1 B1 C1 D1 E1 F1 G1 H1
A2 B2 C2 D2 E2 F2 G2 H2
A3 B3 C3 D3 E3 F3 G3 H3
A4 B4 C4 D4 E4 F4 G4 H4
A5 B5 C5 D5 E5 F5 G5 H5
A6 B6 C6 D6 E6 F6 G6 H6
DQ15/A-1 V
SS
BYTE#A16A15A14A12A13
DQ13 DQ6DQ14DQ7A11A10A8A9
V
CC
DQ4DQ12DQ5NCNCRESET#WE#
DQ11 DQ3DQ10DQ2NCA18NCRY/BY#
DQ9 DQ1DQ8DQ0A5A6A17A7
OE# V
SS
CE#A0A1A2A4A3
SO
21490E-3
FBGA
Bump Side (Bottom) View
Page 6
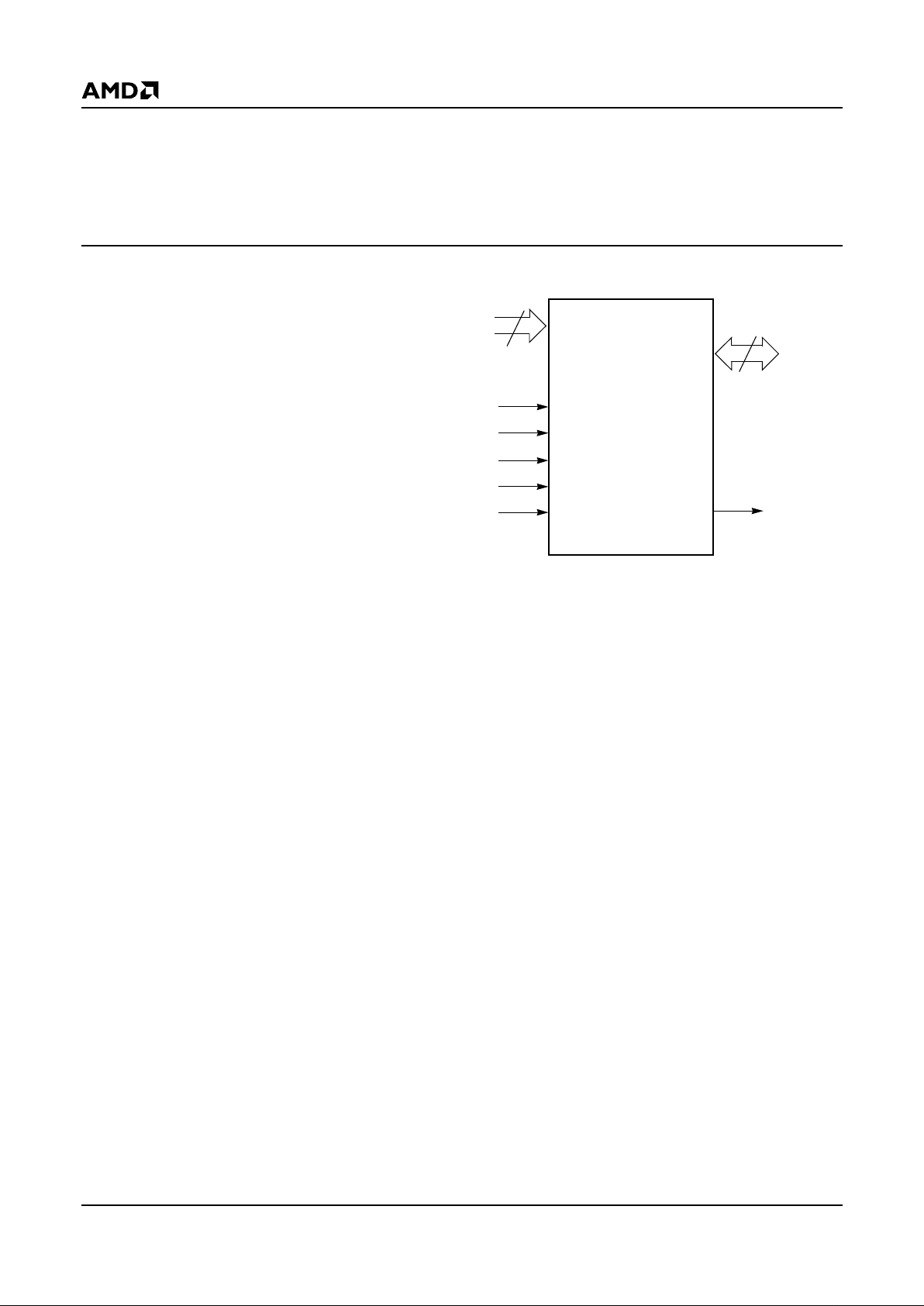
6 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Special Handling Instructions for FBGA
Package
Special handling is required for Flash Memory products
in FBGA packages.
Flash memory devices in FBGA packages may be
damaged if exposed to ultrasonic cleaning methods.
The package and/or data integrity may be
compromised if the package bod y is ex posed to
temperatures above 150°C for prolonged periods of
time.
PIN CONFIGURATION
A0–A18 = 19 addresses
DQ0–DQ14 = 15 data inputs/outputs
DQ15/A-1 = DQ15 (data inp ut/ output, word mode),
A-1 (LSB address input, byte mode)
BYTE# = Selects 8-bit or 16-bit mode
CE# = Chip enable
OE# = Output enable
WE# = Write enable
RESET# = Hardwa r e reset pin, active low
RY/BY# = Ready/Busy# output
V
CC
= 3.0 volt-only single power supply
(see Product Selector Guide for speed
options and voltage supply toleranc es)
V
SS
= Device ground
NC = Pin not connected internally
LOGIC SYMBOL
21490E-4
19
16 or 8
DQ0–DQ15
(A-1)
A0–A18
CE#
OE#
WE#
RESET#
BYTE# RY/BY#
Page 7
Am29LV800B 7
PRELIMINARY
ORDERING INFORMATION
Standard Pr od ucts
AMD standard products are available in s everal packages and operating ranges. The order number (Valid Combination) is formed by a combination of the elements below.
Valid Combinations
Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be supported in volume for this device. Consult the local AMD sales
office to confirm availability of specific valid combinations and
to check on newly released combinations.
DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION
Am29LV800B
8 Megabit (1 M x 8-Bit/512 K x 16-Bit) CMOS Flash Memory
3.0 Volt-only Read, Program, and Erase
CE70RAm29LV800B T
OPTIONAL PROCESSING
Blank = Standard Processing
B = Burn-in
(Contact an AMD representative for more information)
TEMPERATURE RANGE
C=Commercial (0°C to +70°C)
I = Industrial (–40°C to +85°C)
E = Extended (–55°C to +125°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
E = 48-Pin Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP)
Standard Pinout (TS 048)
F = 48-Pin Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP)
Reverse Pinout (TSR048)
S = 44-Pin Small Outline Package (SO 044)
WB = 48-ball Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA)
0.80 mm pitch, 6 x 9 mm package
SPEED OPTION
See Product Selector Guide and Valid Combinations
BOOT CODE SECTOR ARCHITECTURE
T = Top Sector
B = Bottom Sector
Valid Combinations
Am29LV800BT70R,
Am29LV800BB70R
EC, EI, FC, FI, SC, SI, WBC
Am29LV800BT80,
Am29LV800BB80
EC, EI, EE,
FC, FI, FE,
SC, SI, SE,
WBC, WBI, WBE
Am29LV800BT90,
Am29LV800BB90
Am29LV800BT120,
Am29LV800BB120
Page 8
8 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
DEVICE BUS OPERATIONS
This section describes the requirements and use of the
device bus operations, which are initiated through the
internal command register. The command register itself
does not occupy any addressable memory loc ation.
The register is composed of latches that store the commands, along with the address and data information
needed to execute the command. The contents of the
register serve as inputs to the internal state machine.
The state machine outputs d ictate the function of the
device. Table 1 lists the device bus operations, the
inputs and control lev els t he y requ ire , and t he resulting
output. The following subsections describe each of
these operations in further detail.
Table 1. Am29LV800B Device Bus Operations
Legend:
L = Logic Low = V
IL
, H = Logic High = VIH, VID = 12.0 ± 0.5 V, X = Don’t Care, AIN = Address In, DIN = Data In, D
OUT
= Data Out
Notes:
1. Addresses are A18:A0 in word mode (BYTE# = V
IH
), A18:A-1 in byte mode (BYTE# = VIL).
2. The sector protect and sector unprotect functions may also be implemented via programming equipment. See the “Sector
Protection/Unprotection” section.
Word/Byte Configuration
The BYTE# pin controls whether the device data I/O
pins DQ15–DQ0 operate in the by te or word configur ation. If the BYTE# pin is set at logic ‘1’, the device is in
word configuration, DQ15–DQ0 are activ e and c ontrolled by CE# and OE#.
If the BYTE# pin is set at logic ‘0’, the device is in byte
configuration, and only data I/O pins DQ0–DQ7 are active and controlled by CE# and OE#. The data I /O pins
DQ8–DQ14 are tri-stated, and the DQ15 pin is used as
an input for the LSB (A-1) address function.
Requirements for Reading Array Data
To read array data from the outputs, the system must
drive the CE# and OE# pins to V
IL
. CE# is the power
control and selects the device. OE# is the output control and gates array data to the output pins. WE#
should remain at VIH. The BYTE# pin determines
whether the device outputs array data in words or
bytes.
The internal state machine is set for reading array
data upon device po wer-u p , or after a hardw are res et.
This ensure s that no sp urious alteration of the memory content occurs dur ing the power transition. No
command is nece ssary in this mode to ob tain array
data. Standard microprocessor read cycles that assert valid addresses on the de vice addr ess inputs produce valid data on the device data outputs. The
device remains enab led f or read access until t he command register contents are altered.
See “Reading Array Data” for more information. Refer
to the AC Read Operations table for timing specifications and to Figure 13 for the timing diagram. I
CC1
in
the DC Characteristics table represents the active current specification for reading array data.
Operation CE# OE# WE# RESET#
Addresses
(Note 1)
DQ0–
DQ7
DQ8–DQ15
BYTE#
= V
IH
BYTE#
= V
IL
Read L L H H A
IN
D
OUT
D
OUT
DQ8–DQ14 = High-Z,
DQ15 = A-1
Write L H L H A
IN
D
IN
D
IN
Standby
V
CC
±
0.3 V
XX
VCC ±
0.3 V
X High-Z High-Z High-Z
Output Disable L H H H X High-Z High-Z High-Z
Reset X X X L X High-Z High-Z High-Z
Sector Protect (Note 2) L H L V
ID
Sector Address,
A6 = L, A1 = H,
A0 = L
D
IN
XX
Sector Unprotect (Note 2) L H L V
ID
Sector Address,
A6 = H, A1 = H,
A0 = L
D
IN
XX
Temporary Sector Unprotect X X X V
ID
A
IN
D
IN
D
IN
High-Z
Page 9

Am29LV800B 9
PRELIMINARY
Writing Commands/Command Sequences
To write a command or command sequence (which includes programming data to the device and erasing
sectors of memory), the system must drive WE# and
CE# to V
IL
, and OE# to VIH.
For program operations, the BYT E# pin determin es
whether the device accepts program data in bytes or
words. Refer to “Word/Byte Configuration” for more
information.
The device features an Unlock Bypass mode to facili-
tate faster programming. Once the device enters the Unlock Bypass mode, only two write cycles are required to
program a word or byte, instead of four. The “Word/Byte
Program Command Sequence” section has details on
programming data to the device using both standard and
Unlock Bypass command sequences.
An erase operation can erase one sect or, multiple sectors, or the entire device. Tables 2 and 3 indicate the
address space that each sector occupies. A “sector address” consists of the addres s bits required t o un iquely
select a sector. The “Command Definitions” section
has details on erasing a sector or the entire chip, or
suspending/resuming the erase operation.
After the system writes the autoselect command sequence, the device enters the autoselect mode. The
system can then read autoselect codes from the internal register (which is separate from the memory array)
on DQ7–DQ0. Standard read cycle timings apply in this
mode. Refer to the “Autoselect Mode” and “Autoselect
Command Sequence” sections for more information.
I
CC2
in the DC Characteristics table represents the active current specification for the w rite mode. The “AC
Characteristics” section contains timing specification
tables and timing diagrams for write operations.
Program and Erase Operation Status
During an erase or program operation, the system ma y
check the status of the operation by reading the status
bits on DQ7–DQ0. Standard read cycle timings and I
CC
read specifications apply. Refer to “Write Operation
Status” for more information, and to “AC Characteristics” for timing diagrams.
Standby Mode
When the system is not reading or writing to the device ,
it can place the device in the standby mode. In this
mode, current consumption is great ly reduc ed, and the
outputs are placed in the high impedance state, independent of the OE# input.
The device enters the CMOS standby mode when the
CE# and RESET# pin s are both held at V
CC
± 0.3 V.
(Note that this is a more restricted voltage range than
V
IH
.) If CE# and RESET# ar e held a t VIH, but not within
V
CC
± 0.3 V, the device will be in the standb y mode, b ut
the standby current will be grea ter. The device requires
standard access time (t
CE
) for read access when the
device is in either of these standby modes, before it is
ready to read data.
If the device is deselected during erasure or programming, the device draws active current until the
operation is completed.
In the DC Characteristics table, I
CC3
and I
CC4
repre-
sents the standby current specification.
Automatic Sleep Mode
The automatic sleep mode minimizes Flash device
energy consumption. The device automatically
enables this mode when addres ses remain stable for
t
ACC
+ 30 ns. The automatic sleep mode is
independent of the CE#, WE#, and OE# control
signals. Standard address access timings provide new
data when addresses are chan ged. While in sleep
mode, output data is latched and always available to
the system. I
CC4
in the DC Characteristics table
represents the automatic sleep mode current
specification.
RESET#: Hardware Reset Pin
The RESET# pin provides a hardw are method of resetting the device to reading array data. When the RESET# pin is driven low for at least a period of t
RP
, the
device immediately terminates any operation in
progress, tristates all output pins, and ignores all
read/write commands for the duration of the RESET#
pulse. The device also resets the inter nal state machine to reading array data. The operation that was interrupted should be reinitiated once the device is ready
to accept another command sequence, to ensure data
integrity.
Current is reduced for the duration of the RESET#
pulse. When RESET# is held at V
SS
±0.3 V, the device
draws CMOS standby c urrent (I
CC4
). If RESET# is held
at V
IL
but not within VSS±0.3 V, the standby current will
be greater.
The RESET# pin may be tied to the system reset cir-
cuitry. A system reset would thus also reset the Flash
memory, enabling the system to read the boot-up
firmware from the Flash memory.
If RESET# is asserted during a program or erase operation, the RY/BY# pin remains a “0” (busy) until the
internal reset operation is complete, which requires a
time of t
READY
(during Embedded Algorithms). The
system can thus monitor RY/BY# to determine
whether the reset oper ation is c omplete . If RESE T# is
asserted when a program or erase oper ation is not e xecuting (RY/BY# pin is “1”), the reset operation is
completed within a time of t
READY
(not during Embed-
ded Algorithms). The system can read data t
RH
after
the RESET# pin returns to V
IH
.
Page 10
10 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Refer to the AC Characteristics tables for RESET# parameters and to Figure 14 for the timing diagram.
Output Disable Mode
When the OE# input is at VIH, output from the device is
disabled. The output pins are placed in t he high impedance state.
Table 2. Am29LV800BT Top Boot Block Sector Address Table
Sector A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13 A12
Sector Size
(Kbytes/
Kwords)
Address Range (in hexadecim al )
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
Address Range
SA00000XXX 64/32 00000h–0FFFFh 00000h–07FFFh
SA10001XXX 64/32 10000h–1FFFFh08000h–0FFFFh
SA20010XXX 64/32 20000h–2FFFFh10000h–17FFFh
SA30011XXX 64/32 30000h–3FFFFh18000h–1FFFFh
SA40100XXX 64/32 40000h–4FFFFh20000h–27FFFh
SA50101XXX 64/32 50000h–5FFFFh28000h–2FFFFh
SA60110XXX 64/32 60000h–6FFFFh30000h–37FFFh
SA70111XXX 64/32 70000h–7FFFFh38000h–3FFFFh
SA81000XXX 64/32 80000h–8FFFFh40000h–47FFFh
SA91001XXX 64/32 90000h–9FFFFh48000h–4FFFFh
SA101010XXX 64/32 A0000h–AFFFFh50000h–57FFFh
SA111011XXX 64/32 B0000h–BFFFFh58000h–5FFFFh
SA121100XXX 64/32 C0000h–CFFFFh60000h–67FFFh
SA131101XXX 64/32 D0000h–DFFFFh68000h–6FFFFh
SA141110XXX 64/32 E0000h–EFFFFh70000h–77FFFh
SA1511110XX 32/16 F0000h–F7FFFh78000h–7BFFFh
SA161111100 8/4 F8000h–F9FFFh7C000h–7CFFFh
SA171111101 8/4 FA000h–FBFFFh7D000h–7DFFFh
SA18111111X 16/8 FC000h–FFFFFh7E000h–7FFFFh
Page 11
Am29LV800B 11
PRELIMINARY
Table 3. Am29LV800BB Bottom Boot Block Sector Address Table
Note for Tables 2 and 3: Address range is A18:A-1 in byte mode and A18:A0 in word mode. See “Word/Byte Configuration”
section for more information.
Autoselect Mode
The autoselect mode provides manufacturer and device identification, and sector protection verification,
through identifier codes output on DQ7–DQ0. This
mode is primarily intended for progr amming equipment
to automatically match a device to be progr ammed with
its correspondi ng programming al gorithm. However,
the autoselect codes can also be accessed in-system
through the command register.
When using programming equipment, the autoselect
mode requires V
ID
(11.5 V to 12.5 V) on address pin A9.
Address pins A6, A1, and A0 must be as shown in Table
4. In addition, when verifying sector protection, the sec-
tor address must appear on the appr opriate highest
order address bits (see Tables 2 and 3). Table 4 shows
the remaining address bits that are don’t care. When all
necessary bits have been set as required, the programming equipment may then read the corresponding identifier code on DQ7–DQ0.
To access the autoselect codes in-system, the host
system can issue the autoselect command via the
command register, as shown in Table 5. This method
does not require V
ID
. See “Command Definitions” for
details on using the autoselect mode.
Sector A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13 A12
Sector Size
(Kbytes/
Kwords)
Address Range (in hexadecim al )
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
Address Range
SA0000000X 16/8 00000h–03FFFh 00000h–01FFFh
SA10000010 8/4 04000h–05FFFh02000h–02FFFh
SA20000011 8/4 06000h–07FFFh03000h–03FFFh
SA300001XX 32/16 08000h–0FFFFh04000h–07FFFh
SA40001XXX 64/32 10000h–1FFFFh08000h–0FFFFh
SA50010XXX 64/32 20000h–2FFFFh10000h–17FFFh
SA60011XXX 64/32 30000h–3FFFFh18000h–1FFFFh
SA70100XXX 64/32 40000h–4FFFFh20000h–27FFFh
SA80101XXX 64/32 50000h–5FFFFh28000h–2FFFFh
SA90110XXX 64/32 60000h–6FFFFh30000h–37FFFh
SA100111XXX 64/32 70000h–7FFFFh38000h–3FFFFh
SA111000XXX 64/32 80000h–8FFFFh40000h–47FFFh
SA121001XXX 64/32 90000h–9FFFFh48000h–4FFFFh
SA131010XXX 64/32 A0000h–AFFFFh50000h–57FFFh
SA141011XXX 64/32 B0000h–BFFFFh58000h–5FFFFh
SA151100XXX 64/32 C0000h–CFFFFh60000h–67FFFh
SA161101XXX 64/32 D0000h–DFFFFh68000h–6FFFFh
SA171110XXX 64/32 E0000h–EFFFFh70000h–77FFFh
SA181111XXX 64/32 F0000h–FFFFFh78000h–7FFFFh
Page 12
12 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Table 4. Am29LV800B Autoselect Codes (High Voltage Method)
L = Logic Low = VIL, H = Logic High = VIH, SA = Sector Address, X = Don’t care.
Sector Protection/Unprotection
The hardware sector protection feature disables both
program and erase operations in any sect or. The hardware sector unprotection feature re-enables both program and erase operations in previously protected
sectors.
The device is shipped with all sectors unprotected.
AMD offers the option of programming and protecting
sectors at its factory prior to shipping the device
through AMD’s ExpressFlash™ Servic e. Contact an
AMD representative for details.
It is possible to determine whether a sector is protected
or unprotected. See “Autoselect Mode” for details.
Sector Protection/unprotection can be implemented via
two methods.
The primary method requires V
ID
on the RESET# pin
only, and c an be implemented either in-system or via
programming equipment. Figure 2 shows the algorithms and Figure 23 shows the timing diagram. This
method uses standard m icroprocessor bus cycle timing. For sector unprotect, all unprotected sectors must
first be protected prior to the first sector unpro tect write
cycle.
The alternate method intended on ly for programming
equipment requires V
ID
on address pin A9 and OE#.
This method is compatible with programmer routines
written for earlier 3.0 v olt-only AMD flash de vices. Publication number 20536 contains further details; contact
an AMD representative to request a copy.
Temporary Sector Unprotect
This feature allows temporary unpr otection of previously protected sectors to change data in-system. The
Sector Unprotect mode is activated by setting the RESET# pin to V
ID
. During this mode, formerly protected
sectors can be programmed or erased b y selecting the
sector addresses. Once V
ID
is removed from the RESET# pin, all the previously protected sectors are
protected again. Figure 1 shows the algorithm, and
Figure 22 shows the tim ing diagrams, for this feature.
Figure 1. Temporary Sector Unprotect Operation
Description Mode CE# OE# WE#
A18
to
A12
A11
to
A10 A9
A8
to
A7 A6
A5
to
A2 A1 A0
DQ8
to
DQ15
DQ7
to
DQ0
Manufacturer ID: AMD L L H X X V
ID
XLXLL X 01h
Device ID:
Am29LV800B
(Top Boot Block)
Word L L H
XXV
ID
XLXLH
22h DAh
Byte L L H X DAh
Device ID:
Am29LV800B
(Bottom Boot
Block)
Word L L H
XXV
ID
XLXLH
22h 5Bh
Byte L L H X 5Bh
Sector Protection V erification L L H SA X V
ID
XLXHL
X
01h
(protected)
X
00h
(unprotected)
START
Perform Erase or
Program Operations
RESET# = V
IH
Temporary Sector
Unprotect Completed
(Note 2)
RESET# = V
ID
(Note 1)
Notes:
1. All protected sectors unprotected.
2. All previously protected sectors are protected once
again.
21490E-5
Page 13
Am29LV800B 13
PRELIMINARY
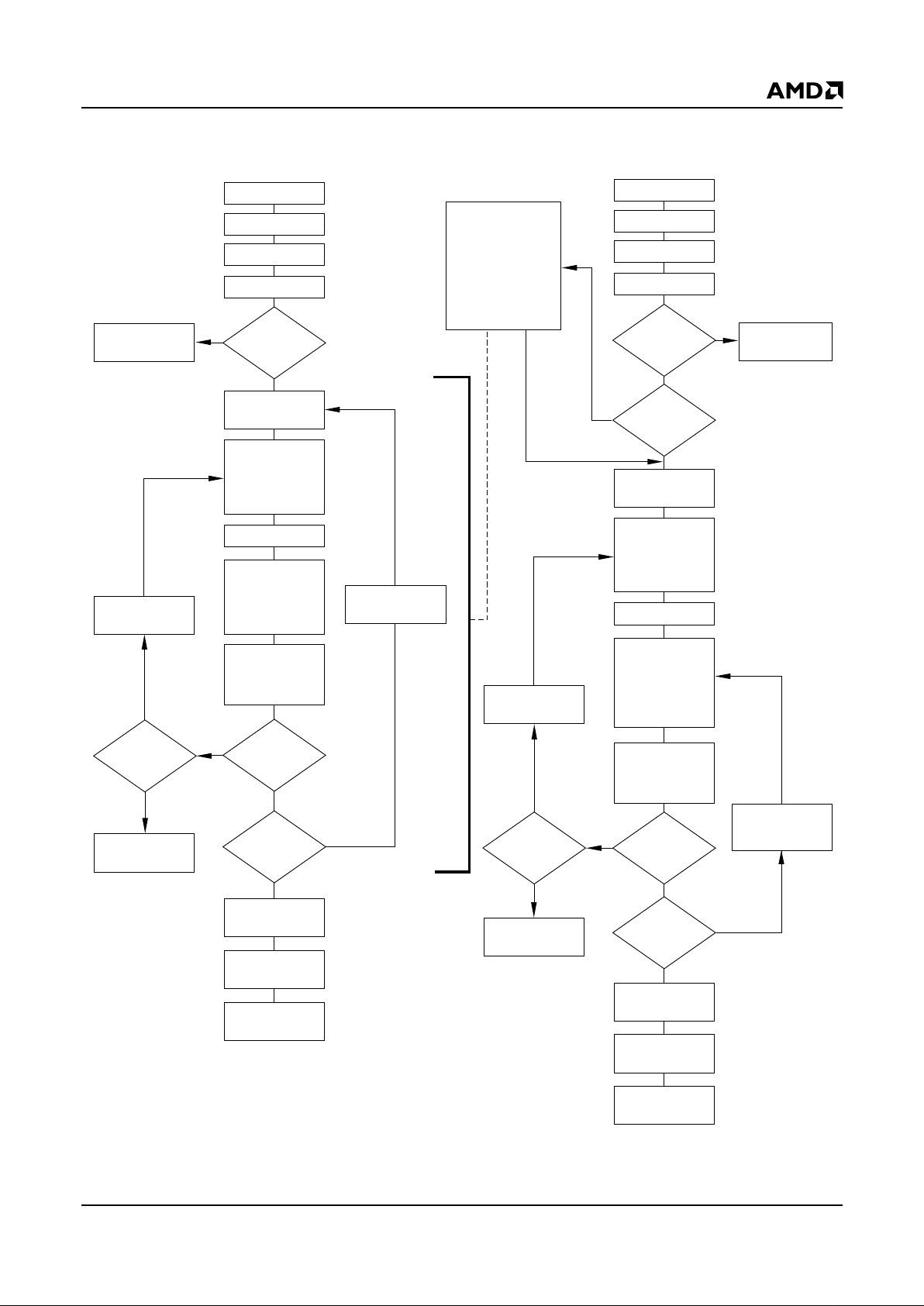
Figure 2. In-System Sector Protect/Unprotect Algorithms
Sector Protect:
Write 60h to sector
address with
A6 = 0, A1 = 1,
A0 = 0
Set up sector
address
Wait 150 µs
Verify Sector
Protect: Write 40h
to sector address
with A6 = 0,
A1 = 1, A0 = 0
Read from
sector address
with A6 = 0,
A1 = 1, A0 = 0
START
PLSCNT = 1
RESET# = V
ID
Wait 1 µs
First Write
Cycle = 60h?
Data = 01h?
Remove V
ID
from RESET#
Write reset
command
Sector Protect
complete
Yes
Yes
No
PLSCNT
= 25?
Yes
Device failed
Increment
PLSCNT
Temporary Sector
Unprotect Mode
No
Sector Unprotect:
Write 60h to sector
address with
A6 = 1, A1 = 1,
A0 = 0
Set up first sector
address
Wait 15 ms
Verify Sector
Unprotect: Write
40h to sector
address with
A6 = 1, A1 = 1,
A0 = 0
Read from
sector address
with A6 = 1,
A1 = 1, A0 = 0
START
PLSCNT = 1
RESET# = V
ID
Wait 1 µs
Data = 00h?
Last sector
verified?
Remove V
ID
from RESET#
Write reset
command
Sector Unprotect
complete
Yes
No
PLSCNT
= 1000?
Yes
Device failed
Increment
PLSCNT
Temporary Sector
Unprotect Mode
No
All sectors
protected?
Yes
Protect all sectors:
The indicated portion
of the sector protect
algorithm must be
performed for all
unprotected sectors
prior to issuing the
first sector
unprotect address
Set up
next sector
address
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
Sector Protect
Algorithm
Sector Unprotect
Algorithm
First Write
Cycle = 60h?
Protect another
sector?
Reset
PLSCNT = 1
21490E-6
Page 14

14 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Hardware Data Protection
The command sequence requirement of unlock cycles
for programming or erasing provides data protection
against inadvertent wri tes (refer to Table 5 for command definitions). In additio n, the following hardware
data protection mea sures prevent accidental erasure
or programming, which might otherwise be caused by
spurious system level signals during V
CC
power-up
and power-down transitions, or from system noise.
Low V
CC
Write Inhibit
When V
CC
is less than V
LKO
, the device does not ac-
cept any write cycles. This protects data during V
CC
power-up and power-down. The command register and
all internal program/erase circuits are disabled, and the
device resets. Subsequent writes are ignored until V
CC
is greater than V
LKO
. The system must provide the
proper signals to the control pins to prevent unintentional writes when V
CC
is greater than V
LKO
.
Write Pulse “Glitch” Protection
Noise pulses of less than 5 ns (typical) on OE#, CE# or
WE# do not initiate a write cycle.
Logical Inhibit
Write cycles are inhibited by holding any one of OE# =
V
IL
, CE# = VIH or WE# = VIH. To initiate a write cycle,
CE# and WE# must be a logical zero while OE# is a
logical one.
Power-Up Write Inhibit
If WE# = CE# = V
IL
and OE# = VIH during power up , the
device does not accept commands on the rising edge
of WE#. The internal state mac hine is automatically
reset to reading array data on power-up.
COMMAND DEFINITIONS
Writing specific addre ss and data commands or sequences into the command register initiates device operations. Table 5 de fines the valid registe r command
sequences. Writing incorrect address and data val-
ues or writing them in the improper sequence resets
the device to reading array data.
All addresses are latched on the falling edge of WE# or
CE#, whichever happens later. All data is latched on
the rising edge of WE# or CE#, whichever happens
first. Refer to the appropriate timing diagrams in the
“AC Characteristics” section.
Reading Array Data
The device is automatically set to reading array data
after device power-up. No commands are required to
retrieve data. The device is also ready to read array
data after comp leting an Embe dded Program or Embedded Erase algorithm.
After the device accepts an Erase Suspend command, the devic e enters the Erase Suspend mode.
The system can read array data using the standard
read timings, except that if it reads at an address
within erase-suspended sectors, the device outputs
status data. After completing a programming operation in the Erase Suspend mode, the system may
once again read array data with the same exception.
See “Erase Suspend/Erase Resume Commands” for
more information on this mode.
The system
must
issue the reset command to re-enable the device for reading array data if DQ5 goes high,
or while in the autoselect mode. See the “Reset Command” section, next.
See also “Requirements for Reading Arr a y Data” in the
“Device Bus Operations” section for more infor mation.
The Read Operations table provides the read parameters, and Figure 13 shows the timing diagram.
Reset Command
Writing the reset command to the devi ce resets the device to reading array data. Address bits are don’t care
for this command.
The reset command may be written between the sequence cycles in an erase command sequence before
erasing begins. This resets the device to reading array
data. Once erasure begins, however, the device ignores reset commands until the operation is complete.
The reset command may be written between the sequence cycles in a program command sequence before programming begins. This resets the device to
reading array data (also applies to programming in
Erase Suspend mode). Once programming begins,
however, the device ignores reset commands until the
operation is complete.
The reset command may be written between the sequence cycles in an autoselect command sequence.
Once in the autoselect mode, t he reset c ommand
must
be written to return to reading array data (also applies
to autoselect during Erase Suspend).
If DQ5 goes high during a program or erase operation,
writing the reset command returns the device to reading array data (also applies during Erase Suspend).
Autoselect Command Sequence
The autoselect c ommand sequenc e allows the host
system to access the manufacturer and devices codes,
and determine whether or not a sector is protected.
T ab le 5 shows the address and data requirements. This
method is an alternative to that shown in Table 4, which
is intended for PROM programmers and requi res V
ID
on address bit A9.
The autoselect command sequence is initiated by writ-
ing two unlock cycles, followed by the autoselect com-
Page 15

Am29LV800B 15
PRELIMINARY
mand. The device then enters the autoselect m ode,
and the system may read at any address any number
of times, without initiating ano ther command sequence.
A read cycle at address XX00h retrieves the manufacturer code. A read cycle at address XX01h in word
mode (or 02h in byte mode) returns the device code. A
read cycle containing a sector address (SA) and the
address 02h in word mode (or 0 4h in byte mode) r eturns 01h if that sector is protected, or 00h if it is unprotected. Refer to Tables 2 and 3 for valid sector
addresses.
The system must write the reset command to exit the
autoselect mode and return to reading array data.
Word/Byte Program Command Sequence
The system may program the device by word or byte,
depending on the state of the BYTE# pin. Programming is a four-bus-cycle operation. The program command sequence is initiated by writing two unlock write
cycles, followed by the program set-up command. The
program address and data are written next, which in
turn initiate the Embedded Program algorithm. The
system is
not
required to provide further controls or timings. The device automatically provides internally generated program pulses and verifies the programm ed
cell margin. Table 5 shows the address and data requirements for the byte program command sequence.
When the Embedded Program algorithm is complete,
the device then returns to reading array data and addresses are no longer latched. The system can determine the status of the program operation by using
DQ7, DQ6, or RY/BY#. See “Write Operation Status”
for information on these status bits.
Any commands written to the device during the Embedded Program Algorithm are ignored. Note that a
hardware reset immediately terminates the programming operation. The program command sequence
should be reinitiated once the de vi ce has reset t o reading array data, to ensure data integrity.
Programming is allowed in any sequence an d across
sector boundaries. A bit cannot be programmed
from a “0” back to a “1”. Attempting to do so may halt
the operation and set DQ5 to “1”, or cause the Data#
Polling algorithm to indic ate the operation was successful. However, a succeeding read will show that the
data is still “0”. Only erase operations can convert a “0”
to a “1”.
Unlock Bypass Command Sequence
The unlock bypass feature allows the system to program bytes or w ords t o the device faster than using the
standard program command sequence. The unloc k b ypass command sequence is initiated by first writing two
unlock cycles. This is followed by a third write cycle
containing the unlock bypass command, 20h. The device then enters the unlock bypass mode. A two-cycle
unlock bypass program command sequence is all that
is required to program in this mode. The first cycle in
this sequence contains the unlock bypass program
command, A0h; the second cycle contains the prog ram
address and data. Additional data is programmed in
the same manner. This mode dispenses with t he i nitial
two unlock cycles required in the standard program
command sequence, resulting in faster total programming time. Table 5 sho ws the requirements f or the command sequence.
During the unlo ck bypass mode, only the Unlock Bypass Program and Unlock Bypass Reset commands
are valid. To exit the unlock bypass mode, the system
must issue the two-cycle unlock bypass reset command sequence. The first cycle must contain the data
90h; the second cycle the data 00h. Add resses are
don’t care for both cycles. The device then returns to
reading array data.
Figure 3 illustrates the algorithm for the program operation. See the Erase/Program Operations table in “AC
Characteristics” for parameters, and to Figure 17 for
timing diagrams.
Page 16

16 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Note: See Table 5 for program command sequence.
Figure 3. Program Operation
Chip Erase Command Sequence
Chip erase is a six bus cycle oper ation. The chip er ase
command sequence is initiated by writing two unlock
cycles, followed by a set-up command. Two additional
unlock write cycles are then followed by the chip erase
command, which in turn invokes the Embedded Erase
algorithm. The device does
not
require the system to
preprogram prior to erase. The Embedded Erase algorithm automatically preprograms and ve rifies the entire
memory for an all zero data patter n prior to electr ical
erase. The system is not required to provide any controls or timings during these operations. Table 5 show s
the address and data requirements for the chip erase
command sequence.
Any commands written to the chip during the Embedded Erase algorithm are ignored. Note that a har dware
reset during the chip erase operation immediately terminates the operation. The Chip Erase command sequence should be reinitiated once the device has
returned to reading array data, t o ensure data int eg rity.
The system can determine the status of the erase operation by using DQ7, DQ6, DQ2, or RY/BY#. See
“Write Operation Status” for information on these status bits. When the Embedded Erase algorithm is complete, the device returns to reading array data and
addresses are no longer latched.
Figure 4 illustrates the algorithm for the erase operation. See the Erase/Program Operations tables in “AC
Characteristics” for parameters, and to Figure 18 for
timing diagrams.
Sector Erase Command Sequence
Sector erase is a six bus cycle operation. The sector
erase command sequence is initiated by writing two
unlock cycles, followed by a set-up command. Two additional unlock write cycles are t hen f ollo wed b y the address of the sector to be erased, and the sector erase
command. Table 5 shows the address and data requirements for the sector erase command sequence.
The device does
not
require the system to preprogram
the memory prior to erase. The Embedded Erase algorithm automatically programs and verifies the s ector for
an all zero data pattern prior to electrical erase. The
system is not required to provide a ny controls or timings during these operations.
After the command sequence is written, a sector erase
time-out of 50 µs begins. During the time-out period,
additional sector addresses and sector erase commands may be written. Loading the sector erase buffer
may be done in any sequence, and the number of sectors may be from one sector to all sector s. The time between these additional cycl es must be less than 50 µs,
otherwise the last address and command might not be
accepted, and erasure may begin. It is recommended
that processor interrupts be disab led during this time to
ensure all commands are accepted. The interrupts can
be re-enabled after the last Sector Eras e command is
written. If the time between additional sector erase
commands can be assumed to be less than 50 µs, the
system need not monitor DQ3. Any command other
than Sector Erase or Erase Suspend during the
time-out period resets the device to reading array
data. The system must rewrite the command sequence
and any additional sector addresses and commands.
The system can monitor DQ3 to determine if the s ector
erase timer has timed out. (See the “DQ3 : Sector Erase
Timer” section.) The tim e-out begins from the rising
edge of the final WE# pulse in the command sequence.
Once the sector erase operation has begun, on ly the
Erase Suspend command is valid. All other commands
are ignored. Note that a hardware reset during the
sector erase operation immediately terminates the operation. The Sector Erase command sequence should
be reinitiated once the device has returned to reading
array data, to ensure data integrity.
START
Write Program
Command Sequence
Data Poll
from System
Verify Data?
No
Yes
Last Address?
No
Yes
Programming
Completed
Increment Address
Embedded
Program
algorithm
in progress
21490E-7
Page 17

Am29LV800B 17
PRELIMINARY
When the Embedded Erase algorithm is complete, the
device returns to reading arra y data and addresses are
no longer latched. The system can determine the status of the erase operation b y usi ng DQ7, DQ6, DQ2, or
RY/BY#. Refer to “Write Operation Status” for information on these status bits.
Figure 4 illustrates the algorithm for the erase operation. Refer to the Erase/Program Operations tables in
the “AC Characteristics” section for parameters, and to
Figure 18 for timing diagrams.
Erase Suspend/Erase Resume Commands
The Erase Suspend command allows the s yst em to interrupt a sector erase operation and then read data
from, or program data to, any sector not selected for
erasure. This command is valid only during the sector
erase operation, including the 50 µs time-out period
during the sector erase command sequence. The
Erase Suspend comm and is ignored if written dur ing
the chip erase operation or Embedded Program algorithm. Writing the Erase Suspend command during the
Sector Erase time-out immediately terminates the
time-out period and suspends the er ase oper at ion. Addresses are “don’t-cares” when writing the Erase Suspend command.
When the Erase Suspend command is written during a
sector erase operation, the de vice requires a maximum
of 20 µs to suspend the erase operation. However,
when the Erase Suspend command is written during
the sector erase time-out, the device immediately terminates the time-out period and suspends the erase
operation.
After the erase operation has been suspended, the
system can read array data from or program data to
any sector not selected for erasure . (The devi ce “erase
suspends” all sectors selected for erasure.) Normal
read and write timings and command definitions apply.
Reading at any address within erase-suspended sectors produces status data on DQ7–DQ0. The system
can use DQ7, or DQ6 and DQ2 together, to determ ine
if a sector is actively erasing or is erase-suspended.
See “Write Operation Status” for information on these
status bits.
After an erase-suspended program operation is complete, the system can once again read arra y data within
non-suspended sectors. The system ca n determine the
status of the program operation using the DQ7 or DQ6
status bits, just as in the standard program operation.
See “Write Operation Status” for more information.
The system may also write the autoselect command
sequence when the device is in the Erase Suspend
mode. The device allows reading autoselect codes
even at addresses within erasing sectors, since the
codes are not stored in the memory array. When the
device exits the autoselect mode, the device reverts to
the Erase Suspend mode, and is ready for another
valid operation. See “Autoselect Command Sequence”
for more information.
The system must write the Erase Resume command
(address bits are “don’t care”) to exit the erase suspend
mode and continue the sector erase operati on. Further
writes of the Resume command are ignored. Another
Erase Suspend command can be written after the device has resumed erasing.
Notes:
1. See Table 5 for erase command sequence.
2. See “DQ3: Sector Erase Timer” for more information.
Figure 4. Erase Operation
START
Write Erase
Command Sequence
Data Poll
from System
Data = FFh?
No
Yes
Erasure Completed
Embedded
Erase
algorithm
in progress
21490E-8
Page 18

18 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Table 5. Am29LV800B Command Definitions
Legend:
X = Don’t care
RA = Address of the memory location to be read.
RD = Data read from location RA during read operation.
PA = Address of the memory location to be programmed.
Addresses latch on the falling edge of the WE# or CE# pulse,
whichever happens later.
PD = Data to be programmed at location PA. Data latches on the
rising edge of WE# or CE# pulse, whichever happens first.
SA = Address of the sector to be verified (in autoselect mode) or
erased. Address bits A18–A12 uniquely select any sector.
Notes:
1. See Table 1 for description of bus operatio n s.
2. All values are in hexadecimal.
3. Except when reading array or autoselect data, all bus cycles
are write operations.
4. Data bits DQ15–DQ8 are don’t cares for unlock and
command cycles.
5. Address bits A18–A11 are don’t cares for unlock and
command cycles, unless PA or SA required.
6. No unlock or command cycles required when reading array
data.
7. The Reset command is required to return to reading array
data when device is in the autoselect mode, or if DQ5 goes
high (while the device is providing status da ta).
8. The fourth cycle of the autoselect command sequence is a
read cycle.
9. The data is 00h for an unprotected sector and 01h for a
protected sector. See “Autoselect Command Sequence” for
more information.
10. The Unlock Bypass command is required prior to the Unlock
Bypass Program command.
11. The Unlock Bypass Reset command is required to return to
reading array data when the device is in the unlock bypass
mode.
12. The system may read and program in non-erasing sectors, or
enter the autoselect mode, when in the Erase Suspend
mode. The Erase Suspend command is valid only during a
sector erase operation.
13. The Erase Resume command is valid only during the Erase
Suspend mode.
Command
Sequence
(Note 1)
Bus Cycles (Notes 2-5)
First Second Third Fourth Fifth Sixth
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
Read (Note 6) 1 RA RD
Reset (Note 7) 1 XXX F0
Manufacturer ID
Word
4
555
AA
2AA
55
555
90 X00 01
Byte AAA 555 AAA
Device ID,
Top Boot Block
Word
4
555
AA
2AA
55
555
90
X01 22DA
Byte AAA 555 AAA
X02
DA
Device ID,
Bottom Boot Block
Word
4
555
AA
2AA
55
555
90
X01 225B
Byte AAA 555 AAA
X02 5B
Sector Protect Verify
(Note 9)
Word
4
555
AA
2AA
55
555
90
(SA)
X02
XX00
XX01
Byte AAA 555 AAA
(SA)
X04
00
01
Program
Word
4
555
AA
2AA
55
555
A0 PA PD
Byte AAA 555 AAA
Unlock Bypass
Word
3
555
AA
2AA
55
555
20
Byte AAA 555 AAA
Unlock Bypass Program (Note 10) 2 XXX A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass Reset (Note 11) 2 XXX 90 XXX 00
Chip Erase
Word
6
555
AA
2AA
55
555
80
555
AA
2AA
55
555
10
Byte AAA 555 AAA AAA 555 AAA
Sector Erase
Word
6
555
AA
2AA
55
555
80
555
AA
2AA
55 SA 30
Byte AAA 555 AAA AAA 555
Erase Suspend (Note 12) 1 XXX B0
Erase Resume (Note 13) 1 XXX 30
Cycles
Autoselect (Note 8)
Page 19

Am29LV800B 19
PRELIMINARY
WRITE OPERATION STATUS
The device provides several bits to determine the status of a write operation: DQ2, DQ3, DQ5, DQ6, DQ7,
and RY/BY#. Table 6 and t he f ollowing s ubsections describe the functions of these bits. DQ7, RY/BY#, and
DQ6 each offer a method for determining whether a
program or erase operation is complete or in progress.
These three bits are discussed first.
DQ7: Data# Polling
The Data# Polling bit, DQ7, indicates to the host system
whether an Embedded Algorithm is in progress or completed, or whether the device is in Erase Suspend.
Data# Polling is valid after the rising edge of the final
WE# pulse in the program or erase command sequence.
During the Em bedded Program algor ithm, the device
outputs on DQ7 the complement of the datum programmed to DQ7. This DQ7 status also applies to programming during Erase Suspend. When the
Embedded Program algorithm is complete, the device
outputs the datum programmed to DQ7. The system
must provide the program address to read valid status
information on DQ7. If a program address falls within a
protected sector, Data# Polling on DQ7 is active for approximately 1 µs, then the device returns to reading
array data.
During the Embedded Erase algorithm, Data# Polling
produces a “0” on DQ7. When the Embedded Erase algorithm is complete, or if the device enters the Erase
Suspend mode, Data# Polling produces a “1” on DQ7.
This is analogous to the complement/true datum output
described for the Embedded Program algorithm: the
erase function changes all the bits in a sector to “1”;
prior to this, the device outputs the “complement,” o r
“0.” The system must provide an address within any of
the sectors selected for erasure to read valid status information on DQ7.
After an erase command sequence is written, if all s ectors selected for erasing are protected, Data# Polling
on DQ7 is active f or appro ximately 100 µs , the n the device returns to reading array data. If not all selected
sectors are protected, the Embedded Erase algorithm
erases the unprotected sectors, and ignores the selected sectors that are protected.
When the system detects DQ7 has changed from the
complement to true data, it can read va lid data at DQ7–
DQ0 on the
following
read cycles. This is because DQ7
may change asynchronously with DQ0–DQ6 while
Output Enable (OE#) is as serted low. Figure 19, Data#
Polling Timings (During Embedded Algorithms), in the
“AC Characteristics” section illustrates this.
Table 6 shows the outputs for Data# Polling on DQ7.
Figure 5 shows the Data# Polling algorithm.
DQ7 = Data?
Yes
No
No
DQ5 = 1?
No
Yes
Yes
FAIL
PASS
Read DQ7–DQ0
Addr = VA
Read DQ7–DQ0
Addr = VA
DQ7 = Data?
START
Notes:
1. VA = Valid address for programming. During a sector
erase operation, a valid address is an address within any
sector selected for erasure. During chip erase, a valid
address is any non-protected sector address.
2. DQ7 should be rechecked even if DQ5 = “1” because
DQ7 may change simultaneously with DQ5.
21490E-9
Figure 5. Data# Polling Algorithm
Page 20

20 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
RY/BY#: Ready/Busy#
The RY/BY# is a dedicated, open-drain output pin that
indicates whether an Embedded Algorithm is in
progress or complete. The RY/BY# status is valid after
the rising edge of the final WE# pulse in the command
sequence. Since RY/BY# is an open-drain output, several RY/BY# pins can be tied together in parallel with a
pull-up resistor to V
CC
.
If the output is low (Busy ), the de vice is activ ely er asing
or programming. (T his includes programming in the
Erase Suspend mode.) If th e output is high (Ready) ,
the device is ready to read array data (including during
the Erase Suspend mode), or is in the standby mode.
Table 6 shows the outputs for RY/BY#. Figures 13, 14,
17 and 18 shows R Y/BY# for read, reset, program, and
erase operations, respectively.
DQ6: Toggle Bit I
Toggle Bit I on DQ6 indicates whethe r an Embedded
Program or Erase algorithm is in progress or complete,
or whether the device has entered the Erase Suspend
mode. Toggle Bit I may be read at any address, and is
valid after the rising edge of the final WE# pulse in the
command sequence (prior to the program or eras e operation), and during the sector erase time-out.
During an Embedded Program or Erase algorithm operation, successive read cycles to any address cause
DQ6 to toggle. (The system may use either OE# or
CE# to control the read cycles.) When the operation is
complete, DQ6 stops toggling.
After an erase command sequence is written, if all s ectors selected for eras ing are protected , DQ6 toggles for
approximately 100 µs, then returns to readi ng array
data. If not all selected sectors are protected, the Embedded Erase algorithm erases the unprotected sectors, and ignores the selected sectors that are
protected.
The system can use DQ6 and DQ2 together to determine whether a sector is actively erasing or is erasesuspended. When the device is actively erasing (that
is, the Embedded Erase algorithm is in progress), DQ6
toggles. When the device enters the Erase Suspend
mode, DQ6 stops toggling. However, the system must
also use DQ2 to determine which sectors are erasing
or erase-suspended. Alternatively, the system can use
DQ7 (see the subsection on “DQ7: Data# Polling”).
If a program address falls within a pro tected sector,
DQ6 toggles for approximately 1 µs after the program
command sequence is written, then returns to reading
array data.
DQ6 also toggles during the erase-suspend-program
mode, and stops toggling once the Embedded Program algorithm is complete.
Table 6 shows the outputs for Toggle Bit I on DQ6. Figure 6 shows the toggle bit algorithm. Figure 20 in the
“AC Characteristics” section shows the toggle bit ti ming
diagrams. Figure 21 shows the differences between
DQ2 and DQ6 in graphical for m. See also the subsection on “DQ2: Toggle Bit II”.
DQ2: Toggle Bit II
The “Toggle Bit II” on DQ2, when used with DQ6, indicates whether a par ticular sect or is actively erasing
(that is, the Embedded Erase algo rithm is in pro gress),
or whether that sector is erase-suspended. Toggle Bit
II is valid after the rising edge of t he final WE# pulse in
the command sequence.
DQ2 toggles w hen the system reads at addresses
within those sectors that have been selected for erasure. (The system may use either OE# or CE# to control
the read cycles.) But DQ2 cannot distinguish whether
the sector is actively erasing or is erase-suspended.
DQ6, by comparison, indicates whether the device is
actively erasing, or is in Erase Suspend, but cannot
distinguish which s ectors are selected for erasure.
Thus, both status bits are requ ired f or sector and mode
information. Refer to Table 6 to compare outputs for
DQ2 and DQ6.
Figure 6 shows the toggle bit algorithm in flowchar t
form, and the section “DQ2: Toggle Bit II” explains the
algorithm. See also the “DQ6: Toggle Bit I” subse ct ion.
Figure 20 shows the toggle bit timing diagram. Figure
21 shows the differences between DQ2 and DQ6 in
graphical form.
Reading Toggle Bits DQ6/DQ2
Refer to Figure 6 for the following discussion. Whenever
the system initially begins rea ding toggle bit status, it
must read DQ7–DQ0 at least twice in a row to determine
whether a toggle bit is toggling. Typically, the system
would note and store the value of the toggle bit after the
first read. After the second read, the system would compare the new value of the toggle bit with the first. If the
toggle bit is not toggling, the device has completed the
program or erase operation. The system can read array
data on DQ7–DQ0 on the following read cycle.
However, if after the initial two read cycles, the system
determines that the toggle bit is still toggling, the system also should note whether the value of DQ5 is high
(see the section on DQ5). If it is, the system should
then determine again whether the toggle bit is toggling,
since the toggle bit may have stopped toggling just as
DQ5 went high. If the toggle bit is no longer toggling,
the device has successfully completed the program or
erase operation. If it is still toggling, the device did not
completed the operation successfully, and the system
must write the reset command to return to readi ng
array data.
Page 21

Am29LV800B 21
PRELIMINARY
The remaining scenario is that the system initially determines that the toggle bit is toggling and DQ5 has not
gone high. The system may continue to monitor the
toggle bit and DQ5 through success ive read cycle s, determining the status as described in the previous paragraph. Alterna tively, it may choose to perfor m other
system tasks. In this case, the system must start at the
beginning of the algorithm when it returns to determine
the status of the operation (top of Figure 6).
DQ5: Exceeded Timing Limits
DQ5 indicates whether the program or erase time has
exceeded a specified internal pulse count limit. Under
these conditions DQ5 produces a “1.” This is a failure
condition that indicates the pro gram or er ase cycle w as
not successfully completed.
The DQ5 failure condition may appear if the system
tries to program a “1” to a location that is previously
programmed to “0.” Only an erase o peration can
change a “0” back to a “1.” Under this condition, the
device halts the oper ation, and when the operatio n has
exceeded the timing limits, DQ5 produces a “1.”
Under both these conditions, the system must issue
the reset command to return th e device to reading
array data.
DQ3: Sector Erase Timer
After writing a sector erase command sequence, the
system may read DQ3 to determine w hether or not an
erase operation has begun. (The sector erase timer
does not apply to the chip erase command.) If additional
sectors are selected for erasure, the entire time-out also
applies after each additional sector erase command.
When the time-out is complete, DQ3 switches from “0”
to “1.” The system may ignore DQ3 if the system can
guarantee that the time between additional sector
erase commands will always be less than 50 µs. See
also the “Sector Erase Command Sequence” section.
After the sector erase command sequenc e is written,
the system should read the status on DQ7 (Data# Polling) or DQ6 (Toggle Bit I) to ensure the device has accepted the command sequence, and then read DQ3. If
DQ3 is “1”, the internally controlled erase cycle has begun; all further commands (other than Erase Sus pend)
are ignored until the erase operation is complete. If
DQ3 is “0”, the device will accept additional sector
erase commands. To ensure the command has been
accepted, the system software should che ck the s tatus
of DQ3 prior to and following each subsequent sector
erase command. If DQ3 is high on the second status
check, the last command might not have been accepted. Table 6 shows the outputs for DQ3.
START
No
Yes
Yes
DQ5 = 1?
No
Yes
Toggle Bit
= Toggle?
No
Program/Erase
Operation Not
Complete, Write
Reset Command
Program/Erase
Operation Complete
Read DQ7–DQ0
Toggle Bit
= Toggle?
Read DQ7–DQ0
Twice
Read DQ7–DQ0
Notes:
1. Read toggle bit twice to determine whether or not it is
toggling. See text.
2. Recheck toggle bit because it may stop toggling as DQ5
changes to “1” . See text.
21490E-10
Figure 6. Toggle Bit Algorithm
(Notes
1, 2)
(Note 1)
Page 22

22 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
Table 6. Write Operation Status
Notes:
1. DQ5 switches to ‘1’ when an Embedded Program or Embedded Erase operation has exceeded the maximum timing limits.
See “DQ5: Exceeded Timing Limits” for more information.
2. DQ7 and DQ2 require a valid address when reading status information. Refer to the appropriate subsection for further details.
Operation
DQ7
(Note 2) DQ6
DQ5
(Note 1) DQ3
DQ2
(Note 2) RY/BY#
Standard
Mode
Embedded Program Algorithm DQ7# Toggle 0 N/A No toggle 0
Embedded Erase Algorithm 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Erase
Suspend
Mode
Reading within Erase
Suspended Sector
1 No toggle 0 N/A Toggle 1
Reading within Non-Erase
Suspended Sector
Data Data Data Data Data 1
Erase-Suspend-Program DQ7# Toggle 0 N/A N/A 0
Page 23

Am29LV800B 23
PRELIMINARY
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Storage Temperature
Plastic Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature
with Power Applied. . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Voltage with Respect to Ground
V
CC
(Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.5 V to +4.0 V
A9, OE#, and
RESET# (Note 2). . . . . . . . . . . .–0.5 V to +12.5 V
All other pins (Note 1) . . . . . –0.5 V to V
CC
+0.5 V
Output Short Circuit Current (Note 3) . . . . . . 200 mA
Notes:
1. Minimum DC voltage on input or I/O pins is –0.5 V . During
voltage transitions, input or I/O pins may undershoot V
SS
to –2.0 V for periods of up to 20 ns. See Figure 7.
Maximum DC voltage on input or I/O pins is V
CC
+0.5 V.
During voltage transitions, input or I/O pins may overshoot
to V
CC
+2.0 V for periods up to 20 ns. See Figure 8.
2. Minimum DC input voltage on pins A9, OE#, and RESET#
is –0.5 V. During voltage transitions, A9, OE#, and
RESET# may undershoot V
SS
to –2.0 V for periods of up
to 20 ns. See Figure 7. Maximum DC input voltage on pin
A9 is +12.5 V which may overshoot to 14.0 V for periods
up to 20 ns.
3. No more than one output may be shorted to ground at a
time. Duration of the short circuit should not be greater
than one second.
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at
these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational sections of this data sheet is not implied.
Exposure of the device to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Figure 7. Maximum Negative Overshoot
Waveform
Figure 8. Maximum Positive Overshoot
Waveform
OPERATING RANGES
Commercial (C) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
Industrial (I) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Extended (E) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
V
CC
Supply Voltages
V
CC
for regulated voltage range. . . . .+3.0 V to +3.6 V
VCC for full v oltage range. . . . . . . . . .+2.7 V to +3.6 V
Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the device is guaranteed.
20 ns
20 ns
+0.8 V
–0.5 V
20 ns
–2.0 V
21490E-11
20 ns
20 ns
V
CC
+2.0 V
V
CC
+0.5 V
20 ns
2.0 V
21490E-12
Page 24

24 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
DC CHARACTERISTICS
CMOS Compatible
Notes:
1. The I
CC
current listed is typically less than 2 mA/MHz, with OE# at VIH. Typical VCC is 3.0 V.
2. I
CC
active while Embedded Erase or Embedded Program is in progress.
3. Automatic sleep mode enables the low power mode when addresses remain stable for t
ACC
+ 30 ns.
4. Not 100% tested.
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
I
LI
Input Load Current
V
IN
= VSS to VCC,
V
CC
= VCC
max
±1.0 µA
I
LIT
A9 Input Load Current VCC = V
CC max
; A9 = 12.5 V 35 µA
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
V
OUT
= VSS to VCC,
V
CC
= V
CC max
±1.0 µA
I
CC1
VCC Active Read Current
(Note 1)
CE# = V
IL,
OE#
= VIH,
Byte Mode
5 MHz 7 12
mA
1 MHz 2 4
CE# = V
IL,
OE#
= VIH,
Word Mode
5 MHz 7 12
1 MHz 2 4
I
CC2
VCC Active Write Current
(Notes 2 and 4)
CE# = V
IL,
OE#
= VIH
15 30 mA
I
CC3
VCC Standby Current
VCC = V
CC max
;
CE#, RESET# = V
CC
±0.3 V
0.2 5 µA
I
CC4
VCC Reset Current
V
CC
= V
CC max
;
RESET# = V
SS
± 0.3 V
0.2 5 µA
I
CC5
Automatic Sleep Mode (Note 3)
VIH = V
CC
± 0.3 V;
V
IL
= V
SS
± 0.3 V
0.2 5 µA
V
IL
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
V
IH
Input High Voltage 0.7 x V
CC
VCC + 0.3 V
V
ID
Voltage for Autoselect and
Temporary Sector Unprotect
V
CC
= 3.3 V 11.5 12.5 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage IOL = 4.0 mA, VCC = V
CC min
0.45 V
V
OH1
Output High Voltage
IOH = –2.0 mA, VCC = V
CC min
0.85 V
CC
V
V
OH2
IOH = –100 µA, VCC = V
CC min
VCC–0.4
V
LKO
Low VCC Lock-Out Voltage
(Note 4)
2.3 2.5 V
Page 25

Am29LV800B 25
PRELIMINARY
DC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Zero Power Flash
20
15
10
5
0
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
Supply Current in mA
Time in ns
Note: Addresses are switching at 1 MHz
21490E-13
Figure 9. I
CC1
Current vs. Time (Showing Active and Automatic Sleep Currents)
10
8
2
0
12345
Frequency in MHz
Supply Current in mA
Note: T = 25 °C
21490E-14
Figure 10. Typical I
CC1
vs. Frequency
2.7 V
3.6 V
4
6
Page 26

26 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
TEST CONDITIONS
Table 7. Test Specifications
KEY TO SWITCHING WAVEFORMS
2.7 kΩ
C
L
6.2 kΩ
3.3 V
Device
Under
Test
21490E-15
Figure 11. Test Setup
Note: Diodes are IN3064 or equivalent
Test Condition
70R,
80
90,
120 Unit
Output Load 1 TTL gate
Output Load Capacitance, C
L
(including jig capacitance)
30 100 pF
Input Rise and Fall Times 5 ns
Input Pulse Levels 0.0–3.0 V
Input timing measurement
reference levels
1.5 V
Output timing measurement
reference levels
1.5 V
KS000010-PAL
WAVEFORM INPUTS OUTPUTS
Steady
Changing from H to L
Changing from L to H
Don’t Care, Any Change Permitted Changing, State Unknown
Does Not Apply Center Line is High Impedance State (High Z)
3.0 V
0.0 V
1.5 V 1.5 V
OutputMeasurement LevelInput
21490E-16
Figure 12. Input Waveforms and Measurement Levels
Page 27

Am29LV800B 27
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Read Operations
Notes:
1. Not 100% tested.
2. See Figure 11 and Table 7 for test specifications.
Parameter
Description
Speed Option
JEDEC Std Test Setup 70R 80 90 120 Unit
t
AVAV
t
RC
Read Cycle Time (Note 1) Min 70 80 90 120 ns
t
AVQV
t
ACC
Address to Output Delay
CE# = V
IL
OE# = V
IL
Max 70 80 90 120 ns
t
ELQV
t
CE
Chip Enable to Output Delay OE# = V
IL
Max 70 80 90 120 ns
t
GLQV
t
OE
Output Enable to Output Delay Max 30 30 35 50 ns
t
EHQZ
t
DF
Chip Enable to Output High Z (Note 1) Max 25 25 30 30 ns
t
GHQZ
t
DF
Output Enable to Output High Z (Note 1) Max 25 25 30 30 ns
t
OEH
Output Enable
Hold Time (Note 1)
Read Min 0 ns
Toggle and
Data# Polling
Min 10 ns
t
AXQX
t
OH
Output Hold Time From Addresses, CE# or
OE#, Whichever Occurs First (Note 1)
Min 0 ns
t
CE
Outputs
WE#
Addresses
CE#
OE#
HIGH Z
Output Valid
HIGH Z
Addresses Stable
t
RC
t
ACC
t
OEH
t
OE
0 V
RY/BY#
RESET#
t
DF
t
OH
21490E-17
Figure 13. Read Operations Timings
Page 28

28 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Hardware Reset (RESET#)
Note: Not 100% tested.
Parameter
Description All Speed OptionsJEDEC Std Test Setup Unit
t
READY
RESET# Pin Low (During Embedded
Algorithms) to Read or Write (See Note)
Max 20 µs
t
READY
RESET# Pin Low (NOT During Embedded
Algorithms) to Read or Write (See Note)
Max 500 ns
t
RP
RESET# Pulse Width Min 500 ns
t
RH
RESET# High Time Before Read (See Note) Min 50 ns
t
RPD
RESET# Low to Standby Mode Min 20 µs
t
RB
RY/BY# Recovery Time Min 0 ns
RESET#
RY/BY#
RY/BY#
t
RP
t
Ready
Reset Timings NOT during Embedded Algorithms
t
Ready
CE#, OE#
t
RH
CE#, OE#
Reset Timings during Embedded Algorithms
RESET#
t
RP
t
RB
21490E-18
Figure 14. RESET# Timings
Page 29

Am29LV800B 29
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Word/Byte Configuration (BYTE#)
Parameter
70R 80 90 120JEDEC Std Description Unit
t
ELFL/tELFH
CE# to BYTE# Switching Low or High Max 5 ns
t
FLQZ
BYTE# Switching Low to Output HIGH Z Max 25 25 30 30 ns
t
FHQV
BYTE# Switching High to Output Active Min 70 80 90 120 ns
DQ15
Output
Data Output
(DQ0–DQ7)
CE#
OE#
BYTE#
t
ELFL
DQ0–DQ14
Data Output
(DQ0–DQ14)
DQ15/A-1
Address
Input
t
FLQZ
BYTE#
Switching
from word
to byte
mode
DQ15
Output
Data Output
(DQ0–DQ7)
BYTE#
t
ELFH
DQ0–DQ14
Data Output
(DQ0–DQ14)
DQ15/A-1
Address
Input
t
FHQV
BYTE#
Switching
from byte
to word
mode
21490E-19
Figure 15. BYTE# Timings for Read Operations
Note: Refer to the Erase/Program Operations table for tAS and tAH specifications.
21490E-20
Figure 16. BYTE# Timings for Write Operations
CE#
WE#
BYTE#
The falling edge of the last WE# signal
t
HOLD
(tAH)
t
SET
(tAS)
Page 30

30 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Erase/Program Operations
Notes:
1. Not 100% tested.
2. See the “Erase and Programming Performance” section for more information.
Parameter
70R 80 90 120JEDEC Std Description Unit
t
AVAV
t
WC
Write Cycle Time (Note 1) Min 70 80 90 120 ns
t
AVWL
t
AS
Address Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
WLAX
t
AH
Address Hold Time Min 45 45 45 50 ns
t
DVWH
t
DS
Data Setup Time Min 35 35 45 50 ns
t
WHDX
t
DH
Data Hold Time Min 0 ns
t
OES
Output Enable Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
GHWL
t
GHWL
Read Recovery Time Before Write
(OE# High to WE# Low)
Min 0 ns
t
ELWL
t
CS
CE# Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
WHEH
t
CH
CE# Hold Time Min 0 ns
t
WLWH
t
WP
Write Pulse Width Min 35 35 35 50 ns
t
WHWL
t
WPH
Write Pulse Width High Min 30 ns
t
WHWH1tWHWH1
Programming Operation (Note 2)
Byte Typ 9
µs
Word Typ 11
t
WHWH2tWHWH2
Sector Erase Operation (Note 2) Typ 0.7 sec
t
VCS
VCC Setup Time (Note 1) Min 50 µs
t
RB
Recovery Time from RY/BY# Min 0 ns
t
BUSY
Program/Erase Valid to RY/BY# Delay Min 90 ns
Page 31

Am29LV800B 31
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
OE#
WE#
CE#
V
CC
Data
Addresses
t
DS
t
AH
t
DH
t
WP
PD
t
WHWH1
t
WC
t
AS
t
WPH
t
VCS
555h
PA PA
Read Status Data (last two cycles)
A0h
t
GHWL
t
CS
Status
D
OUT
Program Command Sequence (last two cycles)
RY/BY#
t
RB
t
BUSY
t
CH
PA
Notes:
1. PA = program address, PD = program data, D
OUT
is the true data at the program address.
2. Illustration shows device in word mode.
21490E-21
Figure 17. Program Operation Timings
Page 32

32 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
OE#
CE#
Addresses
V
CC
WE#
Data
2AAh SA
t
GHWL
t
AH
t
WP
t
WC
t
AS
t
WPH
555h for chip erase
10 for Chip Erase
30h
t
DS
t
VCS
t
CS
t
DH
55h
t
CH
In
Progress
Complete
t
WHWH2
VA
VA
Erase Command Sequence (last two cycles) Read Status Data
RY/BY#
t
RB
t
BUSY
Notes:
1. SA = sector address (for Sector Erase), VA = Valid Address for reading status data (see “Write Operation Status”).
2. Illustration shows device in word mode.
21490E-22
Figure 18. Chip/Sector Erase Operation Timings
Page 33

Am29LV800B 33
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
WE#
CE#
OE#
High
Z
t
OE
High
Z
DQ7
DQ0–DQ6
RY/BY#
t
BUSY
Complement
True
Addresses
VA
t
OEH
t
CE
t
CH
t
OH
t
DF
VA VA
Status Data
Complement
Status Data
True
Valid Data
Valid Data
t
ACC
t
RC
Note: VA = Valid address. Illustration shows first status cycle after command sequence, last status read cycle, and array data
read cycle.
21490E-23
Figure 19. Data# Polling Timings (During Embedded Algorithms)
WE#
CE#
OE#
High Z
t
OE
DQ6/DQ2
RY/BY#
t
BUSY
Addresses
VA
t
OEH
t
CE
t
CH
t
OH
t
DF
VA VA
t
ACC
t
RC
Valid DataValid StatusValid Status
(first read) (second read) (stops toggling)
Valid Status
VA
Note: V A = Valid address; not required for DQ6. Illustration shows first two status cycle after command sequence, last status read
cycle, and array data read cycle.
21490E-24
Figure 20. Toggle Bit Timings (During Embedded Algorithms)
Page 34

34 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Temporary Sector Unprotect
Note: Not 100% tested.
Parameter
All Speed OptionsJEDEC Std Description Unit
t
VIDR VID
Rise and Fall Time (See Note) Min 500 ns
t
RSP
RESET# Setup Time for Temporary Sector
Unprotect
Min 4 µs
Note: The system may use CE# or OE# to toggle DQ2 and DQ6. DQ2 toggles only when read at an address within an
erase-suspended sector.
21490E-25
Figure 21. DQ2 vs. DQ6
Enter
Erase
Erase
Erase
Enter Erase
Suspend Program
Erase Suspend
Read
Erase Suspend
Read
Erase
WE#
DQ6
DQ2
Erase
Complete
Erase
Suspend
Suspend
Program
Resume
Embedded
Erasing
RESET#
t
VIDR
12 V
0 or 3 V
CE#
WE#
RY/BY#
t
VIDR
t
RSP
Program or Erase Command Sequence
0 or 3 V
21490E-26
Figure 22. Temporary Sector Unprotect Timing Diagram
Page 35

Am29LV800B 35
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Sector Protect: 100 µs
Sector Unprotect: 10 ms
1 µs
RESET#
SA, A6,
A1, A0
Data
CE#
WE#
OE#
60h 60h 40h
Valid* Valid* Valid*
Status
Sector Protect/Unprotect Verify
V
ID
V
IH
* For sector protect, A6 = 0, A1 = 1, A0 = 0. For sector unprotect, A6 = 1, A1 = 1, A0 = 0.
21490E-27
Figure 23. Sector Protect/Unprotect Timing Diagram
Page 36

36 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Alternate CE# Controlled Erase/Program Operations
Notes:
1. Not 100% tested.
2. See the “Erase and Programming Performance” section for more information.
Parameter
70R 80 90 120JEDEC Std Description Unit
t
AVAV
t
WC
Write Cycle Time (Note 1) Min 70 80 90 120 ns
t
AVEL
t
AS
Address Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
ELAX
t
AH
Address Hold Time Min 45 45 45 50 ns
t
DVEH
t
DS
Data Setup Time Min 35 35 45 50 ns
t
EHDX
t
DH
Data Hold Time Min 0 ns
t
OES
Output Enable Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
GHEL
t
GHEL
Read Recovery Time Before Write
(OE# High to WE# Low)
Min 0 ns
t
WLEL
t
WS
WE# Setup Time Min 0 ns
t
EHWH
t
WH
WE# Hold Time Min 0 ns
t
ELEH
t
CP
CE# Pulse Width Min 35 35 35 50 ns
t
EHEL
t
CPH
CE# Pulse Width High Min 30 ns
t
WHWH1
t
WHWH1
Programming Operation
(Note 2)
Byte Typ 9
µs
Word T yp 11
t
WHWH2
t
WHWH2
Sector Erase Operation (Note 2) Typ 0.7 sec
Page 37

Am29LV800B 37
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
t
GHEL
t
WS
OE#
CE#
WE#
RESET#
t
DS
Data
t
AH
Addresses
t
DH
t
CP
DQ7# D
OUT
t
WC
t
AS
t
CPH
PA
Data# Polling
A0 for program
55 for erase
t
RH
t
WHWH1 or 2
RY/BY#
t
WH
PD for program
30 for sector erase
10 for chip erase
555 for program
2AA for erase
PA for program
SA for sector erase
555 for chip erase
t
BUSY
Notes:
1. P A = program address, PD = program data, DQ7# = complement of the data written to the device, D
OUT
= data written to the
device.
2. Figure indicates the last two bus cycles of command sequence.
3. Word mode address used as an example.
21490E-28
Figure 24. Alternate CE# Controlled Write Operation Timings
Page 38

38 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
ERASE AND PROGRAMMING PERFORMANCE
Notes:
1. Typical program and erase times assume the following conditions: 25
°
C, 3.0 V VCC, 1,000,000 cycles. Additionally,
programming typicals assume checkerboard pattern.
2. Under worst case conditions of 90°C, V
CC
= 2.7 V, 1,000,000 cycles.
3. The typical chip programming time is considerably less than the maximum chip programming time listed, since most bytes
program faster than the maximum program times listed.
4. In the pre-programming step of the Embedded Erase algorithm, all bytes are programmed to 00h before erasure.
5. System-level overhead is the time required to execute the two- or four-bus-cycle sequence for the program command. See
Table 5 for further information on command definitions.
6. The device has a guaranteed minimum erase and program cycle endurance of 1,000,000 cycles.
LATCHUP CHARACTERISTICS
Includes all pins except VCC. Test conditions: VCC = 3.0 V, one pin at a time.
TSOP AND SO PIN CAPACITANCE
Notes:
1. Sampled, not 100% tested.
2. Test conditions T
A
= 25°C, f = 1.0 MHz.
DATA RETENTION
Parameter Typ (Note 1) Max (Note 2) Unit Comments
Sector Erase Time 0.7 15 s
Excludes 00h programming
prior to erasure
Chip Erase Time 14 s
Byte Programming Time 9 300 µs
Excludes system level
overhead (Note 5)
Word Programming Time 11 360 µs
Chip Programming Time
(Note 3)
Byte Mode 9 27 s
Word Mode 5.8 17 s
Description Min Max
Input voltage with respect to V
SS
on all pins except I/O pins
(including A9, OE#, and RESE T#)
–1.0 V 12.5 V
Input voltage with respect to V
SS
on all I/O pins –1.0 V VCC + 1.0 V
V
CC
Current –100 mA +100 mA
Parameter
Symbol Parameter Description Test Setup Typ Max Unit
C
IN
Input Capacitance VIN = 0 6 7.5 pF
C
OUT
Output Capacitance V
OUT
= 0 8.5 12 pF
C
IN2
Control Pin Capacitance VIN = 0 7.5 9 pF
Parameter Test Conditions Min Unit
Minimum Pattern Data Retention Time
150°C 10 Years
125°C 20 Years
Page 39

Am29LV800B 39
PRELIMINARY
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS*
TS 048—48-Pin Standard TSOP (measured in millimeters)
* For reference only. BSC is an ANSI standard for Basic Space Centering.
TSR048—48-Pin Reverse TSOP (measured in millimeters)
* For reference only. BSC is an ANSI standard for Basic Space Centering.
48
25
1
24
18.30
18.50
19.80
20.20
11.90
12.10
0.05
0.15
0.50 BSC
0.95
1.05
16-038-TS48-2
TS 048
DT95
8-8-96 lv
Pin 1 I.D.
1.20
MAX
0.50
0.70
0.10
0.21
0.25MM (0.0098") BSC
0˚
5˚
0.08
0.20
48
25
1
24
18.30
18.50
19.80
20.20
11.90
12.10
SEATING PLANE
0.05
0.15
0.50 BSC
0.95
1.05
16-038-TS48
TSR048
DT95
8-8-96 lv
Pin 1 I.D.
1.20
MAX
0.50
0.70
0.10
0.21
0.25MM (0.0098") BSC
0˚
5˚
0.08
0.20
Page 40

40 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
FGB—48-Ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA) 6 x 9 mm (measured in mm)
5.80
6.20
8.80
9.20
DATUM B
DATUM A
INDEX
0.025
CHAMFER
0.15
M
Z
B
M
0.15
M
Z
B
M
5.60
BSC
0.40
4.00
BSC
0.08
M
ZA
B
0.10 Z
0.25
0.45
0.80
DETAIL A
0.20 Z
DETAIL A
1.20 MAX
0.40 ± 0.08 (48x) 0.40
16-038-FGB-2
EG137
12-2-97 lv
Page 41

Am29LV800B 41
PRELIMINARY
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
SO 044—44-Pin Small Outline Package (measured in millimeters)
44
23
1
22
13.10
13.50
15.70
16.30
1.27 NOM.
28.00
28.40
2.17
2.45
0.35
0.50
0.10
0.35
2.80
MAX.
SEATING
PLANE
16-038-SO44-2
SO 044
DF83
8-8-96 lv
0.10
0.21
0.60
1.00
0˚
8˚
END VIEW
SIDE VIEW
TOP VIEW
Page 42

42 Am29LV800B
PRELIMINARY
REVISION SUMMARY FOR AM29LV800B
Revision E
Distinctive Characteristics
Changed typical read and program/era se current specifications.
Device now has a guaranteed minimum endurance of
1,000,000 write cycles.
Figure 1, In-System Sector Protect/Unprotect
Algorithm
Corrected A6 to 0, Changed wait specification to 150
µs on sector protect and 15 ms on sector unprotect.
DC Characteristics
Changed typical read and program/era se current specifications.
AC Characteristics
Alternate CE# Controlled Erase/Program Operations:
Changed tCP to 35 ns for 70R, 80, and 90 speed
options.
Erase and Programming Performance
Device now has a guaranteed minimum endurance of
1,000,000 write cycles.
Physical Dimensions
Corrected dimensions for package length and width in
FBGA illustration (standalone data sheet version).
Revision E+1
Figure 2, In-System Sector Protect/Unprotect
Algorithms
In the sector protect algorithm, added a “Reset
PLSCNT=1” box in the path from “Protect anot her sector?” back to setting up the next sector address.
DC Characteristics
Changed Note 1 to indicate that OE# is at V
IH
for t he
listed current.
AC Characteristics
Erase/Program Operations; Altern ate CE# Controlled
Erase/Program Operations:
Corrected the notes refer-
ence for t
WHWH1
and t
WHWH2
. These parameters are
100% tested. Corrected the note reference for t
VCS
.
This parameter is not 100% tested.
Temporary Sector Unprotect Table
Added note reference for t
VIDR
. This parameter is not
100% tested.
Figure 23, Sector Protect/Unprotect Timing
Diagram
A valid address is not required for the first write cycle;
only the data 60h.
Erase and Programming Performance
In Note 2, the worst case endurance is now 1 million cycles.
Trademarks
Copyright © 1998 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
AMD, the AMD logo, and combinations thereof are registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
ExpressFlash is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.
 Loading...
Loading...