Page 1

AL422 Data Sheets
(Revision V1.1)
Page 2

AL422
Amendments (Since April 2, 1999)
05-13-99 DC/AC characteristics (including current consumption) updated.
07-02-99 Pinout diagram (5.0) and DC external load (7.4) modified.
08-03-99 Description about TST pin added in sections 6.0 & 8.1.
09-02-99 8.3.2 rewritten.
10-26-99 Capacitance provided in the AC characteristics section.
12-15-99 Remove TST pin restriction.
01-18-01 1. Revised section “8.3.2 Read Enable during Reset Cycles” to “8.3.2 The Proper
Manipulation of FIFO Access”.
2. Add section “8.3.3 Single Field Write with Multiple Read Operation”
3. Add section “8.3.4 One Field Delay Line (The Old Data Read)”
AL422B January 23, 2001 2
Page 3

AL422
AL422 3M-Bits FIFO Field Memory
Contents:
1.0 Description ________________________________________________________________ 4
2.0 Features___________________________________________________________________ 4
3.0 Applications ________________________________________________________________ 4
4.0 Ordering Information________________________________________________________ 4
5.0 Pinout Diagram ____________________________________________________________ 5
6.0 Pin Description _____________________________________________________________ 5
7.0 Electrical Characteristics _____________________________________________________ 6
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings________________________________________________________ 6
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ________________________________________________ 6
7.3 DC Characteristics _______________________________________________________________ 6
7.4 AC Characteristics _______________________________________________________________ 7
7.5 Timing Diagrams_________________________________________________________________ 9
8.0 Functional Description______________________________________________________ 13
8.1 Memory Operation______________________________________________________________ 14
8.2 5V and 3.3V applications _________________________________________________________ 15
8.3 Application Notes _______________________________________________________________ 16
8.3.1 Irregular Read/Write _________________________________________________________________ 16
8.3.2 The Proper Manipulation of FIFO Access_________________________________________________ 17
8.3.3 Single Field Write with Multiple Read Operation___________________________________________ 17
8.3.4 One Field Delay Line (The Old Data Read) _______________________________________________ 17
9.0 Mechanical Drawing _______________________________________________________ 19
AL422B January 23, 2001 3
Page 4
AL422
1.0 Description
The AL422 consists of 3M-bits of DRAM, and is configured as 393,216 words x 8 bit FIFO (first in
first out). The interface is very user-friendly since all complicated DRAM operations are already
managed by the internal DRAM controller.
Current sources of similar memory (field memory) in the market provide limited memory size which
is only enough for holding one TV field, but not enough to hold a whole PC video frame which
normally contains 640x480 or 720x480 bytes. The AverLogic AL422 provides 50% more memory
to support high resolution for digital PC graphics or video applications. The 50% increase in speed
also expands the range of applications.
2.0 Features
• 384K (393,216) x 8 bits FIFO organization
• Support VGA, CCIR, NTSC, PAL and
HDTV resolutions
• Independent read/write operations (different
I/O data rates acceptable)
• High speed asynchronous serial access
• Read/write cycle time: 20ns
• Access time: 15ns
• Output enable control (data skipping)
• Self refresh
• 5V or 3.3V power supply
• Standard 28-pin SOP package
4.0 Ordering Information
3.0 Applications
• Multimedia systems
• Video capture systems
• Video editing systems
• Scan rate converters
• TV’s picture in picture feature
• Time base correction (TBC)
• Frame synchronizer
• Digital video camera
• Buffer for communications systems
Part number Package Power Supply Status
AL422B 28-pin plastic SOP +5/+3.3 volt Shipping
AL422V5 28-pin plastic SOP +5 volt Replaced by AL422B
AL422V3 28-pin plastic SOP +3.3 volt Replaced by AL422B
AL422B January 23, 2001 4
Page 5
AL422
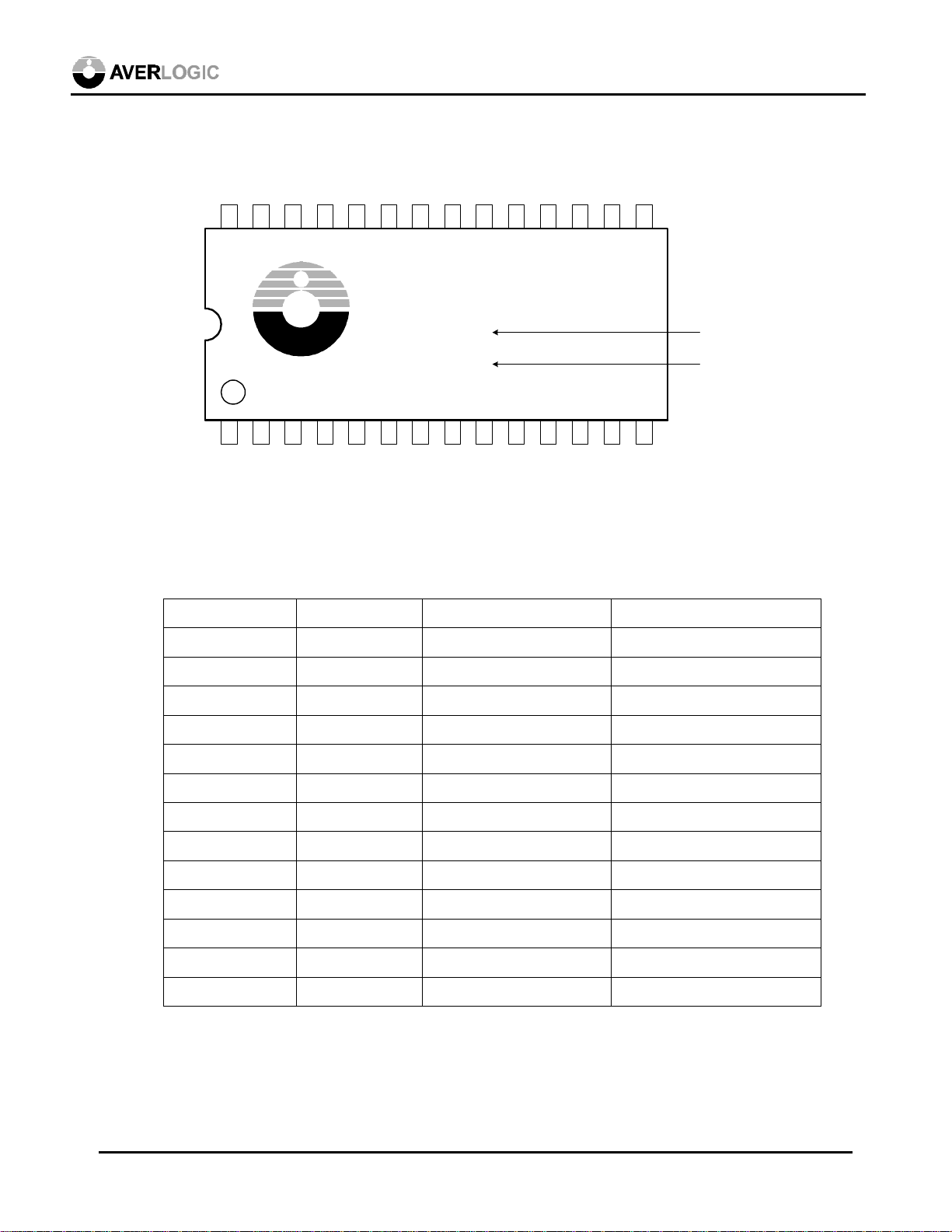
5.0 Pinout Diagram
DO1 DO2 DO3 /RE
DO0
28 27 26
2 3 4 5
1
DI1 DI2 DI3 /WE
DI0
25 24
6.0 Pin Description
Pin name Pin # I/O type Function
/OE /RRST RCK DEC
GND
22 21 20 19
23
AVERLOGIC
AL422B
XXXXX
XXXX
7 8 9 10
6
TST /WRST WCK VDD
GND
DO5 DO6 DO7
DO4
17 16 15
18
12 13 14
11
DI5 DI6 DI7
DI4
AL422-04 422B pinout diagram
Lot Number
Date Code
DI0~DI7 1~4, 11~14 input Data input
WCK 9 Input Write clock
/WE 5 Input (active low) Write enable
/WRST 8 Input (active low) Write reset
DO0~DO7 15~18, 25~28 Output (tristate) Data output
RCK 20 Input Read clock
/RE 24 Input (active low) Read enable
/RRST 21 Input (active low) Read reset
/OE 22 Input (active low) Output enable
TST 7 Input Test pin (pulled-down)*
VDD 10 5V or 3.3V
DEC/VDD 19 Decoupling cap input
GND 6, 23 Ground
AL422B January 23, 2001 5
Page 6
AL422
7.0 Electrical Characteristics
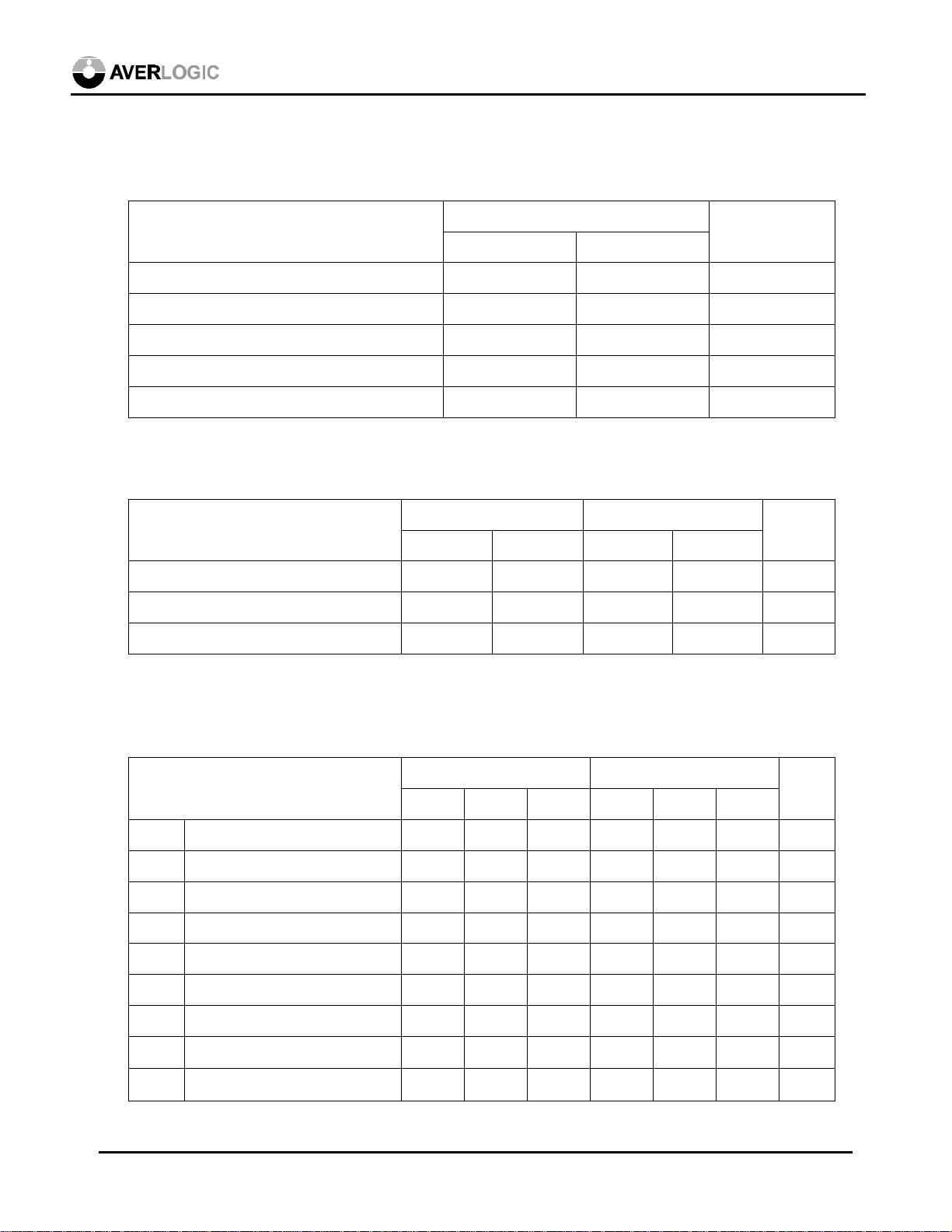
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter
Ratings
3.3V application 5V application
VDD Supply Voltage -1.0 ~ +4.5 -1.0 ~ +7.0 V
VP Pin Voltage -1.0 ~ +5.5 -1.0 ~ VDD +0.5 V
IO Output Current -20 ~ +20 -20 ~ +20 mA
T
Ambient Op. Temperature 0 ~ +70 0 ~ +70 °C
AMB
T
Storage temperature -55 ~ +125 -55 ~ +125 °C
stg
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter
VDD Supply Voltage +3.0 +3.6 +4.5 +5.25 V
VIH High Level Input Voltage +2.0 +5.5 +3.0 VDD +0.5 V
VIL Low Level Input Voltage -1.0 +0.8 -1.0 +0.8 V
3.3V application 5V application
Min Max Min Max
Unit
Unit
7.3 DC Characteristics
(VDD =5V or 3.3V, Vss=0V. T
Parameter
IDD Operating Current @20MHz - 33 - - 50 - mA
IDD Operating Current @30MHz - 45 - - 66 - mA
IDD Operating Current @40MHz - 57 - - 82 - mA
IDD Operating Current @50MHz - 68 - - 97 - mA
I
Standby Current - 7 - - 12 - mA
DDS
VOH Hi-level Output Voltage 0.7V
VOL Lo-level Output Voltage - - +0.4 - - +0.4 V
ILI Input Leakage Current -10 - +10 -10 - +10
ILO Output Leakage Current -10 - +10 -10 - +10
AL422B January 23, 2001 6
= 0 to 70°C)
AMB
3.3V application 5V application
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
DD
- VDD +3.0 - VDD V
Unit
µA
µA
Page 7

AL422
7.4 AC Characteristics
(VDD =5V or 3.3V, Vss=0V, T
= 0 to 70°C)
AMB
3.3V application 5V application
Parameter
Unit
Min Max Min Max
TWC WCK Cycle Time 20 1000 20 1000 ns
T
WCK High Pulse Width 7 - 7 - ns
WPH
T
WCK Low Pulse Width 7 - 7 - ns
WPL
TRC RCK Cycle Time 20 1000 20 1000 ns
T
RCK High Pulse Width 7 - 7 - ns
RPH
T
RCK Low Pulse Width 7 - 7 - ns
RPL
TAC Access Time - 15 - 15 ns
TOH Output Hold Time 4 - 4 - ns
THZ Output High-Z Setup Time 3 15 4 15 ns
TLZ Output Low-Z Setup Time 3 15 4 15 ns
T
/WRST Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
WRS
T
/WRST Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
WRH
T
/RRST Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
RRS
T
/RRST Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
RRH
TDS Input Data Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
TDH Input Data Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
T
/WE Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
WES
T
/WE Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
WEH
T
/WE Pulse Width 10 - 10 - ns
WPW
T
/RE Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
RES
T
/RE Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
REH
T
/RE Pulse Width 10 - 10 - ns
RPW
T
/OE Setup Time 5 - 6 - ns
OES
T
/OE Hold Time 2 - 3 - ns
OEH
T
/OE Pulse Width 10 - 10 - ns
OPW
TTR Transition Time 2 20 3 20 ns
CI Input Capacitance - 7 - 7 pF
CO Output Capacitance - 7 - 7 pF
AL422B January 23, 2001 7
Page 8

AL422
• Input voltage levels are defined as VIH=3.0V and VIL=0.4V.
• The read address needs to be at least 128 cycles after the write address.
DO external load:
AL422B January 23, 2001 8
Page 9

AL422
Reset
Reset
7.5 Timing Diagrams
WCK
/WRST
DI7~0
/WE = "L"
cycle n
T
TR
T
WRS
n-1 n 0 1
cycle (s)
cycle 0 cycle 1
T
WRH
TDST
DH
AL422-05 Write Cycle Timing (Write Reset)
cycle n
cycle (s)
T
RPL
cycle 0 cycle 1
RCK
T
RPH
T
RRS
T
RRH
/RRST
T
AC
T
OH
DO7~0
n-1 n
0 1
0
/RE = /OE = "L"
AL422-07 Read Cycle Timing (Read Reset)
AL422B January 23, 2001 9
Page 10

AL422
cycle n cycle n+1 Disable cycle (s)
T
RPL
cycle n+2
RCK
T
RPH
T
T
RC
RES
T
REH
/RE
T
RPW
T
AC
T
OH
DO7~0
/OE = "L"
RCK
n-1 n
AL422-08 Read Cycle Timing (Read Enable)
cycle n cycle n+1 cycle n+3
T
RPL
T
RPH
T
T
RC
OES
cycle n+2
n+1
n+2
cycle n+4
T
OEH
/OE
T
OPW
T
AC
T
DO7~0
n-1 n
n+1
HZ
Hi-Z
T
OH
T
LZ
n+4
/RE = "L"
AL422-09 Read Cycle Timing (Output Enable)
AL422B January 23, 2001 10
Page 11

WCK
/WE
AL422
cycle n cycle n+1 Disable cycle (s)
TWPL
TWPH
TWES TWEHTWC
TWPW
TDS TDH
cycle n+2
DI7~0
RCK
/RRST
/RE
n-1 n
n+1 n+2
AL422-06 Write Cycle Timing (Write Enable)
cycle n cycle n+1 Disable cycle (s)
TRPL
TRPH
TRC
TRRS TRRH
TRES TREH
RPW
T
TAC
TOH
cycle 0
DO7~0
n-1 n
n+1
0
/OE = "L"
AL422-14 Read Cycle Timing (RE, RRST)
AL422B January 23, 2001 11
Page 12

AL422
WCK
/WRST
/WE
DI7~0
cycle n cycle n+1 Disable cycle (s)
TWPL
TWPH
TWC
TWES TWEH
TWPW
TDS TDH
n-1 n
n+1 1
AL422-15 Write Cycle Timing (WE, WRST)
cycle 0
TWRS TWRH
cycle 1
0
AL422B January 23, 2001 12
Page 13

AL422
8.0 Functional Description
The AL422 is a video frame buffer consisting of DRAM that works like a FIFO which is long enough
to hold up to 819x480 bytes of picture information and fast enough to operate at 50MHz. The
functional block diagram is as follows:
SRAM
Cache
DI7~
DI0
Input
Buffer
WCK
/WRST
/WE
Write
Data
Register
Write
Address
Counter
384k x8
Memory Cell Array
Timing Generator
& Arbiter
Refresh Address
Counter
Read
Data
Register
Read
Address
Counter
AL422-03 Block Diagram
Output
Buffer
RCK
/RRST
/RE
DO7~
DO0
/OE
The I/O pinouts and functions are described as follows:
DI7~DI0 Data Input: Data is input on the rising edge of the cycle of WCK when /WE is pulled low
(enabled).
DO7~DO0 Data Output: Data output is synchronized with the RCK clock. Data is obtained at the
rising edge of the RCK clock when /RE is pulled low. The access time is defined from the rising edge
of the RCK cycle.
WCK Write Clock Input: The write data input is synchronized with this clock. Write data is input at
the rising edge of the WCK cycle when /WE is pulled low (enabled). The internal write address
pointer is incremented automatically with this clock input.
RCK Read Clock Input: The read data output is synchronized with this clock. Read data output at
the rising edge of the RCK cycle when /OE is pulled low (enabled). The internal read address pointer
is incremented with this clock input.
/WE Write Enable Input: /WE controls the enabling/disabling of the data input. When /WE is
pulled low, input data is acquired at the rising edge of the WCK cycle. When /WE is pulled high, the
AL422B January 23, 2001 13
Page 14

AL422
memory does not accept data input. The write address pointer is stopped at the current position. /WE
signal is fetched at the rising edge of the WCK cycle.
/RE Read Enable Input: /RE controls the operation of the data output. When /RE is pulled low,
output data is provided at the rising edge of the RCK cycle and the internal read address is
incremented automatically. /RE signal is fetched at the rising edge of the RCK cycle.
/OE Output Enable Input: /OE controls the enabling/disabling of the data output. When /OE is
pulled low, output data is provided at the rising edge of the RCK cycle. When /OE is pulled high, data
output is disabled and the output pins remain at high impedance status. /OE signal is fetched at the
rising edge of RCK cycle.
/WRST Write Reset Input: This reset signal initializes the write address to 0, and is fetched at the
rising edge of the WCK input cycle.
/RRST Write Reset Input: This reset signal initializes the read address to 0, and is fetched at the
rising edge of the RCK input cycle.
TST Test Pin: For testing purpose only. It should be pulled low for normal applications.
DEC: Decoupling cap pin, should be connected to a 1µF or 2.2µF capacitor to ground for 5V
application. For 3.3V application, the DEC pin can be simply connected to the 3.3V power with
regular 0.1µF bypass capacitor.
8.1 Memory Operation
Initialization
Apply /WRST and /RRST 0.1ms after power on, then follow the following instructions for normal
operation.
Reset Operation
The reset signal can be given at any time regardless of the /WE, /RE and /OE status, however, they
still need to meet the setup time and hold time requirements with reference to the clock input. When
the reset signal is provided during disabled cycles, the reset operation is not executed until cycles are
enabled again. When /WRST signal is pulled low, the data input address will be set to 0 and the data
in the Input Buffer will be flushed into memory cell array. When /RRST signal is pulled low, the data
output address will be set to 0 and pre-fetch the data from memory cell array to Output Buffer.
AL422B January 23, 2001 14
Page 15

AL422
Write Operation
Data input DI7~DI0 is written into the write register at the WCK input when /WE is pulled low. The
write data should meet the setup time and hold time requirements with reference to the WCK input
cycle.
Write operation is prohibited when /WE is pulled high, and the write address pointer is stopped at the
current position. The write address starts from there when the /WE is pulled low again. The /WE
signal needs to meet the setup time and hold time requirements with reference to the WCK input cycle.
Read Operation
Data output DO7~DO0 is written into the read register at the RCK input when both /RE and /OE are
pulled low. The output data is ready after TAC (access time) from the rising edge of the RCK input
cycle.
The read address pointer is stopped at the current position when /RE is pulled high, and starts there
when /RE is pulled low again.
/OE needs to be pulled low for read operations. When /OE is pulled high, the data outputs will be at
high impedance stage. The read address pointer still increases synchronously with RCK regardless of
the /OE status. The /RE and /OE signals need to meet the setup time and hold time requirements with
reference to the RCK input cycle.
When the new data is read, the read address should be between 128 to 393,247 cycles after the write
address, otherwise the output may not be new data.
8.2 5V and 3.3V applications
The AL422 can accept either 3.3V or 5V power with slightly different external configuration. The
internal voltage regulator can convert 5V power to 3.3V for the embedded DRAM and logic circuitry
when 5V power is applied to VDD pin (#10) only and leave the DEC pin (#19) decoupled by a
capacitor of 1µF or 2.2µF to ground. The regulator can also be bypassed when 3.3V power is applied
to both VDD and DEC pins. In either case the AL422 is 5V or 3.3V I/O tolerant. The 3.3V
configuration consumes less power and is free from noise interference from the voltage regulator so
may be more ideal for high-speed applications.
Please note that using the AL422B with 5V configuration can directly replace the previous AL422V5;
using it with 3.3V configuration can directly replace the previous AL422V3. No additional
modification is required.
AL422B January 23, 2001 15
Page 16

AL422
The 5V configuration (direct replacement of the previous AL422V5) is as follows:
5V
AL422B
VDD DEC
0.1uF 2.2uF
The 3.3V configuration (direct replacement of the previous AL422V3) is as follows:
3.3V
3.3V
AL422B
10 19
VDD DEC
0.1uF 0.1uF
8.3 Application Notes
8.3.1 Irregular Read/Write
It is recommended that the WCK and RCK are kept running at least 1MHz at all times. The faster one
of WCK and RCK is used as the DRAM refresh timing clock and has to be kept free running. When
irregular FIFO I/O control is needed, keep the clock free running and use /WE or /RE to control the
I/O as follows:
WCK
Data
/WE
AL422-17 Slow Write - Correct
The following drawing shows irregular clock and should be avoided:
AL422B January 23, 2001 16
Page 17

AL422
WCK
Data
/WE
AL422-16 Slow Write - Incorrect
8.3.2 The Proper Manipulation of FIFO Access
The FIFO memory is designed to allow easy field delay, time-base conversion, and other types of
signal processing. To ensure the expectant data can be read out from the AL422 FIFO, the proper
manipulation on the AL422 FIFO memory is highly recommended
1. The read address should be between 128 to 393,247 cycles after the write address to read the
current field data. (The restriction is indicated in the “Read Operation” Section).
2. The proper FIFO access must make sure after read reset, the read operation will either read all the
old data (last field data) until next read reset, or follow the constraint 1 above to read newly update
data. In any 2 read resets interval, the FIFO access can not read old data (the field data are written
before last write reset), and stop for a period then read the newly update data (even at that time,
write counter is ahead of read counter by more than 128 cycles).
If the FIFO memory manipulations violate the above conditions, some amount of consecutive
unexpected data (old data) will be read at the FIFO data bus.
8.3.3 Single Field Write with Multiple Read Operation
It is one of the functions for FIFO memory that can buffer a field data and do multiple times of fields
read access. In some applications, such as still image capturing, require one field write and multiple
field data read operations. In order not to violate the 128 cycles of write to read delay latency rule,
the write address (pointer) needs to be reset to 0 for the coming multiple read operations so that FIFO
can provide the expectant data at DO bus.
8.3.4 One Field Delay Line (The Old Data Read)
As the design shown in diagram by applying the reset every 1-field cycle (with the common signal for
/WRST and /RRST) and a constant read/write operation (with all /WE, /RE and /OE are tied to
ground), “1 field delay line” timing is shown in timing chart below. When the difference between the
AL422B January 23, 2001 17
Page 18

AL422
write address and the read address is 0 (the read address and the write address are the same), the old
field data are read as shown in the timing chart.
Reset
AL422
8-bit Input 8-bit OutputDI[7:0]
/WE
/RRST/WRST
DO[7:0]
/OE
/RE
WCK
RCK
Clock
AL422 1 Field Delay Line Diagram
RCK
WCK
/RRST
/WRST
DI7~0
DO7~0
Field m Field m + 1
cycle 0 cycle 1 cycle n
0
1 n
AL422-08 1 Field Delay Line Timing Diagram
cycle 0
tAC
0
0
Data of field m
cycle 1
1
1
AL422B January 23, 2001 18
Page 19

AL422
9.0 Mechanical Drawing
28 PIN PLASTIC SOP:
AL422B January 23, 2001 19
Page 20

CONTACT INFORMATION
AverLogic Technologies, Inc.
6840 Via Del Oro
Suite 160
San Jose, CA 95119
USA
Tel : 1 408 361-0400
Fax : 1 408 361-0404
E-mail : sales@averlogic.com
URL : www.averlogic.com
 Loading...
Loading...