Page 1
CMOS, 240 MHz
D9–D0
GND R
SET
I
OUT
I
OUT
COMP
ADV7127
V
REF
VOLTAGE*
REFERENCE
CIRCUIT
PDOWN*
POWER–
DOWN
MODE
V
AA
10
DAC
10
DATA
REGISTER
CLOCK
PSAVE
*ON TSSOP VERSION ONLY
a
FEATURES
240 MSPS Throughput Rate
10-Bit D/A Converters
SFDR
–70 dB typ: f
–53 dB typ: f
RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Output
Complementary Outputs
DAC Output Current Range: 2 mA to 26 mA
TTL Compatible Inputs
Internal Voltage Reference (1.23 V) on TSSOP Package
Single Supply +5 V/+3.3 V Operation
28-Lead SOIC Package and 24-Lead TSSOP Package
Low Power Dissipation (30 mW min @ 3 V)
Low Power Standby Mode (10 mW min @ 3 V)
Power-Down Mode (60 mW min @ 3 V)
Power-Down Mode Available on TSSOP Package
Industrial Temperature Range (–408C to +858C)
APPLICATIONS
Digital Video Systems (1600 3 1200 @ 100 Hz)
High Resolution Color Graphics
Digital Radio Modulation
Image Processing
Instrumentation
Video Signal Reconstruction
Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Wireless LAN
= 50 MHz; f
CLK
= 140 MHz; f
CLK
= 1 MHz
OUT
= 40 MHz
OUT
10-Bit High Speed Video DAC
ADV7127
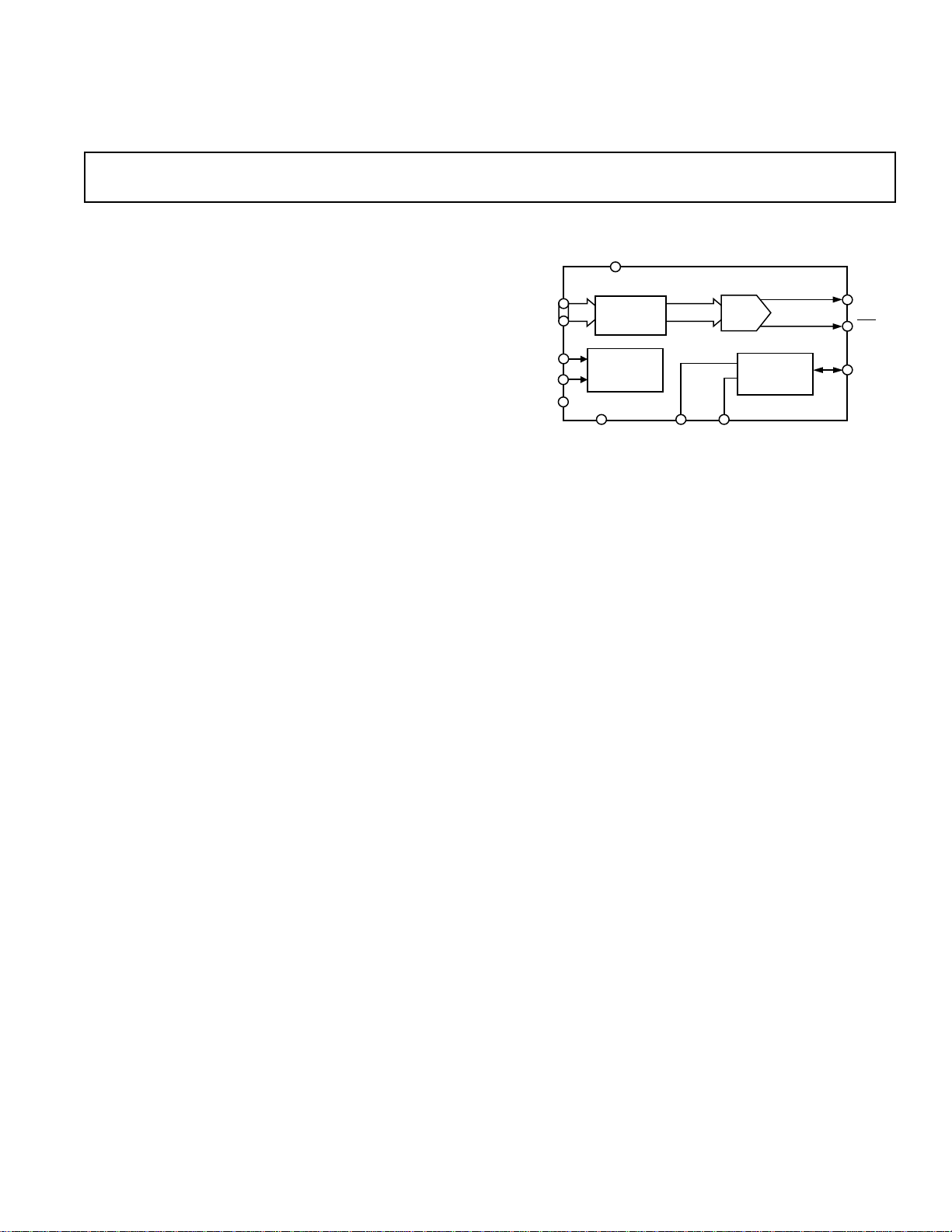
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV7127 (ADV®) is a high speed, digital-to-analog convertor on a single monolithic chip. It consists of a 10-bit,
video D/A converter with on-board voltage reference, complementary outputs, a standard TTL input interface and high
impedance analog output current sources.
The ADV7127 has a 10-bit wide input port. A single +5 V/
+3.3 V power supply and clock are all that are required to make
the part functional.
The ADV7127 is fabricated in a CMOS process. Its monolithic
CMOS construction ensures greater functionality with lower
power dissipation. The ADV7127 is available in a small outline
28-lead SOIC or 24-lead TSSOP package.
ADV is a registered trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The ADV7127 TSSOP package also has a power-down mode.
Both ADV7127 packages have a power standby mode.
The ADV7127 TSSOP package has an on-board voltage reference circuit. The ADV7127 SOIC package requires an external
reference.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. 240 MSPS Throughput.
2. Guaranteed monotonic to 10 bits.
3. Compatible with a wide variety of high resolution color
graphics systems including RS-343A and RS-170A.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1998
Page 2
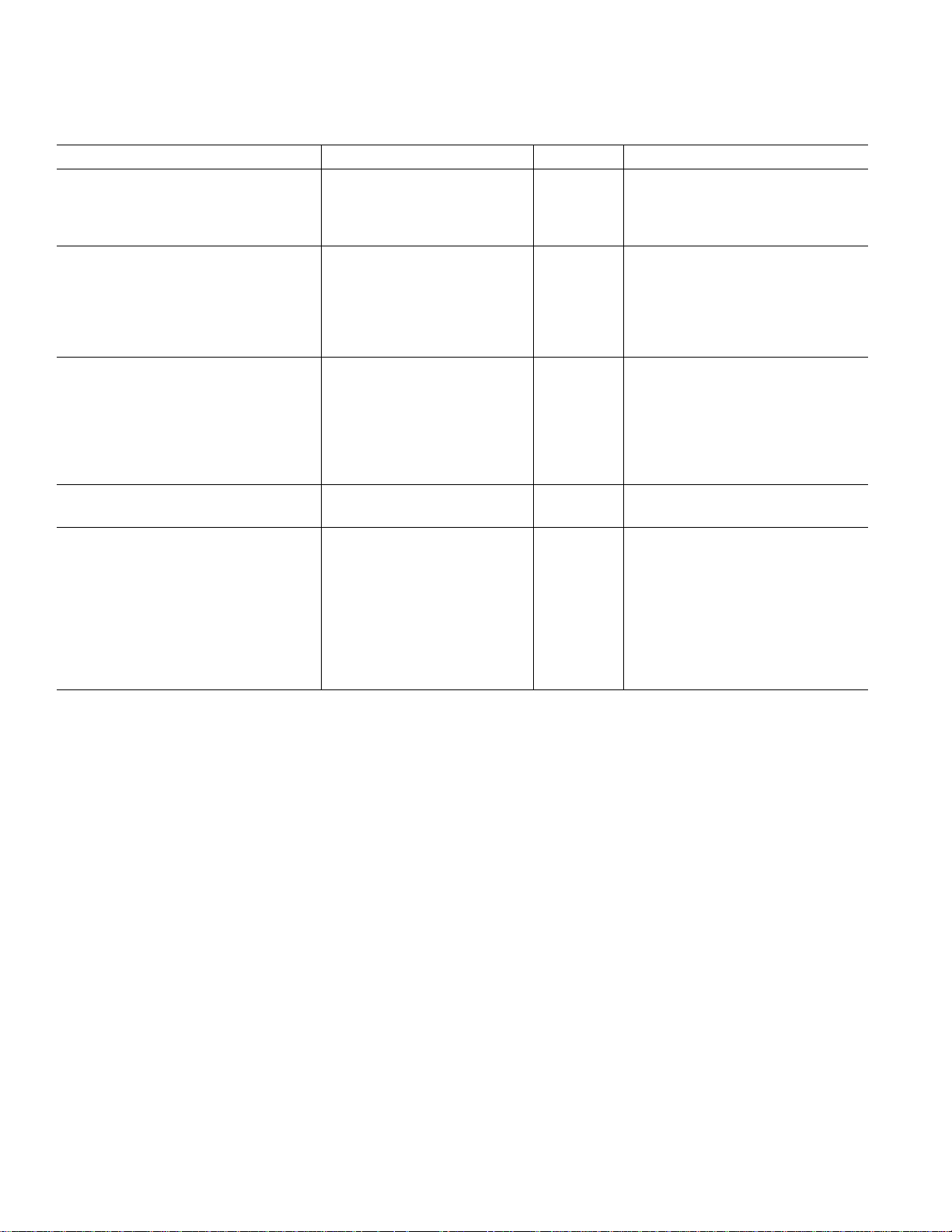
ADV7127–SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = +5 V 6 5%, V
5 V SOIC SPECIFICATIONS
otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 10 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity (BSL) –1 0.4 +1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity –1 0.25 +1 LSB Guaranteed Monotonic
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
IL
IN
IH
2V
–1 +1 µAV
PSAVE Pull-Up Current 20 µA
Input Capacitance, C
IN
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Output Current 2.0 18.5 mA
Output Compliance Range, V
Output Impedance, R
OUT
Output Capacitance, C
Offset Error –0.025 +0.025 % FSR Tested with DAC Output = 0 V
Gain Error
2
OC
OUT
0 +1.4 V
–5.0 +5.0 % FSR FSR = 17.62 mA
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (Ext.)
Reference Range, V
REF
POWER DISSIPATION
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
3
3
3
1.12 1.235 1.35 V
Analog Supply Current 33 37 mA R
Analog Supply Current 5 mA R
Standby Supply Current
4
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.1 0.5 %/%
NOTES
1
Temperature range T
2
Gain error = ((Measured (FSC)/Ideal (FSC) –1) × 100), where Ideal = V
3
Digital supply is measured with continuous clock with data input corresponding to a ramp pattern and with an input level at 0 V and VDD.
4
These max/min specifications are guaranteed by characterization to be over 4.75 V to 5.25 V range.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
to T
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70° C at 240 MHz.
MAX
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 1108C)
MAX
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications T
SET
MIN
to T
MAX1
0.8 V
= 0.0 V or V
IN
AA
10 pF
100 kΩ
10 pF I
3.4 9 mA f
10.5 15 mA f
18 25 mA f
= 0 mA
OUT
= 50 MHz
CLK
= 140 MHz
CLK
= 240 MHz
CLK
= 560 Ω
SET
= 4933 Ω
SET
2.1 5.0 mA PSAVE = Low, Digital and Control
× K × (3FFH) and K = 7.9896.
REF /RSET
Inputs at V
AA
unless
–2– REV. 0
Page 3
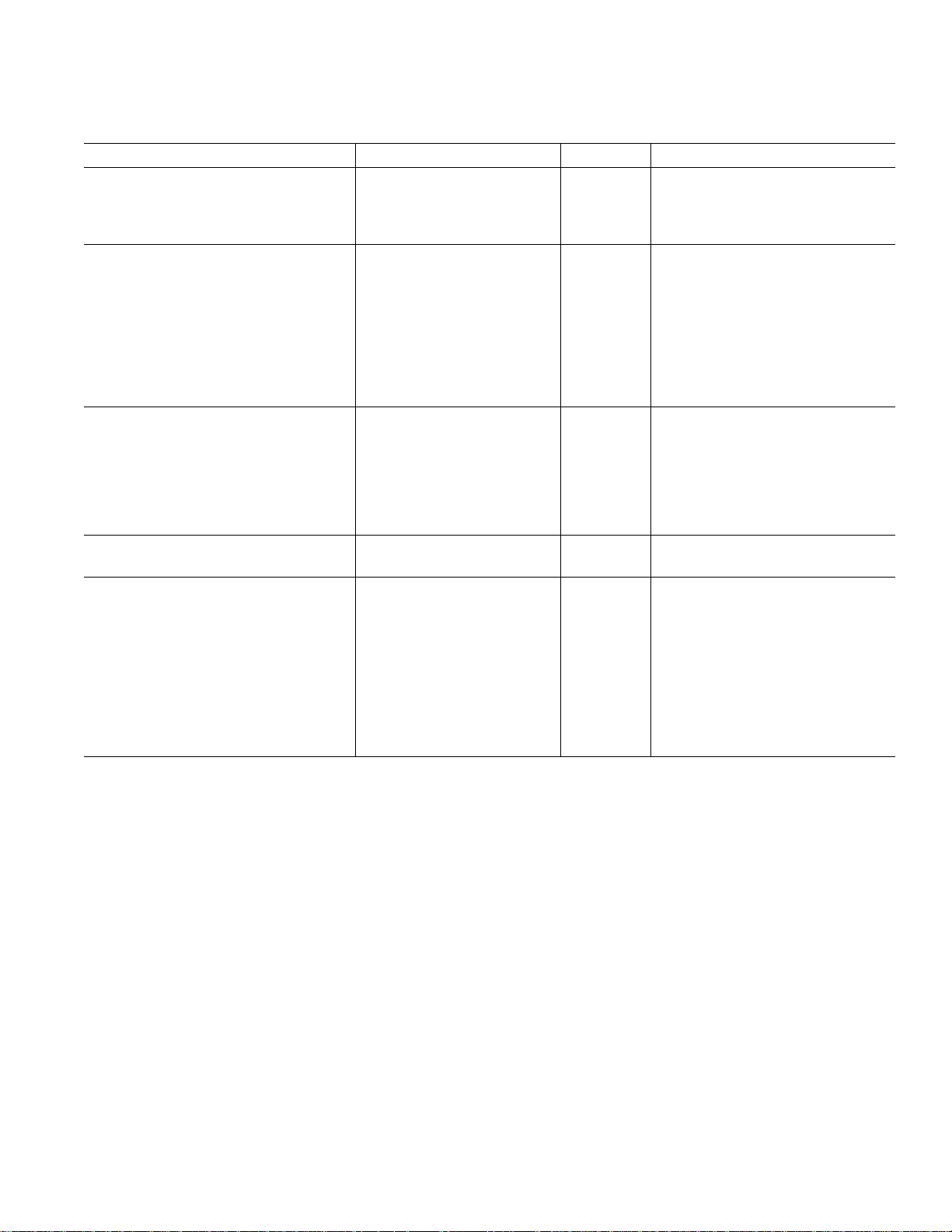
ADV7127
(VAA = +5 V 6 5%, V
5 V TSSOP SPECIFICATIONS
otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 10 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity (BSL) –1 0.4 +1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity –1 0.25 +1 LSB Guaranteed Monotonic
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
PDOWN Input High Voltage
PDOWN Input Low Voltage
Input Current, I
IH
IL
2
2
IN
2V
–1 +1 µAV
PSAVE Pull-Up Current 20 µA
PDOWN Pull-Up Current 20 µA
Input Capacitance, C
IN
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Output Current 2.0 18.5 mA
Output Compliance Range, V
Output Impedance, R
OUT
Output Capacitance, C
Offset Error –0.025 +0.025 % FSR Tested with DAC Output = 0 V
Gain Error
3
OC
OUT
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (Ext. and Int.)
Reference Range, V
POWER DISSIPATION
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
REF
5
5
5
0 +1.4 V
–5.0 +5.0 % FSR FSR = 17.62 mA
4
1.12 1.235 1.35 V
Analog Supply Current 23 27 mA R
Analog Supply Current 5 mA R
Standby Supply Current
PDOWN Supply Current
6
2
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.1 0.5 %/%
NOTES
1
Temperature range T
2
This power-down feature is only available on the ADV7127 in the TSSOP package.
3
Gain error = ((Measured (FSC)/Ideal (FSC) –1) × 100), where Ideal = V
4
Internal voltage reference is available only on the ADV7127 TSSOP package.
5
Digital supply is measured with continuous clock with data input corresponding to a ramp pattern and with an input level at 0 V and VDD.
6
These max/min specifications are guaranteed by characterization to be over 4.75 V to 5.25 V range.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
to T
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70° C at 240 MHz.
MAX
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 1108C)
MAX
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications T
SET
MIN
to T
MAX1
0.8 V
3V
1V
= 0.0 V or V
IN
AA
10 pF
100 kΩ
10 pF I
1.5 3 mA f
46 mA f
6.5 10 mA f
= 0 mA
OUT
= 50 MHz
CLK
= 140 MHz
CLK
= 240 MHz
CLK
= 560 Ω
SET
= 4933 Ω
SET
3.8 6 mA PSAVE = Low, Digital and Control
Inputs at V
AA
1mA
× K × (3FFH ) and K = 7.9896.
REF /RSET
unless
–3–REV. 0
Page 4
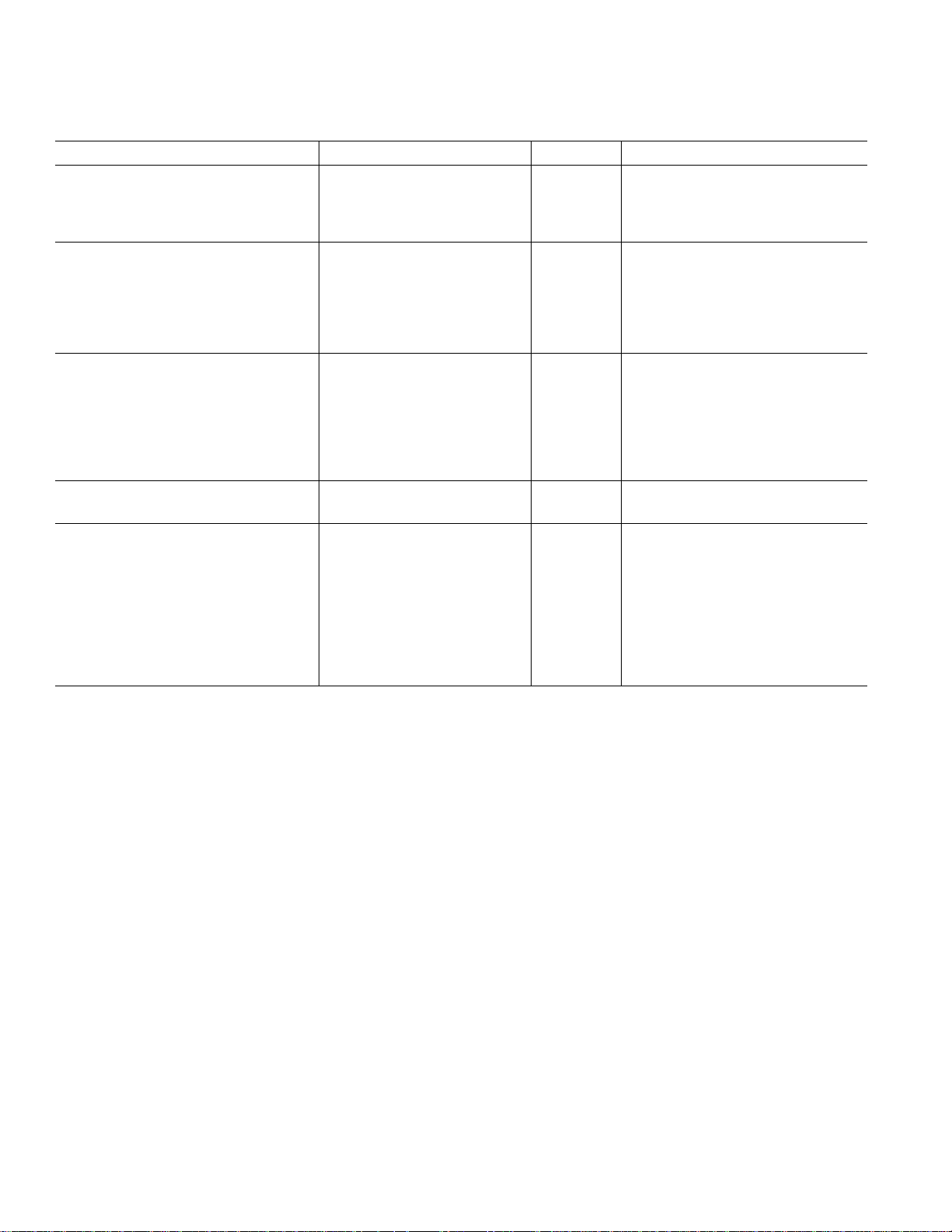
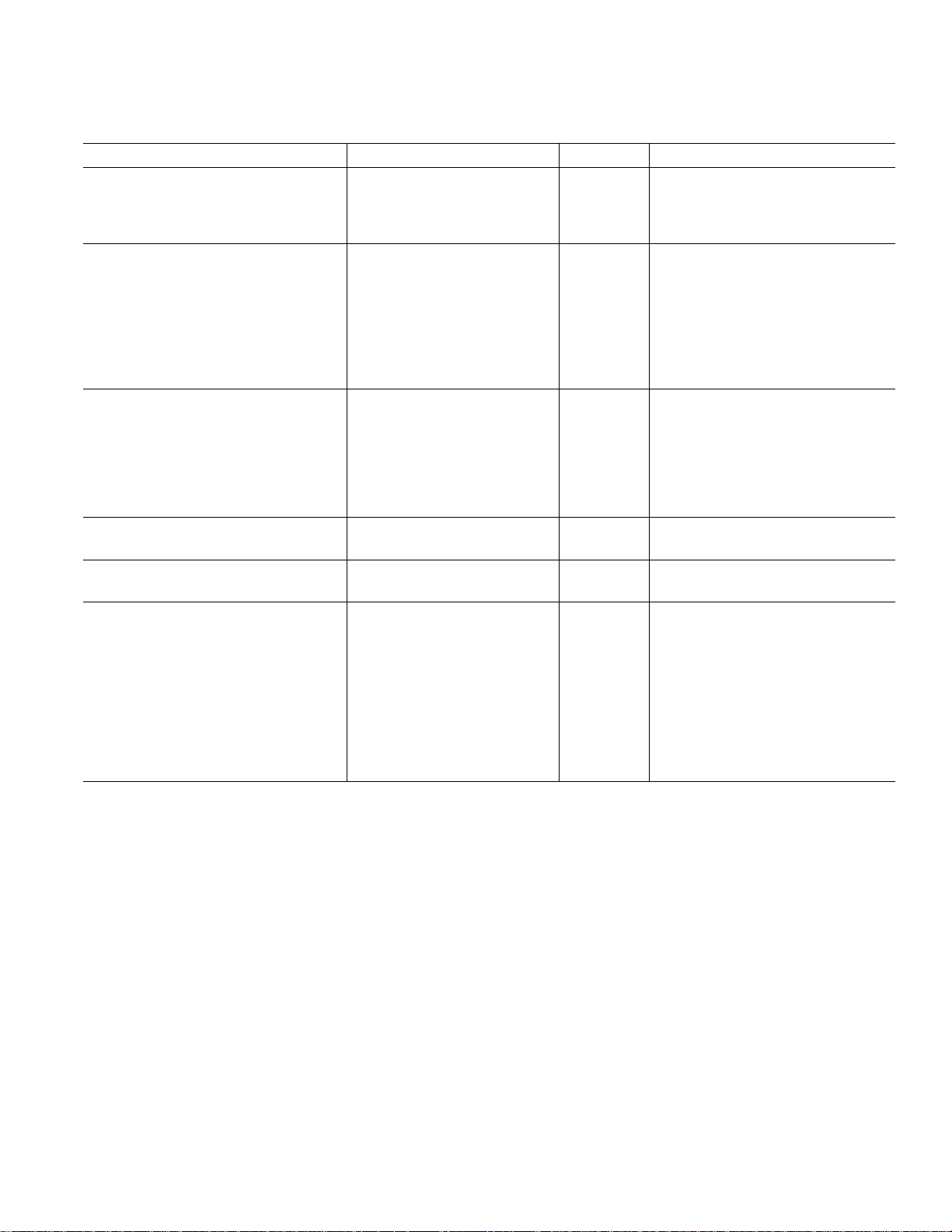
ADV7127–SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = +3.0 V–3.6 V, V
3.3 V SOIC SPECIFICATIONS
1
unless otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 10 Bits R
Integral Nonlinearity (BSL) –1 0.5 +1 LSB R
Differential Nonlinearity –1 0.25 +1 LSB R
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
IL
IN
IH
2.0 V
0.8 V
–1 +1 µAV
PSAVE Pull-Up Current 20 µA
Input Capacitance, C
IN
10 pF
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Output Current 2.0 18.5 mA
Output Compliance Range, V
Output Impedance, R
OUT
Output Capacitance, C
Offset Error 0 0 % FSR Tested with DAC Output = 0 V
Gain Error
3
OC
OUT
0 +1.4 V
70 kΩ
10 pF
0 % FSR FSR = 17.62 mA
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (Ext.)
Reference Range, V
POWER DISSIPATION
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
REF
4
4
4
1.12 1.235 1.35 V
2.2 5.0 mA f
6.5 12.0 mA f
11 15 mA f
Analog Supply Current 32 35 mA R
Analog Supply Current 5 mA R
Standby Supply Current 2.4 5.0 mA PSAVE = Low, Digital and Control
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.1 0.5 %/%
NOTES
1
These max/min specifications are guaranteed by characterization to be over 3.0 V to 3.6 V range.
2
Temperature range T
3
Gain error = ((Measured (FSC)/Ideal (FSC) –1) × 100) , where Ideal = V
4
Digital supply is measured with continuous clock with data input corresponding to a ramp pattern and with an input level at 0 V and VDD.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
to T
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70° C at 240 MHz.
MAX
REF /RSET
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 1108C)
MAX
× K × (3FFH) and K = 7.9896.
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications T
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 0.0 V or V
IN
= 50 MHz
CLK
= 140 MHz
CLK
= 240 MHz
CLK
= 560 Ω
SET
= 4933 Ω
SET
Inputs at V
DD
DD
MIN
to T
MAX
2
–4– REV. 0
Page 5
ADV7127
(VAA = +3.0 V–3.6 V, V
3.3 V TSSOP SPECIFICATIONS
1
unless otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 10 Bits R
Integral Nonlinearity (BSL) –1 0.5 +1 LSB R
Differential Nonlinearity –1 0.25 +1 LSB R
DIGITAL AND CONTROL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
PDOWN Input High Voltage
PDOWN Input Low Voltage
Input Current, I
IH
IL
IN
3
3
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.1 V
0.6 V
–1 +1 µAV
PSAVE Pull-Up Current 20 µA
Input Capacitance, C
IN
10 pF
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Output Current 2.0 18.5 mA
Output Compliance Range, V
Output Impedance, R
OUT
Output Capacitance, C
Offset Error 0 0 % FSR Tested with DAC Output = 0 V
Gain Error
4
OC
OUT
0 +1.4 V
70 kΩ
10 pF
0 % FSR FSR = 17.62 mA
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (Ext.)
Reference Range, V
VOLTAGE REFERENCE (Int.)
Reference Range, V
POWER DISSIPATION
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
Digital Supply Current
REF
5
REF
6
6
6
1.12 1.235 1.35 V
1.235 V
12 mA f
2.5 4.5 mA f
46 mA f
Analog Supply Current 22 25 mA R
Analog Supply Current 5 mA R
Standby Supply Current 2.6 3 mA PSAVE = Low, Digital and Control
PDOWN Supply Current 20 µA
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.1 0.5 %/%
NOTES
1
These max/min specifications are guaranteed by characterization to be over 3.0 V to 3.6 V range.
2
Temperature range T
3
This power-down feature is only available on the ADV7127 in the TSSOP package.
4
Gain error = ((Measured (FSC)/Ideal (FSC) –1) × 100), where Ideal = V
5
Internal voltage reference is available only on the ADV7127 TSSOP package.
6
Digital supply is measured with continuous clock with data input corresponding to a ramp pattern and with an input level at 0 V and VDD.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
to T
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70° C at 240 MHz.
MAX
REF /RSET
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 1108C)
MAX
× K × (3FFH) and K = 7.9896.
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications T
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 680 Ω
SET
= 0.0 V or V
IN
= 50 MHz
CLK
= 140 MHz
CLK
= 240 MHz
CLK
= 560 Ω
SET
= 4933 Ω
SET
Inputs at V
DD
DD
MIN
to T
MAX
2
–5–REV. 0
Page 6

ADV7127–SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = (3 V–5.25 V)1, V
5 V/3.3 V DYNAMIC SPECIFICATIONS
are for TA = +258C unless otherwise noted, TJ
Parameter Min Typ Max Units
DAC PERFORMANCE
Glitch Impulse
Data Feedthrough
Clock Feedthrough
NOTES
1
These max/min specifications are guaranteed by characterization.
2
TTL input values are for 0 V and 3 V with input rise/fall times ≤ 3 ns, measured at the 10% and 90% points. Timing reference points at 50% for inputs and outputs.
3
Clock and data feedthrough is a function of the amount of overshoot and undershoot on the digital inputs. Glitch impulse includes clock and data feedthrough.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
2, 3
2, 3
2, 3
= 1.235 V, R
REF
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications
SET
= 1108C)
MAX
10 pVs
22 dB
33 dB
5 V TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = +5 V 6 5%2, V
1
unless otherwise noted, TJ
= 1.235 V, R
REF
MAX
= 1108C)
= 560 V, CL = 10 pF. All specifications T
SET
MIN
to T
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Condition
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Analog Output Delay, t
Analog Output Rise/Fall Time, t
Analog Output Transition Time, t
Analog Output Skew, t
CLOCK CONTROL
7
f
CLK
7
f
CLK
7
f
CLK
Data and Control Setup, t
Data and Control Hold, t
Clock Pulsewidth High, t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Clock Pulsewidth High t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Clock Pulsewidth High t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Pipeline Delay, t
PSAVE Up Time, t
PDOWN Up Time, t
NOTES
1
Timing specifications are measured with input levels of 3.0 V (VIH) and 0 V (VIL) 0 for both 5 V and 3.3 V supplies.
2
These maximum and minimum specifications are guaranteed over this range.
3
Temperature range: T
4
Rise time was measured from the 10% to 90% point of zero to full-scale transition, fall time from the 90% to 10% point of a full-scale transition.
5
Measured from 50% point of full-scale transition to 2% of final value.
6
Guaranteed by characterization.
7
f
max specification production tested at 125 MHz and 5 V. Limits specified here are guaranteed by characterization.
CLK
8
This power-down feature is only available on the ADV7127 in the TSSOP package.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
PD
MIN
6
6
9
4
7
5
8
0.5 50 MHz 50 MHz Grade
0.5 140 MHz 140 MHz Grade
0.5 240 MHz 240 MHz Grade
1
2
4
5
4
5
4
5
6
6
10
8
11
to T
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70°C at 240 MHz.
MAX
1.5 ns
2.5 ns
1.875 1.1 ns f
1.875 1.25 ns f
2.85 ns f
2.85 ns f
8.0 ns f
8.0 ns f
1.0 1.0 1.0 Clock Cycles
5.5 ns
1.0 ns
15 ns
12 ns
210 ns
320 ns
= 240 MHz
MAX
= 240 MHz
MAX
= 140 MHz
MAX
= 140 MHz
MAX
= 50 MHz
MAX
= 50 MHz
MAX
MAX
3
–6– REV. 0
Page 7

ADV7127
3.3 V TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
(VAA = +3.0 V–3.6 V2, V
1
otherwise noted, TJ
REF
= 1108C)
MAX
= 1.235 V, R
= 560 V. All specifications T
SET
MIN
to T
MAX3
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Condition
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Analog Output Delay, t
Analog Output Rise/Fall Time, t
Analog Output Transition Time, t
Analog Output Skew, t
CLOCK CONTROL
7
f
CLK
7
f
CLK
7
f
CLK
Data and Control Setup, t
Data and Control Hold, t
Clock Pulsewidth High, t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Clock Pulsewidth High t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Clock Pulsewidth High t
Clock Pulsewidth Low t
Pipeline Delay, t
PSAVE Up Time, t
PDOWN Up Time, t
NOTES
1
Timing specifications are measured with input levels of 3.0 V (VIH) and 0 V (VIL) 0 for both 5 V and 3.3 V supplies.
2
These maximum and minimum specifications are guaranteed over this range.
3
Temperature range: T
4
Rise time was measured from the 10% to 90% point of zero to full-scale transition, fall time from the 90% to 10% point of a full-scale transition.
5
Measured from 50% point of full-scale transition to 2% of final value.
6
Guaranteed by characterization.
7
f
max specification production tested at 125 MHz and 5 V limits specified here are guaranteed by characterization.
CLK
8
This power-down feature is only available on the ADV7127 in the TSSOP package.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
PD
MIN
6
10
to T
6
6
9
2
4
6
5
6
4
6
5
6
4
6
5
6
8
11
MAX
4
7
5
8
6
2
6
1.5 ns
2.5 ns
2.85 ns f
2.85 ns f
8.0 ns f
8.0 ns f
1.0 1.0 1.0 Clock Cycles
: –40°C to +85°C at 50 MHz and 140 MHz, 0°C to +70°C at 240 MHz.
7.5 ns
1.0 ns
15 ns
12 ns
50 MHz 50 MHz Grade
140 MHz 140 MHz Grade
240 MHz 240 MHz Grade
1.1 ns f
1.4 ns f
410 ns
320 ns
= 240 MHz
MAX
= 240 MHz
MAX
= 140 MHz
MAX
= 140 MHz
MAX
= 50 MHz
MAX
= 50 MHz
MAX
unless
CLOCK
DIGITAL INPUTS
(D9–D0)
ANALOG OUTPUTS
I
, )
(I
OUT
OUT
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
2
DATA
t
1
NOTES:
1. OUTPUT DELAY (t6) MEASURED FROM THE 50% POINT OF THE RISING
EDGE OF CLOCK TO THE 50% POINT OF FULL SCALE TRANSITION.
2. OUTPUT RISE/FALL TIME (
90% POINTS OF FULL SCALE TRANSITION.
3. TRANSITION TIME (
SCALE TRANSITION TO WITHIN 2% OF THE FINAL OUTPUT VALUE.
t
) MEASURED BETWEEN THE 10% AND
7
t
) MEASURED FROM THE 50% POINT OF FULL
8
t
8
t
6
t
7
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
–7–REV. 0
Page 8

ADV7127
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
VAA to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +7 V
Voltage on any Digital Pin . . . . . GND – 0.5 V to V
Ambient Operating Temperature (T
Storage Temperature (T
Junction Temperature (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
S
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+150°C
J
) . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
A
+ 0.5 V
AA
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . .+300°C
Vapor Phase Soldering (1 Minute) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
to GND2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 V to V
I
OUT
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
AA
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Analog Output Short Circuit to any Power Supply or Common can be of an
indefinite duration.
ORDERING GUIDE
Package 50 MHz 140 MHz 240 MHz
2
R-28
3
RU-24
NOTES
1
50 MHz and 140 MHz devices are specified for –40°C to +85°C operation; 240 MHz devices are specified for 0°C to +70°C.
2
SOIC Package.
3
TSSOP Package.
ADV7127KR50 ADV7127KR140 ADV7127JR240
ADV7127KRU50 ADV7127KRU140 ADV7127JRU240
24-Lead TSSOP 28-Lead SOIC
1
D1
2
D2
3
D3
D4
4
5
D5
ADV7127
6
D6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
D7
8
D8
D9
9
V
10
AA
11
PDOWN
NC
12
NC = NO CONNECT
1
Speed Options
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
V
1
AA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
V
AA
V
AA
V
AA
2
3
4
5
6
7
(Not to Scale)
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
D0
PSAVE
R
SET
V
REF
COMP
I
OUT
I
OUT
V
AA
GND
GND
CLOCK
NC
ADV7127
TOP VIEW
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
V
AA
V
AA
PSAVE
R
SET
V
REF
COMP
V
AA
I
OUT
V
AA
GND
GND
CLOCK
V
AA
V
AA
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the ADV7127 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–8– REV. 0
Page 9

ADV7127
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin
Mnemonic Function
CLOCK Clock Input (TTL Compatible). The rising edge of CLOCK latches the R0–R9, G0–G9, B0–B9, SYNC and
BLANK pixel and control inputs. It is typically the pixel clock rate of the video system. CLOCK should be driven
by a dedicated TTL buffer.
D0–D9 Data Inputs (TTL Compatible). Data is latched on the rising edge of CLOCK. D0 is the least significant data bit.
Unused data inputs should be connected to either the regular PCB power or ground plane.
I
OUT
R
SET
COMP Compensation Pin. This is a compensation pin for the internal reference amplifier. A 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor
V
REF
V
AA
GND Ground. All GND pins must be connected.
I
OUT
PSAVE Power Save Control Pin. The part is put into standby mode when PSAVE is low. The internal voltage reference
PDOWN Power-Down Control Pin (24-Lead TSSOP Only). The ADV7127 completely powers down, including the voltage
Current Output. This high impedance current source is capable of directly driving a doubly terminated 75 Ω
coaxial cable.
Full-Scale Adjust Control. A resistor (R
) connected between this pin and GND controls the magnitude of the
SET
full-scale video signal. Note that the IRE relationships are maintained, regardless of the full-scale output current.
The relationship between R
I
OUT
must be connected between COMP and V
and the full-scale output current on I
SET
(mA) = 7968 × V
REF
AA
(V)/R
.
SET
(Ω)
is given by:
OUT
Voltage Reference Input. An external 1.23 V voltage reference must be connected to this pin. The use of an exter-
nal resistor divider network is not recommended. A 0.1 µF decoupling ceramic capacitor should be connected
between V
Analog Power Supply (5 V ± 5%). All V
and VAA.
REF
pins on the ADV7127 must be connected.
AA
Differential Current Output. Capable of directly driving a doubly terminated 75 Ω load. If not required, this out-
put should be tied to ground.
circuit is still active on the TSSOP in this case.
reference circuit, when PDOWN is low.
TERMINOLOGY
Color Video (RGB)
This usually refers to the technique of combining the three
primary colors of red, green and blue to produce color pictures
within the usual spectrum. In RGB monitors, three DACs are
required, one for each color.
Gray Scale
The discrete levels of video signal between reference black and
reference white levels. A 10-bit DAC contains 1024 different
levels, while an 8-bit DAC contains 256.
Raster Scan
The most basic method of sweeping a CRT one line at a time to
generate and display images.
Reference Black Level
The maximum negative polarity amplitude of the video signal.
Reference White Level
The maximum positive polarity amplitude of the video signal.
Video Signal
That portion of the composite video signal which varies in gray
scale levels between reference white and reference black. Also
referred to as the picture signal, this is the portion that may be
visually observed.
–9–REV. 0
Page 10

ADV7127
TEMPERATURE – 8C
72.0
71.8
70.4
–10 +25 +85
71.2
71.0
70.8
70.6
71.6
71.4
72.2
SFDR – dBc
5 V–Typical Performance Characteristics
(VAA = +5 V, V
= 1.235 V, I
REF
= 17.62 mA, 50 V Doubly Terminated Load, Differential Output Loading, TA = +258C)
OUT
70
60
50
40
30
SFDR – dBc
20
10
0
0.1 1001.0 2.51 5.04 20.2 40.4
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 2. SFDR vs. f
SFDR (DE)
SFDR (SE)
OUT
@ f
CLOCK
=
140 MHz (Single-Ended and
Differential)
76
74
72
70
4th HARMONIC
68
66
THD – dBc
64
62
60
58
0 16050 100 140
f
Figure 5. THD vs. f
CLOCK
2nd HARMONIC
3rd HARMONIC
– MHz
@ f
CLOCK
OUT
=
2 MHz (2nd, 3rd and 4th Harmonics)
80
70
60
50
40
SFDR – dBc
30
20
10
0
0.1 1001.0 2.51 5.04 20.2 40.4
SFDR (SE)
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 3. SFDR vs. f
SFDR (DE)
@ f
OUT
50 MHz (Single-Ended and
Differential)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
LINEARITY – LSBs
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
LINEARITY vs. I
0202 17.62
I
OUT
/mA
OUT
ERROR
Figure 6. Linearity vs. I
CLOCK
OUT
=
Figure 4. SFDR vs. Temperature @
f
= 50 MHz (f
CLOCK
1.00
0.50
0.00
ERROR – LSB
–0.50
–1.00
= 1 MHz)
OUT
CODE – INL
Figure 7. Typical Linearity
0.75
1023
–0.16
–5.0
2
–45.0
SFDR – dBm
1
–85.0
0kHz
START
VAA = 5V
CLK = 140MHz
f
= 2.5MHz
OUT
SING O/P
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
Figure 8. SFDR (Single-Tone) @
f
= 140 MHz (f
CLOCK
= 2 MHz)
OUT1
STOP
–5.0
VAA = 5V
–45.0
SFDR – dBm
–85.0
0kHz
START
2
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
CLK = 140MHz
f
SING O/P
1
OUT
= 20MHz
Figure 9. Single-Tone SFDR @ f
= 140 MHz (f
= 20 MHz)
OUT1
–10– REV. 0
STOP
CLOCK
–5.0
–45.0
SFDR – dBc
–85.0
0kHz
START
2
VAA = 5V
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
CLK = 140MHz
DUAL TONE
DIFF O/P
1
Figure 10. Dual-Tone SFDR @ f
= 140 MHz (f
= 13.5 MHz, f
OUT1
OUT2
14.5 MHz)
STOP
CLOCK
=
Page 11

3 V–Typical Performance Characteristics
TEMPERATURE – 8C
72.0
71.8
70.4
0 16520 85 145
71.2
71.0
70.8
70.6
71.6
71.4
SFDR (f
OUT
= 1MHz)
SFDR – dBc
1.00
0.50
0.00
–0.50
0.75
1023
–0.42
ERROR – LSB
–1.00
CODE– INL
VAA = 3.3V
1
–5.0
–45.0
–85.0
0kHz
START
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
STOP
SFDR – dBm
CLK = 140MHz
DUAL TONE
SING O/P
2
(VAA = +3 V, V
= 1.235 V, I
REF
=17.62 mA, 50 V Doubly Terminated Load, Differential Output Loading, TA = +258C)
OUT
ADV7127
70
60
50
40
30
SFDR – dBc
20
10
0
0.1 2.51 5.04 20.2 40.4 100
Figure 11. SFDR vs. f
SFDR (DE)
SFDR (SE)
FREQUENCY – MHz
OUT
@ f
CLOCK
=
140 MHz (Single-Ended and
Differential)
76
74
72
70
3rd HARMONIC
68
66
64
THD – dBc
62
60
58
56
0 16050 100 140
Figure 14. THD vs. f
2nd HARMONIC
4th HARMONIC
FREQUENCY – MHz
CLOCK
@ f
OUT
=
2 MHz (2nd, 3rd and 4th Harmonics)
80
70
60
50
40
SFDR – dBc
30
20
10
0
0.1 1001.0 2.51 5.04 20.2 40.4
Figure 12. SFDR vs. f
SFDR (DE)
SFDR (SE)
FREQUENCY – MHz
OUT
@ f
50 MHz (Single-Ended and
Differential)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
LINEARITY – LSBs
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
0202 17.62
I
OUT
– mA
Figure 15. Linearity vs. I
CLOCK
OUT
=
Figure 13. SFDR vs. Temperature @
f
= 50 MHz, (f
CLOCK
= 1 MHz)
OUT
Figure 16. Typical Linearity
–5.0
–45.0
SFDR – dBm
–85.0
0kHz
START
Figure 17. Single-Tone SFDR @
f
CLOCK
2
VAA = 3.3V
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
= 140 MHz (f
OUT1
CLK = 140MHz
f
= 2.5MHz
OUT
SING O/P
1
= 2 MHz)
STOP
–5.0
VAA = 3.3V
–45.0
SFDR – dBm
–85.0
0kHz
START
2
35.0MHz 70.0MHz
CLK = 140MHz
f
= 20MHz
OUT
SING O/P
1
Figure 18. Single-Tone SFDR @
f
= 140 MHz (f
CLOCK
= 20 MHz)
OUT1
–11–REV. 0
STOP
Figure 19. Dual-Tone SFDR @ f
= 140 MHz (f
= 13.5 MHz, f
OUT1
OUT2
14.5 MHz)
CLOCK
=
Page 12

ADV7127
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The ADV7127 contains one 10-bit D/A converter, with one
input channel containing a 10-bit register. A reference amplifier
is also integrated on board the part.
Digital Inputs
Ten bits of data (color information) D0–D9 are latched into the
device on the rising edge of each clock cycle. This data is presented to the 10-bit DAC and is then converted to an analog
output waveform. See Figure 20.
CLOCK
DIGITAL INPUTS
D0–D9
ANALOG OUTPUTS
I
, I
OUT
OUT
DATA
Figure 20.␣ Video Data Input/Output
All these digital inputs are specified to accept TTL logic levels.
Clock Input
The CLOCK input of the ADV7127 is typically the pixel clock
rate of the system. It is also known as the dot rate. The dot rate,
and hence the required CLOCK frequency, will be determined
by the on-screen resolution, according to the following equation:
Dot Rate = (Horiz Res) × (Vert Res) × (Refresh Rate)/
(Retrace Factor)
Horiz Res = Number of Pixels/Line.
Vert Res = Number of Lines/Frame.
Refresh Rate = Horizontal Scan Rate. This is the rate at
which the screen must be refreshed, typically
60 Hz for a noninterlaced system or 30 Hz
for an interlaced system.
Retrace Factor = Total Blank Time Factor. This takes into
account that the display is blanked for a
certain fraction of the total duration of each
frame (e.g., 0.8).
Therefore, if we have a graphics system with
a 1024 × 1024 resolution, a noninterlaced
60 Hz refresh rate and a retrace factor of 0.8,
then:
Dot Rate = 1024 × 1024 × 60/0.8
= 78.6 MHz
The required CLOCK frequency is thus 78.6 MHz.
All video data and control inputs are latched into the ADV7127
on the rising edge of CLOCK, as previously described in the
Digital Inputs section. It is recommended that the CLOCK
input to the ADV7127 be driven by a TTL buffer (e.g., 74F244).
I
OUT
mA V
17.61 0.66
0 0
100 IRE
Figure 21. I
Video Output Waveform
OUT
WHITE
LEVEL
BLACK
LEVEL
Table I. Video Output Truth Table (RSET = 560 V,
R
= 37.5 V)
LOAD
Description DAC
Data I
OUT
I
OUT
Input
WHITE LEVEL 17.62 0 3FF
VIDEO Video 17.62 – Video Data
BLACK LEVEL 0 17.62 000H
Power Management
The PSAVE input of the ADV7127 puts the part into standby
mode. It is used to reduce power consumption. When PSAVE
is low, the power may be reduced to approximately 10 mW at
3 V. The ADV7127 in TSSOP package also has a power-down
feature where the entire part, including the voltage reference
circuit, is powered down. In this case, power on the ADV7127
can be reduced to 60 µW at 3 V.
Table II. Power Management
Mode ADV7127 TSSOP ADV7127 SOIC
Power-Save 10 mW Typically at 3 V 10 mW Typically at 3 V
Power-Down Power 60 µW at 3 V Not Available
Reference Input
The ADV7127 has an on-board voltage reference. The V
pin is normally terminated to V
through a 0.1 µF capacitor.
AA
REF
Alternatively, the part could, if required, be overdriven by an
external 1.23 V reference (AD1580).
A resistance R
connected between the R
SET
pin and GND
SET
determines the amplitude of the output video level according to
the following equation:
(mA) = 7,968 × V
I
OUT
Using a variable value of R
(V)/R
REF
, as shown in Figure 22, allows
SET
(Ω) (1)
SET
for accurate adjustment of the analog output video levels. Use
of a fixed 560 Ω R
resistor yields the analog output levels
SET
as quoted in the specification page. These values typically
correspond to the RS-343A video waveform values as shown in
Figure 21.
–12– REV. 0
Page 13

ADV7127
AD848
0.1mF
I
OUT
Z
1
Z
2
ZO = 75V
(CABLE)
Z
S
= 75V
(SOURCE
TERMINATION)
Z
L
= 75V
(MONITOR)
DAC
75V
–V
S
+V
S
0.1mF
GAIN (G) = 1 +
Z
1
Z
2
D/A Converter
The ADV7127 contains a 10-bit D/A converter. The DAC is
designed using an advanced, high speed, segmented architecture. The bit currents corresponding to each digital input are
routed to either the analog output (bit = “1”) or GND (bit =
“0”) by a sophisticated decoding scheme. The use of identical
current sources in a monolithic design guarantees monotonicity
and low glitch. The on-board operational amplifier stabilizes the
full-scale output current against temperature and power supply
variations.
Analog Output
The analog output of the ADV7127 is a high impedance current
source. The current output is capable of directly driving a
37.5 Ω load, such as a doubly terminated 75 Ω coaxial cable.
Figure 22 shows the required configuration for the output con-
nected into a doubly terminated 75 Ω load. This arrangement
will develop RS-343A video output voltage levels across a 75 Ω
monitor.
I
DAC
Z
= 75V
S
(SOURCE
TERMINATION)
OUT
ZO = 75V
(CABLE)
= 75V
Z
L
(MONITOR)
Video Output Buffer
The ADV7127 is specified to drive transmission line loads,
which is what most monitors are rated as. The analog output
configurations to drive such loads are described in the Analog
Interface section and illustrated in Figure 23. However, in some
applications it may be required to drive long “transmission line”
cable lengths. Cable lengths greater than 10 meters can attenuate and distort high frequency analog output pulses. The inclusion of output buffers will compensate for some cable distortion.
Buffers with large full power bandwidths and gains between two
and four will be required. These buffers will also need to be able
to supply sufficient current over the complete output voltage
swing. Analog Devices produces a range of suitable op amps for
such applications. These include the AD84x series of monolithic
op amps. In very high frequency applications (80 MHz), the
AD9617 is recommended. More information on line driver
buffering circuits is given in the relevant op amp data sheets.
Use of buffer amplifiers also allows implementation of other
video standards besides RS-343A and RS-170. Altering the gain
components of the buffer circuit will result in any desired
video level.
Figure 22. Analog Output Termination for RS-343A
A suggested method of driving RS-170 video levels into a 75 Ω
monitor is shown in Figure 23. The output current level of the
DAC remains unchanged, but the source termination resistance,
, on the DAC is increased from 75 Ω to 150 Ω.
Z
S
I
DAC
Z
= 150V
S
(SOURCE
TERMINATION)
OUT
ZO = 75V
(CABLE)
Z
= 75V
L
(MONITOR)
Figure 23. Analog Output Termination for RS-170
More detailed information regarding load terminations for various output configurations, including RS-343A and RS-170, is
available in an Application Note entitled “Video Formats &
Required Load Terminations” available from Analog Devices,
publication no. E1228-15-1/89.
Figure 21 shows the video waveforms associated with the current
output driving the doubly terminated 75 Ω load of Figure 22.
Gray Scale Operation
The ADV7127 can be used for stand-alone, gray scale (monochrome) or composite video applications (i.e., only one channel
used for video information).
Figure 24.␣ AD848 As an Output Buffer
PC Board Layout Considerations
The ADV7127 is optimally designed for lowest noise performance, both radiated and conducted noise. To complement the
excellent noise performance of the ADV7127 it is imperative
that great care be given to the PC board layout. Figure 25 shows
a recommended connection diagram for the ADV7127.
The layout should be optimized for lowest noise on the ADV7127
power and ground lines. This can be achieved by shielding the
digital inputs and providing good decoupling. The lead length
between groups of V
and GND pins should be minimized to
AA
inductive ringing.
Ground Planes
The ADV7127 and associated analog circuitry, should have a
separate ground plane referred to as the analog ground plane.
This ground plane should connect to the regular PCB ground
plane at a single point through a ferrite bead, as illustrated in
Figure 25. This bead should be located as close as possible
(within 3 inches) to the ADV7127.
The analog ground plane should encompass all ADV7127
ground pins, voltage reference circuitry, power supply bypass
circuitry, the analog output traces and any output amplifiers.
The regular PCB ground plane area should encompass all the
digital signal traces, excluding the ground pins, leading up to
the ADV7127.
–13–REV. 0
Page 14

ADV7127
Power Planes
The PC board layout should have two distinct power planes,
one for analog circuitry and one for digital circuitry. The analog
power plane should encompass the ADV7127 (V
) and all
AA
associated analog circuitry. This power plane should be connected to the regular PCB power plane (V
) at a single point
CC
through a ferrite bead, as illustrated in Figure 25. This bead
should be located within three inches of the ADV7127.
The PCB power plane should provide power to all digital logic
on the PC board, and the analog power plane should provide
power to all ADV7127 power pins, voltage reference circuitry
and any output amplifiers.
The PCB power and ground planes should not overlay portions
of the analog power plane. Keeping the PCB power and ground
planes from overlaying the analog power plane will contribute to
a reduction in plane-to-plane noise coupling.
VIDEO
DATA
INPUTS
ADV7127
D0
D9
PDOWN
PSAVE
CLOCK
COMP
V
V
REF
GND
R
SET
I
OUT
AA
R
SET
560V
C6
0.1mF
ANALOG POWER PLANE
R1
75V
C4
0.1mF
C3
0.1mF
Supply Decoupling
Noise on the analog power plane can be further reduced by the
use of multiple decoupling capacitors (see Figure 25).
Optimum performance is achieved by the use of 0.1 µF ceramic
capacitors. Each of the two groups of V
should be individually
AA
decoupled to ground. This should be done by placing the capacitors as close as possible to the device with the capacitor
leads as short as possible, thus minimizing lead inductance.
It is important to note that while the ADV7127 contains circuitry to reject power supply noise, this rejection decreases with
frequency. If a high frequency switching power supply is used,
the designer should pay close attention to reducing power supply noise. A dc power supply filter (Murata BNX002) will provide EMI suppression between the switching power supply and
the main PCB. Alternatively, consideration could be given to
using a three terminal voltage regulator.
C5
0.1mF
ANALOG GROUND PLANE
L1 (FERRITE BEAD)
C2
10mF
L2 (FERRITE BEAD)
VIDEO
OUTPUT
+5V (VCC)
C1
33mF
GROUND
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION VENDOR PART NUMBER
C1 33mF TANTALUM CAPACITOR
C3, C4, C5, C6 0.1mF CERAMIC CAPACITOR
C2 10mF TANTALUM
L1, L2 FERRITE BEAD FAIR-RITE 274300111 OR MURATA BL01/02/03
R1 75V 1% METAL FILM RESISTOR DALE CMF-55C
R
560V 1% METAL FILM RESISTOR DALE CMF-55C
SET
Figure 25. Typical Connection Diagram and Component List
–14– REV. 0
Page 15

ADV7127
Digital Signal Interconnect
The digital signal lines to the ADV7127 should be isolated as
much as possible from the analog outputs and other analog
circuitry. Digital signal lines should not overlay the analog
power plane.
Due to the high clock rates used, long clock lines to the ADV7127
should be avoided so as to minimize noise pickup.
Any active pull-up termination resistors for the digital inputs
should be connected to the regular PCB power plane (V
not the analog power plane.
Analog Signal Interconnect
The ADV7127 should be located as close as possible to the
output connectors thus minimizing noise pickup and reflections
due to impedance mismatch.
CC
), and
The video output signals should overlay the ground plane, and
not the analog power plane, thereby maximizing the high frequency power supply rejection.
For optimum performance, the analog outputs should each
have a source termination resistance to ground of 75 Ω (doubly
terminated 75 Ω configuration). This termination resistance
should be as close as possible to the ADV7127 so as to minimize reflections.
Additional information on PCB design is available in an application note entitled “Design and Layout of a Video Graphics
System for Reduced EMI.” This application note is available
from Analog Devices, publication number E1309-15-10/89.
–15–REV. 0
Page 16

ADV7127
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
28-Lead SOIC
(R-28)
0.7125 (18.10)
0.6969 (17.70)
28 15
PIN 1
0.0192 (0.49)
24
0.177 (4.50)
0.169 (4.30)
1
PIN 1
0.0256 (0.65)
0.0500
(1.27)
BSC
BSC
0.0138 (0.35)
0.311 (7.90)
0.303 (7.70)
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0040 (0.10)
0.006 (0.15)
0.002 (0.05)
SEATING
PLANE
141
0.1043 (2.65)
0.0926 (2.35)
SEATING
PLANE
24-Lead TSSOP
(RU-24)
13
0.256 (6.50)
12
0.0433
(1.10)
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0075 (0.19)
MAX
0.2992 (7.60)
0.2914 (7.40)
0.4193 (10.65)
0.0125 (0.32)
0.0091 (0.23)
0.246 (6.25)
0.0079 (0.20)
0.0035 (0.090)
0.3937 (10.00)
0.0291 (0.74)
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0500 (1.27)
8°
0°
0.0157 (0.40)
0.028 (0.70)
8°
0°
0.020 (0.50)
C3259–8–4/98
x 45°
–16–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...