Page 1
Dual 3 MHz, 800 mA Buck
Data Sheet
FEATURES
Main input voltage range: 2.3 V to 5.5 V
Two 800 mA buck regulators and one 300 mA LDO
24-lead, 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP package
Regulator accuracy: ±3%
Factory programmable or external adjustable VOUTx
3 MHz buck operation with forced PWM and auto PWM/PSM
modes
BUCK1/BUCK2: output voltage range from 0.8 V to 3.8 V
LDO: output voltage range from 0.8 V to 4.75 V
LDO: low input supply voltage from 1.7 V to 5.5 V
LDO: high PSRR and low output noise
APPLICATIONS
Power for processors, ASIC, FPGAs, and RF chipsets
Portable instrumentation and medical devices
Space constrained devices
Regulators with One 300 mA LDO
ADP5023
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADP5023 combines two high performance buck regulators
and one low dropout (LDO) regulator in a small, 24-lead 4 mm ×
4 mm LFCSP to meet demanding performance and board space
requirements.
The high switching frequency of the buck regulators enables tiny
multilayer external components and minimizes the board space.
When the MODE pin is set high, the buck regulators operate in
forced PWM mode. When the MODE pin is set low, the buck
regulators operate in PWM mode when the load current is
above a predefined threshold. When the load current falls below
a predefined threshold, the regulator operates in power save
mode (PSM) improving the light-load efficiency.
The two bucks operate out of phase to reduce the input capacitor requirement. The low quiescent current, low dropout voltage,
and wide input voltage range of the ADP5023 LDO extends the
battery life of portable devices. The ADP5023 LDO maintains
power supply rejection greater than 60 dB for frequencies as
high as 10 kHz while operating with a low headroom voltage.
Regulators in the ADP5023 are activated though dedicated
enable pins. The default output voltages can be externally set in
the adjustable version or factory programmable to a wide range
of preset values in the fixed voltage version.
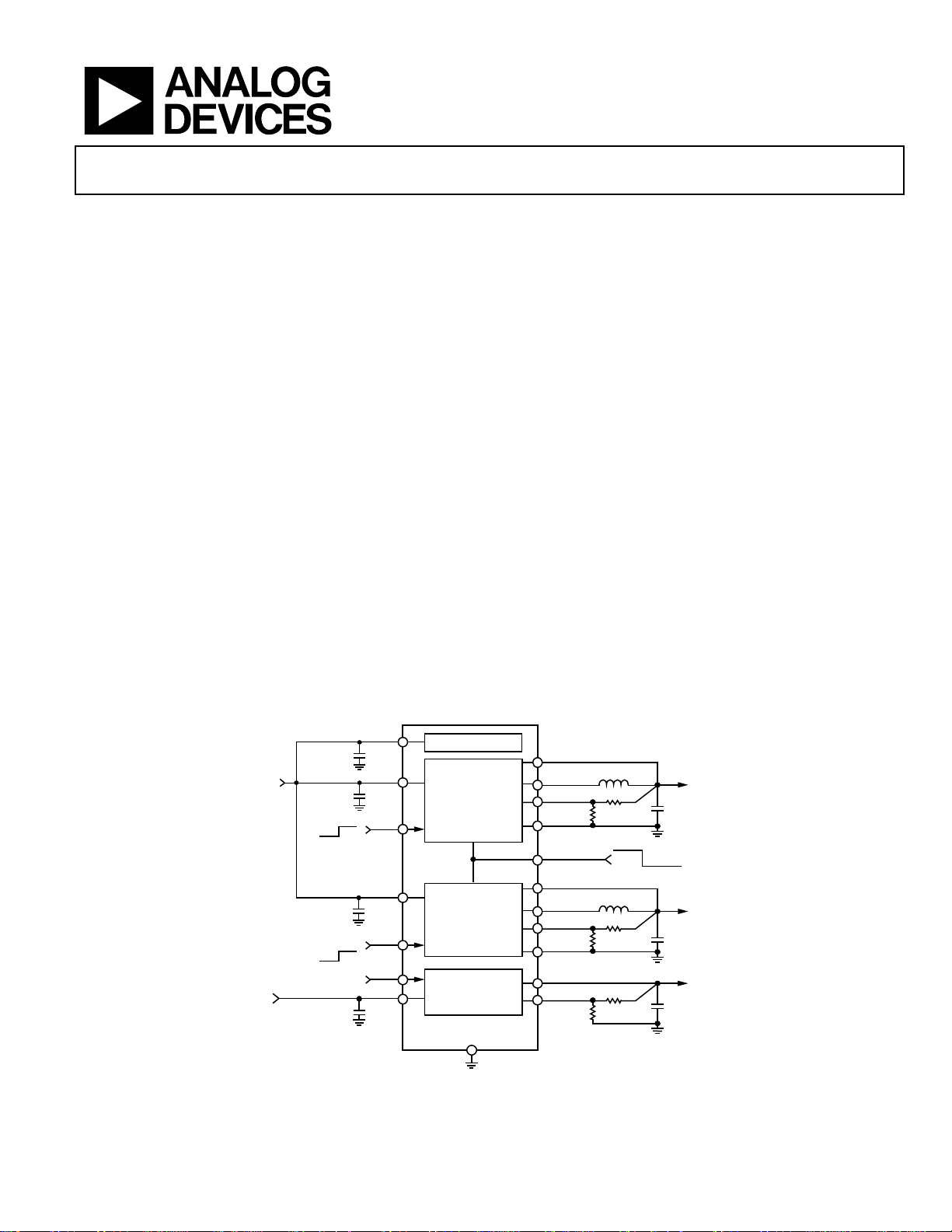
TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
AVIN
C
FILT
0.1µF
2.3V TO
5.5V
1.7V TO
5.5V
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
4.7µF
OFF
4.7µF
OFF
1µF
VIN1
C1
ON
EN1
VIN2
C2
EN2
ON
EN3
VIN3
C3
HOUSEKEEPING
EN1
EN2
EN3
ADP5023
AGND
BUCK1
MODE
MODE
BUCK2
LDO
Figure 1.
VOUT1
SW1
FB1
PGND1
MODE
VOUT2
SW2
FB2
PGND2
VOUT3
FB3
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
L1 1µH
R1
R2
PWM
L2 1µH
R3
R4
R5
R6
C5
10µF
PSM/PWM
C6
10µF
C7
1µF
V
OUT1
800mA
V
OUT2
800mA
V
OUT3
300mA
AT
AT
AT
09889-001
Page 2

ADP5023 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Typical Application Circuit ............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
General Specifications ................................................................. 3
BUCK1 and BUCK2 Specifications ........................................... 4
LDO Specifications ...................................................................... 5
Input and Output Capacitor, Recommended Specifications.. 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 6
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 6
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 6
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
REVISION HISTORY
8/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Power Dissipation and Thermal Considerations....................... 15
Buck Regulator Power Dissipation .......................................... 15
Junction Temperature................................................................ 16
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 17
Power Management Unit........................................................... 17
BUCK1 and BUCK2 .................................................................. 19
LDO.............................................................................................. 20
Applications Information.............................................................. 21
Buck External Component Selection....................................... 21
LDO External Component Selection ...................................... 23
PCB Layout Guidelines.................................................................. 24
Typical Application Schematics.................................................... 25
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 26
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 27
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 28
Page 3
Data Sheet ADP5023
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
V
= V
= V
AVI N
IN1
= 2.3 V to 5.5 V; V
IN2
typical specifications, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE V
THERMAL SHUTDOWN
Threshold TSSD T
Hysteresis TS
START-UP TIME1
BUCK1, LDO t
BUCK2 t
EN1, EN2, EN3, MODE INPUTS
Input Logic High VIH 1.1 V
Input Logic Low VIL 0.4 V
Input Leakage Current V
INPUT CURRENT
All Channels Enabled I
All Channels Disabled I
VIN1 UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
High UVLO Input Voltage Rising UVLO
High UVLO Input Voltage Falling UVLO
Low UVLO Input Voltage Rising UVLO
Low UVLO Input Voltage Falling UVLO
1
Start-up time is defined as the time from EN1 = EN2 = EN3 from 0 V to V
shorter for individual channels if another channel is already enabled. See the section for more information. Typical Performance Characteristics
= 1.7 V to 5.5 V; TJ = −40°C to +125°C for minimum/maximum specifications, and TA = 25°C for
IN3
, V
, V
AVIN
SD-HYS
START1
START2
I-LEAKAGE
STBY-NOSW
SHUTDOWN
2.3 5.5 V
IN1
IN2
rising 150 °C
J
20 °C
250 µs
300 µs
0.05 1 µA
No load, no buck switching 108 175 µA
T
VIN1RISE
VIN1FALL
VIN1RISE
VIN1FALL
= −40°C to +85°C 0.3 1 µA
J
3.9 V
3.1 V
2.275 V
1.95 V
to VOUT1, VOUT2, and VOUT3 reaching 90% of their nominal level. Start-up times are
AVIN
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 28
Page 4
ADP5023 Data Sheet
BUCK1 AND BUCK2 SPECIFICATIONS
V
= V
= V
AVI N
IN1
specifications, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Accuracy V
Line Regulation
Load Regulation
VOLTAGE FEEDBACK V
OPERATING SUPPLY CURRENT MODE = ground
BUCK1 Only IIN
BUCK2 Only IIN
BUCK1 and BUCK2 IIN
PSM CURRENT THRESHOLD I
SW CHARACTERISTICS
SW On Resistance R
R
R
R
Current Limit I
ACTIVE PULL-DOWN R
OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY fSW 2.5 3.0 3.5 MHz
1
All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard statistical quality control (SQC).
= 2.3 V to 5.5 V; TJ = −40°C to +125°C for minimum/maximum specifications, and TA = 25°C for typical
IN2
OUT1
(∆V
(∆V
(∆V
(∆V
FB1
1
, V
PWM mode; I
OUT2
OUT1/VOUT1
OUT2/VOUT2
OUT1/VOUT1
OUT2/VOUT2
, V
)/∆V
)/∆V
)/∆I
)/∆I
Models with adjustable outputs 0.485 0.5 0.515 V
FB2
PWM mode −0.05 %/V
,
IN1
IN2
PWM mode; I
,
OUT1
OUT2
= 0 mA, device not switching, all
I
LOAD 1
= I
LOAD 1
LOAD
= 0 mA to 800 mA −3 +3 %
LOAD 2
= 0 mA to 800 mA −0.1 %/A
44 A
other channels disabled
= 0 mA, device not switching, all
I
LOAD 2
55 A
other channels disabled
I
LOAD 1
= I
= 0 mA, device not switching,
LOAD 2
67 A
LDO channels disabled
PSM to PWM operation 100 mA
PSM
V
PFET
V
NFET
V
PFET
V
NFET
, I
LIMIT1
LIMIT2
Channel disabled 75 Ω
PDWN-B
= V
= 3.6 V 155 240 mΩ
IN1
IN2
= V
= 3.6 V 205 310 mΩ
IN1
IN2
= V
= 5.5 V 162 204 mΩ
IN1
IN2
= V
= 5.5 V 137 243 mΩ
IN1
IN2
pFET switch peak current limit 1600 1950 2300 mA
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 28
Page 5
Data Sheet ADP5023
LDO SPECIFICATIONS
V
= (V
IN3
specifications, and T
Table 3.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE V
OPERATING SUPPLY CURRENT
Bias Current per LDO2 I
I
I
Total System Input Current
LDO Only I
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Accuracy
Line Regulation I
Load Regulation3
VOLTAGE FEEDBACK
DROPOUT VOLTAGE4 V
(∆V
(∆V
CURRENT-LIMIT THRESHOLD5 I
ACTIVE PULL-DOWN R
OUTPUT NOISE
Regulator LDO NOISE
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
RATIO
Regulator LDO 10 kHz, V
100 kHz, V
1 MHz, V
1
All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard statistical quality control (SQC).
2
This is the input current into VIN3, which is not delivered to the output load.
3
Based on an endpoint calculation using 1 mA and 300 mA loads.
4
Dropout voltage is defined as the input-to-output voltage differential when the input voltage is set to the nominal output voltage. This applies only to output voltages
above 1.7 V.
5
Current-limit threshold is defined as the current at which the output voltage drops to 90% of the specified typical value. For example, the current limit for a 3.0 V
output voltage is defined as the current that causes the output voltage to drop to 90% of 3.0 V, or 2.7 V.
+ 0.5 V) or 1.7 V (whichever is greater) to 5.5 V; CIN = C
OUT3
= 25°C for typical specifications, unless otherwise noted.1
A
1.7 5.5 V
IN3
I
VIN3BIAS
IIN
OUT3
OUT3
OUT3
Includes all current into AVIN, VIN1, VIN2, and
VIN3
OUT3
V
100 µA < I
OUT3
OUT3
V
FB3
V
DROPOUT
OUT3/VOUT3
OUT3/VOUT3
LIMIT3
PDWN-L
)/∆V
)/∆I
335 600 mA
Channel disabled 600 Ω
10 Hz to 100 kHz, V
LDO
I
OUT3
0.485 0.5 0.515 V
OUT3
V
IN3
OUT3
V
OUT3
OUT3
PSRR
= 1 µF; TJ = −40°C to +125°C for minimum/maximum
OUT
= 0 µA 10 30 µA
= 10 mA 60 100 µA
= 300 mA 165 245 µA
= 0 µA, all other channels disabled 53 µA
< 300 mA −3 +3 %
OUT3
= 1 mA −0.03 +0.03 %/ V
= 1 mA to 300 mA 0.001 0.003 %/mA
= 3.3 V, I
= 2.5 V, I
= 1.8 V, I
IN3
IN3
= 300 mA 75 140 mV
OUT3
= 300 mA 100 mV
OUT3
= 300 mA 180 mV
OUT3
= 3.3 V, V
= 3.3 V, V
IN3
= 3.3 V, V
= 5 V, V
IN3
OUT3
OUT3
= 2.8 V, I
OUT3
= 2.8 V, I
= 2.8 V, I
= 2.8 V 100 µV rms
OUT3
= 1 mA 60 dB
OUT3
= 1 mA 62 dB
OUT3
= 1 mA 63 dB
OUT3
INPUT AND OUTPUT CAPACITOR, RECOMMENDED SPECIFICATIONS
TA = −40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise specified.
Table 4.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SUGGESTED INPUT AND OUTPUT CAPACITANCE
BUCK1, BUCK2 Input Capacitor C
BUCK1, BUCK2 Output Capacitor C
LDO1 Input and Output Capacitor C
CAPACITOR ESR R
1
The minimum input and output capacitance should be greater than 0.70 µF over the full range of operating conditions. The full range of operating conditions in
the application must be considered during device selection to ensure that the minimum capacitance specification is met. X7R- and X5R-type capacitors are
recommended; Y5V and Z5U capacitors are not recommended for use because of their poor temperature and dc bias characteristics.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 28
, C
MIN1
MIN1
MIN3
ESR
4.7 40 µF
MIN2
, C
10 40 µF
MIN2
, C
0.70 µF
MIN4
0.001 1 Ω
Page 6
ADP5023 Data Sheet
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
Parameter Rating
AVIN to AGND −0.3 V to +6 V
VIN1, VIN2 to AVIN −0.3 V to +0.3 V
PGND1, PGND2 to AGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
VIN3, VOUT1, VOUT2, VOUT3, FB1,
FB2, FB3, EN1, EN2, EN3, MODE to
AGND
VOUT3 to AGND −0.3 V to (VIN3 + 0.3 V)
SW1 to PGND1 −0.3 V to (VIN1 + 0.3 V)
SW2 to PGND2 −0.3 V to (VIN2 + 0.3 V)
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Junction Temperature
Range
Soldering Conditions JEDEC J-STD-020
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
For detailed information on power dissipation, see the Power
Dissipation and Thermal Considerations section.
−0.3 V to (AVIN + 0.3 V)
−40°C to +125°C
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 6. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA θJC Unit
24-Lead, 0.5 mm pitch LFCSP 35 3 °C/W
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 28
Page 7
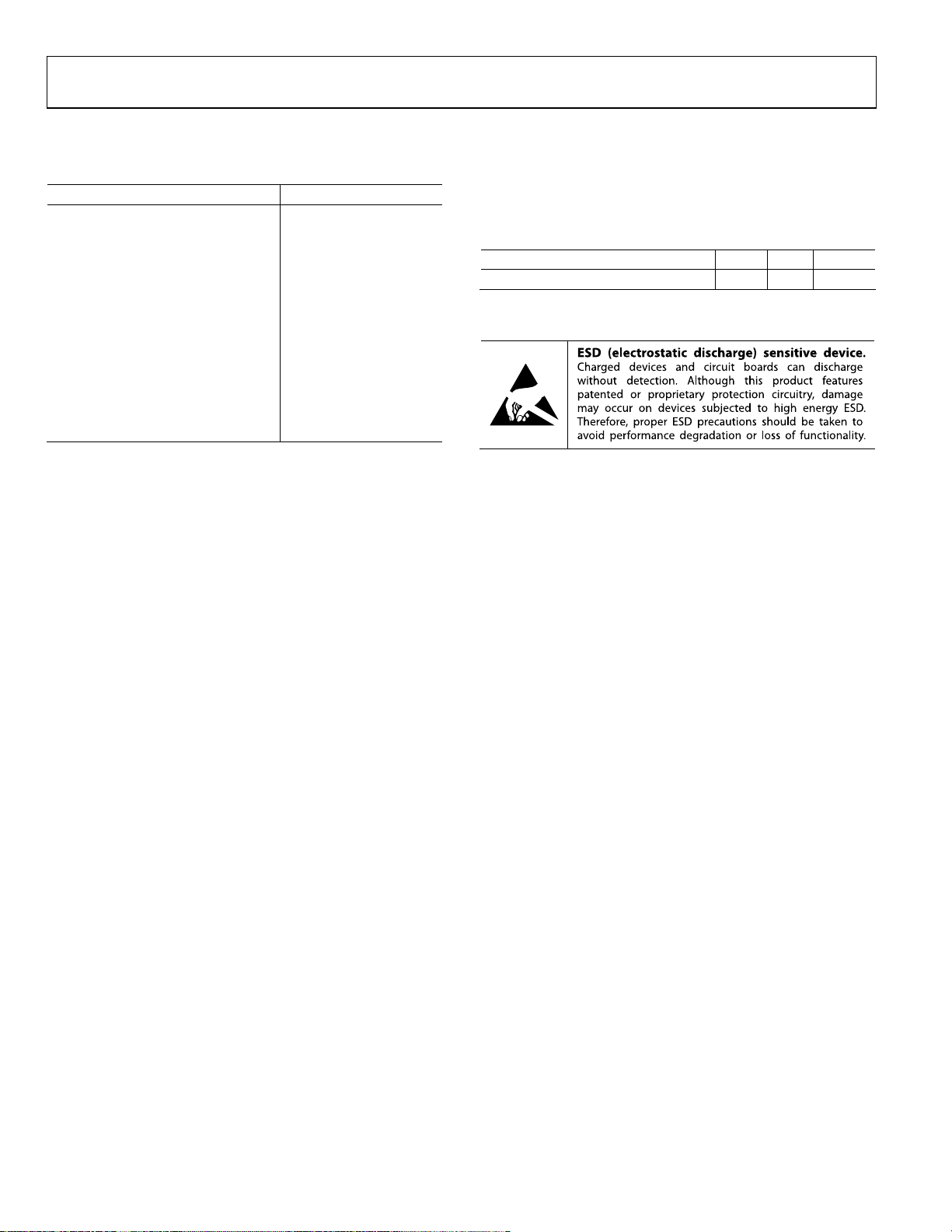
ADP5023
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AGND
AGND
EN3
VIN3
VOUT3
21
10
VOUT1
FB3
20
19
11
12
FB1
EN1
THE EX
18
AGND
AVIN
17
VIN1
16
SW
1
15
PGND1
14
MODE
13
POSED PAD
09889-002
24
23
22
1
AGND
AGND
2
3
VIN2
SW
PGND2
NC
NOTES
1. NC = NO CO
2. IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT
BE SOLDERED TO
ADP5023
2
TOP VIEW
4
(Not to Scale)
5
6
9
8
7
FB2
EN2
VOUT2
NNECT. DO NOT CONNECT TO THIS PIN.
THE GROUND PLANE.
Figure 2. Pin Configuration—View from Top of Die
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 AGND Analog Ground.
2 AGND Analog Ground.
3 VIN2 BUCK2 Input Supply (2.3 V to 5.5 V). Connect VIN2 to VIN1 and AVIN.
4 SW2 BUCK2 Switching Node.
5 PGND2 Dedicated Power Ground for BUCK2.
6 NC No Connect. Leave this pin unconnected.
7 EN2 BUCK2 Enable Pin. High level turns on this regulator, and low level turns it off.
8 FB2
BUCK2 Feedback Input. For device models with adjustable output voltage, connect this pin to the middle of the
BUCK2 resistor divider. For device models with fixed output voltage, leave this pin unconnected.
9 VOUT2 BUCK2 Output Voltage Sensing Input. Connect VOUT2 to the top of the capacitor on VOUT2.
10 VOUT1 BUCK1 Output Voltage Sensing Input. Connect VOUT1 to the top of the capacitor on VOUT1.
11 FB1
BUCK1 Feedback Input. For device models with adjustable output voltage, connect this pin to the middle of the
BUCK1 resistor divider. For device models with fixed output voltage, leave this pin unconnected.
12 EN1 BUCK1 Enable Pin. High level turns on this regulator, and low level turns it off.
13 MODE BUCK1/BUCK2 Operating Mode. MODE = high: forced PWM operation. MODE = low: auto PWM/PSM operation.
14 PGND1 Dedicated Power Ground for BUCK1.
15 SW1 BUCK1 Switching Node
16 VIN1 BUCK1 Input Supply (2.3 V to 5.5 V). Connect VIN1 to VIN2 and AVIN.
17 AVIN Analog Input Supply (2.3 V to 5.5 V). Connect AVIN to VIN1 and VIN2.
18 AGND Analog Ground.
19 FB3
LDO Feedback Input. For device models with adjustable output voltage, connect this pin to the middle of the LDO
resistor divider. For device models with fixed output voltage, leave this pin unconnected.
20 VOUT3 LDO Output Voltage.
21 VIN3 LDO Input Supply (1.7 V to 5.5 V).
22 EN3 LDO Enable Pin. High level turns on this regulator, and low level turns it off.
23 AGND Analog Ground.
24 AGND Analog Ground.
EPAD (EP) Exposed Pad. It is recommended that the exposed pad be soldered to the ground plane.
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 28
Page 8
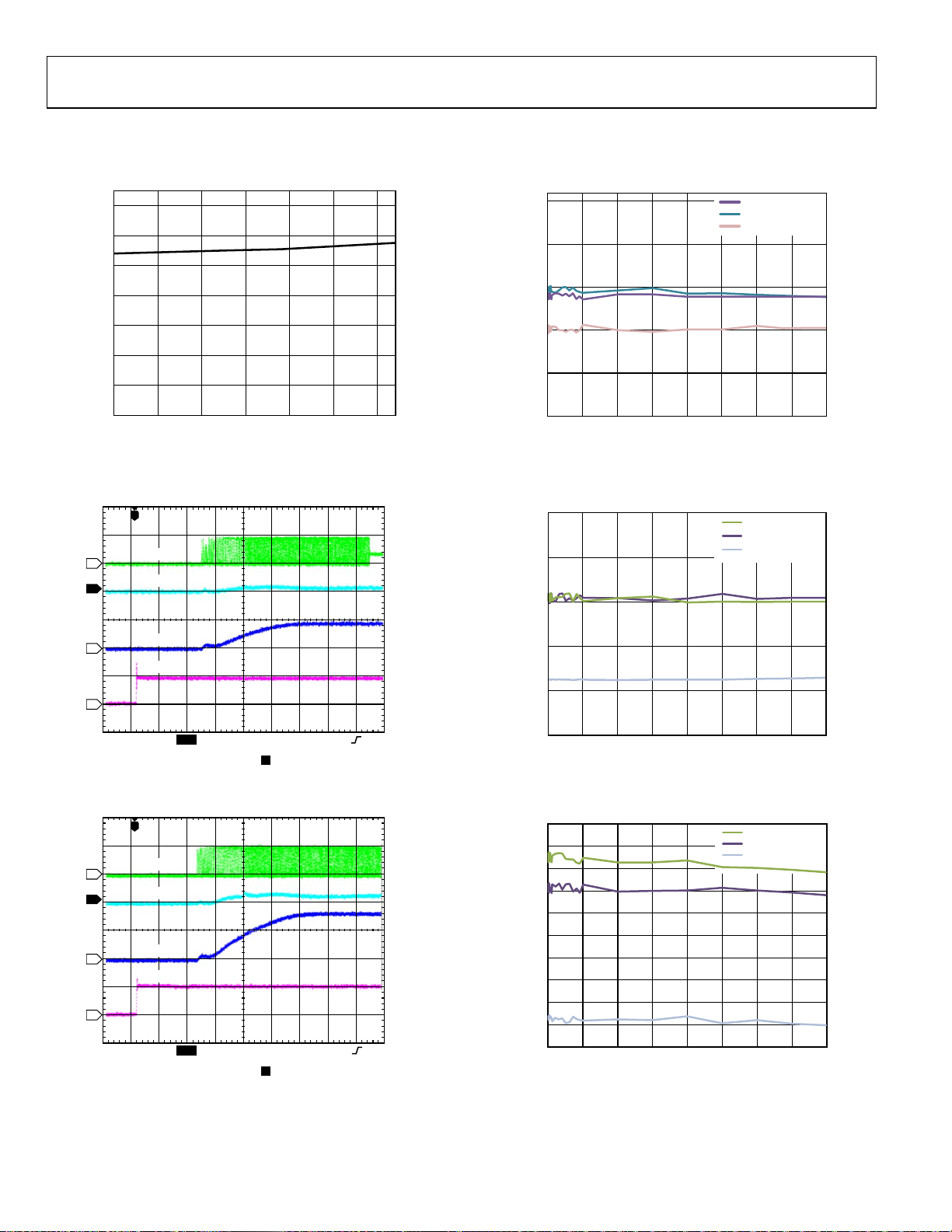
ADP5023 Data Sheet
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
V
= V
= V
IN1
IN2
= 3.6 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
IN3
140
120
100
80
60
40
QUIESCENT CURRENT (µA)
20
0
2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8 4.3 4.8 5.3
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 3. System Quiescent Current vs. Input Voltage, V
V
4
2
1
3
= 1.8 V, V
OUT2
T
SW
IOUT
VOUT
EN
= 1.2 V, V
OUT3
= 3.3 V, All Channels Unloaded
OUT4
OUT1
= 3.3 V,
3.35
3.33
3.31
(V)
OUT
V
3.29
3.27
3.25
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
09889-139
I
OUT
(A)
Figure 6. BUCK1 Load Regulation Across Temperature, V
VIN = 4.2V, +85°C
VIN = 4.2V, +25°C
VIN = 4.2V, –40°C
= 3.3 V,
OUT1
09889-058
Auto Mode
(V)
OUT
V
1.864
1.844
1.824
1.804
1.784
VIN = 3.6V, +85°C
VIN = 3.6V, +25°C
VIN = 3.6V, –40°C
CH1 2.00V
CH3 5.00V
Figure 4. BUCK1 Startup, V
T
4
2
1
3
CH1 2.00V
CH3 5.00V
SW
IOUT
VOUT
EN
Figure 5. BUCK2 Startup, V
CH2 50.0mA Ω
CH4 5.00V
CH2 50.0mA Ω
CH4 5.00V
M 40.0µs A CH3 2. 2V
T 11. 20%
= 1.8 V, I
OUT1
M 40.0µs A CH3 2.2V
T 11. 20%
= 3.3 V, I
OUT2
OUT1
OUT2
= 5 mA
= 10 mA
09889-021
09889-020
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 28
1.764
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
I
OUT
(A)
Figure 7. BUCK2 Load Regulation Across Temperature, V
Auto Mode
0.799
0.798
0.797
0.796
0.795
(V)
0.794
OUT
V
0.793
0.792
0.791
0.790
0.789
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 3.6V, +85°C
VIN = 3.6V, +25°C
VIN = 3.6V, –40°C
Figure 8. BUCK1 Load Regulation Across Input Voltage, V
PWM Mode
OUT2
OUT1
= 1.8 V,
= 3.3 V,
09889-057
09889-054
Page 9
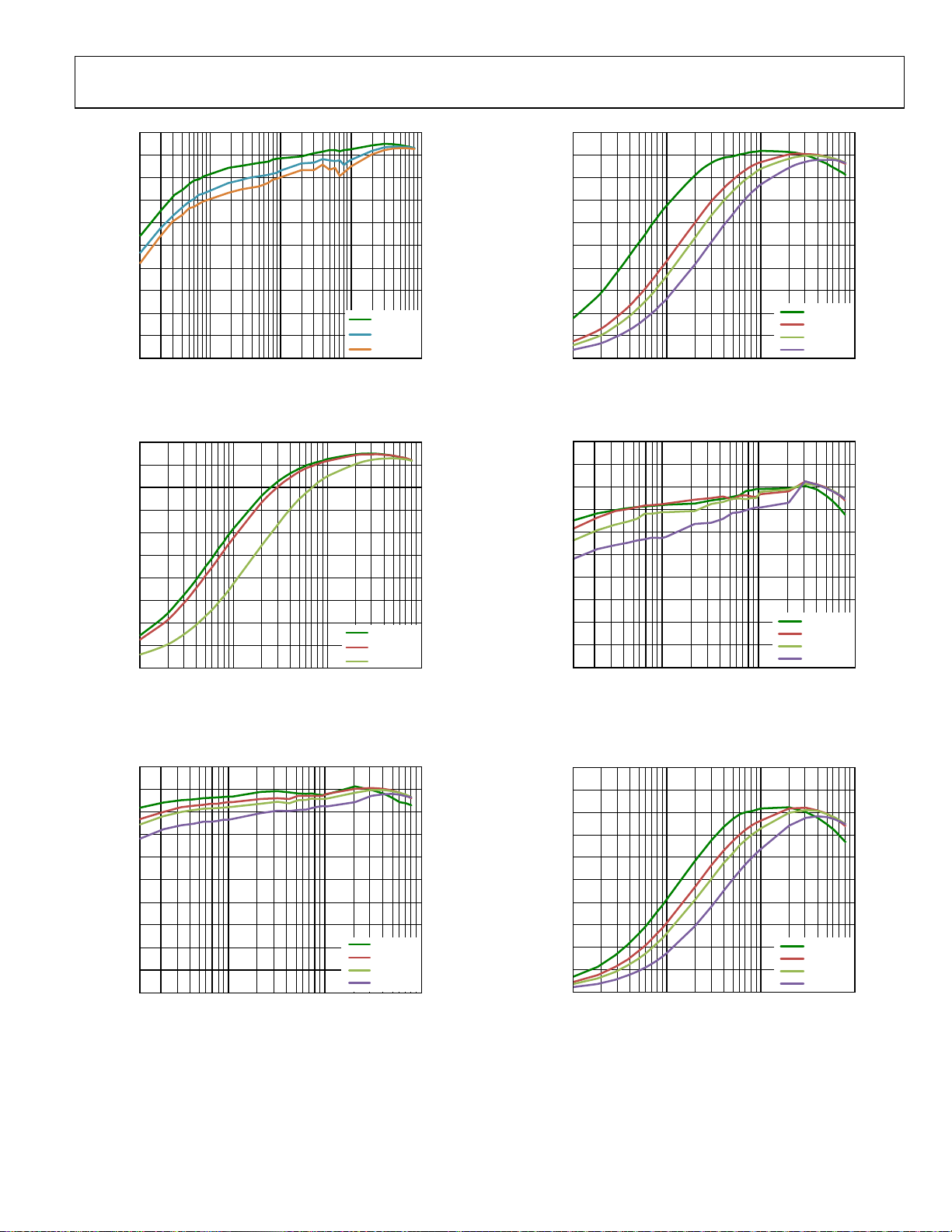
Data Sheet ADP5023
C
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 3.9V
VIN = 4.2V
VIN = 5.5V
Figure 9. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 3.3 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT1
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 3.9V
VIN = 4.2V
VIN = 5.5V
Figure 10. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 3.3 V, PWM Mode
V
OUT1
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 2.3V
VIN = 3.6V
VIN = 4.2V
VIN = 5.5V
Figure 11. BUCK2 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 1.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT2
09889-038
09889-039
09889-036
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 2.4V
V
= 3.6V
IN
V
= 4.5V
IN
V
= 5.5V
IN
Figure 12. BUCK2 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 1.8 V, PWM Mode
V
OUT2
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 2.3V
V
= 3.6V
IN
V
= 4.2V
IN
V
= 5.5V
IN
Figure 13. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 0.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT1
100
90
80
70
60
Y (%)
50
40
EFFICIEN
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
VIN = 2.3V
V
= 3.6V
IN
V
= 4.2V
IN
V
= 5.5V
IN
Figure 14. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 0.8 V, PWM Mode
V
OUT1
09889-035
09889-034
09889-035
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 28
Page 10

ADP5023 Data Sheet
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
+25°C
+85°C
–40°C
Figure 15. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Temperature,
= 3.9 V, V
V
IN
= 3.3 V, Auto Mode
OUT1
09889-062
3.3
3.2
3.1
3.0
2.9
2.8
FREQUENC Y (MHz)
2.7
2.6
2.5
011.00.80.60.40.2
I
OUT
(A)
TA= +25°C
= –40°C
T
A
= +85°C
T
A
.2
Figure 18. BUCK2 Switching Frequency vs. Output Current, Across
Temperature, V
= 1.8 V, PWM Mode
OUT2
09889-040
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
+85°C
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 16. BUCK2 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Temperature,
= 1.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT2
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
I
OUT
(A)
+85°C
+25°C
–40°C
Figure 17. BUCK1 Efficiency vs. Load Current, Across Temperature,
= 0.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT1
T
VOUT
1
I
SW
2
SW
4
CH1 50.0mV M 4.00µs A CH2 240mA
09889-063
Figure 19. Typical Waveforms, V
CH2 500mA Ω
CH4 2.00V
OUT1
T 28.40%
= 3.3 V, I
= 30 mA, Auto Mode
OUT1
09889-025
T
VOUT
1
I
2
4
CH1 50.0mV M 4.00µs A CH2 220mA
09889-200
Figure 20. Typical Waveforms, V
SW
SW
CH2 500mA Ω
CH4 2.00V
OUT2
T 28.40%
= 1.8 V, I
= 30 mA, Auto Mode
OUT2
09889-024
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 28
Page 11

Data Sheet ADP5023
T
T
VOUT
I
SW
SW
VOUT
I
SW
SW
CH2 500mA Ω
CH4 2.00V
T
OUT1
T 28.40%
= 3.3 V, I
= 30 mA, PWM Mode
OUT1
1
2
4
CH1 50mV M 400ns A CH2 220mA
Figure 21. Typical Waveforms, V
1
2
VIN
1
4
3
09889-027
Figure 24. BUCK2 Response to Line Transient, V
4
1
VOUT
SW
CH1 50.0mV
CH3 1.00V CH4 2.00V
V
= 1.8 V, PWM Mode
OUT2
T
SW
VOUT
M 1.00ms A CH3 4.80V
T 30.40%
= 4.5 V to 5.0 V,
IN
09889-013
4
CH1 50mV M 400ns A CH2 220mA
Figure 22. Typical Waveforms, V
CH2 500mA Ω
CH4 2.00V
OUT2
T 28.40%
= 1.8 V, I
T
VIN
1
3
VOUT
SW
CH1 50.0mV
CH3 1.00V CH4 2.00V
M 1.00ms A CH3 4.80V
T 30.40%
Figure 23. BUCK1 Response to Line Transient, V
PWM Mode
= 30 mA, PWM Mode
OUT2
= 4.5 V to 5.0 V, V
IN
OUT1
09889-026
09889-112
= 3.3 V,
I
OUT
2
CH1 50.0mV
CH2 50.0m A Ω
CH4 5.00V
M 20.0µs A CH2 356mA
T 60.000µs
Figure 25. BUCK1 Response to Load Transient, I
V
= 3.3 V, Auto Mode
OUT1
T
SW
4
VOUT
1
I
OUT
2
CH1 50.0mV
CH2 50.0m A Ω
CH4 5.00V
M 20.0µs A CH2 379mA
T 22.20%
Figure 26. BUCK2 Response to Load Transient, I
= 1.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT2
= 1 mA to 50 mA,
OUT1
= 1 mA to 50 mA,
OUT2
09889-016
09889-015
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 28
Page 12

ADP5023 Data Sheet
T
SW
4
1
VOUT
I
OUT
T
I
2
1
IN
VOUT
EN
2
CH1 50.0mV
CH2 200mA Ω
CH4 5.00V
M 20.0µs A CH2 408mA
T 20.40%
Figure 27. BUCK1 Response to Load Transient, I
= 3.3 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT1
T
SW
4
1
2
CH1 100mV
VOUT
I
OUT
CH2 200mA Ω
CH4 5.00V
M 20.0µs A CH2 88.0mA
T 19.20%
Figure 28. BUCK2 Response to Load Transient, I
= 1.8 V, Auto Mode
V
OUT2
T
VOUT2
2
3
1
SW1
VOUT1
SW2
= 20 mA to 180 mA,
OUT1
= 20 mA to 180 mA,
OUT2
3
CH1 2.00V M 40.0µs A CH3 2.2V
09889-017
CH3 5.00V
Figure 30. LDO Startup, V
2.820
2.815
2.810
2.805
C (V)
2.800
OUT
V
2.795
2.790
2.785
2.780
0 0.05 0. 10 0. 15 0.2 0 0.25 0.30
09889-018
Figure 31. LDO Load Regulation Across Input Voltage, V
CH2 50.0mA Ω
I
OUT
T 11.2 0%
OUT3
(A)
= 3.0 V, I
OUT3
= 5 mA
VIN = 3.3V
VIN = 4.5V
VIN = 5.0V
VIN = 5.5V
OUT3
= 2.8 V
09889-022
09889-046
400
350
300
250
(mΩ)
200
ON
RDS
150
100
+25°C
–40°C
+125°C
4
CH1 5.00V
CH3 5.00V
CH2 5.00V
CH4 5.00V
M 400ns A CH4 1.90V
T 50.00%
09889-066
Figure 29. VOUT and SW Waveforms for BUCK1 and BUCK2 in PWM Mode
Showing Out-of-Phase Operation
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 28
50
0
2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8 4.3 4.8 5.3
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 32. NMOS RDS
vs. Input Voltage Across Temperature
ON
09703-037
Page 13

Data Sheet ADP5023
250
200
150
(mΩ)
ON
100
RDS
50
0
2.32.83.33.84.34.85.3
Figure 33. PMOS RDS
ON
–40°C
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
vs. Input Voltage Across Temperature
+25°C
+125°C
09703-038
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
GROUND CURRENT (µA)
10
5
0
0 0.050.100.150.200.25
I
(A)
OUT
Figure 36. LDO Ground Current vs. Output Load, V
= 3.3 V, V
IN3
OUT3
09889-136
= 2.8 V
3.45
3.40
3.35
(V)
3.30
OUT
V
3.25
3.20
3.15
000.250.200.150.100.05
I
OUT
(A)
Figure 34. LDO Load Regulation Across Temperature, V
3.0
2.5
2.0
(V)
1.5
OUT
V
1.0
0.5
0
2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 5.4
(V)
V
IN
Figure 35. LDO Line Regulation Across Output Load, V
VIN = 4.2V, +85°C
VIN = 4.2V, +25°C
VIN = 4.2V, –40°C
= 3.3 V, V
IN3
I
= 300mA
OUT
I
= 150mA
OUT
I
= 100mA
OUT
I
= 10mA
OUT
I
= 1mA
OUT
I
= 100µA
OUT
= 2.8 V
OUT3
T
I
OUT
2
1
.30
09889-049
OUT3
= 2.8 V
09889-045
Figure 37. LDO Response to Load Transient, I
2
1
3
VOUT
CH1 100mV M 40.0µs A CH2 52.0mA
CH1 20.0mV
CH3 1.00V
CH2 100mA Ω
T
VIN
VOUT
Figure 38. LDO Response to Line Transient, V
T 19.20%
= 2.8 V
V
OUT3
M 100µs A CH3 4.80V
T 28.40%
OUT3
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, V
IN
= 1 mA to 80 mA,
= 2.8 V
OUT3
09889-019
09889-014
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 28
Page 14

ADP5023 Data Sheet
60
55
50
45
40
RMS NOISE (µV)
35
30
25
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100
VIN = 5V
VIN = 3.3V
I
OUT
(mA)
Figure 39. LDO Output Noise vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 2.8 V
V
OUT3
09889-047
0
–20
–40
–60
PSRR (dB)
–80
–100
–120
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1 M 10M
FREQUENC Y (Hz)
Figure 42. LDO PSRR Across Output Load, V
100µA
1mA
10mA
50mA
100mA
150mA
IN3
= 3.3 V, V
OUT3
= 3.0 V
09889-051
65
V
= 5V
60
55
50
45
40
RMS NOISE (µV)
35
30
25
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100
IN
VIN = 3.3V
I
OUT
(mA)
Figure 40. LDO Output Noise vs. Load Current, Across Input Voltage,
= 3.0 V
V
OUT3
0
100µA
–10
1mA
10mA
–20
50mA
100mA
–30
150mA
–40
–50
PSRR (dB)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
Figure 41. LDO PSRR Across Output Load, V
FREQUENC Y (Hz)
= 3.3 V, V
IN3
OUT3
09889-048
09889-050
= 2.8 V
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 28
0
100µA
–20
–40
–60
PSRR (dB)
–80
–100
–120
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1 M 10M
1mA
10mA
50mA
100mA
150mA
FREQUENC Y (Hz)
Figure 43. LDO PSRR Across Output Load, V
0
100µA
1mA
10mA
50mA
100mA
150mA
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1 M 10M
FREQUENC Y (Hz)
PSRR (dB)
–100
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
Figure 44. LDO PSRR Across Output Load, V
= 5.0 V, V
IN3
= 5.0 V, V
IN3
OUT3
OUT3
= 2.8 V
= 3.0 V
09889-053
09889-052
Page 15

Data Sheet ADP5023
P
POWER DISSIPATION AND THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
The ADP5023 is a highly efficient µPMU, and, in most cases,
the power dissipated in the device is not a concern. However,
if the device operates at high ambient temperatures and maximum loading condition, the junction temperature can reach
the maximum allowable operating limit (125°C).
When the temperature exceeds 150°C, the ADP5023 turns off
all the regulators, allowing the device to cool down. When the
die temperature falls below 130°C, the ADP5023 resumes
normal operation.
This section provides guidelines to calculate the power dissipated in the device and ensure that the ADP5023 operates
below the maximum allowable junction temperature.
The efficiency for each regulator on the ADP5023 is given by
OUT
η
100%×=
P
IN
(1)
where:
η is the efficiency.
P
is the input power.
IN
P
is the output power.
OUT
Power loss is given by
P
= PIN − P
LOSS
(2a)
OUT
or
P
= P
LOSS
(1− η)/η (2b)
OUT
Power dissipation can be calculated in several ways. The most
intuitive and practical is to measure the power dissipated at the
input and all the outputs. Perform the measurements at the
worst-case conditions (voltages, currents, and temperature).
The difference between input and output power is dissipated in
the device and the inductor. Use Equation 4 to derive the power
lost in the inductor, and from this use Equation 3 to calculate
the power dissipation in the ADP5023 buck converter.
A second method to estimate the power dissipation uses the
efficiency curves provided for the buck regulator, and the power
lost on the LDO can be calculated using Equation 12. When the
buck efficiency is known, use Equation 2b to derive the total
power lost in the buck regulator and inductor, use Equation 4 to
derive the power lost in the inductor, and then calculate the
power dissipation in the buck converter using Equation 3. Add
the power dissipated in the buck and in the LDO to find the
total dissipated power.
Note that the buck efficiency curves are typical values and may
, V
not be provided for all possible combinations of V
. To account for these variations, it is necessary to include a
I
OUT
, and
IN
OUT
safety margin when calculating the power dissipated in the buck.
A third way to estimate the power dissipation is analytical and
involves modeling the losses in the buck circuit provided by
Equation 8 to Equation 11 and the losses in the LDO provided
by Equation 12.
BUCK REGULATOR POWER DISSIPATION
The power loss of the buck regulator is approximated by
P
= P
LOSS
where:
P
is the power dissipation on one of the ADP5023 buck
DBUCKx
regulators.
P
is the inductor power losses.
L
The inductor losses are external to the device and do not have
any effect on the die temperature.
The inductor losses are estimated (without core losses) by
P
≈ I
L
OUT1(RMS)
where:
DCRL is the inductor series resistance.
I
is the rms load current of the buck regulator.
OUT1(RMS)
where r is the normalized inductor ripple current
r = V
OUT1
where:
L is the inductance.
f
is the switching frequency.
SW
D is the duty cycle.
D = V
OUT1/VIN1
ADP5023 buck regulator power dissipation, P
power switch conductive losses, the switch losses, and the transition losses of each channel. There are other sources of loss, but
these are generally less significant at high output load currents,
where the thermal limit of the application is. Equation 8
captures the calculation that must be made to estimate the
power dissipation in the buck regulator.
P
DBUCK
The power switch conductive losses are due to the output current,
I
, flowing through the P-MOSFET and the N-MOSFET
OUT1
power switches that have internal resistance, RDS
RDS
. The amount of conductive power loss is found by
ON-N
P
= [RDS
COND
where RDS
mately 0.16 Ω at 125°C junction temperature and VIN1 = VIN2 =
3.6 V. At VIN1 = VIN2 = 2.3 V, these values change to 0.31 Ω and
0.21 Ω, respectively, and at VIN1 = VIN2 = 5.5 V, the values are
0.16 Ω and 0.14 Ω, respectively.
+ P
DBUCK1
2
× DCRL (4)
II
OUT1
)(1
RMSOUT
× (1 − D)/(I
+ PL (3)
DBUCK2
r
+1
×=
(5)
12
× L × fSW) (6)
OUT1
(7)
, includes the
DBUCK
= P
+ PSW + P
COND
× D + RDS
ON-P
is approximately 0.2 Ω, and RDS
ON-P
(8)
TRAN
and
ON-P
× (1 − D)] × I
ON-N
OUT1
is approxi-
ON-N
2
(9)
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 28
Page 16

ADP5023 Data Sheet
Switching losses are associated with the current drawn by the
driver to turn on and turn off the power devices at the switching
frequency. The amount of switching power loss is given by
P
SW
= (C
GATE-P
+ C
GATE-N
) × V
IN1
2
× f
SW
(10)
where:
C
is the P-MOSFET gate capacitance.
GATE-P
C
is the N-MOSFET gate capacitance.
GATE-N
For the ADP5023, the total of (C
GATE-P
+ C
GATE-N
) is
approximately 150 pF.
The transition losses occur because the P-channel power
MOSFET cannot be turned on or off instantaneously, and the
SW node takes some time to slew from near ground to near
V
(and from V
OUT1
to ground). The amount of transition
OUT1
loss is calculated by
P
= V
× I
× (t
+ t
where t
TRAN
RISE
and t
IN1
OUT1
RISE
are the rise time and the fall time of the
FALL
FALL
) × f
SW
(11)
switching node, SW. For the ADP5023, the rise and fall times of
SW are in the order of 5 ns.
If the preceding equations and parameters are used for estimating the converter efficiency, it must be noted that the equations
do not describe all of the converter losses, and the parameter
values given are typical numbers. The converter performance
also depends on the choice of passive components and board
layout; therefore, a sufficient safety margin should be included
in the estimate.
LDO Regulator Power Dissipation
The power loss of a LDO regulator is given by
P
= [(VIN − V
DLDO
OUT
) × I
] + (VIN × I
LOAD
) (12)
GND
where:
I
is the load current of the LDO regulator.
LOAD
V
and V
IN
are input and output voltages of the LDO,
OUT
respectively.
I
is the ground current of the LDO regulator.
GND
Power dissipation due to the ground current is small and it
can be ignored.
The total power dissipation in the ADP5023 simplifies to
P
D
= P
DBUCK1
+ P
DBUCK2
+ P
(13)
DLDO
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
In cases where the board temperature TA is known, the thermal
resistance parameter, θ
temperature rise. T
formula
T
= TA + (PD × θJA) (14)
J
The typical θ
value for the 24-lead, 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP is
JA
35°C/W (see Tabl e 6 ). A very important factor to consider is
that θ
is based on 4-layer, 4 in × 3 in, 2.5 oz copper, as per
JA
JEDEC standard, and real applications may use different sizes
and layers. It is important to maximize the copper used to remove
the heat from the device. Copper exposed to air dissipates heat
better than copper used in the inner layers. The exposed pad
should be connected to the ground plane with several vias.
If the case temperature can be measured, the junction
temperature is calculated by
T
= TC + (PD × θJC) (15)
J
where T
is the case temperature and θJC is the junction-to-case
C
thermal resistance provided in Table 6 .
When designing an application for a particular ambient
temperature range, calculate the expected ADP5023 power
dissipation (P
) due to the losses of all channels by using
D
Equation 8 to Equation 13. From this power calculation, the
junction temperature, T
The reliable operation of the converter and the two LDO regulators
can be achieved only if the estimated die junction temperature of
the ADP5023 (Equation 14) is less than 125°C. Reliability and
mean time between failures (MTBF) is highly affected by increasing the junction temperature. Additional information about
product reliability can be found from the ADI Reliability Handbook,
which can be found at www.analog.com/reliability_handbook.
, can be used to estimate the junction
JA
is calculated from TA and PD using the
J
, can be estimated using Equation 14.
J
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 28
Page 17

Data Sheet ADP5023
V
THEORY OF OPERATION
AND
ENBK1
ENBK2
ENLDO
GM ERROR
CONTROL
VDDA
AVI N
VIN1
SW1
PGND1
EN1
EN2
EN3
ENABLE
AND MODE
CONTROL
PWM
COMP
I
LIMIT
LOW
CURRENT
DRIVER
ANTISHOOT
THROUGH
PWM/
PSM
BUCK1
AMP
SOFT START
ENBK1
COMP
UNDERVOLTAGE
PSM
LDO
LOCK OUT
75Ω
LDO
CONTROL
OUT1 FB1 FB2VOUT2
OSCILLATOR
SYSTEM
UNDERVOLTAGE
LOCKOUT
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
R1
75Ω
ENBK2
SOFT START
PSM
COMP
GM ERROR
AMP
PWM/
PSM
CONTROL
BUCK2
SEL
CURRENT
DRIVER
ANTISHOOT
THROUGH
OPMODE
B
Y
A
PWM
COMP
I
LIMIT
LOW
AND
MODE2
ADP5023
VIN2
SW2
PGND2
MODE
VIN3 AGND
Figure 45. Functional Block Diagram
POWER MANAGEMENT UNIT
The ADP5023 is a micropower management unit (micro PMU)
combining two step-down (buck) dc-to-dc converters and one
low dropout linear regulator (LDO). The high switching
frequency and tiny 24-lead LFCSP package allows a small
power management solution.
To combine these high performance regulators into the micro
PMU, there is a system controller allowing them to operate
together.
The buck regulators can operate in forced PWM mode if the
MODE pin is at a logic high level. In forced PWM mode, the
buck switching frequency is always constant and does not
change with the load current. If the MODE pin is at a logic
low level, the switching regulators operate in auto PWM/PSM
mode. In this mode, the regulators operate at fixed PWM
frequency when the load current is above the PSM current
threshold. When the load current falls below the PSM current
threshold, the regulator in question enters PSM, where the
switching occurs in bursts. The burst repetition rate is a
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 28
ENLDO
R2
FB3 VOUT3
600Ω
09889-003
function of the current load and the output capacitor value.
This operating mode reduces the switching and quiescent
current losses. The auto PWM/PSM mode transition is
controlled independently for each buck regulator. The two
bucks operate synchronized to each other.
ADP5023 has individual enable pins (EN1 to EN3) control-
The
ling the activation of each regulator. The regulators are activated
by a logic level high applied to the respective EN pin. EN1 controls
BUCK1, EN2 controls BUCK2, and EN3 controls LDO.
Regulator output voltages are set through external resistor
dividers or can be optionally factory programmed to default
values (see the Ordering Guide section).
When a regulator is turned on, the output voltage ramp rate is
controlled though a soft start circuit to avoid a large inrush
current due to the charging of the output capacitors.
Thermal Protection
In the event that the junction temperature rises above 150°C,
the thermal shutdown circuit turns off all the regulators.
Extreme junction temperatures can be the result of high current
Page 18

ADP5023 Data Sheet
operation, poor circuit board design, or high ambient
temperature. A 20°C hysteresis is included so that when thermal
shutdown occurs, the regulators do not return to operation until
the on-chip temperature drops below 130°C. When coming out
of thermal shutdown, all regulators restart with soft-start
control.
Undervoltage Lockout
To protect against battery discharge, undervoltage lockout
(UVLO) circuitry is integrated into the system. If the input
voltage on VIN1 drops below a typical 2.15 V UVLO threshold,
all channels shut down. In the buck channels, both the power
switch and the synchronous rectifier turn off. When the voltage
on VIN1 rises above the UVLO threshold, the part is enabled
once more.
Alternatively, the user can select device models with a UVLO
set at a higher level, suitable for USB applications. For these
models, the device reaches the turn-off threshold when the
input supply drops to 3.65 V typical.
In case of a thermal or UVLO event, the active pull-downs (if
factory enabled) are enabled to discharge the output capacitors
quickly. The pull-downs remain engaged until the input supply
voltage or thermal fault event is no longer present.
Enable/Shutdown
The ADP5023 has an individual control pin for each regulator.
A logic level high applied to the ENx pin activates a regulator,
whereas a logic level low turns off a regulator.
Figure 46 shows the regulator activation timings for the
ADP5023 when all enable pins are connected to AVIN. Also
shown is the active pull-down activation.
AVI N
VOUT1
VOUT3
VOUT2
BUCK1, LDO1
PULL-DOWNS
BUCK2
PULL-DOWN
30µs (MIN)
50µs (MIN)
Figure 46. Regulator Sequencing on ADP5023 (
VUVLO
EN1 = EN2 = EN3 = V
VPOR
AVIN
30µs (MIN )
50µs (MIN)
09889-148
)
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 28
Page 19

Data Sheet ADP5023
BUCK1 AND BUCK2
The buck uses a fixed frequency and high speed current mode
architecture. The buck operates with an input voltage of 2.3 V
to 5.5 V.
The buck output voltage is set through external resistor
dividers, shown in Figure 47 for BUCK1. The output voltage
can optionally be factory programmed to default values as
indicated in the Ordering Guide section. In this event, R1 and
R2 are not needed, and FB1 can be left unconnected. In all
cases, VOUT1 must be connected to the output capacitor. FB1
is 0.5 V.
VIN1
BUCK
V
= V
OUT1
FB1
Figure 47. BUCK1 External Output Voltage Setting
Control Scheme
The bucks operate with a fixed frequency, current mode PWM
control architecture at medium to high loads for high efficiency,
but shift to a power save mode (PSM) control scheme at light
loads to lower the regulation power losses. When operating in
fixed frequency PWM mode, the duty cycle of the integrated
switches is adjusted and regulates the output voltage. When
operating in PSM at light loads, the output voltage is controlled
in a hysteretic manner, with higher output voltage ripple. During
part of this time, the converter is able to stop switching and
enters an idle mode, which improves conversion efficiency.
PWM Mode
In PWM mode, the bucks operate at a fixed frequency of 3 MHz
set by an internal oscillator. At the start of each oscillator cycle,
the pFET switch is turned on, sending a positive voltage across
the inductor. Current in the inductor increases until the current
sense signal crosses the peak inductor current threshold that
turns off the pFET switch and turns on the nFET synchronous
rectifier. This sends a negative voltage across the inductor,
causing the inductor current to decrease. The synchronous
rectifier stays on for the rest of the cycle. The buck regulates the
output voltage by adjusting the peak inductor current threshold.
Power Save Mode (PSM)
The bucks smoothly transition to PSM operation when the load
current decreases below the PSM current threshold. When
either of the bucks enters PSM, an offset is induced in the PWM
regulation level, which makes the output voltage rise. When the
output voltage reaches a level approximately 1.5% above the
PWM regulation level, PWM operation is turned off. At this
point, both power switches are off, and the buck enters an idle
mode. The output capacitor discharges until the output voltage
falls to the PWM regulation voltage, at which point the device
VOUT1
L1
1µH
SW1
FB1
PGND
R1
+ 1
R2
R1
R2
C5
10µF
VOUT1
09889-008
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 28
drives the inductor to make the output voltage rise again to the
upper threshold. This process is repeated while the load current
is below the PSM current threshold.
The ADP5023 has a dedicated MODE pin controlling the PSM
and PWM operation. A high logic level applied to the MODE
pin forces both bucks to operate in PWM mode. A logic level
low sets the bucks to operate in auto PSM/PWM.
PSM Current Threshold
The PSM current threshold is set to 100 mA. The bucks employ
a scheme that enables this current to remain accurately
controlled, independent of input and output voltage levels. This
scheme also ensures that there is very little hysteresis between
the PSM current threshold for entry to and exit from the PSM.
The PSM current threshold is optimized for excellent efficiency
over all load currents.
Oscillator/Phasing of Inductor Switching
The ADP5023 ensures that both bucks operate at the same
switching frequency when both bucks are in PWM mode.
Additionally, the ADP5023 ensures that when both bucks are
in PWM mode, they operate out of phase, whereby the BUCK2
pFET starts conducting exactly half a clock period after the
BUCK1 pFET starts conducting.
Short-Circuit Protection
The bucks include frequency foldback to prevent output current
runaway on a hard short. When the voltage at the feedback pin
falls below half the target output voltage, indicating the possibility of a hard short at the output, the switching frequency is
reduced to half the internal oscillator frequency. The reduction
in the switching frequency allows more time for the inductor to
discharge, preventing a runaway of output current.
Soft Start
The bucks have an internal soft start function that ramps the
output voltage in a controlled manner upon startup, thereby
limiting the inrush current. This prevents possible input voltage
drops when a battery or a high impedance power source is
connected to the input of the converter.
Current Limit
Each buck has protection circuitry to limit the amount of
positive current flowing through the pFET switch and the
amount of negative current flowing through the synchronous
rectifier. The positive current limit on the power switch limits
the amount of current that can flow from the input to the
output. The negative current limit prevents the inductor
current from reversing direction and flowing out of the load.
100% Duty Operation
With a drop in input voltage, or with an increase in load
current, the buck may reach a limit where, even with the pFET
switch on 100% of the time, the output voltage drops below the
desired output voltage. At this limit, the buck transitions to a
mode where the pFET switch stays on 100% of the time. When
Page 20

ADP5023 Data Sheet
the input conditions change again and the required duty cycle
falls, the buck immediately restarts PWM regulation without
allowing overshoot on the output voltage.
Active Pull-Downs
All regulators have optional, factory-programmable, active pulldown resistors discharging the respective output capacitors
when the regulators are disabled. The pull-down resistors are
connected between VOUTx and AGND. Active pull-downs are
disabled when the regulators are turned on. The typical value of
the pull-down resistor is 600 for the LDO and 75 for the
bucks. Figure 46 shows the activation timings for the active
pull-downs during regulator activation and deactivation.
LDO
The ADP5023 contains one LDO with low quiescent current
and low dropout voltage, and provides up to 300 mA of output
current. Drawing a low 10 A quiescent current (typical) at no
load makes the LDO ideal for battery-operated portable
equipment.
The LDO operates with an input voltage of 1.7 V to 5.5 V. The
wide operating range makes these LDO suitable for cascading
configurations where the LDO supply voltage is provided from
one of the buck regulators.
The LDO output voltage is set through external resistor dividers
as shown in Figure 48 for LDO. The output voltage can
optionally be factory programmed to default values as indicated
in the Ordering Guide section. In this event, Ra and Rb are not
needed, and FB3 can be left unconnected. FB3 is 0.5 V.
VIN3
LDO1
V
= V
OUT3
FB3
Figure 48. LDO External Output Voltage Setting
VOUT3
Ra
FB3
Rb
Ra
+ 1
Rb
C7
1µF
VOUT3
09889-009
The LDO also provides high power supply rejection ratio
(PSRR), low output noise, and excellent line and load transient
response with only a small 1 µF ceramic input and output
capacitor.
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 28
Page 21

Data Sheet ADP5023
A
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
BUCK EXTERNAL COMPONENT SELECTION
Trade-offs between performance parameters such as efficiency
and transient response can be made by varying the choice of
external components in the applications circuit, as shown in
Figure 1.
Feedback Resistors
For the adjustable model, referring to Figure 47, the total
combined resistance for R1 and R2 is not to exceed 400 kΩ.
Inductor
The high switching frequency of the ADP5023 bucks allows the
selection of small chip inductors. For best performance, use
inductor values between 0.7 H and 3 H. Suggested inductors
are shown in Ta ble 8.
The peak-to-peak inductor current ripple is calculated using
the following equation:
VVV
−×
I
RIPPLE
)(
OUT
LfV
××
2
I
RIPPLE
OUT
=
IN
IN
SW
where:
is the switching frequency.
f
SW
L is the inductor value.
The minimum dc current rating of the inductor must be greater
than the inductor peak current. The inductor peak current is
calculated using the following equation:
II +=
PEAK
)(
MAXLOAD
Inductor conduction losses are caused by the flow of current
through the inductor, which has an associated internal dc
resistance (DCR). Larger sized inductors have smaller DCR,
which may decrease inductor conduction losses. Inductor core
losses are related to the magnetic permeability of the core material.
Because the bucks are high switching frequency dc-to-dc
converters, shielded ferrite core material is recommended for
its low core losses and low EMI.
Output Capacitor
Higher output capacitor values reduce the output voltage ripple
and improve load transient response. When choosing this value,
it is also important to account for the loss of capacitance due to
output voltage dc bias.
Ceramic capacitors are manufactured with a variety of dielectrics, each with a different behavior over temperature and
applied voltage. Capacitors must have a dielectric adequate
to ensure the minimum capacitance over the necessary
temperature range and dc bias conditions. X5R or X7R
dielectrics with a voltage rating of 6.3 V or 10 V are recommended for best performance. Y5V and Z5U dielectrics are
not recommended for use with any dc-to-dc converter because
of their poor temperature and dc bias characteristics.
The worst-case capacitance accounting for capacitor variation
over temperature, component tolerance, and voltage is calculated using the following equation:
= C
C
EFF
× (1 − TEMPCO) × (1 − TOL)
OUT
where:
is the effective capacitance at the operating voltage.
C
EFF
TEMPCO is the worst-case capacitor temperature coefficient.
TOL is the worst-case component tolerance.
In this example, the worst-case temperature coefficient
(TEMPCO) over −40°C to +85°C is assumed to be 15% for an
X5R dielectric. The tolerance of the capacitor (TOL) is assumed
to be 10% and C
is 9.2 F at 1.8 V, as shown in Figure 49.
OUT
Substituting these values in the equation yields
C
= 9.2 F × (1 − 0.15) × (1 − 0.1) = 7.0 F
EFF
To guarantee the performance of the bucks, it is imperative
that the effects of dc bias, temperature, and tolerances on the
behavior of the capacitors be evaluated for each application.
12
10
8
6
PACITANCE (µF)
4
C
2
0
0123456
DC BIAS VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 49. Capacitance vs. Voltage Characteristic
09889-010
Table 8. Suggested 1.0 μH Inductors
Vendor Model Dimensions (mm) I
Murata LQM2MPN1R0NG0B 2.0 × 1.6 × 0.9 1400 85
Murata LQM18FN1R0M00B 3.2 × 2.5 × 1.5 2300 54
Taiyo Yuden CBC3225T1R0MR 3.2 × 2.5 × 2.5 2000 71
Coilcraft XFL4020-102ME 4.0 × 4.0 × 2.1 5400 11
Coilcraft XPL2010-102ML 1.9 × 2.0 × 1.0 3750 89
Toko MDT2520-CN 2.5 × 2.0 × 1.2 1350 85
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 28
(mA) DCR (mΩ)
SAT
Page 22

ADP5023 Data Sheet
The peak-to-peak output voltage ripple for the selected output
capacitor and inductor values is calculated using the following
equation:
V
RIPPLE
I
RIPPLE
=
8
≈
Cf
××
()
2
OUTSW
V
IN
π
2
CLf
×××
OUTSW
Capacitors with lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) are
preferable to guarantee low output voltage ripple, as shown in
the following equation:
V
ESR ≤
COUT
RIPPLE
I
RIPPLE
The effective capacitance needed for stability, which includes
temperature and dc bias effects, is a minimum of 7 µF and a
maximum of 40 µF.
The buck regulators require 10 µF output capacitors to guarantee stability and response to rapid load variations and to transition
into and out of the PWM/PSM modes. A list of suggested capacitors is shown in Table 9. In certain applications where one or
both buck regulator powers a processor, the operating state is
known because it is controlled by software. In this condition,
the processor can drive the MODE pin according to the operating
state; consequently, it is possible to reduce the output capacitor
from 10 µF to 4.7 µF because the regulator does not expect a
large load variation when working in PSM mode (see Figure 50).
Input Capacitor
Higher value input capacitors help to reduce the input voltage
ripple and improve transient response. Maximum input
capacitor current is calculated using the following equation:
VVV
)(
−
IN
II
≥
CIN
OUT
MAXLOAD
)(
OUT
V
IN
2.3V TO
5.5V
1.7V TO
5.5V
AVI N
C
FILT
0.1µF
4.7µF
OFF
4.7µF
OFF
C2
C3
1µF
VIN1
C1
ON
EN1
VIN2
EN2
ON
EN3
VIN3
Figure 50. Processor System Power Management with PSM/PWM Control
HOUSEKEEPING
EN1
EN2
EN3
ADP5023
AGND
BUCK1
MODE
MODE
BUCK2
LDO
(ANALOG)
To minimize supply noise, place the input capacitor as close as
possible to the VINx pin of the buck. As with the output
capacitor, a low ESR capacitor is recommended.
The effective capacitance needed for stability, which includes
temperature and dc bias effects, is a minimum of 3 µF and a
maximum of 10 µF. A list of suggested capacitors is shown in
Tabl e 10 .
Table 9. Suggested 10 μF Capacitors
Voltage
Case
Rating
Vendor Type Model
Size
(V)
Murata X5R GRM188R60J106 0603 6.3
Taiyo Yuden X5R JMK107BJ475 0603 6.3
TDK X5R C1608JB0J106K 0603 6.3
Panasonic X5R ECJ1VB0J106M 0603 6.3
Table 10. Suggested 4.7 μF Capacitors
Voltage
Rating
Vendor Type Model
Case
Size
(V)
Murata X5R GRM188R60J475ME19D 0402 6.3
Taiyo Yuden X5R JMK107BJ475 0402 6.3
Panasonic X5R ECJ-0EB0J475M 0402 6.3
Table 11. Suggested 1.0 μF Capacitors
Voltage
Rating
Vendor Type Model
Case
Size
(V)
Murata X5R GRM155B30J105K 0402 6.3
TDK X5R C1005JB0J105KT 0402 6.3
Panasonic X5R ECJ0EB0J105K 0402 6.3
Taiyo
X5R LMK105BJ105MV-F 0402 10.0
Yuden
VOUT1
SW1
FB1
PGND1
MODE
VOUT2
SW2
FB2
PGND2
VOUT3
FB3
L1 1µH
R1
R2
PWM
L2 1µH
R3
R4
R5
R6
C5
10µF
PSM/PWM
C6
10µF
C7
1µF
V
OUT1
800mA
V
OUT2
800mA
V
OUT3
300mA
AT
AT
AT
09889-248
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 28
Page 23

Data Sheet ADP5023
A
LDO EXTERNAL COMPONENT SELECTION
Feedback Resistors
For the adjustable model, the maximum value of Rb is not to
exceed 200 kΩ (see Figure 48).
Output Capacitor
The ADP5023 LDO is designed for operation with small, spacesaving ceramic capacitors, but functions with most commonly
used capacitors as long as care is taken with the ESR value. The
ESR of the output capacitor affects stability of the LDO control
loop. A minimum of 0.70 µF capacitance with an ESR of 1 Ω or
less is recommended to ensure stability of the ADP5023. Transient
response to changes in load current is also affected by output
capacitance. Using a larger value of output capacitance improves
the transient response of the ADP5023 to large changes in load
current.
Input Bypass Capacitor
Connecting a 1 µF capacitor from VIN3 to ground reduces
the circuit sensitivity to printed circuit board (PCB) layout,
especially when long input traces or high source impedance
are encountered. If greater than 1 µF of output capacitance is
required, increase the input capacitor to match it.
Input and Output Capacitor Properties
Use any good quality ceramic capacitors with the ADP5023 as
long as they meet the minimum capacitance and maximum ESR
requirements. Ceramic capacitors are manufactured with a variety
of dielectrics, each with a different behavior over temperature
and applied voltage. Capacitors must have a dielectric adequate
to ensure the minimum capacitance over the necessary temperature range and dc bias conditions. X5R or X7R dielectrics with a
voltage rating of 6.3 V or 10 V are recommended for best performance. Y5V and Z5U dielectrics are not recommended for use
with any LDO because of their poor temperature and dc bias
characteristics.
Figure 51
of a 0402 1 µF, 10 V, X5R capacitor. The voltage stability of a
capacitor is strongly influenced by the capacitor size and voltage
rating. In general, a capacitor in a larger package or higher voltage
rating exhibits better stability. The temperature variation of the
depicts the capacitance vs. voltage bias characteristic
X5R dielectric is about ±15% over the −40°C to +85°C temperature range and is not a function of package or voltage rating.
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
PACITANCE (µF)
0.4
C
0.2
0
0123456
Figure 51. Capacitance vs. Voltage Characteristic
DC BIAS VOLTAGE (V)
09889-012
Use the following equation to determine the worst-case capacitance accounting for capacitor variation over temperature,
component tolerance, and voltage.
= C
C
EFF
× (1 − TEMPCO) × (1 − TOL)
BIAS
where:
is the effective capacitance at the operating voltage.
C
BIAS
TEMPCO is the worst-case capacitor temperature coefficient.
TOL is the worst-case component tolerance.
In this example, the worst-case temperature coefficient
(TEMPCO) over −40°C to +85°C is assumed to be 15% for an
X5R dielectric. The tolerance of the capacitor (TOL) is assumed
to be 10% and C
is 0.85 F at 1.8 V as shown in Figure 51.
BIAS
Substituting these values into the following equation:
C
= 0.85 F × (1 − 0.15) × (1 − 0.1) = 0.65 F
EFF
Therefore, the capacitor chosen in this example meets the
minimum capacitance requirement of the LDO over
temperature and tolerance at the chosen output voltage.
To guarantee the performance of the ADP5023, it is imperative
that the effects of dc bias, temperature, and tolerances on the
behavior of the capacitors are evaluated for each application.
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 28
Page 24

ADP5023 Data Sheet
PCB LAYOUT GUIDELINES
Poor layout can affect ADP5023 performance, causing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) problems, ground bounce, and voltage losses. Poor
layout can also affect regulation and stability. A good layout is
implemented using the following guidelines. Also, refer to User
Guide UG-271
• Place the inductor, input capacitor, and output capacitor
close to the IC using short tracks. These components carry
high switching frequencies, and large tracks act as antennas.
• Route the output voltage path away from the inductor and
SW node to minimize noise and magnetic interference.
.
• Maximize the size of ground metal on the component side
to help with thermal dissipation.
• Use a ground plane with several vias connecting to the
component side ground to further reduce noise
interference on sensitive circuit nodes.
• Connect VIN1, VIN2, and AVIN together close to the IC
using short tracks.
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 28
Page 25

Data Sheet ADP5023
TYPICAL APPLICATION SCHEMATICS
AVIN
C
FILT
2.3V TO
5.5V
1.7V TO
5.5V
0.1µF
4.7µF
OFF
4.7µF
OFF
1µF
VIN1
C1
ON
EN1
VIN2
C2
EN2
ON
EN3
VIN3
C3
Figure 52. ADP5023 Fixed Output Voltages with Enable Pins
AVI N
C
FILT
2.3V TO
5.5V
1.7V TO
5.5V
0.1µF
4.7µF
OFF
4.7µF
OFF
1µF
VIN1
C1
ON
EN1
VIN2
C2
EN2
ON
EN3
VIN3
C3
Figure 53. ADP5023 Adjustable Output Voltages with Enable Pins
HOUSEKEEPING
EN1
EN2
EN3
(ANALOG)
ADP5023
AGND
HOUSEKEEPING
EN1
EN2
EN3
(ANALOG)
ADP5023
AGND
BUCK1
MODE
MODE
BUCK2
LDO
BUCK1
MODE
MODE
BUCK2
LDO
VOUT1
SW1
FB1
PGND1
MODE
VOUT2
SW2
FB2
PGND2
VOUT3
FB3
VOUT1
SW1
FB1
PGND1
MODE
VOUT2
SW2
FB2
PGND2
VOUT3
FB3
L1 1µH
PWM
L2 1µH
L1 1µH
R1
R2
PWM
L2 1µH
R3
R4
R5
R6
C5
10µF
PSM/PWM
C6
10µF
C7
1µF
C5
10µF
PSM/PWM
C6
10µF
C7
1µF
V
OUT1
800mA
V
OUT2
800mA
V
OUT3
300mA
V
OUT1
800mA
V
OUT2
800mA
V
OUT3
300mA
AT
AT
AT
09889-150
AT
AT
AT
09889-151
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 28
Page 26

ADP5023 Data Sheet
BILL OF MATERIALS
Table 12.
Reference Value Part Number Vendor Package or Dimension (mm)
C
0.1 µF, X5R, 6.3 V JMK105BJ104MV-F Taiyo-Yuden 0402
AVIN
C3, C7 1 µF, X5R, 6.3 V LMK105BJ105MV-F Taiyo-Yuden 0402
C1, C2 4.7 µF, X5R, 6.3 V ECJ-0EB0J475M Panasonic-ECG 0402
C5, C6 10 µF, X5R, 6.3 V JMK107BJ106MA-T Taiyo-Yuden 0603
L1, L2 1 µH, 0.18 Ω, 850 mA BRC1608T1R0M Taiyo-Yuden 0603
1 µH, 0.085 Ω, 1400 mA LQM2MPN1R0NG0B Murata 2.0 × 1.6 × 0.9
1 µH, 0.059 Ω, 900 mA EPL2014-102ML Coilcraft 2.0 × 2.0 × 1.4
1 µH, 0.086 Ω, 1350 mA MDT2520-CN Toko 2.5 × 2.0 × 1.2
IC1 Three-regulator micro PMU ADP5023 Analog Devices 24-lead LFCSP
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 28
Page 27

Data Sheet ADP5023
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
PIN 1
INDICATOR
0.80
0.75
0.70
SEATING
PLANE
4.10
4.00 SQ
3.90
0.50
BSC
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
COPLANARITY
0.08
0.30
0.25
0.20
19
18
EXPOSED
13
12
BOTTOM VIEWTOP VIEW
24
PAD
7
FOR PROPER CONNECTION OF
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONFIGURATION AND
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
N
I
1
P
A
R
O
T
D
C
I
N
I
1
2.20
2.10 SQ
2.00
6
0.25 MIN
COMPLIANTTOJEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-WGGD-8.
Figure 54. 24-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_WQ]
4 mm × 4 mm Body, Very Very Thin Quad
(CP-24-10)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature
Model1
Range
ADP5023ACPZ-R7 −40°C to +125°C Adjustable 2.25 V
ADP5023ACPZ-1-R7 −40°C to +125°C
ADP5023CP-EVALZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
2
For additional options, contact a local sales or distribution representative. Additional options available are:
BUCK1 and BUCK2: 3.3 V, 3.0 V, 2.8 V, 2.5 V, 2.3 V, 2.0 V, 1.82 V, 1.8 V, 1.6 V, 1.5 V, 1.3 V, 1.2 V, 1.1 V, 1.0 V, 0.9 V, 0.8 V, or adjustable.
LDO: 3.3 V, 3.0 V, 2.9 V, 2.8 V, 2.775 V, 2.5 V, 2.0 V, 1.875 V, 1.8 V, 1.75 V, 1.7 V, 1.65 V, 1.6 V, 1.55 V, 1.5 V, 1.2 V, or adjustable.
3
UVLO: 2.25 V or 3.9 V.
4
BUCK1, BUCK2, LDO: Active pull-down resistor is programmable to be either enabled or disabled.
Output
Vol tage2 UVLO3
VOUT1 = 1.2 V
2.25 V
VOUT2 = 3.3 V
VOUT3 = 2.8 V
Active
Pull-Down4 Package Description
Enabled on
all channels
Enabled on
all channels
24-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package
[LFCSP_WQ]
24-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package
[LFCSP_WQ]
Evaluation Board for
ADP5023ACPZ-R7
072809A
Package
Option
CP-24-10
CP-24-10
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 28
Page 28

ADP5023 Data Sheet
NOTES
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D09889-0-8/11(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...