Page 1
2300 MHz to 2900 MHz Balanced Mixer,
V
FEATURES
RF frequency range of 2300 MHz to 2900 MHz
IF frequency range of dc to 450 MHz
Power conversion loss: 7.7 dB
SSB noise figure of 7.6 dB
Input IP3 of 31 dBm
Typical LO drive of 0 dBm
Single-ended, 50 Ω RF and LO input ports
High isolation SPDT LO input switch
Single-supply operation: 3.3 V to 5 V
Exposed pad, 5 mm × 5 mm 20-lead LFCSP
1500 V HBM/1250 V FICDM ESD performance
APPLICATIONS
Cellular base station receivers
Transmit observation receivers
Radio link downconverters
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADL5363 uses a highly linear, doubly balanced passive
mixer core along with integrated RF and local oscillator (LO)
balancing circuitry to allow for single-ended operation. The
ADL5363 incorporates an RF balun to provide optimal
performance over a 2300 MHz to 2900 MHz input frequency
range. The balanced passive mixer arrangement provides good
LO-to-RF leakage, typically better than −30 dBm, and excellent
intermodulation performance. The balanced mixer core also
provides extremely high input linearity, allowing the device to
be used in demanding cellular applications where in-band
blocking signals might otherwise result in the degradation of
dynamic performance.
LO Buffer and RF Balun
ADL5363
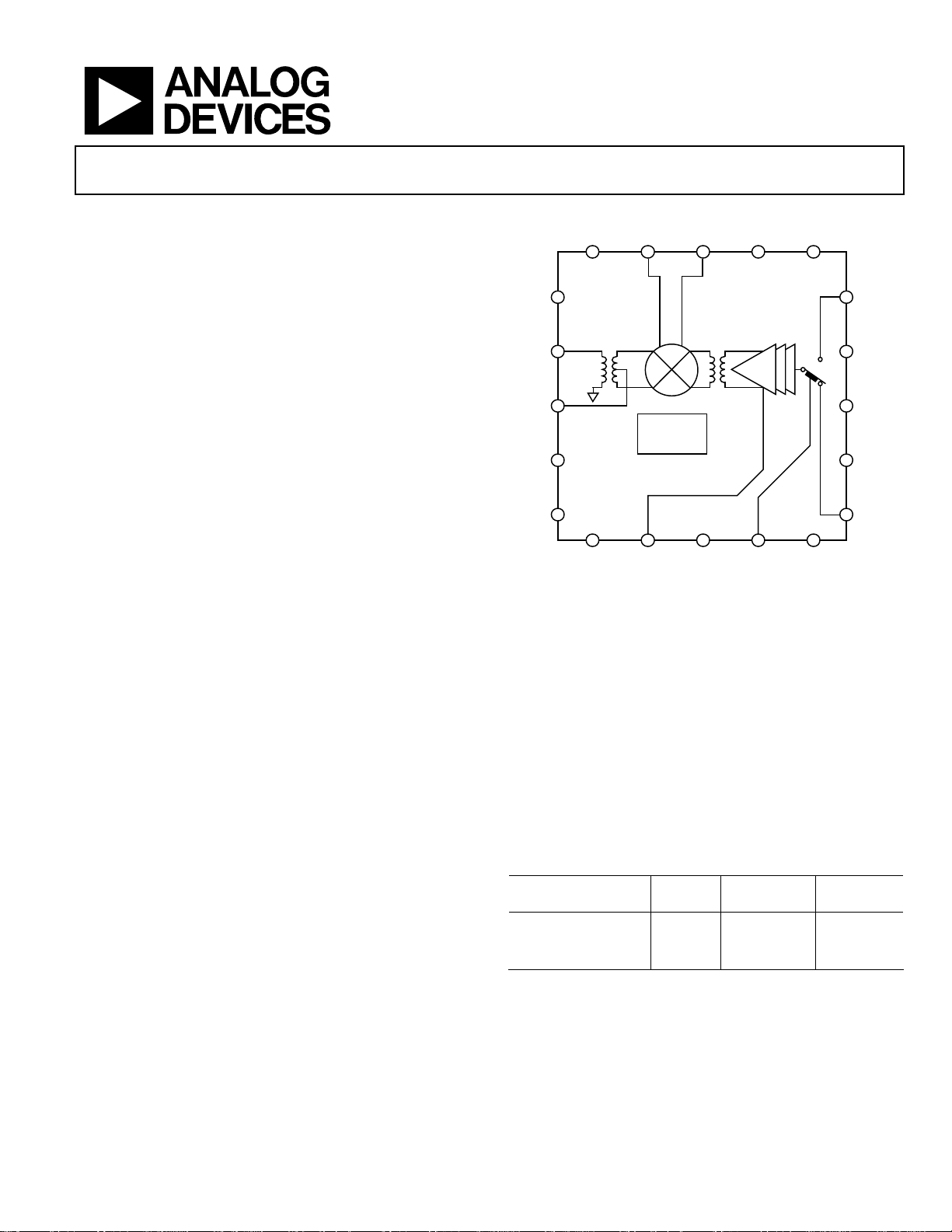
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
CMI IFOP IFON PWDN COMM
20 19 18 17 16
1
VPMX
2
RFIN
3
RFCT
BIAS
GENERATOR
4
COMM
5
COMM
6 7 8 9 10
VLO3 LGM3 VLO2 LOSW NC
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 1.
The ADL5363 provides two switched LO paths that can be used
in TDD applications where it is desirable to rapidly switch between
two local oscillators. LO current can be externally set using a
resistor to minimize dc current commensurate with the desired
level of performance. For low voltage applications, the ADL5363 is
capable of operation at voltages down to 3.3 V with substantially
reduced current. For low voltage operation, an additional logic
pin is provided to power down (<200 µA) the circuit when desired.
The ADL5363 is fabricated using a BiCMOS high performance
IC process. The device is available in a 5 mm × 5 mm, 20-lead
LFCSP and operates over a −40°C to +85°C temperature range.
An evaluation board is also available.
ADL5363
15
LOI2
14
VPSW
13
VGS1
12
VGS0
11
LOI1
9914-001
Table 1. Passive Mixers
RF Frequency (MHz)
Single
Mixer
Single Mixer
and IF Amp
Dual Mixer
and IF Amp
500 to 1700 ADL5367 ADL5357 ADL5358
1200 to 2500 ADL5365 ADL5355 ADL5356
2300 to 2900 ADL5363 ADL5353 ADL5354
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

ADL5363
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
5 V Performance........................................................................... 4
3.3 V Performance........................................................................ 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 7
5 V Performance........................................................................... 7
3.3 V Performance...................................................................... 14
Upconversion.............................................................................. 15
Spurious Performance ............................................................... 16
Circuit Description......................................................................... 17
RF Subsystem.............................................................................. 17
LO Subsystem ............................................................................. 18
Applications Information.............................................................. 19
Basic Connections...................................................................... 19
IF Port.......................................................................................... 19
Bias Resistor Selection ............................................................... 19
Mixer VGS Control DAC.......................................................... 19
Evaluation Board............................................................................ 20
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 23
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 23
REVISION HISTORY
7/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 24
Page 3
ADL5363
SPECIFICATIONS
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, ZO = 50 Ω, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
RF INPUT INTERFACE
Return Loss Tunable to >20 dB over a limited bandwidth 16 dB
Input Impedance 50 Ω
RF Frequency Range 2300 2900 MHz
OUTPUT INTERFACE
Output Impedance Differential impedance, f = 200 MHz 33||-0.3 Ω||pF
IF Frequency Range dc 450 MHz
DC Bias Voltage1 Externally generated 3.3 5.0 5.5 V
LO INTERFACE
LO Power −6 0 +10 dBm
Return Loss 15 dB
Input Impedance 50 Ω
LO Frequency Range 2330 3350 MHz
POWER-DOWN (PWDN) INTERFACE
PWDN Threshold 1.0 V
Logic 0 Level 0.4 V
Logic 1 Level 1.4 V
PWDN Response Time Device enabled, IF output to 90% of its final level 160 ns
Device disabled, supply current <5 mA 220 ns
PWDN Input Bias Current Device enabled 0.0 μA
Device disabled 70 μA
1
Apply the supply voltage from the external circuit through the choke inductors.
2
The PWDN function is intended for use with VS ≤ 3.6 V only.
2
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 24
Page 4
ADL5363
5 V PERFORMANCE
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Power Conversion Loss Including 1:1 IF port transformer and PCB loss 7.7 dB
SSB Noise Figure 7.6 dB
Input Third-Order Intercept (IIP3)
= 2534.5 MHz, f
f
RF1
= 2535.5 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz,
RF2
each RF tone at 0 dBm
Input Second-Order Intercept (IIP2)
= 2535 MHz, f
f
RF1
= 2585 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz,
RF2
each RF tone at 0 dBm
Input 1 dB Compression Point (IP1dB)1 Exceeding 20 dBm RF power results in damage to the device 25 dBm
LO-to-IF Leakage Unfiltered IF output −22 dBm
LO-to-RF Leakage −32 dBm
RF-to-IF Isolation −44 dBc
IF/2 Spurious −10 dBm input power −61 dBc
IF/3 Spurious −10 dBm input power −70 dBc
POWER SUPPLY
Positive Supply Voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V
Quiescent Current VS = 5 V 100 mA
1
Exceeding 20 dBm RF power results in damage to the device.
31 dBm
62 dBm
3.3 V PERFORMANCE
VS = 3.3 V, IS = 60 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, R9 = 226 Ω, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω,
unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Power Conversion Loss Including 1:1 IF port transformer and PCB loss 7.4 dB
SSB Noise Figure 6.8 dB
Input Third-Order Intercept (IIP3)
= 2534.5 MHz, f
f
RF1
= 2535.5 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz,
RF2
each RF tone at 0 dBm
Input Second-Order Intercept (IIP2)
= 2535 MHz, f
f
RF1
= 2585 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz,
RF2
each RF tone at 0 dBm
POWER SUPPLY
Positive Supply Voltage 3.3 V
Quiescent Current VS = 5 V 60 mA
26 dBm
56 dBm
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 24
Page 5

ADL5363
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage, VS 5.5 V
RF Input Level 20 dBm
LO Input Level 13 dBm
IFOP, IFON Bias Voltage 6.0 V
VGS0, VGS1, LOSW, PWDN 5.5 V
Internal Power Dissipation 0.5 W
Thermal Resistance, θJA 25°C/W
Temperature
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) 260°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 24
Page 6
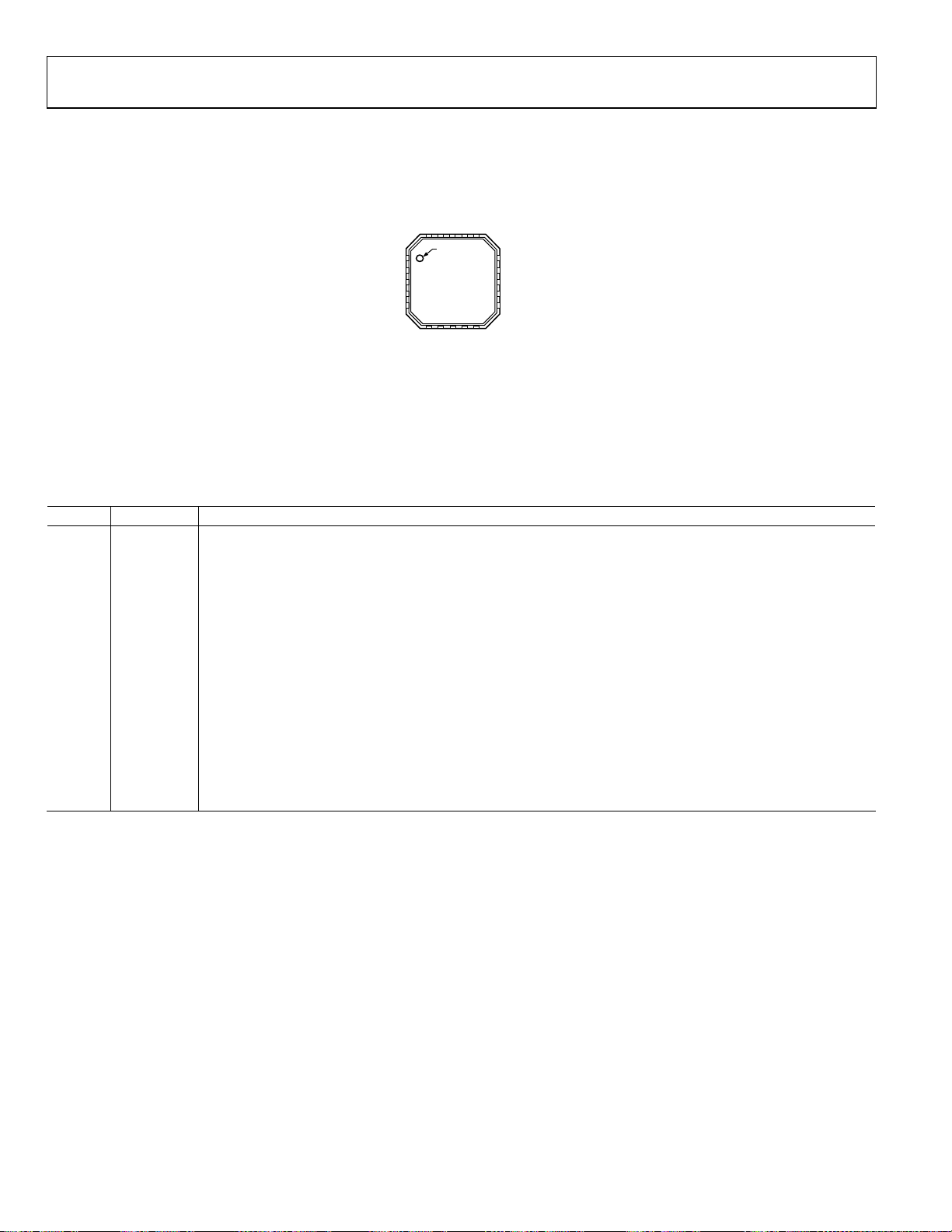
ADL5363
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DN
VCMI
IFOP
COMM
IFON
PW
17
19
18
PIN 1
INDICATOR
9
8
7
VLO2
LGM3
LOSW
16
10
NC
15 LOI2
14 VPSW
13 VGS1
12 VGS0
11 LOI1
09914-002
20
1VPMX
2RFIN
ADL5363
3RFCT
TOP VIEW
4COMM
(Not to Scale)
5COMM
6
NOTES
1.2 NC = NO CONNECT . DO NOT CONNECT
TO THIS PIN.
. EXPOSED PAD. MUST BE SOLDERED
TO GROUND.
VLO3
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 VPMX Positive Supply Voltage.
2 RFIN RF Input. Must be ac-coupled.
3 RFCT RF Balun Center Tap (AC Ground).
4, 5,16 COMM Device Common (DC Ground).
6, 8 VLO3, VLO2 Positive Supply Voltages for LO Amplifier.
7 LGM3 LO Amplifier Bias Control.
9 LOSW LO Switch. LOI1 selected for 0 V, and LOI2 selected for 3 V.
10 NC No Connect.
11, 15 LOI1, LOI2 LO Inputs. Must be ac-coupled.
12, 13 VGS0, VGS1 Mixer Gate Bias Controls. 3 V logic. Ground these pins for nominal setting.
14 VPSW Positive Supply Voltage for LO Switch.
17 PWDN Power Down. Connect this pin to ground for normal operation and connect this pin to 3.0 V for disable mode.
18, 19 IFON, IFOP Differential IF Outputs.
20 VCMI No Connect. This pin can be grounded.
EPAD (EP) Exposed pad. Must be soldered to ground.
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 24
Page 7
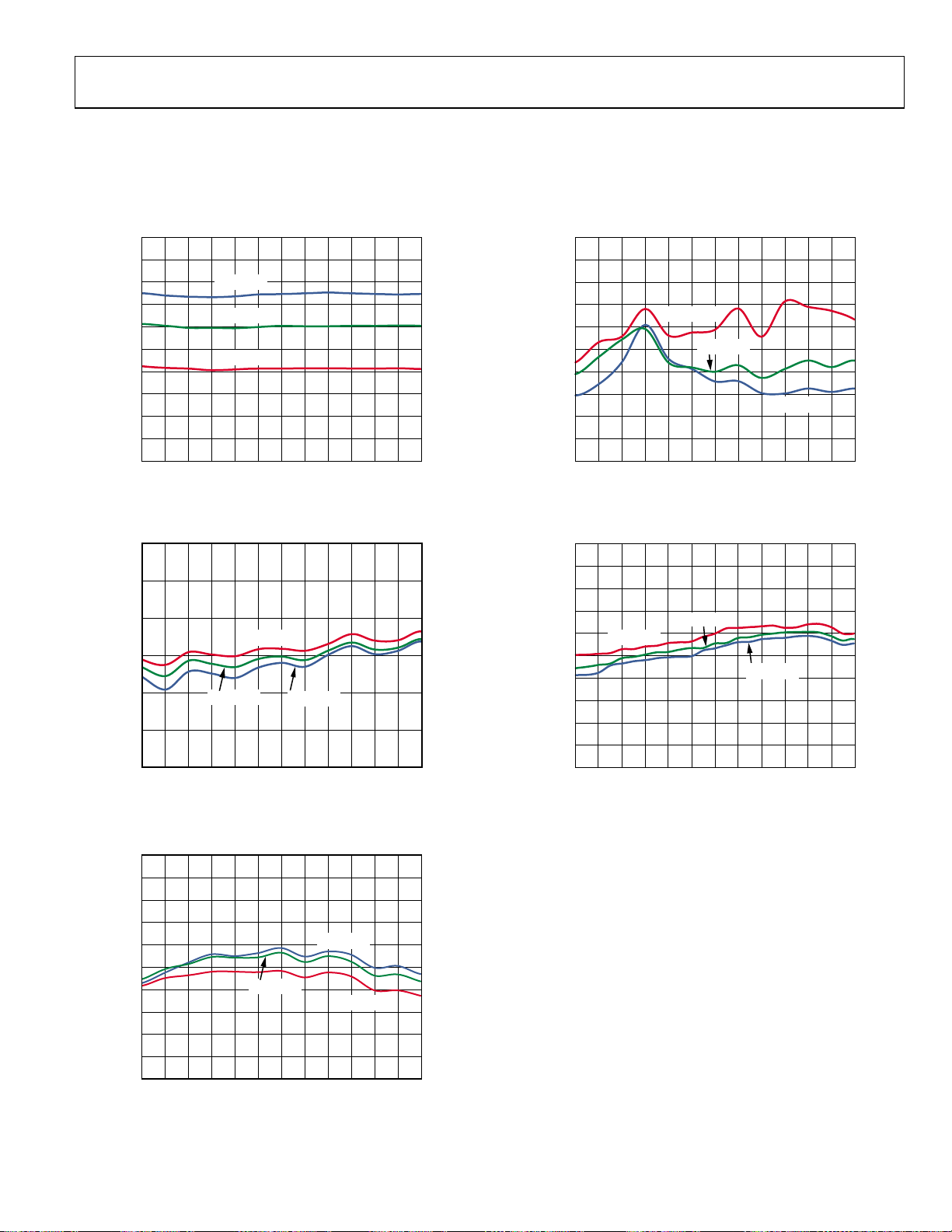
ADL5363
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
5 V PERFORMANCE
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
97
96
95
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902.852.802. 752.70
TA = –40°C
T
= +25°C
A
T
= +85°C
A
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
09914-003
Figure 3. Supply Current vs. RF Frequency
11
10
9
TA = +85°C
8
7
CONVERSION L OSS (dB)
6
5
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
TA = –40°C
09914-004
Figure 4. Power Conversion Loss vs. RF Frequency
40
38
36
34
32
30
28
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
26
24
22
20
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
TA = –40°C
TA = +85°C
09914-005
Figure 5. Input IP3 vs. RF Frequency
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 24
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
INPUT IP2 (dBm)
55
50
45
40
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 6. Input IP2 vs. RF Frequency
10.0
9.5
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
SSB NOISE FIGURE (dB)
6.0
5.5
5.0
TA = +85°C
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 7. SSB Noise Figure vs. RF Frequency
TA = –40°C
TA = –40°C
09914-006
09914-007
Page 8
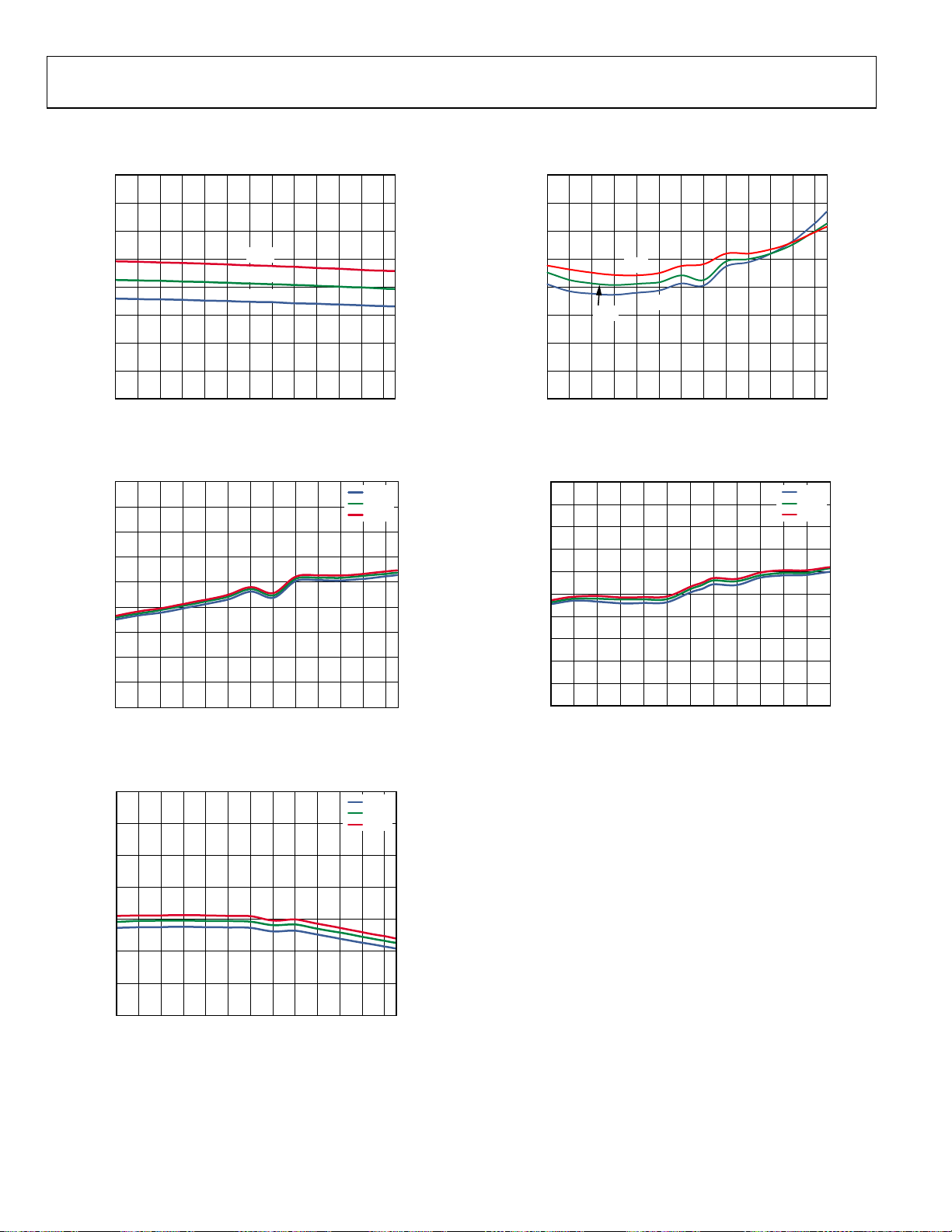
ADL5363
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
140
74
130
120
110
100
90
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
80
70
60
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 8070605040
5.25V
5.00V
4.75V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 8. Supply Current vs. Temperature
9.1
8.8
8.5
8.2
7.9
7.6
7.3
CONVERSION LOSS (dB)
7.0
6.7
6.4
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 8070605040
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 9. Power Conversion Loss vs. Temperature
39
37
4.75V
5.00V
5.25V
4.75V
5.00V
5.25V
71
68
65
62
59
INPUT IP2 (dBm)
56
53
50
09914-008
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 8070605040
5.00V
5.25V
4.75V
TEMPERATURE (° C)
09914-011
Figure 11. Input IP2 vs. Temperature
10.0
9.5
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
SSB NOISE FIGURE (dB)
6.0
5.5
5.0
09914-009
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 8070605040
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
4.75V
5.00V
5.25V
09914-012
Figure 12. SSB Noise Figure vs. Temperature
35
33
31
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
29
27
25
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 8070605040
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
Figure 10. Input IP3 vs. Temperature
09914-010
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 24
Page 9

ADL5363
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
120
100
115
110
105
100
95
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
90
85
80
30 80 130 180 230 280 430380330
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 13. Supply Current vs. IF Frequency
8.4
8.2
8.0
7.8
7.6
7.4
CONVERSION L OSS (dB)
7.2
TA = +85°C
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
TA = –40°C
90
80
70
INPUT IP2 (dBm)
60
50
40
09914-013
30 80 130 180 230 280 430380330
TA = +85°C
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40°C
09914-016
Figure 16. Input IP2 vs. IF Frequency
10.0
9.5
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
SSB NOISE FIGURE (dB)
7.0
6.5
7.0
30 80 130 180 230 280 430380330
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 14. Power Conversion Loss vs. IF Frequency
41
38
35
32
29
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
26
23
20
30 80 130 180 230 280 430380330
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 15. Input IP3 vs. IF Frequency
09914-014
09914-015
6.0
30 80 130 180 230 280 430380330
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 17. SSB Noise Figure vs. IF Frequency
09914-017
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 24
Page 10

ADL5363
–
–
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
12
11
10
9
8
7
CONVERSION LOS S (dB)
6
5
4
–6 –4 –2 0 2 4 6 8 10
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
LO POWER (dBm)
TA = –40°C
Figure 18. Power Conversion Loss vs. LO Power
36
09914-018
30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
IF/2 SPURIOUS (dBc)
–65
–70
–75
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
TA = –40°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 21. IF/2 Spurious vs. RF Frequency
20
09914-021
34
32
30
28
26
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
24
22
20
–6–4–20246810
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
LO POWER (dBm)
Figure 19. Input IP3 vs. LO Power
80
70
60
50
40
30
INPUT IP2 (dBm)
20
TA = –40°C
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
–30
–40
–50
–60
IF/3 SPURIOUS (dBc)
–70
–80
–90
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
09914-019
Figure 22. IF/3 Spurious vs. RF Frequency
TA = +85°C
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
09914-022
10
0
–6–4–20246810
Figure 20. Input IP2 vs. LO Power
LO POWER (dBm)
09914-020
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 24
Page 11

ADL5363
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
100
80
60
40
PERCENTAGE (%)
20
MEAN: 101.06
SD: 0.0008%
0
I
(mA)
SUPPLY
12011010080 90
09914-023
Figure 23. Supply Current Distribution
100
80
60
40
PERCENTAGE (%)
20
MEAN: 7.7
SD: 0.104%
0
CONVERSION LOSS DISTRIBUTION (dB)
7.27.6 7. 47.88.2 8.0
09914-024
Figure 24.Conversion Loss Distribution
100
80
60
40
PERCENTAGE (%)
20
MEAN: 31.13
SD: 0.286%
0
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
3930 33 362721 24
09914-025
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
RESISTANCE (Ω)
15
10
5
0
80 130 180 230 280 330 380
30 430
RESISTANCE (Ω)
CAPACITANCE (pF)
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 26. IF Output Impedance (R Parallel, C Equivalent)
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
–12
–14
RF RETURN LOSS (dB)
–16
–18
–20
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 27. RF Port Return Loss, Fixed IF
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
–24
–27
–30
LO RETURN LOSS (dB)
–33
–36
–39
–42
–45
2.50 3.10
2.55 2.60 2.65 2.70 2.75 2.80 2.85 2.90 2.95 3.00 3. 05
LO FREQUENCY (GHz)
SELECTED
UNSELECTED
50
4
3
2
1
0
–1
CAPACITANCE (pF )
–2
–3
–4
0
09914-027
09914-028
09914-026
Figure 25. Input IP3 Distribution
Figure 28. LO Return Loss, Selected and Unselected
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 24
Page 12

ADL5363
–
–
–
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
60
57
54
51
48
45
42
39
LO SWITCH ISOLATION (dB)
36
33
30
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.902.852.802.752.70
TA = +85°C
T
= +25°C
A
RF FREQUENCY (GHz )
Figure 29. LO Switch Isolation vs. RF Frequency
30
–35
–40
–45
–50
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dBc)
–55
–60
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 30. RF-to-IF Isolation vs. RF Frequency
5
TA = –40°C
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
09914-029
09914-030
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
TA = +85°C
–30
LO-TO -IF LEAKAG E (dBm)
–35
–40
–45
TA = +25°C
2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.70 2.75 2.80 3.103.00 3.052.952.902.85
TA = –40°C
LO FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 32. LO-to-RF Leakage vs. LO Frequency
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
2xLO LEAKAGE (dBm)
–45
–50
–55
–60
2.50 3.10
2.55 2.60 2.65 2.70 2.75 2.80 2.85 2.90 2.95 3.00 3.05
2xLO TO RF
2xLO TO IF
LO FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 33. 2LO Leakage vs. LO Frequency
52
09914-032
09914-033
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
LO-TO -IF LEAKAG E (dBm)
–35
–40
2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.70 2.75 2.80 3.103.00 3.052.952.902.85
LO FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 31. LO-to-IF Leakage vs. LO Frequency
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
09914-031
–55
–58
–61
–64
–67
3xLO LEAKAGE (dBm)
–70
–73
–76
2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.70 2.75 2.80 2.85 2.90 2.95 3.00 3.05
3xLO TO RF
3xLO TO IF
LO FREQUE NCY (GHz)
Figure 34. 3LO Leakage vs. LO Frequency
3.10
09914-034
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 24
Page 13

ADL5363
m
R
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
12
VGS = 0, 0
VGS = 0, 1
11
VGS = 1, 0
VGS = 1, 1
10
9
8
7
6
5
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
4
3
2
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.902. 852. 802.752.70
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
GAIN
NOISE FIGURE
Figure 35. Power Conversion Loss and SSB Noise Figure vs. RF Frequency
40
VGS = 0, 0
VGS = 0, 1
38
VGS = 1, 0
VGS = 1, 1
36
34
)
32
30
28
INPUT IP3 (dB
26
24
22
20
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
RF FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 36. Input IP3 vs. RF Frequency
23
21
19
17
15
13
11
9
SSB NOISE FIGURE (dB)
7
5
3
09914-035
11.0
E(dB)
10.5
10.0
9.5
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
CONVERSION LOSS AND SSB NOISE FIGU
7.0
600 700 900800 1000 1100 1200 1300 1 400 1500 1600 1700 1800
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
CONVERSION LOSS (dB)
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
BIAS RESI STOR VALUE (Ω)
32
31
30
29
28
27
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
26
25
24
Figure 37. Power Conversion Loss, SSB Noise Figure, and
Input IP3 vs. IF Bias Resistor Value
140
130
120
110
100
90
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
80
70
60
600 1800
09914-036
700 900800 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700
BIAS RESIST OR VALUE (Ω)
09914-038
Figure 38. Supply Current vs. Bias Resistor Value
09914-037
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 24
Page 14

ADL5363
3.3 V PERFORMANCE
VS = 3.3 V, IS = 60 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
67
100
65
63
TA = +85°C
61
59
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
TA = +25°C
57
56
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = –40°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 39. Supply Current vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
CONVERSION L OSS (dB)
6.0
5.5
5.0
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
TA = –40°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 40. Power Conversion Loss vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V
34
31
90
80
70
60
50
INPUT IP2 (dBm)
40
30
20
09914-039
TA = –40°C
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
09914-042
Figure 42. Input IP2 vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
SSB NOISE FIGURE (dB)
5.0
4.5
4.0
09914-040
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
FREQUENCY (GHz)
TA = –40°C
09914-043
Figure 43. SSB Noise Figure vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V
28
25
22
19
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
16
13
10
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 41. Input IP3 vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V
TA = –40°C
TA = +85°C
09914-041
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 24
Page 15

ADL5363
UPCONVERSION
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and ZO = 50 Ω, unless
otherwise noted.
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
CONVERSION LOSS (dB)
5
4
3
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.902. 852.802.752.70
TA = –40°C
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
RF FREQ UENCY (GHz)
Figure 44. Power Conversion Loss vs. RF Frequency, V
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
23
22
21
20
Figure 45. Input IP3 vs. RF Frequency, V
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
TA = –40°C
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902.852.802.752.70
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
S
= 5 V, Upconversion
= 5 V, Upconversion
S
09914-044
09914-045
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
CONVERSION LOSS (dB)
5.0
4.5
4.0
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
TA = –40°C
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 2.902.852.802.752. 70
RF FREQUENCY (GHz )
Figure 46. Power Conversion Loss vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V, Upconversion
35
33
31
29
TA = –40°C
27
25
23
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
21
19
17
15
2.30 2.35 2.40 2.45 2.50 2.55 2. 60 2.65 2.902.852.802.752.70
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 47. Input IP3 vs. RF Frequency at 3.3 V, Upconversion
09914-046
09914-047
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 24
Page 16

ADL5363
SPURIOUS PERFORMANCE
(N × fRF) − (M × fLO) spur measurements were made using the standard evaluation board. Mixer spurious products are measured in dBc
from the IF output power level. Data was measured only for frequencies less than 6 GHz. Typical noise floor of the measurement system
= −100 dBm.
5 V Performance
VS = 5 V, IS = 100 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, RF power = 0 dBm, VGS0 = VGS1 = 0 V, and
Z
= 50 , unless otherwise noted.
O
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
0 −10.9 −28.3 −44.5
1 −42.2 0.0 −49.3 −31.2 −49.8
2 −75.8 −76.5 −64.6 −78.4 −78.5 −94.7
3 <−100 −83.0 <−100 −73.5 −90.9 −89.8 <−100
4 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
5 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
6 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
7 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
N
8 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
9 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
10 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
11 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
12 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
13 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
14 <−100 <−100 <−100
15 <−100 <−100
M
3.3 V Performance
VS = 3.3 V, IS = 56 mA, TA = 25°C, fRF = 2535 MHz, fLO = 2738 MHz, LO power = 0 dBm, RF power = 0 dBm, R9 = 226 Ω, VGS0 = VGS1 =
0 V, and Z
= 50 Ω, unless otherwise noted.
O
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
0 −16.9 −35.1 −61.4
1 −41.9 0.0 −49.1 −30.4 −52.6
2 −72.3 −80.3 −62.7 −68.5 −71.9 <−100
3 −94.6 −71.6 <−100 −61.2 −92.7 −75.1
4 <−100 <−100
5
6
7
N
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
M
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100 <−100
<−100 <−100 <−100
<−100
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 24
Page 17

ADL5363
V
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ADL5363 consists of two primary components: the radio
frequency (RF) subsystem and the local oscillator (LO) subsystem.
The combination of design, process, and packaging technology
allows the functions of these subsystems to be integrated
into a single die, using mature packaging and interconnection
technologies to provide a high performance, low cost design
with excellent electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties.
In addition, the need for external components is minimized,
optimizing cost and size.
The RF subsystem consists of an integrated, low loss RF balun,
passive MOSFET mixer, sum termination network.
The LO subsystem consists of an SPDT-terminated FET switch
and a three-stage limiting LO amplifier. The purpose of the LO
subsystem is to provide a large, fixed amplitude, balanced signal
to drive the mixer independent of the level of the LO input.
A block diagram of the device is shown in Figure 48.
1
VPMX
2
RFIN
3
RFCT
4
COMM
5
COMM
VLO3 LGM3 VLO2 LOSW NC
NC = NO CO NNECT
CMI
20 19 18 17 16
6 7 8 9 10
IFOP IFON PWDN CO MM
ADL5363
BIAS
GENERATOR
Figure 48. Simplified Schematic
15
LOI2
14
VPSW
13
VGS1
12
VGS0
11
LOI1
09914-051
RF SUBSYSTEM
The single-ended, 50 Ω RF input is internally transformed to a
balanced signal using a low loss (<1 dB) unbalanced-to-balanced
(balun) transformer. This transformer is made possible by an
extremely low loss metal stack, which provides both excellent
balance and dc isolation for the RF port. Although the port can
be dc connected, it is recommended that a blocking capacitor be
used to avoid running excessive dc current through the part.
The RF balun can easily support an RF input frequency range
of 2300 MHz to 2900 MHz.
The resulting balanced RF signal is applied to a passive mixer
that commutates the RF input with the output of the LO subsystem.
The passive mixer is essentially a balanced, low loss switch that
adds minimum noise to the frequency translation. The only
noise contribution from the mixer is due to the resistive loss
of the switches, which is in the order of a few ohms.
As the mixer is inherently broadband and bidirectional, it
is necessary to properly terminate all the idler (M × N product)
frequencies generated by the mixing process. Terminating the
mixer avoids the generation of unwanted intermodulation
products and reduces the level of unwanted signals at the IF
output. This termination is accomplished by the addition of a
sum network between the IF output and the mixer.
The IP3 performance can be optimized by adjusting the supply
current with an external resistor. Figure 37 and 38 illustrate how
the bias resistor affects the performance with a 5 V supply.
Additionally, dc current can be saved by increasing either or
both resistors. It is permissible to reduce the dc supply voltage
to as low as 3.3 V, further reducing the dissipated power of the
part. (Note that no performance enhancement is obtained by
reducing the value of these resistors and excessive dc power
dissipation may result.)
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 24
Page 18

ADL5363
LO SUBSYSTEM
The ADL5363 has two LO inputs permitting multiple synthesizers
to be rapidly switched with extremely short switching times
(<40 ns) for frequency agile applications. The two inputs are
applied to a high isolation SPDT switch that provides a constant
input impedance, regardless of whether the port is selected, to
avoid pulling the LO sources. This multiple section switch also
ensures high isolation to the off input, minimizing any leakage
from the unwanted LO input that may result in undesired IF
responses.
The single-ended LO input is converted to a fixed amplitude
differential signal using a multistage, limiting LO amplifier.
This results in consistent performance over a range of LO input
power. Optimum performance is achieved from −6 dBm to
+10 dBm, but the circuit continues to function at considerably
lower levels of LO input power.
The performance of this amplifier is critical in achieving a
high intercept passive mixer without degrading the noise floor
of the system. This is a critical requirement in an interferer rich
environment, such as cellular infrastructure, where blocking
interferers can limit mixer performance. The bandwidth of the
intermodulation performance is somewhat influenced by the
current in the LO amplifier chain. For dc current sensitive
applications, it is permissible to reduce the current in the
LO amplifier by raising the value of the external bias control
resistor. For dc current critical applications, the LO chain
can operate with a supply voltage as low as 3.3 V, resulting in
substantial dc power savings.
In addition, when operating with supply voltages below 3.6 V,
ADL5363 has a power-down mode that permits the dc
the
current to drop to <200 µA.
All of the logic inputs are designed to work with any logic family
that provides a Logic 0 input level of less than 0.4 V and a Logic 1
input level that exceeds 1.4 V. All logic inputs are high impedance
up to Logic 1 levels of 3.3 V. At levels exceeding 3.3 V, protection
circuitry permits operation up to 5.5 V, although a small bias
current is drawn.
All pins, including the RF pins, are ESD protected and have
been tested up to a level of 1500 V HBM and 1250 V CDM.
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 24
Page 19

ADL5363
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
BASIC CONNECTIONS
The ADL5363 mixer is designed to downconvert radio frequencies (RF) primarily between 2300 MHz and 2900 MHz to lower
intermediate frequencies (IF) between 30 MHz and 450 MHz.
Figure 49 depicts the basic connections of the mixer. To prevent
nonzero dc voltages from damaging the RF balun or LO input
circuit, ac-couple the RF and LO input ports. The RFIN
matching network consists of a series 1.5 pF capacitor and a
shunt 12 nH inductor to provide the optimized RF input return
loss for the desired frequency band.
IF PORT
The real part of the output impedance is approximately 50 , as
seen in Figure 26, which matches many commonly used SAW
filters without the need for a transformer. This results in a
voltage conversion loss that is approximately the same as the
power conversion loss, as shown in Tabl e 3.
IF1_OUT
T1
BIAS RESISTOR SELECTION
An external resistor, R
of the integrated amplifiers at the LO terminals. It is necessary
to have a sufficient amount of current to bias the internal LO
amplifier to optimize dc current vs. optimum IIP3 performance.
Figure 37 and Figure 38 provide the reference for the bias
resistor selection when lower power consumption is considered
at the expense of conversion gain and IP3 performance.
, is used to adjust the bias current
BIAS LO
MIXER VGS CONTROL DAC
The ADL5363 features two logic control pins, VGS0 (Pin 12) and
VGS1 (Pin 13), that allow programmability for internal gate-tosource voltages for optimizing mixer performance over desired
frequency bands. The evaluation board defaults both VGS0 and
VGS1 to ground.
R1
0Ω
C25
560pF
+5V
4.7µF
0.01µF
10pF
+5V
10µH
1.5pF
RF-IN +5V
12nH
10pF
+5V
20
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8 9 10
C24
560pF
19 18 17 16
10kΩ
ADL5363
BIAS
GENERATOR
R
BIAS LO
10pF10pF
10kΩ
22pF
15
14
13
12
11
22pF
10pF
LO2_IN
LO1_IN
09914-052
Figure 49. Typical Application Circuit
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 24
Page 20

ADL5363
EVALUATION BOARD
An evaluation board is available for the family of double balanced mixers. The standard evaluation board schematic is shown in Figure 50.
The evaluation board is fabricated using Rogers® RO3003 material. Table 7 describes the various configuration options of the evaluation
board. Evaluation board layout is shown in Figure 51 to Figure 54.
IF1_OUT
R1
T1
0Ω
RF-IN
VPOS
C1
1.5pF
C2
10µF
Z1
12nH
C5
0.01µFC410pF
C21
10pF
VPOS
10pF
R14
0Ω
VPMX
RFIN
RFCT
COMM
COMM
C6
C25
560pF
1.1kΩ
VCMI
VLO3
R9
C24
560pF
IFOP
IFON
ADL5363
LO2
LGM3
V
C8
10pF
DN
PW
LOSW
VPOS
Figure 50. Evaluation Board Schematic
COMM
NC
L3
0Ω
LOI2
VPSW
VGS1
VGS0
LOI1
R4
10kΩ
R21
10kΩ
VGS0
C12
22pF
LOSEL
PWR_UP
VGS1
C10
22pF
LO2_IN
C20
10pF
C22
1nF
VPOS
LO1_IN
R22
10kΩ
R23
15kΩ
9914-053
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 24
Page 21

ADL5363
Table 7. Evaluation Board Configuration
Components Function Description Default Conditions
C2, C6, C8,
C20, C21
C1, C4, C5, Z1 RF input interface
T1, R1, C24, C25 IF output interface
C10, C12, R4 LO interface
R21 PWDN interface
C22, L3, R9, R14,
R22, R23, VGS0,
VGS1
Power supply
decoupling
Bias control
Power Supply Decoupling. Nominal supply decoupling
consists of a 10 μF capacitor to ground in parallel with a
10 pF capacitor to ground positioned as close to the device
as possible.
RF Input Interface. The input channels are ac-coupled
through C1. C4 and C5 provide bypassing for the center taps
of the RF input baluns.
IF Output Interface. T1 is a 1:1 impedance transformer used
to provide a single-ended IF output interface. Remove R1
for balanced output operation. C24 and C25 are used to
block the dc bias at the IF ports.
LO Interface. C10 and C12 provide ac coupling for the
LO1_IN and LO2_IN local oscillator inputs. LOSEL selects
the appropriate LO input for both mixer cores. R4 provides
a pull-down to ensure that LO1_IN is enabled when the
LOSEL test point is logic low. LO2_IN is enabled when
LOSEL is pulled to logic high.
PWDN Interface. R21 pulls the PWDN logic low and enables
the device. The PWR_UP test point allows the PWDN
interface to be exercised using the an external logic
generator. Grounding the PWDN pin for nominal operation
is allowed. Using the PWDN pin when supply voltages
exceed 3.3 V is not allowed.
Bias Control. R22 and R23 form a voltage divider to provide
3 V for logic control, bypassed to ground through C22.
VGS0 and VGS1 jumpers provide programmability at the
VGS0 and VGS1 pins. It is recommended to pull these two
pins to ground for nominal operation. R9 sets the bias
point for the internal LO buffers.
C2 = 10 μF (size 0603),
C6, C8, C20, C21 = 10 pF (size 0402)
C1 = 1.5 pF (size 0402),
C4 = 10 pF (size 0402),
C5 = 0.01 μF (size 0402)
Z1= 12 nH (size 0402)
T1 = TC1-1-13M+ (Mini-Circuits),
R1 = 0 Ω (size 0402),
C24, C25 = 560 pF (size 0402)
C10, C12 = 22 pF (size 0402),
R4 = 10 kΩ (size 0402)
R21 = 10 kΩ (size 0402)
C22 = 1 nF (size 0402),
L3 = 0 Ω (size 0603),
R9 = 1.1 kΩ (size 0402),
R14 = 0 Ω (size 0402),
R22 = 10 kΩ (size 0402),
R23 = 15 kΩ (size 0402),
VGS0 = VGS1 = 3-pin shunt
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 24
Page 22

ADL5363
Figure 51. Evaluation Board Top Layer
Figure 52. Evaluation Board Ground Plane, Internal Layer 1
09914-152
09914-154
Figure 53. Evaluation Board Power Plane, Internal Layer 2
09914-153
09914-155
Figure 54. Evaluation Board Bottom Layer
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 24
Page 23

ADL5363
C
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.05
0.65
BSC
0.75
0.60
0.50
0.60 MAX
15
16
10
11
20
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
6
2.60 BSC
FOR PROPER CONNECTION O F
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONF IGURATIO N AND
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIO NS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
N
I
1
P
R
O
T
N
D
C
I
A
I
1
3.20
3.10 SQ
3.00
5
042209-B
5.00
INDI
0.90
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
PIN 1
ATO R
12° MAX
BSC SQ
TOP VIEW
0.70
0.65
0.60
0.35
0.28
0.23
COMPLIANTTOJEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VHHC
4.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.60 MAX
0.05 MAX
0.01 NOM
COPLANARITY
Figure 55. 20-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
5 mm × 5 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-20-5)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option Ordering Quantity
ADL5363ACPZ-R7 −40°C to +85°C
20-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
7” Tape and Reel
ADL5363-EVALZ Evaluation Board 1
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
CP-20-5 1,500
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 24
Page 24

ADL5363
NOTES
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D09914-0-7/11(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...