Page 1
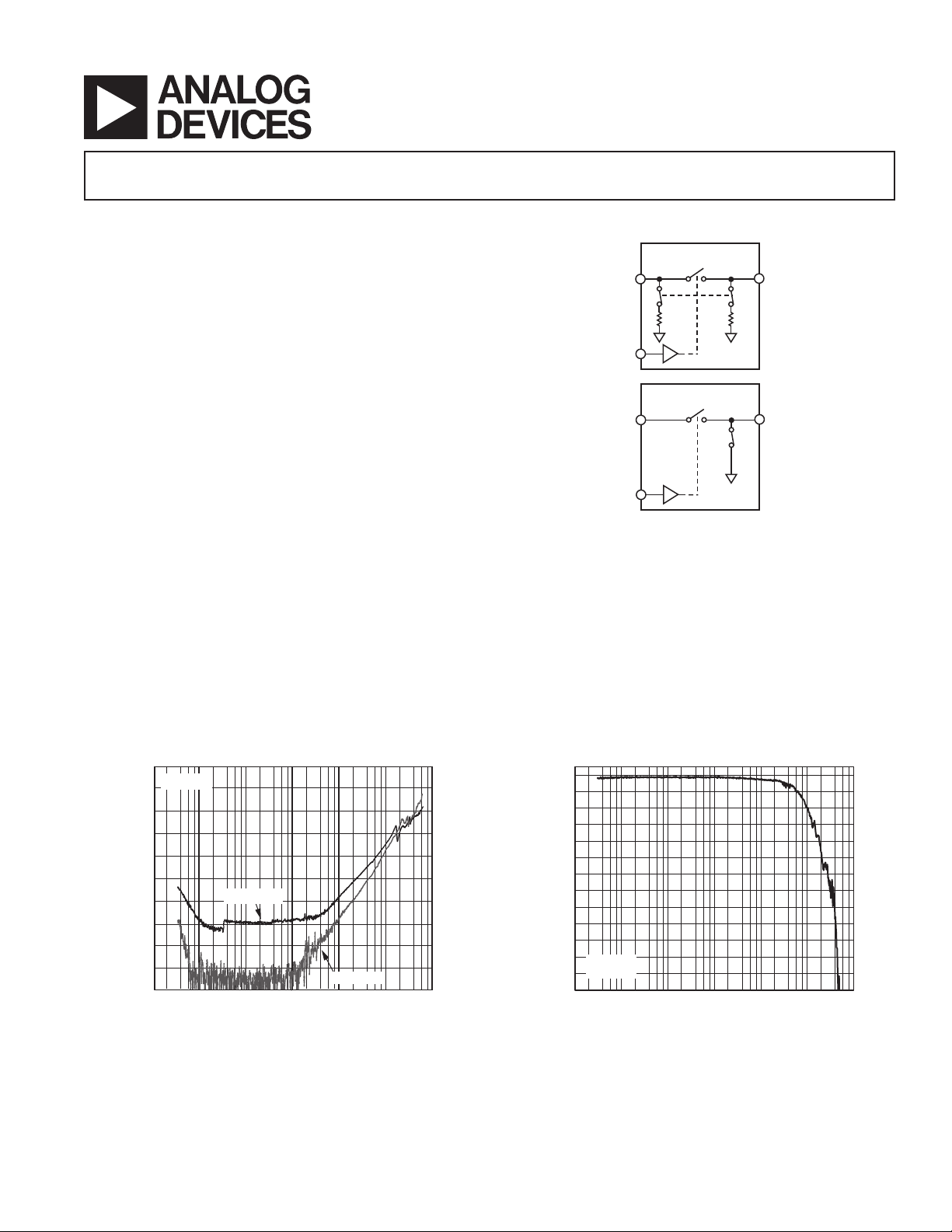
Wideband, 40 dB Isolation at 1 GHz, CMOS
RF2
CTRL
ADG901
RF1
50
50
RF2
CTRL
ADG902
RF1
1.65 V to 2.75 V, SPST Switches
ADG901/ADG902
FEATURES
Wideband Switch: –3 dB @ 4.5 GHz
Absorptive/Reflective Switches
High Off Isolation (40 dB @ 1 GHz)
Low Insertion Loss (0.8 dB @1 GHz)
Single 1.65 V to 2.75 V Power Supply
CMOS/LVTTL Control Logic
8-Lead MSOP and Tiny 3 mm 3 mm LFCSP Packages
Low Power Consumption (<1 A)
APPLICATIONS
Wireless Communications
General-Purpose RF Switching
Dual-Band Applications
High Speed Filter Selection
Digital Transceiver Front End Switch
IF Switching
Tuner Modules
Antenna Diversity Switching
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADG901/ADG902 are wideband switches that use a
CMOS process to provide high isolation and low insertion loss to
1 GHz. The ADG901 is an absorptive (matched) switch with
50 Ω terminated shunt legs, while the ADG902 is a reflective
switch. These devices are designed such that the isolation is
high over the dc to 1 GHz frequency range. They have on-board
CMOS control logic, thus eliminating the need for external
controlling circuitry. The control inputs are both CMOS and
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAMS
LVTTL compatible. The low power consumption of these
CMOS devices makes them ideally suited to wireless applications and general-purpose high frequency switching.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. –40 dB Off Isolation @ 1 GHz
2. 0.8 dB Insertion Loss @ 1 GHz
3. Tiny 8-Lead MSOP/LFCSP Packages
0
TA = 25C
–10
20
–
–30
–40
–50
VDD = 2.5 V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
V
DD
= 1.8 V
–60
ISOLATION (dB)
–70
–80
–90
–100
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
Figure 1. Off Isolation vs. Frequency
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
–0.4
–0.6
0.8
–
–1.0
–1.2
–1.4
–1.6
–1.8
–2.0
–2.2
INSERTION LOSS (dB)
–2.4
–2.6
VDD = 2.5V
= 25C
T
–2.8
A
–3.0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 2. Insertion Loss vs. Frequency
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
(VDD = 1.65 V to 2.75 V, GND = 0 V, input power = 0 dBm,
1
ADG901/ADG902–SPECIFICATIONS
all specifications T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
B Version
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ2Max Unit
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Operating Frequency
–3 dB Frequency
Input Power
4
3
4
DC 2.5 GHz
4.5 GHz
0 V dc Bias 7 dBm
+0.5 V dc Bias 16 dBm
Insertion Loss S
, S
21
Isolation—RF1 to RF2 S21, S
DC to 100 MHz; VDD = 2.5 V ± 10% 0.4 0.7 dB
12
500 MHz; V
1000 MHz; V
100 MHz 60 61 dB
12
= 2.5 V ± 10% 0.5 0.8 dB
DD
= 2.5 V ± 10% 0.8 1.25 dB
DD
(CP Package) 500 MHz 43 45 dB
1000 MHz 34 40 dB
Isolation—RF1 to RF2 S
, S
21
100 MHz 51 60 dB
12
(RM Package) 500 MHz 37.5 47 dB
1000 MHz 31 37 dB
DC to 100 MHz 20 28 dB
22
Return Loss (On Channel)
4
S11, S
500 MHz 23 29 dB
Return Loss (Off Channel)
4
S11, S
1000 MHz 25 28 dB
DC to 100 MHz 18 23 dB
22
500 MHz 17 21 dB
On Switching Time
Off Switching Time
Rise Time
Fall Time
4
4
1 dB Compression
Third Order Intermodulation Intercept IP
Video Feedthrough
4
4
4
5
t
t
t
t
P
ON
OFF
RISE
FALL
–1 dB
3
1000 MHz 15 19 dB
50% CTRL to 90% RF 3.6 6 ns
50% CTRL to 10% RF 5.8 9.5 ns
10% to 90% RF 3.1 5.5 ns
90% to 10% RF 6.0 8.5 ns
1000 MHz 17 dBm
900 MHz/901 MHz, 4 dBm 30 36 dBm
2.5 mV p-p
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
CAPACITANCE
4
INH
V
INH
INL
V
INL
I
VDD = 2.25 V to 2.75 V 1.7 V
VDD = 1.65 V to 1.95 V 0.65 V
CC
V
VDD = 2.25 V to 2.75 V 0.7 V
VDD = 1.65 V to 1.95 V 0.35 VCCV
0 ≤ VIN ≤ 2.75 V ± 0.1 ±1 µA
RF1/RF2, RF Port On Capacitance CRF ON f = 1 MHz 1.2 pF
CTRL Input Capacitance C
CTRL
f = 1 MHz 2.1 pF
POWER REQUIREMENTS
V
DD
Quiescent Power Supply Current I
NOTES
1
Temperature range B Version: –40°C to +85°C.
2
Typical values are at VDD = 2.5 V and 25°C, unless otherwise stated.
3
Point at which insertion loss degrades by 1 dB.
4
Guaranteed by design, not subject to production test.
5
The dc transience at the output of any port of the switch when the control voltage is switched from high to low or low to high in a 50 Ω test setup, measured with
1 ns rise time pulses and 500 MHz bandwidth.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
DD
Digital inputs = 0 V or V
DD
1.65 2.75 V
0.1 1 µA
REV. A–2–
Page 3
ADG901/ADG902
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
VDD to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to +4 V
Inputs to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
Continuous Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 mA
Input Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 dBm
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (B Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
MSOP Package
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206°C/W
JA
1
+ 0.3 V
DD
LFCSP Package
Thermal Impedance (2-layer board) . . . . . . . . . . 84°C/W
JA
Thermal Impedance (4-layer board) . . . . . . . . . . 48°C/W
2
JA
Lead Temperature, Soldering (10 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300°C
IR Reflow, Peak Temperature (<20 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . 235°C
ESD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 kV
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of
the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Only one absolute
maximum rating may be applied at any one time.
2
RF1/2 Off Port Inputs to Ground ................................... –0.5 V to VDD – 0.5 V
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option Branding
ADG901BRM –40°C to +85°CMini Small Outline Package (MSOP) RM-8 W6B
ADG901BRM-500RL7 –40°C to +85°CMini Small Outline Package (MSOP) RM-8 W6B
ADG901BRM-REEL7 –40°C to +85°CMini Small Outline Package (MSOP) RM-8 W6B
ADG901BCP-500RL7 –40°C to +85°CLead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) CP-8 W6B
ADG901BCP-REEL7 –40°C to +85°CLead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) CP-8 W6B
ADG902BRM –40°C to +85°CMini Small Outline Package (MSOP) RM-8 W7B
ADG902BRM-500RL7 –40°C to +85°CMini Small Outline Package (MSOP) RM-8 W7B
ADG902BRM-REEL7 –40°C to +85°CLead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) RM-8 W7B
ADG902BCP-500RL7 –40°C to +85°CLead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) CP-8 W7B
ADG902BCP-REEL7 –40°C to +85°CLead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) CP-8 W7B
EVAL-ADG901EB Evaluation Board
EVAL-ADG902EB Evaluation Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
ADG901/ADG902 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
PIN CONFIGURATION
8-Lead MSOP (RM-8)
8-Lead 3 mm 3 mm LFCSP (CP-8)
V
CTRL
GND
RF1
DD
1
ADG901/
2
ADG902
3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
4
8
RF2
7
GND
6
GND
5
GND
Pin No. Mnemonic Function
1V
2 CTRL CMOS or TTL Logic Level.
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DD
Power Supply Input. These parts can
be operated from 1.65 V to 2.75 V;
should be decoupled to GND.
V
DD
0
➞
RF1 Isolated from RF2
➞
RF1 to RF2
1
3, 5, 6, 7 GND Ground Reference Point for All
Circuitry on the Part.
Table I. Truth Table
4 RF1 RF1 Port.
8 RF2 RF2 Port.
CTRL Signal Path
0 RF1 isolated from RF2
1 RF1 to RF2
REV. A
–3–
Page 4

ADG901/ADG902
TERMINOLOGY
Parameter Description
V
DD
I
DD
GND Ground (0 V) reference.
CTRL Logic control input.
V
INL
V
INH
I
INL (IINH
C
t
ON
t
OFF
t
RISE
t
FALL
) Input current of the digital input.
IN
Off Isolation The attenuation between input and output ports of the switch when the switch control voltage is in the
Insertion Loss The attenuation between input and output ports of the switch when the switch control voltage is in the
P
–1 dB
IP
3
Return Loss The amount of reflected power relative to the incident power at a port. Large return loss indicates good matching.
Video Feedthrough Spurious signals present at the RF ports of the switch when the control voltage is switched from high to low
Most positive power supply potential.
Positive supply current.
Maximum input voltage for Logic 0.
Minimum input voltage for Logic 1.
Digital input capacitance.
Delay between applying the digital control input and the output switching on.
Delay between applying the digital control input and the output switching off.
Rise time. Time for the RF signal to rise from 10% to 90% of the ON level.
Fall time. Time for the RF signal to fall from 90% to 10% of the ON level.
OFF condition.
ON condition.
1 dB compression point. The RF input power level at which the switch insertion loss increases by 1 dB over its
low level value. It is a measure of how much power the ON switch can handle before the insertion loss increases
by 1 dB.
Third order intermodulation intercept. This is a measure of the power in false tones that occur when closely spaced
tones are passed through a switch, whereby the nonlinearity of the switch causes these false tones to be generated.
By measuring Return Loss the VSWR can be calculated from conversion charts. VSWR (voltage standing wave ratio)
indicates degree of matching present at a switch RF port.
or low to high without an RF signal present.
REV. A–4–
Page 5

Typical Performance Characteristics–ADG901/ADG902
–0.4
–0.6
0.8
–
VDD = 2.5V
–1.0
–1.2
–1.4
–1.6
–1.8
–2.0
INSERTION LOSS (dB)
–2.2
–2.4
–2.6
TA = 25C
–2.8
–3.0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
VDD = 2.25V
VDD = 2.75V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 1. Insertion Loss vs. Frequency
over Supplies (S12 and S21)
–0.4
–0.6
+25C
0.8
–
–1.0
–1.2
–1.4
–1.6
–1.8
–2.0
–2.2
INSERTION LOSS (dB)
–2.4
–2.6
VDD = 2.5V
–2.8
–3.0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
+85C
FREQUENCY (Hz)
–40C
TPC 4. Insertion Loss vs. Frequency
over Temperature (S12 and S21)
–0.40
–0.45
0.50
–
–0.55
VDD = 2.5V
–0.60
–0.65
–0.70
–0.75
–0.80
INSERTION LOSS (dB)
–0.85
–0.90
TA = 25C
–0.95
–1.00
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
VDD = 2.25V
VDD = 2.75V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 2. Insertion Loss vs. Frequency
over Supplies (S12 and S21)
(Zoomed TPC 1 Plot)
0
–5
TA = 25C
–10
–15
20
–
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
–70
ISOLATION (dB)
–75
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
VDD = 2.5V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
V
DD
= 1.8V
TPC 5. OFF Isolation vs. Frequency
over Supplies (S12 and S21)
–0.4
–0.6
0.8
–
VDD = 1.8V
–1.0
–1.2
–1.4
–1.6
–1.8
–2.0
–2.2
–2.4
INSERTION LOSS (dB)
–2.6
TA = 25C
–2.8
–3.0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
VDD = 1.95V
VDD = 1.65V
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 3. Insertion Loss vs. Frequency
over Supplies (S12 and S21)
0
VDD = 2.5V
–5
–10
–15
20
–
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
ISOLATION (dB)
–65
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G 10G
+85C
+25C
–40C
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 6. OFF Isolation vs. Frequency
over Temperature (S12 and S21)
0
TA = 25C
2.5V
V
–5
DD =
10
–
–15
–20
–25
RETURN LOSS (dB)
–30
–35
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M 1G
OFF SWITCH
ON SWITCH
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TPC 7. Return Loss vs. Frequency
(S11)
REV. A
10G
CH1
CH2
CH1 = CTRL = 1V/DIV t
CH2 = RFx = 100mV/DIV t
TPC 8. Switch Timing
–5–
RISE
FALL
= 2.8ns
= 5.1ns
CTRL
RFx
CH2 pk-pk
2.016mV
CH1 500mV CH2 1mV 10.0ns
TPC 9. Video Feedthrough
Page 6

ADG901/ADG902
40
35
30
25
20
(dBm)
3
IP
15
10
5
0
250 350 450 550
FREQUENCY (MHz)
650 750 850
TPC 10. IP3 vs. Frequency
VDD = 2.5V
= 25C
T
A
20
18
16
14
12
(dBm)
10
–1dB
8
P
6
4
2
0
0 250 500 750 1000 1250
TPC 11. P
FREQUENCY (MHz)
vs. Frequency
–1dB
VDD = 2.5V
= 25C
T
A
1500
REV. A–6–
Page 7

ADG901/ADG902
Test Circuits*
V
DD
0.1F
V
DD
RF1
V
S
CTRL
GND
Test Circuit 1. Switching Timing: tON, t
V
DD
0.1F
V
DD
RF1
V
S
CTRL
GND
RF2
RF2
R
50
V
R
50
V
DD
0.1F
V
OUT
R
50
L
50
50
NETWORK
ANALYZER
RF2
V
S
NC
V
ADG901
V
OUT
V
CTRL
L
V
OUT
50% 50%
90%
t
ON
t
10%
OFF
OFF
OUT
V
CTRL
L
V
OUT
10%
t
RISE
50%
90%
90%
t
FALL
50%
10%
RF1
CTRL
V
CTRL
OSCILLOSCOPE
50
DD
RF2
50
GND
INSERTION LOSS
= 20
LOG
V
OUT
V
Test Circuit 4. Insertion Loss
V
DD
0.1F
V
DD
GND
V
ADG901
RF1
50
CTRL
CTRL
S
V
RF1
CTRL
CTRL
Test Circuit 2. Switch Timing: t
V
DD
0.1F
V
50
DD
50
GND
OFF ISOLATION =20 LOG
RF2
ADG901
Test Circuit 3. Off Isolation
, t
RISE
FALL
V
OUT
R
L
50
50
V
S
NETWORK
ANALYZER
V
OUT
V
S
Test Circuit 5. Video Feedthrough
*Similiar setups for ADG902.
REV. A
–7–
Page 8

ADG901/ADG902
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
CTRL
V
CTRL
RF1
V
DD
0.1F
V
ADG901
50
DD
GND
Test Circuit 6. IP
50
RF2
3
COMBINER
RF
SOURCE
RF
SOURCE
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
CTRL
V
CTRL
0.1F
ADG901
RF1
50
Test Circuit 7. P
GND
V
DD
V
DD
RF
SOURCE
RF2
50
–1dB
V
S
REV. A–8–
Page 9

ADG901/ADG902
APPLICATIONS
The ADG901/ADG902 are ideal solutions for low power, high
frequency applications. The low insertion loss, high isolation
between ports, low distortion, and low current consumption of
these parts make them excellent solutions for many high frequency
switching applications.
Applications include switching between high frequency filters,
ASK generator, and FSK generator.
Absorptive vs. Reflective Switches
The ADG901 is an absorptive (matched) switch with 50 Ω termi-
nated shunt legs, and the ADG902 is a reflective switch with 0 Ω
terminated shunts to ground. The ADG901 absorptive switch
has a good VSWR on each port, regardless of the switch mode.
An absorptive switch should be used when there is a need for a
good VSWR that is looking into the port but not passing the
through signal to the common port. The ADG901 is therefore
ideal for applications that require minimum reflections back to
the RF source. It also ensures that the maximum power is transferred to the load.
The ADG902 reflective switch is suitable for applications where
high off port VSWR does not matter and the switch has some
other desired performance feature. It can be used in many applications, including high speed filter selection. In most cases, an
absorptive switch can be used instead of a reflective switch, but
not vice versa.
ADG9xx EVALUATION BOARD
The ADG9xx evaluation board allows designers to evaluate the
high performance wideband switches with a minimum of effort.
To prove that these devices meet user requirements, the user
requires only a power supply and a network analyzer along with
the evaluation board. An application note is available with the
evaluation board and provides complete information on operating
the evaluation board.
The RF1 port (see Figure 3) is connected through a 50 Ω trans-
mission line to the top left SMA connector J1. RF2 is connected
through a 50 Ω transmission line to the top SMA connector J2.
J3 is connected to GND. A through transmission line connects
J4 and J5 and this transmission line is used to estimate the loss
of the PCB over the environmental conditions being evaluated.
The board is constructed of a 4-layer, FR4 material with a dielectric constant of 4.3 and an overall thickness of 0.062 inches. Two
ground layers with grounded planes provide ground for the RF
transmission lines. The transmission lines were designed using a
coplanar waveguide with ground plane model using a trace width
of 0.052 inches, clearance to ground plane of 0.030 inches,
dielectric thickness of 0.029 inches, and a metal thickness of
0.014 inches.
REV. A
Figure 3. ADG9xx Evaluation Board Top View
–9–
Page 10

ADG901/ADG902
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
(RM-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
3.00
BSC
PIN 1
INDICATOR
85
3.00
BSC
1
PIN 1
0.65 BSC
0.15
0.00
0.38
0.22
COPLANARITY
0.10
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-187AA
4.90
BSC
4
SEATING
PLANE
1.10 MAX
0.23
0.08
8
0
0.80
0.60
0.40
8-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP]
3 mm 3 mm Body
(CP-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
0.50
0.40
BOTTOM
VIEW
0.30
4
PIN 1 INDICATOR
1
1.50
REF
3.00
BSC SQ
TOP
VIEW
2.75
BSC SQ
0.45
0.50
BSC
0.60 MAX
8
5
1.90
1.75
1.60
0.90
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
12 MAX
0.30
0.23
0.18
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
0.25
MIN
1.60
1.45
1.30
REV. A–10–
Page 11

ADG901/ADG902
Revision History
Location Page
10/04—Data Sheet changed from REV. 0 to REV. A.
Changes to FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Changes to PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Changes to SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Changes to ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Change to ADG9xx EVALUATION BOARD section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Updated OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
REV. A
–11–
Page 12

C03336–0–10/04(A)
–12–
 Loading...
Loading...