Page 1

CMOS 1.8 V to 5.5 V, 2.5
a
FEATURES
1.8 V to 5.5 V Single Supply
4 (Max) On Resistance
0.75 (Typ) On Resistance Flatness
Automotive Temperature Range: –40°C to +125°C
–3 dB Bandwidth > 200 MHz
Rail-to-Rail Operation
6-Lead SOT-23 Package and 8-Lead SOIC Package
Fast Switching Times:
= 12 ns
t
ON
= 6 ns
t
OFF
Typical Power Consumption (< 0.01 W)
TTL/CMOS Compatible
APPLICATIONS
Battery-Powered Systems
Communication Systems
Sample-and-Hold Systems
Audio Signal Routing
Video Switching
Mechanical Reed Relay Replacement
2:1 Mux/SPDT Switch in SOT-23
ADG719
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADG719
S2
S1
IN
SWITCHES SHOWN FOR A LOGIC “1” INPUT
D
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADG719 is a monolithic CMOS SPDT switch. This switch
is designed on a submicron process that provides low power
dissipation yet gives high switching speed, low on resistance, and
low leakage currents.
The ADG719 can operate from a single-supply range of 1.8 V to
5.5 V, making it ideal for use in battery-powered instruments and
with the new generation of DACs and ADCs from Analog Devices.
Each switch of the ADG719 conducts equally well in both
directions when on. The ADG719 exhibits break-before-make
switching action.
Because of the advanced submicron process, –3 dB bandwidths
of greater than 200 MHz can be achieved.
The ADG719 is available in a 6-lead SOT-23 package and an
8-lead µSOIC package.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. 1.8 V to 5.5 V Single-Supply Operation. The ADG719 offers
high performance, including low on resistance and fast switching
times, and is fully specified and guaranteed with 3 V and 5 V
supply rails.
2. Very Low R
At 1.8 V operation, R
ture range.
3. Automotive Temperature Range: –40°C to +125°C
4. On Resistance Flatness (R
5. –3 dB Bandwidth > 200 MHz.
6. Low Power Dissipation. CMOS construction ensures low
power dissipation.
7. Fast t
8. Tiny 6-lead SOT-23 and 8-lead µSOIC packages.
ON/tOFF.
(4 Ω Max at 5 V and 10 Ω Max at 3 V).
ON
is typically 40 Ω over the tempera-
ON
FLAT(ON)
) (0.75 Ω typ).
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
Page 2
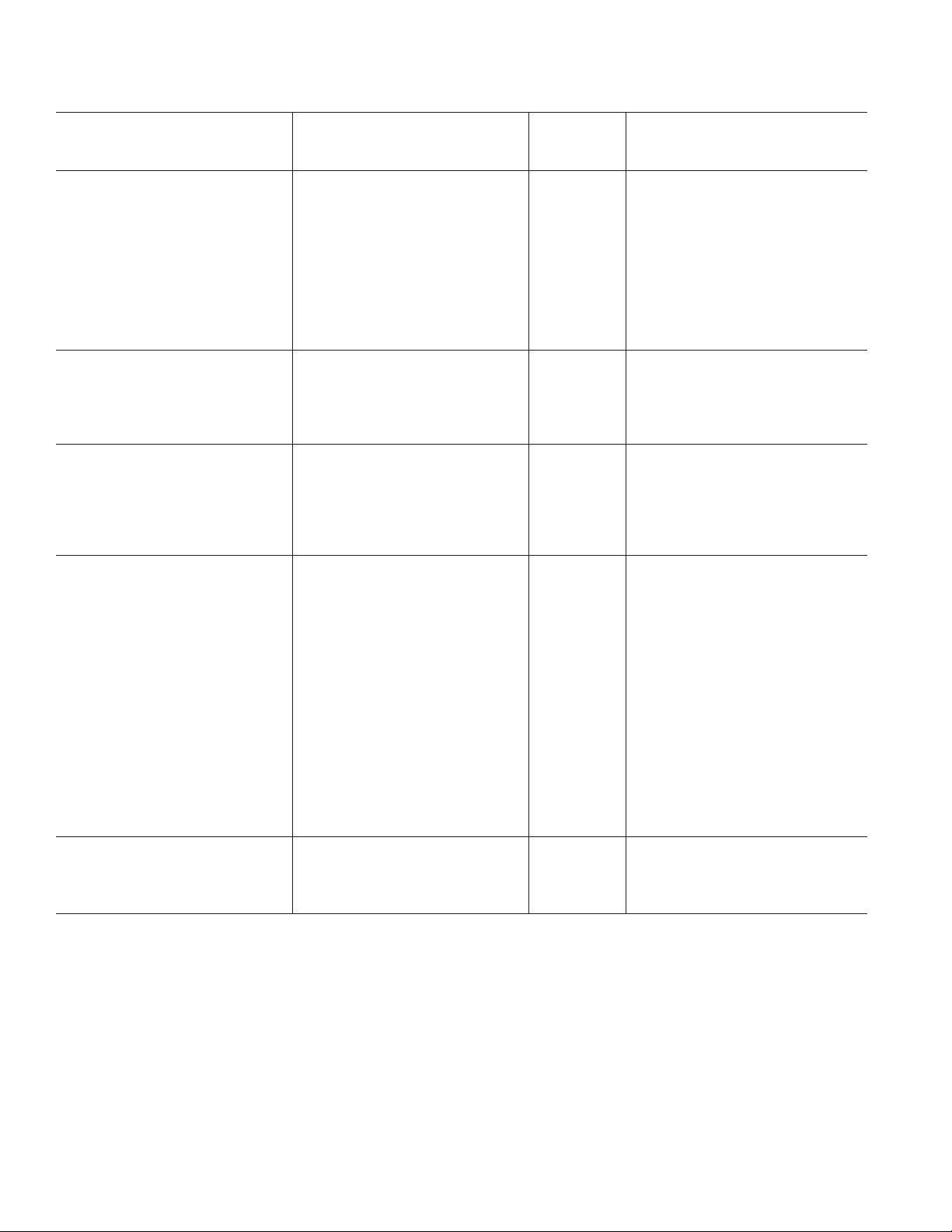
ADG719–SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter +25C +85C +125C Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ANALOG SWITCH
Analog Signal Range 0 V to VDDV
On Resistance (R
On Resistance Match Between
Channels (∆R
On Resistance Flatness (R
LEAKAGE CURRENTS V
Source Off Leakage I
Channel On Leakage I
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current
or I
I
INL
INH
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
t
ON
t
OFF
Break-Before-Make Time Delay, t
Off Isolation –67 dB typ R
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk –62 dB typ R
Bandwidth –3 dB 200 MHz typ R
C
(Off) 7 pF typ
S
CD, CS (On) 27 pF typ
POWER REQUIREMENTS V
I
DD
NOTES
1
Temperature range is as follows: B Version: – 40°C to +125°C.
2
Guaranteed by design, not subject to production test.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
)V
ON
2.5 Ω typ Test Circuit 1
45 7 Ω max
) 0.1 Ω typ VS = 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA
ON
FLAT(ON)
(Off) ±0.01 nA typ VS = 4.5 V/1 V, VD = 1 V/4.5 V;
S
)0.75 Ω typ VS = 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA
±0.25 ± 0.35 1 nA max Test Circuit 2
, IS (On) ±0.01 nA typ VS = VD = 1 V or VS = VD = 4.5 V;
D
±0.25 ± 0.35 5 nA max Test Circuit 3
INH
INL
0.005 µA typ VIN = V
2
7 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF
3 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF
8 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF,
D
–87 dB typ R
–82 dB typ R
0.001 µA typ
(VDD = 5 V 10%, GND = 0 V.)
B Version
–40C to –40C to
0.4 0.4 Ω max
1.2 1.5 Ω max
2.4 V min
0.8 V max
±0.1 µA max
12 ns max V
6 ns max V
1 ns min V
1.0 µA max
= 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA;
S
= 5.5 V
DD
or V
INL
= 3 V; Test Circuit 4
S
= 3 V; Test Circuit 4
S
= VS2 = 3 V; Test Circuit 5
S1
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 10 MHz
L
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 1 MHz;
L
INH
Test Circuit 6
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 10 MHz
L
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 1 MHz;
L
Test Circuit 7
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF; Test Circuit 8
L
= 5.5 V
DD
Digital Inputs = 0 V or 5.5 V
1
–2–
REV. B
Page 3
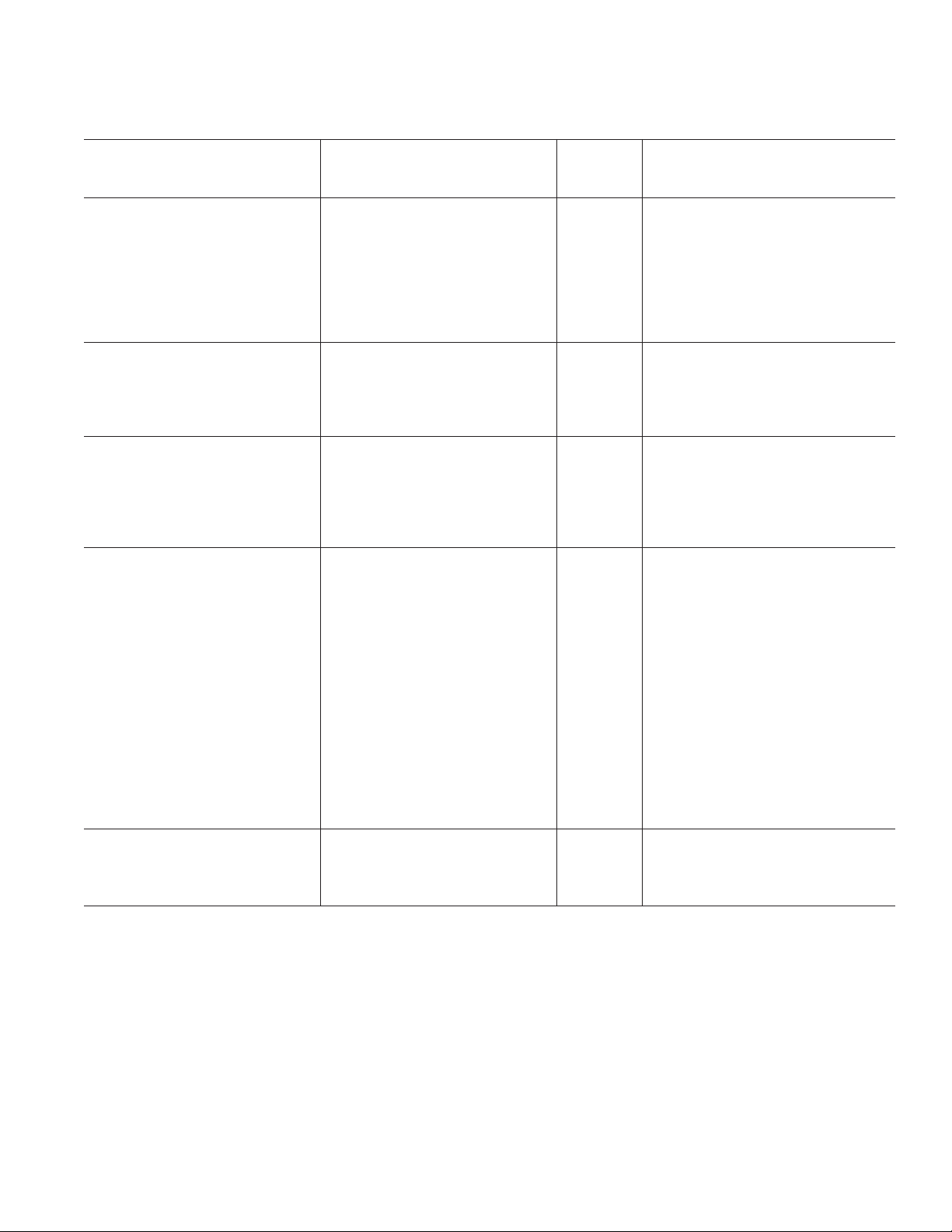
ADG719
1
SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter +25C +85C +125C Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ANALOG SWITCH
Analog Signal Range 0 V to V
On Resistance (R
On Resistance Match Between
Channels (∆R
On Resistance Flatness (R
LEAKAGE CURRENTS V
Source Off Leakage I
Channel On Leakage I
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current
or I
I
INL
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
t
ON
t
OFF
Break-Before-Make Time Delay, t
Off Isolation –67 dB typ R
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk –62 dB typ R
Bandwidth –3 dB 200 MHz typ R
(Off) 7 pF typ
C
S
CD, CS (On) 27 pF typ
POWER REQUIREMENTS V
I
DD
NOTES
1
Temperature range is as follows: B Version: –40°C to +125°C.
2
Guaranteed by design, not subject to production test.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
INH
ON
) 0.1 Ω typ VS = 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA
ON
(VDD = 3 V 10%, GND = 0 V.)
B Version
–40C to –40C to
V
DD
)67 Ω typ VS = 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA;
10 12 Ω max Test Circuit 1
0.4 0.4 Ω max
FLAT(ON)
(Off) ±0.01 nA typ VS = 3 V/1 V, VD = 1 V/3 V;
S
) 2.5 Ω typ VS = 0 V to VDD, IS = –10 mA
= 3.3 V
DD
±0.25 ±0.35 1 nA max Test Circuit 2
, IS (On) ±0.01 nA typ VS = VD = 1 V or VS = VD = 3 V;
D
±0.25 ±0.35 5 nA max Test Circuit 3
INH
INL
0.005 µA typ VIN = V
2.0 V min
0.8 V max
INL
or V
INH
±0.1 µA max
2
10 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF
15 ns max V
= 2 V; Test Circuit 4
S
4 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF
8 ns max V
8 ns typ RL = 300 Ω, CL = 35 pF
D
1 ns min V
–87 dB typ R
= 2 V; Test Circuit 4
S
= VS2 = 2 V; Test Circuit 5
S1
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 10 MHz
L
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 1 MHz;
L
Test Circuit 6
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 10 MHz
L
–82 dB typ R
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF, f = 1 MHz;
L
Test Circuit 7
= 50 Ω, CL = 5 pF; Test Circuit 8
L
= 3.3 V
DD
Digital Inputs = 0 V or 3.3 V
0.001 µA typ
1.0 µA max
REV. B
–3–
Page 4
ADG719
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
VDD to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
Analog, Digital Inputs
2
. . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V or
1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 mA, Whichever Occurs First
Peak Current, S or D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 mA
(Pulsed at 1 ms, 10% Duty Cycle Max)
Continuous Current, S or D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 mA
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (B Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
µSOIC Package, Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315 mW
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206°C/W
θ
JA
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44°C/W
θ
JC
SOT-23 Package, Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282 mW
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229.6°C/W
θ
JA
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.99°C/W
θ
JC
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
ESD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 kV
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Only one absolute
maximum rating may be applied at any one time.
2
Overvoltages at IN, S, or D will be clamped by internal diodes. Current should be
limited to the maximum ratings given.
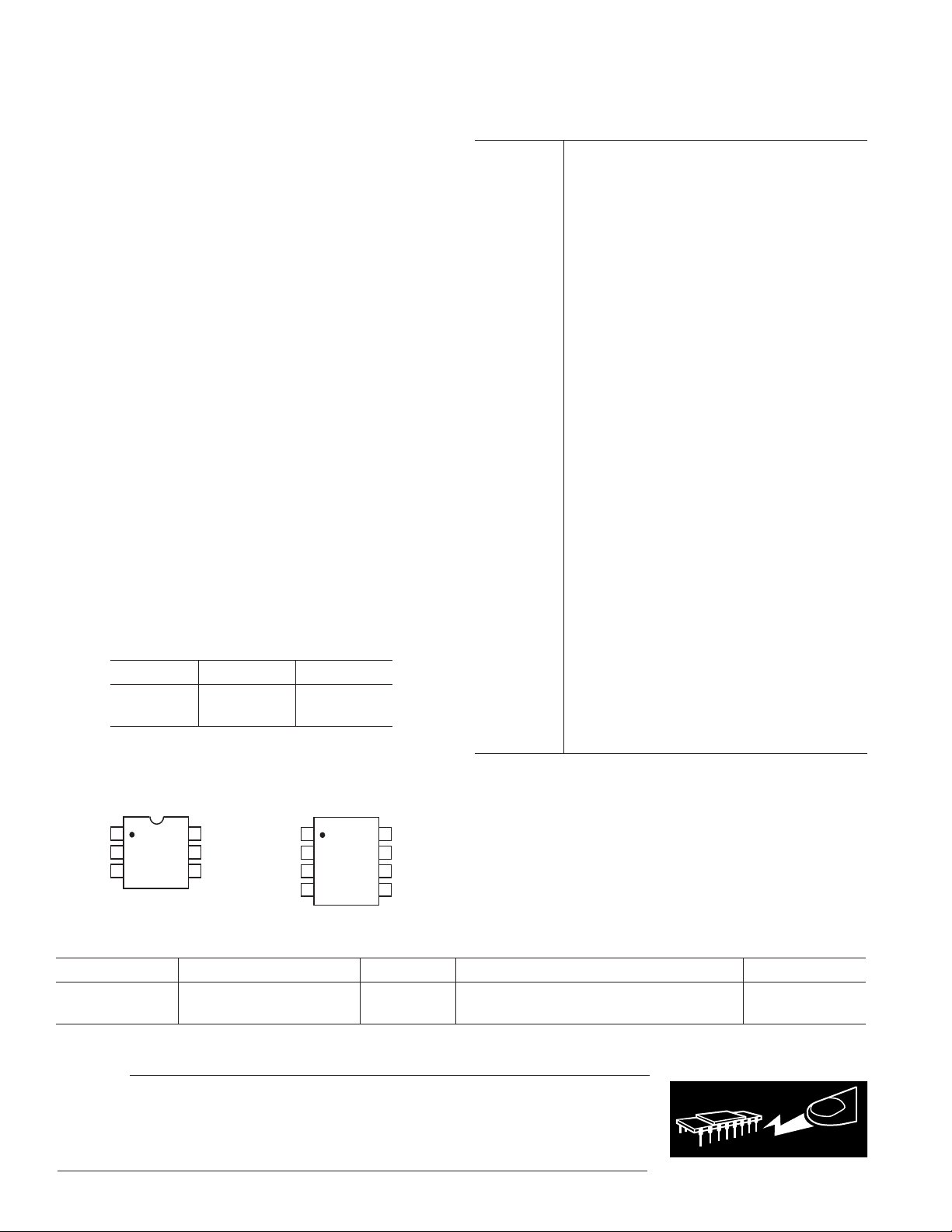
Table I. Truth Table
ADG719 IN Switch S1 Switch S2
0ONOFF
1 OFF ON
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
TERMINOLOGY
V
DD
Most Positive Power Supply Potential
GND Ground (0 V) Reference
S Source Terminal. May be an input or output.
DDrain Terminal. May be an input or output.
IN Logic Control Input
R
ON
∆R
ON
R
FLAT(ON)
Ohmic Resistance between D and S
On Resistance Match between Any Two Channels
i.e., R
max – R
ON
ON
min
Flatness is defined as the difference between the
maximum and minimum value of on resistance,
as measured over the specified analog signal range.
I
(Off) Source Leakage Current with the Switch Off
S
I
, IS (On) Channel Leakage Current with the Switch On
D
V
)Analog Voltage on Terminals D and S
D (VS
C
(Off) Off Switch Source Capacitance
S
C
, CS (On) On Switch Capacitance
D
t
ON
Delay between Applying the Digital Control
Input and the Output Switching On
t
OFF
Delay between Applying the Digital Control
Input and the Output Switching Off
t
D
Off Time or On Time Measured between the
90% Points of Both Switches, when Switching
From One Address State to Another
Crosstalk A Measure of Unwanted Signal That Is Coupled
through from One Channel to Another as a Result
of Parasitic Capacitance
Off Isolation A Measure of Unwanted Signal Coupling through
an Off Switch
Bandwidth The Frequency at Which the Output is Attenuated
by –3 dBs
On Response The Frequency Response of the On Switch
Insertion Loss Loss due to On Resistance of Switch
6-Lead SOT-23
(RT-6)
1
IN
ADG719
2
V
TOP VIEW
DD
(Not to Scale)
3
GND
6
S2
5
D
4
S1
8-Lead SOIC
(RM-8)
1
D
2
ADG719
S1
TOP VIEW
3
GND
(Not to Scale)
4
DD
NC = NO CONNECT
8
S2
7
NC
6
IN
5
NCV
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Brand* Package Description Package Option
ADG719BRM –40°C to +125°C S5B µSOIC (MicroSmall Outline IC) [MSOP] RM-8
ADG719BRT –40°C to +125°C S5B SOT-23 (Plastic Surface Mount) RT-6
*Branding on these packages is limited to three characters due to space constraints.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
WARNING!
Although the ADG719 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. B
Page 5

Typical Performance Characteristics–
FREQUENCY – Hz
1n
10
I
SUPPLY
– A
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
10n
100n
1
10
100
1m
10m
1
VDD = 5V
ADG719
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
–
3.0
ON
R
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
VDD = 3.0V
0 5.00.5
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
VD OR VS – DRAIN OR SOURCE VOLTAGE – V
VDD = 2.7V
VDD = 5.0V
TA = 25C
VDD = 4.5V
TPC 1. On Resistance vs. VD (VS), Single Supplies
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
–
3.0
ON
R
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0 3.00.5
+85C
+25C
–40C
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
VD OR VS – DRAIN OR SOURCE VOLTAGE – V
VDD = 3V
TPC 2. On Resistance vs. VD (VS) for Different
Temperatures, V
DD
= 3 V
0.15
0.10
0.05
CURRENT – nA
0
–0.05
09010
I
D
IS (OFF)
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
TEMPERATURE – C
, IS (ON)
V
DD
V
= 4.5V/1V
D
V
= 1V/4.5V
S
= 5V
TPC 4. Leakage Currents vs. Temperature
0.15
0.10
0.05
CURRENT – nA
0
–0.05
09010
I
, IS (ON)
D
IS (OFF)
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
TEMPERATURE – C
V
DD
V
D
V
S
= 3V
= 3V/1V
= 1V/3V
TPC 5. Leakage Currents vs. Temperature
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
–
R
ON
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0 5.00.5
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
VD OR VS – DRAIN OR SOURCE VOLTAGE – V
+85C
+25C
–40C
TPC 3. On Resistance vs. VD (VS) for Different
Temperatures, VDD = 5 V
REV. B
VDD = 5V
3.5 4.0 4.5
TPC 6. Supply Current vs. Input Switching Frequency
–5–
Page 6

ADG719
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
OFF ISOLATION – dB
–100
–110
–120
–130
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY – Hz
VDD = 5V, 3V
TPC 7. Off Isolation vs. Frequency
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
CROSSTALK – dB
–100
–110
–120
–130
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY – Hz
VDD = 5V, 3V
TPC 8. Crosstalk vs. Frequency
0
VDD = 5V
–2
–4
ON RESPONSE – dB
–6
100k 1M 100M
FREQUENCY – Hz
10M10k
TPC 9. On Response vs. Frequency
12
10
8
6
– pC
4
INJ
Q
2
0
–2
–4
05
VDD 3V
V
5V
DD
1234
V
– V
S
TPC 10. Charge Injection vs. Source Voltage
–6–
REV. B
Page 7

Test Circuits
ADG719
I
DS
V1
SD
V
S
RON = V1/ I
DS
Test Circuit 1. On Resistance
V
S
V
S1
V
S2
V
IN
0.1F
S1
S2
IN
IN
IS (OFF) ID (OFF)
V
S
SD
A A
Test Circuit 2. Off Leakage
V
DD
0.1F
V
DD
SD
GND
R
L
300
C
L
35pF
V
OUT
V
IN
V
OUT
Test Circuit 4. Switching Times
V
DD
V
V
DD
GND
D2
D
R
L2
300
C
L2
35pF
V
OUT
IN
0V
V
OUT
0V
Test Circuit 5. Break-Before-Make Time Delay, t
V
D
50% 50%
90%
t
ON
50% 50%
50% 50%
t
D
D
SD
V
S
ID (ON)
Test Circuit 3. On Leakage
90%
t
OFF
t
D
A
V
D
V
DD
0.1F
V
DD
IN
V
IN
S
GND
50
D
OFF ISOLATION = 20 LOG
Test Circuit 6. Off Isolation
NETWORK
ANALYZER
50
V
OUT
R
L
50
V
OUT
V
V
IN
V
S
0.1F
IN
V
DD
0.1F
NETWORK
ANALYZER
R
V
L
OUT
50
S
50
V
S
V
DD
S1
S2
IN
GND
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL
CROSSTALK = 20
LOG
D
R
50
V
OUT
V
S
Test Circuit 7. Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
V
DD
NETWORK
V
DD
S
D
GND
ANALYZER
50
V
V
OUT
R
L
50
S
REV. B
INSERTION LOSS = 20 LOG
V
Test Circuit 8. Bandwidth
–7–
WITH SWITCH
V
OUT
WITHOUT SWITCH
OUT
Page 8

ADG719
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The ADG719 belongs to Analog Devices’ new family of
CMOS switches. This series of general-purpose switches has
improved switching times, lower on resistance, higher bandwidths, low power consumption, and low leakage currents.
ADG719 Supply Voltages
Functionality of the ADG719 extends from 1.8 V to 5.5 V single
supply, which makes it ideal for battery-powered instruments
where power efficiency and performance are important design
parameters.
It is important to note that the supply voltage effects the input
signal range, the on resistance, and the switching times of the part.
By taking a look at the Typical Performance Characteristics and the
Specifications, the effects of the power supplies can be clearly seen.
For V
= 1.8 V operation, RON is typically 40 Ω over the
DD
temperature range.
On Response vs. Frequency
Figure 1 illustrates the parasitic components that affect the ac performance of CMOS switches (the switch is shown surrounded by a
box). Additional external capacitances will further degrade some
performance. These capacitances affect feedthrough, crosstalk,
and system bandwidth.
C
DS
S
R
V
IN
ON
D
C
D
C
LOAD
R
LOAD
V
OUT
Figure 1. Switch Represented by Equivalent Parasitic
Components
The transfer function that describes the equivalent diagram of
the switch (Figure 1) is of the form A(s) shown below:
As R
()
=
sR C
()
ON DS
T
sR R C
()
TONT
+
1
+
1
where:
RR R R
=+
T LOAD LOAD ON
=++
CC C C
T LOAD D DS
()
The signal transfer characteristic is dependent on the switch
channel capacitance, CDS. This capacitance creates a frequency
zero in the numerator of the transfer function A(s). Because the
switch on resistance is small, this zero usually occurs at high
frequencies. The bandwidth is a function of the switch output
capacitance combined with CDS and the load capacitance. The
frequency pole corresponding to these capacitances appears in
the denominator of A(s).
The dominant effect of the output capacitance, C
, causes the
D
pole breakpoint frequency to occur first. Therefore, in order to
maximize bandwidth, a switch must have a low input and
output capacitance and low on resistance. The On Response
vs. Frequency plot for the ADG719 can be seen in TPC 9.
Off Isolation
Off isolation is a measure of the input signal coupled through an
off switch to the switch output. The capacitance, C
, couples the
DS
input signal to the output load when the switch is off, as shown
in Figure 2.
C
DS
S
V
IN
D
C
D
C
LOAD
R
LOAD
V
OUT
Figure 2. Off Isolation Is Affected by External Load
Resistance and Capacitance
The larger the value of CDS, the larger the values of feedthrough
that will be produced. TPC 7 illustrates the drop in off isolation as
a function of frequency. From dc to roughly 200 kHz, the switch
shows better than –95 dB isolation. Up to frequencies of 10 MHz,
the off isolation remains better than –67 dB. As the frequency
increases, more and more of the input signal is coupled through to
the output. Off isolation can be maximized by choosing a switch
with the smallest C
possible. The values of load resistance and
DS
capacitance also affect off isolation, since they contribute to the
coefficients of the poles and zeros in the transfer function of the
switch when open.
As
()
=
sR C C C
()( )
sR C
()
LOAD DS
LOAD LOAD D DS
++ +
1
–8–
REV. B
Page 9

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
8-Lead Small Outline Package [MSOP]
(RM-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
3.00
BSC
ADG719
85
3.00
BSC
1
PIN 1
0.65 BSC
0.15
0.00
0.38
0.22
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-187AA
4
SEATING
PLANE
4.90
BSC
1.10 MAX
0.23
0.08
8ⴗ
0ⴗ
6-Lead Plastic Surface Mount Package [SOT-23]
(RT-6)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
2.90 BSC
1.90
BSC
0.50
0.30
4 5
2.80 BSC
2
0.95 BSC
1.45 MAX
SEATING
PLANE
0.22
0.08
10ⴗ
0ⴗ
1.60 BSC
1.30
1.15
0.90
0.15 MAX
6
1 3
PIN 1
0.80
0.40
0.60
0.45
0.30
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-178AB
–9–REV. B
Page 10

ADG719
Revision History
Location Page
7/02 Data Sheet changed from REV. A to REV. B.
Changes to Product Name ...............................................................................................................................................................1
Changes to FEATURES..................................................................................................................................................................1
Additions to PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS ....................................................................................................................................... 1
Changes to SPECIFICATIONS ......................................................................................................................................................2
Edits to ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ................................................................................................................................ 4
Changes to TERMINOLOGY.........................................................................................................................................................4
Edits to ORDERING GUIDE .........................................................................................................................................................4
Added new TPCs 4 and 5 ................................................................................................................................................................5
Replaced TPC 10 ............................................................................................................................................................................6
TEST CIRCUITs 6, 7, and 8 replaced ............................................................................................................................................7
Updated RM-8 and RT-6 package outlines ...................................................................................................................................... 9
–10–
REV. B
Page 11

–11–
Page 12

C00044–0–7/02(B)
–12–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...