Page 1
24-Bit Capacitance-to-Digital Converter
V
FEATURES
Capacitance-to-digital converter
New standard in single chip solutions
Interfaces to single or differential grounded sensors
Resolution down to 20 aF (that is, up to 19.5-bit ENOB)
Accuracy: 10 fF
Linearity: 0.01%
Common-mode (not changing) capacitance up to 17 pF
Full-scale (changing) capacitance range ±8 pF
Update rate: 5 Hz to 45 Hz
Simultaneous 50 Hz and 60 Hz rejection at 8.1 Hz update
Active shield for shielding sensor connection
Temperature sensor on-chip
Resolution: 0.1°C, accuracy: ±2°C
Voltage input channel
Internal clock oscillator
2-wire serial interface (I
Power
2.7 V to 5.25 V single-supply operation
0.7 mA current consumption
Operating temperature: −40°C to +125°C
16-lead TSSOP package
APPLICATIONS
Automotive, industrial, and medical systems for
Pressure measurement
Position sensing
Proximity sensing
Level sensing
Flow metering
Impurity detection
2
C® compatible)
with Temperature Sensor
AD7747
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7747 is a high-resolution, Σ- capacitance-to-digital
converter (CDC). The capacitance to be measured is connected
directly to the device inputs. The architecture features inherent
high resolution (24-bit no missing codes, up to 19.5-bit effective
resolution), high linearity (±0.01%), and high accuracy (±10 fF
factory calibrated). The AD7747 capacitance input range is
±8 pF (changing), and it can accept up to 17 pF common-mode
capacitance (not changing), which can be balanced by a programmable on-chip digital-to-capacitance converter (CAPDAC).
The AD7747 is designed for single-ended or differential
capacitive sensors with one plate connected to ground. For
floating (not grounded) capacitive sensors, the AD7745 or
AD7746 are recommended.
The part has an on-chip temperature sensor with a resolution of
0.1°C and accuracy of ±2°C. The on-chip voltage reference and
the on-chip clock generator eliminate the need for any external
components in capacitive sensor applications. The part has a
standard voltage input that, together with the differential reference
input, allows easy interface to an external temperature sensor,
such as an RTD, thermistor, or diode.
2
The AD7747 has a 2-wire, I
part can operate with a single power supply of 2.7 V to 5.25 V.
It is specified over the automotive temperature range of
−40°C to +125°C and is housed in a 16-lead TSSOP package.
C-compatible serial interface. The
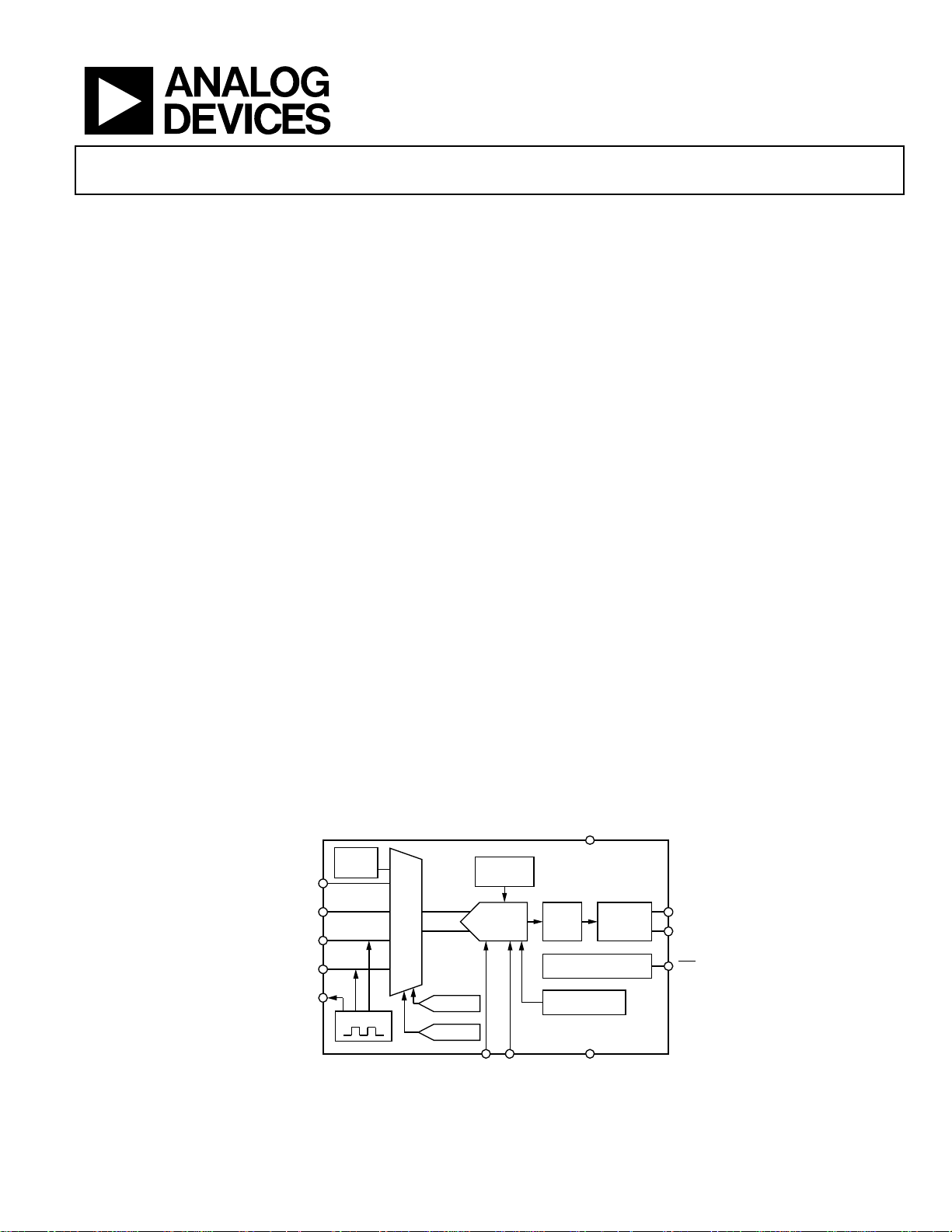
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DD
TEMP
SENSOR
VIN(+)
VIN(–)
CIN1(+)
CIN1(–)
SHLD
EXCITATION
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
MUX
CAP DAC 1
CAP DAC 2
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
GENERATOR
REFIN( +) REFIN( –)
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
AD7747
DIGITAL
FILTER
CONTROL LOG IC
CALIBRATION
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
GND
I2C
SERIAL
INTERFACE
SDA
SCL
RDY
05469-001
Page 2

AD7747
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 6
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 6
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Output Noise and Resolution Specifications ..............................11
Serial Interface ................................................................................ 12
Read Operation........................................................................... 12
Write Operation.......................................................................... 12
AD7747 Reset.............................................................................. 13
General Call................................................................................. 13
Register Descriptions ..................................................................... 14
Status Register............................................................................. 15
Cap Data Register....................................................................... 15
VT Data Register ........................................................................15
Cap Setup Register ..................................................................... 16
VT Setup Register....................................................................... 16
EXC Setup Register ....................................................................17
Configuration Register .............................................................. 18
Cap DAC A Register .................................................................. 19
Cap DAC B Register................................................................... 19
Cap Offset Calibration Register ............................................... 20
Cap Gain Calibration Register.................................................. 20
Volt Gain Calibration Register ................................................. 20
Circuit Description......................................................................... 21
Overview ..................................................................................... 21
Capacitance-to-Digital Converter............................................ 21
Active AC Shield Concept......................................................... 21
CAPDAC..................................................................................... 21
Single-Ended Capacitive Configuration ................................. 22
Differential Capacitive Configuration..................................... 22
Parasitic Capacitance................................................................. 23
Parasitic Resistance.................................................................... 23
Parasitic Serial Resistance ......................................................... 23
Capacitive Gain Calibration ..................................................... 23
Capacitive System Offset Calibration...................................... 24
Internal Temperature Sensor .................................................... 24
External Temperature Sensor ................................................... 24
Voltage Input............................................................................... 25
V
Monitor................................................................................ 25
DD
Typical Application Diagram.................................................... 26
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 27
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 27
REVISION HISTORY
1/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 28
Page 3
AD7747
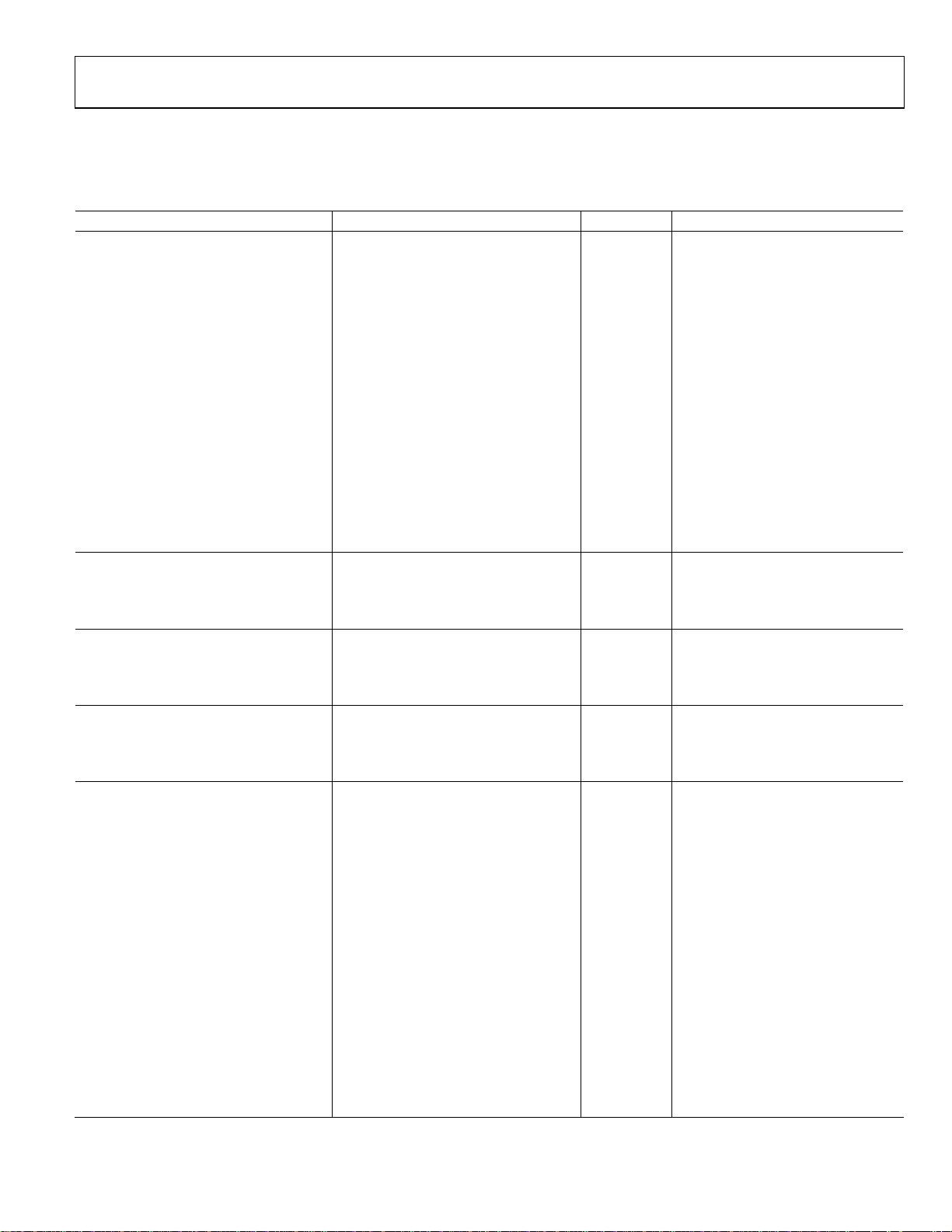
SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V or 4.75 V to 5.25 V; GND = 0 V; EXC = ±V
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CAPACITIVE INPUT
Conversion Input Range ±8.192 pF1 Factory calibrated
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)2 ±0.01 % of FSR1
No Missing Codes2 24 Bit Conversion time ≥ 124 ms
Resolution, p-p 16.5 Bit Conversion time 124 ms, see Table 5
Resolution Effective 19.1 Bit Conversion time 124 ms, see Table 5
Output Noise, rms 11.0
Absolute Error3 ±10 fF1 25°C, VDD = 5 V, after offset calibration
Offset Error
4, 5
32 aF1
System Offset Calibration Range5 ±1 pF
Offset Deviation over Temperature2 0.4 fF See Figure 6
Gain Error6 0.02 0.11 % of FS1 25°C, VDD = 5 V
Gain Drift vs. Temperature2 −23 −26 −29 ppm of FS/°C
Power Supply Rejection2 0.5 4 fF/V
Normal Mode Rejection5 72 dB 50 Hz ± 1%, conversion time 124 ms
60 dB 60 Hz ± 1%, conversion time 124 ms
CAPDAC
Full Range 17 21 pF 6-bit CAPDAC
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) 0.3 LSB See Figure 16
Drift vs. Temperature2 26 ppm of FS/°C
EXCITATION
Frequency 16 kHz
AC Voltage Across Capacitance ±VDD × 3/8 V To be configured via digital interface
Average DC Voltage Across Capacitance VDD/2 V
TEMPERATURE SENSOR7 V
Resolution 0.1 °C
Error2 ±0.5 ±2 °C Internal temperature sensor
±2 °C External sensing diode8
VOLTAGE INPUT7 V
Differential VIN Voltage Range ±V
Absolute VIN Voltage2 GND − 0.03 VDD + 0.03 V
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) ±3 ±15 ppm of FS
No Missing Codes2 24 Bit Conversion time = 122.1 ms
Resolution, p-p 16 Bits
Output Noise 3 μV rms
Offset Error ±3 μV
Offset Drift vs. Temperature 15 nV/°C
Full-Scale Error
2, 9
0.025 0.1 % of FS
Full-Scale Drift vs. Temperature 5 ppm of FS/°C Internal reference
0.5 ppm of FS/°C External reference
Average VIN Input Current 300 nA/V
Analog VIN Input Current Drift ±50 pA/V/°C
Power Supply Rejection 80 dB Internal reference, VIN = V
90 dB External reference, VIN = V
× 3/8; −40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted.
DD
aF/√Hz
Conversion time 124 ms, see Table 5
After system offset calibration,
excluding effect of noise
REF
REF
V
REF
Conversion time = 62 ms,
see Table 6 and Table 7
Conversion time = 62 ms,
see Table 6 and Table 7
internal
internal or V
= 2.5 V
REF
4
/2
REF
/2
REF
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 28
Page 4
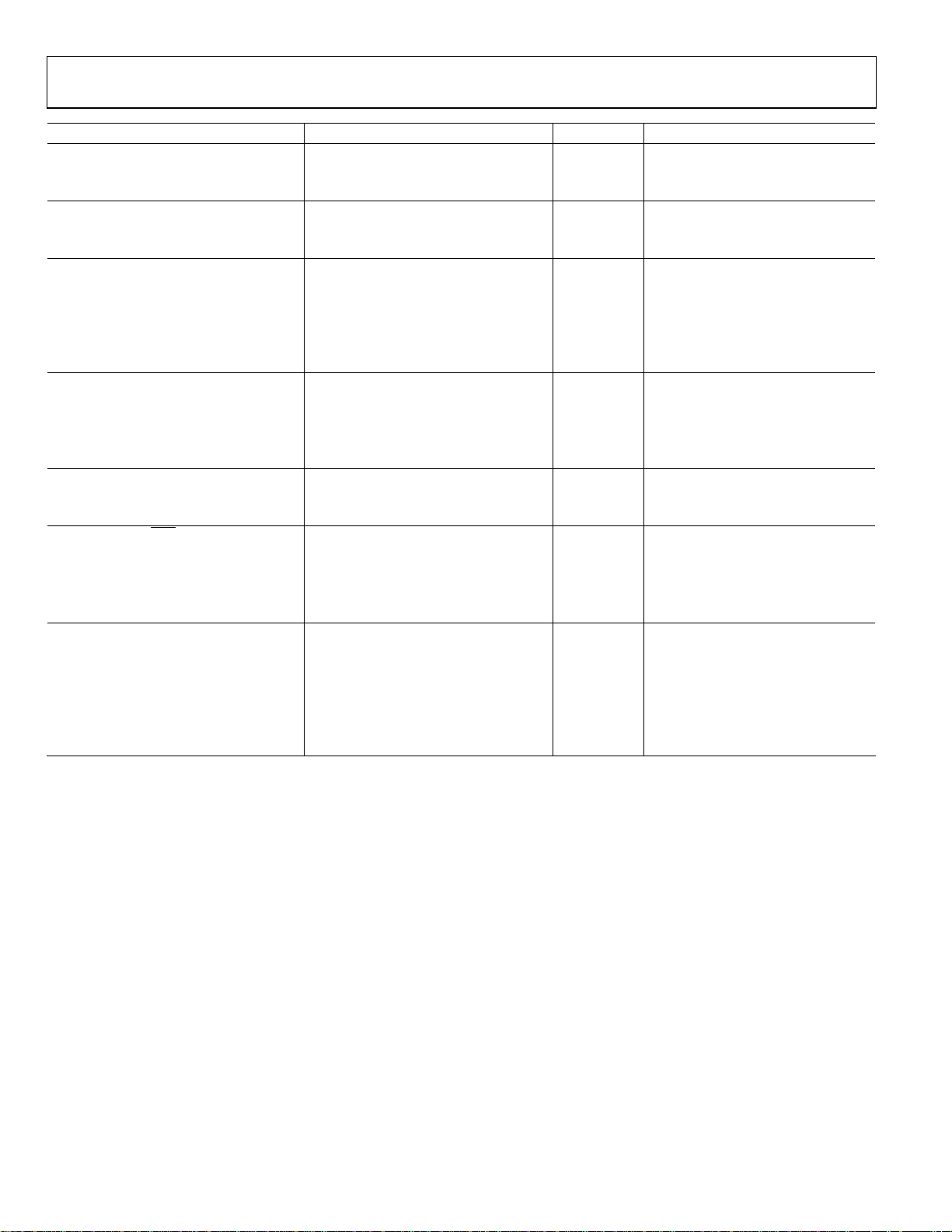
AD7747
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Normal Mode Rejection5 75 dB 50 Hz ± 1%, conversion time = 122.1 ms
50 dB 60 Hz ± 1%, conversion time = 122.1 ms
Common-Mode Rejection2 95 dB VIN = 1 V
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Voltage 1.169 1.17 1.171 V TA = 25°C
Drift vs. Temperature 5 ppm/°C
EXTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT
Differential REFIN Voltage2 0.1 2.5 VDD V
Absolute REFIN Voltage2 GND − 0.03 VDD + 0.03 V
Average REFIN Input Current 400 nA/V
Average REFIN Input Current Drift ±50 pA/V/°C
Common-Mode Rejection 80 dB
SERIAL INTERFACE LOGIC INPUTS (SCL, SDA)
VIH Input High Voltage 2.1 V
VIL Input Low Voltage 0.8 V
Hysteresis 150 mV
Input Leakage Current (SCL) ±0.1 ±1 μA
OPEN-DRAIN OUTPUT (SDA)
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
IOH Output High Leakage Current 0.1 1 μA V
LOGIC OUTPUT (
RDY
)
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
VOH Output High Voltage 4.0 V I
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
VOH Output High Voltage VDD − 0.6 V I
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD-to-GND Voltage 4.75 5.25 V VDD = 5 V, nominal
2.7 3.6 V VDD = 3.3 V, nominal
IDD Current 850 μA Digital inputs equal to VDD or GND
750 μA VDD = 5 V
700 μA VDD = 3.3 V
IDD Current Power-Down Mode 0.5 2 μA Digital inputs equal to VDD or GND
1
Capacitance units: 1 pF = 10
2
Specification is not production tested, but is supported by characterization data at initial product release.
3
Factory calibrated. The absolute error includes factory gain calibration error, integral nonlinearity error, and offset error after system offset calibration, all at 25°C.
At different temperatures, compensation for gain drift over temperature is required.
4
The capacitive input offset can be eliminated using a system offset calibration. The accuracy of the system offset calibration is limited by the offset calibration register
LSB size (32 aF) or by converter + system p-p noise during the system capacitive offset calibration, whichever is greater. To minimize the effect of the converter +
system noise, longer conversion times should be used for system capacitive offset calibration. The system capacitance offset calibration range is ±1 pF; the larger
offset can be removed using CAPDACs.
5
Specification is not production tested, but guaranteed by design.
6
The gain error is factory calibrated at 25°C. At different temperatures, compensation for gain drift over temperature is required.
7
The VTCHOP bit in the VT SETUP register must be set to 1 for the specified temperature sensor and voltage input performance.
8
Using an external temperature sensing diode 2N3906, with nonideality factor nf = 1.008, connected as in Figure 37, with total serial resistance <100 Ω.
9
Full-scale error applies to both positive and negative full scale.
−12
F; 1 fF = 10
−15
F; 1 aF = 10
−18
F. Full scale (FS) = 8.192 pF; full-scale range (FSR) = ±8.192 pF.
= −6.0 mA
SINK
= VDD
OUT
= 1.6 mA, VDD = 5 V
SINK
= 200 μA, VDD = 5 V
SOURCE
= 100 μA, VDD = 3 V
SINK
= 100 μA, VDD = 3 V
SOURCE
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 28
Page 5
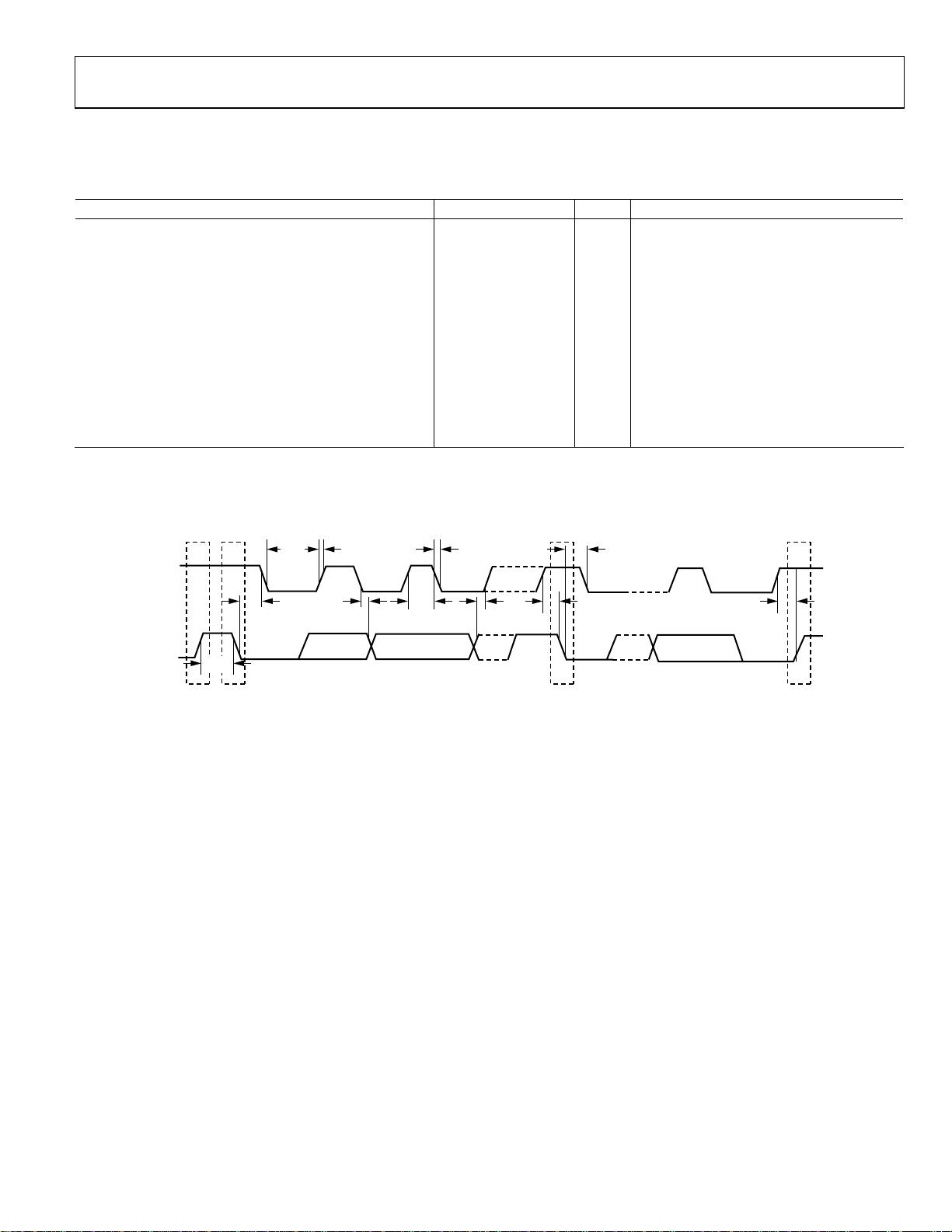
AD7747
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, or 4.75 V to 5.25 V; GND = 0 V; Input Logic 0 = 0 V; Input Logic 1 = VDD; −40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SERIAL INTERFACE
SCL Frequency 0 400 kHz
SCL High Pulse Width, t
SCL Low Pulse Width, t
SCL, SDA Rise Time, tR 0.3 μs
SCL, SDA Fall Time, t
Hold Time (Start Condition), t
Setup Time (Start Condition), t
Data Setup Time, t
Setup Time (Stop Condition), t
Data Hold Time, t
Bus-Free Time (Between Stop and Start Condition, t
1
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance.
2
All input signals are specified with input rise/fall times = 3 ns, measured between the 10% and 90% points. Timing reference points at 50% for inputs and outputs.
Output load = 10 pF.
1, 2
See Figure 2
0.6 μs
HIGH
1.3 μs
LOW
F
0.6 μs After this period, the first clock is generated
HD;STA
0.6 μs Relevant for repeated start condition
SU;STA
0.1 μs
SU;DAT
0.6 μs
SU;STO
(Master) 0 μs
HD;DAT
t
R
t
LOW
0.3 μs
) 1.3 μs
BUF
t
F
t
HD;STA
SCL
t
SDA
t
t
BUF
PS
HD;STA
t
HD;DAT
HIGH
t
SU;DAT
t
SU;STA
S
t
SU;STO
P
05469-002
Figure 2. Serial Interface Timing Diagram
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 28
Page 6
AD7747
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Positive Supply Voltage VDD to GND −0.3 V to +6.5 V
Voltage on any Input or Output Pin to
GND
ESD Rating (ESD Association Human Body
Model, S5.1)
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
TSSOP Package θ
(Thermal Impedance-to-Air)
TSSOP Package θJC
(Thermal Impedance-to-Case)
Peak Reflow Soldering Temperature
Pb Free (20 sec to 40 sec) 260°C
JA
−0.3 V to V
2000 V
128°C/W
14°C/W
+ 0.3 V
DD
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only and functional operation of the device at these or
any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 28
Page 7
AD7747
V
V
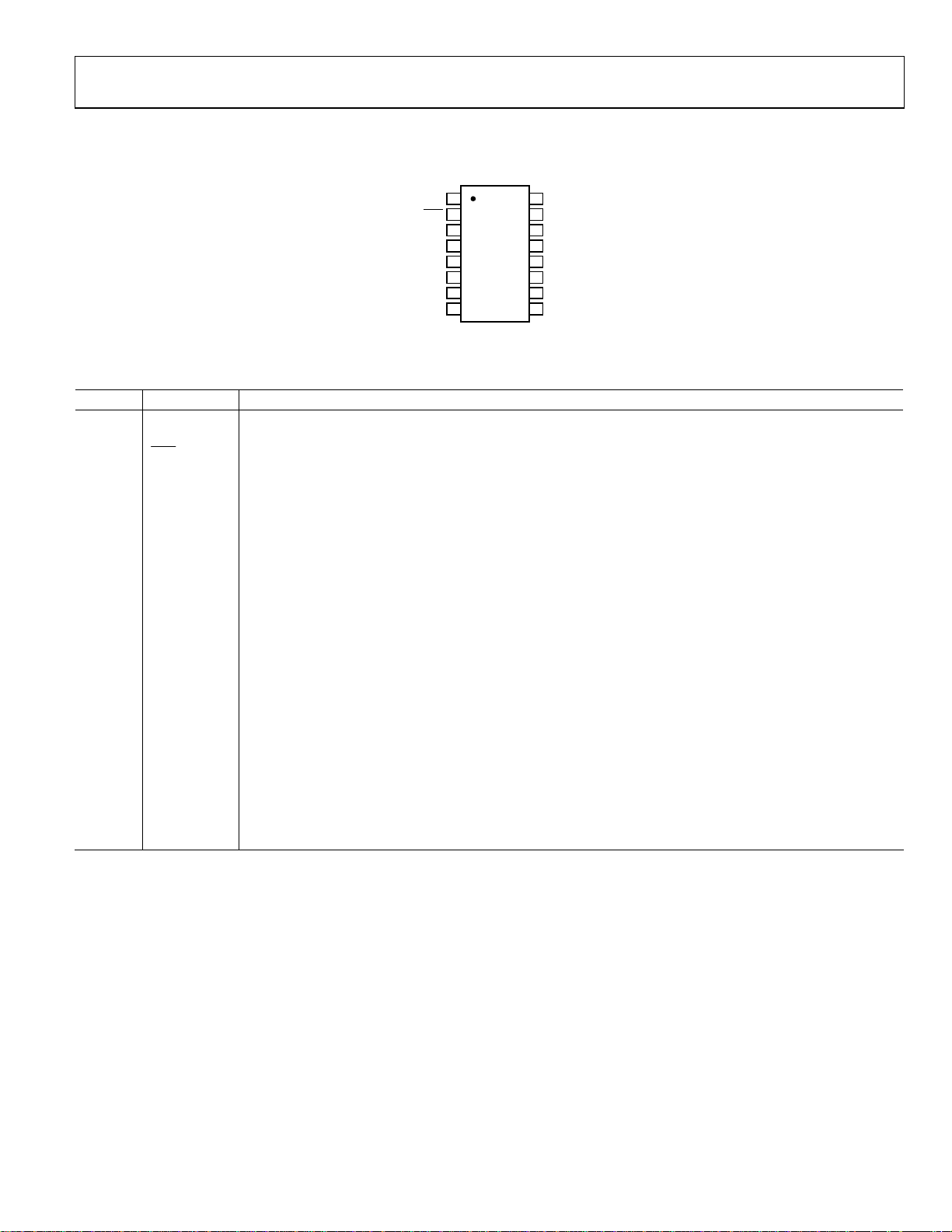
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
SCL
1
2
RDY
3
SHLD
TST
REFIN(+)
REFIN(–)
CIN1(–)
CIN1(+)
AD7747
4
TOP VIEW
5
(Not to Scale)
6
7
8
NC = NO CONNECT
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 SCL
Serial Interface Clock Input. Connects to the master clock line. Requires pull-up resistor if not already provided
in the system.
2
Logic Output. A falling edge on this output indicates that a conversion on enabled channel(s) has been finished
RDY
and the new data is available. Alternatively, the status register can be read via the 2-wire serial interface and the
relevant bit(s) decoded to query the finished conversion. If not used, this pin should be left as an open circuit.
3 SHLD
Capacitive Input Active AC Shielding. To eliminate the CIN parasitic capacitance to ground, the SHLD signal
can be used for shielding the connection between the sensor and CIN. If not used, this pin should be left as an
open circuit.
4 TST This pin must be left as an open circuit for proper operation.
5, 6
REFIN(+),
REFIN(−)
Differential Voltage Reference Input for the Voltage Channel (ADC). Alternatively, the on-chip internal reference
can be used for the voltage channel. These reference input pins are not used for conversion on capacitive
channel(s) (CDC). If not used, these pins can be left as an open circuit or connected to GND.
7 CIN1(−)
CDC Negative Capacitive Input. The measured capacitance is connected between the CIN1(−) pin and GND. If
not used, this pin should be left as an open circuit.
8 CIN1(+)
CDC Positive Capacitive Input. The measured capacitance is connected between the CIN1(+) pin and GND. If not
used, this pin should be left as an open circuit.
9, 10 NC Not Connected. These pins should be left as an open circuit.
11, 12 VIN(+), VIN(−)
Differential Voltage Input for the Voltage Channel (ADC). These pins are also used to connect an external
temperature sensing diode. If not used, these pins can be left as an open circuit or connected to GND.
13 GND Ground Pin.
14 VDD
Power Supply Voltage. This pin should be decoupled to GND, using a low impedance capacitor, for example in
combination with a 10 μF tantalum and a 0.1 μF multilayer ceramic.
15 NC Not Connected. This pin should be left as an open circuit.
16 SDA
Serial Interface Bidirectional Data. Connects to the master data line. Requires a pull-up resistor if not provided
elsewhere in the system.
SDA
16
15
NC
14
VDD
13
GND
12
IN(–)
11
IN(+)
10
NC
9
NC
05469-003
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 28
Page 8
AD7747
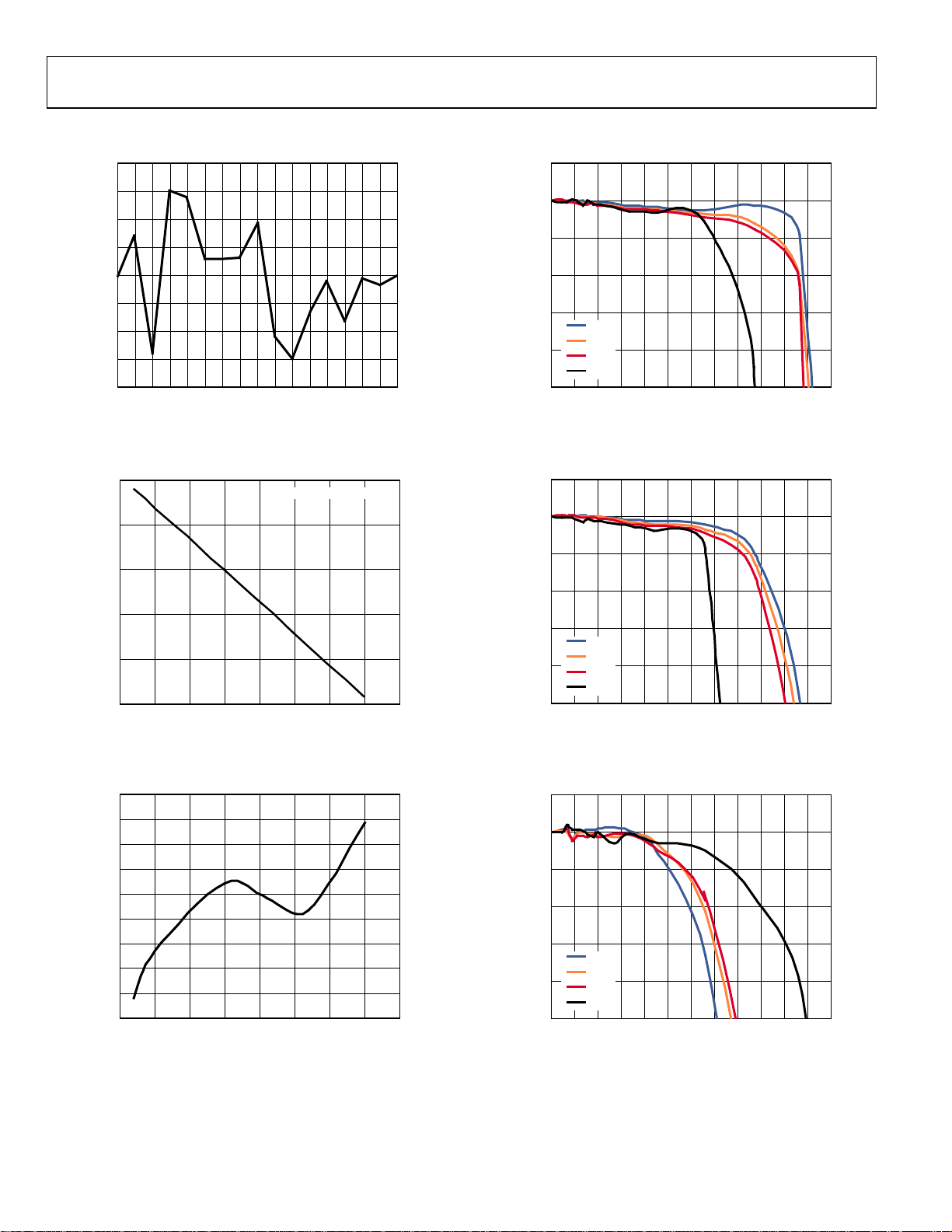
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
80
10
60
40
20
0
INL (ppm)
–20
–40
–60
–80
–8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –1–2 8
INPUT CAPACIT ANCE (pF)
01234567
Figure 4. Capacitance Input Integral Nonlinearity;
= 5 V, CAPDAC = 0x3F
V
DD
2000
1000
0
–1000
GAIN ERROR (ppm)
–2000
–3000
–50 150
–25 0 25 50 75 100 125
TEMPERATURE (ºC)
GAIN TC ≈ –28ppm/ºC
Figure 5. Capacitance Input Gain Drift vs. Temperature;
V
= 5 V, CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF
DD
.20
.15
.10
.050
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
OFFSET ERROR (fF)
–0.20
–0.25
–0.30
–50 150
–25 0 25 50 75 100 125
TEMPERATURE (ºC)
0
–10
–20
CAP ERROR (fF)
–30
–40
05469-004
–50
2.7V
3.0V
3.3V
5.0V
0 600500
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 550
CAPACITANCE SHLD T O GND (pF )
05469-007
Figure 7. Capacitance Input Error vs. Capacitance Between SHLD and GND;
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF, V
10
0
–10
–20
CAP ERROR (fF)
–30
–40
05469-005
–50
2.7V
3.0V
3.3V
5.0V
0 600500
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 550
CAPACITANCE SHLD T O GND (pF )
= 2.7 V, 3 V, 3.3 V, and 5 V
DD
05469-008
Figure 8. Capacitance Input Error vs. Capacitance Between SHLD and GND;
CIN(+) to GND = 25 pF, V
10
0
–10
–20
CAP ERROR (fF)
–30
–40
05469-006
–50
2.7V
3.0V
3.3V
5.0V
0 600500
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 550
CAPACITANCE CIN TO SHLD (pF )
= 2.7 V, 3 V, 3.3 V, and 5 V
DD
05469-009
Figure 6. Capacitance Input Offset Drift vs. Temperature;
= 5 V, CIN(+) Open
V
DD
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 28
Figure 9. Capacitance Input Error vs. Capacitance Between CIN(+) and SHLD;
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF, V
= 2.7 V, 3 V, 3.3 V, and 5V
DD
Page 9
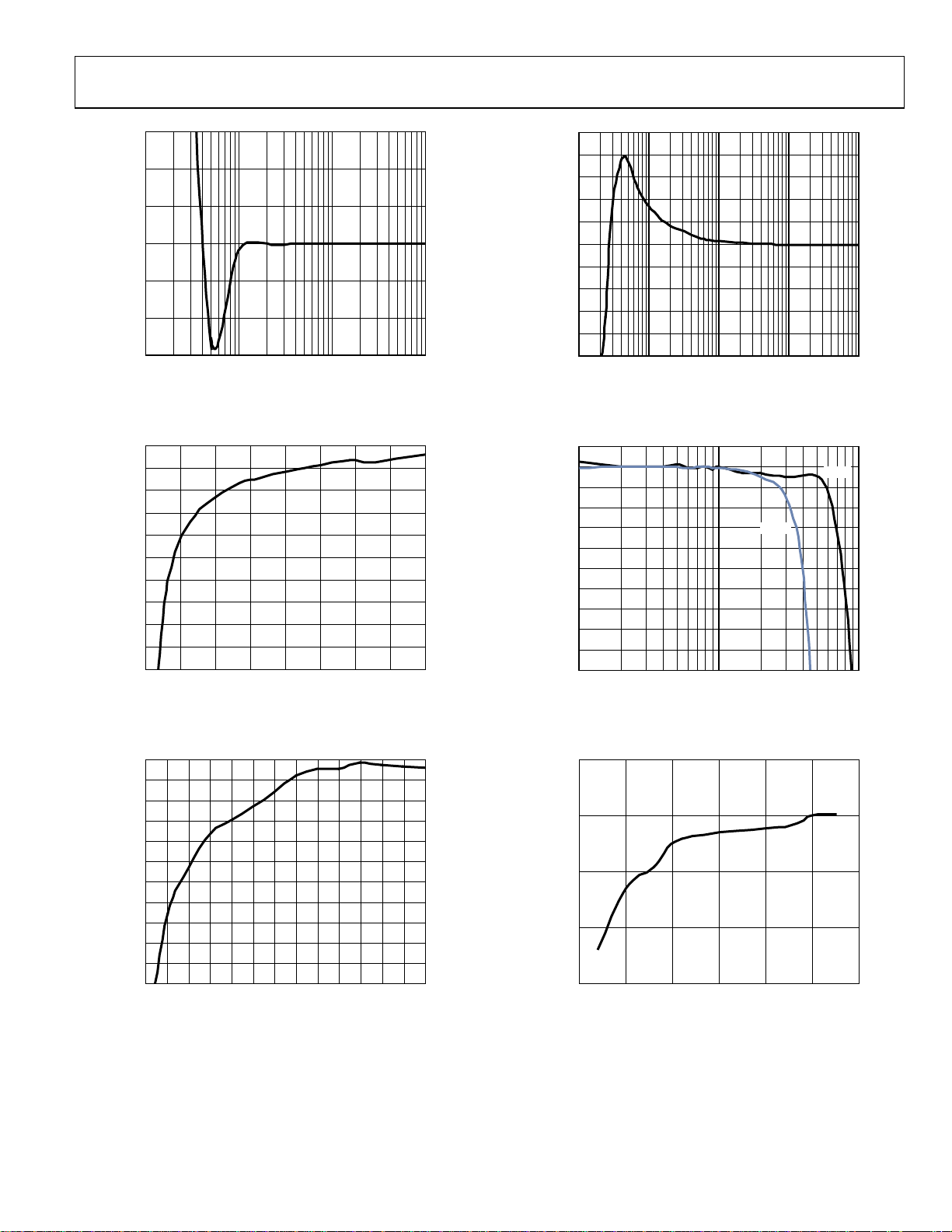
AD7747
150
100
50
0
CAP ERROR (fF)
–50
–100
–150
01k
10 100
PARALLEL RESISTANCE (MΩ)
05469-010
Figure 10. Capacitance Input Error vs. Parallel Resistance;
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF, V
0
–100
–200
–300
–400
–500
–600
CAP ERROR (fF)
–700
–800
–900
–1000
0 200
25 50 75 1 00 125 150 175
CIN TO SHLD RE SISTANCE (kΩ)
= 5 V
DD
05469-058
Figure 11. Capacitance Input Error vs. Resistance Between CIN1(+) and SHLD;
DD
= 5 V
05469-059
100
–100
–200
–300
–400
–500
–600
CAP ERROR (fF)
–700
–800
–900
–1000
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF, V
0
0.091
0.27 0. 48 0. 96 5 25 100
CIN TO SHLD RE SISTANCE (MΩ)
Figure 12. Capacitance Input Error vs. Resistance Between CIN(+) and SHLD;
CIN(+) to GND = 25 pF, V
DD
= 5 V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
CAP ERROR (pF)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0.01
0.1 1.0 10.0
SHLD TO GND RESI STANCE (MΩ)
100
05469-066
Figure 13. Capacitance Input Error vs. Resistance Between SHLD and GND;
= 5 V
DD
8 pF
25 pF
05469-067
10
100
CAP ERROR (fF)
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF; V
10
0
1
SERIAL RESISTANCE (kΩ)
Figure 14. Capacitance Input Error vs. Serial Resistance;
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF and 25pF, V
0.2
0
–0.2
CAP ERROR (fF)
–0.4
–0.6
3.0 3.5 4. 0 4.5 5.0
2.5 5.5
VDD (V)
DD
= 5 V
05469-062
Figure 15. Capacitance Input Power Supply Rejection (PSR);
CIN(+) to GND = 8 pF
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 28
Page 10

AD7747
200
0
150
100
50
0
–50
CAPDAC DNL (fF)
–100
–150
–200
8 162432404856
064
CAPDAC CODE
05469-050
Figure 16. CAPDAC Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
ERROR (°C)
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
–50
–25 0 25 50 75 100 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
150
05469-034
Figure 17. Internal Temperature Sensor Error vs. Temperature
–20
–40
–60
GAIN (dB)
–80
–100
–120
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
01k
Figure 19. Capacitive Channel Frequency Response;
0
–20
–40
–60
GAIN (dB)
–80
–100
–120
25 50 75 1 00 125 150 175
0 200
Figure 20. Capacitive Channel Frequency Response;
INPUT SIGNAL FREQUENCY ( Hz)
Conversion Time = 22 ms
INPUT SIGNAL FREQUENCY ( Hz)
Conversion Time = 124 ms
05469-051
05469-052
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
ERROR (°C)
–1.5
–2.0
–2.5
–3.0
–50
–25 0 25 50 75 100 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 18. External Temperature Sensor Error vs. Temperature
05469-035
150
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 28
0
–20
–40
–60
GAIN (dB)
–80
–100
–120
0
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
INPUT SIGNAL FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 21. Voltage Channel Frequency Response;
Conversion Time = 122.1 ms
400
05469-039
Page 11

AD7747
OUTPUT NOISE AND RESOLUTION SPECIFICATIONS
The AD7747 resolution is limited by noise. The noise
performance varies with the selected conversion time.
Table 5 shows typical noise performance and resolution for the
capacitive channel. These numbers were generated from 1000
data samples acquired in continuous conversion mode, at an
excitation of 16 kHz, ±V
× 3/8, and with all CIN and SHLD
DD
pins connected only to the evaluation board (no external
capacitors).
Table 5. Typical Capacitive Input Noise and Resolution vs. Conversion Time (Bold line represents default setting)
Conversion
Time (ms)
22.0 45.5 43.6 28.8 190 821 16.4 14.3
23.9 41.9 39.5 23.2 146 725 16.8 14.5
40.0 25.0 21.8 11.1 52 411 18.3 15.3
76.0 13.2 10.9 11.2 37 262 18.7 15.9
124.0 8.1 6.9 11.0 29 174 19.1 16.5
154.0 6.5 5.3 10.4 24 173 19.3 16.5
184.0 5.4 4.4 10.0 21 141 19.6 16.8
219.3 4.6 4.0 9.0 18 126 19.9 17.0
Output Data
Rate (Hz)
−3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
RMS Noise
(aF/√Hz)
Table 6 and Table 7 show typical noise performance and
resolution for the voltage channel. These numbers were
generated from 1000 data samples acquired in continuous
conversion mode with VIN pins shorted to ground.
RMS noise represents the standard deviation and p-p noise
represents the difference between minimum and maximum
results in the data. Effective resolution is calculated from rms
noise, and p-p resolution is calculated from p-p noise.
RMS
Noise (aF)
P-P
Noise (aF)
Effective Resolution
(Bits)
P-P Resolution
(Bits)
Table 6. Typical Voltage Input Noise and Resolution vs. Conversion Time, Internal Voltage Reference
Conversion
Time (ms)
20.1 49.8 26.4 11.4 62 17.6 15.2
32.1 31.2 15.9 7.1 42 18.3 15.7
62.1 16.1 8.0 4.0 28 19.1 16.3
122.1 8.2 4.0 3.0 20 19.5 16.8
Output Data
Rate (Hz)
−3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
RMS Noise
(μV)
P-P Noise
(μV)
Effective Resolution
(Bits)
P-P Resolution
(Bits)
Table 7. Typical Voltage Input Noise and Resolution vs. Conversion Time, External 2.5 V Voltage Reference
Conversion
Time (ms)
20.1 49.8 26.4 14.9 95 18.3 15.6
32.1 31.2 15.9 6.3 42 19.6 16.8
62.1 16.1 8.0 3.3 22 20.5 17.7
122.1 8.2 4.0 2.1 15 21.1 18.3
Output Data
Rate (Hz)
−3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
RMS Noise
(μV)
P-P Noise
(μV)
Effective Resolution
(Bits)
P-P Resolution
(Bits)
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 28
Page 12

AD7747
SERIAL INTERFACE
The AD7747 supports an I2C-compatible 2-wire serial interface.
The two wires on the I
(data). These two wires carry all addressing, control, and data
information one bit at a time over the bus to all connected
peripheral devices. The SDA wire carries the data, while the
SCL wire synchronizes the sender and receiver during the data
transfer. I
A device that initiates a data transfer message is called a master,
while a device that responds to this message is called a slave.
To control the AD7747 device on the bus, the following
protocol must be followed. First, the master initiates a data
transfer by establishing a start condition, defined by a high-tolow transition on SDA while SCL remains high. This indicates
that the start byte follows. This 8-bit start byte is made up of a
7-bit address plus an R/W bit indicator.
All peripherals connected to the bus respond to the start
condition and shift in the next 8 bits (7-bit address + R/W bit).
The bits arrive MSB first. The peripheral that recognizes the
transmitted address responds by pulling the data line low
during the ninth clock pulse. This is known as the acknowledge
bit. All other devices withdraw from the bus at this point and
maintain an idle condition. An exception to this is the general
call address, which is described later in this document. The idle
condition is where the device monitors the SDA and SCL lines
waiting for the start condition and the correct address byte. The
R/W bit determines the direction of the data transfer. A Logic 0
LSB in the start byte means that the master writes information
to the addressed peripheral. In this case, the AD7747 becomes a
slave receiver. A Logic 1 LSB in the start byte means that the
master reads information from the addressed peripheral. In this
case, the AD7747 becomes a slave transmitter. In all instances, the
AD7747 acts as a standard slave device on the I
The start byte address for the AD7747 is 0x90 for a write and
0x91 for a read.
2
C devices are classified as either master or slave devices.
2
C bus are called SCL (clock) and SDA
2
C bus.
READ OPERATION
When a read is selected in the start byte, the register that is
currently addressed by the address pointer is transmitted on to
the SDA line by the AD7747. This is then clocked out by the
master device and the AD7747 awaits an acknowledge from the
master.
If an acknowledge is received from the master, the address autoincrementer automatically increments the address pointer
register and outputs the next addressed register content on to
the SDA line for transmission to the master. If no acknowledge
is received, the AD7747 returns to the idle state and the address
pointer is not incremented.
The address pointer’s auto-incrementer allows block data to be
written or read from the starting address and subsequent
incremental addresses.
In continuous conversion mode, the address pointer’s autoincrementer should be used for reading a conversion result.
That means the three data bytes should be read using one
multibyte read transaction rather than three separate single byte
transactions. The single byte data read transaction may result in
the data bytes from two different results being mixed. The same
applies for six data bytes if both the capacitive and the
voltage/temperature channel are enabled.
The user can also access any unique register (address) on a oneto-one basis without having to update all the registers. The
address pointer register’s contents cannot be read.
If an incorrect address pointer location is accessed, or if the user
allows the auto-incrementer to exceed the required register
address, the following applies:
• In read mode, the AD7747 continues to output various
internal register contents until the master device issues a
no acknowledge, start, or stop condition. The address
pointer auto-incrementer’s contents are reset to point to
the status register at Address 0x00 when a stop condition is
received at the end of a read operation. This allows the
status register to be read (polled) continually without
having to constantly write to the address pointer.
• In write mode, the data for the invalid address is not
loaded into the AD7747 registers, but an acknowledge is
issued by the AD7747.
WRITE OPERATION
When a write is selected, the byte following the start byte is
always the register address pointer (subaddress) byte, which
points to one of the internal registers on the AD7747. The
address pointer byte is automatically loaded into the address
pointer register and acknowledged by the AD7747. After the
address pointer byte acknowledge, a stop condition, a repeated
start condition, or another data byte can follow from the master.
A stop condition is defined by a low-to-high transition on SDA
while SCL remains high. If a stop condition is ever encountered
by the AD7747, it returns to its idle condition and the address
pointer is reset to Address 0x00.
If a data byte is transmitted after the register address pointer
byte, the AD7747 loads this byte into the register that is
currently addressed by the address pointer register, sends an
acknowledge, and the address pointer auto-incrementer
automatically increments the address pointer register to the
next internal register address. Thus, subsequent transmitted
data bytes are loaded into sequentially incremented addresses.
If a repeated start condition is encountered after the address
pointer byte, all peripherals connected to the bus respond
exactly as outlined above for a start condition, that is, a repeated
start condition is treated the same as a start condition. When a
master device issues a stop condition, it relinquishes control of
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 28
Page 13

AD7747
the bus, allowing another master device to take control of the
bus. Therefore, a master wanting to retain control of the bus
issues successive start conditions known as repeated start
conditions.
AD7747 RESET
To reset the AD7747 without having to reset the entire I2C bus,
an explicit reset command is provided. This uses a particular
address pointer word as a command word to reset the part and
upload all default settings. The AD7747 does not respond to the
2
C bus commands (do not acknowledge) during the default
I
values upload for approximately 150 µs (max 200 µs).
The reset command address word is 0xBF.
SDATA
GENERAL CALL
When a master issues a slave address consisting of seven 0s with
the eighth bit (R/W bit) set to 0, this is known as the general call
address. The general call address is for addressing every device
connected to the I
address and read in the following data byte.
If the second byte is 0x06, the AD7747 is reset, completely
uploading all default values. The AD7747 does not respond to
2
the I
C bus commands (do not acknowledge) during the default
values upload for approximately 150 µs (200 µs maximum).
The AD7747 does not acknowledge any other general call
commands.
2
C bus. The AD7747 acknowledges this
SCLOCK
1–7
START ADDR ACK ACK DATA ACK STOPSUBADDRESS
R/W
P981–7981–798S
05469-011
Figure 22. Bus Data Transfer
WRITE
SEQUENCE
READ
SEQUENCE
LSB = 0
S SLAVE ADDR A(S) SUB ADDR A(S) S SLAVE ADDR A(S) DATA
S = START BIT
P = STOP BIT
A(S) = ACKNOWLEDGE BY SLAVE
A(M) = ACKNOWLEDGE BY MASTER
Figure 23. Write and Read Sequences
DATA A(S)S SLAVE ADDR A(S) SUB ADDR A(S)
LSB = 1
A(S) = NO ACKNOWLEDGE BY SLAVE
A(M) = NO ACKNOWLEDGE BY MASTER
DATA P
A(M)
A(S)
DATA P
A(M)
05469-012
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 28
Page 14

AD7747
REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
The master can write to or read from all of the AD7747 registers
except the address pointer register, which is a write-only
register. The address pointer register determines which register
the next read or write operation accesses. All communications
with the part through the bus start with an access to the address
pointer register. After the part has been accessed over the bus
Table 8. Register Summary
Address
Pointer
Register (Dec) (Hex) Dir Default Value
Cap Data H 1 0x01 R Capacitive channel data—high byte, 0x00
Cap Data M 2 0x02 R Capacitive channel data—middle byte, 0x00
Cap Data L 3 0x03 R Capacitive channel data—low byte, 0x00
VT Data H 4 0x04 R Voltage/temperature channel data—high byte, 0x00
VT Data M 5 0x05 R Voltage/temperature channel data—middle byte, 0x00
VT Data L 6 0x06 R Voltage/temperature channel data—low byte, 0x00
Cap Offset H 13 0x0D R/W Capacitive offset calibration—high byte, 0x80
Cap Offset L 14 0x0E R/W Capacitive offset calibration—low byte, 0x00
Cap Gain H 15 0x0F R/W Capacitive gain calibration—high byte, factory calibrated
Cap Gain L 16 0x10 R/W Capacitive gain calibration—low byte, factory calibrated
Volt Gain H 17 0x11 R/W Voltage gain calibration—high byte, factory calibrated
Volt Gain L 18 0x12 R/W Voltage gain calibration—low byte, factory calibrated
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
– – – – – RDY RDYVT RDYCAP Status 0 0x00 R
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
CAPEN – CAPDIFF – – – – – Cap Setup 7 0x07 R/W
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
VTEN VTMD1 VTMD0 EXTREF – – VTSHORT VTCHOP VT Setup 8 0x08 R/W
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
– – – – EXCDAC EXCEN EXCLVL1 EXCLVL0 EXC Setup 9 0x09 R/W
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
VTFS1 VTFS0 CAPFS2 CAPFS1 CAPFS0 MD2 MD1 MD0 Configuration 10 0x0A R/W
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
DACAENA – DACA—6-Bit Value Cap DAC A 11 0x0B R/W
0 0 0x00
DACBENB – DACB—6-Bit Value Cap DAC B 12 0x0C R/W
0 0 0x00
and a read/write operation is selected, the address pointer
register is set up. The address pointer register determines from
or to which register the operation takes place. A read/write
operation is performed from/to the target address, which then
increments to the next address until a stop command on the bus
is performed.
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 28
Page 15

AD7747
STATUS REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x00, Read Only, Default Value 0x07
This register indicates the status of the converter. The status register can be read via the 2-wire serial interface to query a finished
conversion.
RDY
The
pin reflects the status of the RDY bit. Therefore, the
the finished conversion.
Table 9. Status Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic – – – – – RDY RDYVT RDYCAP
Default 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
Table 10.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 to 3 – Not used, always read 0.
2 RDY
1 RDYVT
0 RDYCAP RDYCAP = 0 indicates that a conversion on the capacitive channel is complete and new unread data is available.
RDY = 0 indicates that conversion on the enabled channel(s) is complete and new unread data is available.
If both capacitive and voltage/temperature channels are enabled, the RDY bit is changed to 0 after conversion
on both channels is complete. The RDY bit returns to 1 either when data is read or prior to finishing the next
conversion. If, for example, only the capacitive channel is enabled, then the RDY bit reflects the RDYCAP bit.
RDYVT = 0 indicates that a conversion on the voltage/temperature channel is complete and new unread data
is available.
RDY
pin high-to-low transition can be used as an alternative indication of
CAP DATA REGISTER
24 Bits, Address Pointer 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, Read-Only, Default Value 0x000000
This register contains the capacitive channel output data. The
register is updated after finished conversion on the capacitive
channel, with one exception: When the serial interface read
operation from the Cap Data register is in progress, the data
register is not updated and the new capacitance conversion
result is lost.
The stop condition on the serial interface is considered to be the
end of the read operation. Therefore, to prevent data corruption,
all three bytes of the data register should be read sequentially
using the register address pointer auto-increment feature of the
serial interface.
To prevent losing some of the results, the Cap Data register
should be read before the next conversion on the capacitive
channel is finished.
The 0x000000 code represents negative full scale (−8.192 pF),
the 0x800000 code represents zero scale (0 pF), and the
0xFFFFFF code represents positive full scale (+8.192 pF).
VT DATA REGISTER
24 Bits, Address Pointer 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, Read-Only, Default Value 0x000000
This register contains the voltage/temperature channel output
data. The register is updated after finished conversion on the
voltage channel or temperature channel, with one exception:
When the serial interface read operation from the VT Data
register is in progress, the data register is not updated and the
new voltage/temperature conversion result is lost.
The stop condition on the serial interface is considered to be the
end of the read operation. Therefore, to prevent data corruption,
all three bytes of the data register should be read sequentially
using the register address pointer auto-increment feature of the
serial interface.
For voltage input, Code 0 represents negative full scale (−V
the 0x800000 code represents zero scale (0 V), and the
0xFFFFFF code represents positive full scale (+V
REF
).
To prevent losing some of the results, the VT Data register
should be read before the next conversion on the voltage/
temperature channel is complete.
For the temperature sensor, the temperature can be calculated
from code using the following equation:
Temperature (°C) = (Code/2048) − 4096
REF
),
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 28
Page 16

AD7747
CAP SETUP REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x07, Default Value 0x00
Capacitive channel setup.
Table 11. Cap Setup Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic CAPEN – CAPDIFF – – – – –
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 12.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 CAPEN CAPEN = 1 enables capacitive channel for single conversion, continuous conversion, or calibration.
6 – This bit must be 0 for proper operation.
5 CAPDIFF This bit must be set to 1 for proper operation.
4 to 0 – These bits must be 0 for proper operation.
VT SETUP REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x08, Default Value 0x00
Voltage/Temperature channel setup.
Table 13. VT Setup Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic VTEN VTMD1 VTMD0 EXTREF – – VTSHORT VTCHOP
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 14.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 VTEN VTEN = 1 enables voltage/temperature channel for single conversion, continuous conversion, or calibration.
6
5
4 EXTREF
3 to 2 – These bits must be 0 for proper operation.
1 VTSHORT VTSHORT = 1 internally shorts the voltage/temperature channel input for test purposes.
0 VTCHOP = 1
VTMD1
VTMD0
Voltage/temperature channel input configuration.
VTMD1 VTMD0 Channel Input
0 0 Internal temperature sensor
0 1 External temperature sensor diode
1 0 VDD monitor
1 1 External voltage input (VIN)
EXTREF = 1 selects an external reference voltage connected to REFIN(+), REFIN(−) for the voltage input or the
monitor.
V
DD
EXTREF = 0 selects the on-chip internal reference. The internal reference must be used with the internal
temperature sensor for proper operation.
VTCHOP = 1 sets internal chopping on the voltage/temperature channel.
The VTCHOP bit must be set to 1 for the specified voltage/temperature channel performance.
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 28
Page 17

AD7747
EXC SETUP REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x09, Default Value 0x03
Capacitive channel excitation setup.
Table 15. EXC Setup Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic – – – – EXCDAC EXCEN EXCLVL1 EXCLVL0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
Table 16.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 to 4 – These bits must be 0 for proper operation.
3 EXCDAC CAPDAC excitation. This bit must be set to 1 for the proper capacitive channel operation.
2 EXCEN CIN and AC SHLD excitation. This bit must be set to 1 for the proper capacitive channel operation.
1
0
EXCLVL1,
EXCLVL0
Excitation Voltage Level. Must be set to ±VDD × 3/8 to allow operation for specified performance.
EXCLVL1 EXCLVL0 Voltage on Cap EXC Low Level EXC High Level
0 0 ±VDD/8 V
0 1 ±VDD/4 V
1 0 ±V
1 1 ±V
× 3/8 V
DD
/2 0 VDD
DD
× 3/8 V
DD
× 1/4 V
DD
× 1/8 V
DD
DD
DD
DD
× 5/8
× 3/4
× 7/8
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 28
Page 18

AD7747
CONFIGURATION REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x0A, Default Value 0xA0
Converter update rate and mode of operation setup.
Table 17. Configuration Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic VTFS1 VTFS0 CAPFS2 CAPFS1 CAPFS0 MD2 MD1 MD0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 18.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
VTFS1
VTFS0
CAPFS2
CAPFS1
CAPFS0
MD2
MD1
MD0
Voltage/temperature channel digital filter setup—conversion time/update rate setup.
VTFS1 VTFS0 Conversion Time (ms) Update Rate (Hz) −3 dB Frequency (Hz)
0 0 20.1 49.8 26.4
0 1 32.1 31.2 15.9
1 0 62.1 16.1 8.0
1 1 122.1 8.2 4.0
Capacitive channel digital filter setup—conversion time/update rate setup.
CAPFS2 CAPFS1 CAPFS0 Conversion Time (ms) Update Rate −3 dB Frequency (Hz)
0 0 0 22.0 45.5 43.6
0 0 1 23.9 41.9 39.5
0 1 0 40.0 25.0 21.8
0 1 1 76.0 13.2 10.9
1 0 0 124.0 8.1 6.9
1 0 1 154.0 6.5 5.3
1 1 0 184.0 5.5 4.4
1 1 1 219.3 4.6 4.0
Converter mode of operation setup.
MD2 MD1 MD0 Mode
0 0 0 Idle
0 0 1 Continuous conversion
0 1 0 Single conversion
0 1 1 Power-down
1 0 0 –
1 0 1 Capacitance system offset calibration
1 1 0 Capacitance or voltage system gain calibration
1 1 1 –
VTCHOP = 1
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 28
Page 19

AD7747
CAP DAC A REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x0B, Default Value 0x00
Capacitive DAC setup.
Table 19. Cap DAC A Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic DACAENA – DACA—6-Bit Value
Default 0 0 0x00
Table 20.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 DACAENA DACAENA = 1 connects capacitive DACA to the positive capacitance input.
6 – This bit must be 0 for proper operation.
5 to 1 DACA
CAP DAC B REGISTER
Address Pointer 0x0C, Default Value 0x00
Capacitive DAC setup.
DACA value, Code 0x00 ≈ 0 pF, Code 0x3F ≈ full range.
Table 21. Cap DAC B Register Bit Map
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic DACBENB – DACB—6-Bit Value
Default 0 0 0x00
Table 22.
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 DACBENB DACBENB = 1 connects capacitive DACB to the negative capacitance input.
6 – This bit must be 0 for proper operation.
5 to 1 DACB
DACB value, Code 0x00 ≈ 0 pF, Code 0x3F ≈ full range.
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 28
Page 20

AD7747
CAP OFFSET CALIBRATION REGISTER
16 Bits, Address Pointer 0x0D, 0x0E, Default Value 0x8000
The capacitive offset calibration register holds the capacitive
channel zero-scale calibration coefficient. The coefficient is
used to digitally remove the capacitive channel offset. The
register value is updated automatically following the execution
of a capacitance offset calibration. The capacitive offset calibration resolution (cap offset register LSB) is less than 32 aF; the
full range is ±1 pF.
CAP GAIN CALIBRATION REGISTER
16 Bits, Address Pointer 0x0F, 0x10, Default Value 0xXXXX
Capacitive gain calibration register. The register holds the
capacitive channel full-scale factory calibration coefficient.
VOLT GAIN CALIBRATION REGISTER
16 Bits, Address Pointer 0x11,0x12, Default Value 0xXXXX
Voltage gain calibration register. The register holds the voltage
channel full-scale factory calibration coefficient.
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 28
Page 21

AD7747
V
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DD
TEMP
VIN(+)
VIN(–)
CIN1(+)
CIN1(–)
SHLD
SENSOR
EXCITATION
MUX
CAP DAC 1
CAP DAC 2
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
GENERATOR
REFIN(+) REF IN(–)
AD7747
DIGITAL
FILTER
CONTROL LOG IC
CALIBRATION
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
GND
I2C
SERIAL
INTERFACE
SDA
SCL
RDY
Figure 24. AD7747 Block Diagram
OVERVIEW
The AD7747 core is a high precision converter consisting of a
second-order (Σ- or charge balancing) modulator and a thirdorder digital filter. It works as a CDC for the capacitive inputs
and as a classic ADC for the voltage input or for the voltage
from a temperature sensor.
In addition to the converter, the AD7747 integrates a multiplexer, an excitation source and CAPDACs for the capacitive
inputs, a temperature sensor and a voltage reference for the
voltage and temperature inputs, a complete clock generator,
a control and calibration logic, and an I
2
C-compatible serial
interface.
CAPACITANCE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
Figure 25 shows the CDC simplified functional diagram. The
measured capacitance C
lator input and ground. A square-wave excitation signal is
applied on the C
X
continuously samples the charge going through the C
digital filter processes the modulator output, which is a stream
of 0s and 1s containing the information in 0 and 1 density. The
data from the digital filter is scaled, applying the calibration
coefficients, and the final result can be read through the serial
interface.
CIN
C
X
SHLD
Figure 25. CDC Simplified Block Diagram
is connected between the Σ- modu-
X
during the conversion and the modulator
. The
X
CAPACITANCE TO DIGITAL CONVERTER
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
MODULATOR
EXCITATION
(CDC)
DIGITAL
FILTER
DATA
05469-014
05469-013
ACTIVE AC SHIELD CONCEPT
The AD7747 measures capacitance between CIN and ground.
That means any capacitance to ground on signal path between
the AD7747 CIN pin(s) and sensor is included in the AD7747
conversion result.
The parasitic capacitance of the sensor connections can easily
be in the same, if not even higher, order as the capacitance of
the sensor itself. If that parasitic capacitance is stable, it can be
treated as a nonchanging capacitive offset. However, the parasitic capacitance of sensor connections is often changing as a
result of mechanical movement, changing ambient temperature,
ambient humidity, etc. These changes are seen as drift in the
conversion result and may significantly compromise the system
accuracy.
To eliminate the CIN parasitic capacitance to ground, the
AD7747 SHLD signal can be used for shielding the connection
between the sensor and CIN, as shown in
Figure 25. The SHLD
output is basically the same signal waveform as the excitation of
the CIN pin; the SHLD is driven to the same voltage potential
as the CIN pin. Therefore, there is no ac current between CIN
and SHLD pins, and any capacitance between these pins does
not affect the CIN charge transfer. Ideally, the CIN to SHLD
capacitance does not have any contribution to the AD7747 result.
To get the best result, locate the AD7747 as close as possible to
the capacitive sensor. Keep the connection between the sensor
and AD7747 CIN pin, and also the return path between sensor
ground and the AD7747 GND pin, short. Shield the PCB track
to the CIN pin and connect the shielding to the AD7747 SHLD
pin. In addition, if a shielded cable is used for sensor connection,
the shield should be connected to the AD7747 SHLD pin.
CAPDAC
The AD7747 CDC full-scale input range is ±8.192 pF. For simplicity of calculation, however, the following text and figures use
±8 pF. The part can accept a higher capacitance on the input
and the common-mode or offset (nonchanging component)
capacitance can be balanced by programmable on-chip CAPDACs.
CAPDAC(+)
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
CAPDAC(–)
C
C
Y
X
SHLD
CDC
Figure 26. Using a CAPDAC
DATA
05649-015
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 28
Page 22

AD7747
The CAPDAC can be understood as a negative capacitance
connected internally to the CIN pin. There are two independent
CAPDACs, one connected to the CIN(+) and the second connected to the CIN(−). The relation between the capacitance
input and output data can be expressed as
()()
YX
)()( −−−+−≈ CAPDACCCAPDACCDATA
The CAPDACs have a 6-bit resolution, monotonic transfer
function, are well matched to each other, and have a defined
temperature coefficient. The CAPDAC full range (absolute
value) is not factory calibrated and can vary up to ±20% with
the manufacturing process. See the
Specifications section and
Figure 16 of the typical performance characteristics.
SINGLE-ENDED CAPACITIVE CONFIGURATION
The AD7747 can be used for interfacing to a single-ended
capacitive sensor. In this configuration the sensor should be
connected to one of the AD7747 CIN pins, for example CIN(+)
and the other pin should be left open circuit. Note that the
CAPDIFF bit in the Cap Setup register must be set to 1 at all
times for the correct operation.
It is recommended to guard the unused CIN input with the
active shield to ensure the best performance in terms of noise,
offset, and offset drift.
The CDC (without using the CAPDACs) measure the positive
(or the negative) input capacitance in the range of 0 pF to 8 pF
Figure 27).
(see
0...8pF
CDC
0x800000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
C
X
0...8pF
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
CAPDAC(+)
OFF
CAPDIFF = 1
CAPDAC(–)
OFF
Figure 29 shows how to shift the input range further, up to
25 pF absolute value of capacitance connected to the CIN(+).
±8pF
CDC
0x000000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
05469-018
CAPDAC(+)
17pF
CAPDIFF = 1
CAPDAC(–)
0pF
C
X
9...25p F
(17pF ± 8pF)
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
SHLD
Figure 29. Using CAPDAC in Single-Ended Configuration
DIFFERENTIAL CAPACITIVE CONFIGURATION
When the AD7747 is used for interfacing to a differential
capacitive sensor, each of the two input capacitances, C
must be less than 8 pF (without using the CAPDACs) or must
be less than 25 pF and balanced by the CAPDACs. Balancing
by the CAPDACs means that both C
C
− CAPDAC(−) are less than 8 pF.
Y
− CAPDAC(+) and
X
If the unbalanced capacitance connected to CIN pins is higher
than 8 pF, the CDC introduces a gain error, an offset error, and
nonlinearity error.
See the examples shown in
C
X
0...8pF
C
Y
0...8pF
Figure 30, Figure 31, and Figure 32.
CAPDAC(+)
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
OFF
CAPDIFF = 1
CAPDAC(–)
OFF
±8pF
CDC
and CY,
X
0x000000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
SHLD
05469-016
Figure 27. CDC Single-Ended Input Configuration
The CAPDAC can be used for programmable shifting of the
input range. The example in
Figure 28 shows how to use the full
±8 pF CDC span to measure capacitance between 0 pF to 16 pF.
±8pF
CDC
0x000000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
05469-017
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 28
CAPDAC(+)
8pF
CAPDIFF = 1
CAPDAC(–)
0pF
C
X
0...16pF
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
SHLD
Figure 28. Using CAPDAC in Single-Ended Configuration
SHLD
Figure 30. CDC Differential Input Configuration
CAPDAC(+)
17pF
CIN(+)
CAPDIFF = 1
CIN(–)
CAPDAC(–)
C
X
13...21pF
(17pF ± 4pF)
C
Y
13...21pF
(17pF ± 4pF)
17pF
SHLD
Figure 31. Using CAPDAC in Differential Configuration
±8pF
CDC
0x000000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
05469-019
05469-020
Page 23

AD7747
Parasitic resistances, as shown in Figure 34, cause leakage
currents, which affect the CDC result. The AD7747 CDC
measures the charge transfer between the CIN pin and ground.
Any resistance connected in parallel to the measured
capacitance, C
, such as the parasitic resistance, RP1, also
X
transfers charge. Therefore, the parallel resistor is seen as an
additional capacitance in the output data. A resistance in the
range of R
≥ 10 M causes an offset error in the CDC result.
P1
An offset calibration can be used to compensate for the effect of
small leakage currents. A higher leakage current to ground,
≤ 10 M, results in a gain error, an offset error, and a
R
P1
nonlinearity error. See
Figure 10 in the Ty p i cal Performanc e
Characteristics section.
A parasitic resistance, R
as R
between the CIN pin and the active shield, as shown in
P3
, between SHLD and ground, as well
P2
Figure 34, cause a leakage current, which affects the CDC result
and is seen as an offset in the data. An offset calibration can be
used to compensate for effect of the small leakage current
caused by a resistance R
and RP3 ≥ 200 k. See Figure 11,
P2
Figure 12, and Figure 13 in the Typic a l Pe r fo r mance
Characteristics section.
PARASITIC SERIAL RESISTANCE
±8pF
CDC
0x000000
TO
0xFFFFFF
DATA
C
X
9 TO 25pF
(17pF ± 8pF)
C
Y
17pF
CIN(+)
CIN(–)
SHLD
CAPDAC(+)
17pF
CAPDIFF = 1
CAPDAC(–)
17pF
Figure 32. Using CAPDAC in Differential Configuration
PARASITIC CAPACITANCE
The CDC architecture used in the AD7747 measures the
capacitance C
Most applications use the active shield to avoid external influences during the CDC. However, any parasitic capacitance, C
as shown in
C
P1
connected between the CIN pin and ground.
X
Figure 33, can affect the CDC result.
CIN
C
C
X
P2
C
P3
CDC
DATA
05469-021
,
P
SHLD
Figure 33. Parasitic Capacitance
A parasitic capacitance, CP1, coupled in between CIN and
ground adds directly to the value of the capacitance C
therefore, the CDC result is: DATA ≈ C
+ CP1. An offset cali-
X
and,
X
bration might be sufficient to compensate for a small parasitic
capacitance (C
≤ 1pF). For a larger parasitic capacitance, the
P1
CAPDAC can be used to compensate, followed by an offset
calibration to ensure the full range of ±8pF is available for
the system.
Other parasitic capacitances, such as C
and ground as well as C
between the CIN pin and SHLD,
P3
between active shield
P2
could influence the conversion result. However, the graphs in
the
Typical Performance Characteristics section show that the
effect of parasitic capacitance of type C
insignificant to the CDC result.
gain error caused by C
by C
.
P3
P2
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the
. Figure 9 shows the gain error caused
below 250 pF is
P2/CP3
PARASITIC RESISTANCE
CIN
R
C
R
P1
X
P2
R
P3
SHLD
CDC
Figure 34. Parasitic Resistance on CIN
DATA
R
05469-041
S
C
X
CIN
SHLD
CDC
DATA
5469-043
Figure 35. Parasitic Serial Resistance
The AD7747 CDC result is affected by a resistance in series
with the measured capacitance. The serial resistance should be
less than 10 kΩ for the specified performance. See
the
Typical Performance Characteristics section.
Figure 14 in
CAPACITIVE GAIN CALIBRATION
The AD7747 gain is factory calibrated for the full scale of
±8.192 pF in the production for each part individually. The
factory gain coefficient is stored in a one-time programmable
(OTP) memory and is copied to the capacitive gain register at
power-up or after reset.
The gain can be changed by executing a capacitance gain calibration mode, for which an external full-scale capacitance needs
to be connected to the capacitance input, or by writing a user
value to the capacitive gain register. This change would be only
temporary, and the factory gain coefficient would be reloaded
back after power-up or reset. The part is tested and specified for
use only with the default factory calibration coefficient.
05649-042
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 28
Page 24

AD7747
CAPACITIVE SYSTEM OFFSET CALIBRATION
The capacitive offset is dominated by the parasitic offset in the
application, such as the initial capacitance of the sensor, any
parasitic capacitance of tracks on the board, and the capacitance
of any other connections between the sensor and the CDC.
Therefore, the AD7747 is not factory calibrated for capacitive
offset. It is the user’s responsibility to calibrate the system
capacitance offset in the application.
Any offset in the capacitance input larger than ±1 pF should
first be removed using the on-chip CAPDACs. The small offset
within ±1 pF can then be removed by using the capacitance
offset calibration register.
One method of adjusting the offset is to connect a zero-scale
capacitance to the input and execute the capacitance offset
calibration mode. The calibration sets the midpoint of the
±8.192 pF range (that is, Output Code 0x800000) to that
zero-scale input.
Another method is to calculate and write the offset calibration
17
register value; the LSB value is 31.25 aF (8.192 pF/2
).
The offset calibration register is reloaded by the default value at
power-on or after reset. Therefore, if the offset calibration is not
repeated after each system power-up, the calibration coefficient
value should be stored by the host controller and reloaded as
part of the AD7747 setup.
INTERNAL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
INTERNAL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
IN × I
CLOCK
GENERATOR
BE
24-BIT Σ-Δ
MODULATOR
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
ΔV
Figure 36. Internal Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensing method used in the AD7747 is to
measure a difference in ∆V
two different currents (see
BE
Figure 36). The ∆VBE change with
temperature is linear and can be expressed as
KT
nV
BE
×=Δ
f
q
VDD
FILTER
AND
DATA
05469-026
DIGITAL
SCALING
voltage of a transistor operated at
)ln()( N
where:
K is Boltzmann’s constant (1.38 × 10
−23
).
T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin.
−19
q is the charge on the electron (1.6 × 10
coulombs).
N is the ratio of the two currents.
is the ideality factor of the thermal diode.
n
f
The AD7747 uses an on-chip transistor to measure the
temperature of the silicon chip inside the package. The Σ-
ADC converts the ∆V
to digital; the data are scaled using
BE
factory calibration coefficients. Thus, the output code is
proportional to temperature.
Code
()
CeTemperatur
2048
−=°
4096
The AD7747 has a low power consumption resulting in only a
small effect due to the part self-heating (less than 0.5°C at
= 5 V).
V
DD
If the capacitive sensor can be considered to be at the same
temperature as the AD7747 chip, the internal temperature
sensor can be used as a system temperature sensor. That means
the complete system temperature drift compensation can be
based on the AD7747 internal temperature sensor without need
for any additional external components. See Figure 17 in the
Typical Performance Characteristics section.
EXTERNAL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
× I
N
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
MODULATOR
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
VDD
CLOCK
DIGITAL
SCALING
DATA
FILTER
AND
method, which
BE
+ RS2 in
S1
EXTERNAL
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
R
2N3906
ΔV
BE
VIN(+)
S1
R
S2
VIN(–)
Figure 37. Transistor as an External Temperature Sensor
I ...
The AD7747 provides the option of using an external transistor
as a temperature sensor in the system. The ∆V
is similar to the internal temperature sensor method, is used.
However, it is modified to compensate for the serial resistance
of connections to the sensor. Total serial resistance (R
Figure 37) up to 100 Ω is compensated. The VIN(−) pin must
be grounded for proper external temperature sensor operation.
The AD7747 is factory calibrated for Transistor 2N3906 with
the ideality factor n
Figure 18 in the Typical Performance Characteristics section.
See
= 1.008.
f
05469-027
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 28
Page 25

AD7747
VOLTAGE INPUT
VIN(+)
R
T
RTD
VIN(–)
REFIN(+)
R
REF
REFIN(–)
VDD
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER
MODULATOR
(ADC)
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
DIGITAL
FILTER
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
DATA
The AD7747 Σ- core can work as a high resolution (up to
21 ENOB) classic ADC with a fully differential voltage input.
The ADC can be used either with the on-chip high precision,
low drift, 1.17 V voltage reference, or with an external reference
connected to the fully differential reference input pins.
The voltage and reference inputs are continuously sampled by
a Σ- modulator during the conversion. Therefore, the input
source impedance should be kept low. See the application
example in
Figure 38.
VDD MONITOR
Along with converting external voltages, the AD7747 Σ- ADC
can be used for monitoring the V
the VDD pin is internally attenuated by 6.
voltage. The voltage from
DD
GND
Figure 38. Resistive Temperature Sensor Connected to the Voltage Input
05469-028
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 28
Page 26

AD7747
V
/5V
TYPICAL APPLICATION DIAGRAM
3
POWER SUPPLY
10kΩ
VDD
+
0.1µF 10µF
10kΩ
VIN (+)
VIN (–)
CIN1( +)
CIN1(–)
SHLD
TEMP
SENSOR
EXCITATION
MUX
GENERATOR
24-BIT Σ-Δ
GENERATOR
CAP DAC 1
CAP DAC 2
REFIN(+) REFIN(–)
CLOCK
AD7747
DIGITAL
FILTER
CONTROL LOGIC
CALIBR ATION
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
I2C
SERIAL
INTERFACE
GND
SDA
SCL
RDY
HOST
SYSTEM
5469-029
Figure 39. Basic Application Diagram for a Differential Capacitive Sensor
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 28
Page 27

AD7747
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
5.10
5.00
4.90
0.15
0.05
4.50
4.40
4.30
PIN 1
16
0.65
BSC
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153-AB
0.10
0.30
0.19
9
81
1.20
MAX
SEATING
PLANE
6.40
BSC
0.20
0.09
8°
0°
0.75
0.60
0.45
Figure 40. 16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP]
(RU-16)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD7747ARUZ1 −40°C to +125°C 16-Lead TSSOP RU-16
AD7747ARUZ-REEL1 −40°C to +125°C 16-Lead TSSOP RU-16
AD7747ARUZ-REEL71 −40°C to +125°C 16-Lead TSSOP RU-16
EVAL-AD7747EBZ1 Evaluation Board
1
Z = Pb-free part.
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 28
Page 28

AD7747
NOTES
Purchase of licensed I2C components of Analog Devices or one of its sublicensed Associated Companies conveys a license for the purchaser under the Philips I2C Patent
Rights to use these components in an I
2
C system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05469-0-1/07(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...