Page 1
LC2MOS Signal Conditioning ADC
a
FEATURES
Charge Balancing ADC
24 Bits No Missing Codes
ⴞ0.0015% Nonlinearity
Two-Channel Programmable Gain Front End
Gains from 1 to 128
Differential Inputs
Low-Pass Filter with Programmable Filter Cutoffs
Ability to Read/Write Calibration Coefficients
Bidirectional Microcontroller Serial Interface
Internal/External Reference Option
Single or Dual Supply Operation
Low Power (25 mW typ) with Power-Down Mode
(7 mW typ)
APPLICATIONS
RTD Transducers
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7711A is a complete analog front end for low frequency
measurement applications. The device accepts low level signals
directly from a transducer and outputs a serial digital word. It
employs a sigma-delta conversion technique to realize up to
24 bits of no missing codes performance. The input signal is
applied to a proprietary programmable gain front end based
around an analog modulator. The modulator output is processed by an on-chip digital filter. The first notch of this digital
filter can be programmed via the on-chip control register allowing adjustment of the filter cutoff and settling time.
The part features two differential analog inputs and a differential reference input. Normally, one of the channels will be used
as the main channel with the second channel used as an auxiliary input to periodically measure a second voltage. It can be
operated from a single supply (by tying the V
provided that the input signals on the analog inputs are more
positive than –30 mV. By taking the V
can convert signals down to –V
SS
on its inputs. The part also
REF
provides a 400 µA current source that can be used to provide
excitation for RTD transducers. The AD7711A thus performs
all signal conditioning and conversion for a single or dual channel system.
The AD7711A is ideal for use in smart, microcontroller-based
systems. Input channel selection, gain settings and signal polarity can be configured in software using the bidirectional serial
port. The AD7711A contains self-calibration, system calibration
and background calibration options and also allows the user to
read and write the on-chip calibration registers.
*Protected by U.S. Patent No. 5,134,401.
pin to AGND)
SS
pin negative, the part
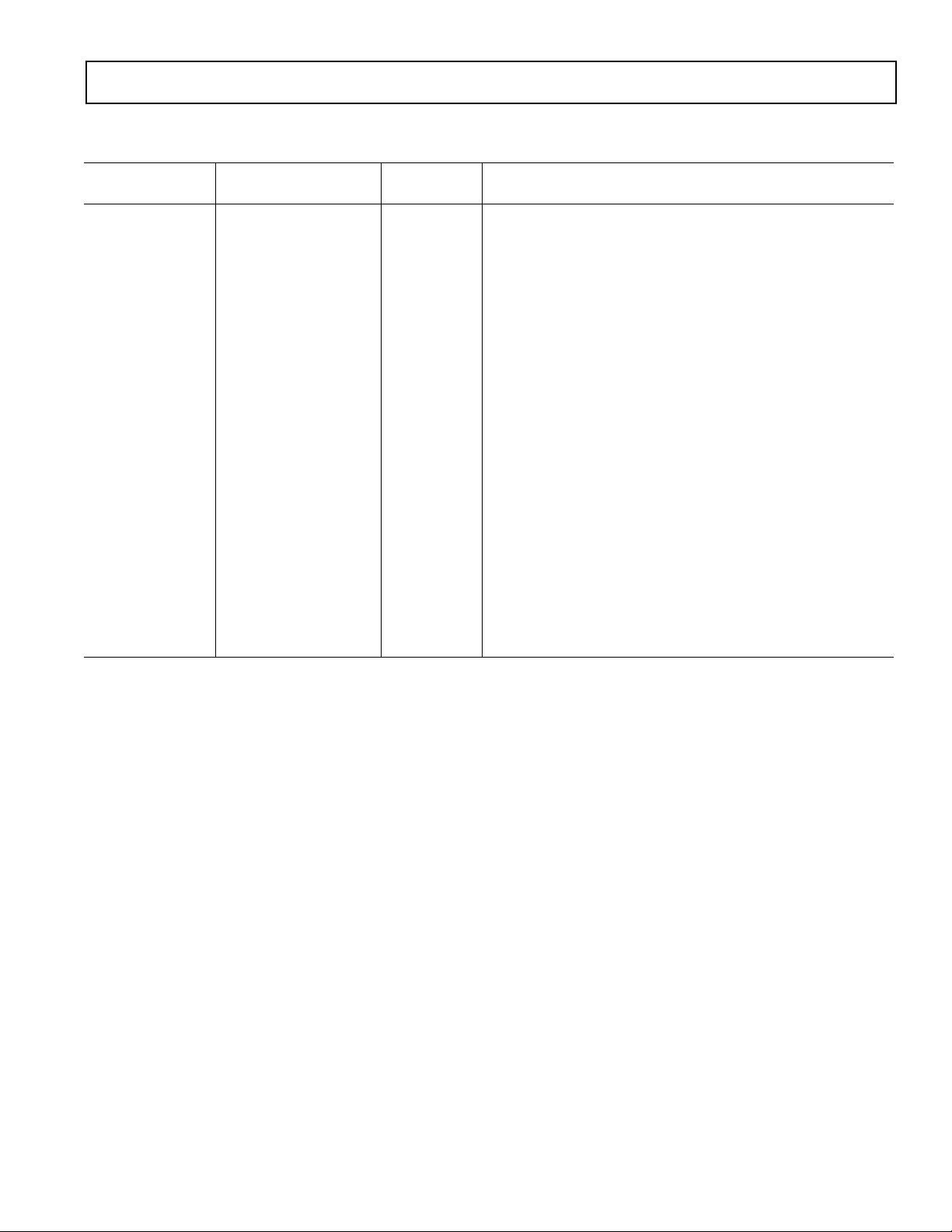
with RTD Current Source
AD7711A*
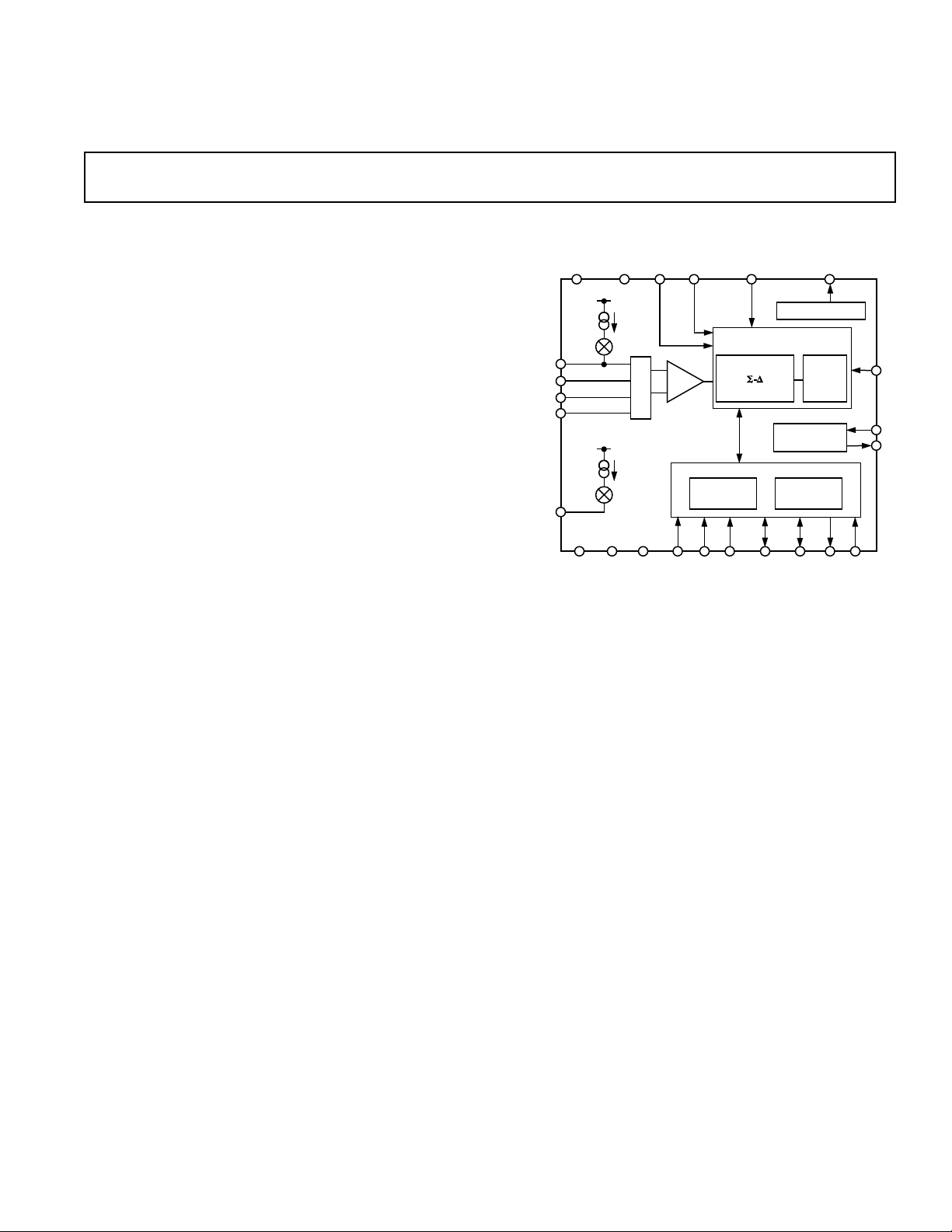
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REF
AV
DD
AV
DD
AIN1(+)
AIN1(–)
AIN2(+)
AIN2(–)
AV
DD
RTD
CURRENT
AD7711A
AGND DGND MODE SDATA SCLK A0
CMOS construction ensures low power dissipation, and a software programmable power-down mode reduces the standby
power consumption to only 7 mW typical. The part is available
in a 24-lead, 0.3 inch-wide, hermetic dual-in-line package
(cerdip) as well as a 24-lead small outline (SOIC) package.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The programmable gain front end allows the AD7711A
to accept input signals directly from an RTD transducer,
removing a considerable amount of signal conditioning. An
on-chip current source provides the excitation current for
the RTD.
2. The part features excellent static performance specifications
with 24-bit no missing codes, ±0.0015% accuracy and low
rms noise (<250 nV). Endpoint errors and the effects of
temperature drift are eliminated by on-chip calibration options, which remove zero-scale and full-scale errors.
3. The AD7711A is ideal for microcontroller or DSP processor
applications with an on-chip control register that allows
control over filter cutoff, input gain, channel selection, signal
polarity, RTD current control and calibration modes.
4. The AD7711A allows the user to read and to write the
on-chip calibration registers. This means that the microcontroller has much greater control over the calibration
procedure.
DV
4.5mA
400mA
DD
M
U
X
V
SS
REF
IN (–)
PGA
A = 1 – 128
IN (+)
V
BIAS
CHARGE-BALANCING A/D
AUTO-ZEROED
MODULATOR
SERIAL INTERFACE
CONTROL
REGISTER
2.5V REFERENCE
CONVERTER
CLOCK
GENERATION
OUTPUT
REGISTER
REF OUT
DIGITAL
FILTER
DRDYTFSRFS
SYNC
MCLK
IN
MCLK
OUT
REV. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1998
Page 2
AD7711A–SPECIFICATIONS
REF␣ IN(–) = AGND; MCLK IN = 10␣ MHz unless otherwise stated. All specifications T
Parameter A, S Versions
(AVDD = +5␣ V ⴞ 5%; DVDD = +5␣ V ⴞ 5%; VSS = 0 V or –5␣ V ⴞ 5%; REF IN(+) = +2.5␣ V;
to T
MIN
1
Units Conditions/Comments
unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
STATIC PERFORMANCE
No Missing Codes 24 Bits min Guaranteed by Design. For Filter Notches ≤ 60 Hz
22 Bits min For Filter Notch = 100 Hz
18 Bits min For Filter Notch = 250 Hz
15 Bits min For Filter Notch = 500 Hz
12 Bits min For Filter Notch = 1 kHz
Output Noise See Tables I and II Depends on Filter Cutoffs and Selected Gain
Integral Nonlinearity @ +25°C ±0.0015 % FSR max Filter Notches ≤ 60 Hz
T
to T
MIN
Positive Full Scale Error
Full-Scale Drift
Unipolar Offset Error
Unipolar Offset Drift
Bipolar Zero Error
Bipolar Zero Drift
MAX
5
2
5
2
5
2, 3
0.003 % FSR max Typically ±0.0003%
See Note 4 Excluding Reference
1 µV/°C typ Excluding Reference. For Gains of 1, 2
0.3 µV/°C typ Excluding Reference. For Gains of 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
See Note 4
0.5 µV/°C typ For Gains of 1, 2
0.25 µV/°C typ For Gains of 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
See Note 4
0.5 µV/°C typ For Gains of 1, 2
0.25 µV/°C typ For Gains of 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
Gain Drift 2 ppm/°C typ
Bipolar Negative Full-Scale Error
Bipolar Negative Full-Scale Drift
T
to T
MIN
MAX
2
@ +25°C ±0.003 % FSR max Excluding Reference
5
±0.006 % FSR max Typically ±0.0006%
1 µV/°C typ Excluding Reference. For Gains of 1, 2
0.3 µV/°C typ Excluding Reference. For Gains of 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
ANALOG INPUTS/REFERENCE INPUTS
Common-Mode Rejection (CMR) 100 dB min At DC
Common-Mode Voltage Range
Normal-Mode 50 Hz Rejection
Normal-Mode 60 Hz Rejection
Common-Mode 50 Hz Rejection
Common-Mode 60 Hz Rejection
DC Input Leakage Current
T
to T
MIN
Sampling Capacitance
Analog Inputs
MAX
8
Input Voltage Range
Input Sampling Rate, f
Reference Inputs
REF IN(+) – REF IN(–) Voltage
Input Sampling Rate, f
6
7
7
7
7
7
@ +25°C 10 pA max
7
9
S
11
S
VSS to AV
DD
100 dB min For Filter Notches of 10, 25, 50 Hz, ±0.02 × f
100 dB min For Filter Notches of 10, 30, 60 Hz, ±0.02 × f
150 dB min For Filter Notches of 10, 25, 50 Hz, ±0.02 × f
150 dB min For Filter Notches of 10, 30, 60 Hz, ±0.02 × f
1 nA max
20 pF max
REF
REF
10
0 to +V
±V
See Table III
+2.5 to +5 V min to V max For Specified Performance. Part Functions with
f
/256
CLK IN
V min to V max
NOTCH
NOTCH
NOTCH
NOTCH
For Normal Operation. Depends on Gain Selected
nom Unipolar Input Range (B/U Bit of Control Register = 1)
nom Bipolar Input Range (B/U Bit of Control Register = 0)
Lower V
Voltages
REF
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Output Voltage 2.5 V nom
Initial Tolerance @ +25°C ±1 % max
Drift 20 ppm/°C typ
Output Noise 30 µV typ pk-pk Noise 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Bandwidth
Line Regulation (AVDD) 1 mV/V max
Load Regulation 1.5 mV/mA max Maximum Load Current 1 mA
External Current 1 mA max
NOTES
1
Temperature ranges are as follows: A Version, –40°C to +85°C; S Version, –55°C to +125°C.
2
Applies after calibration at the temperature of interest.
3
Positive full-scale error applies to both unipolar and bipolar input ranges.
4
These errors will be of the order of the output noise of the part as shown in Table I when using system calibration. These errors are 20 µV typical when using selfcalibration or background calibration.
5
Recalibration at any temperature or use of the background calibration mode will remove these drift errors.
6
This common-mode voltage range is allowed provided that the input voltage on AIN(+) and AIN(–) does not exceed AV
7
These numbers are guaranteed by design and/or characterization.
8
The analog inputs present a very high impedance dynamic load which varies with clock frequency and input sample rate. The maximum recommended source
resistance depends on the selected gain (see Tables IV and V).
9
The analog input voltage range on the AIN1(+) and AIN2(+) inputs is given here with respect to the voltage on the AIN1(–) and AIN2(–) inputs. The absolute
voltage on the analog inputs should not go more positive than AVDD + 30 mV or go more negative than VSS – 30 mV.
10
V
= REF IN(+) – REF IN(–).
REF
11
The reference input voltage range may be restricted by the input voltage range requirement on the V
BIAS
input.
+ 30 mV and VSS – 30 mV.
DD
–2– REV. C
Page 3
AD7711A
Parameter A, S Versions
INPUT
12
DD
V
BIAS
Input Voltage Range AV
1
– 0.85 × V
Units Conditions/Comments
REF
See V
BIAS
Input Section
or AVDD – 3.5 V max Whichever Is Smaller; +5 V/–5 V or +10 V/0 V
or AVDD – 2.1 V max Whichever Is Smaller; +5 V/0 V Nominal AVDD/V
Nominal AVDD/V
V
+ 0.85 × V
SS
REF
See V
BIAS
SS
SS
Input Section
or VSS + 3 V min Whichever Is Greater; +5 V/–5 V or +10 V/0 V
or VSS + 2.1 V min Whichever Is Greater; +5 V/0 V Nominal AVDD/V
Nominal AVDD/V
V
Rejection 65 to 85 dB typ Increasing with Gain
BIAS
SS
SS
LOGIC INPUTS
Input Current ±10 µA max
All Inputs except MCLK IN
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 V max
INL
V
, Input High Voltage 2.0 V min
INH
MCLK IN Only
V
, Input Low Voltage 0.8 V max
INL
V
, Input High Voltage 3.5 V min
INH
LOGIC OUTPUTS
VOL, Output Low Voltage 0.4 V max I
VOH, Output High Voltage DVDD – 1 V min I
Floating State Leakage Current ±10 µA max
Floating State Output Capacitance
13
9 pF typ
= 1.6 mA
SINK
SOURCE
= 100 µA
TRANSDUCER BURNOUT
Current 4.5 µA nom
Initial Tolerance @ +25°C ±10 % typ
Drift 0.1 %/°C typ
RTD EXCITATION CURRENT
Output Current 400 µA nom
Initial Tolerance @ +25°C ±20 % max
Drift 20 ppm/°C typ
Line Regulation (AVDD) 400 nA/V max AVDD = +5 V
Load Regulation 400 nA/V max
Output Compliance AVDD – 2 V max
SYSTEM CALIBRATION
Positive Full-Scale Calibration Limit
Negative Full-Scale Calibration Limit
Offset Calibration Limit
Input Span
NOTES
12
The AD7711A is tested with the following V
with AVDD = +5 V and VSS = –5 V, V
13
Guaranteed by design, not production tested.
14
After calibration, if the analog input exceeds positive full scale, the converter will output all 1s. If the analog input is less than negative full scale, then the device will
output all 0s.
15
These calibration and span limits apply provided the absolute voltage on the analog inputs does not exceed AVDD + 30 mV or go more negative than VSS – 30 mV.
15
15
BIAS
14
14
= 0 V.
(1.05 × V
–(1.05 × V
–(1.05 × V
0.8 × V
(2.1 × V
voltages. With AVDD = +5 V and VSS = 0 V, V
BIAS
)/GAIN V max GAIN Is the Selected PGA Gain (Between 1 and 128)
REF
)/GAIN V max GAIN Is the Selected PGA Gain (Between 1 and 128)
REF
)/GAIN V max GAIN Is the Selected PGA Gain (Between 1 and 128)
REF
/GAIN V min GAIN Is the Selected PGA Gain (Between 1 and 128)
REF
)/GAIN V max GAIN Is the Selected PGA Gain (Between 1 and 128)
REF
= +2.5 V, with AVDD = +10 V and VSS = 0 V, V
BIAS
= +5 V and
BIAS
The offset calibration limit applies to both the unipolar zero point and the bipolar zero point.
REV. C
–3–
Page 4
AD7711A–SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter A, S Versions Units Conditions/Comments
POWER REQUIREMENTS
Power Supply Voltages
AVDD Voltage
DVDD Voltage
AVDD–V
Power Supply Currents
AVDD Current 4 mA max
DV
DD
VSS Current 1.5 mA max VSS = –5 V
Power Supply Rejection
Positive Supply (AV
Negative Supply (VSS) 90 dB typ
Power Dissipation
Normal Mode 45 mW max AV
Normal Mode 52.5 mW max AV
Standby (Power-Down) Mode 15 mW max AV
NOTES
16
The AD7711A is specified with a 10 MHz clock for AV
than 10.5 V.
17
The ±5% tolerance on the DV
18
Measured at dc and applies in the selected passband. PSRR at 50 Hz will exceed 120 dB with filter notches of 10 Hz, 25 Hz or 50 Hz. PSRR at 60 Hz will exceed
120 dB with filter notches of 10 Hz, 30 Hz or 60 Hz.
19
PSRR depends on gain: Gain of 1: 70 dB typ; Gain of 2: 75 dB typ; Gain of 4: 80 dB typ; Gains of 8 to 128: 85 dB typ. These numbers can be improved (to 95 dB
typ) by deriving the V
Specifications subject to change without notice.
16
17
Voltage +10.5 V max For Specified Performance
SS
+5 to +10 V nom ±5% for Specified Performance
+5 V nom ±5% for Specified Performance
Current 4.5 mA max
18
and DVDD) See Note 19 dB typ
DD
voltages of +5 V ± 5%. It is specified with an 8 MHz clock for AV
DD
input is allowed provided that DVDD does not exceed AVDD by more than 0.3 V.
DD
voltage (via Zener diode or reference) from the AVDD supply.
BIAS
Rejection w.r.t. AGND; Assumes V
= DV
DD
DD
DD
= +5␣ V, VSS = 0 V; Typically 25 mW
DD
= DV
= +5␣ V, VSS = –5 V; Typically 30 mW
DD
= DV
= +5␣ V, VSS = 0 V or –5 V; Typically 7 mW
DD
Is Fixed
BIAS
voltages greater than 5.25 V and less
DD
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(T
= +25°C, unless otherwise noted)
A
AVDD to DVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +12 V
to VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +12 V
AV
DD
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +12 V
AV
DD
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +12 V
AV
DD
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +6 V
DV
DD
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +6 V
DV
DD
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +0.3 V to –6 V
V
SS
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +0.3 V to –6 V
V
SS
Analog Input Voltage to AGND
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
– 0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
SS
Reference Input Voltage to AGND
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
REF OUT to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to AV
– 0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
SS
DD
Digital Input Voltage to DGND . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND . . . –0.3 V to DV
+ 0.3 V
DD
Operating Temperature Range
Commercial (A Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Extended (S Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 secs) . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C
Power Dissipation (Any Package) to +75°C . . . . . . . . 450 mW
Derates Above +75°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 mW/°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Options*
AD7711AAR –40°C to +85°C R-24
AD7711ASQ –55°C to +125°CQ-24
*R = SOIC, Q = Cerdip.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD7711A features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. C
Page 5
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
AD7711A
(DVDD = +5␣ V ⴞ 5%; AVDD = +5␣ V or +10␣ V3, ⴞ 5%; VSS = 0 V or –5 V ⴞ 10%; AGND = DGND
1, 2
= 0 V; f
= 10␣ MHz; Input Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = DVDD unless otherwise noted)
CLKIN
Limit at T
MIN
, T
MAX
Parameter (A, S Versions) Units Conditions/Comments
4, 5
f
CLK IN
Master Clock Frequency: Crystal Oscillator or Externally
400 kHz min Supplied for Specified Performance
= +5 V ± 5%
DD
= +5.25 V to +10.5 V
DD
t
CLK IN LO
t
CLK IN HI
6
t
r
6
t
f
t
1
10 MHz max AV
8 MHz max AV
0.4 × t
0.4 × t
CLK IN
CLK IN
ns min Master Clock Input Low Time. t
ns min Master Clock Input High Time
50 ns max Digital Output Rise Time. Typically 20 ns
50 ns max Digital Output Fall Time. Typically 20 ns
1000 ns min SYNC Pulsewidth
Self-Clocking Mode
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
7
t
7
7
t
8
t
9
t
10
t
14
t
15
t
16
t
17
t
18
t
19
0 ns min DRDY to RFS Setup Time
0 ns min DRDY to RFS Hold Time
2 × t
CLK IN
ns min A0 to RFS Setup Time
0 ns min A0 to RFS Hold Time
4 × t
4 × t
t
CLK IN
t
CLK IN/2
t
CLK IN
3 × t
+ 20 ns max RFS Low to SCLK Falling Edge
CLK IN
+ 20 ns max Data Access Time (RFS Low to Data Valid)
CLK IN
/2 ns min SCLK Falling Edge to Data Valid Delay
+ 30 ns max
/2 ns nom SCLK High Pulsewidth
/2 ns nom SCLK Low Pulsewidth
CLK IN
50 ns min A0 to TFS Setup Time
0 ns min A0 to TFS Hold Time
4 × t
4 × t
+ 20 ns max TFS to SCLK Falling Edge Delay Time
CLK IN
CLK IN
ns min TFS to SCLK Falling Edge Hold Time
0 ns min Data Valid to SCLK Setup Time
10 ns min Data Valid to SCLK Hold Time
CLK IN
= 1/f
2
CLK IN
–5–REV. C
Page 6
AD7711A
Limit at T
MIN
, T
MAX
Parameter (A, S Versions) Units Conditions/Comments
External Clocking Mode
f
SCLK
t
20
t
21
t
22
t
23
7
t
24
7
t
25
t
26
t
27
t
28
8
t
29
t
30
8
t
31
t
32
t
33
t
34
t
35
t
36
NOTES
1
Guaranteed by design, not production tested. All input signals are specified with tr = tf = 5 ns (10% to 90% of 5 V) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
2
See Figures 10 to 13.
3
The AD7711A is specified with a 10 MHz clock for AV
than 10.5 V.
4
CLK IN duty cycle range is 45% to 55%. CLK IN must be supplied whenever the AD7711A is not in STANDBY mode. If no clock is present in this case, the device
can draw higher current than specified and possibly become uncalibrated.
5
The AD7711A is production tested with f
6
Specified using 10% and 90% points on waveform of interest.
7
These numbers are measured with the load circuit of Figure 1 and defined as the time required for the output to cross 0.8 V or 2.4 V.
8
These numbers are derived from the measured time taken by the data output to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 1. The measured number is then
extrapolated back to remove effects of charging or discharging the 100 pF capacitor. This means that the times quoted in the timing characteristics are the true bus
relinquish times of the part and as such are independent of external bus loading capacitances.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
f
/5 MHz max Serial Clock Input Frequency
CLK IN
0 ns min DRDY to RFS Setup Time
0 ns min DRDY to RFS Hold Time
2 × t
CLK IN
ns min A0 to RFS Setup Time
0 ns min A0 to RFS Hold Time
4 × t
CLK IN
ns max Data Access Time (RFS Low to Data Valid)
10 ns min SCLK Falling Edge to Data Valid Delay
2 × t
2 × t
2 × t
t
CLK IN
+ 20 ns max
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
ns min SCLK High Pulsewidth
ns min SCLK Low Pulsewidth
+ 10 ns max SCLK Falling Edge to DRDY High
10 ns min SCLK to Data Valid Hold Time
+ 10 ns max
t
CLK IN
10 ns min RFS/TFS to SCLK Falling Edge Hold Time
5 × t
/2 + 50 ns max RFS to Data Valid Hold Time
CLK IN
0 ns min A0 to TFS Setup Time
0 ns min A0 to TFS Hold Time
4 × t
2 × t
CLK IN
– SCLK High ns min Data Valid to SCLK Setup Time
CLK IN
ns min SCLK Falling Edge to TFS Hold Time
30 ns min Data Valid to SCLK Hold Time
voltages of +5 V ± 5%. It is specified with an 8 MHz clock for AV
DD
at 10 MHz (8 MHz for AVDD > +5.25 V). It is guaranteed by characterization to operate at 400 kHz.
CLK IN
voltages greater than 5.25 V and less
DD
1.6mA
TO OUTPUT
PIN
100pF
200mA
+2.1V
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Access Time and Bus Relinquish
Time
–6–
PIN CONFIGURATION
DIP and SOIC
1
SCLK
2
MCLK IN
SYNC
MODE
AIN1(+)
AIN1(–)
AIN2(+)
AIN2(–)
V
AV
A0
SS
DD
3
4
5
AD7711A
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
MCLK OUT
24
DGND
23
DV
DD
22
SDATA
21
DRDY
20
RFS
19
TFS
18
AGND
RTD CURRENT
17
16
REF OUT
15
REF IN(+)
14
REF IN(–)
13
V
BIAS
REV. C
Page 7
AD7711A
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Mnemonic Function
1 SCLK Serial Clock. Logic Input/Output depending on the status of the MODE pin. When MODE is high, the
device is in its self-clocking mode and the SCLK pin provides a serial clock output. This SCLK becomes
active when RFS or TFS goes low and it goes high impedance when either RFS or TFS returns high or when
the device has completed transmission of an output word. When MODE is low, the device is in its external
clocking mode and the SCLK pin acts as an input. This input serial clock can be a continuous clock with all
data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the
information being transmitted to the AD7711A in smaller batches of data.
2 MCLK IN Master Clock signal for the device. This can be provided in the form of a crystal or external clock. A crystal can
be tied across the MCLK IN and MCLK OUT pins. Alternatively, the MCLK IN pin can be driven with a
CMOS compatible clock and MCLK OUT left unconnected. The clock input frequency is nominally 10 MHz.
3 MCLK OUT When the master clock for the device is a crystal, the crystal is connected between MCLK IN and MCLK OUT.
4 A0 Address Input. With this input low, reading and writing to the device is to the control register. With this input
high, access is to either the data register or the calibration registers.
5 SYNC Logic Input which allows for synchronization of the digital filters when using a number of AD7711As. It resets
the nodes of the digital filter.
6 MODE Logic Input. When this pin is high, the device is in its self-clocking mode; with this pin low, the device is in its
external clocking mode.
7 AIN1(+) Analog Input Channel 1. Positive input of the programmable gain differential analog input. The AIN1(+) input
is connected to an output current source which can be used to check that an external transducer has burned out
or gone open circuit. This output current source can be turned on/off via the control register.
8 AIN1(–) Analog Input Channel 1. Negative input of the programmable gain differential analog input.
9 AIN2(+) Analog Input Channel 2. Positive input of the programmable gain differential analog input.
10 AIN2(–) Analog Input Channel 2. Negative input of the programmable gain differential analog input.
11 V
12 AV
13 V
SS
DD
BIAS
14 REF IN(–) Reference Input. The REF IN(–) can lie anywhere between AV
15 REF IN(+) Reference Input. The reference input is differential providing that REF IN(+) is greater than REF IN(–).
16 REF OUT Reference Output. The internal +2.5 V reference is provided at this pin. This is a single ended output
17 RTD CURRENT Constant Current Output. A nominal 400 µA constant current is provided at this pin, and this can be used
18 AGND Ground reference point for analog circuitry.
Analog Negative Supply, 0 V to –5 V. Tied to AGND for single supply operation. The input voltage on AIN1
or AIN2 should not go > 30 mV negative w.r.t. V
for correct operation of the device.
SS
Analog Positive Supply Voltage, +5 V to +10 V.
Input Bias Voltage. This input voltage should be set such that V
× V
REF >VSS
where V
and VSS. Thus with AV
–5 V, it can be tied to AGND while with AV
is REF IN(+) – REF IN(–). Ideally, this should be tied halfway between AV
REF
= +5 V and VSS = 0 V, it can be tied to REF OUT; with AVDD = +5 V and VSS =
DD
= +10 V, it can be tied to +5 V.
DD
+ 0.85 × V
BIAS
and VSS provided REF IN(+) is greater
DD
< AVDD and V
REF
BIAS
– 0.85
DD
than REF IN(–).
REF IN(+) can lie anywhere between AV
and VSS.
DD
which is referred to AGND. It is a buffered output which is capable of providing 1 mA to an external load.
as the excitation current for RTDs. This current can be turned on/off via the control register.
2
–7–REV. C
Page 8
AD7711A
Pin Mnemonic Function
19 TFS Transmit Frame Synchronization. Active low logic input used to write serial data to the device with serial data
expected after the falling edge of this pulse. In the self-clocking mode, the serial clock becomes active after
TFS goes low. In the external clocking mode, TFS must go low before the first bit of the data word is written
to the part.
20 RFS Receive Frame Synchronization. Active low logic input used to access serial data from the device. In the
self-clocking mode, the SCLK and SDATA lines both become active after RFS goes low. In the external
clocking mode, the SDATA line becomes active after RFS goes low.
21 DRDY Logic Output. A falling edge indicates that a new output word is available for transmission. The DRDY pin
will return high upon completion of transmission of a full output word. DRDY is also used to indicate when
the AD7711A has completed its on-chip calibration sequence.
22 SDATA Serial Data. Input /Output with serial data being written to either the control register or the calibration
registers and serial data being accessed from the control register, calibration registers or the data register.
During an output data read operation, serial data becomes active after RFS goes low (provided DRDY is low).
During a write operation, valid serial data is expected on the rising edges of SCLK when TFS is low. The
output data coding is natural binary for unipolar inputs and offset binary for bipolar inputs.
23 DV
DD
24 DGND Ground reference point for digital circuitry.
Digital Supply Voltage, +5 V. DVDD should not exceed AVDD by more than 0.3 V in normal operation.
TERMINOLOGY
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
This is the maximum deviation of any code from a straight line
passing through the endpoints of the transfer function. The endpoints of the transfer function are zero-scale (not to be confused
with bipolar zero), a point 0.5 LSB below the first code transition (000 . . . 000 to 000 . . . 001) and full scale, a point 0.5 LSB
above the last code transition (111 . . . 110 to 111 . . . 111). The
error is expressed as a percentage of full scale.
POSITIVE FULL-SCALE ERROR
Positive Full-Scale Error is the deviation of the last code transition (111 . . . 110 to 111 . . . 111) from the ideal AIN(+) voltage
(AIN(–) + V
/GAIN – 3/2 LSBs). It applies to both unipolar
REF
and bipolar analog input ranges.
UNIPOLAR OFFSET ERROR
Unipolar Offset Error is the deviation of the first code transition
from the ideal AIN(+) voltage (AIN(–) + 0.5 LSB) when operating in the unipolar mode.
BIPOLAR ZERO ERROR
This is the deviation of the midscale transition (0111 . . . 111
to 1000 . . . 000) from the ideal AIN(+) voltage (AIN(–)
– 0.5 LSB) when operating in the bipolar mode.
BIPOLAR NEGATIVE FULL-SCALE ERROR
This is the deviation of the first code transition from the ideal
AIN(+) voltage (AIN(–) – V
/GAIN + 0.5␣ LSB), when oper-
REF
ating in the bipolar mode.
POSITIVE FULL-SCALE OVERRANGE
Positive Full-Scale Overrange is the amount of overhead available to handle input voltages on AIN(+) input greater than
AIN(–) + V
/GAIN (for example, noise peaks or excess volt-
REF
ages due to system gain errors in system calibration routines)
without introducing errors due to overloading the analog modulator or overflowing the digital filter.
NEGATIVE FULL-SCALE OVERRANGE
This is the amount of overhead available to handle voltages on
AIN(+) below AIN(–) – V
/GAIN without overloading the
REF
analog modulator or overflowing the digital filter. Note that the
analog input will accept negative voltage peaks even in the unipolar mode provided that AIN(+) is greater than AIN(–) and
greater than V
OFFSET CALIBRATION RANGE
– 30␣ mV.
SS
In the system calibration modes, the AD7711A calibrates its
offset with respect to the analog input. The Offset Calibration
Range specification defines the range of voltages that the
AD7711A can accept and still accurately calibrate offset.
FULL-SCALE CALIBRATION RANGE
This is the range of voltages that the AD7711A can accept in
the system calibration mode and still correctly calibrate full-scale.
INPUT SPAN
In system calibration schemes, two voltages applied in sequence
to the AD7711A’s analog input define the analog input range.
The input span specification defines the minimum and maximum input voltages from zero to full-scale that the AD7711A
can accept and still calibrate accurately gain.
–8–
REV. C
Page 9
AD7711A
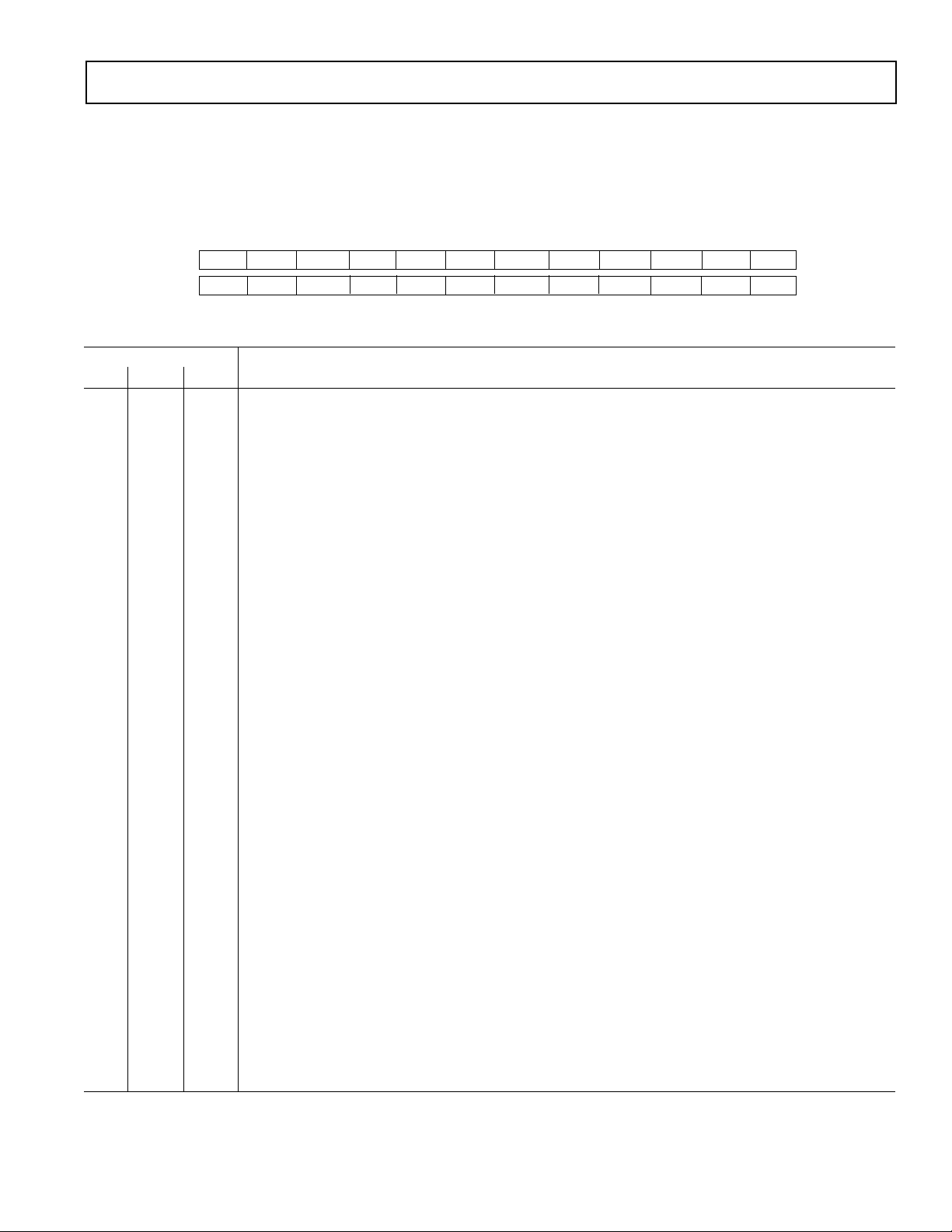
CONTROL REGISTER (24 BITS)
A write to the device with the A0 input low writes data to the control register. A read to the device with the A0 input low accesses the
contents of the control register. The control register is 24 bits wide and when writing to the register 24 bits of data must be written
otherwise the data will not be loaded to the control register. In other words, it is not possible to write just the first 12 bits of data into
the control register. If more than 24 clock pulses are provided before TFS returns high, then all clock pulses after the 24th clock
pulse are ignored. Similarly, a read operation from the control register should access 24 bits of data.
MSB
MD2 MD1 MD0 G2 G1 G0 CH PD WL IO BO B/U
FS11* FS10 FS9 FS8 FS7 FS6 FS5 FS4 FS3 FS2 FS1 FS0
*Must always be 0 to ensure correct operation of the device.
LSB
2
Operating Mode
MD2 MD1 MD0 Operating Mode
0 0 0 Normal Mode. This is the normal mode of operation of the device whereby a read to the device with A0
high accesses data from the data register. This is the default condition of these bits after the internal
power on reset.
0 0 1 Activate Self-Calibration. This activates self-calibration on the channel selected by CH. This is a one-step
calibration sequence, and when complete, the part returns to normal mode (with MD2, MD1, MD0 of
the control register returning to 0, 0, 0). The DRDY output indicates when this self-calibration is complete
and valid data is available in the output register. For this calibration type, the zero scale calibration is done
internally on shorted (zeroed) inputs and the full-scale calibration is done internally on V
REF
.
0 1 0 Activate System Calibration. This activates system calibration on the channel selected by CH. This is a
two-step calibration sequence, with the zero scale calibration done first on the selected input channel and
DRDY indicating when this zero scale calibration is complete. The part returns to normal mode at the
end of this first step in the two-step sequence.
0 1 1 Activate System Calibration. This is the second step of the system calibration sequence with full-scale
calibration being performed on the selected input channel. Once again, DRDY indicates when the full-
scale calibration is complete. When this calibration is complete, the part returns to normal mode.
1 0 0 Activate System Offset Calibration. This activates system offset calibration on the channel selected by
CH. This is a one-step calibration sequence and, when complete, the part returns to normal mode with
DRDY indicating when this system offset calibration is complete. For this calibration type, the zero scale
calibration is done on the selected input channel and the full-scale calibration is done internally on V
REF
.
1 0 1 Activate Background Calibration. This activates background calibration on the channel selected by CH. If
the background calibration mode is on, then the AD7711A provides continuous self-calibration of the
reference and shorted (zeroed) inputs. This calibration takes place as part of the conversion sequence,
extending the conversion time and reducing the word rate by a factor of six. Its major advantage is that
the user does not have to worry about recalibrating the device when there is a change in the ambient
temperature. In this mode, the shorted (zeroed) inputs and V
, as well as the analog input voltage, are
REF
continuously monitored and the calibration registers of the device are automatically updated.
1 1 0 Read/Write Zero Scale Calibration Coefficients. A read to the device with A0 high accesses the contents
of the zero scale calibration coefficients of the channel selected by CH. A write to the device with A0 high
writes data to the zero-scale calibration coefficients of the channel selected by CH. The word length for
reading and writing these coefficients is 24 bits, regardless of the status of the WL bit of the control
register. Therefore, when writing to the calibration register 24 bits of data must be written, otherwise the
new data will not be transferred to the calibration register.
1 1 1 Read/Write Full-Scale Calibration Coefficients. A read to the device with A0 high accesses the contents of
the full-scale calibration coefficients of the channel selected by CH. A write to the device with A0 high
writes data to the full-scale calibration coefficients of the channel selected by CH. The word length for
reading and writing these coefficients is 24 bits, regardless of the status of the WL bit of the control
register. Therefore, when writing to the calibration register 24 bits of data must be written, otherwise the
new data will not be transferred to the calibration register.
–9–REV. C
Page 10

AD7711A
PGA GAIN
G2 Gl G0 Gain
0001(Default Condition After the Internal Power-On Reset)
0012
0104
0118
10016
10132
11064
111128
Channel Selection
CH Channel
0 AIN1 (Default Condition After the Internal Power-On Reset)
1 AIN2
Power-Down
PD
0 Normal Operation (Default Condition After the Internal Power-On Reset)
1 Power-Down
Word Length
WL Output Word Length
0 16-Bit (Default Condition After Internal Power-On Reset)
1 24-Bit
RTD Excitation Current
IO
0 Off (Default Condition After Internal Power-On Reset)
1On
Burnout Current
BO
0 Off (Default Condition After Internal Power-On Reset)
1On
Bipolar/Unipolar Selection (Both Inputs)
B/U
0 Bipolar (Default Condition After Internal Power-On Reset)
1 Unipolar
Filter Selection (FS11–FS0)
The on-chip digital filter provides a Sinc3 (or (Sinx/x)3) filter response. The 12 bits of data programmed into these bits determine
the filter cutoff frequency, the position of the first notch of the filter and the data rate for the part. In association with the gain selection, it also determines the output noise (and hence the effective resolution) of the device.
The first notch of the filter occurs at a frequency determined by the relationship: filter first notch frequency = (f
where code is the decimal equivalent of the code in bits FS0 to FS11 and is in the range 19 to 2,000. With the nominal f
10 MHz, this results in a first notch frequency range from 9.76 Hz to 1.028 kHz. To ensure correct operation of the AD7711A, the
value of the code loaded to these bits must be within this range. Failure to do this will result in unspecified operation of the device.
Changing the filter notch frequency, as well as the selected gain, impacts resolution. Tables I and II and Figure 2 show the effect of
the filter notch frequency and gain on the effective resolution of the AD7711A. The output data rate (or effective conversion time)
for the device is equal to the frequency selected for the first notch of the filter. For example, if the first notch of the filter is selected
at 50 Hz, then a new word is available at a 50 Hz rate or every 20 ms. If the first notch is at 1 kHz, a new word is available every 1 ms.
The settling time of the filter to a full-scale step input change is worst case 4 × 1/(output data rate). This settling time is to 100% of
the final value. For example, with the first filter notch at 50 Hz, the settling time of the filter to a full-scale step input change is
80 ms max. If the first notch is at 1 kHz, the settling time of the filter to a full-scale input step is 4 ms max. This settling time can be
reduced to 3 × l/(output data rate) by synchronizing the step input change to a reset of the digital filter. In other words, if the step
input takes place with SYNC low, the settling time will be 3 × l/(output data rate). If a change of channels takes place, the settling
time is 3 × l/(output data rate) regardless of the SYNC input.
The –3 dB frequency is determined by the programmed first notch frequency according to the relationship: filter –3 dB frequency
= 0.262 × first notch frequency.
CLK IN
/512)/code
of
CLK IN
–10–
REV. C
Page 11

AD7711A
Tables I and II show the output rms noise for some typical notch and –3 dB frequencies. The numbers given are for the bipolar
input ranges with a V
noise from the part comes from two sources. First, there is the electrical noise in the semiconductor devices used in the implementation of the modulator (device noise). Secondly, when the analog input signal is converted into the digital domain, quantization noise
is added. The device noise is at a low level and is largely independent of frequency. The quantization noise starts at an even lower
level but rises rapidly with increasing frequency to become the dominant noise source. Consequently, lower filter notch settings
(below 60 Hz approximately) tend to be device noise dominated while higher notch settings are dominated by quantization noise.
Changing the filter notch and cutoff frequency in the quantization noise dominated region results in a more dramatic improvement
in noise performance than it does in the device noise dominated region as shown in Table I. Furthermore, quantization noise is
added after the PGA, so effective resolution is independent of gain for the higher filter notch frequencies. Meanwhile, device noise is
added in the PGA and, therefore, effective resolution suffers a little at high gains for lower notch frequencies.
At the lower filter notch settings (below 60 Hz), the no missing codes performance of the device is at the 24-bit level. At the higher
settings, more codes will be missed until at 1 kHz notch setting, no missing codes performance is only guaranteed to the 12-bit level.
However, since the effective resolution of the part is 10.5 bits for this filter notch setting, this no missing codes performance should
be more than adequate for all applications.
The effective resolution of the device is defined as the ratio of the output rms noise to the input full scale. This does not remain
constant with increasing gain or with increasing bandwidth. Table II shows the same table as Table I except that the output is now
expressed in terms of effective resolution (the magnitude of the rms noise with respect to 2 × V
is possible to do post filtering on the device to improve the output data rate for a given –3 dB frequency and also to further reduce
the output noise (see Digital Filtering section).
of +2.5 V. These numbers are typical and are generated with an analog input voltage of 0 V. The output
REF
/GAIN, i.e., the input full scale). It
REF
2
Table I. Output Noise vs. Gain and First Notch Frequency
First Notch of
Filter & O/P –3␣ dB Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of
Data Rate
10␣ Hz
25␣ Hz
30␣ Hz
50␣ Hz
60␣ Hz
100␣ Hz
250␣ Hz
500␣ Hz
1␣ kHz
NOTES
1
The default condition (after the internal power-on reset) for the first notch of filter is 60 Hz.
2
For these filter notch frequencies, the output rms noise is primarily dominated by device noise and as a result is independent of the value of the reference voltage.
Therefore, increasing the reference voltage will give an increase in the effective resolution of the device (i.e., the ratio of the rms noise to the input full scale is increased since the output rms noise remains constant as the input full-scale increases).
3
For these filter notch frequencies, the output rms noise is dominated by quantization noise and as a result is proportional to the value of the reference voltage.
1
Frequency 1248163264128
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
3
2.62␣ Hz 1.0 0.78 0.48 0.33 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25
6.55␣ Hz 1.8 1.1 0.63 0.5 0.44 0.41 0.38 0.38
7.86␣ Hz 2.5 1.31 0.84 0.57 0.45 0.43 0.4 0.4
13.1␣ Hz 4.33 2.06 1.2 0.64 0.54 0.46 0.46 0.46
15.72␣ Hz 5.28 2.36 1.33 0.87 0.63 0.62 0.6 0.56
26.2␣ Hz 13 6.4 3.7 1.8 1.1 0.9 0.65 0.65
65.5␣ Hz 130 75 25 12 7.5 4.0 2.7 1.7
131␣ Hz 0.6 × 10
262␣ Hz 3.1 × 10
3
3
0.26 × 10
1.6 × 10
Typical Output RMS Noise (V)
3
140 70 35 25 15 8
3
0.7 × 10
3
0.29 × 10
3
180 120 70 40
Table II. Effective Resolution vs. Gain and First Notch Frequency
First Notch of
Effective Resolution
1
(Bits)
Filter & O/P –3␣ dB Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of Gain of
Data Rate Frequency 1248163264128
10␣ Hz 2.62␣ Hz 22.5 21.5 21.5 21 20.5 19.5 18.5 17.5
25␣ Hz 6.55␣ Hz 21.5 21 21 20 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5
30␣ Hz 7.86␣ Hz 21 21 20.5 20 19.5 18.5 17.5 16.5
50␣ Hz 13.1␣ Hz 20 20 20 20 19 18.5 17.5 16.5
60␣ Hz 15.72␣ Hz 20 20 20 19.5 19 18 17 16
100␣ Hz 26.2␣ Hz 18.5 18.5 18.5 18.5 18 17.5 17 16
250␣ Hz 65.5␣ Hz 15 15 15.5 15.5 15.5 15.5 15 14.5
500␣ Hz 131␣ Hz 13 13 13 13 13 12.5 12.5 12.5
1␣ kHz 262␣ Hz 10.5 10.5 11 11 11 10.5 10 10
NOTE
1
Effective resolution is defined as the magnitude of the output rms noise with respect to the input full scale (i.e., 2 × V
of +2.5 V and resolution numbers are rounded to the nearest 0.5 LSB.
/GAIN). The above table applies for a V
REF
REF
–11–REV. C
Page 12

ANALOG
+5V SUPPLY
10mF 0.1mF 0.1mF
AVDDDV
DD
AIN1(+)
AIN1(–)
AGND
V
SS
DGND
REF OUT
REF IN(+)
V
BIAS
REF IN(–)
RTD CURRENT
DRDY
TFS
RFS
SDATA
SCLK
A0
MODE
SYNC
MCLK OUT
MCLK IN
AD7711A
DIFFERENTIAL
ANALOG INPUT
DIFFERENTIAL
ANALOG INPUT
ANALOG GROUND
DIGITAL GROUND
DATA READY
TRANSIT (WRITE)
RECEIVE (READ)
SERIAL DATA
SERIAL CLOCK
ADDRESS INPUT
+5V
AIN2(+)
AIN2(–)
AD7711A
Figures 2a and 2b give information similar to that outlined in Table I. In these plots, the output rms noise is shown for the full
range of available cutoffs frequencies rather than for some typical cutoff frequencies as in Tables I and II. The numbers given in
these plots are typical values at +25°C.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The AD7711A is a sigma-delta A/D converter with on-chip
digital filtering, intended for the measurement of wide dynamic
range, low frequency signals such as those in weigh scale, industrial control or process control applications. It contains a sigmadelta (or charge balancing) ADC, a calibration microcontroller
with on-chip static RAM, a clock oscillator, a digital filter and a
bidirectional serial communications port.
The part contains two programmable gain differential analog
input channels. The gain range is from 1 to 128 allowing the
part to accept unipolar signals of between 0 mV to +20 mV and
0 V to +2.5 V or bipolar signals in the range from ±20 mV to
±2.5 V when the reference input voltage equals +2.5 V. The
input signal to the selected analog input channel is continuously
sampled at a rate determined by the frequency of the master
clock, MCLK IN, and the selected gain (see Table III). A
charge balancing A/D converter (Sigma-Delta Modulator) converts the sampled signal into a digital pulse train whose duty
cycle contains the digital information. The programmable gain
function on the analog input is also incorporated in this sigmadelta modulator with the input sampling frequency being modified to give the higher gains. A sinc
processes the output of the sigma-delta modulator and updates
the output register at a rate determined by the first notch frequency of this filter. The output data can be read from the serial
port randomly or periodically at any rate up to the output register update rate. The first notch of this digital filter (and hence
its –3 dB frequency) can be programmed via an on-chip control
register. The programmable range for this first notch frequency
is from 9.76 Hz to 1.028 kHz, giving a programmable range for
the –3 dB frequency of 2.58 Hz to 269 Hz.
10000
GAIN OF 1
1000
100
10
OUTPUT NOISE – mV
1
0.1
10 10000100
NOTCH FREQUENCY – Hz
GAIN OF 2
GAIN OF 4
GAIN OF 8
1000
Figure 2a. Plot of Output Noise vs. Gain and Notch
Frequency (Gains of 1 to 8)
3
digital low-pass filter
10000
1000
100
10
OUTPUT NOISE – mV
1
0.1
10 10000100
NOTCH FREQUENCY – Hz
GAIN OF 16
GAIN OF 32
GAIN OF 64
GAIN OF 128
1000
Figure 2b. Plot of Output Noise vs. Gain and Notch
Frequency (Gains of 16 to 128)
The basic connection diagram for the part is shown in Figure 3.
This shows the AD7711A in the external clocking mode with
both the AV
and DVDD pins of the AD7711A being driven
DD
from the analog +5 V supply. Some applications will have
separate supplies for both AV
and DVDD, and in some of
DD
these cases, the analog supply will exceed the +5 V digital supply (see Power Supplies and Grounding section).
Figure 3. Basic Connection Diagram
–12–
REV. C
Page 13

AD7711A
The AD7711A provides a number of calibration options which
can be programmed via the on-chip control register. A calibration cycle may be initiated at any time by writing to this control
register. The part can perform self-calibration using the on-chip
calibration microcontroller and SRAM to store calibration parameters. Other system components may also be included in the
calibration loop to remove offset and gain errors in the input
channel using the system calibration mode. Another option is a
background calibration mode where the part continuously performs self-calibration and updates the calibration coefficients.
Once the part is in this mode, the user does not have to worry
about issuing periodic calibration commands to the device or
ask the device to recalibrate when there is a change in the ambient temperature or power supply voltage.
The AD7711A gives the user access to the on-chip calibration
registers allowing the microprocessor to read the device’s calibration coefficients and also to write its own calibration coefficients to the part from prestored values in E
2
PROM. This gives
the microprocessor much greater control over the AD7711A’s
calibration procedure. It also means that the user can verify that
the device has performed its calibration correctly by comparing the
coefficients after calibration with prestored values in E
2
PROM.
The AD7711A can be operated in single supply systems provided that the analog input voltage does not go more negative
than –30 mV. For larger bipolar signals, a V
of –5 V is re-
SS
quired by the part. For battery operation, the AD7711A also
offers a software programmable standby mode that reduces idle
power consumption to typically 7 mW.
THEORY OF OPERATION
The general block diagram of a sigma-delta ADC is shown in
Figure 4. It contains the following elements:
1. A sample-hold amplifier.
2. A differential amplifier or subtracter.
3. An analog low-pass filter.
4. A 1-bit A/D converter (comparator).
5. A 1-bit DAC.
6. A digital low-pass filter.
S/H AMP
+
–
ANALOG
LOW-PASS
FILTER
DAC
COMPARATOR
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
DATA
Figure 4. General Sigma-Delta ADC
In operation, the analog signal sample is fed to the subtracter,
along with the output of the 1-bit DAC. The filtered difference
signal is fed to the comparator, whose output samples the difference signal at a frequency many times that of the analog signal
sampling frequency (oversampling).
Oversampling is fundamental to the operation of sigma-delta
ADCs. Using the quantization noise formula for an ADC:
SNR = (6.02 × number of bits + 1.76) dB,
a 1-bit ADC or comparator yields an SNR of 7.78 dB.
The AD7711A samples the input signal at a frequency of
19.5 kHz or greater (see Table III). As a result, the quantization
noise is spread over a much wider frequency than that of the
band of interest. The noise in the band of interest is reduced
still further by analog filtering in the modulator loop, which
shapes the quantization noise spectrum to move most of the
noise energy to frequencies outside the bandwidth of interest.
The noise performance is thus improved from this 1-bit level to
the performance outlined in Tables I and II and in Figure 2.
The output of the comparator provides the digital input for the
1-bit DAC, so that the system functions as a negative feedback
loop that tries to minimize the difference signal. The digital
data that represents the analog input voltage is contained in the
duty cycle of the pulse train appearing at the output of the
comparator. It can be retrieved as a parallel binary data word
using a digital filter.
Sigma-delta ADCs are generally described by the order of the
analog low-pass filter. A simple example of a first order sigmadelta ADC is shown in Figure 5. This contains only a first
order low-pass filter or integrator. It also illustrates the derivation of the alternative name for these devices: Charge Balancing
ADCs.
DIFFERENTIAL
V
IN
AMPLIFIER
INTEGRATOR
e
+FS
DAC
–FS
COMPARATOR
Figure 5. Basic Charge-Balancing ADC
It consists of a differential amplifier (whose output is the difference between the analog input and the output of a 1-bit DAC),
an integrator and a comparator. The term, charge balancing,
comes from the fact that this system is a negative feedback loop
that tries to keep the net charge on the integrator capacitor at
zero by balancing charge injected by the input voltage with
charge injected by the 1-bit DAC. When the analog input is
zero, the only contribution to the integrator output comes from
the 1-bit DAC. For the net charge on the integrator capacitor
to be zero, the DAC output must spend half its time at +FS
and half its time at –FS. Assuming ideal components, the duty
cycle of the comparator will be 50%.
When a positive analog input is applied, the output of the 1-bit
DAC must spend a larger proportion of the time at +FS, so the
duty cycle of the comparator increases. When a negative input
voltage is applied, the duty cycle decreases.
The AD7711A uses a second order sigma-delta modulator and
a digital filter that provides a rolling average of the sampled
output. After power-up, or if there is a step change in the input
voltage, there is a settling time that must elapse before valid
data is obtained.
2
–13–REV. C
Page 14

FREQUENCY – Hz
0
–240
07010
GAIN
20 30 40 50 60
–20
–120
–180
–200
–220
–60
–100
–40
–80
–140
–160
AD7711A
Input Sample Rate
The modulator sample frequency for the device remains at
/512 (19.5 kHz @ f
f
CLK IN
selected gain. However, gains greater than ×1 are achieved by a
combination of multiple input samples per modulator cycle and
a scaling of the ratio of reference capacitor to input capacitor.
As a result of the multiple sampling, the input sample rate of
the device varies with the selected gain (see Table III). The
effective input impedance is 1/C × f
pling capacitance and f
S
Table III. Input Sampling Frequency vs. Gain
Gain Input Sampling Frequency (fS)
1f
22 × f
44 × f
88 × f
16 8 × f
32 8 × f
64 8 × f
128 8 × f
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
DIGITAL FILTERING
The AD7711A’s digital filter behaves like a similar analog filter,
with a few minor differences.
First, since digital filtering occurs after the A-to-D conversion
process, it can remove noise injected during the conversion
process. Analog filtering cannot do this.
On the other hand, analog filtering can remove noise superimposed on the analog signal before it reaches the ADC. Digital
filtering cannot do this and noise peaks riding on signals near
full scale have the potential to saturate the analog modulator
and digital filter, even though the average value of the signal is
within limits. To alleviate this problem, the AD7711A has
overrange headroom built into the sigma-delta modulator and
digital filter which allows overrange excursions of 5% above the
analog input range. If noise signals are larger than this, consideration should be given to analog input filtering, or to reducing
the input channel voltage so that its full scale is half that of the
analog input channel full scale. This will provide an overrange
capability greater than 100% at the expense of reducing the
dynamic range by 1 bit (50%).
Filter Characteristics
The cutoff frequency of the digital filter is determined by the
value loaded to bits FS0 to FS11 in the control register. At the
maximum clock frequency of 10 MHz, the minimum cutoff
frequency of the filter is 2.58 Hz while the maximum programmable cutoff frequency is 269 Hz.
Figure 6 shows the filter frequency response for a cutoff frequency of 2.62 Hz, which corresponds to a first filter notch frequency of 10 Hz. This is a (sinx/x)
that provides >100 dB of 50 Hz and 60 Hz rejection. Programming a different cutoff frequency via FS0–FS11 does not alter
the profile of the filter response, it changes the frequency of the
notches as outlined in the Control Register section.
= 10 MHz) regardless of the
CLK IN
where C is the input sam-
S
is the input sample rate.
/256 (39 kHz @ f
/256 (78 kHz @ f
/256 (156 kHz @ f
/256 (312 kHz @ f
/256 (312 kHz @ f
/256 (312 kHz @ f
/256 (312 kHz @ f
/256 (312 kHz @ f
3
response (also called sinc3)
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
CLK IN
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
= 10 MHz)
Figure 6. Frequency Response of AD7711A Filter
Since the AD7711A contains this on-chip, low-pass filtering,
there is a settling time associated with step function inputs, and
data on the output will be invalid after a step change until the
settling time has elapsed. The settling time depends upon the
notch frequency chosen for the filter. The output data rate
equates to this filter notch frequency, and the settling time of
the filter to a full-scale step input is four times the output data
period. In applications using both input channels, the settling
time of the filter must be allowed to elapse before data from the
second channel is accessed.
Post Filtering
The on-chip modulator provides samples at a 19.5 kHz output
rate. The on-chip digital filter decimates these samples to
provide data at an output rate that corresponds to the programmed first notch frequency of the filter. Since the output
data rate exceeds the Nyquist criterion, the output rate for a
given bandwidth will satisfy most application requirements.
However, there may be some applications which require a
higher data rate for a given bandwidth and noise performance.
Applications that need this higher data rate will require some
post filtering following the digital filter of the AD7711A.
For example, if the required bandwidth is 7.86 Hz but the required update rate is 100 Hz, the data can be taken from the
AD7711A at the 100 Hz rate giving a –3 dB bandwidth of
26.2 Hz. Post filtering can be applied to this to reduce the bandwidth and output noise, to the 7.86 Hz bandwidth level, while
maintaining an output rate of 100 Hz.
Post filtering can also be used to reduce the output noise from
the device for bandwidths below 2.62 Hz. At a gain of 128, the
output rms noise is 250 nV. This is essentially device noise or
white noise, and since the input is chopped, the noise has a flat
frequency response. By reducing the bandwidth below 2.62 Hz,
the noise in the resultant passband can be reduced. A reduction
in bandwidth by a factor of two results in a √2 reduction in the
output rms noise. This additional filtering will result in a longer
settling time.
–14–
REV. C
Page 15

AD7711A
Antialias Considerations
The digital filter does not provide any rejection at integer mul-
tiples of the modulator sample frequency (n × 19.5 kHz, where
n = 1, 2, 3 . . . ). This means that there are frequency bands,
±f
3 dB
wide (f
is cutoff frequency selected by FS0 to FS11)
3 dB
where noise passes unattenuated to the output. However, due to
the AD7711A’s high oversampling ratio, these bands occupy
only a small fraction of the spectrum and most broadband noise
is filtered. In any case, because of the high oversampling ratio a
simple, RC, single pole filter is generally sufficient to attenuate
the signals in these bands on the analog input and thus provide
adequate antialiasing filtering.
If passive components are placed in front of the AD7711A, care
must be taken to ensure that the source impedance is low enough
so as not to introduce gain errors in the system. The dc input
impedance for the AD7711A is over 1 GΩ. The input appears
as a dynamic load which varies with the clock frequency and
with the selected gain (see Figure 7). The input sample rate, as
shown in Table III, determines the time allowed for the analog
input capacitor, C
, to be charged. External impedances result
IN
in a longer charge time for this capacitor and this may result
in gain errors being introduced on the analog inputs. Table IV
shows the allowable external resistance/capacitance values such
that no gain error to the 16-bit level is introduced while Table V
shows the allowable external resistance/capacitance values such
that no gain error to the 20-bit level is introduced. Both inputs
of the differential input channels look into similar input circuitry.
AD7711A
R
INT
AIN
7kV TYP
C
INT
11.5pF TYP
V
SWITCHING FREQUENCY DEPENDS
f
AND SELECTED GAIN
ON
CLKIN
BIAS
HIGH
IMPEDANCE
1GV
Figure 7. Analog Input Impedance
Table IV. Typical External Series Resistance That Will Not
Introduce 16-Bit Gain Error
External Capacitance (pF)
Gain 0 50 100 500 1000 5000
1 184 kΩ 45.3 kΩ 27.1 kΩ 7.3 kΩ 4.1 kΩ 1.1 kΩ
2 88.6 kΩ 22.1 kΩ 13.2 kΩ 3.6 kΩ 2.0 kΩ 560 Ω
4 41.4 kΩ 10.6 kΩ 6.3 kΩ 1.7 kΩ 970 Ω 270 Ω
8–128 17.6 kΩ 4.8 kΩ 2.9 kΩ 790 Ω 440 Ω
120 Ω
Table V. Typical External Series Resistance That Will Not
Introduce 20-Bit Gain Error
External Capacitance (pF)
Gain 0 50 100 500 1000 5000
1 145 kΩ 34.5 kΩ 20.4 kΩ 5.2 kΩ 2.8 kΩ 700 Ω
2 70.5 kΩ 16.9 kΩ 10 kΩ 2.5 kΩ 1.4 kΩ 350 Ω
4 31.8 kΩ 8.0 kΩ 4.8 kΩ 1.2 kΩ 670 Ω 170 Ω
8–128 13.4 kΩ 3.6 kΩ 2.2 kΩ 550 Ω 300 Ω 80 Ω
The numbers in the above tables assume a full-scale change on
the analog input. In any case, the error introduced due to longer
charging times is a gain error which can be removed using the
system calibration capabilities of the AD7711A provided that
the resultant span is within the span limits of the system calibration techniques for the AD7711A.
ANALOG INPUT FUNCTIONS
Analog Input Ranges
Both analog inputs are differential, programmable gain, input
channels which can handle either unipolar or bipolar input
signals. The common-mode range of these inputs is from V
provided that the absolute value of the analog input volt-
AV
DD
age lies between V
–30 mV and AVDD +30 mV.
SS
to
SS
The dc input leakage current is 10 pA maximum at 25°C
(±1 nA over temperature). This results in a dc offset voltage
developed across the source impedance. However, this dc offset
effect can be compensated for by a combination of the differential input capability of the part and its system calibration mode.
Burnout Current
The AIN1(+) input of the AD7711A contains a 4.5 µA current
source that can be turned on/off via the control register. This
current source can be used in checking that a transducer has not
burned out or gone open circuit before attempting to take measurements on that channel. If the current is turned on and allowed flow into the transducer and a measurement of the input
voltage on the AIN1 input is taken, it can indicate that the
transducer has burnout or gone open circuit. For normal operation, this burnout current is turned off by writing a 0 to the BO
bit in the control register.
RTD Excitation Current
The AD7711A also contains a 400 µA constant current source,
which is provided at the RTD current pin of the device. This
current can be turned on/off via the control register. Writing a 1
to the IO bit of the control register enables the excitation current.
The temperature coefficient of the RTD current is typical
20 ppm/°C. For applications where this coefficient is too large,
the following scheme can be used to remove the drift error. The
conversion result from the AD7711A is ratiometric to the V
voltage. Therefore, if the V
voltage varies with the RTD
REF
REF
temperature coefficient, the temperature drift of the current
source will be removed. Hence, the reference voltage for the
part should be generated by placing a low t.c. resistor (6.25 kΩ
for 2.5 V reference) in series with the constant current. The
RTD current source can be driven to within 2 V of AV
DD
. The
reference input of the AD7711A is differential so the REF
IN(+) and REF IN(–) of the AD7711A are driven from either
side of the resistor.
2
–15–REV. C
Page 16

AD7711A
Bipolar/Unipolar Inputs
The two analog inputs on the AD7711A can accept either unipolar or bipolar input voltage ranges. Bipolar or unipolar options are chosen by programming the B/U bit of the control
register. This programs both channels for either unipolar or
bipolar operation. Programming the part for either unipolar or
bipolar operation does not change any of the input signal conditioning; it simply changes the data output coding. The data
coding is binary for unipolar inputs and offset binary for bipolar
inputs.
The input channels are differential and, as a result, the voltage
to which the unipolar and bipolar signals are referenced is the
voltage on the AIN(–) input. For example, if AIN(–) is +1.25 V
and the AD7711A is configured for unipolar operation with a
gain of 1 and a V
of +2.5 V, the input voltage range on the
REF
AIN(+) input is +1.25 V to +3.75 V. If AIN(–) is +1.25 V and
the AD7711A is configured for bipolar mode with a gain of 1
and a V
of +2.5 V, the analog input range on the AIN(+)
REF
input is –1.25 V to +3.75 V.
REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT
The AD7711A contains a temperature compensated +2.5 V
reference which has an initial tolerance of ±1%. This reference
voltage is provided at the REF OUT pin and it can be used as
the reference voltage for the part by connecting the REF OUT
pin to the REF IN(+) pin. This REF OUT pin is a single-ended
output, referenced to AGND, which is capable of providing up
to 1 mA to an external load. In applications where REF OUT is
connected to REF IN(+), REF IN(–) should be tied to AGND
to provide the nominal +2.5 V reference for the AD7711A.
The reference inputs of the AD7711A, REF IN(+) and REF
IN(–), provide a differential reference input capability. The
common-mode range for these differential inputs is from V
. The nominal differential voltage, V
AV
DD
(REF IN(+) –
REF
to
SS
REF IN(–)), is +2.5 V for specified operation, but the reference
voltage can go to +5 V with no degradation in performance provided that the absolute value of REF IN(+) and REF IN(–) does
not exceed its AV
and VSS limits and the V
DD
range limits are obeyed. The part is also functional with V
input voltage
BIAS
REF
voltages down to 1 V but with degraded performance as the
output noise will, in terms of LSB size, be larger. REF IN(+) must
always be greater than REF IN(–) for correct operation of the
AD7711A.
Both reference inputs provide a high impedance, dynamic load
similar to the analog inputs. The maximum dc input leakage
current is 10 pA (±1 nA over temperature) and source resis-
tance may result in gain errors on the part. The reference inputs
look like the analog input (see Figure 7). In this case, R
5 kΩ typ and C
/256 and does not vary with gain. For gains of 1 to 8 C
f
CLK IN
varies with gain. The input sample rate is
INT
INT
is
INT
is 20 pF; for a gain of 16 it is 10 pF; for a gain of 32 it is 5 pF;
for a gain of 64 it is 2.5 pF; and for a gain of 128 it is 1.25 pF.
The digital filter of the AD7711A removes noise from the reference input just as it does with the analog input, and the same
limitations apply regarding lack of noise rejection at integer
multiples of the sampling frequency. The output noise performance outlined in Tables I and II assumes a clean reference. If
the reference noise in the bandwidth of interest is excessive, it
can degrade the performance of the AD7711A. Using the onchip reference as the reference source for the part (i.e., connecting REF OUT to REF IN) results in somewhat degraded output
noise performance from the AD7711A for portions of the noise
table which are dominated by the device noise. The on-chip
reference noise effect is eliminated in ratiometric applications
where the reference is used to provide the excitation voltage for
the analog front end. The connection scheme shown in Figure 8
is recommended when using the on-chip reference. Recommended reference voltage sources for the AD7711A include the
AD780 and AD680 2.5 V references.
REF OUT
AD7711A
REF IN(+)
REF IN(–)
Figure 8. REF OUT/REF IN Connection
V
Input
BIAS
The V
input determine at what voltage the internal analog
BIAS
circuitry is biased. It essentially provides the return path for
analog currents flowing in the modulator and, as such, it should
be driven from a low impedance point to minimize errors.
For maximum internal headroom, the V
set halfway between AV
AV
and (V
DD
+ 0.85 × V
BIAS
headroom the circuit has at the upper end, while the difference
between V
and (V
SS
and VSS. The difference between
BIAS
DD
) determines the amount of
REF
– 0.85 × V
REF
voltage should be
BIAS
) determines the amount
of headroom the circuit has at the lower end. Care should be
taken in choosing a V
prescribed limits. For single +5 V operation, the selected V
voltage must ensure that V
or VSS or that the V
AV
DD
voltage to ensure that it stays within
BIAS
± 0.85 × V
BIAS
voltage itself is greater than V
BIAS
does not exceed
REF
BIAS
SS
+ 2.1 V and less than AVDD – 2.1 V. For single +10 V operation
or dual ±5 V operation, the selected V
that V
the V
AV
and V
± 0.85 × V
BIAS
voltage itself is greater than VSS + 3 V or less than
BIAS
–3 V. For example, with AVDD = +4.75 V, VSS = 0 V
DD
= +2.5 V, the allowable range for the V
REF
+2.125 V to +2.625 V. With AV
= +5 V, the range for V
V
REF
= +4.75 V, VSS = –4.75 V and V
AV
DD
does not exceed AVDD or VSS or that
REF
DD
is +4.25 V to +5.25 V. With
BIAS
voltage must ensure
BIAS
voltage is
BIAS
= +9.5 V, VSS = 0 V and
= +2.5 V, the V
REF
BIAS
range is –2.625 V to +2.625 V.
The V
ply rejection performance of the AD7711A. If the V
tracks the AV
from the AV
ternal Zener diode, connected between the AV
as the source for the V
AV
voltage does have an effect on the AVDD power sup-
BIAS
supply, it improves the power supply rejection
DD
supply line from 80 dB to 95 dB. Using an ex-
DD
voltage gives the improvement in
power supply rejection performance.
DD
BIAS
DD
voltage
BIAS
line and V
BIAS
–16–
REV. C
Page 17

AD7711A
USING THE AD7711A
SYSTEM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
The AD7711A operates differently from successive approximation ADCs or integrating ADCs. Since it samples the signal
continuously, like a tracking ADC, there is no need for a start
convert command. The output register is updated at a rate
determined by the first notch of the filter and the output can be
read at any time, either synchronously or asynchronously.
Clocking
The AD7711A requires a master clock input, which may be an
external TTL/CMOS compatible clock signal applied to the
MCLK IN pin with the MCLK OUT pin left unconnected.
Alternatively, a crystal of the correct frequency can be connected between MCLK IN and MCLK OUT, in which case the
clock circuit will function as a crystal controlled oscillator. For
lower clock frequencies, a ceramic resonator may be used instead of the crystal. For these lower frequency oscillators, external capacitors may be required on either the ceramic resonator
or on the crystal.
The input sampling frequency, the modulator sampling frequency, the –3 dB frequency, output update rate and calibration
time are all directly related to the master clock frequency,
Reducing the master clock frequency by a factor of two
f
CLK IN.
will halve the above frequencies and update rate and will double
the calibration time.
The current drawn from the DV
related to f
the DV
DD
power supply.
AV
DD
System Synchronization
. Reducing f
CLK IN
current but will not affect the current drawn from the
power supply is also directly
DD
by a factor of two will halve
CLK IN
If multiple AD7711As are operated from a common master
clock, they can be synchronized to update their output registers
simultaneously. A falling edge on the SYNC input resets the
filter and places the AD7711A into a consistent, known state. A
common signal to the AD7711As’ SYNC inputs will synchronize their operation. This would normally be done after each
AD7711A has performed its own calibration or has had calibration coefficients loaded to it.
The SYNC input can also be used to reset the digital filter in
systems where the turn-on time of the digital power supply
(DVDD) is very long. In such cases, the AD7711A will start
operating internally before the DV
mum operating level, +4.75 V. With a low DV
line has reached its mini-
DD
voltage, the
DD
AD7711A’s internal digital filter logic does not operate correctly. Thus, the AD7711A may have clocked itself into an
incorrect operating condition by the time that DV
DD
has
reached its correct level. The digital filter will be reset upon
issue of a calibration command (whether it is self-calibration,
system calibration or background calibration) to the AD7711A.
This ensures correct operation of the AD7711A. In systems
where the power-on default conditions of the AD7711A are
acceptable, and no calibration is performed after power-on,
issuing a SYNC pulse to the AD7711A will reset the AD7711A’s
digital filter logic. An R, C on the SYNC line, with R, C time
constant longer than the DV
power-on time, will perform the
DD
SYNC function.
ACCURACY
Sigma-delta ADCs, like VFCs and other integrating ADCs, do
not contain any source of nonmonotonicity and inherently offer
no missing codes performance. The AD7711A achieves excellent linearity by the use of high quality, on-chip silicon dioxide
capacitors, which have a very low capacitance/voltage coefficient. The device also achieves low input drift through the use
of chopper stabilized techniques in its input stage. To ensure
excellent performance over time and temperature, the AD7711A
uses digital calibration techniques which minimize offset and
gain error.
AUTOCALIBRATION
Autocalibration on the AD7711A removes offset and gain errors
from the device. A calibration routine should be initiated on the
device whenever there is a change in the ambient operating
temperature or supply voltage. It should also be initiated if there
is a change in the selected gain, filter notch or bipolar/unipolar
input range. However, if the AD7711A is in its background
calibration mode, the above changes are all automatically taken
care of (after allowing for the settling time of the filter).
The AD7711A offers self-calibration, system calibration and
background calibration facilities. For calibration to occur on the
selected channel, the on-chip microcontroller must record the
modulator output for two different input conditions. These are
“zero-scale” and “full-scale” points. With these readings, the
microcontroller can calculate the gain slope for the input to
output transfer function of the converter. Internally, the part
works with a resolution of 33 bits to determine its conversion
result of either 16 bits or 24 bits.
The AD7711A also provides the facility to write to the on-chip
calibration registers and in this manner the span and offset for
the part can be adjusted by the user. The offset calibration register contains a value which is subtracted from all conversion
results, while the full-scale calibration register contains a value
which is multiplied by all conversion results. The offset calibration coefficient is subtracted from the result prior to the multiplication by the full-scale coefficient. In the first three modes
outlined here, the DRDY line indicates that calibration is complete by going low. If DRDY is low before (or goes low during)
the calibration command, it may take up to one modulator cycle
before DRDY goes high to indicate that calibration is in progress.
Therefore, DRDY should be ignored for up to one modulator
cycle after the last bit of the calibration command is written to
the control register.
2
–17–REV. C
Page 18

AD7711A
Self-Calibration
In the self-calibration mode with a unipolar input range, the
zero scale point used in determining the calibration coefficients
is with both inputs shorted (i.e., AIN(+) = AIN(–) = V
the full-scale point is V
. The zero scale coefficient is deter-
REF
mined by converting an internal shorted inputs node. The full
scale coefficient is determined from the span between this
shorted inputs conversion and a conversion on an internal V
node. The self-calibration mode is invoked by writing the appropriate values (0, 0, 1) to the MD2, MD1 and MD0 bits of the
control register. In this calibration mode, the shorted inputs
node is switched in to the modulator first and a conversion is
performed; the V
node is then switched in and another con-
REF
version is performed. When the calibration sequence is complete, the calibration coefficients updated and the filter resettled
to the analog input voltage, the DRDY output goes low. The
self-calibration procedure takes into account the selected gain
on the PGA.
For bipolar input ranges in the self-calibrating mode, the sequence is very similar to that just outlined. In this case, the two
points which the AD7711A calibrates are midscale (bipolar
zero) and positive full scale.
System Calibration
System calibration allows the AD7711A to compensate for
system gain and offset errors as well as its own internal errors.
System calibration performs the same slope factor calculations
as self-calibration but uses voltage values presented by the system to the AIN inputs for the zero and full-scale points. System
calibration is a two-step process. The zero scale point must be
presented to the converter first. It must be applied to the converter before the calibration step is initiated and remain stable
until the step is complete. System calibration is initiated by
writing the appropriate values (0, 1, 0) to the MD2, MD1 and
MD0 bits of the control register. The DRDY output from the
device will signal when the step is complete by going low. After
the zero-scale point is calibrated, the full-scale point is applied
and the second step of the calibration process is initiated by
again writing the appropriate values (0, 1, 1) to MD2, MD1 and
MD0. Again the full-scale voltage must be set up before the
calibration is initiated and it must remain stable throughout the
calibration step. DRDY goes low at the end of this second step
to indicate that the system calibration is complete. In the unipolar mode, the system calibration is performed between the two
endpoints of the transfer function; in the bipolar mode, it is
performed between midscale and positive full scale.
This two-step system calibration mode offers another feature.
After the sequence has been completed, additional offset or gain
calibrations can be performed by themselves to adjust the zero
reference point or the system gain. This is achieved by performing the first step of the system calibration sequence (by writing
0, 1, 0 to MD2, MD1, MD0). This will adjust the zero-scale or
offset point but will not change the slope factor from what was
set during a full system calibration sequence.
System calibration can also be used to remove any errors from
an antialiasing filter on the analog input. A simple R, C antialiasing filter on the front end may introduce a gain error on the
analog input voltage but the system calibration can be used to
remove this error.
BIAS
) and
REF
System Offset Calibration
System offset calibration is a variation of both the system calibration and self-calibration. In this case, the zero scale point
for the system is presented to the AIN input of the converter.
System-offset calibration is initiated by writing 1, 0, 0 to MD2,
MD1, MD0. The system zero scale coefficient is determined by
converting the voltage applied to the AIN input, while the fullscale coefficient is determined from the span between this AIN
conversion and a conversion on V
. The zero scale point
REF
should be applied to the AIN input for the duration of the calibration sequence. This is a one-step calibration sequence with
DRDY going low when the sequence is completed. In the unipolar mode, the system offset calibration is performed between
the two endpoints of the transfer function; in the bipolar mode,
it is performed between midscale and positive full scale.
Background Calibration
The AD7711A also offers a background calibration mode where
the part interleaves its calibration procedure with its normal
conversion sequence. In the background calibration mode, the
same voltages are used as the calibration points as are used in
the self-calibration mode, i.e., shorted inputs and V
REF
. The
background calibration mode is invoked by writing 1, 0, 1 to
MD2, MD1, MD0 of the control register. When invoked, the
background calibration mode reduces the output data rate of the
AD7711A by a factor of six while the –3 dB bandwidth remains
unchanged. Its advantage is that the part is continually performing calibration and automatically updating its calibration coefficients. As a result, the effects of temperature drift, supply
sensitivity and time drift on zero and full scale errors are automatically removed. When the background calibration mode is
turned on, the part will remain in this mode until bits MD2,
MD1 and MD0 of the control register are changed. With background calibration mode on, the first result from the AD7711A
will be incorrect as the full-scale calibration will not have been
performed. For a step change on the input, the second output
update will have settled to 100% of the final value.
Table VI summarizes the calibration modes and the calibration
points associated with them. It also gives the duration from
when the calibration is invoked to when valid data is available to
the user.
Span and Offset Limits
Whenever a system calibration mode is used, there are limits on
the amount of offset and span that can be accommodated. The
range of input span in both the unipolar and bipolar modes has
a minimum value of 0.8 × V
REF
/GAIN.
2.1 × V
/GAIN and a maximum value of
REF
The amount of offset that can be accommodated depends on
whether the unipolar or bipolar mode is being used. This offset
range is limited by the requirement that the positive full-scale
calibration limit is ≤ 1.05 × V
range plus the span range cannot exceed 1.05 × V
the span is at its minimum (0.8 × V
the offset can be is (0.25 × V
/GAIN. Therefore, the offset
REF
/GAIN).
REF
/GAIN) the maximum
REF
/GAIN. If
REF
–18–
REV. C
Page 19

AD7711A
AV
DD
DV
DD
0.1mF10mF
ANALOG
SUPPLY
0.1mF
DIGITAL +5V
SUPPLY
AD7711A
Table VI. Calibration Truth Table
Cal Type MD2, MD1, MD0 Zero Scale Cal Full-Scale Cal Sequence Duration
Self-Cal 0, 0, 1 Shorted Inputs V
REF
System Cal 0, 1, 0 AIN – Two Step 4 × 1/Output Rate
System Cal 0, 1, 1 – AIN Two Step 4 × 1/Output Rate
System Offset Cal 1, 0, 0 AIN V
Background Cal 1, 0, 1 Shorted Inputs V
REF
REF
One Step 9 × 1/Output Rate
One Step 9 × 1/Output Rate
One Step 6 × 1/Output Rate
2
In the bipolar mode, the system offset calibration range is again
restricted by the span range. The span range of the converter in
bipolar mode is equidistant around the voltage used for the zero
scale point thus the offset range plus half the span range cannot
exceed (1.05 × V
/GAIN). If the span is set to 2 × V
REF
the offset span cannot move more than ±(0.05 × V
REF
/GAIN)
REF
/GAIN,
before the endpoints of the transfer function exceed the input
overrange limits ±(1.05 × V
to the minimum ±(0.4 × V
offset range is ±(0.65
/GAIN). If the span range is set
REF
/GAIN) the maximum
REF
× V
/GAIN).
REF
allowable
POWER-UP AND CALIBRATION
On power-up, the AD7711A performs an internal reset which
sets the contents of the control register to a known state. However, to ensure correct calibration for the device a calibration
routine should be performed after power-up.
The power dissipation and temperature drift of the AD7711A
are low and no warm up time is required before the initial calibration is performed. However, if an external reference is being
used, this reference must have stabilized before calibration is
initiated.
Drift Considerations
The AD7711A uses chopper stabilization techniques to minimize input offset drift. Charge injection in the analog switches
and dc leakage currents at the sampling node are the primary
sources of offset voltage drift in the converter. The dc input
leakage current is essentially independent of the selected gain.
Gain drift within the converter depends primarily upon the
temperature tracking of the internal capacitors. It is not affected
by leakage currents.
Measurement errors due to offset drift or gain drift can be eliminated at any time by recalibrating the converter or by operating
the part in the background calibration mode. Using the system
calibration mode can also minimize offset and gain errors in the
signal conditioning circuitry. Integral and differential linearity
errors are not significantly affected by temperature changes.
The analog and digital supplies to the AD7711A are independent and separately pinned out to minimize coupling between
the analog and digital sections of the device. The digital filter
will provide rejection of broadband noise on the power supplies,
except at integer multiples of the modulator sampling frequency.
The digital supply (DV
supply (AV
) by more than 0.3 V in normal operation. If sepa-
DD
) must not exceed the analog positive
DD
rate analog and digital supplies are used, the recommended
decoupling scheme is shown in Figure 9. In systems where
= +5 V and DVDD = +5 V, it is recommended that AV
AV
DD
DD
and DVDD are driven from the same +5 V supply, although each
supply should be decoupled separately as shown in Figure 9. It
is preferable that the common supply is the system’s analog +5 V
supply.
It is also important that power is applied to the AD7711A before signals at REF IN, AIN or the logic input pins in order to
avoid excessive current. If separate supplies are used for the
AD7711A and the system digital circuitry, then the AD7711A
should be powered up first. If it is not possible to guarantee this,
then current limiting resistors should be placed in series with the
logic inputs.
Figure 9. Recommended Decoupling Scheme
POWER SUPPLIES AND GROUNDING
Since the analog inputs and reference input are differential,
most of the voltages in the analog modulator are common-mode
voltages. V
provides the return path for most of the analog
BIAS
currents flowing in the analog modulator. As a result, the V
input should be driven from a low impedance to minimize errors
due to charging/discharging impedances on this line. When the
internal reference is used as the reference source for the part,
AGND is the ground return for this reference voltage.
BIAS
–19–REV. C
Page 20

AD7711A
DIGITAL INTERFACE
The AD7711A’s serial communications port provides a flexible
arrangement to allow easy interfacing to industry-standard
microprocessors, microcontrollers and digital signal processors.
A serial read to the AD7711A can access data from the output
register, the control register or from the calibration registers. A
serial write to the AD7711A can write data to the control register or the calibration registers.
Two different modes of operation are available, optimized for
different types of interface where the AD7711A can act either as
master in the system (it provides the serial clock) or as slave (an
external serial clock can be provided to the AD7711A). These
two modes, labelled self-clocking mode and external clocking
mode, are discussed in detail in the following sections.
Self-Clocking Mode
The AD7711A is configured for its self-clocking mode by tying
the MODE pin high. In this mode, the AD7711A provides the
serial clock signal used for the transfer of data to and from the
AD7711A. This self-clocking mode can be used with processors
that allow an external device to clock their serial port including
most digital signal processors and microcontrollers such as the
68HC11 and 68HC05. It also allows easy interfacing to serial
parallel conversion circuits in systems with parallel data communication, allowing interfacing to 74XX299 Universal Shift registers without any additional decoding. In the case of shift registers,
the serial clock line should have a pull-down resistor instead of
the pull-up resistor shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
Read Operation
Data can be read from either the output register, the control
register or the calibration registers. A0 determines whether the
data read accesses data from the control register or from the
output/calibration registers. This A0 signal must remain valid
for the duration of the serial read operation. With A0 high, data
is accessed from either the output register or from the calibration registers. With A0 low, data is accessed from the control
register.
The function of the DRDY line is dependent only on the output
update rate of the device and the reading of the output data
register. DRDY goes low when a new data word is available in
the output data register. It is reset high when the last bit of data
(either 16th bit or 24th bit) is read from the output register. If
data is not read from the output register, the DRDY line will
remain low. The output register will continue to be updated at
the output update rate but DRDY will not indicate this. A read
from the device in this circumstance will access the most recent
word in the output register. If a new data word becomes available to the output register while data is being read from the
output register, DRDY will not indicate this and the new data
word will be lost to the user. DRDY is not affected by reading
from the control register or the calibration registers.
Data can only be accessed from the output data register when
DRDY is low. If RFS goes low with DRDY high, no data trans-
fer will take place. DRDY does not have any effect on reading
data from the control register or from the calibration registers.
Figure 10 shows a timing diagram for reading from the AD7711A
in the self-clocking mode. This read operation shows a read
from the AD7711A’s output data register. A read from the
control register or calibration registers is similar but in these
cases the DRDY line is not related to the read function. Depending on the output update rate, it can go low at any stage in
the control/calibration register read cycle without affecting the
read and its status should be ignored. A read operation from
either the control or calibration registers must always read 24
bits of data from the respective register.
Figure 10 shows a read operation from the AD7711A. For the
timing diagram shown, it is assumed that there is a pull-up
resistor on the SCLK output. With DRDY low, the RFS input
is brought low. RFS going low enables the serial clock of the
AD7711A and also places the MSB of the word on the serial
data line. All subsequent data bits are clocked out on a high to
low transition of the serial clock and are valid prior to the following rising edge of this clock. The final active falling edge of
SCLK clocks out the LSB and this LSB is valid prior to the final
active rising edge of SCLK. Coincident with the next falling
edge of SCLK, DRDY is reset high. DRDY going high turns off
the SCLK and the SDATA outputs. This means that the data
hold time for the LSB is slightly shorter than for all other bits.
DRDY (O)
A0 (I)
RFS (I)
SCLK (O)
SDATA (O)
t
2
t
4
t
t
6
t
7
t
8
MSB LSB
9
t
10
Figure 10. Self-Clocking Mode, Output Data Read Operation
–20–
t
3
t
5
THREE-STATE
REV. C
Page 21

AD7711A
Write Operation
Data can be written to either the control register or calibration
registers. In either case, the write operation is not affected by
the DRDY line and the write operation does not have any effect
on the status of DRDY. A write operation to the control register
or the calibration register must always write 24 bits to the respective register.
Figure 11 shows a write operation to the AD7711A. A0 determines whether a write operation transfers data to the control
register or to the calibration registers. This A0 signal must remain valid for the duration of the serial write operation. The
falling edge of TFS enables the internally generated SCLK
output. The serial data to be loaded to the AD7711A must be
valid on the rising edge of this SCLK signal. Data is clocked
into the AD7711A on the rising edge of the SCLK signal with
the MSB transferred first. On the last active high time of SCLK,
the LSB is loaded to the AD7711A. Subsequent to the next
falling edge of SCLK, the SCLK output is turned off. (The
timing diagram of Figure 11 assumes a pull-up resistor on the
SCLK line.)
External Clocking Mode
The AD7711A is configured for its external clocking mode by
tying the MODE pin low. In this mode, SCLK of the AD7711A
is configured as an input and an external serial clock must be
provided to this SCLK pin. This external clocking mode is
designed for direct interface to systems which provide a serial
clock output which is synchronized to the serial data output,
including microcontrollers such as the 80C51, 87C51, 68HC11
and 68HC05 and most digital signal processors.
Read Operation
As with the self-clocking mode, data can be read from either the
output register, the control register or the calibration registers.
A0 determines whether the data read accesses data from the
control register or from the output/calibration registers. This A0
signal must remain valid for the duration of the serial read operation. With A0 high, data is accessed from either the output
register or from the calibration registers. With A0 low, data is
accessed from the control register.
The function of the DRDY line is dependent only on the output
update rate of the device and the reading of the output data
register. DRDY goes low when a new data word is available in
the output data register. It is reset high when the last bit of data
(either 16th bit or 24th bit) is read from the output register. If
data is not read from the output register, the DRDY line will
remain low. The output register will continue to be updated at
the output update rate but DRDY will not indicate this. A read
from the device in this circumstance will access the most recent
word in the output register. If a new data word becomes available to the output register while data is being read from the
output register, DRDY will not indicate this and the new data
word will be lost to the user. DRDY is not affected by reading
from the control register or the calibration register.
Data can only be accessed from the output data register when
DRDY is low. If RFS goes low while DRDY is high, no data
transfer will take place. DRDY does not have any effect on reading
data from the control register or from the calibration registers.
2
A0 (I)
t
TFS (I)
SCLK (O)
SDATA (O)
14
t
16
t
18
MSB LSB
t
9
t
19
t
10
t
15
t
17
Figure 11. Self-Clocking Mode, Control/Calibration Register Write Operation
–21–REV. C
Page 22

AD7711A
Figures 12a and 12b show timing diagrams for reading from the
AD7711A in the external clocking mode. Figure 12a shows a
situation where all the data is read from the AD7711A in one
read operation. Figure 12b shows a situation where the data is
read from the AD7711A over a number of read operations. Both
read operations show a read from the AD7711A’s output data
register. A read from the control register or calibration registers
is similar but in these cases the DRDY line is not related to the
read function. Depending on the output update rate, it can go
low at any stage in the control/calibration register read cycle
without affecting the read and its status should be ignored. A
read operation from either the control or calibration registers
must always read 24 bits of data from the respective register.
Figure 12a shows a read operation from the AD7711A where
RFS remains low for the duration of the data word transmission.
With DRDY low, the RFS input is brought low. The input
SCLK signal should be low between read and write operations.
RFS going low places the MSB of the word to be read on the
serial data line. All subsequent data bits are clocked out on a
high to low transition of the serial clock and are valid prior to
the following rising edge of this clock. The penultimate falling
DRDY (O)
t
20
A0 (I)
t
22
edge of SCLK clocks out the LSB and the final falling edge
resets the DRDY line high. This rising edge of DRDY turns off
the serial data output.
Figure 12b shows a timing diagram for a read operation where
RFS returns high during the transmission of the word and returns low again to access the rest of the data word. Timing
parameters and functions are very similar to that outlined for
Figure 12a but Figure 12b has a number of additional times to
show timing relationships when RFS returns high in the middle
of transferring a word.
RFS should return high during a low time of SCLK. On the
rising edge of RFS, the SDATA output is turned off. DRDY
remains low and will remain low until all bits of the data word
are read from the AD7711A, regardless of the number of times
RFS changes state during the read operation. Depending on the
time between the falling edge of SCLK and the rising edge of
RFS, the next bit (BIT N+1) may appear on the databus before
RFS goes high. When RFS returns low again, it activates the
SDATA output. When the entire word is transmitted, the
DRDY line will go high turning off the SDATA output as per
Figure 12a.
t
21
t
23
RFS (I)
SCLK (I)
SDATA (O)
DRDY (O)
A0 (I)
RFS (I)
SCLK (I)
SDATA (O)
t
26
t
24
t
25
MSB LSB
t
27
t
t
29
Figure 12a. External-Clocking Mode, Output Data Read Operation
t
20
t
22
t
26
t
24
MSB
t
25
t
27
BIT N BIT N+1
t
30
t
31
THREE-STATE
t
24
28
THREE-STATE
t
25
Figure 12b. External-Clocking Mode, Output Data Read Operation (
–22–
RFS
Returns High During Read Operation)
REV. C
Page 23

AD7711A
Write Operation
Data can be written to either the control register or calibration
registers. In either case, the write operation is not affected by
the DRDY line and the write operation does not have any effect
on the status of DRDY. A write operation to the control register
or the calibration register must always write 24 bits to the
respective register.
Figure 13a shows a write operation to the AD7711A with TFS
remaining low for the duration of the write operation. A0 determines whether a write operation transfers data to the control
register or to the calibration registers. This A0 signal must remain valid for the duration of the serial write operation. As
before, the serial clock line should be low between read and
write operations. The serial data to be loaded to the AD7711A
must be valid on the high level of the externally applied SCLK
signal. Data is clocked into the AD7711A on the high level of
this SCLK signal with the MSB transferred first. On the last
active high time of SCLK, the LSB is loaded to the AD7711A.
A0 (I)
t
32
TFS (I)
t
26
SCLK (I)
t
36
SDATA (I)
t
MSB
35
Figure 13b shows a timing diagram for a write operation to the
AD7711A with TFS returning high during the write operation
and returning low again to write the rest of the data word. Timing parameters and functions are very similar to that outlined for
Figure 13a but Figure 13b has a number of additional times to
show timing relationships when TFS returns high in the middle
of transferring a word.
Data to be loaded to the AD7711A must be valid prior to the
rising edge of the SCLK signal. TFS should return high during
the low time of SCLK. After TFS returns low again, the next bit
of the data word to be loaded to the AD7711A is clocked in on
next high-level of the SCLK input. On the last high time of the
SCLK input, the LSB is loaded to the AD7711A.
t
33
t
34
t
27
LSB
2
Figure 13a. External-Clocking Mode, Control/Calibration Register Write Operation
A0 (I)
t
32
TFS (I)
SCLK (I)
SDATA (I)
t
26
t
t
35
MSB BIT N BIT N+1
27
t
30
t
36
t
35
Figure 13b. External-Clocking Mode, Control/Calibration Register Write Operation (
During Write Operation)
t
36
TFS
Returns High
–23–REV. C
Page 24

AD7711A
SIMPLIFYING THE EXTERNAL CLOCKING MODE INTERFACE
In many applications, the user may not require the facility of
writing to the on-chip calibration registers. In this case, the
serial interface to the AD7711A in external clocking mode can
be simplified by connecting the TFS line to the A0 input of the
AD7711A (see Figure 14). This means that any write to the
device will load data to the control register (since A0 is low
while TFS is low) and any read to the device will access data
from the output data register or from the calibration registers
(since A0 is high while RFS is low). It should be noted that in
this arrangement the user does not have the capability of reading
from the control register.
RFS
FOUR
INTERFACE
LINES
Figure 14. Simplified Interface with
SDATA
SCLK
TFS
A0
AD7711A
TFS
Connected to A0
Another method of simplifying the interface is to generate the
TFS signal from an inverted RFS signal. However, generating
the signals the opposite way around (RFS from an inverted
TFS) will cause writing errors.
MICROCOMPUTER/MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
The AD7711A’s flexible serial interface allows for easy interface
to most microcomputers and microprocessors. Figure 15 shows
a flowchart diagram for a typical programming sequence for
reading data from the AD7711A to a microcomputer while
Figure 16 shows a flowchart diagram for writing data to the
AD7711A. Figures 17, 18 and 19 show some typical interface
circuits.
The flowchart of Figure 15 is for continuous read operations
from the AD7711A output register. In the example shown, the
DRDY line is continuously polled. Depending on the microprocessor configuration, the DRDY line may come to an interrupt
input in which case the DRDY will automatically generate an
interrupt without being polled. The reading of the serial buffer
could be anything from one read operation up to three read
operations (where 24 bits of data are read into an 8-bit serial
register). A read operation to the control/calibration registers is
similar but in this case the status of DRDY can be ignored. The
A0 line is brought low when the RFS line is brought low when
reading from the control register.
The flowchart also shows the bits being reversed after they have
been read in from the serial port. This depends on whether the
microprocessor expects the MSB of the word first or the LSB of
the word first. The AD7711A outputs the MSB first.
The flowchart in Figure 16 is for a single 24-bit write operation
to the AD7711A control or calibration registers. This shows
data being transferred from data memory to the accumulator
before being written to the serial buffer. Some microprocessor
systems will allow data to be written directly to the serial buffer
from data memory. The writing of data to the serial buffer from
the accumulator will generally consist of either two or three
write operations, depending on the size of the serial buffer.
START
CONFIGURE &
INITIALIZE mC/mP
SERIAL PORT
BRING
RFS, TFS HIGH
POLL DRDY
DRDY
LOW?
NO
YES
BRING
RFS LOW
33
READ
SERIAL BUFFER
BRING
RFS HIGH
REVERSE
ORDER OF BITS
Figure 15. Flowchart for Continuous Read Operations to
the AD7711A
The flowchart also shows the option of the bits being reversed
before being written to the serial buffer. This depends on
whether the first bit transmitted by the microprocessor is the
MSB or the LSB. The AD7711A expects the MSB as the first
bit in the data stream. In cases where the data is being read or
being written in bytes and the data has to be reversed, the bits
will have to be reversed for every byte.
–24–
REV. C
Page 25

AD7711A
START
CONFIGURE &
INITIALIZE mC/mP
SERIAL PORT
BRING
RFS, TFS & A0 HIGH
LOAD DATA FROM
ADDRESS TO
ACCUMULATOR
REVERSE
ORDER OF
BITS
BRING
TFS & A0 LOW
WRITE DATA FROM
ACCUMULATOR TO
SERIAL BUFFER
BRING
TFS & A0 HIGH
END
33
Figure 16. Flowchart for Single Write Operation to the
AD7711A
AD7711A–8051 Interface
Figure 17 shows an interface between the AD7711A and the
8XC51 microcontroller. The AD7711A is configured for its external clocking mode while the 8XC51 is configured in its Mode 0
serial interface mode. The DRDY line from the AD7711A is
connected to the Port P1.2 input of the 8XC51 so the DRDY
DV
DD
SYNC
8XC51
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P3.0
P3.1
RFS
TFS
DRDY
A0
SDATA
SCLK
MODE
AD7711A
Figure 17. AD7711A to 8XC51 Interface
line is polled by the 8XC51. The DRDY line can be connected
to the INT1 input of the 8XC51 if an interrupt driven system is
preferred.
Table VII shows some typical 8XC51 code used for a single 24bit read from the output register of the AD7711A. Table VIII
shows some typical code for a single write operation to the control register of the AD7711A. The 8XC51 outputs the LSB first
in a write operation while the AD7711A expects the MSB first
so the data to be transmitted has to be rearranged before being
written to the output serial register. Similarly, the AD7711A
outputs the MSB first during a read operation while the 8XC51
expects the LSB first. Therefore, the data which is read into the
serial buffer needs to be rearranged before the correct data word
from the AD7711A is available in the accumulator.
Table VII. 8XC51 Code for Reading from the AD7711A
MOV SCON,#00010001B; Configure 8051 for MODE 0
Operation
MOV IE,#00010000B; Disable All Interrupts
SETB 90H; Set P1.0, Used as RFS
SETB 91H; Set P1.1, Used as TFS
SETB 93H; Set P1.3, Used as A0
MOV R1,#003H; Sets Number of Bytes to Be Read in
A Read Operation
MOV R0,#030H; Start Address for Where Bytes Will
Be Loaded
MOV R6,#004H; Use P1.2 as DRDY
WAIT:
NOP;
MOV A,P1; Read Port 1
ANL A,R6; Mask Out All Bits Except DRDY
JZ READ; If Zero Read
SJMP WAIT; Otherwise Keep Polling
READ:
CLR 90H; Bring RFS Low
CLR 98H; Clear Receive Flag
POLL:
JB 98H, READ1 Tests Receive Interrupt Flag
SJMP POLL
READ 1:
MOV A,SBUF; Read Buffer
RLC A; Rearrange Data
MOV B.0,C; Reverse Order of Bits
RLC A; MOV B.1,C; RLC A; MOV B.2,C;
RLC A; MOV B.3,C; RLC A; MOV B.4,C;
RLC A; MOV B.5,C; RLC A; MOV B.6,C;
RLC A; MOV B.7,C;
MOV A,B;
MOV @R0,A; Write Data to Memory
INC R0; Increment Memory Location
DEC R1 Decrement Byte Counter
MOV A,Rl
JZ END Jump if Zero
JMP WAIT Fetch Next Byte
END:
SETB 90H Bring RFS High
FIN:
SJMP FIN
2
–25–REV. C
Page 26

AD7711A
SDATA
SCLK
A0
RFS
TFS
PC0
MISO
SCK
PC1
PC2
MODE
PC3
DRDY
SYNC
68HC11
MOSI
SS
DV
DD
DV
DD
AD7711A
SDATA
SCLK
A0
RFS
TFS
DR
SCLK
MODE
A0
DRDY
ADSP-2105
DT
DMWR
TFS
DV
DD
RFS
D
74HC74
Q
Q
AD7711A
Table VIII. 8XC51 Code for Writing to the AD7711A
MOV SCON,#00000000B; Configure 8051 for MODE 0
Operation & Enable Serial Reception
MOV IE,#10010000B; Enable Transmit Interrupt
MOV IP,#00010000B; Prioritize the Transmit Interrupt
SETB 91H; Bring TFS High
SETB 90H; Bring RFS High
MOV R1,#003H; Sets Number of Bytes to Be Written
in a Write Operation
MOV R0,#030H; Start Address in RAM for Bytes
MOV A,#00H; Clear Accumulator
MOV SBUF,A; Initialize the Serial Port
WAIT:
JMP WAIT; Wait for Interrupt
INT ROUTINE:
NOP; Interrupt Subroutine
MOV A,R1; Load R1 to Accumulator
JZ FIN; If Zero Jump to FIN
DEC R1; Decrement R1 Byte Counter
MOV A,@R; Move Byte into the Accumulator
INC R0; Increment Address
RLC A; Rearrange Data—From LSB First
to MSB First
MOV B.0,C; RLC A; MOV B.1,C; RLC A;
MOV B.2,C; RLC A; MOV B.3,C; RLC A;
MOV B.4,C; RLC A; MOV B.5,C; RLC A;
MOV B.6,C; RLC A: MOV B.7,C:MOV A,B;
CLR 93H; Bring A0 Low
CLR 91H; Bring TFS Low
MOV SBUF,A; Write to Serial Port
RETI; Return from Subroutine
FIN:
SETB 91H; Set TFS High
SETB 93H; Set A0 High
RETI; Return from Interrupt Subroutine
AD7711A-ADSP-2105 Interface
An interface circuit between the AD7711A and the ADSP-2105
microprocessor is shown in Figure 19. In this interface, the
AD7711A is configured for its self-clocking mode while the RFS
and TFS pins of the ADSP-2105 are configured as inputs and
the ADSP-2105 serial clock line is also configured as an input.
Figure 18. AD7711A to 68HC11 Interface
When the ADSP-2105’s serial clock is configured as an input it
needs a couple of clock pulses to initialize itself correctly before
accepting data. Therefore, the first read from the AD7711A
may not read correct data. In the interface shown, a read operation to the AD7711A accesses either the output register or the
calibration registers. Data cannot be read from the control register. A write operation always writes to the control or calibration
registers.
DRDY is used as the frame synchronization pulse for read operations from the output register and it is decoded with A0 to
drive the RFS inputs of both the AD7711A and the ADSP-
2105. The latched A0 line drives the TFS inputs of both the
AD7711A and the ADSP-2105 as well as the AD7711A
A0 input.
AD7711A–68HC11 Interface
Figure 18 shows an interface between the AD7711A and the
68HC11 microcontroller. The AD7711A is configured for its
external clocking mode while the SPI port is used on the 68HC11
which is in its single chip mode. The DRDY line from the
AD7711A is connected to the Port PC0 input of the 68HC11 so
the DRDY line is polled by the 68HC11. The DRDY line can
be connected to the IRQ input of the 68HC11 if an interrupt
driven system is preferred. The 68HC11 MOSI and MISO lines
should be configured for wired-or operation. Depending on the
interface configuration, it may be necessary to provide bidirectional buffers between the 68HC11’s MOSI and MISO lines.
The 68HC11 is configured in the master mode with its CPOL
bit set to a logic zero and its CPHA bit set to a logic one. With a
10 MHz master clock on the AD7711A, the interface will operate with all four serial clock rates of the 68HC11.
–26–
Figure 19. AD7711A to ADSP-2105 Interface
REV. C
Page 27

AD7711A
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions are shown in inches and (mm).
Cerdip (Q-24)
1.290 (32.77) MAX
0.225 (5.715)
MAX
0.125 (3.175)
MIN
24
1
PIN 1
0.021 (0.533)
0.015 (0.381)
1. LEAD NO. 1 IDENTIFIED BY DOT OR NOTCH.
2. CERDIP LEADS WILL BE EITHER TIN PLATED OR SOLDER DIPPED.
IN ACCORDANCE WITH MIL-M-38510 REQUIREMENTS.
TYP
0.110 (2.794)
0.090 (2.286)
TYP
13
12
0.070 (1.778)
0.020 (0.508)
0.065 (1.651)
0.055 (1.397)
TYP
0.295
(7.493)
MAX
SEATING
PLANE
0.320 (8.128)
0.290 (7.366)
158
08
0.180
(4.572)
MAX
0.012 (0.305)
0.008 (0.203)
TYP
2
C1996c–0–7/98
0.012 (0.3)
0.004 (0.1)
24
1
PIN 1
0.614 (15.60)
0.598 (15.20)
0.050 (1.27)
BSC
SOIC (R-24)
0.019 (0.49)
0.014 (0.35)
13
0.299 (7.6)
0.291 (7.4)
12
0.104 (2.65)
0.093 (2.35)
SEATING
PLANE
0.419 (10.65)
0.394 (10.00)
0.013 (0.32)
0.009 (0.23)
88
08
0.03 (0.75)
0.01 (0.25)
x 458
0.005 (1.27)
0.016 (0.40)
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
–27–REV. C
 Loading...
Loading...