Page 1
16-Bit, 1 LSB INL,
a
FEATURES
Throughput: 500 kSPS
INL: 1 LSB Max (0.0015% of Full Scale)
16-Bit Resolution with No Missing Codes
S/(N+D): 94 dB Typ @ 45 kHz
THD: –110 dB Typ @ 45 kHz
Differential Input Range: 2.5 V
Both AC and DC Specifications
No Pipeline Delay
Parallel (8 Bits/16 Bits) and Serial 5 V/3 V Interface
SPI™/QSPI™/MICROWIRE™/DSP Compatible
Single 5 V Supply Operation
67 mW Typical Power Dissipation, 15 W @ 100 SPS
Power-Down Mode: 7 W Max
Packages: 48-Lead Quad Flatpack (LQFP)
48-Lead Frame Chip Scale (LFCSP)
Pin-to-Pin Compatible with the AD7675
APPLICATIONS
CT Scanners
Data Acquisition
Instrumentation
Spectrum Analysis
Medical Instruments
Battery-Powered Systems
Process Control
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7676 is a 16-bit, 500 kSPS, charge redistribution SAR,
fully differential analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that operates from a single 5 V power supply. The part contains a high
speed 16-bit sampling ADC, an internal conversion clock,
error correction circuits, and both serial and parallel system
interface ports.
The AD7676 is hardware factory-calibrated and is comprehensively tested to ensure such ac parameters as signal-to-noise ratio
(SNR) and total harmonic distortion (THD), in addition to the
more traditional dc parameters of gain, offset, and linearity.
It is fabricated using Analog Devices’ high performance, 0.6 micron
CMOS process and is available in a 48-lead LQFP or a tiny
48-lead LFCSP with operation specified from –40°C to +85°C.
*Patent pending
SPI and QSPI are trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
MIRCOWIRE is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
500 kSPS, Differential ADC
AD7676
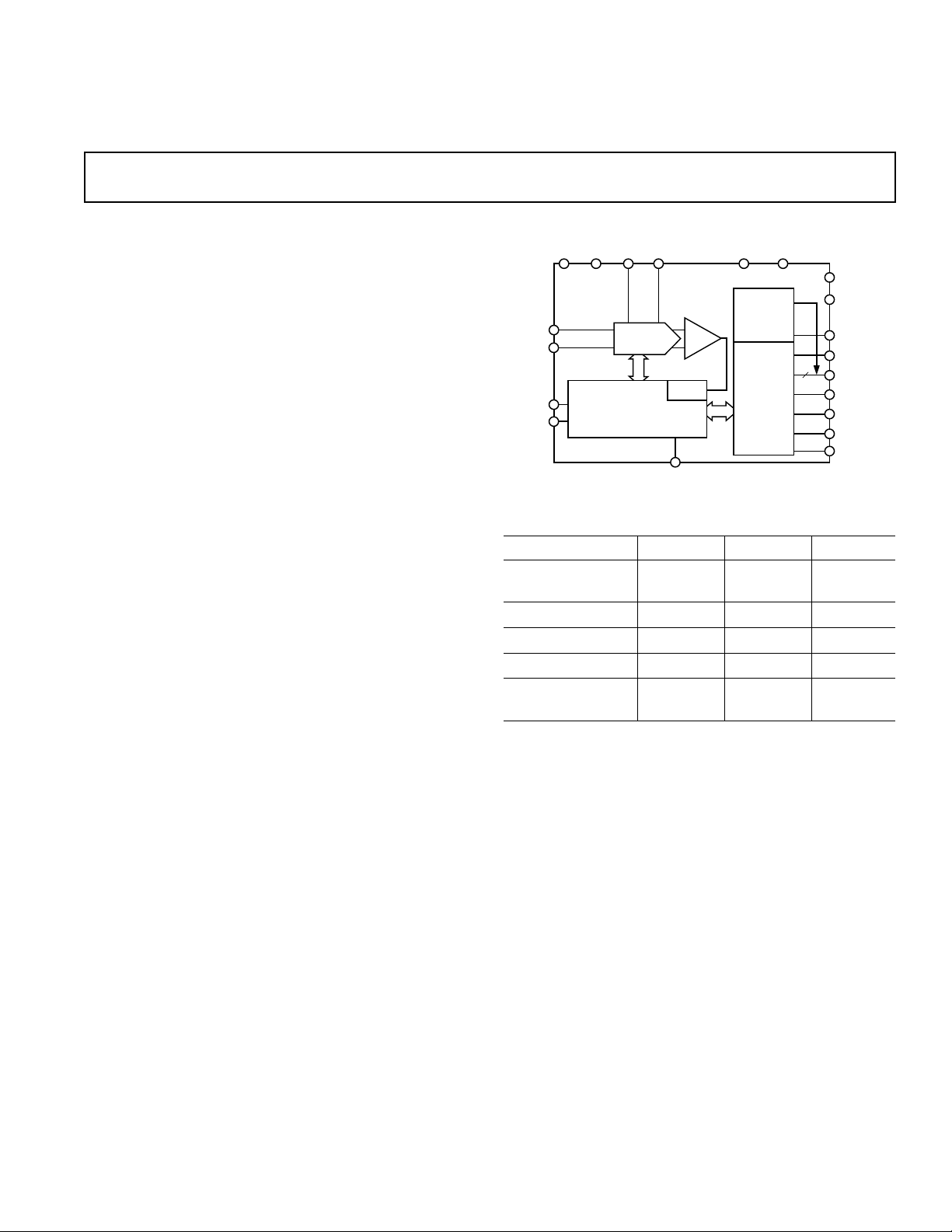
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AV DD AGND REF REFGND
AD7676
IN+
IN–
PD
RESET
SWITCHED
CAP DAC
CLOCK
CONTROL LOGIC AND
CALIBRATION CIRCUITRY
CNVST
Table I. PulSAR Selection
Type/kSPS 100–250 500–570 800–1000
Pseudo Differential AD7660 AD7650
True Bipolar AD7663 AD7665 AD7671
True Differential AD7675 AD7676 AD7677
18-Bit AD7678 AD7679 AD7674
Simultaneous/ AD7654
Multichannel
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Excellent INL
The AD7676 has a maximum integral nonlinearity of 1.0 LSB
with no missing 16-bit code.
2. Superior AC Performances
The AD7676 has a minimum dynamic of 92 dB, 94 dB typical.
3. Fast Throughput
The AD7676 is a 500 kSPS, charge redistribution, 16-bit
SAR ADC with internal error correction circuitry.
4. Single-Supply Operation
The AD7676 operates from a single 5 V supply and typically
dissipates only 67 mW. It consumes 7 µW maximum when in
power-down.
5. Serial or Parallel Interface
Versatile parallel (8 bits or 16 bits) or 2-wire serial interface
arrangement compatible with either 3 V or 5 V logic.
DGNDDVD D
SERIAL
PORT
PARALLEL
INTERFACE
AD7664
16
*
OVD D
OGND
SER/PAR
BUSY
D[15:0]
CS
RD
OB/2C
BYTESWAP
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
Page 2
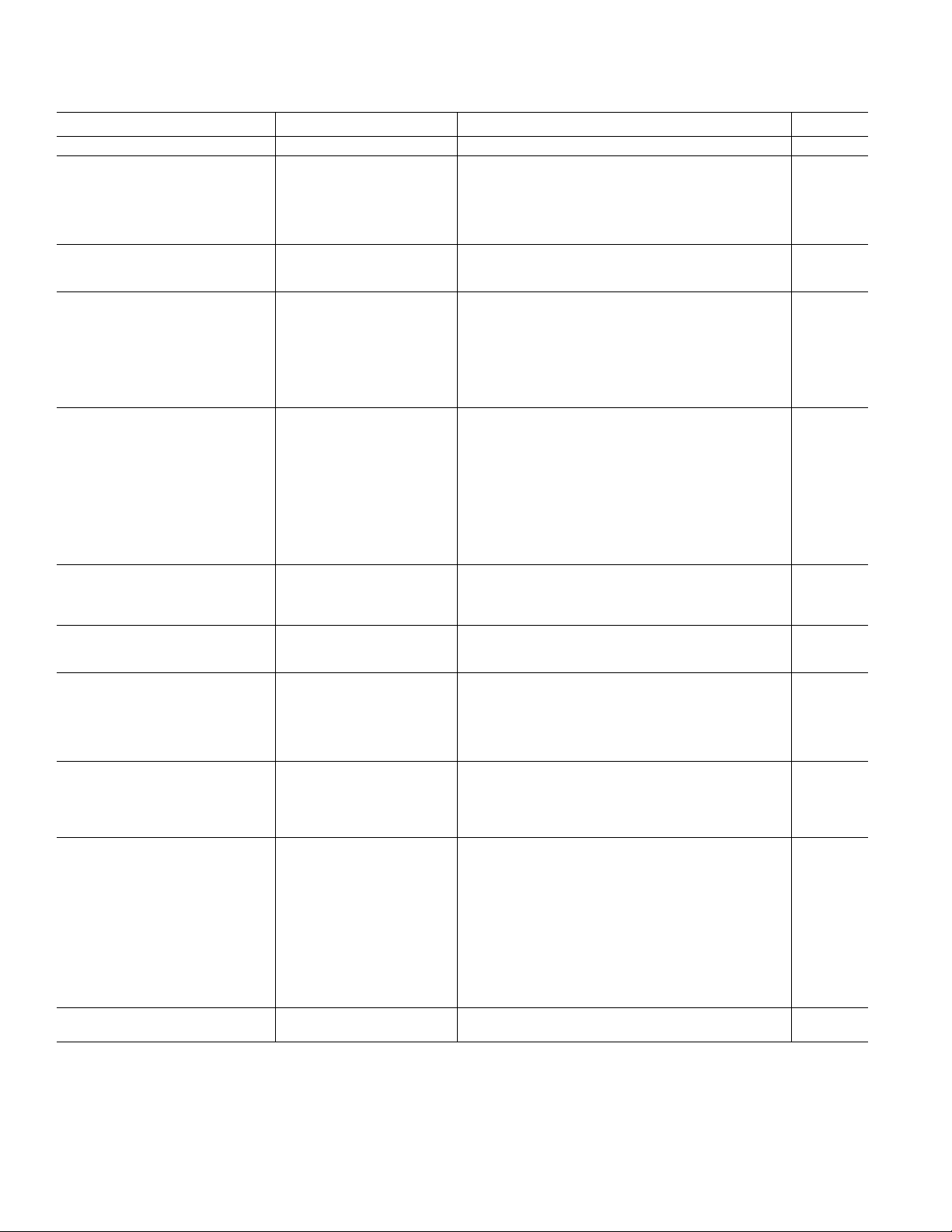
AD7676–SPECIFICATIONS
(–40C to +85C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 16 Bits
ANALOG INPUT
Voltage Range V
Operating Input Voltage V
Analog Input CMRR f
Input Current 500 kSPS Throughput 5 µA
– V
IN+
IN–
to AGND –0.1 +3 V
IN+, VIN–
= 10 kHz 79 dB
IN
–V
REF
+V
REF
V
Input Impedance See Analog Inputs Section
THROUGHPUT SPEED
Complete Cycle 2 µs
Throughput Rate 0 500 kSPS
DC ACCURACY
Integral Linearity Error –1 +1 LSB
1
No Missing Codes 16 Bits
Transition Noise 0.35 LSB
+Full-Scale Error
–Full-Scale Error
Zero Error
2
2
2
–22 +22 LSB
–22 +22 LSB
–8 +8 LSB
Power Supply Sensitivity AVDD = 5 V ± 5% ±0.7 LSB
AC ACCURACY
Signal-to-Noise f
= 20 kHz 92 94 dB
IN
fIN = 45 kHz 94 dB
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range fIN = 20 kHz 104.5 110 dB
fIN = 45 kHz 110 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion fIN = 20 kHz –110 –103.5 dB
fIN = 45 kHz –110 dB
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) fIN = 20 kHz 92 94 dB
fIN = 45 kHz 94 dB
fIN = 45 kHz, –60 dB Input 34 dB
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
–3 dB Input Bandwidth 3.9 MHz
SAMPLING DYNAMICS
Aperture Delay 2ns
Aperture Jitter 5 ps rms
Transient Response Full-Scale Step 750 ns
REFERENCE
External Reference Voltage Range 2.3 2.5 AVDD – 1.85 V
External Reference Current Drain 500 kSPS Throughput 170 µA
DIGITAL INPUTS
Logic Levels
V
IL
V
IH
I
IL
I
IH
–0.3 +0.8 V
+2.0 OVDD + 0.3 V
–1 +1 µA
–1 +1 µA
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Data Format Parallel or Serial 16-Bit Conversion Results Available
Pipeline Delay Immediately after Completed Conversion
I
V
OL
V
OH
= 1.6 mA 0.4 V
SINK
I
= –100 µA OVDD – 0.6 V
SOURCE
POWER SUPPLIES
Specified Performance
AVDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
DVDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
OVDD 2.7 5.25
4
V
Operating Current 500 kSPS Throughput
AVDD 9.5 mA
5
DVDD
5
OVDD
Power Dissipation
In Power-Down Mode
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specified Performance T
NOTES
1
LSB means Least Significant Bit. Within the ± 2.5 V input range, one LSB is 76.3 µV.
2
See Definition of Specifications section. These specifications do not include the error contribution from the external reference.
3
All specifications in dB are referred to a full-scale input FS. Tested with an input signal at 0.5 dB below full-scale unless otherwise specified.
4
The maximum should be the minimum of 5.25 V and DVDD + 0.3 V.
5
Tested in Parallel Reading Mode.
6
With OVDD below DVDD + 0.3 V and all digital inputs forced to DVDD or DGND, respectively.
7
Contact factory for extended temperature range.
5
6
7
500 kSPS Throughput 67 74 mW
100 SPS Throughput 15 µW
MIN
to T
MAX
–40 +85 °C
Specifications subject to change without notice.
3.9 mA
37 µA
7 µW
–2–
REV. B
Page 3
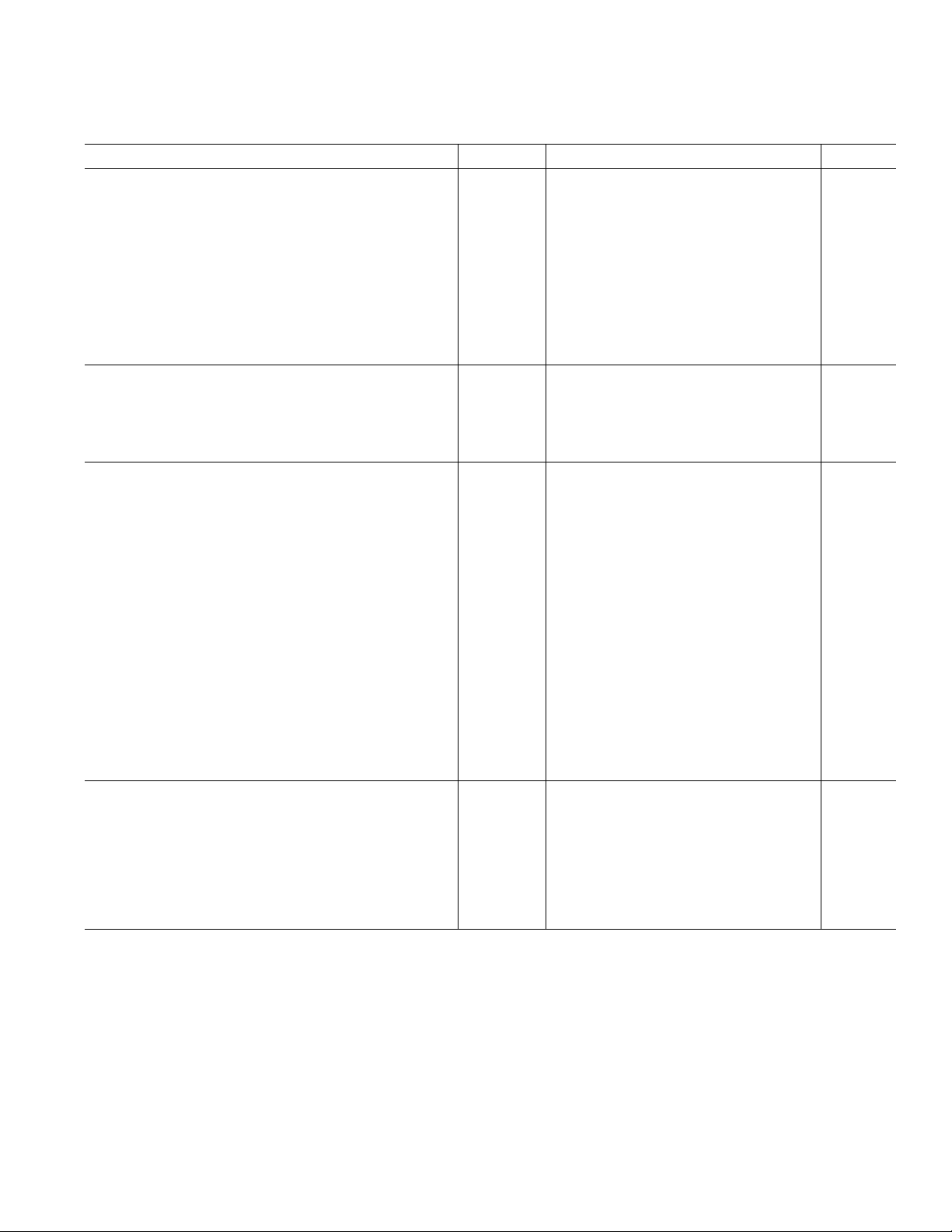
AD7676
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
(–40C to +85C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Refer to Figures 11 and 12
Convert Pulsewidth t
Time between Conversions t
CNVST LOW to BUSY HIGH Delay t
BUSY HIGH All Modes except in Master Serial Read t
1
2
3
4
5ns
2 µs
30 ns
1.25 µs
Convert Mode
Aperture Delay t
End of Conversion to BUSY LOW Delay t
Conversion Time t
Acquisition Time t
RESET Pulsewidth t
5
6
7
8
9
10 ns
750 ns
10 ns
2ns
1.25 µs
Refer to Figures 13, 14, and 15 (Parallel Interface Modes)
CNVST LOW to DATA Valid Delay t
DATA Valid to BUSY LOW Delay t
Bus Access Request to DATA Valid t
Bus Relinquish Time t
Refer to Figures 16 and 17 (Master Serial Interface Modes)
1
CS LOW to SYNC Valid Delay t
CS LOW to Internal SCLK Valid Delay t
CS LOW to SDOUT Delay t
CNVST LOW to SYNC Delay t
SYNC Asserted to SCLK First Edge Delay
Internal SCLK Period
Internal SCLK HIGH
Internal SCLK LOW
SDOUT Valid Setup Time
SDOUT Valid Hold Time
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
CS HIGH to SYNC HI-Z t
CS HIGH to Internal SCLK HI-Z t
CS HIGH to SDOUT HI-Z t
BUSY HIGH in Master Serial Read after Convert
2
CNVST LOW to SYNC Asserted Delay t
SYNC Deasserted to BUSY LOW Delay t
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
t
18
t
19
t
20
t
21
t
22
t
23
t
24
25
26
27
t
28
29
30
45 ns
515ns
525 ns
3ns
25 40 ns
12 ns
7ns
4ns
2ns
3ns
See Table I
1.25 µs
25 ns
1.25 ns
40 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
Refer to Figures 18 and 19 (Slave Serial Interface Modes)
External SCLK Setup Time t
External SCLK Active Edge to SDOUT Delay t
SDIN Setup Time t
SDIN Hold Time t
External SCLK Period t
External SCLK HIGH t
External SCLK LOW t
NOTES
1
In serial interface modes, the SYNC, SCLK, and SDOUT timings are defined with a maximum load CL of 10 pF; otherwise, the load is 60 pF maximum.
2
In Serial Master Read during Convert Mode, see Table II.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
5ns
318ns
5ns
5ns
25 ns
10 ns
10 ns
REV. B
–3–
Page 4
AD7676
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
Table II. Serial Clock Timings in Master Read after Convert
DIVSCLK[1] 0011
DIVSCLK[0] 0101Unit
SYNC to SCLK First Edge Delay Minimum t
Internal SCLK Period Minimum t
Internal SCLK Period Maximum t
Internal SCLK HIGH Minimum t
Internal SCLK LOW Minimum t
SDOUT Valid Setup Time Minimum t
SDOUT Valid Hold Time Minimum t
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay Minimum t
Busy High Width Maximum t
18
19
19
20
21
22
23
24
28
3171717ns
25 50 100 200 ns
40 70 140 280 ns
12 22 50 100 ns
7214999ns
4181818ns
243089ns
360140 300 ns
2 2.5 3.5 5.75 µs
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Analog Inputs
2
IN+
, IN–2, REF, REFGND
1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . AVDD + 0.3 V to AGND – 0.3 V
Ground Voltage Differences
AGND, DGND, OGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V
Supply Voltages
AVDD, DVDD, OVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
AVDD to DVDD,
AVDD to OVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±7 V
DVDD to OVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Internal Power Dissipation
Internal Power Dissipation
3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 700 mW
4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 W
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range
(Soldering 10 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
See Analog Inputs section.
3
Specification is for device in free air: 48-Lead LQFP: JA = 91°C/W, JC = 30°C/W.
4
Specification is for device in free air: 48-Lead LFCSP: JA = 26°C/W.
ORDERING GUIDE
I
1.6mA
TO OUTPUT
PIN
C
L
*
60pF
500A
*
IN SERIAL INTERFACE MODES, THE SYNC, SCLK, AND
SDOUT TIMINGS ARE DEFINED WITH A MAXIMUM LOAD
OF 10pF; OTHERWISE, THE LOAD IS 60pF MAXIMUM.
C
L
OL
1.4V
I
OH
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Digital Interface Timing
0.8V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
2V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
Figure 2. Voltage Reference Levels for Timings
Model Temperature Range Package Description Option
AD7676AST –40°C to +85°CQuad Flatpack (LQFP) ST-48
AD7676ASTRL –40°C to +85°CQuad Flatpack (LQFP) ST-48
AD7676ACP –40°C to +85°CChip Scale (LFCSP) CP-48
AD7676ACPRL –40°C to +85°CChip Scale (LFCSP) CP-48
EVAL-AD7676CB
EVAL-CONTROL BRD2
NOTES
1
This board can be used as a standalone evaluation board or in conjunction with the EVAL-CONTROL BRD2 for
evaluation/demonstration purposes.
2
This board allows a PC to control and communicate with all Analog Devices evaluation boards ending in the CB designators.
1
2
Evaluation Board
Controller Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD7676 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
Package
REV. B
Page 5
AD7676
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
1 AGND P Analog Power Ground Pin
2 AVDD P Input Analog Power Pins. Nominally 5 V.
3, 6, 7, NC No Connect
40–42,
44–48
4 BYTESWAP DI Parallel Mode Selection (8-Bit/16-Bit). When LOW, the LSB is output on D[7:0] and the MSB is
output on D[15:8]. When HIGH, the LSB is output on D[15:8] and the MSB is output on D[7:0].
5OB/2C DI Straight Binary/Binary Twos Complement. When OB/2C is HIGH, the digital output is straight
binary. When LOW, the MSB is inverted resulting in a twos complement output from its internal
shift register.
8 SER/PAR DI Serial/Parallel Selection Input. When LOW, the Parallel Port is selected. When HIGH, the
Serial Interface Mode is selected and some bits of the DATA bus are used as a Serial Port.
9, 10 D[0:1] DO Bit 0 and Bit 1 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. When SER/PAR is HIGH, these outputs are in
high impedance.
11, 12 D[2:3] or DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, these outputs are used as Bit 2 and Bit 3 of the Parallel Port Data
Output Bus.
DIVSCLK[0:1] When SER/PAR is HIGH, EXT/INT is LOW and RDC/SDIN is LOW, which is the Serial Master
Read after Convert Mode. These inputs, part of the Serial Port, are used to slow down, if desired,
the internal serial clock that clocks the data output. In the other serial modes, these pins are high
impedance outputs.
13 D[4] DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as the Bit 4 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or EXT/INT When SER/PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used as a digital select input for
choosing the internal or an external data clock. With EXT/INT tied LOW, the internal clock is
selected on the SCLK output. With EXT/INT set to a logic HIGH, output data is synchronized to
an external clock signal connected to the SCLK input.
14 D[5] DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 5 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or INVSYNC When SER/PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the Serial Port, is used to select the active state of
the SYNC signal. When LOW, SYNC is active HIGH. When HIGH, SYNC is active LOW.
15 D[6] DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 6 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or INVSCLK
16 D[7] DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 7 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or RDC/SDIN When SER/PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the Serial Port, is used as either an external data
17 OGND P Input/Output Interface, Digital Power Ground
18 OVDD P Input/Output Interface, Digital Power. Nominally at the same supply as the supply of the host
19 DVDD P Digital Power. Nominally at 5 V.
20 DGND P Digital Power Ground
When SER/PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the Serial Port, is used to invert the SCLK signal.
It is active in both Master and Slave Modes.
input or a Read Mode selection input depending on the state of EXT/INT.
When EXT/INT is HIGH, RDC/SDIN could be used as a data input to daisy-chain the conversion
results from two or more ADCs onto a single SDOUT line. The digital data level on SDIN is
output on DATA with a delay of 16 SCLK periods after the initiation of the read sequence. When
EXT/INT is LOW, RDC/SDIN is used to select the Read Mode. When RDC/SDIN is HIGH,
the data is output on SDOUT during conversion. When RDC/SDIN is LOW, the data is output
on SDOUT only when the conversion is complete.
interface (5 V or 3 V).
REV. B
–5–
Page 6
AD7676
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
21 D[8] DO When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 8 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. When
or SDOUT SER/PAR is HIGH, this output, part of the Serial Port, is used as a serial data output synchronized
to SCLK. Conversion results are stored in an on-chip register. The AD7676 provides the conversion
result, MSB first, from its internal shift register. The DATA format is determined by the logic level
of OB/2C. In Serial Mode, when EXT/INT is LOW, SDOUT is valid on both edges of SCLK.
In Serial Mode, when EXT/INT is HIGH:
If INVSCLK is LOW, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK rising edge and valid on the next falling edge.
If INVSCLK is HIGH, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK falling edge and valid on the next rising edge.
22 D[9] DI/O When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 9 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or SCLK When SER/PAR is HIGH, this pin, part of the Serial Port, is used as a serial data clock input or
output, depending on the logic state of the EXT/INT pin. The active edge where the data SDOUT
is updated depends on the logic state of the INVSCLK pin.
23 D[10] DO When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 10 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or SYNC When SER/PAR is HIGH, this output, part of the Serial Port, is used as a digital output frame
synchronization for use with the internal data clock (EXT/INT = Logic LOW). When a read
sequence is initiated and INVSYNC is LOW, SYNC is driven HIGH and remains HIGH while
SDOUT output is valid. When a read sequence is initiated and INVSYNC is HIGH, SYNC is
driven LOW and remains LOW while SDOUT output is valid.
24 D[11] DO When SER/PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 11 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
or RDERROR When SER/PAR is HIGH and EXT/INT is HIGH, this output, part of the Serial Port, is used as
an incomplete read error flag. In Slave Mode, when a data read is started and not complete when
the following conversion is complete, the current data is lost and RDERROR is pulsed HIGH.
25–28 D[12:15] DO Bit 12 to Bit 15 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. These pins are always outputs regardless
of the state of SER/PAR.
29 BUSY DO Busy Output. Transitions HIGH when a conversion is started and remains HIGH until the conversion
is complete and the data is latched into the on-chip shift register. The falling edge of BUSY could
be used as a data-ready clock signal.
30 DGND P Must Be Tied to Digital Ground
31 RD DI Read Data. When CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled.
32 CS DI Chip Select. When CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled.
CS is also used to gate the external serial clock.
33 RESET DI Reset Input. When set to a logic HIGH, resets the AD7676. Current conversion if any is aborted.
34 PD DI Power-Down Input. When set to a logic HIGH, power consumption is reduced and conversions
are inhibited after the current one is completed.
35 CNVST DI Start Conversion. If CNVST is HIGH when the acquisition phase (t
edge on CNVST puts the internal sample-and-hold into the hold state and initiates a conversion.
This mode is the most appropriate if low sampling jitter is desired. If CNVST is LOW when the
acquisition phase (t
) is complete, the internal sample-and-hold is put into the hold state and a
8
conversion is started immediately.
36 AGND P Must Be Tied to Analog Ground
37 REF AI Reference Input Voltage
38 REFGND AI Reference Input Analog Ground
39 IN– AI Differential Negative Analog Input
43 IN+ AI Differential Positive Analog Input
NOTES
AI = Analog Input
DI = Digital Input
DI/O = Bidirectional Digital
DO = Digital Output
P = Power
) is complete, the next falling
8
–6–
REV. B
Page 7

PIN CONFIGURATION
AD7676
NCNCNCNCNC
48 47 46 45 44 39 38 3743 42 41 40
1
AGND
AV DD
NC
BYTESWAP
OB/2C
NC
NC
SER/PAR
D0
D1
D2/DIVSCLK[0]
D3/DIVSCLK[1]
NC = NO CONNECT
PIN 1
2
IDENTIFIER
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
D4/EXT/INT
D6/INVSCLK
D5/INVSYNC
(Not to Scale)
D7/RDC/SDIN
DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONS
Integral Nonlinearity Error (INL)
Integral nonlinearity is the maximum deviation of a straight line
drawn through the transfer function of the actual ADC. The
deviation is measured from the middle of each code.
Differential Nonlinearity Error (DNL)
In an ideal ADC, code transitions are 1 LSB apart. Differential
nonlinearity is the maximum deviation from this ideal value. It is
often specified in terms of resolution for which no missing codes
are guaranteed.
+Full-Scale Error
The last transition (from 011 ...10 to 011 . . . 11 in twos complement coding) should occur for an analog voltage 1 1/2 LSB below
the nominal +full scale (+2.499886 V for the ±2.5 V range). The
+full-scale error is the deviation of the actual level of the last
transition from the ideal level.
–Full-Scale Error
The first transition (from 100 ...00 to 100 . . . 01 in twos complement coding) should occur for an analog voltage 1/2 LSB above
the nominal –full scale (–2.499962 V for the ±2.5 V range). The
–full-scale error is the deviation of the actual level of the last
transition from the ideal level.
Bipolar Zero Error
The bipolar zero error is the difference between the ideal midscale
input voltage (0 V) and the actual voltage producing the midscale
output code.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The difference, in decibels (dB), between the rms amplitude of
the input signal and the peak spurious signal.
IN+NCNCNCIN–
AD7676
TOP VIEW
DVD D
OVD D
OGND
DGND
D8/SDOUT
REFGND
REF
D9/SCLK
D10/SYNC
D11/RDERROR
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
AGND
CNVST
PD
RESET
CS
RD
DGND
BUSY
D15
D14
D13
D12
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
ENOB is a measurement of the resolution with a sine wave
input. It is related to S/(N+D) by the following formula:
ENOB S N D
=+
/–./.176 602
[]
()
dB
and is expressed in bits.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is the ratio of the rms sum of the first five harmonic
components to the rms value of a full-scale input signal and is
expressed in decibels.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the rms value of the actual input signal to the
rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding harmonics and dc. The value for SNR is
expressed in decibels (dB).
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) Ratio (S/[N+D])
S/(N+D) is the ratio of the rms value of the actual input signal
to the rms sum of all other spectral components below the
Nyquist frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc. The
value for S/(N+D) is expressed in decibels (dB).
Aperture Delay
Aperture delay is a measure of the acquisition performance and
is measured from the falling edge of the CNVST input to when
the input signal is held for a conversion.
Transient Response
The time required for the AD7676 to achieve its rated accuracy
after a full-scale step function is applied to its input.
REV. B
–7–
Page 8

AD7676
–Typical Performance Characteristics
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
INL – LSB
–0.25
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 16384 32768 49152 65536
CODE
TPC 1. Integral Nonlinearity vs. Code
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
COUNTS
3000
2000
1000
0000
0
7FFB
7FFC07FFD07FFE87FFF
8271
8094
8000
CODE IN HEXA
0
80011180020800308004
TPC 2. Histogram of 16,384 Conversions of a DC Input at
the Code Transition
16000
14000
12000
10000
8000
COUNTS
6000
4000
2000
0000
0
7FFA
0
7FFB
7FFC07FFD07FFE
14640
880
CODE IN HEXA
863
7FFF 8000
0
8001080020800308004
TPC 4. Histogram of 16,384 Conversions of a DC Input at
the Code Center
20
16
12
8
NUMBER OF UNITS
4
0
–0.9
–0.8 –0.7 –0.6 –0.5 –0.4 –0.3 –0.2 –0.1–1.0 0.0
NEGATIVE INL – LSB
TPC 5. Typical Negative INL Distribution (199 Units)
20
16
12
8
NUMBER OF UNITS
4
0
0.1
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.90
POSITIVE INL – LSB
1.0
TPC 3. Typical Positive INL Distribution (199 Units)
–8–
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
AMPLITUDE – dB of Full Scale
–160
–180
050100 150 250
FREQUENCY – kHz
f
= 500kSPS
S
f
= 45.01kHz
IN
SNR = 94dB
THD = –110dB
SFDR = 110dB
SINAD = 93.9dB
200
TPC 6. FFT Plot
REV. B
Page 9

AD7676
100
95
90
85
80
SNR AND S/(ND) – dB
75
70
10 10001 100
FREQUENCY – kHz
SNR
S/(ND)
ENOB
TPC 7. SNR, S/(N+D), and ENOB vs. Frequency
96
SNR
93
90
S/(ND)
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
ENOB – Bits
50
40
30
DELAY – ns
20
12
t
10
0
OVDD = 2.7V @ 25C
OVDD = 2.7V @ 85C
OVDD = 5.0V @ 85C
OVDD = 5.0V @ 25C
10050 150
CL – pF
TPC 10. Typical Delay vs. Load Capacitance C
100k
10k
1k
100
10
AV DD
DVD D
2000
L
87
SNR (REFERENCED TO FULL SCALE) – dB
83
–40 0–60 –20
–50 –30 –10
INPUT LEVEL – dB
TPC 8. SNR and S/(N+D) vs. Input Level
96
SNR
93
90
SNR – dB
87
84
–35 45 10525–15 65
THD
0 125–55 85
TEMPERATURE – C
TPC 9. SNR, THD vs. Temperature
–104
–106
–108
–110
–112
THD – dB
OPERATING CURRENTS – A
0.01
0.001
1
0.1
1k100 10k
SAMPLING RATE – SPS
OVD D
100k
1M10
TPC 11. Operating Currents vs. Sample Rate
250
200
150
100
50
POWER-DOWN OPERATING CURRENTS – nA
0
–35 5 8525 65
–15 105–55 45
TEMPERATURE – C
DVD D
AV DD
OVD D
TPC 12. Power-Down Operating Currents vs. Temperature
REV. B
–9–
Page 10

AD7676
5
4
3
2
1
0
LSB
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
–55 135–35
–FS
OFFSET
+FS
–15 –5 15 35 55 75 95
TEMPERATURE – C
115
TPC 13. Drift vs. Temperature
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
The AD7676 is a fast, low power, single-supply, precise 16-bit
analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The AD7676 is capable of
converting 500,000 samples per second (500 kSPS) and allows
power saving between conversions. When operating at 100 SPS,
for example, it typically consumes only 15 µW. This feature
makes the AD7676 ideal for battery-powered applications.
The AD7676 provides the user with an on-chip track-and-hold,
successive-approximation ADC that does not exhibit any pipeline
or latency, making it ideal for multiple multiplexed channel
applications.
The AD7676 can be operated from a single 5 V supply and be
interfaced to either 5 V or 3 V digital logic. It is housed in a
48-lead LQFP package or a 48-lead LFCSP package that combines
space savings and allows flexible configurations as either serial
or parallel interface. The AD7676 is pin-to-pin compatible with
the AD7675.
CONVERTER OPERATION
The AD7676 is a successive-approximation analog-to-digital
converter based on a charge redistribution DAC. Figure 3 shows
the simplified schematic of the ADC. The capacitive DAC consists
of two identical arrays of 16 binary weighted capacitors.
During the acquisition phase, terminals of the array tied to the
comparator’s input are connected to AGND via SW
and SW–.
+
All independent switches are connected to the analog inputs.
Thus, the capacitor arrays are used as sampling capacitors and
acquire both analog signals.
When the acquisition phase is complete and the CNVST input
goes or is low, a conversion phase is initiated. When the conversion
phase begins, SW+ and SW– are opened first. The two capacitor
arrays are then disconnected from the inputs and connected to
the REFGND input. Therefore, the differential voltage between
the output of IN+ and IN– captured at the end of the acquisition
phase is applied to the comparator inputs, causing the comparator
to become unbalanced.
By switching each element of the capacitor array between
REFGND or REF, the comparator input varies by binary
weighted voltage steps (V
REF
/2, V
/4 ...V
REF
/65536). The
REF
control logic toggles these switches, starting with the MSB first,
in order to bring the comparator back into a balanced condition.
After the completion of this process, the control logic generates
the ADC output code and brings BUSY output LOW.
Transfer Functions
Using the OB/2C digital input, the AD7676 offers two output
codings: straight binary and twos complement. The ideal transfer
characteristic for the AD7676 is shown in Figure 4.
111...111
111...110
111...101
ADC CODE – Straight Binary
000...010
000...001
000...000
–FS + 1 LSB–FS
–FS + 0.5 LSB
+FS – 1 LSB
+FS – 1.5 LSB
ANALOG INPUT
Figure 4. ADC Ideal Transfer Function
IN+
REF
REFGND
IN–
32,768C 16,384C
MSB
32,768C 16,384C
MSB
4C 2C C C
4C 2C C C
Figure 3. ADC Simplified Schematic
–10–
LSB
LSB
SW
SW
+
COMP
–
SWITCHES
CONTROL
CONTROL
LOGIC
CNVST
BUSY
OUTPUT
CODE
REV. B
Page 11

AD7676
FREQUENCY – Hz
CMRR – dB
45
75
10k 10M1k 1M
80
65
100k
55
85
70
60
50
40
ANALOG
SUPPLY
ADR421
2.5V REF
NOTE 1
ANALOG INPUT+
ANALOG INPUT–
(5V)
1M
100nF
NOTE 4
AD8021
NOTE 4
AD8021
NOTE 3
–
+
–
+
50
U1
U2
50
50k
100
+
C
+
REF
NOTE 2
15
C
C
15
C
C
10F
100nF
1F
2.7nF
NOTE 5
2.7nF
NOTE 5
NOTE 6
AV DD AGND DGND
REF
REFGND
IN+
+
10F 100nF
AD7676
IN–
DVD D
DVD D
OVD D OGND
SCLK
SDOUT
BUSY
CNVST
OB/2C
SER/PAR
BYTESWAP
RESET
100nF
CS
RD
PD
+
10F
50
NOTE 7
DVD D
DIGITAL SUPPLY
(3.3V OR 5V)
SERIAL PORT
D
CLOCK
C/P/DSP
NOTES
1. SEE VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT SECTION.
2. WITH THE RECOMMENDED VOLTAGE REFERENCES, C
3. OPTIONAL CIRCUITRY FOR HARDWARE GAIN CALIBRATION.
4. THE AD8021 IS RECOMMENDED. SEE DRIVER AMPLIFIER CHOICE SECTION.
5. SEE ANALOG INPUTS SECTION.
6. OPTION, SEE POWER SUPPLY SECTION.
7. OPTIONAL LOW JITTER CNVST, SEE CONVERSION CONTROL SECTION.
IS 47F. SEE VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT SECTION.
REF
Figure 5. Typical Connection Diagram (±2.5 V Range Shown)
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 5 shows a typical connection diagram for the AD7676.
Different circuitry shown on this diagram is optional and is
discussed below.
Analog Inputs
The AD7676 is specified to operate with a differential ±2.5 V
range. The typical input impedance for each analog input range
is also shown. Figure 6 shows a simplified analog input section
of the AD7676.
AV DD
IN+
IN–
AGND
R+ = 684
R– = 684
C
S
C
S
current. These diodes can handle a forward-biased current of
120 mA maximum. This condition could eventually occur when
the input buffer’s (U1) or (U2) supplies are different from
AVDD. In such a case, an input buffer with a short-circuit
current limitation can be used to protect the part.
This analog input structure is a true differential structure. By
using these differential inputs, signals common to both inputs
are rejected as shown in Figure 7, which represents the typical
CMRR over frequency.
Figure 6. Simplified Analog Input
The diodes shown in Figure 6 provide ESD protection for the
inputs. Care must be taken to ensure that the analog input signal
never exceeds the absolute ratings on these inputs. This will
cause these diodes to become forward-biased and start conducting
REV. B
–11–
Figure 7. Analog Input CMRR vs. Frequency
Page 12

AD7676
During the acquisition phase for ac signals, the AD7676 behaves
like a one-pole RC filter consisting of the equivalent resistance
R+, R–,
and CS. The resistors R+ and R– are typically 684 Ω and
are lumped components made up of some serial resistors and the
on resistance of the switches. The capacitor C
is typically 60 pF
S
and is mainly the ADC sampling capacitor. This one-pole filter
with a typical –3 dB cutoff frequency of 3.88 MHz reduces undesirable aliasing effects and limits the noise coming from the inputs.
Because the input impedance of the AD7676 is very high, the
AD7676 can be driven directly by a low impedance source without
gain error. That allows users to put, as shown in Figure 5, an
external one-pole RC filter between the output of the amplifier
output and the ADC analog inputs to even further improve the
noise filtering done by the AD7676 analog input circuit. However,
the source impedance has to be kept low because it affects the
ac performances, especially the total harmonic distortion (THD).
The maximum source impedance depends on the amount of
THD that can be tolerated. The THD degrades proportionally
to the source impedance.
Single-to-Differential Driver
For applications using unipolar analog signals, a single-ended-todifferential driver will allow for a differential input into the part.
The schematic is shown in Figure 8.
ANALOG INPUT
2.5V REF
(UNIPOLAR)
590
590
U1
590
U2
AD8021
C
C
590
AD8021
C
C
IN+
IN–
AD7676
REF
2.5V REF
Figure 8. Single-Ended-to-Differential Driver Circuit
This configuration, when provided an input signal of 0 to V
REF
,
will produce a differential ±2.5 V with a common mode at 1.25 V.
If the application can tolerate more noise, the AD8138 can be used.
Driver Amplifier Choice
Although the AD7676 is easy to drive, the driver amplifier needs
to meet the following requirements:
• The driver amplifier and the AD7676 analog input circuit have
to be able, together, to settle for a full-scale step of the capacitor array at a 16-bit level (0.0015%). In the amplifier’s data
sheet, the settling at 0.1% or 0.01% is more commonly
specified. It could significantly differ from the settling time
at the 16-bit level and, therefore, it should be verified prior to
the driver selection. The tiny op amp AD8021, which combines ultralow noise and a high gain bandwidth, meets this
settling time requirement even when used with a high gain
up to 13.
• The driver needs to have a THD performance suitable to
that of the AD7676.
• The noise generated by the driver amplifier needs to be kept
as low as possible to preserve the SNR and transition noise
performance of the AD7676. The noise coming from the driver is
filtered by the AD7676 analog input circuit one-pole, low-pass
filter made by R+, R–, and C
. The SNR degradation due to
S
the amplifier is:
SNR LOG
LOSS
=
20
784
28
π
+
()
fNe
−
3
dB
2
N
where:
f
is the –3 dB input bandwidth of the AD7676 (3.9 MHz)
–3 dB
or the cutoff frequency of the input filter if any is used.
N is the noise factor of the amplifier (1 if in buffer
configuration).
e
is the equivalent input noise voltage of the op amp in nV/√Hz .
N
For instance, a driver with an equivalent input noise of
2 nV/√Hz like the AD8021 and configured as a buffer, thus
with a noise gain of +1, will degrade the SNR by only 0.26 dB.
The AD8021 meets these requirements and is usually appropriate
for almost all applications. The AD8021 needs an external
compensation capacitor of 10 pF. This capacitor should have
good linearity as an NPO ceramic or mica type.
The AD8022 could also be used where a dual version is needed
and a gain of 1 is used.
The AD8132 or the AD8138 could also be used to generate
a differential signal from a single-ended signal.
The AD829 is another alternative where high frequency (above
500 kHz) performance is not required. In a gain of 1, it requires
an 82 pF compensation capacitor.
The AD8610 is also another option where low bias current is
needed in low frequency applications.
Voltage Reference Input
The AD7676 uses an external 2.5 V voltage reference.
The voltage reference input REF of the AD7676 has a dynamic
input impedance. Therefore, it should be driven by a low impedance source with an efficient decoupling between the REF and
REFGND inputs. This decoupling depends on the choice of the
voltage reference but usually consists of a low ESR tantalum
capacitor connected to the REF and REFGND inputs with
minimum parasitic inductance. 47 µF is an appropriate value for
the tantalum capacitor when used with one of the recommended
reference voltages:
•
The low noise, low temperature drift ADR421 and AD780
voltage references
•
The low power ADR291 voltage reference
•
The low cost AD1582 voltage reference
For applications using multiple AD7676s, it is more effective to
buffer the reference voltage with a low noise, very stable op amp
like the AD8031.
Care should also be taken with the reference temperature coefficient of the voltage reference, which directly affects the full-scale
accuracy if this parameter matters. For instance, a ±15 ppm/°C
tempco of the reference changes the full scale by ±1 LSB/°C.
–12–
REV. B
Page 13

V
SAMPLING RATE – SPS
1M
POWER DISSIPATION – W
0.1
10k
100 100k10 10k
100
1k
1
100k
1k
10
1M
, as mentioned in the specification table, could be increased
REF
to AVDD – 1.85 V. The benefit here is the increased SNR obtained
as a result of this increase. Since the input range is defined in
terms of V
, this would essentially increase the range to make
REF
it a ±3 V input range with an AVDD above 4.85 V. The theoretical improvement as a result of this increase in reference is
1.58 dB (20 log [3/2.5]). Due to the theoretical quantization noise,
however, the observed improvement is approximately 1 dB. The
AD780 can be selected with a 3 V reference voltage.
Power Supply
The AD7676 uses three sets of power supply pins: an analog 5 V
supply AVDD, a digital 5 V core supply DVDD, and a digital
input/output interface supply OVDD. The OVDD supply allows
direct interface with any logic working between 2.7 V and
DVDD + 0.3 V. To reduce the number of supplies needed, the
digital core (DVDD) can be supplied through a simple RC filter
from the analog supply as shown in Figure 5. The AD7676 is
independent of power supply sequencing once OVDD does not
exceed DVDD by more than 0.3 V and thus free from supply
voltage-induced latch-up. Additionally, it is very insensitive to
power supply variations over a wide frequency range, as shown in
Figure 9.
75
70
65
60
AD7676
Figure 10. Power Dissipation vs. Sample Rate
CONVERSION CONTROL
Figure 11 shows the detailed timing diagrams of the conversion
process. The AD7676 is controlled by the signal CNVST, which
initiates conversion. Once initiated, it cannot be restarted or
aborted, even by the power-down input PD, until the conversion
is complete. The CNVST signal operates independently of CS
and RD signals.
t
2
CNVST
t
1
55
PSRR – dB
50
45
40
35
10k 10M1k 1M
100k
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 9. PSRR vs. Frequency
POWER DISSIPATION
The AD7676 automatically reduces its power consumption at
the end of each conversion phase. During the acquisition phase,
the operating currents are very low, which allows a significant
power savings when the conversion rate is reduced, as shown in
Figure 10. This feature makes the AD7676 ideal for very low
power battery-operated applications.
It should be noted that the digital interface remains active even
during the acquisition phase. To reduce the operating digital
supply currents even further, the digital inputs need to be driven
close to the power rails (i.e., DVDD and DGND) and OVDD
BUSY
t
t
ACQUIRE CONVERT
MODE
3
5
t
4
t
6
ACQUIRE
t
7
t
8
CONVERT
Figure 11. Basic Conversion Timing
For true sampling applications, the recommended operation of
the CNVST signal is the following:
CNVST must be held HIGH from the previous falling edge of
BUSY, and during a minimum delay corresponding to the acquisition time t
; then, when CNVST is brought LOW, a conversion
8
is initiated and the BUSY signal goes HIGH until the completion of the conversion. Although CNVST is a digital signal, it
should be designed with this special care with fast, clean edges,
and levels, with minimum overshoot and undershoot or ringing.
For applications where the SNR is critical, the CNVST signal
should have a very low jitter. To achieve this, some use a dedicated
oscillator for CNVST generation or, at least, to clock it with a
high frequency low jitter clock as shown in Figure 5.
should not exceed DVDD by more than 0.3 V.
REV. B
–13–
Page 14

AD7676
t
9
RESET
BUSY
DATABUS
t
8
CNVST
Figure 12. RESET Timing
For other applications, conversions can be automatically initiated.
If CNVST is held LOW when BUSY is LOW, the AD7676
controls the acquisition phase and then automatically initiates a
new conversion. By keeping CNVST LOW, the AD7676 keeps
the conversion process running by itself. It should be noted that
the analog input has to be settled when BUSY goes LOW. Also,
at power-up, CNVST should be brought LOW once to initiate the
conversion process. In this mode, the AD7676 could sometimes
run slightly faster than the guaranteed limit of 500 kSPS.
DIGITAL INTERFACE
The AD7676 has a versatile digital interface; it can be interfaced
with the host system by using either a serial or parallel interface.
The serial interface is multiplexed on the parallel databus. The
AD7676 digital interface also accommodates both 3 V or 5 V
logic by simply connecting the OVDD supply pin of the AD7676
to the host system interface digital supply. Finally, by using the
OB/2C input pin, either twos complement or straight binary
coding can be used.
The two signals CS and RD control the interface. When at least
one of these signals is HIGH, the interface outputs are in high
impedance. Usually, CS allows the selection of each AD7676 in
multicircuit applications and is held LOW in a single AD7676
design. RD is generally used to enable the conversion result on
the databus.
CS = RD = 0
CNVST
t
1
PARALLEL INTERFACE
The AD7676 is configured to use the parallel interface (Figure 13)
when the SER/PAR is held LOW. The data can be read either
after each conversion, which is during the next acquisition phase,
or during the following conversion as shown, respectively, in
Figures 14 and 15. When the data is read during the conversion,
however, it is recommended that it be read-only during the first
half of the conversion phase. That avoids any potential feedthrough
between voltage transients on the digital interface and the most
critical analog conversion circuitry.
CS
RD
BUSY
DATABUS
t
12
CURRENT
CONVERSION
t
13
Figure 14. Slave Parallel Data Timing for Reading
(Read after Conversion)
CS = 0
CNVST,
RD
BUSY
DATABUS
t
3
t
12
t
1
PREVIOUS
CONVERSION
t
t
4
13
Figure 15. Slave Parallel Data Timing for Reading (Read
during Conversion)
The BYTESWAP pin allows a glueless interface to an 8-bit bus.
As shown in Figure 16, the LSB byte is output on D[7:0] and the
MSB is output on D[15:8] when BYTESWAP is LOW. When
BYTESWAP is HIGH, the LSB and MSB bytes are swapped and
the LSB is output on D[15:8] and the MSB is output on D[7:0].
By connecting BYTESWAP to an address line, the 16-bit data
can be read in two bytes on either D[15:8] or D[7:0].
t
10
BUSY
DATABUS
t
3
PREVIOUS CONVERSION DATA NEW DATA
t
4
t
11
Figure 13. Master Parallel Data Timing for Reading
(Continuous Read)
–14–
CS
RD
BYTE
PINS D[15:8]
PINS D[7:0]
HI-Z
HI-Z
HIGH BYTE LOW BYTE
t
12
LOW BYTE HIGH BYTE
t
12
Figure 16. 8-Bit Parallel Interface
HI-Z
t
13
HI-Z
REV. B
Page 15

AD7676
SERIAL INTERFACE
The AD7676 is configured to use the serial interface when the
SER/PAR is held HIGH. The AD7676 outputs 16 bits of data
MSB first, on the SDOUT pin. This data is synchronized with
the 16 clock pulses provided on the SCLK pin.
MASTER SERIAL INTERFACE
Internal Clock
The AD7676 is configured to generate and provide the serial data
clock SCLK when the EXT/INT pin is held LOW. The AD7676 also
generates a SYNC signal to indicate to the host when the serial
CS, RD
CNVST
BUSY
SYNC
SCLK
SDOUT
EXT/INT = 0
t
3
t
29
t
14
t
20
t
15
t
16
t
22
RDC/SDIN = 0 INVSCLK = INVSYNC = 0
t
18
t
19
t
21
123 141516
D15 D14 D2 D1 D0X
t
23
data is valid. The serial clock SCLK and the SYNC signal can be
inverted if desired. The output data is valid on both the rising
and falling edges of the data clock. Depending on RDC/SDIN
input, the data can be read after each conversion or during the
following conversion. Figures 17 and 18 show the detailed timing
diagrams of these two modes.
Usually, because the AD7676 has a longer acquisition phase
than the conversion phase, the data is read immediately after
conversion. That makes the mode master, read after conversion,
the most recommended serial mode when it can be used.
t
28
t
30
t
25
t
24
t
26
t
27
Figure 17. Master Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read after Conversion)
CS, RD
CNVST
BUSY
SYNC
SCLK
SDOUT
EXT/INT = 0
t
1
t
3
t
17
t
14
t
15
t
18
t
16
t
22
t
19
t20t
21
123 141516
D15 D14 D2 D1 D0X
RDC/SDIN = 1 INVSCLK = INVSYNC = 0
t
23
t
25
t
24
t
26
t
27
Figure 18. Master Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read Previous Conversion during Conversion)
REV. B
–15–
Page 16

AD7676
In Read-after-Conversion Mode, unlike in other modes, it should
be noted that the signal BUSY returns LOW after the 16 data
bits are pulsed out and not at the end of the conversion phase,
which results in a longer BUSY width.
In Read-during-Conversion Mode, the serial clock and data
toggle at appropriate instances, which minimizes potential feedthrough between digital activity and the critical conversion decisions.
SLAVE SERIAL INTERFACE
External Clock
The AD7676 is configured to accept an externally supplied serial
data clock on the SCLK pin when the EXT/INT pin is held HIGH.
In this mode, several methods can be used to read the data. The
external serial clock is gated by CS and the data are output when
both CS and RD are LOW. Thus, depending on CS, the data can
be read after each conversion or during the following conversion.
The external clock can be either a continuous or discontinuous
clock. A discontinuous clock can be either normally HIGH or
normally LOW when inactive. Figures 19 and 20 show the detailed
timing diagrams of these methods. Usually, because the AD7676
has a longer acquisition phase than the conversion phase, the
data are read immediately after conversion.
While the AD7676 is performing a bit decision, it is important
that voltage transients not occur on digital input/output pins or
degradation of the conversion result could occur. This is particularly important during the second half of the conversion phase
because the AD7676 provides error correction circuitry that can
correct for an improper bit decision made during the first half of
the conversion phase. For this reason, it is recommended that when
an external clock is being provided, it is a discontinuous clock
that is toggling only when BUSY is LOW or, more importantly,
that it does not transition during the latter half of BUSY HIGH.
External Discontinuous Clock Data Read after Conversion
This mode is the most recommended of the serial slave modes.
Figure 19 shows the detailed timing diagrams of this method.
After a conversion is complete, indicated by BUSY returning
LOW, the result of this conversion can be read while both CS and
RD are LOW. The data is shifted out, MSB first, with 16 clock
pulses and is valid on both the rising and falling edges of the clock.
Among the advantages of this method, the conversion performance is not degraded because there are no voltage transients
on the digital interface during the conversion process.
Another advantage is to be able to read the data at any speed up to
40 MHz, which accommodates both slow digital host interface
and the fastest serial reading.
Finally, in this mode only, the AD7676 provides a “daisy chain”
feature using the RDC/SDIN input pin for cascading multiple
converters together. This feature is useful for reducing component
count and wiring connections when it is desired as it is, for
instance, in isolated multiconverter applications.
An example of the concatenation of two devices is shown in
Figure 21. Simultaneous sampling is possible by using a common
CNVST
latched on the opposite edge of SCLK of the one used
out the data on SDOUT. Thus, the MSB of the
converter just follows the LSB of the “downstream”
signal. It should be noted that the RDC/SDIN input is
to shift
“upstream”
converter
on the next SCLK cycle.
CS
BUSY
SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
EXT/INT = 1 RD = 0
t
35
t
t
36
37
123 1415161718
t
31
D15 D14 D1 D0D13
t
16
X15 X14 X13 X1 X0 Y15 Y14
t
33
t
32
t
34
INVSCLK = 0
Figure 19. Slave Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read after Conversion)
X15 X14X
–16–
REV. B
Page 17

AD7676
External Clock Data Read During Conversion
Figure 20 shows the detailed timing diagrams of this method.
During a conversion, while both CS and RD are LOW, the result
of the previous conversion can be read. The data is shifted out,
MSB first, with 16 clock pulses, and is valid on both rising and
falling edges of the clock. The 16 bits have to be read before the
current conversion is complete. If that is not done, RDERROR is
pulsed HIGH and can be used to interrupt the host interface to
prevent incomplete data reading. There is no daisy chain feature
in this mode, and RDC/SDIN input should always be tied either
HIGH or LOW.
To reduce performance degradation due to digital activity, a fast
discontinuous clock of at least 18 MHz is recommended to ensure
that all the bits are read during the first half of the conversion
phase. For this reason, this mode is more difficult to use.
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
The AD7676 is ideally suited for traditional dc measurement
applications supporting a microprocessor and ac signal processing
applications interfacing to a digital signal processor. The AD7676
is designed to interface either with a parallel 8-bit or 16-bit wide
EXT/INT = 1 RD = 0
CS
interface or with a general-purpose Serial Port or I/O Ports on a
microcontroller. A variety of external buffers can be used with
the AD7676 to prevent digital noise from coupling into the ADC.
The following sections illustrate the use of the AD7676 with
an SPI-equipped microcontroller, and the ADSP-21065L and
ADSP-218x signal processors.
SPI Interface (MC68HC11)
Figure 22 shows an interface diagram between the AD7676 and an
SPI-equipped microcontroller, such as the MC68HC11. To accommodate the slower speed of the microcontroller, the AD7676 acts
as a slave device and data must be read after conversion. This mode
also allows the daisy chain feature. The convert command could
be initiated in response to an internal timer interrupt. The reading
of output data, one byte at a time if necessary, could be initiated
in response to the end-of-conversion signal (BUSY going LOW)
using an interrupt line of the microcontroller. The serial peripheral interface (SPI) on the MC68HC11 is configured for Master
Mode (MSTR) = 1, Clock Polarity Bit (CPOL) = 0, Clock Phase
Bit (CPHA) = 1, and SPI interrupt enable (SPIE) = 1 by writing
to the SPI Control Register (SPCR). The IRQ is configured for
edge-sensitive-only operation (IRQE = 1 in OPTION register).
INVSCLK = 0
CNVST
BUSY
SCLK
SDOUT
t
3
t
16
t
35
t36t
37
12 3 141516
t
31
t
32
D1 D0X D15 D14 D13
Figure 20. Slave Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read Previous Conversion during Conversion)
BUSY
OUT
BUSY BUSY
AD7676 NO. 2
(UPSTREAM)
RDC/SDIN SDOUT
CNVST
CS
SCLK
AD7676 NO. 1
(DOWNSTREAM)
RDC/SDIN SDOUT
CNVST
SCLK
CS
DATA
OUT
REV. B
SCLK IN
CS IN
CNVST IN
Figure 21. Two AD7676s in a Daisy Chain Configuration
–17–
Page 18

AD7676
DVD D
AD7676*
SER/PAR
EXT/INT
CS
RD
INVSCLK
BUSY
SDOUT
SCLK
CNVST
*ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED FOR CLARITY
MC68HC11*
IRQ
MISO/SDI
SCK
I/O PORT
Figure 22. Interfacing the AD7676 to SPI Interface
ADSP-21065L in Master Serial Interface
As shown in Figure 23, the AD7676 can be interfaced to the
ADSP-21065L using the serial interface in Master Mode without
any glue logic required. This mode combines the advantages of
reducing the wire connections and the ability to read the data during
or after conversion maximum speed transfer (DIVSCLK[0:1]
both LOW).
The AD7676 is configured for the Internal Clock Mode (EXT/INT
LOW) and acts, therefore, as the master device. The convert
command can be generated by either an external low jitter oscillator or, as shown, by a FLAG output of the ADSP-21065L or by
a frame output TFS of one serial port of the ADSP-21065L that
can be used like a timer. The Serial Port on the ADSP-21065L
is configured for external clock (IRFS = 0), rising edge active
(CKRE = 1), external late framed sync signals (IRFS = 0,
LAFS = 1, RFSR = 1), and active HIGH (LRFS = 0). The Serial
Port of the ADSP-21065L is configured by writing to its receive
control register (SRCTL)—see the ADSP-2106x SHARC User’s
Manual. Because the Serial Port within the ADSP-21065L will
be seeing a discontinuous clock, an initial word reading has to
be done after the ADSP-21065L has been reset to ensure that
the Serial Port is properly synchronized to this clock during each
following data read operation.
DVD D
AD7676*
SER/PAR
RDC/SDIN
RD
EXT/INT
CS
INVSYNC
INVSCLK
SYNC
SDOUT
SCLK
CNVST
*ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED FOR CLARITY
ADSP-21065L*
SHARC
RFS
DR
RCLK
FLAG OR TFS
Figure 23. Interfacing to the ADSP-21065L Using
the Serial Master Mode
APPLICATION HINTS
Layout
The AD7676 has very good immunity to noise on the power
supplies as can be seen in Figure 21. However, care should still
be taken with regard to grounding layout.
The printed circuit board that houses the AD7676 should be
designed so the analog and digital sections are separated and
confined to certain areas of the board. This facilitates the use of
ground planes that can be easily separated. Digital and analog
ground planes should be joined in only one place, preferably
underneath the AD7676, or, at least, as close as possible to the
AD7676. If the AD7676 is in a system where multiple devices
require analog to digital ground connections, the connection
should still be made at one point only, a star ground point
that should be established as close as possible to the AD7676.
It is recommended to avoid running digital lines under the device
as these will couple noise onto the die. The analog ground plane
should be allowed to run under the AD7676 to avoid noise
coupling. Fast switching signals like CNVST or clocks should be
shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating noise to other sections of the board and should never run near analog signal paths.
Crossover of digital and analog signals should be avoided. Traces
on different but close layers of the board should run at right
angles to each other. This will reduce the effect of feedthrough
through the board.
The power supply lines to the AD7676 should use as large a
trace as possible to provide low impedance paths and reduce the
effect of glitches on the power supply lines. Good decoupling is
also important to lower the supply’s impedance presented to
the AD7676 and reduce the magnitude of the supply spikes.
Decoupling ceramic capacitors, typically 100 nF, should be
placed on each power supply’s pins, AVDD, DVDD, and OVDD,
close to and ideally right up against these pins and their corresponding ground pins. Additionally, low ESR 10 µF capacitors
should be located in the vicinity of the ADC to further reduce
low frequency ripple.
The DVDD supply of the AD7676 can be either a separate
supply or come from the analog supply, AVDD, or from the
digital interface supply, OVDD. When the system digital supply
is noisy, or fast switching digital signals are present, it is recommended if no separate supply is available, to connect the DVDD
digital supply to the analog supply AVDD through an RC filter as
shown in Figure 5 and to connect the system supply to the interface digital supply OVDD and the remaining digital circuitry.
When DVDD is powered from the system supply, it is useful to
insert a bead to further reduce high frequency spikes.
The AD7676 has four different ground pins: REFGND, AGND,
DGND, and OGND. REFGND senses the reference voltage and
should be a low impedance return to the reference because it
carries pulsed currents. AGND is the ground to which most internal ADC analog signals are referenced. This ground must be
connected with the least resistance to the analog ground plane.
DGND must be tied to the analog or digital ground plane,
depending on the configuration. OGND is connected to the
digital system ground.
The layout of the decoupling of the reference voltage is important.
The decoupling capacitor should be close to the ADC and
connected with short and large traces to minimize parasitic
inductances.
Evaluating the AD7676 Performance
A recommended layout for the AD7676 is outlined in the
evaluation board for the AD7676. The evaluation board package
includes a fully assembled and tested evaluation board,
documentation, and software for controlling the board from a
PC via the Eval-Control BRD2.
–18–
REV. B
Page 19

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
48-Lead Plastic Quad Flatpack [LQFP]
1.4 mm Thick
(ST-48)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
AD7676
1.45
1.40
1.35
0.15
0.05
SEATING
PLANE
ROTATED 90 CCW
VIEW A
0.08 MAX
COPLANARITY
48-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP]
7.00
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1.60 MAX
0.75
0.60
0.45
SEATING
PLANE
0.20
0.09
7
3.5
0
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-026BBC
PIN 1
INDICATOR
VIEW A
1
12
0.50
BSC
(CP-48)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
37
36
0.60 MAX
0.60 MAX
48
13
9.00 BSC
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
0.30
0.23
0.18
37
24
36
25
0.27
0.22
0.17
48
7.00
BSC
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1
1.00
0.90
0.80
0.25
REF
12 MAX
SEATING
PLANE
TOP
VIEW
0.70 MAX
0.65 NOM
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
6.75
BSC SQ
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.08
BOTTOM
VIEW
25
24
5.50
REF
5.25
4.70
2.25
12
13
REV. B
–19–
Page 20

Revision History
Location Page
10/02—Data Sheet changed from REV. A to REV. B.
Added 48-Lead LFCSP to FEATURES and GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Added PulSAR Selection table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Edit to SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Changes to ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Additions to ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Edits to PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Edit to Transfer Functions section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Changes to Power Supply section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Added 48-Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
C02690–0–10/02(B)
–20–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. B
 Loading...
Loading...