Page 1
Low Cost, Low Power
Mono Audio Codec
AD74111
FEATURES
2.5 V Mono Audio Codec with 3.3 V Tolerant
Digital Interface
Supports 8 kHz to 48 kHz Sample Rates
Supports 16-/20-/24-Bit Word Lengths
Multibit - Modulators with
“Perfect Differential Linearity Restoration” for
Reduced Idle Tones and Noise Floor
Data Directed Scrambling DAC – Least Sensitive to Jitter
Performance (20 Hz to 20 kHz)
85 dB ADC Dynamic Range
93 dB DAC Dynamic Range
Programmable ADC Gain
On-Chip Volume Control for DAC Channel
Software Controllable Clickless Mute
Supports 256 f
, 512 fS, and 768 fS Master Mode
S
Clocks
Master Clock Prescaler for Use with DSP Master Clocks
On-Chip Reference
16-Lead TSSOP Package
APPLICATIONS
Digital Video Camcorders (DVC)
®
Portable Audio Devices (Walkman
, PDAs, and so on)
Audio Processing
Voice Processing
Telematic Systems
General-Purpose Analog I/O
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD74111 is a front-end processor for general-purpose audio
and voice applications. It features a multibit ⌺-⌬ A/D conversion
channel and a multibit ⌺-⌬ D/A conversion channel. The ADC
channel provides >67 dB THD+N and the DAC channel provides >88 dB THD+N, both over an audio signal bandwidth.
The AD74111 is particularly suitable for a variety of applications
where mono input and output channels are required, including
audio sections of digital video camcorders, portable personal
audio devices, and telematic applications. Its high quality
performance also makes it suitable for speech and telephony
applications such as speech recognition and synthesis, and modern
feature phones.
An on-chip reference voltage is included but can be powered
down and bypassed by an external reference source if required.
The AD74111 offers sampling rates that, depending on MCLK
selection and MCLK divider ratio, range from 8 kHz in the
voiceband range to 48 kHz in the audio range.
The AD74111 is available in a 16-lead TSSOP package option
and is specified for the automotive temperature range of –40°C
to +105°C.
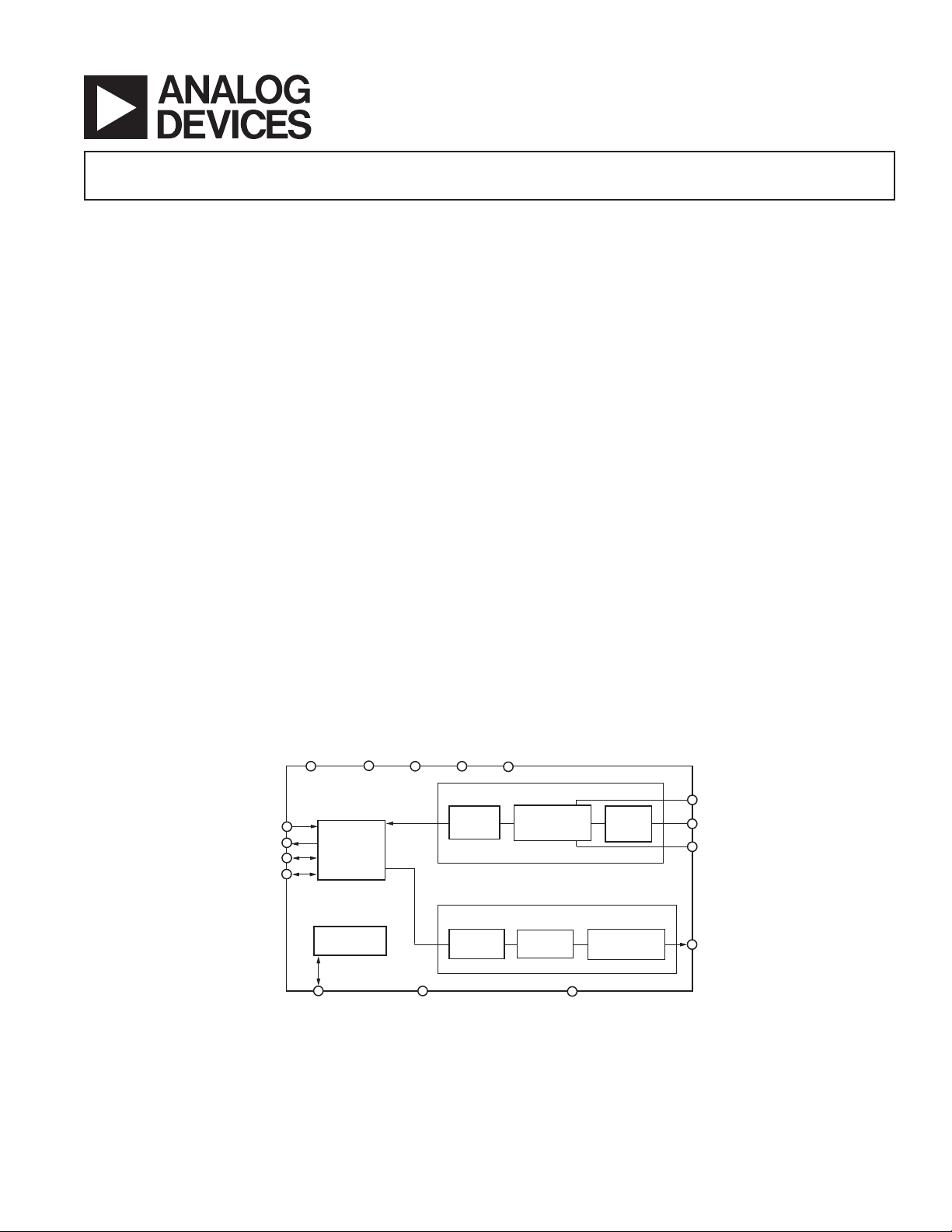
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
RESET
DIN
DOUT
DFS
DCLK
REFCAP
MCLK
SERIAL
DATA
PORT
REFERENCE
DGND
DVDD2 AVDDDVDD1
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
FILTER
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
ADC
AGND
GAIN
STAGE
- DAC
MODULATOR
-
MODULATOR
DAC CHANNEL
VOLUME
CONTROL
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
CAPP
VIN
CAPN
VOUT
Page 2
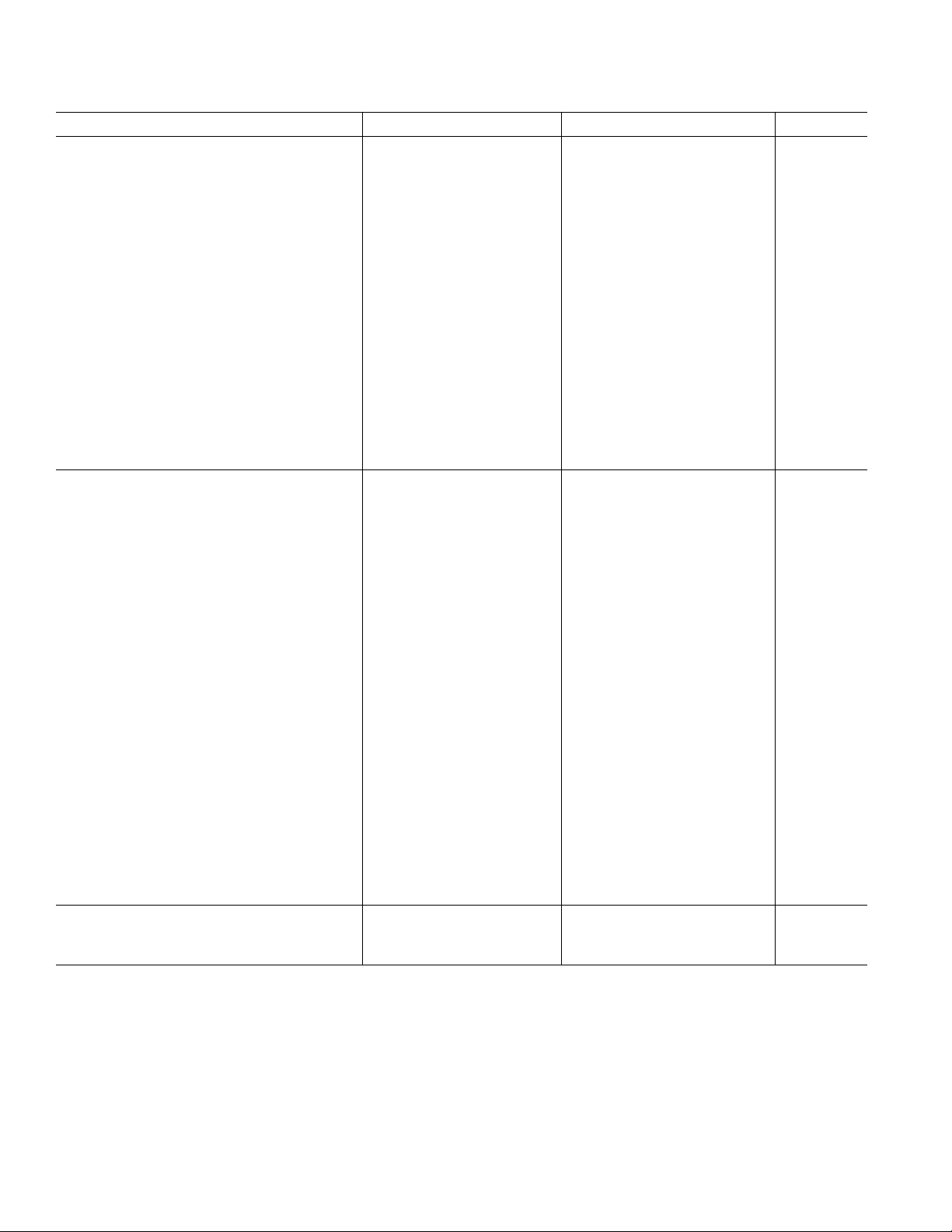
AD74111–SPECIFICATIONS
(AVDD = 2.5 V ± 5%, DVDD2 = 2.5 V ± 5%, DVDD1 = 2.5 V ± 5%, f
fS = 48 kHz, TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
= 12.288 MHz,
MCLK
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
ADC Resolution 24 Bits
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) f
= 16 kHz 70 77 dB
S
Dynamic Range
(20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dB Input)
No Filter fS = 48 kHz 85 dB
f
= 16 kHz 78 85 dB
With A-Weighted Filter f
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise f
S
= 48 kHz 87 dB
S
= 48 kHz, PGA = 0 dB –67 dB
S
f
= 16 kHz –75 dB
S
Programmable Input Gain 12 dB
Gain Step Size 3dB
Offset Error –55 +30 +80 mV
Full-Scale Input Voltage 0.5 V rms
Input Resistance 4kΩ
Input Capacitance 15 pF
Common-Mode Input Volts 1.125 V
Crosstalk
ADC Input Signal = 1.0 kHz,
100 dB
0 dB; DAC Output = DC
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
DAC Resolution 24 Bits
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) f
= 16 kHz 80 89 dB
S
Dynamic Range
(20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dB Input)
No Filter f
With A-Weighted Filter f
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
= 48 kHz 93 dB
S
= 16 kHz 84 93 dB
f
S
= 48 kHz 95 dB
S
fS = 48 kHz –88 dB
f
= 16 kHz –88 –81 dB
S
dB
DC Accuracy
Offset Error –75 –10 +50 mV
Gain Error –0.9 +0.175 +0.8 dB
Volume Control Step Size
(1024 Linear Steps) 0.098 %
Volume Control Range (Max Attenuation) –60 dB
Mute Attenuation –100 dB
De-emphasis Gain Error ± 0.1 dB
Full-Scale Output Voltage 0.5 V rms
Output Resistance 145 Ω
Common Mode Output Volts 1.125 V
Crosstalk
Signal Input ADC = AGND; 95 dB
DAC Output
Level = 1.0 kHz, 0 dB
REFERENCE (Internal)
Absolute Voltage, V
V
TC 50 ppm/°C
REF
REF
1.125 V
REV. 0–2–
Page 3
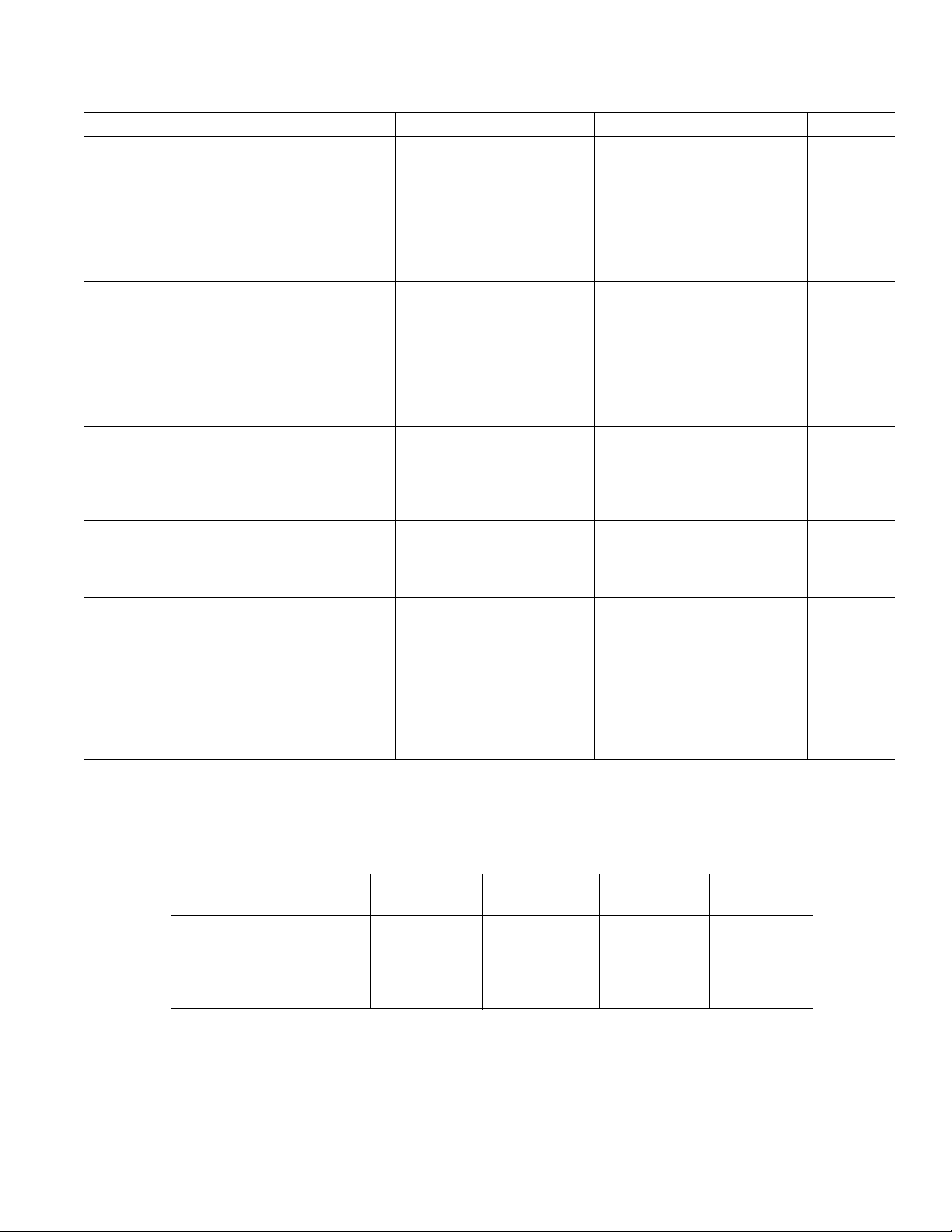
AD74111
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
ADC DECIMATION FILTER* f
Pass Band 21.5 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple 0.2 mdB
Transition Band 5 kHz
Stop Band 26.5 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 120 dB
Group Delay 910 µs
Low Group Delay Mode 87 µs
DAC INTERPOLATION FILTER* f
Pass Band 21.5 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple 10 mdB
Transition Band 5 kHz
Stop Band 26.5 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 75 dB
Group Delay 505 µs
Low Group Delay Mode 55 µs
LOGIC INPUT
, Input High Voltage DVDD1 – 0.8 DVDD1 V
V
INH
V
, Input Low Voltage 0 0.8 V
INL
Input Current –10 +10 µA
Input Capacitance 10 pF
LOGIC OUTPUT
VOH, Output High Voltage DVDD1 – 0.4 DVDD1 V
V
, Output Low Voltage 0 0.4 V
OL
Three-State Leakage Current –10 +10 µA
POWER SUPPLIES
AVDD 2.375 2.625 V
DVDD2 2.375 2.625 V
DVDD1 2.375 3.6 V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
1 kHz, 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog
Supply Pins 72 dB
50/60 Hz, 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog
Supply Pins 73 dB
*Guaranteed by design.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= 48 kHz
S
= 48 kHz
S
REV. 0
Table I. Current Summary (AVDD = 2.5 V, DVDD1 = 2.5 V, DVDD2 = 2.5 V)
1, 2, 3
AVDD DVDD1 DVDD2 Total Current
Conditions Current (mA) Current (mA) Current (mA) (Max)(mA)
ADC, Reference, Ref-Amp On 6.11 (6.11) 0.15 (0.43) 0.72 (2.10)
DAC, Reference, Ref-Amp On 3.80 (4.0) 0.15 (0.43) 0.85 (2.23)
Reference, Ref-Amp On 0.60 (0.60) 0.15 (0.43) 0.27 (0.50)
All Sections On 8.60 0.15 (0.43) 1.72 (4.80) 15.35
Power-Down Mode 0.035 0.15 (0.43) 0.49 (0.49) 2.6
NOTES
1
All values are typical, unless otherwise noted.
2
Max values are quoted with DVDD1 = 3.6 V.
3
Sample rates quoted are for 16 kHz and (48 kHz).
–3–
Page 4
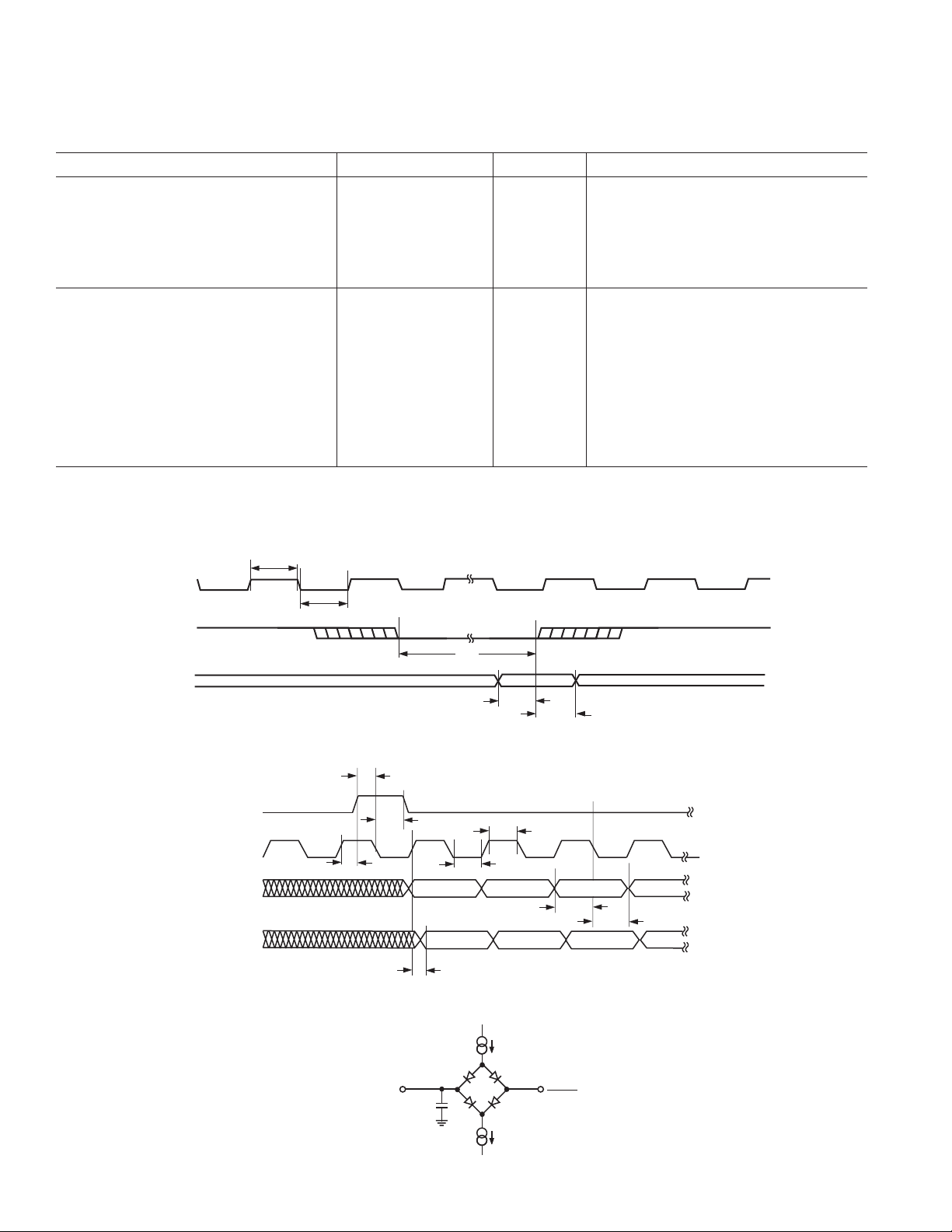
AD74111
(AVDD = 2.5 V ± 5%, DVDD2 = 2.5 V ± 5%, DVDD1 = 3.3 V ± 10%, f
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
Parameter Min Max Unit Comments
MASTER CLOCK AND RESET
t
MH
t
ML
t
RES
t
RS
t
RH
SERIAL PORT
t
CH
t
CL
t
FD
t
FS
t
FH
t
DD
t
DS
t
DH
t
DT
NOTES
1
Determines Master/Slave mode operation.
2
Applies in Slave mode only.
3
Applies in Master mode only.
4
Applies in Multiframe-Sync mode only.
MCLK High 25 ns
MCLK Low 25 ns
RESET Low 10 ns
DIN Setup Time 5 MCLKS To RESET Rising Edge
DIN Setup Time 5 MCLKS To RESET Rising Edge
DCLK High
DCLK Low
2
2
20 ns
20 ns
DFS Delay 5 ns From DCLK Rising Edge
DFS Setup Time 5 ns To DCLK Falling Edge
DFS Hold Time 15 ns From DCLK Falling Edge
DOUT Delay 30 ns From DCLK Rising Edge
DIN Setup Time 5 ns To DCLK Falling Edge
DIN Hold Time 15 ns From DCLK Falling Edge
DOUT Three-State 40 ns From DCLK Rising Edge
t
MH
MCLK
= 12.288 MHz, fS = 48 kHz,
MCLK
1
1
3
4
RESET
DIN
DFS
DCLK
DIN
DOUT
t
ML
Figure 1. MCLK and
t
FS
t
FH
t
FD
t
DD
Figure 2. Serial Port Timing
t
RES
t
RS
t
RH
RESET
Timing
t
CH
t
CL
MSB MSB–1
MSB MSB–2
100A
MSB–1
I
OL
MSB–2
t
DS
t
DH
TO OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
C
L
100A
I
OH
DVDD1
2
Figure 3. Load Circuit for Digital Output Timing Specifications
REV. 0–4–
Page 5
AD74111
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
AVDD, DVDD2 to AGND, DGND . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +3.0 V
DVDD1 to AGND, DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +4.5 V
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
Digital I/O Voltage to DGND . . . . . . –0.3 V to DVDD1 + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Automotive (Y Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +105°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Parameter Min Max Unit
Specifications Guaranteed –40 +105 ºC
Storage –65 +150 ºC
16-Lead TSSOP, θ
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . .150.4°C/W
JA
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Range Package
AD74111YRU –40ºC to +105ºC RU-16
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
AD74111 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. 0
–5–
Page 6
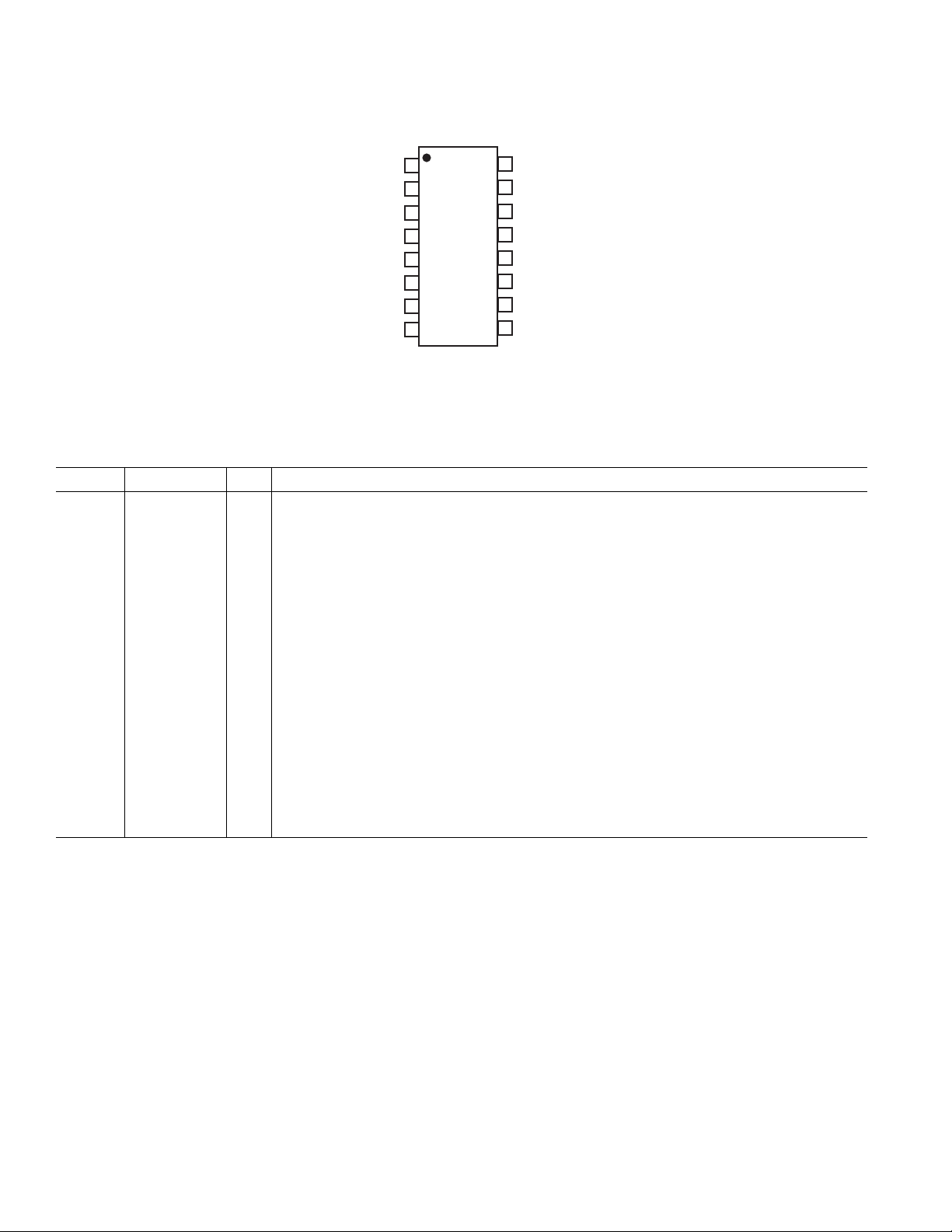
AD74111
R
PIN CONFIGURATION
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
MCLK
DVDD1
DVDD2
DGND
AGND
REFCAP
CAPP
VIN
DCLK
1
DIN
2
DFS
3
DOUT
ESET
AVDD
CAPN
VOUT
AD74111
4
TOP VIEW
(NOT TO SCALE)
5
6
7
8
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No. Mnemonic I/O Description
1 DCLK I/O Serial Clock
2DIN I Serial Data Input. The state of DIN on the rising edge of RESET determines the operating mode
of the interface. See the Selecting Master or Slave Mode section for more information.
3 DFS I/O Frame Synchronization Signal
4 DOUT O Serial Data Output
5 RESET IPower-Down/Reset Input
6 AVDD Analog 2.5 V Power Supply Connection
7 CAPN ADC Filter Capacitor (Negative)
8 VOUT O DAC Analog Output
9VIN I ADC Analog Input
10 CAPP ADC Filter Capacitor (Positive)
11 REFCAP I/O Internal Reference Decoupling Capacitor. Can also be used for connection of an external reference.
12 AGND Analog Ground Connection
13 DGND Digital Ground Connection
14 DVDD2 Digital 2.5 V Power Supply Connection (Core)
15 DVDD1 Digital Power Supply Connection (Interface)
16 MCLK I External Master Clock Input
REV. 0–6–
Page 7

Typical Performance Characteristics–AD74111
0
–50
–100
MAGNITUDE – dB
–150
01.00.25
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO
0.5 0.75
TPC 1. ADC Composite Filter Response
0
–50
0
–40
–80
MAGNITUDE – dB
–120
f
S
0 1.00.25
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO
0.5 0.75
f
s
TPC 4. DAC Composite Filter Response
0
–40
–100
MAGNITUDE – dB
–150
0 1.00.25
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO fS
0.5 0.75
TPC 2. ADC Composite Filter Response
Low Group Delay Enabled
1.0
0.5
0
MAGNITUDE – mdB
–0.5
–1.0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO
TPC 3. ADC Composite Filter Response
(Pass-Band Section)
–80
MAGNITUDE – dB
–120
01.00.25
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO
0.5 0.75
f
s
TPC 5. DAC Composite Filter Response
Low Group Delay Enabled
10
5
0
MAGNITUDE – mdB
–5
–10
f
s
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
FREQUENCY – NORMALIZED TO
f
S
TPC 6. DAC Composite Filter Response
(Pass-Band Section)
REV. 0
–7–
Page 8

AD74111
78
74
70
66
THD+N – dB
62
58
54
84 4816
24 40
SAMPLE RATE – kHz
32
TPC 7. ADC THD+N vs. Sample Rate
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
General Description
The AD74111 is a 2.5 V mono codec. It comprises an ADC and
DAC channel with single-ended input and output. The ADC
has a programmable gain stage and the DAC has programmable
volume control. Each of these sections is described in further
detail below. The AD74111 is controlled by means of a flexible
serial port (SPORT) that can be programmed to accommodate
many industry standard DSPs and microcontrollers. The AD74111
can be set to operate as a master or slave device. The AD74111
can be set to operate with sample rates of 8 kHz to 48 kHz,
depending on the values of MCLK and the MCLK prescalers.
On-chip digital filtering is provided as part of the DAC and
ADC channels with a low group delay option to reduce the delays
through the filters when operating at lower sample rates. Figure 4
shows a block diagram of the DAC and ADC channel in the
AD74111. Figures 5a and 5b show block diagrams of the filter
arrangements of the ADC and DAC filters.
90
88
86
84
THD+N – dB
82
80
78
84816
24 40
SAMPLE RATE – kHz
32
TPC 8. DAC THD+N vs. Sample Rate
ADC Section
The AD74111 contains a multibit sigma-delta ADC. The ADC
has a single input pin with additional pins for decoupling/filter
capacitors. The ADC channel has an independent input amplifier
gain stage that can be programmed in steps of 3 dB, from 0 dB
to 12 dB. The input amplifier gain settings are set by programming the appropriate bits in Control Register E. The ADC can
also be muted under software control. The AD74111 input
channel employs a multibit sigma-delta conversion technique that
provides a high resolution output with system filtering implemented on-chip. Sigma-delta converters employ a technique
known as oversampling, where the sampling rate is many times
the highest frequency of interest. In the case of the AD74111,
the oversampling ratio is 64 and a decimation filter is used to
reduce the output to standard sample rates. The maximum sample
rate is 48 kHz.
MCLK
PRESCALERS
(/1 to /12)
/4
ADC MODULATOR
CLOCK
DAC O/P
ADC
INPUT
MODULATOR
MODULATOR
5 BITS
- ADC
- DAC
DAC MODULATOR
CLOCK
SINC FILTER
/2
INTERPOLATOR
( 16)
(/8)
Figure 4. ADC and DAC Engine
DECIMATOR
INTERPOLATOR
( 8)
(/8)
ADC
DATA
16-/20-/24-
BITS
DAC
DATA
16-/20-/24-
BITS
REV. 0–8–
Page 9

ADC
MODULATOR
64
f
S
5th ORDER
COMB FILTER
8
f
S
HALF-BAND
S
COMB
COMPENSATION
4
f
Figure 5a. ADC Filter Section
2
AD74111
f
S
HALF-BAND
f
S
ADC
RESULT
LOW GROUP
DELAY OUTPUT
DAC
MODULATOR
128
f
8
16 ZERO
S
ORDER HOLD
f
S
HALF-BAND
FILTER
4
f
S
Figure 5b. DAC Filter Section
ADC, CAPP, and CAPN Pins
The ADC channel requires two external capacitors to act as
charge reservoirs for the switched capacitor inputs of the sigmadelta modulator. These capacitors isolate the outputs of the PGA
stage from glitches generated by the sigma-delta modulator. The
capacitor also forms a low-pass filter with the output impedance
of the PGA (approximately 124 Ω), which helps to isolate noise
from the modulator engine. The capacitors should be of good
quality, such as NPO or polypropylene film, with values from
100 pF to 1 nF and should be connected to AGND.
Peak Readback
The AD74111 can store the highest ADC value to facilitate level
adjustment of the input signal. Programming the Peak Enable
bit in Control Register E with a 1 will enable ADC Peak Level
Reading. The peak value is stored as a 6-bit number from 0 dB
to –63 dB in 1 dB steps. Reading Control Register F will give the
highest ADC value since the bit was set. The ADC peak register
is automatically cleared after reading.
Decimator Section
The digital decimation filter has a pass-band ripple of 0.2 mdB
and a stop-band attenuation of 120 dB. The filter is an FIR type
with a linear phase response. The group delay at 48 kHz is
910 µs. Output sample rates up to 48 kHz are supported.
Input Signal Swing
The ADC input has an input range of 0.5 V rms/1.414 V p-p
about a bias point equal to V
. Figure 6 shows a typical
REFCAP
input filter circuit for use with the AD74111.
1.414V p-p
V
AGND
47F
51
10nF
NPO
VIN
Figure 6. Typical Input Circuit
DAC Section
The AD74111 DAC channel has a single-ended, analog output.
The DAC has independent software controllable Mute and Volume
Control functions. Control Register G controls the attenuation
factor for the DAC. This register is 10 bits wide, giving 1024
steps of attenuation. The AD74111 output channel employs a
multibit sigma-delta conversion technique that provides a high
quality output with system filtering implemented on-chip.
ZERO ORDER HOLD
SINC COMPENSATION
FILTER
2
S
HALF-BAND–
FILTER
f
S
DAC
INPUT
LOW GROUP
DELAY INPUT
f
Output Signal Swing
The DAC has an output range of 0.5 V rms/1.414 V p-p about
a bias point equal to V
VOUT
REFCAP
820
(see Figure 7).
V
REFCAP
2n2F
NPO
1.414V p-p
Figure 7. Typical Output Circuit
Low Group Delay
It is possible to bypass much of the digital filtering by enabling
the Low Group Delay function in Control Register C. By reducing the amount of filtering the AD74111 applies to input and
output samples, the time delay between the sampling interval
and when the sample is available is greatly reduced. This can be
of benefit in applications such as telematics, where minimal
time delays are important. When the Low Group Delay function
is enabled, the sample rate becomes IMCLK/128.
Reference
The AD74111 features an on-chip reference whose nominal
value is 1.125 V. A 100 nF ceramic and 10 µF tantalum capacitor
applied at the REFCAP pin are necessary to stabilize the reference.
(See Figure 8.)
10F
0.1F
REFCAP
Figure 8. Reference Decoupling
If required, an external reference can be used as the reference
source of the ADC and DAC sections. This may be desirable in
situations where multiple devices are required to use the same
value of reference or because of a better temperature coefficient
specification. The internal reference can be disabled via Control
Register A and the external reference applied at the REFCAP
pin (see Figure 9). External references should be of a suitable
value such that the voltage swing of the inputs or outputs is not
affected by being too close to the power supply rails and should
be adequately decoupled.
REV. 0
–9–
Page 10

AD74111
1.125V
EXTERNAL
REFERENCE
REFCAP
Figure 9. External Reference
Master Clocking Scheme
The update rate of the AD74111’s ADC and DAC channels
requires an internal master clock (IMCLK) that is 256 times the
sample update rate (IMCLK = 256 ⫻ f
). To provide some flex-
S
ibility in selecting sample rates, the device has a series of three
master clock prescalers that are programmable and allow the
user to choose a range of convenient sample rates from a single
external master clock. The master clock signal to the AD74111 is
applied at the MCLK pin. The MCLK signal is passed through
a series of three programmable MCLK prescaler (divider) circuits
that can be selected to reduce the resulting Internal MCLK
(IMCLK) frequency if required. The first and second MCLK
prescalers provide divider ratios of ⫼1 (pass through), ⫼2, ⫼3;
while the third prescaler provides divider ratios of ⫼1 (pass
through), ⫼2, ⫼4.
PROGRAMMABLE MCLK DIVIDER
MCLK
PRESCALER 1
/1
/2
/3
PRESCALER 2
/1
/2
/3
CONTROL REGISTER
PRESCALER 3
/1
/2
/4
IMCLK
Figure 10. MCLK Divider
The divider ratios allow a more convenient sample rate selection
from a common MCLK, which may be required in many voice
related applications. Control Register B should be programmed
to achieve the desired divider ratios.
Selecting Sample Rates
The sample rate at which the converter runs is always 256 times
the IMCLK rate. IMCLK is the Internal Master Clock and is the
output from the Master Clock Prescaler. The default sample rate
is 48 kHz (based on an external MCLK of 12.288 MHz). In this
mode, the ADC modulator is clocked at 3.072 MHz and the DAC
modulator is clocked at 6.144 MHz. Sample rates that are lower
than MCLK/256 can be achieved by using the MCLK prescaler.
Example 1: f
MCLK = 48 kHz ⫻ 256 = 12.288 MHz to provide 48 kHz f
For f
= 8 kHz, it is necessary to use the ⫼3 setting in
SAMP
= 48 kHz and 8 kHz Required
SAMP
SAMP
.
Prescaler 1, the ⫼2 setting in Prescaler 2, and pass through
in Prescaler 3. This results in an IMCLK = 8 kHz ⫻ 256 =
2.048 MHz (= 12.288 MHz/6).
Example 2: f
MCLK = 44.1 kHz ⫻ 256 = 11.2896 MHz to provide 44.1 kHz f
For f
= 11.025 kHz, it is necessary to use the ⫼1 setting in
SAMP
= 44.1 kHz and 11.025 kHz Required
SAMP
SAMP
.
Prescaler 1 and the ⫼4 setting in Prescaler 2, and pass through
in Prescaler 3. This results in an IMCLK = 11.025 kHz ⫻ 256
= 2.8224 MHz (= 11.2896 MHz/4).
Resetting the AD74111
The AD74111 can be reset by bringing the RESET pin low.
Following a reset, the internal circuitry of the AD74111 ensures
that the internal registers are reset to their default settings and
the on-chip RAM is purged of previous data samples. The DIN
pin is sampled to determine if the AD74111 is required to
operate in Master or Slave mode. The reset process takes 3072
MCLK periods, and the user should not attempt to program the
AD74111 during this time.
Power Supplies and Grounds
The AD74111 features three separate supplies: AVDD, DVDD1,
and DVDD2.
AVDD is the supply to the analog section of the device and must
be of sufficient quality to preserve the AD74111’s performance
characteristics. It is nominally a 2.5 V supply.
DVDD1 is the supply for the digital interface section of the device.
It is fed from the digital supply voltage of the DSP or controller
to which the device is interfaced and allows the AD74111
to interface with devices operating at supplies of between
2.5 V – 5% to 3.3 V + 10%.
DVDD2 is the supply for the digital core of the AD74111. It is
nominally a 2.5 V supply.
Accessing the Internal Registers
The AD74111 has seven registers that can be programmed to
control the functions of the AD74111. Each register is 10 bits
wide and is written to or read from using a 16-bit write or read
operation, with the exception of Control Register F, which is
read-only. Table V shows the format of the data transfer operation.
The Control Word is made up of a Read/Write bit, the register
address, and the data to be written to the device. Note that in a
read operation the data field is ignored by the device. Access to
the control registers is via the serial port through one of the
operating modes described below.
Serial Port
The AD74111 contains a flexible serial interface port that is
used to program and read the control registers and to send and
receive DAC and ADC audio data. The serial port is compatible
with many popular DSPs and can be programmed to operate in
a variety of modes, depending on which one best suits the DSP
being used. The serial port can be set to operate as a Master or
Slave device, as discussed below. Figure 11 shows a timing
diagram of the serial port.
REV. 0–10–
Page 11

AD74111
t
FS
DFS
DCLK
DIN
DOUT
t
FH
t
FD
t
t
MSB MSB–1
MSB MSB–2
DD
Figure 11. Serial Port (SPORT) Timing
Serial Port Operating Modes
The serial port of the AD74111 can be programmed to operate
in a variety of modes depending on the requirements and flexibility of the DSP to which it is connected. The two principal
modes of operation are Mixed mode and Data mode.
Mixed Mode
Mixed mode allows the control registers of the AD74111 to be
programmed and read back. It also allows data to be sent to the
DACs and data to be read from the ADCs. In Mixed mode,
there are separate data slots, each with its own frame synchronization signal (DFS) for control and DAC or ADC information.
The AD74111 powers up in Mixed mode by default to allow
the control registers to be programmed. Figure 13 shows the
default setting for Mixed mode.
Data Mode
Data mode can be used when programming or reading the
control registers is no longer required. Data mode provides a
frame synchronization (DFS) pulse for each sample of data.
Once the part has been programmed into Data mode, the only
way to change the control registers is to perform a hardware reset
to put the AD74111 back into Mixed mode. Figure 15 shows
the default setting for Data mode.
Data-Word Length
The AD74111 can be programmed to send DAC audio data
and receive ADC audio data in different word length formats of
16, 20, or 24 bits. The default mode is 16 bits, but this can be
changed by programming Control Register C for the appropriate
word length.
Selecting Master or Slave Mode
The initial operating mode of the AD74111 is determined by
the state of the DIN pin following a reset. If the DIN pin is high
during this time, Slave mode is selected. In Slave mode, the
DFS and DCLK pins are inputs and the control signals for
these pins must be provided by the DSP or other controller. If
the DIN pin is low immediately following a reset, the AD74111
will operate in Master mode.
t
CH
CL
MSB–2
t
DS
t
DH
MSB–1
Master Mode Operation
In Master mode, the DFS and DCLK pins are outputs from the
AD74111. This is the easiest mode in which to use the AD74111
because the correct timing relationship between sample rate,
DCLK, and DFS is controlled by the AD74111.
Slave Mode Operation
In Slave mode, the DFS and DCLK pins are inputs to the
AD74111. Care needs to be exercised when designing a system
to operate the AD74111 in this mode as the relationship between
the sample rate, DCLK, and DFS needs to be controlled by the
DSP or other controller and must be compatible with the internal DAC/ADC engine of the AD74111. Figure 12 shows a block
diagram of the DAC engine and the AD74111’s serial port. The
sample rate for the DAC engine is determined by the MCLK
and MCLK prescalers. The DAC engine will read data from the
DAC Data register at this rate. It is therefore important that the
serial port is updated at the same rate, as any error between the
two will accumulate and eventually cause the DAC engine to have
to resynchronize with the serial port, which will cause erroneous
values on the DAC output pins.
DFS
DIN
RESYNC*
LOAD DAT
*RESYNC IS ONLY USED WHEN THE DAC BECOMES
UNSYNCHRONIZED WITH THE SERIAL PORT
DAC ENGINE
DAC DATA REGISTER
SERIAL PORT
VOUT
Figure 12. DAC Engine
In most cases, it is easy to keep a DSP in synchronization with
the AD74111 if they are both run from the same clock or the
DSP clock is a multiple of the AD74111’s MCLK. In this case,
REV. 0
–11–
Page 12

AD74111
there will be a fixed relationship between the instruction cycle
time of the DSP program and the AD74111, so a timer could be
used to accurately control the DAC updates. If a timer is not
available, the Multiframe-Sync (MFS) mode could be used to
generate a DFS pulse every 16 or 32 DCLKs, allowing the DSP
to accurately control the number of DCLKs between updates
using an autobuffering or DMA type technique. In all cases for
Slave mode operation, there should be 128 DCLKs (Normal
mode) or 256 DCLKs (Fast mode) between DAC updates. The
ADC operates in a similar manner; however, if the DSP does not
read an ADC result, this will appear only as a missed sample and
will not be audible. Slave mode is most suited to state-machine
type applications where the number of DCLKs and their
relationships to the other interface signals can be controlled.
1/
f
S
DIN
DOUT
DFS
(MM16)
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
STATUS
(16 BITS)
(16 BITS)
DAC
(16 BITS)
ADC
(16 BITS)
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
Figure 13. 16-Bit Mixed Mode, Word Length = 16 Bits
Table II. Serial Mode Selection
CRD:2 CRC:5, 4
CRD:3 DSP Word Operating
DM/MM Mode Width Mode Figure
0016 16-Bit Data Mode 15
0116 32-Bit Data Mode 19
1016 16-Bit Mixed Mode 13
1116 32-Bit Mixed Mode 17
00>16 16-Bit Data Mode 16
01>16 32-Bit Data Mode 20
10>16 16-Bit Mixed Mode 14
11>16 32-Bit Mixed Mode 18
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
STATUS
(16 BITS)
(16 BITS)
DAC
(16 BITS)
ADC
(16 BITS)
DIN
DOUT
DFS
(MM16)
DIN
DOUT
DFS
(MM16)
1/
f
S
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
16 DCLKS
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
Figure 14. 16-Bit Mixed Mode, Word Length = 24 Bits
1/
f
S
DAC
(16 BITS)
ADC
STATUS
(16 BITS)
(16 BITS)
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
DAC
(16 BITS)
ADC
STATUS
(16 BITS)
(16 BITS)
Figure 15. 16-Bit Data Mode, Word Length = 16 Bits
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
REV. 0–12–
Page 13

AD74111
1/f
S
DIN
DOUT
DFS
(MM16)
DIN
DOUT
DFS
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
16 DCLKs
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
Figure 16. 16-Bit Data Mode, Word Length = 24 Bits
1/
f
S
DAC DATA
(16 BITS)
ADC DATA
(16 BITS)
32 DCLKs
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
Figure 17. 32-Bit Mixed Mode, Word Length = 16 Bits
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
DIN
DOUT
DFS
DIN
DOUT
DFS
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
DAC DATA
(16 BITS)
ADC DATA
(16 BITS)
f
1/
S
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
32 DCLKS
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
Figure 18. 32-Bit Mixed Mode, Word Length = 24 Bits
1/
f
S
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
CONTROL
(16 BITS)
STATUS
(16 BITS)
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
REV. 0
Figure 19. 32-Bit Data Mode, Word Length = 16 Bits
–13–
Page 14

AD74111
1/
f
S
DIN
DOUT
DFS
DFS
DIN
DOUT
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
C
S
128 DCLKs (NORMAL MODE)
256 DCLKs (FAST MODE)
DAC DATA
(24 BITS)
ADC DATA
(24 BITS)
Figure 20. 32-Bit Data Mode, Word Length = 24 Bits
1/f
S
32 DCLKs
DAC
ADC ADC
C DAC
S
Figure 21. Multiframe Sync 32-Bit Mixed Mode
1/f
S
32 DCLKs
DFS
DIN
DOUT
DFS
DOUT
DIN
DAC
ADC
C
S
DAC
ADC
Figure 22. Multiframe Sync 32-Bit Data Mode
1/f
16 DCLKS
S
Figure 23. Multiframe Sync 16-Bit Mixed Mode
DAC
ADC
C
S
DAC
ADC
REV. 0–14–
Page 15

1/
f
16 DCLKs
DFS
DIN
DAC DAC
DOUT
ADC ADC
S
Figure 24. Multiframe Sync 16-Bit Data Mode
Table III. Multiframe Sync Selection
CRD:9 CRD:3 CRC:2
MFS DM/MM DSP Mode Operating Mode Figure
10 0 16-Bit Data Mode 24
10 1 32-Bit Data Mode 22
11 0 16-Bit Mixed Mode 23
11 1 32-Bit Mixed Mode 21
AD74111
Table IV. Control Register Map
Address (Binary) Name Description Type Width Reset Setting
0 0 0 0 CRA Control Register A R/W 10 00h
0 0 0 1 CRB Control Register B R/W 10 00h
0 0 1 0 CRC Control Register C R/W 10 00h
0 0 1 1 CRD Control Register D R/W 10 08h or 09h*
0 1 0 0 CRE Control Register E R/W 10 00h
0 1 0 1 CRF Control Register F R 10 00h
0 1 1 0 CRG Control Register G R/W 10 00h
*09h if DIN is low and 08h if DIN is high.
Table V. Control Word Descriptions
Bit Field Description
15 R/W When this bit is high, the contents of the data field will be written to the register specified by the Address
Field. When this bit is low, a read of the register specified by the Address Field will occur at the next
sample interval; the contents of the Data Field are ignored.
14–11 Register Address This 4-bit field is used to select one of the seven control registers of the AD74111.
10 Reserved This bit is reserved and should always be programmed with zero.
9–0 Data Field This 10-bit field holds the data that is to be written to or read from the register specified in the Address Field.
REV. 0
–15–
Page 16

AD74111
Table VI. Control Register A
Function
ADC Input Reference
R/W ADDRESS RES Reserved Amplifier ADC DAC Reference Amplifier Reserved
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7 6 5 4 3 2 1, 0
1 0000 0 0 0 = Off 0 = Off 0 = Off 0 = Off 0 = Off 0
1 = On 1 = On 1 = On 1 = On 1 = On
Table VII. Control Register B
Function
Third MCLK Second MCLK First MCLK
R/W ADDRESS RES Reserved Divider Divider Divider
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6 5, 4 3, 2 1, 0
1 0001 0 0 00 = Divide by 1 00 = Divide by 1 00 = Divide by 1
01 = Divide by 2 01 = Divide by 2 01 = Divide by 2
10 = Divide by 4 10 = Divide by 3 10 = Divide by 3
11 = Divide by 1 11 = Divide by 1 11 = Divide by 1
Table VIII. Control Register C
Function
DAC and ADC Low Group DAC ADC High-
R/W ADDRESS RES Reserved Word Width Delay De-emphasis Pass Filter
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6 5, 4 3 2, 1 0
1 0010 0 0 00 = 16 Bits 0 = Disabled 00 = None 0 = Disabled
01 = 20 Bits 1 = Enabled 01 = 44.1 kHz 1 = Enabled
10 = 24 Bits 10 = 32 kHz
11 = 24 Bits 11 = 48 kHz
Table IX. Control Register D
Function
Master/
R/W ADDRESS RES Multiframe Sync Reserved DM/MM DSP Mode Fast DCLK Slave
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9 8, 7, 6, 5, 4 3 2 1 0
1 0011 0 0 = Normal Mode 0 0 = Data Mode 0 = 16 Bits 0 = 128 ⫻ f
1 = MFS Mode 1 = Mixed Mode 1 = 32 Bits 1 = 256 ⫻ fS1 = Master
0 = Slave
S
REV. 0–16–
Page 17

AD74111
Table X. Control Register E
Function
ADCL Peak ADC DAC
R/W ADDRESS RES Reserved Enable ADC Gain Mute Mute
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6 5 4, 3, 2 1 0
1 0100 0 0 0 = Disabled 000 = 0 dB 0 = Normal 0 = Normal
1 = Peak Enable 001 = 3 dB 1 = Mute 1 = Mute
010 = 6 dB
011 = 9 dB
1XX = 12 dB
Table XI. Control Register F
Function
R/W ADDRESS RES Reserved ADC Input Peak Level
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
000000 = 0 dBFS
000001 = –1 dBFS
0 0101 0 0 000010 = –2 dBFS
111110 = –62 dBFS
111111 = –63 dBFS
Table XII. Control Register G
Function
R/W ADDRESS RES DAC Volume
15 14, 13, 12, 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
0000000000 = 0 dBFS
0000000001 = (1023/1024) dBFS
1 0110 0 0000000010 = (1022/1024) dBFS
1111111110 = (2/1024) dBFS
1111111111 = Mute
REV. 0
–17–
Page 18

AD74111
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP]
(RU-16)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
5.10
5.00
4.90
0.15
0.05
4.50
4.40
4.30
PIN 1
16
0.65
BSC
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153AB
0.10
0.30
0.19
9
81
1.20
MAX
6.40
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
0.20
0.09
0.75
8
0
0.60
0.45
REV. 0–18–
Page 19

–19–
Page 20

C03069–0–2/03(0)
–20–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...