Page 1
Dual Picoampere Input
Current Bipolar Op Amp
AD706
FEATURES
High DC Precision
100 V Max Offset Voltage
1.5 V/C Max Offset Drift
200 pA Max Input Bias Current
0.5 V p-p Voltage Noise, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
750 A Supply Current
Available in 8-Lead Plastic Mini-DlP
and Surface-Mount (SOIC) Packages
Available in Tape and Reel in Accordance with
EIA-481A Standard
Quad Version: AD704
APPLICATIONS
Low Frequency Active Filters
Precision Instrumentation
Precision Integrators
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD706 is a dual, low power, bipolar op amp that has the
low input bias current of a JFET amplifier, but which offers a
significantly lower I
drift over temperature. It utilizes superbeta
B
bipolar input transistors to achieve picoampere input bias current
levels (similar to FET input amplifiers at room temperature),
while its I
JFET amp, for which I
typically only increases by 5⫻ at 125°C (unlike a
B
doubles every 10°C for a 1000⫻
B
increase at 125°C). The AD706 also achieves the microvolt
offset voltage and low noise characteristics of a precision bipolar
input amplifier.
Since it has < 200 pA of bias current, the AD706 does not
require the commonly used “balancing” resistor. Furthermore,
the current noise is only 50 fA/√Hz, which makes this amplifier
usable with very high source impedances. At 600 A max supply
current (per amplifier), the AD706 is well suited for today’s
high density boards.
The AD706 is an excellent choice for use in low frequency
active filters in 12-bit and 14-bit data acquisition systems, in
precision instrumentation, and as a high quality integrator. The
AD706 is internally compensated for unity gain and is available
in five performance grades. The AD706J is rated over the
commercial temperature range of 0°C to +70°C. The AD706A is
rated for the extended industrial temperature range of –40°C
to +85°C.
The AD706 is offered in two varieties of an 8-lead package:
plastic mini-DIP and surface-mount (SOIC).
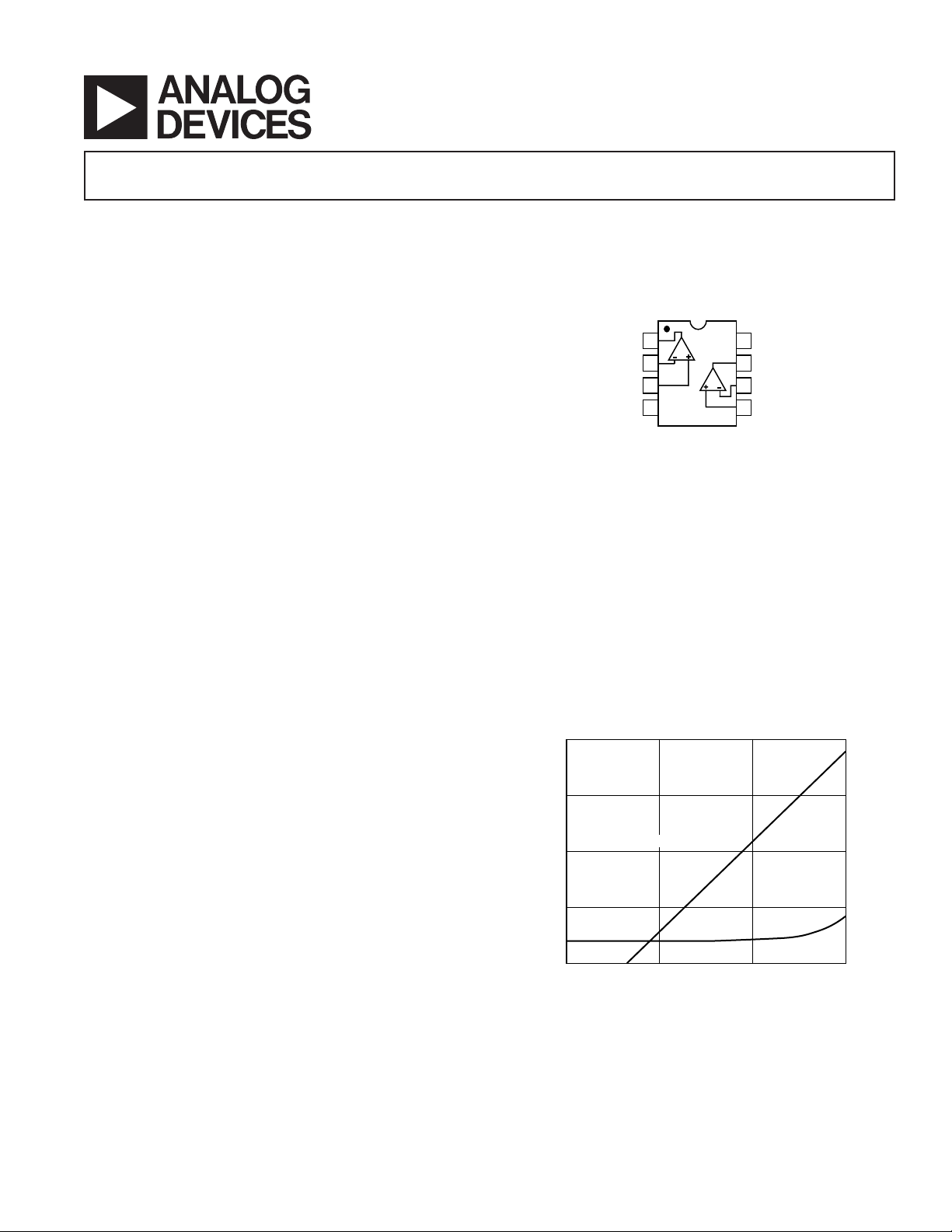
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Plastic Mini-DIP (N) and
Plastic SOIC (R) Packages
AMPLIFIER 1 AMPLIFIER 2
OUTPUT
–IN
IN
1
2
3
4
AD706
TOP VIEW
8
7
6
5
V
OUTPUT
–IN
INV–
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD706 is a dual low drift op amp that offers JFET
level input bias currents, yet has the low I
drift of a bipolar
B
amplifier. It may be used in circuits using dual op amps
such as the LT1024.
2. The AD706 provides both low drift and high dc precision.
3. The AD706 can be used in applications where a chopper
amplifier would normally be required but without the
chopper’s inherent noise.
100
10
– nA
B
1
TYPICAL I
0.1
0.01
–55 +125+25 +110
TYPICAL JFET AMP
AD706
TEMPERATURE – C
Figure 1. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
REV. E
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
AD706–SPECIFICATIONS
(@ TA = +25C, VCM = 0 V and 15 V dc, unless otherwise noted.)
AD706J/A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE
Initial Offset 30 100 µV
Offset T
MIN
to T
MAX
40 150 µV
vs. Temperature, Average TC 0.2 1.5 µV/°C
vs. Supply (PSRR) V
to T
T
MIN
MAX
= ±2 V to ± 18 V 110 132 dB
S
VS = ±2.5 V to ± 18 V 106 126 dB
Long Term Stability 0.3 µV/Month
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
1
VCM = 0 V 50 200 pA
= ±13.5 V 250 pA
V
CM
vs. Temperature, Average TC 0.3 pA/°C
to T
T
MIN
T
MIN
to T
MAX
MAX
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT V
VCM = 0 V 300 pA
VCM = ±13.5 V 400 pA
= 0 V 30 150 pA
CM
= ±13.5 V 250 pA
V
CM
vs. Temperature, Average TC 0.6 pA/°C
to T
T
MIN
T
MIN
to T
MAX
MAX
VCM = 0 V 80 250 pA
VCM = ±13.5 V 80 350 pA
MATCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage 150 µV
Input Bias Current
to T
T
2
MIN
T
MIN
to T
MAX
MAX
250 µV
300 pA
500 pA
Common-Mode Rejection 106 dB
to T
T
MIN
MAX
106 dB
Power Supply Rejection 106 dB
to T
T
MIN
MAX
104 dB
Crosstalk (Figure 2a) @ f = 10 Hz
RL = 2 kΩ 150 dB
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Unity Gain Crossover Frequency 0.8 MHz
Slew Rate G = –1 0.15 V/µs
T
MIN
to T
MAX
0.15 V/µs
INPUT IMPEDANCE
Differential 40||2 MΩ||pF
Common Mode 300||2 GΩ||pF
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Common-Mode Voltage ±13.5 ±14 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio V
= ±13.5 V 110 132 dB
CM
T
MIN
to T
MAX
108 128 dB
INPUT CURRENT NOISE 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 3 pA p-p
f = 10 Hz 50 fA/√Hz
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 0.5 µV p-p
f = 10 Hz 17 nV/√Hz
f = 1 kHz 15 22 nV/√Hz
OPEN-LOOP GAIN V
= ±12 V
O
= 10 kΩ 200 2000 V/mV
R
LOAD
T
MIN
= ±10 V
V
O
R
LOAD =
T
MIN
to T
MAX
2 kΩ 200 1000 V/mV
to T
MAX
150 1500 V/mV
150 1000 V/mV
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Voltage Swing R
= 10 kΩ±13 ±14 V
LOAD
to T
T
MIN
MAX
±13 ± 14 V
Current Short Circuit ±15 mA
Capacitive Load Drive Capability Gain = +1 10,000 pF
REV. E–2–
Page 3
AD706
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
OUTPUT A
–INPUT A
+INPUT A
–V
S
0.074 (1.88)
OUTPUT B
–INPUT B
+INPUT B
0.118 (3.00)
+V
S
SPECIFICATIONS
(continued)
AD706J/A
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
POWER SUPPLY
Rated Performance ±15 V
Operating Range ±2.0 ±18 V
Quiescent Current, Total 0.75 1.2 mA
T
MIN
to T
MAX
0.8 1.4 mA
TRANSISTOR COUNT Number of Transistors 90
NOTES
1
Bias current specifications are guaranteed maximum at either input.
2
Input bias current match is the difference between corresponding inputs (IB of –IN of Amplifier 1 minus IB of –IN of Amplifier 2).
∆∆V
CMRR match is the difference between
PSRR match is the difference between
All min and max specifications are guaranteed.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
OS1
for Amplifier 1 and
V
CM
∆∆V
OS1
V
for Amplifier 1 and
SUPPLY
1
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Internal Power Dissipation
(Total: Both Amplifiers)
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 650 mW
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± V
Differential Input Voltage3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +0.7 V
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite
Storage Temperature Range (N, R) . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range
AD706J . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
AD706A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–40°C to +85°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 10 secs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Specification is for device in free air:
8-Lead Plastic Package: θJA = 100°C/W
8-Lead Small Outline Package: θJA = 155°C/W
3
The input pins of this amplifier are protected by back-to-back diodes. If the
differential voltage exceeds ± 0.7 V, external series protection resistors should be
added to limit the input current to less than 25 mA.
∆∆V
OS2
for Amplifier 2, expressed in dB.
V
CM
∆∆V
OS2
for Amplifier 2, expressed in dB.
V
SUPPLY
Model Range Description Option
AD706JN 0°C to 70°C Plastic DIP N-8
AD706JR 0°C to 70°C SOIC R-8
S
AD706JR-REEL 0°C to 70°CTape and Reel R-8
AD706JR-REEL7 0°C to 70°CTape and Reel R-8
AD706AR –40°C to +85°C SOIC R-8
AD706AR-REEL –40°C to +85°CTape and Reel R-8
AD706AR-REEL7 –40°C to +85°CTape and Reel R-8
AD706ARZ-REEL* –40°C to +85°CTape and Reel R-8
*Lead-free part.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package
METALIZATION PHOTOGRAPH
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
Contact factory for latest dimensions.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
AD706 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. E
–3–
Page 4

AD706–Typical Performance Characteristics
(Default Conditions: 5 V, CL = 5 pF, G = 2, Rg = Rf = 1 kΩ, RL = 2 kΩ, VO = 2 V p-p, Frequency = 1 MHz, TA = 25C)
1000
SAMPLE
SIZE: 3000
800
600
400
NUMBER OF UNITS
200
0
–80 –40 0 40 80
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE –
V
TPC 1. Typical Distribution
of Input Offset Voltage
V
S
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
1.5
1.0
(REFERRED TO SUPPLY VOLTAGES)
0.5
INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE LIMIT – Volts
–V
S
0 5101520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – Volts
TPC 4. Input Common-Mode Voltage
Range vs. Supply Voltage
1000
SAMPLE
SIZE: 5100
800
600
400
NUMBER OF UNITS
200
0
–160 –80 0 80 160
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
TPC 2. Typical Distribution
of Input Bias Current
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE – Volts p-p
0
1k 10k 1M
FREQUENCY – Hz
100k
TPC 5. Large Signal Frequency
Response
1000
SAMPLE SIZE: 2400
800
600
400
NUMBER OF UNITS
200
0
–120 –60 0 60 120
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT – pA
TPC 3. Typical Distribution
of Input Offset Current
100
SOURCE RESISTANCE
MAY BE EITHER BALANCED
10
1.0
OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT – V/C
0.1
OR UNBALANCED
FOR INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
1k 10k 100M
100k 1M 10M
SOURCE RESISTANCE –
TPC 6. Offset Voltage Drift
vs. Source Resistance
200
SAMPLE SIZE: 375
–55C TO 125C
160
120
80
NUMBER OF UNITS
40
0
–0.8
–0.4 0 0.4 0.8
OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT – V/C
TPC 7. Typical Distribution
of Offset Voltage Drift
4
3
2
1
CHANGE IN OFFSET VOLTAGE – V
0
0
1234
WARM-UP TIME – Minutes
TPC 8. Change in Input Offset
Voltage vs. Warm-Up Time
60
40
20
0
–20
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
–40
–60
5
–15
–10 –5 0 5
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE – Volts
POSITIVE I
NEGATIVE I
B
B
10
15
TPC 9. Input Bias Current vs.
Common-Mode Voltage
REV. E–4–
Page 5

AD706
g
1000
100
10
VOLTAGE NOISE – nV/冪Hz
1
110 1000
FREQUENCY – Hz
100
TPC 10. Input Noise Voltage
Spectral Density
1000
900
800
700
QUIESCENT CURRENT – A
600
0
5101520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – Volts
+125C
+25C
–55C
TPC 13. Quiescent Supply
Current vs. Supply Voltage
1000
100
100 10k
10
CURRENT NOISE – fA/冪Hz
1
110 1000
20M
FREQUENCY – Hz
100
V
OUT
TPC 11. Input Noise Current
Spectral Density
160
140
120
100
80
CMRR – dB
60
40
20
0
0.1
110100 10k
1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
100k
1M
TPC 14. Common-Mode Rejection
Ratio vs. Frequency
0.5V
0
5
TIME – Seconds
TPC 12. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
Noise Voltage
180
160
140
120
100
PSRR – dB
80
60
40
20
0.1
110100 10k
+ PSRR
FREQUENCY – Hz
– PSRR
1k
100k
TPC 15. Power Supply Rejection
Ratio vs. Frequency
10
1M
10M
–55C
+25C
+125C
1M
OPEN-LOOP VOLTAGE GAIN
100k
12 46810 100
LOAD RESISTANCE – k
TPC 16. Open-Loop Gain vs. Load
Resistance vs. Load Resistance
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
OPEN-LOOP VOLTAGE GAIN – dB
–20
0.01
0.1 1 10 1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
100
GAIN
PHASE
100k 10M
10k
1M
TPC 17. Open-Loop Gain and
Phase Shift vs. Frequency
0
30
60
rees
90
120
150
180
PHASE SHIFT – De
210
240
+V
S
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
+1.5
+1.0
(REFERRED TO SUPPLY VOLTAGES)
+0.5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – Volts
–V
S
0 5101520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – Volts
TPC 18. Output Voltage Swing vs.
Supply Voltage
REV. E
–5–
Page 6

AD706
–80
–100
–120
CROSSTALK – dB
–140
–160
10
100 1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 2a. Crosstalk vs. Frequency
+V
0.1F
S
2
1/2
AD706
3
4
SINE WAVE
GENERATOR
–V
20k
S
0.1F
1000
100
CLOSED-LOOP OUTPUT IMPEDANCE –
0.001
10
1
0.1
0.01
1
AV = –1000
AV = + 1
I
= +1mA
OUT
10 100 1k 10k
FREQUENCY – Hz
100k
Figure 3. Magnitude of Closed-Loop Output
Impedance vs. Frequency
R
+V
1/2
AD706
F
S
0.1F
8
4
2k
R
L
V
OUT
C
L
V
R
2k
L
OUT1
20V p-p
V
IN
1
+V
S
2.21k
8
6
1/2
AD706
5
CROSSTALK = 20 LOG
1F 0.1F
7
Figure 2b. Crosstalk Test Circuit
Figure 4b. Unity Gain Follower Large
Signal Pulse Response, RF = 10 kΩ,
= 1,000 pF
C
L
V
OUT2
Figure 4a. Unity Gain Follower (For large signal
applications, resistor RF limits the current
through the input protection diodes.)
V
OUT2
V
OUT1
–20dB
10
Figure 4c. Unity Gain Follower
Small Signal Pulse Response,
= 0 Ω, CL = 100 pF
R
F
SQUARE
WAVE
INPUT
0.1F
–V
S
Figure 4d. Unity Gain Follower
Small Signal Pulse Response,
= 0 Ω, CL = 1000 pF
R
F
REV. E–6–
Page 7

10k
+V
S
+
0.1F
R
L
2.5k
0.1µF
S
V
IN
SQUARE
WAVE
INPUT
10k
–
1/2
AD706
+
8
4
–V
Figure 5a. Unity Gain Inverter Connection
AD706
V
OUT
C
L
Figure 5b. Unity Gain Inverter Large
Signal Pulse Response, CL = 1,000 pF
Figure 5c. Unity Gain Inverter Small
Signal Pulse Response, CL = 100 pF
Figure 6 shows an in-amp circuit that has the obvious advantage
of requiring only one AD706, rather than three op amps, with
subsequent savings in cost and power consumption. The transfer
function of this circuit (without R
VVV
for R1 = R4 and R2 = R3.
()1
=− +
OUT IN1 IN2
) is
G
R
4
3
R
Input resistance is high, thus permitting the signal source to
have an unbalanced output impedance.
RG (OPTIONAL)
R1
49.9k
RP*
V
IN1
1k
RP*
V
IN2
1k
*OPTIONAL INPUT PROTECTION RESISTOR FOR GAINS GREATER
THAN 100 OR INPUT VOLTAGES EXCEEDING THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE.
R2 R3
+V
S
0.1F
8
2
–
3
+
V
OUT
FOR R1 = R4, R2 = R3
A1
1/2
AD706
= (V
1
– V
IN1
IN2
) (1+ ) + ( )
R4
49.9k
1/2
AD706
5
–
A2
7
6
+
4
–V
2R4
R
S
G
R4
R3
OUTPUT
0.1F
Figure 6. Two Op Amp Instrumentation Amplifier
Furthermore, the circuit gain may be fine trimmed using an
optional trim resistor, R
. Like the three op amp circuit, CMR
G
increases with gain, once initial trimming is accomplished—but
Figure 5d. Unity Gain Inverter Small
Signal Pulse Response, CL = 1000 pF
CMR is still dependent upon the ratio matching of Resistors R1
through R4. Resistor values for this circuit, using the optional
gain resistor, R
, can be calculated using
G
R1= R4 = 49.9kΩ
R2 = R3 =
RG=
49.9 kΩ
0.9 G −1
99.8 kΩ
0.06 G
where G = The desired circuit gain.
Table I provides practical 1% resistance values. Note that
without resistor R
, R2 and R3 = 49.9 kΩ/G–1.
G
Table I. Operating Gains of Amplifiers A1 and A2 and
Practical 1% Resistor Values for the Circuit of Figure 6
Circuit Gain Gain of A1 Gain of A2 R2, R3 R1, R4
1.10 11.00 1.10 499 kΩ 49.9 kΩ
1.33 4.01 1.33 150 kΩ 49.9 kΩ
1.50 3.00 1.50 100 kΩ 49.9 kΩ
2.00 2.00 2.00 49.9 kΩ 49.9 kΩ
10.1 1.11 10.10 5.49 kΩ 49.9 kΩ
101.0 1.01 101.0 499 Ω 49.9 kΩ
1001 1.001 1001 49.9 Ω 49.9 kΩ
For a much more comprehensive discussion of in-amp applications, refer to the Instrumentation Amplifier Applications Guide—
available free from Analog Devices, Inc.
REV. E
–7–
Page 8

AD706
C2
C1
+
3
1/2
AD706
–
2
–V
R5
2M
4
S
1
0.1F
C5
0.01F
OPTIONAL BALANCE
RESISTOR NETWORKS*
R1
INPUT
*WITHOUT THE NETWORK,
PINS 1 AND 2, AND 6 AND 7
OF THE AD706 ARE TIED
TOGETHER.
CAPACITORS C1 AND C2
ARE SOUTHERN ELECTRONICS
MPCC, POLYCARB 5%, 50V
1M
R2
1M
Figure 7. 1 Hz, 4-Pole Active Filter
1 Hz, 4-Pole, Active Filter
Figure 7 shows the AD706 in an active filter application. An
important characteristic of the AD706 is that both the input bias
current, input offset current, and their drift remain low over
most of the op amp’s rated temperature range. Therefore, for
most applications, there is no need to use the normal balancing
resistor. Adding the balancing resistor enhances performance at
high temperatures, as shown by Figure 8.
R3
1MR41M
180
120
60
–60
–120
+V
S
C3
5
C4
0
AD706
6
R6
2M
0.1F
8
+
1/2
7
–
C6
0.01F
WITHOUT OPTIONAL
BALANCE RESISTOR, R3
WITH OPTIONAL BALANCE
OUTPUT
RESISTOR, R3
OFFSET VOLTAGE OF FILTER CIRCUIT (RTI) – V
–180
–40 0 40
TEMPERATURE – C
80 120
Figure 8. VOS vs. Temperature Performance
of the 1 Hz Filter
Table II. 1 Hz, 4-Pole, Low Pass Filter Recommended Component Values
Section 1 Section 2
Desired Low Frequency Frequency C1 C2 C3 C4
Pass Response (Hz) Q (Hz) Q (F) (F) (F) (F)
Bessel 1.43 0.522 1.60 0.806 0.116 0.107 0.160 0.0616
Butterworth 1.00 0.541 1.00 1.31 0.172 0.147 0.416 0.0609
0.1 dB Chebychev 0.648 0.619 0.948 2.18 0.304 0.198 0.733 0.0385
0.2 dB Chebychev 0.603 0.646 0.941 2.44 0.341 0.204 0.823 0.0347
0.5 dB Chebychev 0.540 0.705 0.932 2.94 0.416 0.209 1.00 0.0290
1.0 dB Chebychev 0.492 0.785 0.925 3.56 0.508 0.206 1.23 0.0242
NOTE
Specified Values are for a –3 dB point of 1.0 Hz. For other frequencies simply scale capacitors C1 through C4 directly, i.e. for 3 Hz
Bessel response, C1 = 0.0387 µF, C2 = 0.0357 µF, C3 = 0.0533 µF, C4 = 0.0205 µF.
REV. E–8–
Page 9

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC]
(R-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
5.00 (0.1968)
4.80 (0.1890)
4.00 (0.1574)
3.80 (0.1497)
85
6.20 (0.2440)
5.80 (0.2284)
41
AD706
1.27 (0.0500)
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0040)
COPLANARITY
0.10
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012AA
1.75 (0.0688)
1.35 (0.0532)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
0.50 (0.0196)
0.25 (0.0099)
8
0
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
8-Lead Plastic Dual-in-Line Package [PDIP]
(N-8)
Dimensions shown in inches and (millimeters)
0.375 (9.53)
0.365 (9.27)
0.355 (9.02)
8
1
0.100 (2.54)
0.180
(4.57)
MAX
0.150 (3.81)
0.130 (3.30)
0.110 (2.79)
0.022 (0.56)
0.018 (0.46)
0.014 (0.36)
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES; MILLIMETER DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF INCH EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-095AA
BSC
5
4
0.295 (7.49)
0.285 (7.24)
0.275 (6.98)
0.015
(0.38)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
0.060 (1.52)
0.050 (1.27)
0.045 (1.14)
0.325 (8.26)
0.310 (7.87)
0.300 (7.62)
0.150 (3.81)
0.135 (3.43)
0.120 (3.05)
0.015 (0.38)
0.010 (0.25)
0.008 (0.20)
45
REV. E
–9–
Page 10

AD706
Revision History
Location Page
10/03–Data Sheet changed from REV. D to REV. E
Removed the K Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Universal
Updated FEATURES list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Updated PRODUCT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Renumbered TPCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Renumbered Figures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Updated OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
10/02–Data Sheet changed from REV. C to REV. D
Deleted 8-Lead CERDIP (Q-8) Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Universal
Edits to FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Edits to PRODUCT DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Edits to SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Edits to ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Edits to ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Updated OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
REV. E–10–
Page 11

–11–
Page 12

C00820–0–10/03(E)
–12–
 Loading...
Loading...