Page 1
Dual-Channel, 12-Bit 125 MSPS
a
FEATURES
Two Independent 12-Bit, 125 MSPS ADCs
Channel-to-Channel Isolation, > 80 dB
AC-Coupled Signal Conditioning Included
Gain Flatness up to Nyquist, < 0.1 dB
Input VSWR 1.1:1 to Nyquist
80 dB Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
Two’s Complement Output Format
3.3 V or 5 V CMOS-Compatible Output Levels
1.5 W Per Channel
Single-Ended or Differential Input
350 MHz Input Bandwidth
APPLICATIONS
Wireless and Wired Broadband Communications
Base Stations and “Zero-IF” or Direct IF Sampling
Subsystems
Wireless Local Loop (WLL)
Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS)
Radar and Satellite Subsystems
IF Sampling A/D Converter
AD10226
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD10226 offers two complete ADC channels with on-module
signal conditioning for improved dynamic performance. Each wide
dynamic range ADC has a transformer coupled front end
optimized for direct-IF sampling. The AD10226 has on-chip
track-and-hold circuitry and utilizes an innovative architecture to
achieve 12-bit, 125 MSPS performance. The AD10226 uses
innovative high density circuit design to achieve exceptional
performance, while still maintaining excellent isolation and providing for board area savings.
The AD10226 operates with 5.0 V analog supply and 3.3 V digital
supply. Each channel is completely independent, allowing operation with independent ENCODE and analog inputs. The AD10226
is available in a 35 mm square 385-lead BGA package.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Guaranteed sample rate of 125 MSPS
2. Input signal conditioning included with full-power bandwidth
to 350 MHz
3. Industry-leading IF sampling performance
D0A
(LSB)
D1A
D2A
D3A
D4A
D5A
D6A
D7A
D8A
D9A
D10A
D11A
(MSB)
DFS_A
SFDR_A
12
ENCODEA
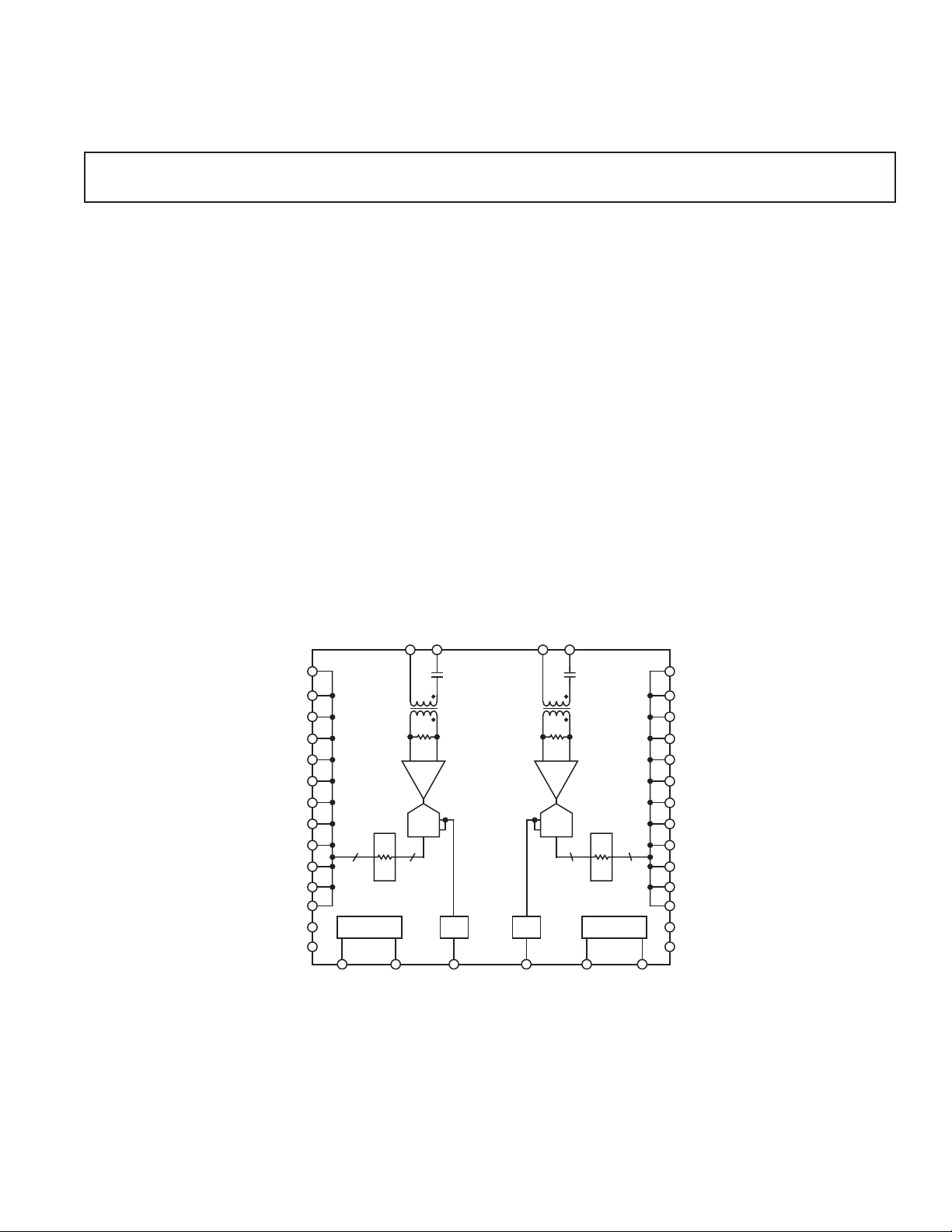
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AINA2
AINA1 AINB1
T1A
50⍀
T/H T/H
ADC
12
OUTPUT
RESISTORS
TIMING
ENCODEA
REF
REF_A_OUT
AD10226
REF_B_OUT
AINB2
50⍀
ADC
REF
T1B
12 12
OUTPUT
RESISTORS
TIMING
ENCODEB
ENCODEB
D0B
(LSB)
D1B
D2B
D3B
D4B
D5B
D6B
D7B
D8B
D9B
D10B
D11B
(MSB)
DFS_B
SFDR_B
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
Page 2
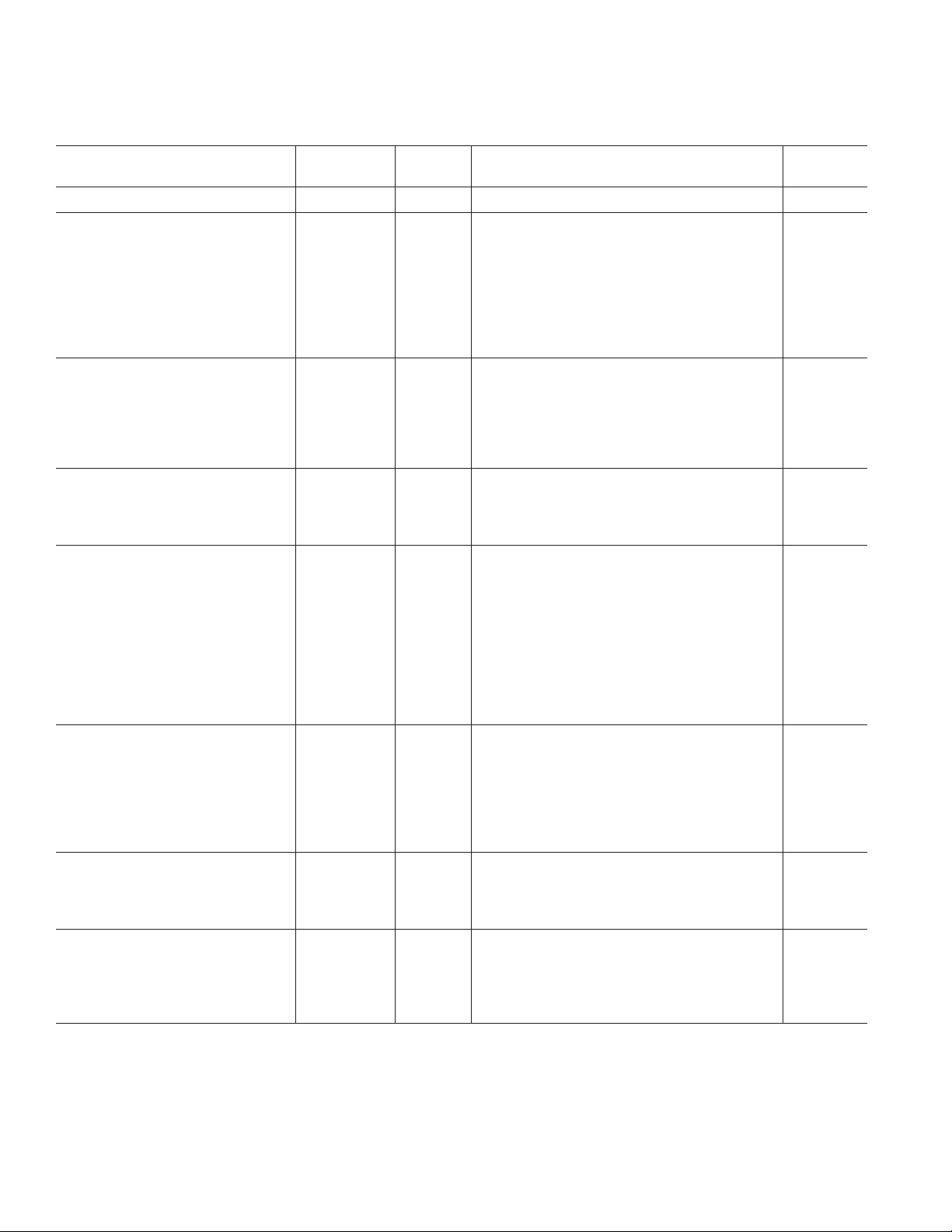
AD10226–SPECIFICATIONS
1
(V
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
= 3.3 V, V
DD
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 12 Bits
DC ACCURACY
Differential Nonlinearity
Integral Nonlinearity
No Missing Codes Full IV Guaranteed
Gain Error
3
2
2
Full IV –0.99 ±0.3 +0.99 LSB
Full IV –1.3 ± 0.75 +1.3 LSB
25°CI –9 ± 1+9% FS
Output Offset 25°CI –12 +2 +12 LSB
Gain Tempco Full V 100 ppm/°C
Offset Tempco Full V –50 ppm/°C
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range 25°CV 1.84 V p-p
Input Impedance 25°CV 50 Ω
Input VSWR
4
Full V 1.1:1 1.25:1 Ratio
Analog Input Bandwidth, High Full IV 300 350 MHz
Analog Input Bandwidth, Low Full IV 1 MHz
ANALOG REFERENCE
Output Voltage 25°CV 2.5 V
Load Current 25°CV 5 mA
Tempco Full V ±80 ppm/°C
SWITCHING PERFORMANCE
5
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 125 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full IV 10 MSPS
Duty Cycle Full IV 45 50 55 %
Aperture Delay (t
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) 25°CV 0.25 ps rms
Output Valid Time (t
Output Propagation Delay (t
Output Rise Time (t
)25°CV 2.1 ns
A
6
)
V
)25°CV 3.5 ns
R
PD
6
)
Full IV 3.0 4.5 ns
Full IV 4.5 6.0 ns
Output Fall Time (tF)25°CV 3.3 ns
DIGITAL INPUTS
ENCODE Input Common-Mode Full IV 3.75 V
Differential Input (ENC, ENC) Full IV 500 mV
Logic “1” Voltage Full IV 2.0 V
Logic “0” Voltage Full IV 0.8 V
Input Resistance Full IV 3 6 kΩ
Input Capacitance 25°CV 3 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Logic “1” Voltage
Logic “0” Voltage
6
6
Full IV 3.1 3.3 V
Full IV 0 0.2 V
Output Coding Two’s Complement
POWER SUPPLY
Power Dissipation
7
8
Full VI 3040 3300 mW
Power Supply Rejection Ratio Full IV ± 0.5 ± 5.0 mV/V
Total I (DV
) Current Full VI 40 60 mA
DD
Total I (AVCC) Current Full VI 540 650 mA
= 5.0 V; ENCODE = 125 MSPS, unless otherwise noted.)
CC
Test
–2–
REV. 0
Page 3
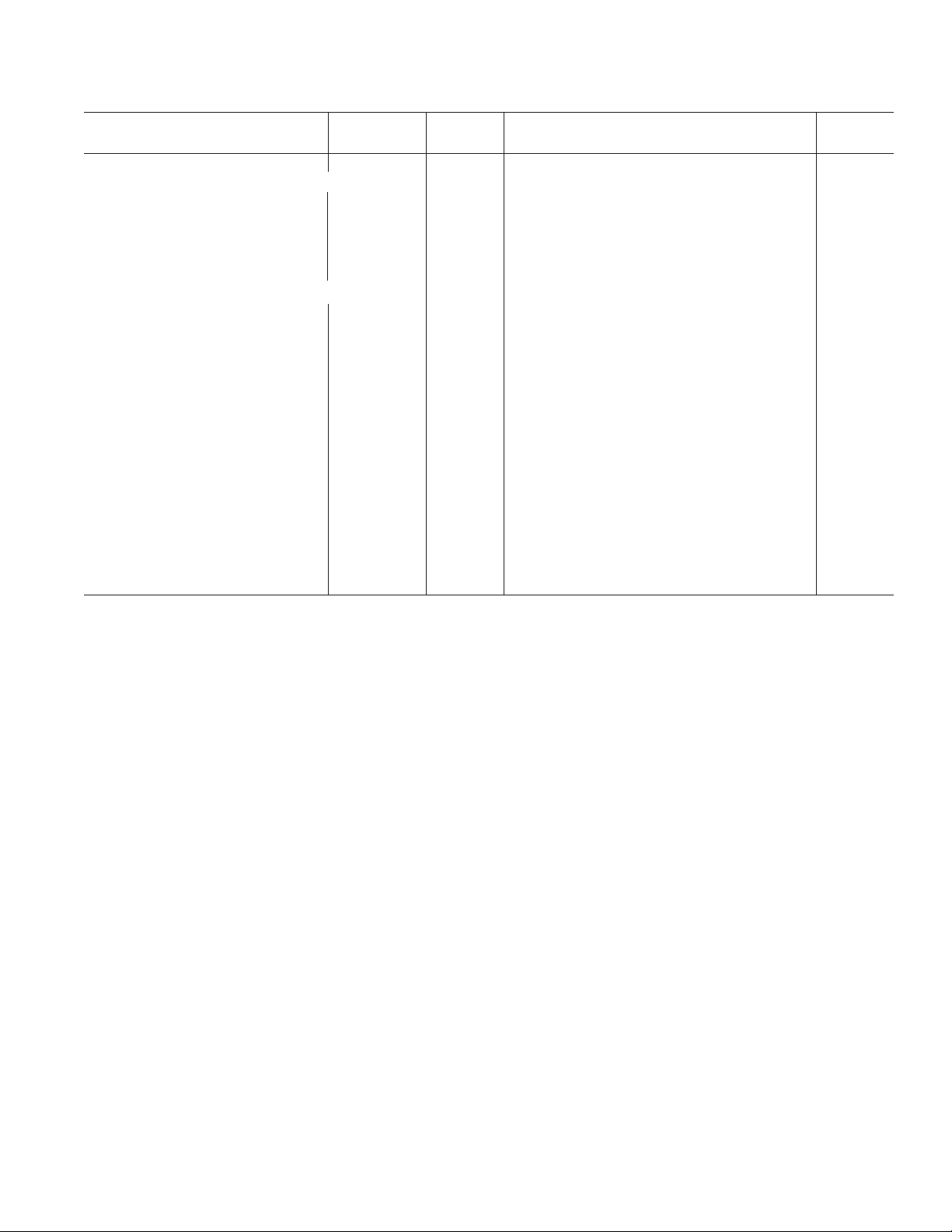
AD10226
Test
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)9 (Without Harmonics)
f
= 10.3 MHz 25°CI 66.5 68.5 dBFS
IN
f
= 49 MHz 25°CV 67 dBFS
IN
= 71 MHz 25°CI 63 66 dBFS
f
IN
f
= 121 MHz 25°CV 64 dBFS
IN
f
= 250 MHz 25°CV 60 dBFS
IN
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SINAD)
= 10.3 MHz 25°CI 65.5 68 dBFS
f
IN
f
= 49 MHz 25°CV 66.5 dBFS
IN
f
= 71 MHz 25°CI 62.5 65 dBFS
IN
= 121 MHz 25°CV 62.5 dBFS
f
IN
f
= 250 MHz 25°CV 59.5 dBFS
IN
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
fIN = 10 MHz 25°CI 76.5 82 dBFS
= 41 MHz 25°CV 77 dBFS
f
IN
f
= 71 MHz 25°CI 66 72 dBFS
IN
f
= 121 MHz 25°CV 71 dBFS
IN
= 250 MHz 25°CV 70 dBFS
f
IN
Two-Tone Intermodulation
Distortion
f
IN
f
IN
12
(IMD)
= 29.3 MHz; fIN = 30.3 MHz 25°CV 78 dBc
= 150 MHz; fIN = 151 MHz 25°CV 70 dBc
Channel-to-Channel Isolation
fIN = 121 MHz Full IV 85 dB
10
(With Harmonics)
11
13
NOTES
1
All ac specifications tested by driving ENCODE and ENCODE differentially, with the analog input applied to AINX1 and AINX2 tied to ground.
2
SFDR enabled (SFDR = 1) for DNL and INL specifications.
3
Gain error measured at 10.3 MHz.
4
Input VSWR, see TPC 14.
5
See Figure 1, Timing Diagram.
6
tV and tPD are measured from the transition points of the ENCODE input to the 50%/50% levels of the digital outputs swing. The digital output load during
test is not to exceed an ac load of 10 pF or a dc current of ± 40 A.
7
Supply voltages should remain stable within ± 5% for normal operation.
8
Power dissipation measures with encode at rated speed.
9
Analog input signal power at –1 dBFS; signal-to-noise (SNR) is the ratio of signal level to total noise (first six harmonics removed). ENCODE = 125 MSPS,
SFDR mode = 1. SNR is reported in dBFS, related back to converter full-scale.
10
Analog input signal power at –1 dBFS; signal-to-noise and distortion (SINAD) is the ratio of signal level to total noise + harmonics. ENCODE = 125 MSPS.
SINAD is reported in dBFS, related back to converter full-scale.
11
Analog input signal equals –1 dBFS; SFDR is ratio of converter full-scale to worst spur.
12
Both input tones at –7 dBFS; two-tone intermodulation distortion (IMD) rejection is the ratio of either tone to the worst third order intermod product.
13
Channel-to-channel isolation tested with A channel/50 Ω terminated (AINA2) grounded and a full-scale signal applied to B channel (AINB2).
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. 0
–3–
Page 4
AD10226
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 V
V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 V
CC
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 V p-p (18 dBm)
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
+ 0.5 V
DD
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 mA
Operating Temperature (Ambient) . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature (Ambient) . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent
damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions outside of those indicated in the operation sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
385-Lead BGA Package:
The typical θ
of the module as determined by an IR scan is
JA
26.25°C/W.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level
I 100% production tested
II 100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at specific
temperatures
III Sample tested only
IV Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization
testing
V Parameter is a typical value only
VI 100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed by design and
characterization testing for industrial temperature range
Table I. Output Coding (V
= 2.5 V) (Two’s Complement)
REF
Code AIN (V) Digital Output
+2047 +0.875 0111 1111 1111
·· ·
·· ·
00 0000 0000 0000
–1 –0.000427 1111 1111 1111
·· ·
·· ·
–2048 –0.875 1000 0000 0000
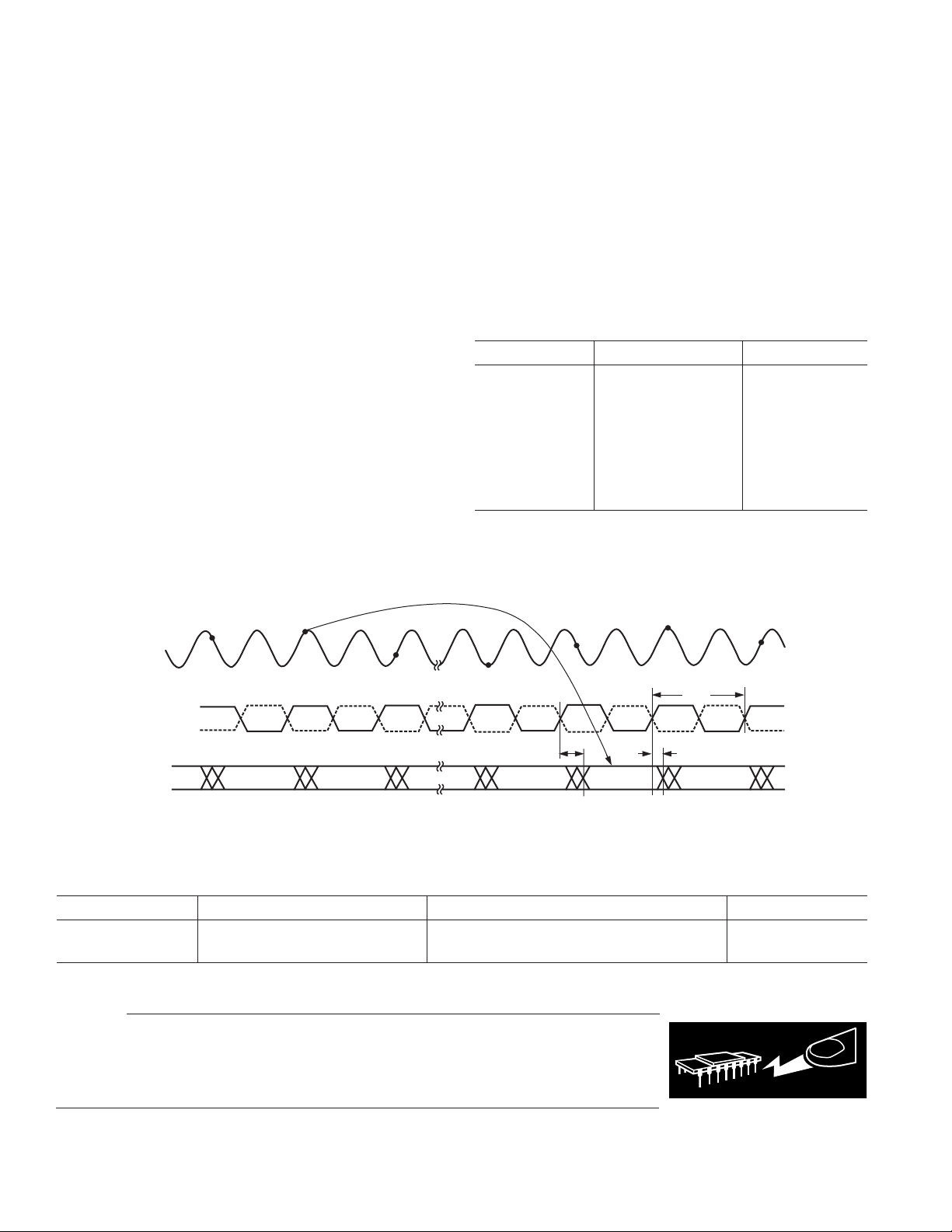
SAMPLE Nⴚ1SAMPLE N SAMPLE Nⴙ10 SAMPLE Nⴙ11
AIN
SAMPLE Nⴙ9SAMPLE Nⴙ1
1/f
ENCODE
ENCODE
D11ⴚD0
t
PD
DATA Nⴚ11 DATA Nⴚ10 Nⴚ9 DATA Nⴚ1 DATA N DATA N ⴙ 1
Nⴚ2
S
t
V
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD10226AB –25°C to +85°C (Ambient) 385-Lead BGA (35 mm 35 mm) B-385
AD10226/PCB 25°CEvaluation Board with AD10226AB
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD10226 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
REV. 0
Page 5
PIN CONFIGURATION
25 23 21 19 17 15 13 11 9 7 5 3 1
24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AD10226
35mm SQUARE
BOTTOM VIEW
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Mnemonic Function
AGNDA A Channel Analog Ground. A and B grounds should be connected as close to the device as possible.
REF_A_OUT A Channel Internal Voltage Reference
NC No connection
A1 Analog Input for A side ADC (– input)
A
IN
A2 Analog Input for A side ADC (+ input)
A
IN
A Analog Positive Supply Voltage (nominally 5.0 V)
AV
CC
DGNDA A Channel Digital Ground
D11A–D0A Digital Outputs for ADC A. D0 (LSB)
ENCODEA Complement of ENCODE
ENCODEA Data conversion initiated on the rising edge of ENCODE input.
A Digital Positive Supply Voltage (nominally 3.3 V)
DV
CC
DGNDB B Channel Digital Ground
D11B–D0B Digital Outputs for ADC B. D0 (LSB)
AGNDB B Channel Analog Ground. A and B grounds should be connected as close to the device as possible.
B Digital Positive Supply Voltage (nominally 3.3 V)
DV
CC
ENCODEB Complement of ENCODE
ENCODEB Data conversion initiated on rising edge of ENCODE input.
REF_B_OUT B Channel Internal Voltage Reference
B1 Analog Input for B side ADC (– input)
A
IN
B2 Analog Input for B side ADC (+ input)
A
IN
B Analog Positive Supply Voltage (nominally 5.0 V)
AV
CC
DFS Data format select. Low = Two’s Complement, High = Binary.
SFDR Mode CMOS control pin that enables (SFDR MODE = 1) a proprietary circuit that may improve the spurious free dynamic
range (SFDR) performance. It is useful in applications where the dynamic range of the system is limited by discrete spurious
frequency content caused by nonlinearities in the ADC transfer function. SFDR Mode = 0 for normal operation.
REV. 0
–5–
Page 6

AD10226
385-LEAD BGA PINOUT
Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal
No. Name No. Name No. Name No. Name No. Name No. Name
A1 AGNDA
A2 AGNDA
A3 AGNDA
A4 AGNDA
A5 AGNDA
A6 AGNDA
A7 DNC
A8 DNC
A9 AGNDA
A10 AV
CC
A
A11 REF_A_OUT
A12 AGNDA
A13 DNC
A14 AGNDB
A15 AGNDB
A16 AV
CC
B
A17 AGNDB
A18 AV
CC
B
A19 DNC
A20 DNC
A21 AGNDB
A22 AGNDB
A23 AGNDB
A24 AGNDB
A25 AGNDB
B1 AGNDA
B2 AGNDA
B3 AGNDA
B4 AGNDA
B5 AGNDA
B6 AGNDA
B7 DNC
B8 DNC
B9 AGNDA
B10 AV
CC
A
B11 REF_A_OUT
B12 AGNDA
B13 DNC
B14 AGNDB
B15 AGNDB
B16 AV
CC
B
B17 AGNDB
B18 AV
CC
B
B19 DNC
B20 DNC
B21 AGNDB
B22 AGNDB
B23 AGNDB
B24 AGNDB
B25 AGNDB
C1 AGNDA
C2 AGNDA
C3 AGNDA
C4 AGNDA
C5 AGNDA
C6 AGNDA
C7 DNC
C8 DNC
C9 AGNDA
C10 AV
CC
A
C11 REF_A_OUT
C12 AGNDA
C13 DNC
C14 AGNDB
C15 AGNDB
C16 AV
CC
B
C17 AGNDB
C18 AV
CC
B
C19 DNC
C20 DNC
C21 AGNDB
C22 AGNDB
C23 AGNDB
C24 AGNDB
C25 AGNDB
D1 AGNDA
D2 AGNDA
D3 AGNDA
D4 AGNDA
D5 AGNDA
D6 AGNDA
D7 A
D8 A
A2
IN
A1
IN
D9 AGNDA
D10 AV
CC
A
D11 REF_A_OUT
D12 AGNDA
D13 DNC
D14 AGNDB
D15 AGNDB
D16 AV
CC
B
D17 AGNDB
D18 AV
D19 A
D20 A
B
CC
B2
IN
B1
IN
D21 AGNDB
D22 AGNDB
D23 AGNDB
D24 AGNDB
D25 AGNDB
E1 AGNDA
E2 AGNDA
E3 AGNDA
E4 AGNDA
E22 AGNDB
E23 AGNDB
E24 AGNDB
E25 AGNDB
F1 AGNDA
F2 AGNDA
F3 AGNDA
F4 AGNDA
F22 AGNDB
F23 AGNDB
F24 AGNDB
F25 AGNDB
G1 AGNDA
G2 AGNDA
G3 AGNDA
G4 AGNDA
G22 AGNDB
G23 AGNDB
G24 AGNDB
G25 AGNDB
H1 AGNDA
H2 AGNDA
H3 AGNDA
H4 AGNDA
H22 AGNDB
H23 AGNDB
H24 AGNDB
H25 AGNDB
J1 AV
J2 AV
J3 AV
J4 AV
CC
CC
CC
CC
A
A
A
A
J22 REF_B_OUT
J23 REF_B_OUT
J24 REF_B_OUT
J25 REF_B_OUT
K1 AGNDA
K2 AGNDA
K3 AGNDA
K4 AGNDA
K10 SFDR_MODE_A
K11 AGNDA
K12 AGNDA
K13 DNC
K14 AGNDB
K15 AGNDB
K16 SFDR_MODE_B
K22 AGNDB
K23 AGNDB
K24 AGNDB
K25 AGNDB
L1 AGNDA
L2 AGNDA
L3 AGNDA
L4 AGNDA
L10 DFS_A
L11 AGNDA
L12 AGNDA
L13 DNC
L14 AGNDB
L15 AGNDB
L16 DFS_B
L22 ENCBB
L23 ENCBB
L24 ENCBB
L25 ENCBB
M1 ENCAB
M2 ENCAB
M3 ENCAB
M4 ENCAB
M10 AGNDA
M11 AGNDA
M12 AGNDA
M13 DNC
M14 AGNDB
M15 AGNDB
M16 AGNDB
M22 ENCB
M23 ENCB
M24 ENCB
M25 ENCB
N1 ENCA
N2 ENCA
N3 ENCA
N4 ENCA
N10 GAIN_A
N11 AGNDA
N12 AGNDA
N13 DNC
N14 AGNDB
N15 AGNDB
N16 AGNDB
N22 AGNDB
N23 AGNDB
N24 AGNDB
N25 AGNDB
P1 AGNDA
P2 AGNDA
P3 AGNDA
P4 AGNDA
P10 AGNDA
P11 AGNDA
P12 AGNDA
P13 DNC
P14 AGNDB
P15 AGNDB
P16 AGNDB
P22 DV
P23 DV
P24 DV
P25 DV
P25 DV
R1 DV
R2 DV
R3 DV
R4 DV
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
R10 AGNDA
R11 AGNDA
R12 AGNDA
R13 DNC
R14 AGNDB
R15 AGNDB
R16 AGNDB
R22 DB0
R23 DB0
R24 DB0
R25 DB0
T1 DA11
T2 DA11
T3 DA11
T4 DA11
T10 AV
CC
A
T11 AGNDA
T12 AGNDA
T13 DNC
T14 AV
CC
B
T15 GAIN_B
T16 AGNDB
T22 DB1
T23 DB1
T24 DB1
T25 DB1
U1 DA10
U2 DA10
U3 DA10
U4 DA10
U22 DB2
U23 DB2
U24 DB2
U25 DB2
V1 DA9
V2 DA9
V3 DA9
V4 DA9
V22 DB3
V23 DB3
V24 DB3
V25 DB3
W1 DA8
W2 DA8
W3 DA8
W4 DA8
W22 DB4
W23 DB4
W24 DB4
W25 DB4
Y1 DA7
Y2 DA7
Y3 DA7
Y4 DA7
Y22 DB5
Y23 DB5
Y24 DB5
Y25 DB5
AA1 DGNDA
AA2 DGNDA
AA3 DGNDA
AA4 DGNDA
AA22 DGNDB
AA23 DGNDB
AA24 DGNDB
AA25 DGNDB
AB1 OVRA
AB2 OVRA
AB3 OVRA
AB4 OVRA
AB5 DGNDA
AB6 DA6
AB7 DA5
AB8 DA4
AB9 DA3
AB10 DA2
AB11 DA1
AB12 DA0
AB13 DGNDA
AB14 DGNDB
AB15 DB11
AB16 DB10
AB17 DB9
AB18 DB8
AB19 DB7
AB20 DB6
AB21 DGNDB
AB22 OVRB
AB23 OVRB
AB24 OVRB
AB25 OVRB
AC1 DGNDA
AC2 DGNDA
AC3 DGNDA
AC4 DGNDA
AC5 DGNDA
AC6 DA6
AC7 DA5
AC8 DA4
AC9 DA3
AC10 DA2
AC11 DA1
AC12 DA0
AC13 DGNDA
AC14 DGNDB
AC15 DB11
AC16 DB10
AC17 DB9
AC18 DB8
AC19 DB7
AC20 DB6
AC21 DGNDB
AC22 DGNDB
AC23 DGNDB
AC24 DGNDB
AC25 DGNDB
AD1 DGNDA
AD2 DGNDA
AD3 DGNDA
AD4 DGNDA
AD5 DGNDA
AD6 DA6
AD7 DA5
AD8 DA4
AD9 DA3
AD10 DA2
AD11 DA1
AD12 DA0
AD13 DGNDA
AD14 DGNDB
AD15 DB11
AD16 DB10
AD17 DB9
AD18 DB8
AD19 DB7
AD20 DB6
AD21 DGNDB
AD22 DGNDB
AD23 DGNDB
AD24 DGNDB
AD25 DGNDB
AE1 DGNDA
AE2 DGNDA
AE3 DGNDA
AE4 DGNDA
AE5 DGNDA
AE6 DA6
AE7 DA5
AE8 DA4
AE9 DA3
AE10 DA2
AE11 DA1
AE12 DA0
AE13 DGNDA
AE14 DGNDB
AE15 DB11
AE16 DB10
AE17 DB9
AE18 DB8
AE19 DB7
AE20 DB6
AE21 DGNDB
AE22 DGNDB
AE23 DGNDB
AE24 DGNDB
AE25 DGNDB
–6–
REV. 0
Page 7

1
2
AGN DA
AGN DA
A
A
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AV
CC
AGN DA
AGN DA
ENCAB
ENCA
AGN DA
DV
CC
DA11
DA10
DA9
DA8
DA7
DGNDA
OVR A
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
A
A
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
ENCAB
AGN DA
DV
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AV
CC
AGN DA
AGN DA
ENCAB
ENCA
AGN DA
DV
CC
DA11
DA10
DA9
DA8
DA7
DGNDA
OVR A
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
AV
CC
ENCA
CC
DA11
DA10
DA9
DA8
DA7
OVR A
AD10226
385-LEAD BGA PINOUT (Top View, PCB Footprint)
22
23
24
ENCB
CC
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
OVRB
B
25
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
REF_B_OUT
AGNDB
ENCBB
ENCB
AGNDB
DV
CC
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DGNDB
OVRB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
B
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
A
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AV
CC
AGN DA
AGN DA
ENCAB
ENCA
AGN DA
DV
CC
DA11
DA10
DA9
DA8
DA7
DGNDA
OVR A
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
A
A
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
DA6
DA6
DA6
DA6
A
DNC
DNC
DNC
IN
DA5
DA5
DA5
DA5
9
10
DNC
AGN DA
AVCCA
REF_A_OUT
DNC
AGN DA
AV
REF_A_OUT
A
CC
DA3
DA3
DA3
DA3
AV
CC
AV
CC
SFDR
Mode A
DFS_A
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AV
CC
DA2
DA2
DA2
DA2
A
REF_A_OUT
A
REF_A_OUT
B
DNC
AGN DA
A2
A1
A
AGN DA
IN
DA4
DA4
DA4
DA4
11
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
DA1
DA1
DA1
DA1
12
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
AGN DA
DA0
DA0
DA0
DA0
13
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDA
14
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNCB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AV
CC
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
B
15
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNCB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
DB11
DB11
DB11
DB11
16
AVCCB
AV
CC
AV
CC
AV
CC
SFDR
Mode B
DFS_B
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
DB10
DB10
DB10
DB10
B
B
B
17
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNCB
DB9
DB9
DB9
DB9
18
AVCCB
AV
CC
AV
CC
AV
CC
DB8
DB8
DB8
DB8
19
DNC
DNC
B
DNC
B
B
AINB2
DB7
DB7
DB7
DB7
20
DNC
DNC
DNC
AINB1
DB6
DB6
DB6
DB6
21
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
REF_B_OUT
AGNDB
ENCBB
ENCB
AGNDB
DV
CC
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DGNDB
OVRB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
B
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
REF_B_OUT
AGNDB
ENCBB
ENCB
AGNDB
DV
CC
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DGNDB
OVRB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
B
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
REF_B_OUT
AGNDB
ENCBB
AGNDB
DV
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
REV. 0
–7–
Page 8

AD10226
– Typical Performance Characteristics
0
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
TPC 1. Single Tone @ 10.3 MHz
0
ENCODE = 125MSPS
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
= 49MHz (–1dBFS)
A
IN
SNR = 67.12dBFS
SFDR = 83.09dBFS
51015202530354045 50
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
ENCODE = 125MSPS
= 10.3MHz (–1dBFS)
A
IN
SNR = 68.19dBFS
SFDR = 85.13dBFS
55 60
55 60
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
0
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
ENCODE = 125MSPS
A
SNR = 63.66dBFS
SFDR = 79.28dBFS
TPC 4. Single Tone @ 121 MHz
0
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
= 121MHz (–1dBFS)
IN
55 60
ENCODE = 125MSPS
= 240MHz (–1dBFS)
A
IN
SNR = 59.06dBFS
SFDR = 74.56dBFS
55 60
0
ENCODE = 125MSPS
ⴚ10
A
IN
SNR = 66.2dBFS
ⴚ20
SFDR = 82.02dBFS
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
0
TPC 2. Single Tone @ 49 MHz
= 71MHz (–1dBFS)
51015202530354045 50
FREQUENCY – MHz
TPC 3. Single Tone @ 71 MHz
55 60
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
TPC 5. Single Tone @ 240 MHz
0
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
ENCODE = 125MSPS
= 29.3MHz AND 30.3MHz
A
IN
SFDR = 79.03dBFS
TPC 6. Two Tone @ 29/30 MHz
55 60
–8–
REV. 0
Page 9

AD10226
3.0
ⴚ3.0
LSB
0.0
0
1.0
2.0
512 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096
ⴚ2.0
ⴚ1.0
ENCODE = 125MSPS
INL MIN = 0.610
INL MAX = 0.702
OUTPUT CODES
0
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
TPC 7. Two Tone @ 150/151 MHz
0
ⴚ10
ⴚ20
ⴚ30
ⴚ40
ⴚ50
ⴚ60
dB
ⴚ70
ⴚ80
ⴚ90
ⴚ100
ⴚ110
ⴚ120
ⴚ130
5101520253035404550
0
FREQUENCY – MHz
ENCODE = 125MSPS
= 150MHz AND 151MHz
A
IN
SFDR = 75.38dBFS
ENCODE = 125MSPS
= 240MHz AND 241MHz
A
IN
SFDR = 67dBFS
55 60
55 60
0
ⴚ
1
ⴚ
2
ⴚ
3
GAIN – dB
ⴚ
4
ⴚ
5
ⴚ6
10
TPC 10. Integral Nonlinearity
100 1000
FREQUENCY – MHz
TPC 8. Two Tone @ 240/241 MHz
3.0
ENCODE = 125MSPS
DNL MIN = 0.530
2.5
DNL MAX = 0.369
2.0
1.5
1.0
LSB
0.5
0.0
ⴚ0.5
ⴚ1.0
512 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096
0
OUTPUT CODES
TPC 9. Differential Nonlinearity
TPC 11. Frequency Response
0
ⴚ
1
GAIN – dB
ⴚ
2
10
100 1000
FREQUENCY – MHz
TPC 12. Gain Flatness*
*Gain flatness measurement is performed by
applying a constant voltage at the device input.
REV. 0
–9–
Page 10

AD10226
10MHz = 52.22 – j0.421
50MHz = 50.69 – j2.84
100MHz = 47.50 – j3.58
150MHz = 44.61 – j0.970
200MHz = 43.70 + j3.70
250MHz = 46.41 + j9.48
300MHz = 53.09 + j14.76
10
9
8
7
6
5
GAIN – dB
4
3
2
1
0
0.1
1MHz = 1.010
10MHz = 1.028
50MHz = 1.045
100MHz = 1.066
140MHz = 1.090
160MHz = 1.126
200MHz = 1.170
1
10
FREQUENCY – MHz
100 1000
TPC 13. Input Impedance S11
Equivalent Circuits
8k⍀
ENCODE
24k⍀
Test Circuit 1. Equivalent ENCODE Input
V
CC
V
CC
100⍀
8k⍀
24k⍀
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
ENCODE
TPC 14. Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)
V
CC
OUTPUT
Q1
NPN
V
CC
V
REF
Test Circuit 3. Equivalent Voltage Reference Output
V
CC
3.75k⍀
AIN2
50⍀
AIN1
15k⍀
3.75k⍀
15k⍀
Test Circuit 2. Equivalent Digital Output
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Analog Bandwidth
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the
fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is
reduced by 3 dB.
Aperture Delay
The delay between the 50% point on the rising edge of the ENCODE
command and the instant at which the analog input is sampled.
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter)
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
–10–
Test Circuit 4. Equivalent Analog Input
Differential Nonlinearity
The deviation of any code from an ideal 1 LSB step.
ENCODE Pulsewidth/Duty Cycle
Pulsewidth high is the minimum amount of time that the
ENCODE pulse should be left in logic “1” state to achieve rated
performance; pulsewidth low is the minimum time ENCODE
pulse should be left in low state. At a given clock rate, these specs
define an acceptable ENCODE duty cycle.
REV. 0
Page 11

AD10226
Harmonic Distortion
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the worst
harmonic component.
Integral Nonlinearity
The deviation of the transfer function from a reference line measured
in fractions of 1 LSB using a “best straight line” determined by
a least square curve fit.
Minimum Conversion Rate
The ENCODE rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal
frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the guaranteed limit.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The ENCODE rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Output Propagation Delay
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of ENCODE
command and the time when all output data bits are within valid
logic levels.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
The ratio of a change in output offset voltage to a change in
power supply voltage.
Signal-to-Noise-and-Distortion (SINAD)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full-scale)
to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components,
excluding the first six harmonics and dc. [May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal levels are lowered) or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full-scale).]
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (without Harmonics)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full-scale)
to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components,
excluding the first six harmonics and dc. [May be reported in
dBc (i.e., degrades as signal levels are lowered) or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full-scale).]
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the peak
spurious spectral component. The peak spurious component may
or may not be a harmonic. [May be reported in dBc (i.e., degrades
as signal levels is lowered) or in dBFS (always related back to
converter full-scale).]
Two-Tone Intermodulation Distortion Rejection
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the worst third order intermodulation product; reported in dBc.
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)
The ratio of the amplitude of the electric field at a voltage maximum
to that at an adjacent voltage minimum.
APPLICATION NOTES
Theory of Operation
The AD10226 is a high-dynamic-range dual 12-bit, 125 MHz
subrange pipeline converter that uses switched capacitor architecture. The analog input section uses A
A2/B2 at 1.84 V p-p
IN
with an input impedance of 50 Ω. The analog input includes an
ac-coupled wideband 1:1 transformer, which provides high dynamic
range and SNR while maintaining VSWR and gain flatness. The
ADC includes a high bandwidth linear track/hold that gives excellent spurious performance up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. The
high bandwidth track/hold has a low jitter of 0.25 ps rms, leading
to excellent SNR and SFDR performance. AC-coupled differential PECL/ECL encode inputs are recommended for optimum
performance.
REV. 0
–11–
USING THE AD10226
ENCODE Input
Any high speed A/D converter is extremely sensitive to the quality
of the sampling clock provided by the user. A track/hold circuit
is essentially a mixer, and any noise, distortion, or timing jitter
on the clock will be combined with the desired signal at the A/D
output. For that reason, considerable care has been taken in the
design of the ENCODE input of the AD10226, and the user is
advised to give commensurate thought to the clock source.
The monolithic converter has an internal clock duty cycle stabilization circuit that locks to the rising edge of ENCODE (falling edge
of ENCODE if driven differentially), and optimizes timing internally. This allows for a wide range of input duty cycles at the input
without degrading performance. Jitter in the rising edge of the input
is still of paramount concern and is not reduced by the internal
stabilization circuit. This circuit is always on and cannot be disabled by the user.
The ENCODE and ENCODE inputs are internally biased to 3.75 V
(nominal) and support either differential or single-ended signals.
For best dynamic performance, a differential signal is recommended.
Good performance is obtained using an MC10EL16 in the circuit
to directly drive the encode inputs, as illustrated in Figure 2.
AD10226
ENCODE
ENCODE
PECL
GATE
510⍀
GND
510⍀
0.1F
0.1F
Figure 2. Using PECL to Drive ENCODE Inputs
Often, the cleanest clock source is a crystal oscillator producing
a pure, single-ended sine wave. In this configuration, or with any
roughly symmetrical, single-ended clock source, the signal can
be ac-coupled to the ENCODE input. To minimize jitter, the
signal amplitude should be maximized within the input range
described in the Table II.
Table II. ENCODE Inputs
Description Min Nom Max
Differential Signal
Amplitude (V
) 200 mV 750 mV 5.5 V
ID
Input Voltage
Range (V
HID, VILD, VHIS
) –5 V V
+ 0.5 V
CC
Internal Common-Mode
Voltage (V
)3.75 V
ICM
External Common-Mode
Bias (V
) 2.0 V 4.25 V
ECM
50⍀
SINE
SOURCE
0.1F
0.1F
50⍀ 50⍀ 50⍀
ENCODE
ENCODE
AD10226
Figure 3. Single-Ended 50 Sine Encode Circuit
The 10 kΩ resistors to ground at each of the inputs, in parallel with
the internal bias resistors, set the common-mode voltage to ~ 2.5 V,
Page 12

AD10226
allowing the maximum swing at the input. The ENCODE input
should be bypassed with a capacitor to ground to reduce noise.
This ensures that the internal bias voltage is centered on the
encode signal (Figure 3). For best dynamic performance, impedances at ENCODE and ENCODE should match.
Figure 4 shows another preferred method for clocking the AD10226.
The clock source (low jitter) is converted from single-ended to
differential using an RF transformer. The back-to-back Schottky
diodes across the transformer secondary limit clock excursions
into the AD10226 to approximately 0.8 V p-p differential. This
helps prevent the large voltage swings of the clock from feeding
through to the other portions of the AD9433, and limits the noise
presented to the ENCODE inputs. A crystal clock oscillator can
also be used to drive the RF transformer if an appropriate limiting
resistor (typically 100 Ω) is placed in the series with the primary.
CLOCK
SOURCE
0.1F
100⍀
AD10226
ENCODE
ENCODE
Figure 4. Double-Ended 50 Sine Encode Circuit
ENCODE Voltage Level Definition
The voltage level definitions for driving ENCODE and ENCODE
in differential mode is shown in Figure 6.
V
V
IHS VILS
V
IHS VILS
IHD
V
ID
V
ILD
V
IHS
V
ILS
ENCODE
ENCODE
ENCODE
ENCODE
0.1F
Figure 5. Differential Input Levels
Analog Input
The analog input is a single-ended ac-coupled high performance
1:1 transformer with an input impedance of 50 Ω to 350 MHz.
The nominal full scale input is 1.87 V p-p.
Special care was taken in the design of the analog input section
of the AD10226 to prevent damage and corruption of data when
the input is overdriven.
SFDR Optimization
The SFDR MODE pin enables (SFDR MODE = 1) a proprietary
circuit that may improve the spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR)
performance of the AD10226. It is useful in applications where the
dynamic range of the system is limited by discrete spurious frequency
content caused by nonlinearities in the ADC transfer function.
Enabling this circuit will give the circuit a dynamic transfer function,
meaning that the voltage threshold between two adjacent output
codes may change from clock cycle to clock cycle. While improving spurious frequency content, this dynamic aspect of the transfer
function may be inappropriate for some time domain applications
of the converter. Connecting the SFDR Mode pin to ground will
disable this function. The Typical Performance Characteristics
section of the data sheet illustrates the improvement in the linearity
of the converter and its effect on spurious-free dynamic range.
–12–
Digital Outputs
The digital outputs are 3.3 V (2.7 V to 3.6 V) TTL/CMOScompatible for lower power consumption. The output data format
is selectable through the data format select (DFS) CMOS input.
DFS = 1 selects offset binary coding (Table III); DFS = 0 selects Two’s Complement coding (Table IV).
Table III. Offset Binary Output Coding (DFS = 1, V
A
– AIN (V) Digital
IN
= 2.5 V)
REF
Code Range = 2 V p-p Output
4095 +0.92 1111 1111 1111
•• •
•• •
2048 0 1000 0000 0000
2047 –0.00045 0111 1111 1111
•• •
•• •
0 –0.92 0000 0000 0000
Table IV. Two’s Complement Output Coding
(DFS = 0, V
A
– AIN (V) Digital
IN
= 2.5 V)
REF
Code Range = 2 V p-p Output
+2047 +0.92 0111 1111 1111
•• •
•• •
00 0000 0000 0000
–1 –0.00045 1111 1111 1111
•• •
•• •
–2048 –0.92 1000 0000 0000
Voltage Reference
A stable and accurate 2.5 V voltage reference is designed into the
AD10226 (V
). An external voltage reference is not required.
REFOUT
Timing
The AD10226 provides latched data outputs, with 10 pipeline
delays. Data outputs are available one propagation delay (t
PD
) after
the rising edge of the ENCODE command (see Figure 1). The
length of the output data lines and loads placed on them should
be minimized to reduce transients within the AD10226; these
transients can detract from the converter’s dynamic performance.
The minimum guaranteed conversion rate of the AD10226 is
10 MSPS. At internal clock rates below 10 MSPS, dynamic performance may degrade. Therefore, input clock rates below 10 MHz
should be avoided.
GROUNDING AND DECOUPLING
Analog and Digital Grounding
Proper grounding is essential in any high-speed, high resolution
system. Multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs) are recommended
to provide optimal grounding and power schemes. The use of
ground and power planes offers distinct advantages:
1. The minimization of the loop area encompassed by a signal
and its return path.
2. The minimization of the impedance associated with ground
and power paths.
3. The inherent distributed capacitor formed by the powerplane,
PCB insulation, and ground plane.
REV. 0
Page 13

AD10226
These characteristics result in both a reduction of electromagnetic
interference (EMI) and an overall improvement in performance.
It is important to design a layout that prevents noise from coupling
to the input signal. Digital signals should not be run in parallel
with input signal traces and should be routed away from the input
circuitry. The PCB should have a ground plane covering all unused
portions of the component side of the board to provide a low
impedance path and manage the power and ground currents. The
ground plane should be removed from the area near the input
pins to reduce stray capacitance.
Solder Reflow Profile
The Solder Reflow Profile for the AD10226 is shown in Figure 6.
250
200
150
100
TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
50
0
050
100 150 200 250 300 350 400
TIME – Seconds
Figure 6. Typical Solder Reflow Profile
LAYOUT INFORMATION
The schematic of the evaluation board (Figures 7a–7d) represents
a typical implementation of the AD10226. The pinout of the
AD10226 is very straightforward and facilitates ease of use and the
implementation of high-frequency/high resolution design practices. It is recommended that high quality ceramic chip capacitors
be used to decouple each supply pin to ground directly at the device.
All capacitors can be standard high quality ceramic chip capacitors.
Care should be taken when placing the digital output runs. Because
the digital outputs have such a high slew rate, the capacitive loading on the digital outputs should be minimized. Circuit traces for
the digital outputs should be kept short and connect directly to
the receiving gate. Internal circuitry buffers the outputs of the
AD9433 ADC through a resistor network to eliminate the need
to externally isolate the device from the receiving gate.
EVALUATION BOARD
The AD10226 evaluation board (Figures 7a–7d) is designed to
provide optimal performance for evaluation of the AD10226
analog-to-digital converter. The board encompasses everything
needed to ensure the highest level of performance for evaluating the
AD10226. The board requires an analog input signal, an ENCODE
clock and power supply inputs. The clock is buffered on-board to
provide clocks for the latches. The digital outputs and out clocks
are available at the standard 40-pin connectors J1 and J2. Power
to the analog supply pins is connected via banana jacks. The analog
supply powers the associated components and analog section of the
AD10226. The digital outputs of the AD10226 are also powered
via banana jacks with 3.3 V. Contact the factory if additional layout
or application assistance is required.
BILL OF MATERIALS LIST FOR AD10226 EVALUATION BOARD
Quantity Reference Designator Value Description Part Number
2 U16, U17 IC, Low Voltage 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flop 74LCX16374MTD
with 5 V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs (Fairchild)
1U1 IC, BGA 35 35 385 AD10226AB
2 U14, U15 IC, Precision Low Dropout any CAP ADP3330ART-3.3-RL7
Voltage Regulator (Analog)
4 R38, R39, R56, R58 33 kΩ RES 33 kΩ 1/10W 0.1% 0805 SMD ERA-6YEB333V (Panasonic)
8 R1, R7, R8, R41, R60, R61, R71, R72 51 Ω RES 51 Ω 1/10W 5% 0805 SMD ERJ-6GEYJ510V (Panasonic)
32 R3, R4, R9–R18, R23–R30, R35, 100 Ω RES 100 Ω 1/10W 1% 0805 SMD ERJ-6ENF1000V
R36, R40, R42–R46, R63–R66 (Panasonic)
23 C1, C2, C5–C10, C12, C16–C18, 0.1 µF CAP 0.1 µF 50 V Ceramic Y5V 0805 ECJ-2VF1H104Z
C20–C26, C28, C33–C35 (Panasonic)
2 C13, C27 0.47 µF CAP 0.47 µF 25 V Ceramic Y5V 0805 ECJ-2YF1E474Z (Panasonic)
2 J1, J2 2 20 Male Connector Strip, 100 Centers TSW-120-08G-D (Samtec)
4 L1, L2, L3, L4 47 Ω SMT Ferrite Bead 2743019447 (Fair Rite)
4 U2, U3, U9, U11 IC, 3.3 V/5 V ECL Differential MC10EP16D
Receiver/Driver (Motorola)
8 E3–E6, E25, E26, E33, E34 Power Jack, Banana Plug 108-0740-001 (Johnson Company)
2 U4, U10 3.3 V Dual Differential SY100ELT23L
LVPECL-to-LVTTL Translator (Micrel-Synergy)
10 C3, C4, C11, C14, C15, C19, 10 µF Solid Tantalum Chip Capacitor, T491C106M016AS
C29, C30–C32 10 µF, 16 V, 20% (KEMET)
8 J3–J7, J10–J12 SMA PLUG 200Mil STR GOLD 142-0801-201
(Johnson Components Inc.)
4 Spacer Aluminum, Hex M–F (Standoff)
4 Nut Hex Stl #4-40 UNC-2B
1 AD10201/AD10226 Evaluation Board GS03983 Rev. A (PCB)
2 C36, C37 CAP 0.047 µF 25 V Ceramic Y5V 0603 ECJ-1VB1C473K
6 JP3, JP4, JP6, JP8, JP9, JP12 0 Ω RES 0 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 ER J-2GEOR00
REV. 0
–13–
Page 14

AD10226
LATCHA
R7
51⍀
MSB D11A
D10A
D9A
D8A
D7A
D6A
D5A
D4A
D3A
D2A
D1A
LSB D0A
DGNDA
U16
25
CP2
24
OE2
26
I15
27
I14
29
I13
30
I12
32
I11
33
I10
35
I9
36
I8
48
CP1
1
OE1
37
I7
38
I6
40
I5
41
I4
43
I3
44
I2
46
I1
47
I0
28
GND
34
GND
39
GND
45
GND
74LCX16374MTD
DUT_3.3VDA
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
O15
O14
O13
O12
O11
O10
O9
O8
O7
O6
O5
O4
O3
O2
O1
O0
GND
GND
GND
GND
42
31
7
18
23
22
20
19
17
16
14
13
12
11
9
8
6
5
3
2
21
15
10
4
DGNDA
R18
100⍀
R17
100⍀
R16
100⍀
R40
100⍀
R44
100⍀
R45
100⍀
R46
100⍀
R15
100⍀
R14
100⍀
R13
100⍀
R24
100⍀
R23
100⍀
B11A MSB
B10A
B9A
B8A
B7A
B6A
B5A
B4A
B3A
B2A
B1A
B0A LSB
3.3VDA
C15
+
10F
16V
DGNDA
BUFLATA
1
MSB B11A
R71
51⍀
LSB B0A
2
3
B10A
4
B9A
5
B8A
6
B7A
7
B6A
8
B5A
9
B4A
10
11
12
B3A
13
B2A
14
B1A
15
16
17
18
19
20
DGNDA DGNDA
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
40
39
39
38
38
37
37
36
36
35
35
34
34
33
33
32
32
31
31
30
30
29
29
28
28
27
27
26
26
25
25
24
24
23
23
22
22
21
21
LATCHB
R8
51⍀
MSB D11B
D10B
D9B
D8B
D7B
D6B
D5B
D4B
D3B
D2B
D1B
LSB D0B
DGNDB
U17
25
CP2
24
OE2
26
I15
27
I14
29
I13
30
I12
32
I11
33
I10
35
I9
36
I8
48
CP1
1
OE1
37
I7
38
I6
40
I5
41
I4
43
I3
44
I2
46
I1
47
I0
28
GND
34
GND
39
GND
45
GND
74LCX16374MTD
R11
DUT_3.3VDB
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
O15
O14
O13
O12
O11
O10
O9
O8
O7
O6
O5
O4
O3
O2
O1
O0
GND
GND
GND
GND
42
31
7
18
23
22
20
19
17
16
14
13
12
11
9
8
6
5
3
2
21
15
10
4
DGNDB
100⍀
R10
100⍀
R30
100⍀
R29
100⍀
R28
100⍀
R27
100⍀
R26
100⍀
R12
100⍀
100⍀
R25
100⍀
R36
100⍀
R35
100⍀
B11B MSB
B10B
B9B
B8B
B7B
B6B
B5B
B4B
R9
B3B
B2B
B1B
B0B LSB
Figure 7a. Evaluation Board Schematic
3.3VDB
C14
+
10F
16V
DGNDB
BUFLATB
1
MSB B11B
R72
51⍀
LSB B0B
2
3
B10B
4
B9B
5
B8B
6
B7B
7
B6B
8
B5B
9
B4B
10
11
12
B3B
13
B2B
14
B1B
15
16
17
18
19
20
DGNDB DGNDB
J2
40
40
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
39
39
38
38
37
37
36
36
35
35
34
34
33
33
32
32
31
31
30
30
29
29
28
28
27
27
26
26
25
25
24
24
23
23
22
22
21
21
–14–
REV. 0
Page 15

AD10226
E4
E6
E5
E34
E25
E3
AGNDA
5VAA
AGNDA
AGNDB
5VAB
AGNDB
DGNDA
3.3VDA
L3
12
47⍀ @ 100MHz
C3
++
10F
16V
L4
12
47⍀ @ 100MHz
C4
++
10F
16V
C29
++
10F
16V
C20
0.1F
C21
0.1F
L1
12
47⍀ @ 100MHz
C12
0.1F
AGNDA
AGNDB
5VAA
C11
10F
16V
5VAB
C19
10F
16V
DUT_3.3VDA
C31
10F
16V
A
IN
AINA2
AINB2
A
IN
A1
AGNDA
AGNDA
AGNDB
B1
J3
J4
J7
J6
JP1
JP2
AINA 1
AINA 2
AINB 2
AINB 1
STITCHES TO TIE GROUNDS TOGETHER
DGNDA DGNDB
DGNDA DGNDB
DGNDA AGNDA
AGNDA AGNDB
DGNDB AGNDB
E78 E77
E7 E12
E10 E9
E8 E11
E1 E2
E41E42
E43E44
E47E48
E65E66
E68E67
E69E70
E71E72
E74E73
E75E76
E82E81
E30E29
E35E36
E37E38
E39E40
E46E45
E80E79
E83E84
AGNDADGNDA
E33
E26
L2
12
DGNDA
DGNDB
DUT_3.3VDB
C32
10F
16V
DGNDA
DGNDB
3.3VDB
47⍀ @ 100MHz
C30
++
10F
16V
DGNDB
C16
0.1F
AGNDB
5VAA
AGNDA
C34
0.1F
DUT_3.3VDA
C10
0.1F
DGNDA
DUT_3.3VDB
C9
0.1F
C18
0.1F
Figure 7b. Evaluation Board Schematic
DGNDB
C17
0.1F
DGNDB
AGNDB
REV. 0
–15–
Page 16

AD10226
ENCODE
ENCA
J5
AGNDA
J12
AGNDA
R1
51⍀
AGNDA
R41
51⍀
AGNDA
C1
0.1F
C2
0.1F
3.3VA
3.3VDA
5VAA
R56
33k⍀
R58
33k⍀
NR
ERR
5
3
8
7
6
5
AGNDA
8
7
6
5
DGNDA
3.3VA
3.3VDA
C13
0.1F
25V
C6
0.1F
U14
21
IN OUT
6
SD
GND
4
AGNDA
U2
1
NC VCC
2
DQ
3
DQ
4
VBB VEE
MC10EP16D
U3
1
NC VCC
2
DQ
3
DQ
4
VBB VEE
MC10EP16D
R42
R43
100⍀
100⍀
AGNDA
R3
100⍀R4100⍀
DGNDA
U4
1
D0 VCC
2
D0
3
D1
4
D1 GND
SY100EPT23L
Q
Q
8
7
6
5
DGNDA
C7
0.1F
C8
0.1F
3.3VDA
C5
0.1F
ENCAB
ENCA
LATCHA
E23
E19
BUFLATA
ENCODE
ENCB
J10
AGNDB
J11
AGNDB
R60
51⍀
AGNDB
R61
51⍀
AGNDB
C22
0.1F
C23
0.1F
3.3VB
3.3VDB
5VAB
R38
33k⍀
R39
33k⍀
NR
ERR
5
3
8
7
6
5
AGNDB
8
7
6
5
DGNDB
3.3VB
3.3VDB
C27
0.47F
25V
C25
0.1F
R63
100⍀
R65
100⍀
AGNDB
DGNDB
R64
100⍀
R66
100⍀
U15
21
IN OUT
6
SD
GND
4
AGNDB
U11
1
NC VCC
2
DQ
3
DQ
4
VBB VEE
MC10EP16D
U9
1
NC VCC
2
DQ
3
DQ
4
VBB VEE
MC10EP16D
Figure 7c. Evaluation Board Schematic
U10
1
D0 VCC
2
D0
3
D1
4
D1 GND
SY100EPT23L
Q
Q
DGNDB
8
7
6
5
C24
0.1F
C28
0.1F
3.3VDB
C26
0.1F
ENCBB
ENCB
LATCHB
E24
E22
BUFLATB
–16–
REV. 0
Page 17

AGN DA
+5VAA
+5VAA
AGN DA
0.047F
JP4
AGN DA
DGNDA
DGNDB
C36
AB13
AC13
AD13
AE13
AA22
AA23
AA24
AA25
AB14
AB21
AC14
AC21
AC22
AC23
AC24
AC25
AD14
AD21
AD22
AD23
AD24
AD25
AE14
AE21
AE22
AE23
AE24
AE25
AD10226
C33
0.1F
AGN DA
AINA1
AINA2
OVR A
D0A
D1A
D2A
D3A
D4A
D5A
D6A
D7A
D8A
D9A
D10A
D11A
ENCA
ENCAB
AB4
AB3
AB2
AB1
AE12
AD12
AC12
AB12
AE11
AD11
AC11
AB11
AE10
AD10
AC10
AB10
AE9
AD9
AC9
AB9
AE8
AD8
AC8
AB8
AE7
AD7
AC7
AB7
AE6
AD6
AC6
A1
AGNDA
A2
AGNDA
A3
OVRA
AGNDA
A4
AGNDA
A5
AGNDA
A6
AGNDA
A9
AGNDA
A12
AGNDA
B1
AGNDA
B2
AGNDA
B3
AGNDA
B4
AGNDA
B5
AGNDA
B6
AGNDA
B9
AGNDA
B12
AGNDA
C1
AGNDA
C2
AGNDA
C3
AGNDA
C4
AGNDA
C5
AGNDA
C6
AGNDA
C9
AGNDA
C12
AGNDA
D1
AGNDA
D2
AGNDA
D3
AGNDA
D4
AGNDA
D5
AGNDA
D6
AGNDA
D9
AGNDA
D12
AGNDA
E1
AGNDA
E2
AGNDA
E3
AGNDA
E4
AGNDA
F1
AGNDA
F2
AGNDA
F3
AGNDA
F4
AGNDA
G1
AGNDA
G2
AGNDA
G3
AGNDA
G4
AGNDA
H1
AGNDA
H2
AGNDA
H3
AGNDA
H4
AGNDA
K1
AGNDA
K2
AGNDA
K3
AGNDA
K4
AGNDA
K10
K11
AGNDA
K12
AGNDA
L1
AGNDA
L2
AGNDA
L3
AGNDA
L4
AGNDA
L10
L11
AGNDA
L12
AGNDA
M10
AGNDA
M11
AGNDA
M12
AGNDA
N10
N11
AGNDA
N12
AGNDA
P1
AGNDA
P2
AGNDA
P3
AGNDA
P4
AGNDA
P10
AGNDA
P11
AGNDA
P12
AGNDA
R10
AGNDA
R11
AGNDA
R12
AGNDA
T10
T11
AGNDA
T12
AGNDA
AA1
DGNDA
AA2
DGNDA
AA3
DGNDA
AA4
DGNDA
AB5
DGNDA
DGNDA
AC1
DGNDA
AC2
DGNDA
AC3
DGNDA
AC4
DGNDA
AC5
DGNDA
DGNDA
AD1
DGNDA
AD2
DGNDA
AD3
DGNDA
AD4
DGNDA
AD5
DGNDA
DGNDA
AE1
DGNDA
AE2
DGNDA
AE3
DGNDA
AE4
DGNDA
AE5
DGNDA
DGNDA
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
DGNDB
OVRB
AB25
OVRA
OVRA
AGN DA
AGN DA
OVRB
OVRB
AB24
AB23
OVRA
OVRB
AB22
AE15
D0A (LSBA)
JP3
JP6
D11B (MSBB)
AD15
D0A (LSBA)
D0A (LSBA)
+5VAA
+5VAA
D11B (MSBB)
D11B (MSBB)
AC15
AB15
D1A
D1A
D1A
D1A
D2A
D2A
D2A
D2A
D3A
D3A
D3A
D3A
D4A
D4A
D4A
D4A
D0A (LSBA)
D11B (MSBB)
D10B
D10B
D10B
D10B
D9B
D9B
D9B
D9B
D8B
D8B
D8B
D8B
D7B
D7B
D7B
AC16
AC17
AC18
AB17
AE18
AD18
AB18
AE19
AD19
AC19
AB19
AE16
AD16
AB16
AE17
AD17
AB6Y4Y3Y2Y1W4W3W2W1V4V3V2V1U4U3U2U1T4T3T2T1N4N3N2N1M4M3M2M1D7C7B7A7D8C8B8A8
D5A
D5A
D5A
D5A
D6A
D6A
D6A
D6A
D7A
D7A
D7A
D7A
D8A
D8A
D8A
D8A
D9A
D9A
D9A
D9A
D10A
D10A
D10A
D10A
D11A (MSBA)
D11A (MSBA)
D11A (MSBA)
AD10226
+5VAB
JP8
AGNDB
D7B
D6B
D6B
D6B
D6B
D5B
D5B
D5B
D5B
D4B
D4B
D4B
D4B
D3B
D3B
D3B
D3B
D2B
D2B
D2B
D2B
D1B
D1B
D1B
D1B
D0B (LSBB)
D0B (LSBB)
D0B (LSBB)
T25
T24
T23
AE20
AD20
Y25
Y24
Y23
Y22
V25
V24
V23
V22
W25
W24
W23
AC20
AB20
W22
T22
U25
U24
U23
U22
R25
R24
R23
R22
ENCA
ENCA
D11A (MSBA)
C37
0.047F
D0B (LSBB)
ENCB
ENCB
M25
M24
ENCA
ENCA
AINA2
AINA2
AINA2
AINA2
AINA1
ENCAB
ENCAB
AINA1
ENCAB
ENCAB
+5VAB
JP9
AGNDB
+5VAB
JP12
AGNDB
ENCB
ENCB
ENCBB
ENCBB
ENCBB
ENCBB
REF_B
REF_B
REF_B
REF_B
AINB1
AINB1
J25
J24
J23
J22
L25
L24
L23
L22
D20
C20
M23
M22
B20
AINA1
AINB1
A20
D11
AINA1
AINB1
D19
C11
REF_A
REF_A
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
5VAA
3.3VDA
3.3VDA
3.3VDA
3.3VDA
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
SHEILD
3.3VDB
3.3VDB
3.3VDB
3.3VDB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
5VAB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AGNDB
AINB2
C19
B11
AINB2
B19
A11
REF_A
REF_A
AINB2
AINB2
A19
J1
J2
J3
J4
A10
B10
C10
D10
R1
R2
R3
R4
A13
B13
C13
D13
K13
L13
M13
N13
P13
R13
T13
P22
P23
P24
P25
A16
B16
C16
D16
A18
B18
C18
D18
A14
A15
A17
A21
A22
A23
A24
A25
B14
B15
B17
B21
B22
B23
B24
B25
C14
C15
C17
C21
C22
C23
C24
C25
D14
D15
D17
D21
D22
D23
D24
D25
E22
E23
E24
E25
F22
F23
F24
F25
G22
G23
G24
G25
H22
H23
H24
H25
K14
K15
K16
K22
K23
K24
K25
L14
L15
L16
M14
M15
M16
N14
N15
N16
N22
N23
N24
N25
P14
P15
P16
R14
R15
R16
T14
T15
T16
E49
+5VAA
DUT_3.3VDA
DUT_3.3VDB
+5VAB
+5VAB
REV. 0
D4B
D5B
D6B
D7B
D8B
D9B
D10B
D11B
OVR B
Figure 7d. Evaluation Board Schematic
–17–
D3B
D2B
D1B
D0B
AGNDB
ENCB
C35
0.1F
ENCBB
E50
AINB2
AINB1
AGNDB
Page 18

AD10226
+5VAB
E5
+
C19
E39
E11
E8
GS03983 REV: A
AD10201/ AD10206
EVALUATION BOARD
J7
GND TIEGND TIE
E47
L3
+
C3
+
+5V
AA
E6
Figure 8a. Mechanical Layout Top View
C4
L4
+
REF_A
J4
AINB2
C11
E3
E49
E4
JP1
AINA2
AGNDB
ENCB
JP2
ENCA
AGNDA
J2
GND TIE
E19
E23
L2
E77
E78
+
DGNDA
E26
+3.3VDB
C16
C30
+
+
R11
R10
R30
R29
R28
R27
R26
R12
R9
R25
R36
R35
E12
GND TIE
E7
J1
R18
R17
R16
R40
R44
R45
R46
R15
R14
R13
R24
R23
C31
L1
C29
+
C12
E25
+3.3VDA
E33 DGNDB
E38
E37
E29
E30
E1
E2
E35
E36
C32
J10
ENCB
E50
REF_B
J6
AINB1
AINA1
J3
GND TIES
E80
E79
E46
E45
E22
J11
E83
BUFLATB
E84
LATCHB
E24
U1
ENCA
E82
E65
E9
J12
J5
E41
E43
E68
E74
E71
E69
E75
BUFLATA
LATCHA
E81
E66
E10
E42
E44
GND TIES
E67
E73
E72
E70
E76
E34
Figure 8c. Top View
+
C14
GND TIE
R72
C26
C17
R8
U17
GND TIE
U16
C15
C9
R7
R71
GND TIES
R39
C6
U9
R64
C18 C24
JP12
+5V
JP6
C10
C7
R42
U3
R58
GND TIES
R61
C23
U11
R38
R63
U15
C28
C35
JP9
C37
JP8
JP3
C36
JP4
C20
C8
R43
C34
C13
U14
U2
C2
R41
R60
C27
C22
C21
C33
R56
C1
R1
U10
R66
R65
C25
R4
R3
U4
C5
Figure 8b. Mechanical Layout Bottom View
GND TIE
GND TIE
Figure 8d. Layer 2
–18–
REV. 0
Page 19

AD10226
Figure 8e. Layer 3
Figure 8g. Ground View 2
REV. 0
Figure 8f. Ground View 1
–19–
Page 20

AD10226
37.00
35.00 BSC SQ
33.00
DETAIL C
AD10201AB
XXXX
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in millimeters (mm).
385-Lead Ball Grid Array (BGA)
(B-385)
30.48 BSC
SQ
DETAIL A
DETAIL B
1.27 TYP
24681012141618202224
135791113151719212325
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
C02927–0–5/02(0)
COMPONENT
VOL UME
DETAIL A
0.75
0.60
0.50
3.20
MAX
1.15
1.02
0.89
DETAIL B
0.90
0.75
0.60
AD10201AB
XXXX
DETAIL C
–20–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...