Page 1

54SX Family FPGAs
v3.1
Leading Edge Performance
• 320 MHz Internal Performance
• 3.7 ns Clock-to-Out (Pin-to-Pin)
• 0.1 ns Input Set-Up
• 0.25 ns Clock Skew
Specifications
• 12,000 to 48,000 System Gates
• Up to 249 User-Programmable I/O Pins
• Up to 1080 Flip-Flops
• 0.35µ CMOS
Features
• 66 MHz PCI
• CPLD and FPGA Integration
• Single Chip Solution
• 100% Resource Utilization with 100% Pin Locking
• 3.3V Operation with 5.0V Input Tolerance
• Very Low Power Consumption
• Deterministic, User-Controllable Timing
• Unique In-System Diagnostic and Debug capability with
Silicon Explorer II
• Boundary Scan Testing in Compliance with IEEE Standard
1149.1 (JTAG)
• Secure Programming Technology Prevents Reverse
Engineering and Design Theft
SX Product Profile
A54SX08 A54SX16 A54SX16P A54SX32
Capacity
Typical Gates
System Gates
Logic Modules
Combinatorial Cells
Register Cells (Dedicated Flip-Flops) 256 528 528 1,080
Maximum User I/Os 130 175 175 249
Clocks 3333
JTAG YesYesYesYes
PCI ——Yes—
Clock-to-Out 3.7 ns 3.9 ns 4.4 ns 4.6 ns
Input Set-Up (External) 0.8 ns 0.5 ns 0.5 ns 0.1 ns
Speed Grades Std, –1, –2, –3 Std, –1, –2, –3 Std, –1, –2, –3 Std, –1, –2, –3
Temperature Grades C, I, M C, I, M C, I, M C, I, M
Packages (by pin count)
PLCC
PQFP
VQFP
TQFP
PBGA
FBGA
8,000
12,000
768
512
84
208
100
144, 176
—
144
16,000
24,000
1,452
924
—
208
100
176
—
—
16,000
24,000
1,452
924
—
208
100
144, 176
—
—
32,000
48,000
2,880
1800
—
208
—
144, 176
313, 329
—
June 2003 1
© 2003 Actel Corporation
Page 2
General Description
Actel’s SX family of FPGAs features a sea-of-modules
architecture that delivers device performance and
integration levels not currently achieved by any other FPGA
architecture. SX devices greatly simplify design time, enable
dramatic reductions in design costs and power
consumption, and further decrease time to market for
performance-intensive applications.
Actel’s SX architecture features two types of logic modules,
the combinatorial cell (C-cell) and the register cell (R-cell),
each optimized for fast and efficient mapping of synthesized
logic functions. The routing and interconnect resources are
in the metal layers above the logic modules, providing
optimal use of silicon. This enables the en tire floor of the
device to be spanned with an uninterrupted grid of
fine-grained, synthesis-friendly logic modules (or
“sea-of-modules”), which reduces the distance signals have
to travel between logic modules. To minimize signal
propagation delay, SX devices employ both local and general
routing resources. The high-speed local routing resources
(DirectConnect and FastConnect) enable very fast local
signal propagation that is optimal for fast counters, state
54SX Family FPGAs
machines, and datapath logic. The general system of
segmented routing tracks allows any logic module in the
array to be connected to any other logic or I/O module.
Within this system, propagation delay is minimized by
limiting the number of antifuse interconnect elements to
five (90 percent of connections typically use only three
antifuses). The unique local and general routing structure
featured in SX devices gives fast and predictable
performance, allows 100percent pin-locking with full logic
utilization, enables concurrent PCB development, reduces
design time, and allows designers to achieve performance
goals with minimum effort.
Further complementing SX’s flexible routing structure is a
hard-wired, constantly loaded clock network that has been
tuned to provide fast clock propagation with minimal clock
skew. Additionally, the high performance of the internal
logic has eliminated the need to embed latches or flip-flops
in the I/O cells to achieve fast clock-to-out or fast input
set-up times. SX devices have easy-to-use I/O cells that do
not require HDL instantiation, facilitating design re-use and
reducing design and verification time.
Ordering Information
A54SX16 – PQ 208
P
2
Application (Temperature Range)
Blank = Commercial (0 to +70°C)
I = Industrial (–40 to +85°C)
M = Military (–55 to +125°C)
PP = Pre-production
Package Lead Count
Package Type
BG = Ball Grid Array
PL = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
PQ = Plastic Quad Flat Pack
TQ = Thin (1.4 mm) Quad Flat Pack
VQ = Very Thin (1.0 mm) Quad Flat Pack
FG = Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array (1.0 mm)
Speed Grade
Blank = Standard Speed
–1 = App roximately 15% Faster than Standard
–2 = App roximately 25% Faster than Standard
–3 = Approximately 35% Faster than Standard
Blank = Not PCI Compliant
P = PCI Compliant
Part Number
A54SX08 = 12,000 System Gates
A54SX16 = 24,000 System Gates
A54SX16P = 24,000 System Gates
A54SX32 = 48,000 System Gates
2 v3.1
Page 3

54SX Family FPGAs
Product Plan
Speed Grade* Application
Std–1–2–3 C I†M
A54SX08 Device
84-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
100-Pin Very Thin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (VQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
144-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
144-Pin Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
176-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
208-Pin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
A54SX16 Device
100-Pin Very Thin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (VQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
176-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
208-Pin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
A54SX16P Device
100-Pin Very Thin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (VQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
144-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
176-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
208-Pin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
A54SX32 Device
144-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
176-Pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
208-Pin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔P
313-Pin Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
329-Pin Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) ✔✔✔✔ ✔✔—
Contact your Actel sales representative for product availability.
Applications:C = CommercialAvailability:✔ = Available*Speed Grade:–1 = Approx. 15% faster than Standard
I = Industrial P = Planned –2 = Approx. 25% faster than Standard
M = Military — = Not Planned –3 = Approx. 35% faster than Standard
† Only Std, –1, –2 Speed Grade
Only Std, –1 Speed Grade
•
•
Plastic Device Resources
User I/Os (including clock buffers)
Device
84-Pin
A54SX08 69 81 130 113 128 — — 111
A54SX16 — 81 175 — 147 — — —
A54SX16P — 81 175 113 147 — — —
A54SX32 — — 174 113 147 249 249 —
Package Definitions (Consult your local Actel sales representative for product availability.)
PLCC = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier, PQFP = Plastic Quad Flat Pack, TQFP = Thin Quad Flat Pack, VQFP = Very Thin Quad Flat Pack,
PBGA = Plastic Ball Grid Array, FBGA = Fine Pitch (1.0 mm) Ball Grid Array
PLCC
VQFP
100-Pin
PQFP
208-Pin
TQFP
144-Pin
v3.1 3
TQFP
176-Pin
PBGA
313-Pin
PBGA
329-Pin
FBGA
144-Pin
Page 4
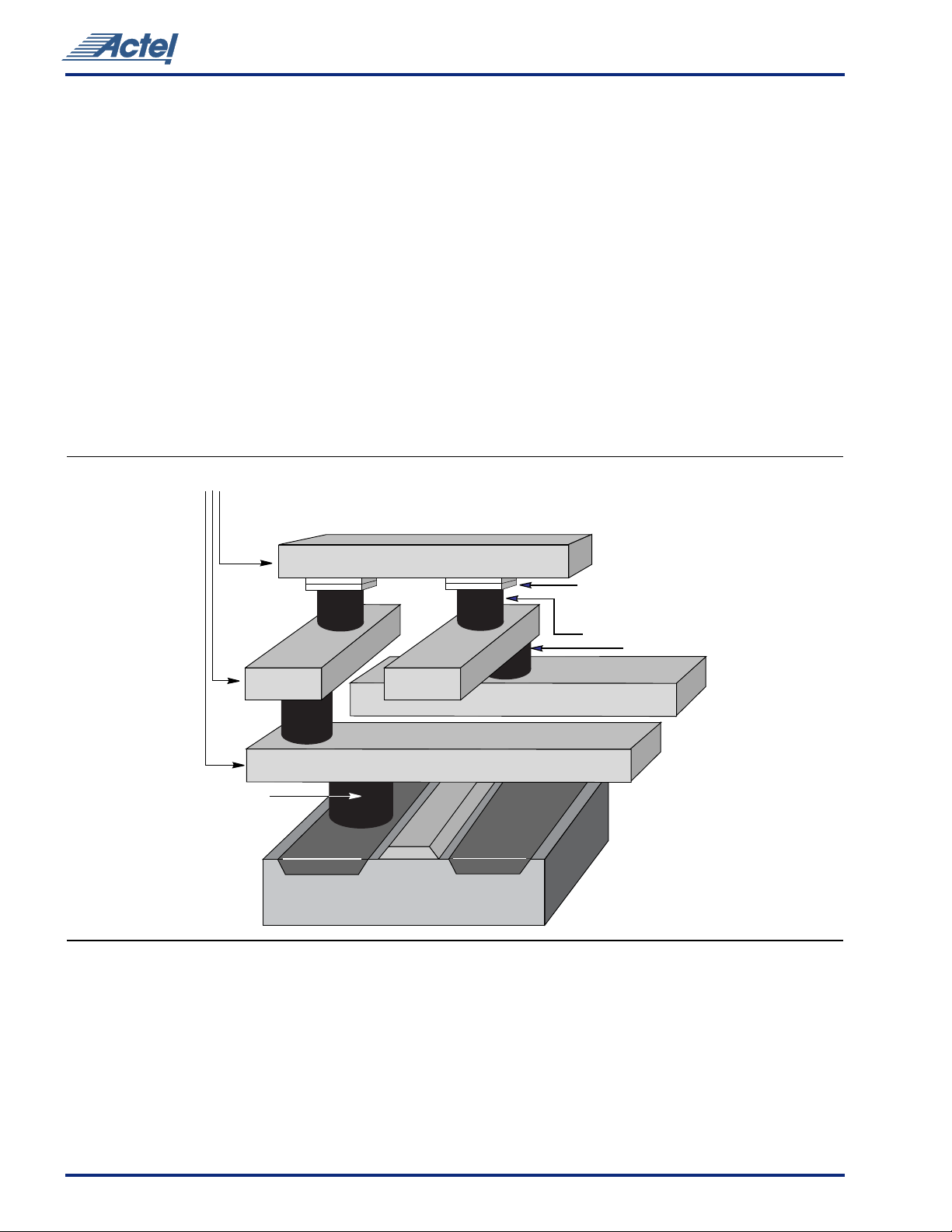
SX Family Architecture
The SX family architecture was designed to satisfy
next-generation performance and integration requirements
for production-volume designs in a broad range of
applications.
Programmable Interconnect Elemen t
The SX family provides efficient use of silicon by locating the
routing interconnect resources between the Metal 2 (M2)
and Metal 3 (M3) layers (Figure1). This completely
eliminates the channels of routing and interconnect
resources between logic modules (as implemented on SRAM
FPGAs and previous generations of antifuse FPGAs), and
enables the entire floor of the device to be spanned with an
uninterrupted grid of logic modules.
Interconnection between these logic modules is achieved
using Actel’s patented metal-to-metal programmable
Routing T rac ks
54SX Family FPGAs
antifuse interconnect elements, which are embedded
between the M2 and M3 layers. The antifuses are normally
open circuit and, when programmed, form a permanent
low-impedance connection.
The extremely small size of these interconnect elements
gives the SX famil y abundant routing resources and provides
excellent protection against design pirating. Reverse
engineering is virtually impossible because it is extremely
difficult to distinguish between programmed and
unprogrammed antifuses, and there is no configuration
bitstream to intercept.
Additionally, the interconnect (i.e., the antifuses and metal
tracks) have lower capacitance and lower resistance than
any other device of similar capacity, leading to the fastest
signal propagation in the industry.
Metal 3
Metal 2
Metal 1
Tungsten Plug
Contact
Silicon Substrate
Figure 1 • SX Family Interconnect Elements
Logic Module Design
The SX family architecture is described as a
“sea-of-modules” architecture because the entire floor of
the device is covered with a grid of logic modules with
virtually no chip area lost to interconnect elements or
routing. Actel’s SX family provides two types of logic
modules, the register cell (R-cell) and the combinatorial
cell (C-cell).
Amorphous Silicon/
Dielectric Antifuse
Tungsten Plug Via
Tungsten Plug Via
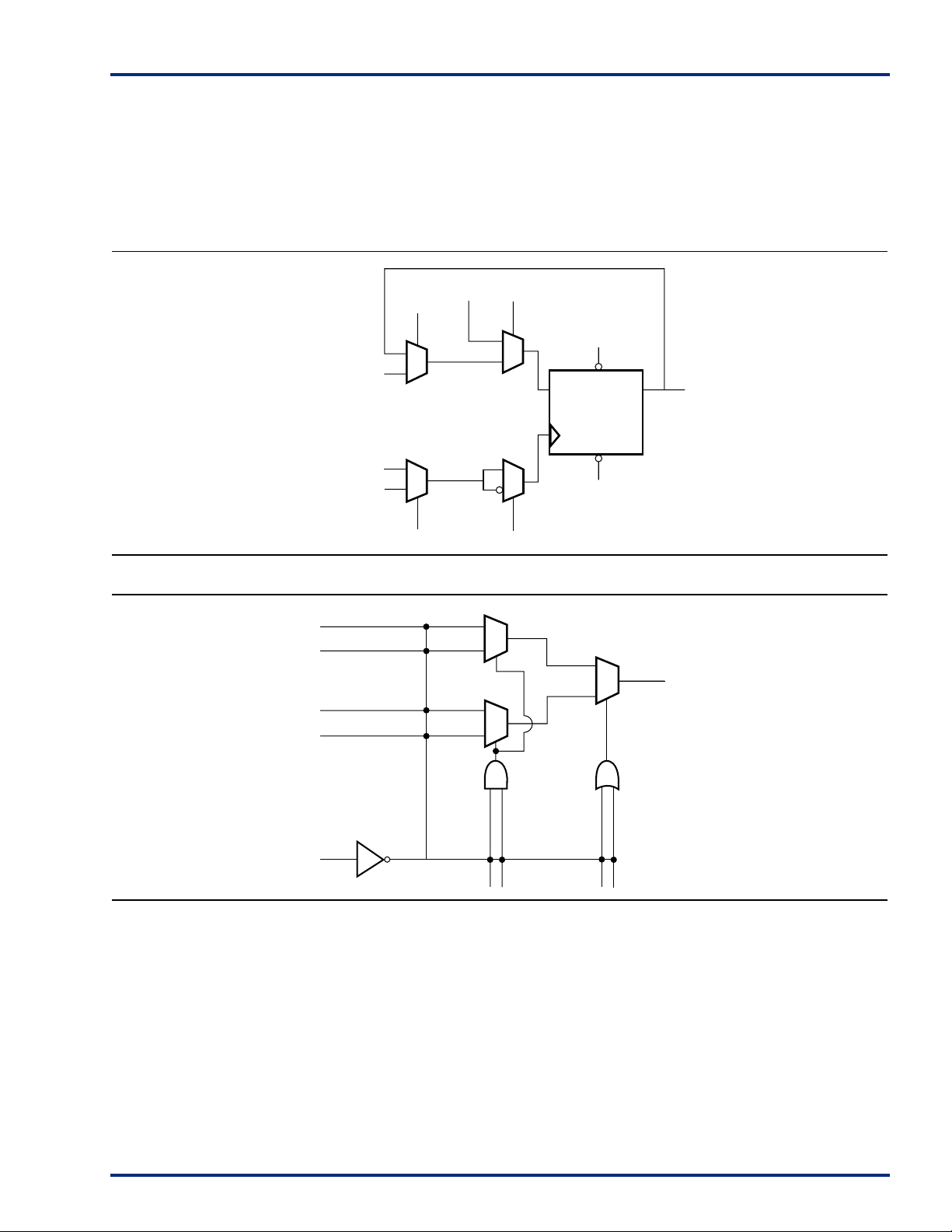
The R-cell contains a flip-flop featuring asynchronous clear,
asynchronous preset, and clock enable (using the S0 and S1
lines) control signals (Figure 2 on page5). The R-cell
registers feature programmable clock polarity selectable on
a register-by-register basis. This provides additional
flexibility while allowing mapping of synthesized functions
into the SX FPGA. The clock source for the R-cell can be
chosen from either the hard-wired clock or the routed clock.
4 v3.1
Page 5
54SX Family FPGAs
The C-cell implements a range of combinatorial functions
up to 5-inputs (Figure 3). Inclusion of the DB input and its
associated inverter function dramatically increases the
number of combinatorial functions that can be
implemented in a single module from 800 options in
previous architectures to more than 4,000 in the SX
architecture. An example of the improved flexibility
Routed
Data Input
S0
Direct
Connect
Input
HCLK
CLKA,
CLKB,
Internal Logic
CKS CKP
enabled by the inversion capability is the ability to integrate
a 3-input exclusive-OR function into a single C-cell. This
facilitates construction of 9-bit parity-tree functions with 2
ns propagation delays. At the same time, the C-cell
structure is extremely synthesis friendly, simplifying the
overall design and reducing synthesis time.
S1
PSETB
YDQ
CLRB
Figure 2 • R-Cell
D0
D1
D2
D3
DB
A0 B0 A1 B1
Figure 3 • C-Cell
Chip Architecture
The SX family’s chip architecture provides a unique
approach to module organization and chip routing that
delivers the best register/logic mix for a wide variety of new
and emerging applications.
Module Organization
Actel has arranged all C-cell and R-cell logic modules into
horizontal banks called Clusters. There are two types of
Clusters: Type 1 contains two C-cells and one R-cell, while
Y
Sa Sb
Type 2 contains one C-cell and two R-cells.
To increase design efficiency and device performance, Actel
has further organized these modules into
SuperClusters
(Figure4 on page 6). SuperCluster 1 is a two-wide grouping
of Type 1 clusters. SuperCluster 2 is a two-wide group
containing one Type 1 cluster and one Type 2 cluster. SX
devices feature more SuperCluster 1 modules than
SuperCluster 2 modules because designers typically require
significantly more combinatorial logic than flip-flops.
v3.1 5
Page 6
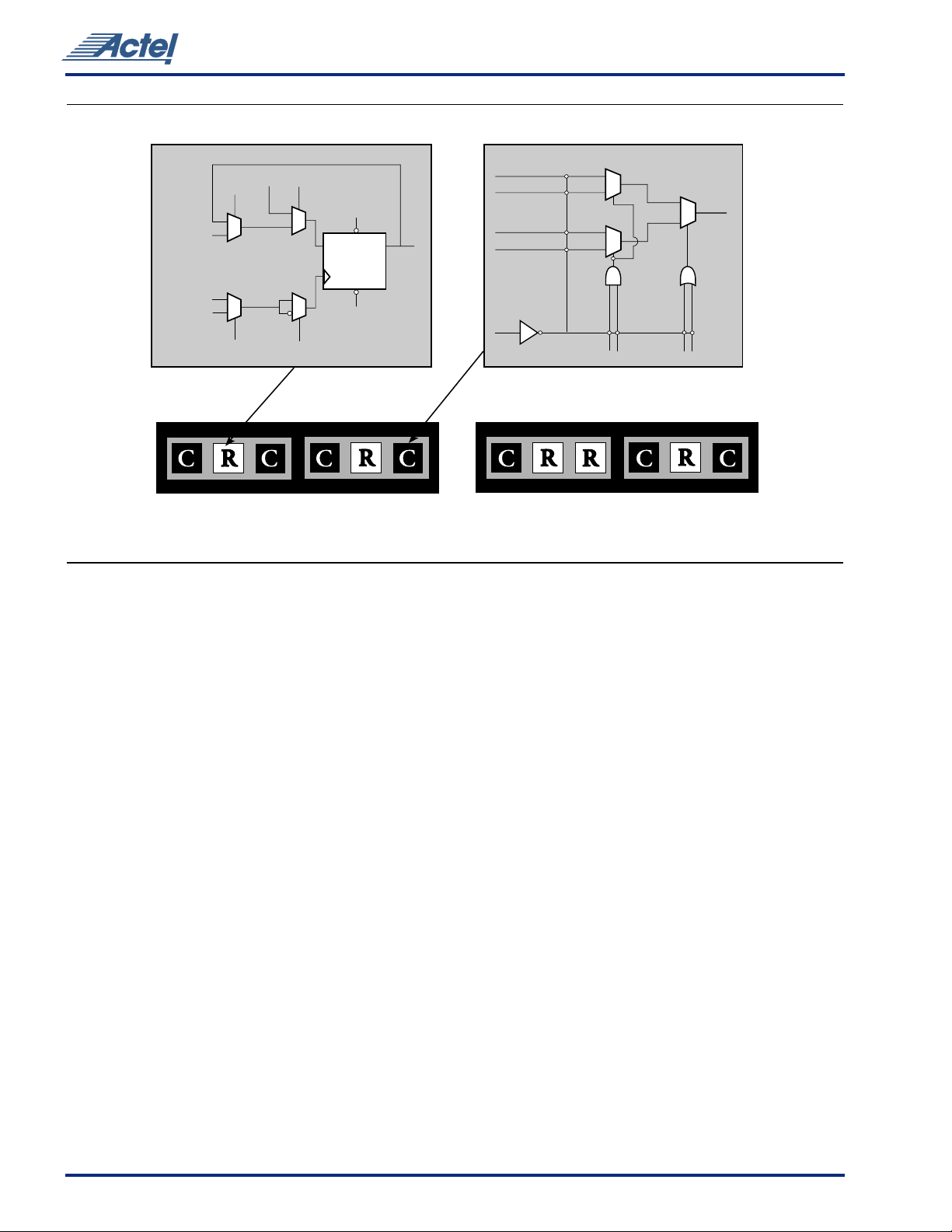
R-Cell C-Cell
54SX Family FPGAs
Routed
Data Input
S0
Direct
Connect
Input
HCLK
CLKA,
CLKB,
Internal Logic
CKS CKP
Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 2 Cluster 1
Type 1 SuperCluster Type 2 SuperCluster
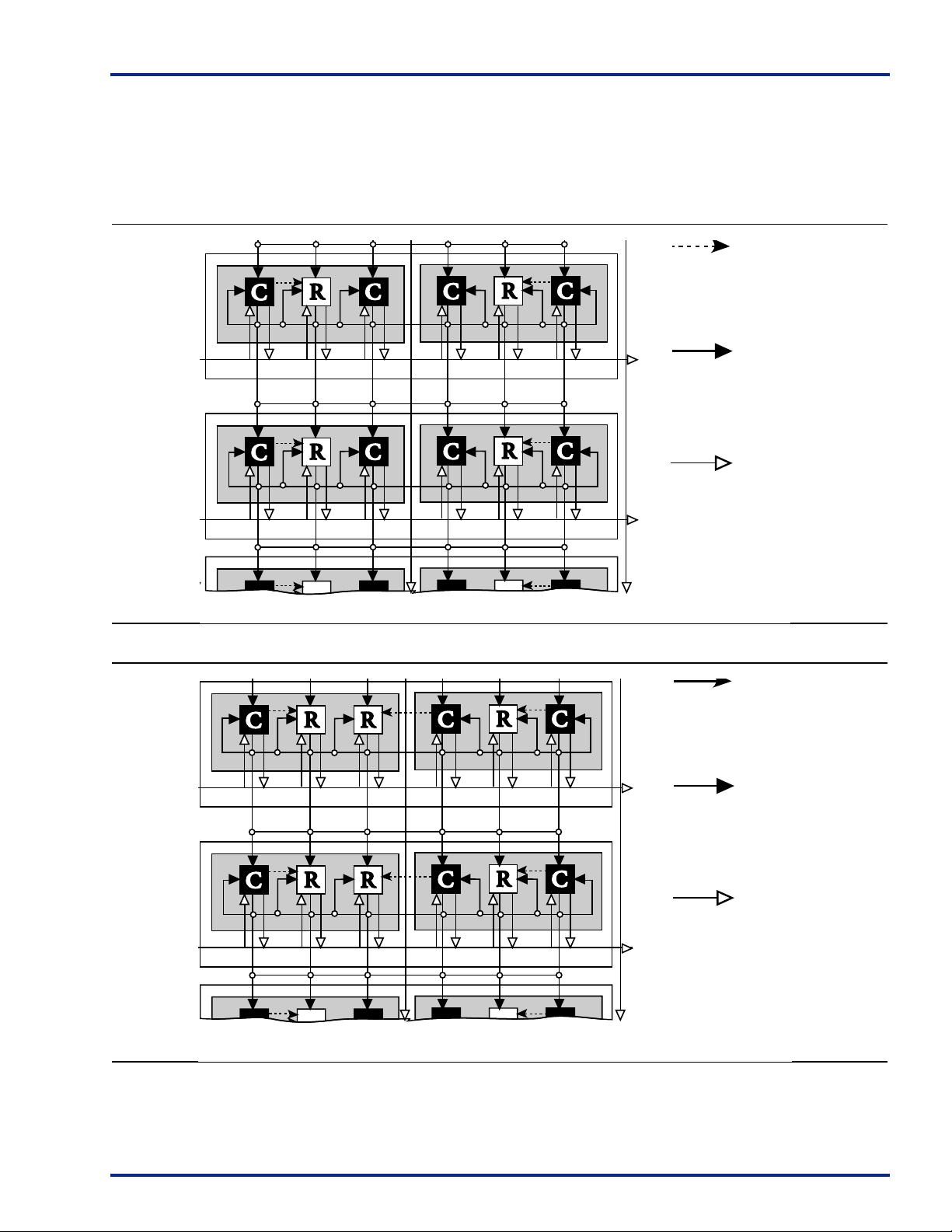
Figure 4 • Cluster Organization
Routing Resources
S1
PSETB
YDQ
CLRB
D0
D1
Y
D2
D3
Sa Sb
DB
A0 B0 A1 B1
Clusters and SuperClusters can be connected through the
use of two innovative local routing resources called
FastConnect and DirectConnect, which enable extremely
fast and predictable interconnection of modules within
Clusters and SuperClusters (Figure 5 and Figure 6 on
page 7). This routing architectu re also dr amaticall y reduces
the number of antifuses required to complete a circuit,
ensuring the highest possible performance.
DirectConnect is a horizontal routing resource that provides
connections from a C-cell to its neighboring R-cell in a given
SuperCluster. DirectConnect uses a hard-wired signal path
requiring no programmable interconnection to achieve its
fast signal propagation time of less than 0.1 ns.
FastConnect enables horizontal routing between any two
logic modules within a given SuperCluster and vertical
routing with the SuperCluster immediately below it. Only
one programmable connection is used in a FastConnect
path, delivering maximum pin-to-pin propagation of 0.4 ns.
In addition to DirectConnect and FastConnect, the
architecture makes use of two globally oriented routing
resources known as segmented routing and high-drive
routing. Actel’s segmented routing structure provides a
variety of track lengths for extremely fast routing between
SuperClusters. The exact combination of track lengths and
antifuses within each path is chosen by the 100 percent
automatic place and route software to minimize signal
propagation delays.
Actel’s high-drive routing structure provides three clock
networks. The first clock, called HCLK, is hard wired from
the HCLK buffer to the clock select MUX in each R-cell. This
provides a fast propagation path for the clock signal,
enabling the 3.7 ns clock-to-out (pin-to-pin) performance of
the SX devices. The hard-wired clock is tuned to provide
clock skew as low as 0.25 ns. The remaining two clocks
(CLKA, CLKB) are global clocks that can be sourced from
external pins or from internal logic signals within the SX
device.
6 v3.1
Page 7
54SX Family FPGAs
Other Architectural Features
Technology
Actel’s SX family is implemented on a high-voltage twin-well
CMOS process using 0.35µ design rules. The metal-to-metal
antifuse is made up of a combination of amorphous silicon
and dielectric material with barrier metals and has a
programmed (“on” state) resistance of 25Ω with
capacitance of 1.0 fF for low signal impedance.
Direct Connect
• No antifuses
• 0.1 ns routing delay
Fast Connect
• One antifuse
• 0.4 ns routing delay
Routing Segments
• Typically 2 antifuses
• Max. 5 antifuses
Figure 5 • DirectConnect and FastConnect for Type 1 SuperClusters
Figure 6 • DirectConnect and FastConnect for Type 2 SuperClusters
Direct Connect
• No antifuses
• 0.1 ns routing delay
Fast Connect
• One antifuse
• 0.4 ns routing delay
Routing Segments
• Typically 2 antifuses
• Max. 5 antifuses
v3.1 7
Page 8
54SX Family FPGAs
Performance
The combination of architectural features described above
enables SX devices to operate with internal clock
frequencies exceeding 300 MHz, enabling very fast
execution of even complex logic functions. Thus, the SX
family is an optimal platform upon which to integrate the
functionality previously contained in multiple CPLDs. In
addition, designs that previously would have required a gate
array to meet performance goals can now be integrated into
an SX device with dramatic improvements in cost and time
to market. Using timing-driven place and route tools,
designers can achieve highly deterministic device
performance. With SX devices, designers do not need to use
complicated performance-enhancing design techniques
such as the use of redundant logic to reduce fanout on
critical nets or the instantiation of macros in HDL code to
achieve high performance.
I/O Modules
Each I/O on an SX device can be configured as an input, an
output, a tristate output, or a bidirectional pin. Even without
the inclusion of dedicated I/O registers, these I/Os, in
combination with array registers, can achieve clock-to-out
(pad-to-pad) timing as fast as 3.7 ns. I/O cells that have
embedded latches and flip-flops require instantiation in
HDL code; this is a design complication not encountered in
SX FPGAs. Fast pin-to-pin timing ensures that the device
will have little trouble interfacing with any other device in
the system, which in turn enables parallel design of system
components and reduces overall design time.
Power Requirements
The SX family supports 3.3V operation and is designed to
tolerate 5.0V inputs. (Table 1). Power consumption is
extremely low due to the very short distances signals are
required to travel to complete a circuit. Power requirements
are further reduced because of the small number of
low-resistance antifuses in the path. The antifuse
architecture does not require active circuitry to hold a
charge (as do SRAM or EPROM), making it the lowest-power
architecture on the market.
Table 1 • Supply Voltages
Maximum
V
CCAVCCIVCCR
A54SX08
A54SX16
A54SX32
A54SX16-P
Note: A54SX16-P has three different entries because it is capable of
3.3V 3.3V 5.0V 5.0V 3.3V
3.3V
3.3V
3.3V
both a 3.3V and a 5V drive.
3.3V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
5.0V
Input
Tolerance
3.3V
5.0V
5.0V
Maximum
Output
Drive
3.3V
3.3V
5.0V
Boundary Scan Testing (BST)
All SX devices are IEEE 1149.1 compliant. SX devices offer
superior diagnostic and testing capabilities by providing
Boundary Scan Testing (BST) and probing capabilities.
These functions are controlled through the special test pins
in conjunction with the program fuse. The functionality of
each pin is described in Table 2.In the dedicated test mode,
TCK, TDI and TDO are dedicated pins and cannot be used as
regular I/Os. In flexible mode, TMS should be set HIGH
through a pull-up resistor of 10kΩ. TMS can be pulled LOW
to initiate the test sequence.
The program fuse determines whether the device is in
dedicated or flexible mode. The default (fuse not blown) is
flexible mode. .
Table 2 • Boundary Scan Pin Functionality
Program Fuse Blown
(Dedicated Test Mode)
TCK, TDI, TDO are
dedicated BST pins
No need for pull-up resistor
for TMS
Development Tool Support
Program Fuse Not Blown
(Flexible Mode)
TCK, TDI, TDO are flexible
and may be used as I/Os
Use a pull-up resistor of 10k
Ω on TMS
The SX devices are fully supported by Actel’s line of FPGA
development tools, including the Actel DeskTOP series and
Designer Advantage tools. The Actel DeskTOP series is an
integrated design environment for PCs that includes design
entry, simulation, synthesis, and place and route tools.
Designer Advantage, Actel’s suite of FPGA development
point tools for PCs and Workstations, includes the ACTgen
Macro Builder, Designer with DirectTime timing driven
place and route and analysis tools, and device programming
software.
In addition, the SX devices contain ActionProbe circuitry
that provides built-in access to every node in a design,
enabling 100-percent real-time observation and analysis of a
device's internal logic nodes without design iteration. The
probe circuitry is accessed by Silicon Explorer II, an
easy-to-use integrated verification and logic analysis tool
that can sample data at 100 M Hz (asynchronous ) or 66 MHz
(synchronous). Silicon Explorer II attaches to a PC’s
standard COM port, turning the PC into a fully functional
18-channel logic analyzer. Silicon Explorer II allows
designers to complete the design verification process at
their desks and reduces verification time from several hours
per cycle to only a few seconds.
8 v3.1
Page 9
54SX Family FPGAs
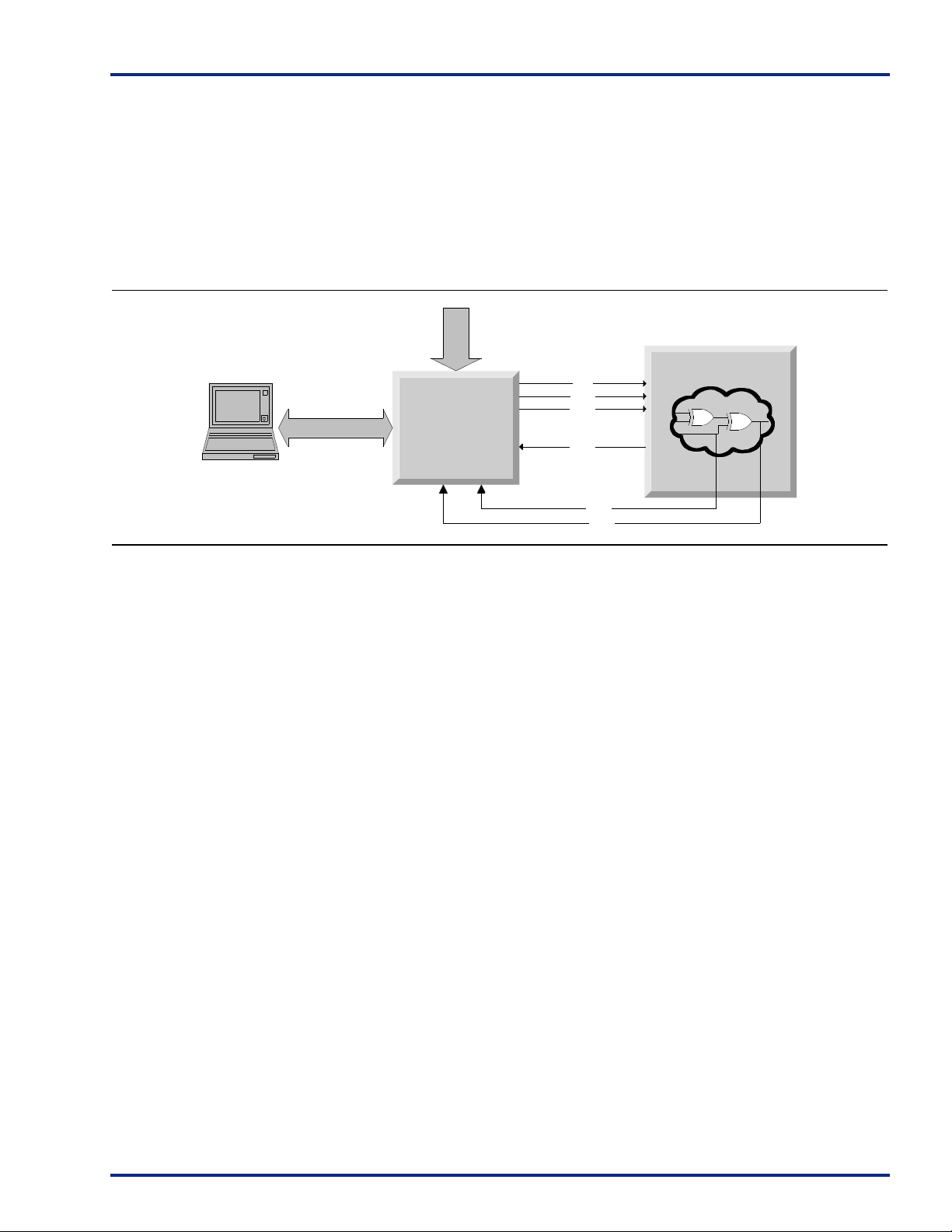
SX Probe Circuit Control Pins
The Silicon Explorer II tool uses the boundary scan ports
(TDI, TCK, TMS and TDO) to select the desired nets for
verification. The selected internal nets are assigned to the
PRA/PRB pins for observation. Figure 7 illustrates the
interconnection between Silicon Expl orer II and the FPGA
to perform in-circuit verification. The TRST pin is equipped
with a pull-up resistor. To remove the boundary scan state
machine from the reset state during probing, it is
16
Serial Connection
Silicon Explorer II
recommended that the TRST pin be left floating.
Design Considerations
The TDI, TCK, TDO, PRA, and PRB pins should not be used
as input or bidirectional ports. Because these pins are
active during probing, critical signals input through these
pins are not available while probing. In addition, the
Security Fuse should not be programmed because doing so
disables the Probe Circuitry.
Channel
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
PRA
PRB
SX FPGA
Figure 7 • Probe Setup
v3.1 9
Page 10
3.3V/5V Operating Conditions Absolute Maximum Ratings
1
Recommended Operating Conditions
54SX Family FPGAs
Symbol Parameter Limits Units
V
V
V
CCR
CCA
CCI
2
DC Supply Voltage
2
DC Supply Voltage –0.3 to +4.0 V
DC Supply Voltage
2
(A54SX08, A54SX16,
3
–0.3 to +6.0 V
–0.3 to +4.0 V
A54SX32)
V
V
V
I
T
IO
CCI
I
O
STG
2
(A54SX16P)
Input Voltage –0.5 to +5.5 V
Output Voltage –0.5 to +3.6 V
I/O Source Sink
3
Current
Storage Temperature –65 to +150 °C
–0.3 to +6.0 V
–30 to +5.0 mA
DC Supply Voltage
Notes:
1. Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device.
Exposure to absolute maximum rated conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability. Device should not be
operated outside the Recommended Operating Conditions.
2. V
in the A54SX16P must be greater than or equal to V
CCR
during power-up and power-down sequences and during
CCI
normal operation.
3. Device inputs are normally high impedance and draw
extremely low current. However, when input voltage is greater
than V
+ 0.5V or less than GND – 0.5V, the internal protection
CC
diodes will forward-bias and can draw excessive current.
Parameter
Temperature
1
Range
cial Industrial Military Units
0 to+70 –40 to +85 –55 to +125 °C
3.3V Power
Commer
Supply
±10 ±10 ±10
Tolerance
5.0V Power
Supply
±5 ±10 ±10
Tolerance
Note:
1. Ambient temperature (T
industrial; case temperature (T
%V
%V
) is used for commercial and
A
) is used for military.
C
C
C
C
C
Electrical Specifications
Commercial Industrial
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
(I
V
OH
V
OL
V
IL
V
IH
t
R
C
IO
I
CC
I
CC(D)
= -20uA) (CMOS)
OH
(I
= -8mA) (TTL)
OH
(I
= -6mA) (TTL)
OH
(IOL= 20uA) (CMOS)
(I
= 12mA) (TTL)
OL
(I
= 8mA) (TTL)
OL
, t
F
Input Transition Time tR, t
F
CIO I/O Capacitance 10 10 pF
Standby Current, ICC 4.0 4.0 mA
I
CC(D) IDynamic VCC
Supply Current See “Evaluating Power in 54SX Devices” on page 18
(V
CCI
– 0.1)
2.4
V
CCI
V
CCI
(V
CCI
– 0.1)
2.4
V
CCI
V
CCI
0.10
0.50
0.50
0.8 0.8 V
2.0 2.0 V
50 50 ns
V
V
10 v3.1
Page 11
54SX Family FPGAs
PCI Compliance for the 54SX Family
The 54SX family supports 3.3V and 5V PCI and is compliant with the PCI Local Bus Specification Rev. 2.1.
A54SX16P DC Specifications (5.0V PCI Operation)
Symbol Parameter Condition Min. Max. Units
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
V
IH
V
IL
I
IH
I
IL
V
OH
V
OL
C
IN
C
CLK
C
IDSEL
Notes:
1. Input leakage currents include hi-Z output leakage for all bi-directional buffers with tri-state outputs.
2. Signals without pull-up resistors must have 3 mA low output current. Signals requiring pull up must have 6 mA; the latter include,
FRAME#, IRDY#, TRDY#, DEVSEL#, STOP#, SERR#, PERR#, LOCK#, and, when used AD[63::32], C/BE[7::4]#, PAR64, REQ64#, and ACK64#.
3. Absolute maximum pin capacitance for a PCI input is 10 pF (except for CLK).
4. Lower capacitance on this input-only pin allows for non-resistive coupling to AD[xx].
Supply Voltage for Array 3.0 3.6 V
Supply Voltage required for Internal Biasing 4.75 5.25 V
Supply Voltage for IOs 4.75 5.25 V
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
1
1
2.0 VCC + 0.5 V
–0.5 0.8 V
Input High Leakage Current VIN = 2.7 70 µA
Input Low Leakage Current VIN = 0.5 –70 µA
Output High Voltage I
Output Low Voltage
Input Pin Capacitance
2
3
= –2 mA 2.4 V
OUT
I
= 3 mA, 6 mA 0.55 V
OUT
10 pF
CLK Pin Capacitance 5 12 pF
IDSEL Pin Capacitance
4
8pF
v3.1 11
Page 12
54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16P AC Specifications for (PCI Operation)
Symbol Parameter Condition Min. Max. Units
1
I
OH(AC)
I
OL(AC)
I
CL
slew
slew
≤ 1.4
OUT
OUT
OUT
= 3.1
≥ 2.2
OUT
OUT
= 0.71
< 2.4
< V
CC
3
1
> 0.55
> 0
3
1, 2
–44 + (V
1, 3
1
1, 3
Switching Current High
(Test Point) V
Switching Current High
(Test Point) V
0 < V
1.4 ≤ V
3.1 < V
OUT
V
OUT
2.2 > V
0.71 > V
OUT
Low Clamp Current –5 < VIN ≤ –1 –25 + (VIN + 1)/0.015 mA
R
F
Output Rise Slew Rate 0.4V to 2.4V load
Output Fall Slew Rate 2.4V to 0.4V load
4
4
–44 mA
– 1.4)/0.024 mA
OUT
Equation A: on
page 13
–142 mA
95 mA
V
/0.023
OUT
Equation B: on
page 13
mA
206 mA
15V/ns
15V/ns
Notes:
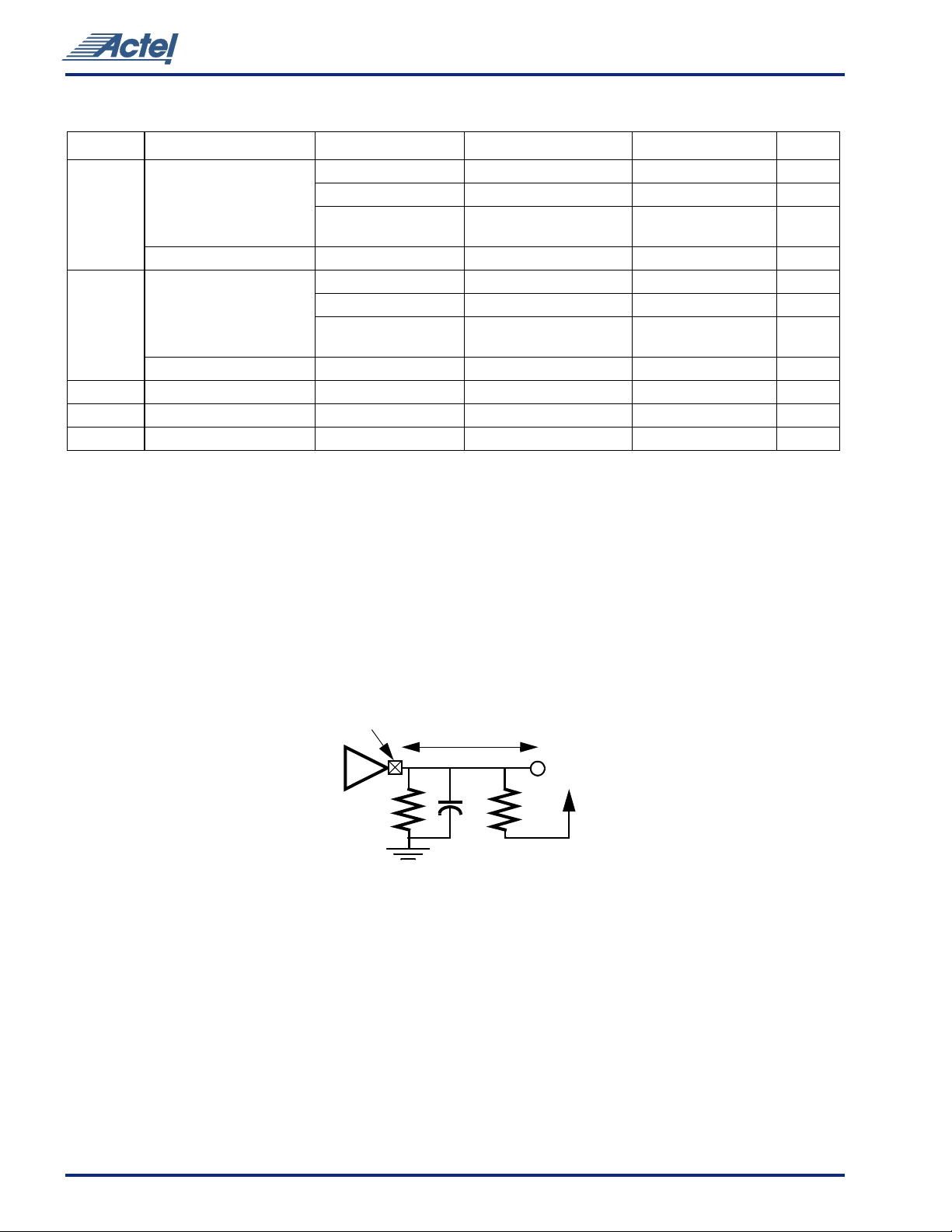
1. Refer to the V/I curves in Figure 8. Switching current characteristics for REQ# and GNT# are permitted to be one half of that specified here;
i.e., half size output drivers may be used on these signals. This specification does not apply to CLK and RST# which are system outputs.
“Switching Current High” specification are not relevant to SERR#, INTA#, INTB#, INTC#, and INTD# which are open drain outputs.
2. Note that this segment of the minimum current curve is drawn from the AC drive point directly to the DC drive point rather than toward
the voltage rail (as is done in the pull-down curve). This difference is intended to allow for an optional N-channel pull-up.
3. Maximum current requirements must be met as drivers pull beyond the last step voltage. Equations defining these maximums (A and B)
are provided with the respective diagrams in Figure 8. The equation defined maxima should be met by design. In order to facilitate
component testing, a maximum current test point is defin ed for each side of the output driver.
4. This parameter is to be interpreted as the cumulative edge rate across the spe cified range, rather than the instantaneous rate at a ny poin t
within the transition range. The specified load (diagram below) is optional; i.e., the designer may elect to meet this parameter with an
unloaded output per revision 2.0 of the PCI Local Bus Specification. However, adherence to both maximum and minimum parameters is
now required (the maximum is no longer simply a guideline). Since adherence to the maximum slew rate was not required prior to
revision 2.1 of the specification, there may be components in the market for some time that have faster edge rates; therefore, motherboard
designers must bear in mind that rise and fall times faster than this specification could occur, and should ensure that signal integrity
modeling accounts for this. Rise slew rate does not apply to open drain outputs.
pin
1/2 in. max.
output
buffer
V
CC
10 pF
1kΩ
1kΩ
12 v3.1
Page 13
54SX Family FPGAs
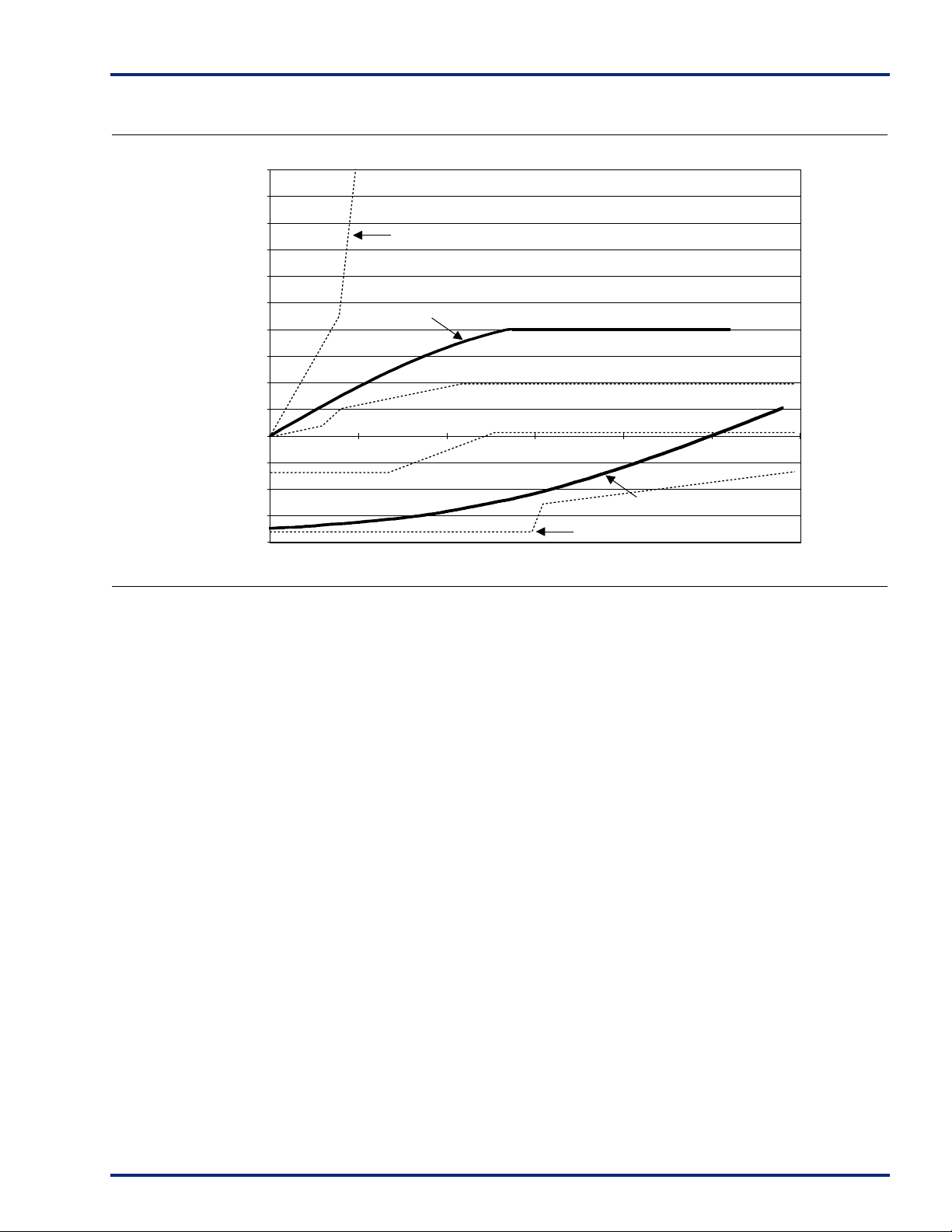
Figure 8 shows the 5.0V PCI V/I curve and the minimum and maximum PCI drive characteristics of the A54SX16P family.
0.50
0.45
0.40
0.35
0.30
0.25
0.20
0.15
Current (A)
0.10
0.05
0
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
–0.20
PCI IOH Mininum
PCI IOL Maximum
SX PCI I
1
OL
Figure 8 • 5.0V PCI Curve for A54SX16P Family
Equation A:
I
= 11.9 * (V
OH
for VCC > V
– 5.25) * (V
OUT
OUT
> 3.1V
OUT
+ 2.45)
PCI IOL Mininum
23456
SX PCI I
PCI IOH Maximum
Voltage Out
OH
Equation B:
IOL = 78.5 * V
for 0V < V
OUT
OUT
* (4.4 – V
< 0.71V
OUT
)
v3.1 13
Page 14
54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16P DC Specifications (3 .3V PCI Operation)
Symbol Parameter Condition Min. Max. Units
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
V
IH
V
IL
I
IPU
I
IL
V
OH
V
OL
C
IN
C
CLK
C
IDSEL
Supply Voltage for Array 3.0 3.6 V
Supply Voltage required for Internal Biasing 3.0 3.6 V
Supply Voltage for IOs 3.0 3.6 V
Input High Voltage 0.5V
CCVCC
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.3V
Input Pull-up Voltage
Input Leakage Current
Output High Voltage I
Output Low Voltage I
Input Pin Capacitance
1
2
3
0 < VIN < V
OUT
OUT
CC
= –500 µA 0.9V
= 1500 µA 0.1V
0.7V
CC
CC
+ 0.5 V
CC
V
V
±10 µA
V
CC
V
10 pF
CLK Pin Capacitance 5 12 pF
IDSEL Pin Capacitance
4
8pF
Notes:
1. This specification should be guaranteed by design. It is the minimum voltage to which pull-up resistors are calculated to pull a floated
network. Applications sensitive to static power utilization should assure that the input buffer is conducting minimum current at this
input voltage.
2. Input leakage currents include hi-Z output leakage for all bi-directional buffers with tri-state outputs.
3. Absolute maximum pin capacitance for a PCI i nput is 10pF ( exc ept f or C LK).
4. Lower capacitance on this input-only pin allows for non-resistive coupling to AD[xx].
14 v3.1
Page 15
54SX Family FPGAs
A 54SX16P AC Specifications (3.3V PCI Operation)
Symbol Parameter Condition Min. Max. Units
CC
< 0.9V
< V
2
CC
≥ 0.6V
> 0.1V
> 0
OUT
2
CC
1
mA
1
CC
1, 2
–17.1 + (VCC – V
CC
1
CC
1
CC
1, 2
–12V
CC
)
OUT
16V
CC
26.7V
OUT on page 16
– 1)/0.015 mA
OUT
Equation C: on
page 16
–32V
CC
38V
CC
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
I
OH(AC)
I
OL(AC)
I
CL
I
CH
slew
slew
OUT
CC
OUT
≤ V
CC
= 0.7V
> V
> V
CC
≤ 0.3V
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
Switching Current High
(Test Point) V
Switching Current High
0 < V
0.3V
0.7VCC < V
V
0.6V
0.18VCC > V
(Test Point) V
OUT
= 0.18V
Low Clamp Current –3 < VIN ≤ –1 –25 + (VIN + 1)/0.015 mA
High Clamp Current –3 < VIN ≤ –1 25 + (VIN – V
Output Rise Slew Rate30.2VCC to 0.6VCC load 1 4 V/ns
R
Output Fall Slew Rate30.6VCC to 0.2VCC load 1 4 V/ns
F
Notes:
1. Refer to the V/I curves in Figure9. Switching current characteristics for REQ# and GNT# are permitted to be one half of that specified here;
i.e., half size output drivers may be used on these signals. This specification does not apply to CLK and RST# which are system outputs.
“Switching Current High” specification are not relevant to SERR#, INTA#, INTB#, INTC#, and INTD# which are open drain outputs.
2. Maximum current requirements must be met as drivers pull beyond the last step voltage. Equations defining these maximums (C and D)
are provided with the respective diagrams in Figure 9. The equation defined maxima should be met by design. In order to facilit ate
component testing, a maximum current test point is defined for each side of t he output driver.
3. This parameter is to be interpreted as the cumulative edge rate across the specified range, rather than the instantaneous rate at any point
within the transition range. The specified load (diagram below) is optional; i.e., the designer may elect to meet this parameter with an
unloaded output per the latest revision of the PCI Local Bus Specification. However, adherence to both maximum and minimum
parameters is required (the maximum is no longer simply a guideline). Rise slew rate does not apply to open drain outputs.
pin
1/2 in. max.
output
buffer
V
CC
10 pF
1kΩ
1kΩ
v3.1 15
Page 16
54SX Family FPGAs
Figure 9 shows the 3.3V PCI V/I curve and the minimum and maximum PCI drive characteristics of the A54SX16P family.
0.50
0.45
0.40
0.35
0.30
0.25
0.20
0.15
Current (A)
0.10
0.05
0
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
–0.20
PCI IOH Minimum
PCI IOL Maximum
SX PCI I
123456
OL
Figure 9 • 3.3V PCI Curve for A54SX16P Family
Equation C:
= (98.0/VCC) * (V
I
OH
for V
CC
> V
– VCC) * (V
OUT
OUT
> 0.7 V
OUT
CC
+ 0.4VCC)
PCI IOH Maximum
Voltage Out
Equation D:
PCI IOL Minimum
I
= (256/VCC) * V
OL
for 0V < V
SX PCI I
OUT
OH
* (VCC – V
OUT
< 0.18 V
CC
OUT
)
16 v3.1
Page 17
54SX Family FPGAs
Power-Up Sequencing
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
Power-Up Sequence Comments
A54SX08, A54SX16, A54SX32
3.3V 5.0V 3.3V
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
No possible damage to device.
Possible damage to device.
A54SX16P
3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V Only No possible damage to device.
3.3V 5.0V 3.3V
3.3V 5.0V 5.0V
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
No possible damage to device.
Possible damage to device.
No possible damage to device.
No possible damage to device.
Power-Down Sequencing
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
Power-Down Sequence Comments
A54SX08, A54SX16, A54SX32
3.3V 5.0V 3.3V
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
No possible damage to device.
Possible damage to device.
A54SX16P
3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V Only No possible damage to device.
3.3V 5.0V 3.3V
3.3V 5.0V 5.0V
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
5.0V First
3.3V Second
3.3V First
5.0V Second
Possible damage to device.
No possible damage to device.
No possible damage to device.
No possible damage to device.
v3.1 17
Page 18

54SX Family FPGAs
Evaluating Power in 54SX Devices
A critical element of system reliability is the ability of
electronic devices to safely dissipate the heat generated
during operation. The thermal characteristics of a circuit
depend on the device and package used, the operating
temperature, the operating current, and the system's ability
to dissipate heat.
You should complete a power evaluation early in the design
process to help identify potential heat-related problems in
the system and to prevent the system from exceeding the
device’s maximum allowed junction temperature.
The actual power dissipated by most applications is
significantly lower than the power the package can
dissipate. However, a thermal analysis should be performed
for all projects. To perform a power evaluation, follow these
steps:
• Estimate the power consumption of the application.
• Calculate the maximum power allowed for the device and
package.
• Compare the estimated power and maximum power
values.
Estimating Power Consumption
The total power dissipation for the 54SX family is the sum of
the DC power dissipation and the AC power dissipation. Use
Equation 1 to calculate the estimated power consumption of
your application.
= PDC + PAC (1)
P
Total
DC Power Dissipation
The power due to standby current is typically a small
component of the overall power. The Standby power is
shown below for commercial, worst case conditions (70°C).
Table 3 •
I
CC
4mA 3.6V 14.4mW
V
CC
Power
The DC power dissipation is defined in Equation 2 as
follows:
= (I
P
DC
(I
standby
AC Power Dissipation
)*V
standby
)*V
CCA
+ x*VOL*IOL + y*(V
CCI
+ (I
standby
)*V
CCI
+
CCR
– VOH)*V
OH
(2)
The power dissipation of the 54SX Family is usually
dominated by the dynamic power dissipation. Dynamic
power dissipation is a function of frequency, equivalent
capacitance and power supply voltage. The AC power
dissipation is defined as follows:
PAC = P
P
Output Buffer
= V
P
AC
(n * C
EQI
(0.5 * (q
(0.5 * (q
(0.5 * (s
Definition of Terms Used in Fo rmula
Module
2
CCA
* fn)
* C
1
* C
2
* C
1
+ P
RCLKA Net
+ P
Input Buffer
* [(m * C
Input Buffer
EQCR
EQCR
EQHV
EQM
* fq1) + (r1 * fq1))
* fq2)+ (r2 * fq2))
* fs1) + (C
+ P
RCLKB Net
+ P
HCLK Net
(3)
* fm)
+ (p * (C
EQHF
Module
EQO
RCLKB
* fs1))
+
+ CL) * fp)
+
RCLKA
+
](4)
HCLK
Output Buffer
m = Number of logic modules switching at f
n = Number of input buffers switching at f
p = Number of output buffers switching at f
q
1
= Number of clock loads on the first routed array
clock
q
2
= Number of clock loads on the second routed
array clock
x = Number of I/Os at logic low
y = Number of I/Os at logic high
r
1
= Fixed capacitance due to first routed array
clock
r
2
= Fixed capacitance due to second routed array
clock
s
1
= N umber of clock loads on the dedicated array
clock
C
C
C
C
EQM
EQI
EQO
EQCR
= Equivalent capacitance of logic modules in pF
= Equivalent capacitance of input buffers in pF
= Equivalent capacitance of output buffers in pF
= Equivalent capacitance of routed array clock in
pF
C
C
C
f
m
f
n
f
p
f
q1
f
q2
f
s1
EQHV
EQHF
L
= Variable capacitance of dedicated array clock
= Fixed capacitance of dedicated array clock
= Output lead capacitance in pF
= Average logic module switching rate in MHz
= Average input buffer switching rate in MHz
= Average output buffer switching rate in MHz
= Average first routed array clock rate in MHz
= Average second routed array clock rate in MHz
= Average dedicated array clock rate in MHz
A54SX08 A54SX16 A54SX16P A54SX32
(pF) 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0
C
EQM
C
(pF) 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4
EQI
(pF) 4.7 4.7 4.7 4.7
C
EQO
(pF) 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.6
C
EQCR
C
EQHV
C
EQHF
(pF) 87 138 138 171
r
1
(pF) 87 138 138 171
r
2
0.615 0.615 0.615 0.615
60 96 96 140
+
+
m
n
p
18 v3.1
Page 19

54SX Family FPGAs
Guidelines for Calculating Pow er Consumption
The following guidelines are meant to represent worst-case
scenarios so that they can be generally used to predict the
upper limits of power dissipation. These guidelines are as
follow:
Logic Modules (m) = 20% of modules
Inputs Switching (n) = # inputs/4
Outputs Switching (p) = # output/4
First Routed Array Clock Loads (q
) = 20% of register
1
cells
Second Routed Array Clock Loads (q
) = 20% of register
2
cells
Load Capacitance (C
Average Logic Module Switching Rate
)
(f
m
Average Input Switching Rate (f
Average Output Switching Rate (f
Average First Routed Array Clock Rate
)
(f
q1
Average Second Routed Array Clock
Rate (f
)
q2
Average Dedicated Array Clock Rate
(f
)
s1
Dedicated Clock Array clock loads (s
)=35 pF
L
=f/10
)=f/5
n
)=f/10
p
=f/2
=f/2
=f
)=20% of regular
1
modules
Sample Power Calculation
One of the designs used to characterize the A54SX family
was a 528 bit serial in serial out shift register. The design
utilized 100% of the dedicated flip-flops of an A54SX16P
device. A pattern of 0101… was clocked into the device at
frequencies ranging from 1 MHz to 200 MHz. Shifting in a
series of 0101… caused 50% of the flip-flops to toggle from
low to high at every clock cycle.
Follow the steps below to estimate power consumption. The
values provided for the sample calculation below are for the
shift register design above. This method for estimating
power consumption is conservative and the actual power
consumption of your design may be less than the estimated
power consumption.
The total power dissipation for the 54SX family is the sum of
the AC power dissipation and the DC power dissipation.
= PAC (dynamic power) + PDC (static power) (5)
P
Total
AC Power Dissipation
PAC = P
P
Output Buffer
= V
P
AC
(n * C
EQI
+
Buffer
(0.5 * (q
(0.5 * (q
(0.5 * (s
Module
2
CCA
* fn)
* C
1
* C
2
* C
1
+ P
RCLKA Net
+ P
Input Buffer
* [(m * C
Input Buffer
EQCR
EQCR
EQHV
EQM
* fq1) + (r1 * fq1))
* fq2)+ (r2 * fq2))
* fs1) + (C
+ P
RCLKB Net
+ P
HCLK Net
(6)
* fm)
+ (p * (C
EQHF
Module
EQO
* fs1))
+
+ CL) * fp)
+
RCLKA
+
RCLKB
HCLK
Output
](7)
Step #1: Define Terms Used in Formula
V
CCA
3.3
Module
Number of logic modules switching at f
m264
m
(Used 50%)
Average logic modules switching rate
f
(MHz) (Guidelines: f/10)
m
Module capacitance C
(pF) C
EQM
f
m
EQM
Input Buffer
Number of input buffers switching at f
Average input switching rate f
(MHz)
n
n
n1
f
n
(Guidelines: f/5)
Input buffer capacitance C
(pF) C
EQI
EQI
Output Buffer
Number of output buffers switching at f
Average output buffers switching rate
(MHz) (Guidelines: f/10)
f
p
Output buffers buffer Capacitance C
Output Load capacitance C
(pF) C
L
EQO
p1
p
f
(pF)C
p
EQO
L
RCLKA
Number of Clock loads q
1
Capacitance of routed array clock (pF) C
Average clock rate (MHz) f
Fixed capacitance (pF) r
q
1
q1
1
EQCR
RCLKB
Number of Clock loads q
2
Capacitance of routed array clock (pF) C
Average clock rate (MHz) f
Fixed capacitance (pF) r
q
2
q2
2
EQCR
HCLK
Number of Clock loads s
Variable capacitance of dedicated
1
C
EQHV
array clock (pF)
Fixed capacitance of dedicated
C
EQHF
array clock (pF)
Average clock rate (MHz) f
s1
+
20
4.0
40
3.4
20
4.7
35
528
1.6
200
138
0
1.6
0
138
0
0.615
96
0
v3.1 19
Page 20

54SX Family FPGAs
Step #2: Calculate Dynamic Power Consumption
V
CCA*VCCA
m*f
m*CEQM
n*f
n*CEQI
p*f
*(C
p
0.5*(q
0.5*(q
0.5 *(s
= 1.461W
P
AC
EQO+CL
1*CEQCR*fq1
2*CEQCR*fq2
* C
1
) 0.000794
* fs1)+(C
EQHV
)+(r1*fq1) 0.11208
)+(r2*fq2)0
EQHF*fs1
)0
10.89
0.02112
0.000136
Step #3: Calculate DC Power Dissipation
DC Power Dissipation
P
DC
X*V
= (I
OL*IOL
standby
+ Y*(V
)*V
+ (I
CCA
– VOH)*V
CCI
)*V
standby
OH (8)
CCR
+ (I
standby
)*V
CCI
+
For a rough estimate of DC Power Dissipation, only use
=(I
P
DC
standby
)*V
. The rest of the formula provides a
CCA
very small number that can be considered negligible.
1200
1000
P
DC
= (I
standby
)*V
CCA
PDC = .55mA*3.3V
P
= 0.001815W
DC
Step #4: Calculate Total Power Consumption
P
= PAC + P
Total
P
= 1.461 + 0.001815
Total
P
= 1.4628W
Total
DC
Step #5: Compare Estimated Power Consumption against
Characterized Power Consumption
The estimated total power consumption for this design is
1.46W. The characterized power consumption for this design
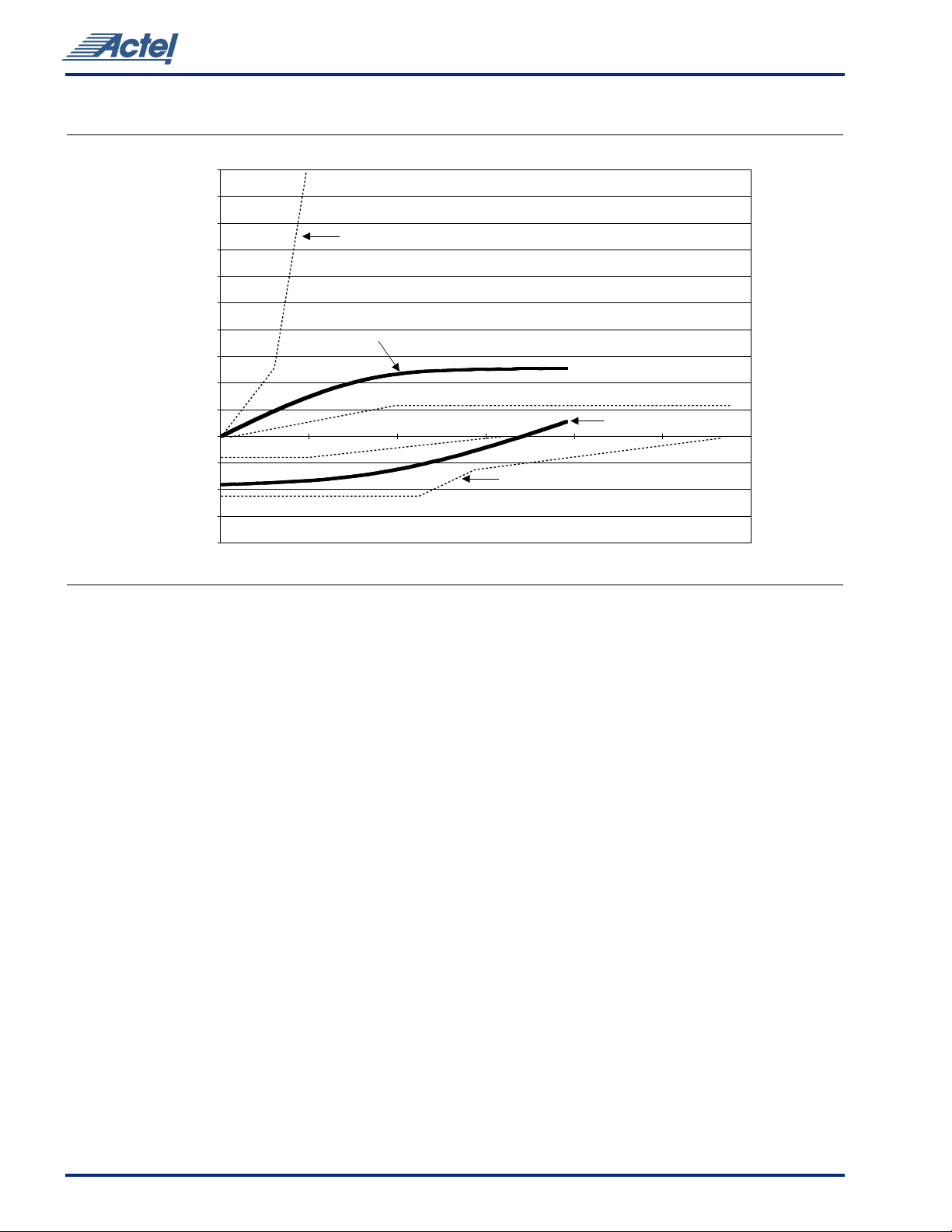
at 200 MHz is 1.0164W. Figure10 shows the characterized
power dissipation numbers for the shift register design
using frequencies ranging from 1 MHz to 200 MHz.
800
600
Power Dissipation mW
400
200
0
Figure 10 • Power Dissipation
200 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
Frequency MHz
20 v3.1
Page 21

54SX Family FPGAs
Junction Temperature (TJ)
The temperature that you select in Designer Series software
is the junction temperature, not ambient temperature. This
is an important distinction because the heat generated from
P = Power calculated from Estimating Power Consumption
section
θ
= Junction to ambient of package. θja numbers are
ja
located in Package Thermal Characteristics section.
dynamic power consumption is usually hotter than the
ambient temperature. Use the equation below to calculate
Package Thermal Characteristics
junction temperature.
The device junction to case thermal characteristic is θjc,
Junction Temperature = ∆T + T
Where:
T
= Ambient Temperature
a
∆T = Temperature gradient between junction (silicon) and
ambient
∆T =
θ
* P
ja
a
and the junction to ambient air characteristic is θ
thermal characteristics for θ
are shown with two different
ja
ja
air flow rates.
The maximum junction temperature is 150°C.
A sample calculation of the absolute maximum power
dissipation allowed for a TQFP 176-pin package at
commercial temperature and still air is as follows:
Max. junction temp. (°C) – Max. ambient temp. (°C)
Maximum Power Allowed
Package Type Pin Count θ
Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) 84 12 32 22 °C/W
Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) 144 11 32 24 °C/W
Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP) 176 11 28 21 °C/W
Very Thin Quad Flatpack (VQFP) 100 10 38 32 °C/W
Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) without Heat Spreader 208 8 30 23 °C/W
Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) with Heat Spreader 208 3.8 20 17 °C/W
Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) 272 3 20 14.5 °C/W
Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) 313 3 23 17 °C/W
Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) 329 3 18 13.5 °C/W
Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA) 144 3.8 38.8 26.7 °C/W
Note:
SX08 does not have a heat spreader.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
θ
(°C/W)
ja
jc
150°C – 70°C
--------------------------------- 2.86W===
28°C/W
θ
ja
Still Air
θ
ja
300 ft/min Units
. The
v3.1 21
Page 22

54SX Timing Model*
54SX Family FPGAs
Routed
Clock
I/O Module
t
= 1.5 ns (100% Load)
RCKH
F
= 250 MHz
MAX
t
INY
= 1.5 ns
= 0.5 ns
t
SUD
t
= 0.0 ns
HD
t
IRD2
= 0.6 ns
Register
Cell
D
t
= 0.8 ns
RCO
Combinatorial
=0.6 ns
t
PD
Q
t
RD1
Cell
= 0.3 ns
Register
t
RCO
Predicted
Routing
Delays
= 0.3 ns
t
RD1
t
= 1.0 ns
RD4
t
= 1.9 ns
RD8
Cell
D
Q
= 0.8 ns
t
RD1
I/O Module
= 0.3 ns
Output DelaysInternal DelaysInput Delays
= 1.6 ns
t
DHL
I/O Module
t
DHL
t
ENZH
= 1.6 ns
= 2.3 ns
Hard-Wired Clock
F
HMAX
= 1.0 ns
t
HCKH
= 320 MHz
*Values shown for A54SX08-3, worst-case commercial conditions.
Hard-Wired Clock
External Set-Up = t
INY
+ t
IRD1
+ t
SUD
– t
HCKH
= 1.5 + 0.3 + 0.5 – 1.0 = 1.3 ns
Clock-to-Out (Pin-to-Pin)
=t
HCKH
+ t
RCO
+ t
RD1
+ t
DHL
= 1.0 + 0.8 + 0.3 + 1.6 = 3.7 ns
Routed Clock
External Set-Up = t
INY
= 1.5 + 0.3 + 0.5 – 1.5 = 0.8 ns
Clock-to-Out (Pin-to-Pin)
=t
RCKH
= 1.52+ 0.8 + 0.3 + 1.6 = 4.2 ns
+ t
+ t
IRD1
RCO
+ t
+ t
SUD
RD1
– t
+ t
RCKH
DHL
22 v3.1
Page 23

54SX Family FPGAs
Output Buffer Delays
E
V
CC
In
Out
V
OL
50%
t
DLH
50%
V
OH
1.5V
AC Test Loads
Load 1
(Used to measure
propagation delay)
To the output
under test
t
DHL
35 pF
GND
1.5V
D
En
Out
TRIBUFF
V
CC
50%
V
CC
1.5V
t
ENZL
50%
V
OL
PAD
t
ENLZ
Load 2
(Used to measure enable delays)
V
CC
GND
R to VCC for t
To the output
under test
R to GND for t
R = 1 kΩ
35 pF
To AC test loads (shown below)
GND
10%
En
Out
50%
GND
t
ENZH
(Used to measure disable delays)
V
PZL
PZH
To the output
under test
V
CC
V
1.5V
Load 3
CC
50%
OH
t
ENHZ
GND
R to VCC for t
R to GND for t
R = 1 kΩ
5 pF
GND
90%
PLZ
PHZ
Input Buffer Delays C-Cell Delays
t
INY
0V
Y
50%
S, A or B
50%
Out
GND
t
Out
v3.1 23
In
Out
GND
PAD
1.5V
t
INY
INBUF
3V
1.5V
V
CC
50%
S
A
Y
B
V
CC
t
PD
GND
t
PD
GND
50%
50%
V
CC
50%
PD
50% 50%
t
PD
V
CC
Page 24

Register Cell Timing Characteristics
Flip-Flops
54SX Family FPGAs
D
CLK
(Positive edge triggere d)
D
t
HPWH
t
RPWH
,
CLK
CLR
PRESET
t
SUD
Q
Timing Characteristics
Timing characteristics for 54SX devices fall into three
categories: family-dependent, device-dependent, and
design-dependent. The input and output buffer
characteristics are common to all 54SX family members.
Internal routing delays are device dependent. Design
dependency means actual delays are not determined until
after placement and routing of the user’s design is complete.
Delay values may then be determined by using the
DirectTime Analyzer utility or performing simulation with
post-layout delays.
PRESET
CLR
t
HD
t
RCO
Long Tracks
Q
t
HPWL
t
RPWL
,
t
CLR
t
WASYN
t
HP
t
PRESET
Some nets in the design use long tracks. Long tracks are
special routing resources that span multiple rows, columns,
or modules. Long tracks employ three and sometimes five
antifuse connections. This increases capacitance and
resistance, resulting in longer net delays for macros
connected to long tracks. Typically up to 6% of nets in a fully
utilized device require long tracks. Long tracks contribute
approximately 4 ns to 8.4 ns delay. This additional delay is
represented statistically in higher fanout (FO=24) routing
delays in the data sheet specifications section.
Critical Nets and Typical Nets
Propagation delays are expressed only for typical nets,
which are used for initial design performance evaluation.
Critical net delays can then be applied to the most
time-critical paths. Critical nets are determined by net
property assignment prior to placement and routing. Up to
6% of the nets in a design may be designated as critical,
while 90% of the nets in a design are typical.
Timing Derating
54SX devices are manufactured in a CMOS process.
Therefore, device performance varies according to
temperature, voltage, and process variations. Minimum
timing parameters reflect maximum operating voltage,
minimum operating temperature, an d best-case processing.
Maximum timing parameters reflect minimum operating
voltage, maximum operating temperature, and worst-case
processing.
Temperature and Voltage Derating Factors
(Normalized to Worst-Case Commercial, TJ = 70°C, V
Junction Temperature (TJ)
V
CCA
3.0
3.3
3.6
24 v3.1
–55 –40 0 25 70 85 125
0.75 0.78 0.87 0.89 1.00 1.04 1.16
0.70 0.73 0.82 0.83 0.93 0.97 1.08
0.66 0.69 0.77 0.78 0.87 0.92 1.02
CCA
= 3.0V)
Page 25

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX08 Timing Characteristics
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions, V
= 4.75V, V
CCR
CCA,VCCI
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
C-Cell Propagation Delays
t
PD
Internal Array Module 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
Predicted Routing Delays
t
DC
t
FC
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RD3
t
RD4
t
RD8
t
RD12
FO=1 Routing Delay, Direct
Connect
FO=1 Routing Delay, Fast Connect 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
1
2
0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 ns
R-Cell Timing
t
RCO
t
CLR
t
PRESET
t
SUD
t
HD
t
WASYN
Sequential Clock-to-Q 0.8 1.1 1.2 1 .4 ns
Asynchronous Clear-to-Q 0.5 0 .6 0.7 0.8 ns
Asynchronous Preset-to-Q 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Set-Up 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.8 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Hold 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
Asynchronous Pulse Width 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Input Module Propagation Delays
t
INYH
t
INYL
Input Module Predicted Routing Delays
t
IRD1
t
IRD2
t
IRD3
t
IRD4
t
IRD8
t
IRD12
Input Data Pad-to-Y HIGH 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Input Data Pad-to-Y LOW 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
2
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
Notes:
1. For dual-module macros, use tPD + t
RD1
+ t
PDn
, t
RCO
+ t
RD1
+ t
PDn
or t
PD1
+ t
RD1
+ t
, whichever is appropriate.
SUD
2. Routing delays are for typical designs across worst-case operating conditions. These parameters should be used for estimating device
performance. Post-route timing analysis or simulation is required to determine actual worst-case performance. Post-route timing is
based on actual routing delay measurements performed on the device prior to shipment.
v3.1 25
Page 26

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX08 Timing Characteristics (continued)
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
Dedicated (Hard-Wired) Array Clock Network
t
HCKH
Input LOW to HIGH
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HCKL
Input HIGH to LOW
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HPWH
t
HPWL
t
HCKSW
t
HP
f
HMAX
Minimum Pulse Width HIGH 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Minimum Pulse Width LOW 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Maximum Skew 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 ns
Minimum Period 2.7 3.1 3.6 4.2 ns
Maximum Frequency 350 320 280 240 MHz
Routed Array Clock Networks
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RPWH
t
RPWL
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
TTL Output Module Timing
Input LOW to HIGH (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Min. Pulse Width HIGH 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Min. Pulse Width LOW 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Maximum Skew (Light Load) 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 ns
Maximum Skew (50% Load) 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.4 ns
Maximum Skew (100% Load) 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.4 ns
1
1.0 1.1 1.3 1.5 ns
1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
1.3 1.5 1.7 2.0 ns
1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
1.5 1.7 2.0 2.3 ns
1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
1.5 1.8 2.0 2.3 ns
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 2.1 2.4 2.8 3.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 2.3 2.7 3.1 3.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 1.3 1.5 1.7 2.0 ns
Note:
1. Delays based on 35 pF loading, except t
26 v3.1
ENZL
and t
ENZH
. For t
ENZL
and t
the loading is 5 pF.
ENZH
Page 27

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16 Timing Characteristics
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions, V
= 4.75V, V
CCR
CCA,VCCI
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
C-Cell Propagation Delays
t
PD
Internal Array Module 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
Predicted Routing Delays
t
DC
t
FC
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RD3
t
RD4
t
RD8
t
RD12
FO=1 Routing Delay, Direct
Connect
FO=1 Routing Delay, Fast Connect 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
1
2
0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 ns
R-Cell Timing
t
RCO
t
CLR
t
PRESET
t
SUD
t
HD
t
WASYN
Sequential Clock-to-Q 0.8 1.1 1.2 1.4 ns
Asynchronous Clear-to-Q 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Asynchronous Preset-to-Q 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Set-Up 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.8 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Hold 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
Asynchronous Pulse Width 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Input Module Propagation Delays
t
INYH
t
INYL
Predicted Input Routing Delays
t
IRD1
t
IRD2
t
IRD3
t
IRD4
t
IRD8
t
IRD12
Input Data Pad-to-Y HIGH 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Input Data Pad-to-Y LOW 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
2
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
Notes:
1. For dual-module macros, use tPD + t
RD1
+ t
PDn
, t
RCO
+ t
RD1
+ t
PDn
or t
PD1
+ t
RD1
+ t
, whichever is appropriate.
SUD
2. Routing delays are for typical designs across worst-case operating conditions. These parameters should be used for estimating device
performance. Post-route timing analysis or simulation is required to determine actual worst-case performance. Post-route timing is
based on actual routing delay measurements performed on the device prior to shipment.
v3.1 27
Page 28

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16 Timing Characteristics (continued)
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
Dedicated (Hard-Wired) Array Clock Network
t
HCKH
Input LOW to HIGH
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HCKL
Input HIGH to LOW
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HPWH
t
HPWL
t
HCKSW
t
HP
f
HMAX
Minimum Pulse Width HIGH 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Minimum Pulse Width LOW 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Maximum Skew 0.2 0.2 0.3 0.3 ns
Minimum Period 2.7 3.1 3.6 4.2 ns
Maximum Frequency 350 320 280 240 MHz
Routed Array Clock Networks
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RPWH
t
RPWL
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
TTL Output ModuleTiming
Input LOW to HIGH (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Min. Pulse Width HIGH 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Min. Pulse Width LOW 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Maximum Skew (Light Load) 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.7 ns
Maximum Skew (50% Load) 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Maximum Skew (100% Load) 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
1
1.2 1.4 1.5 1.8 ns
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.9 ns
1.6 1.8 2.1 2.5 ns
1.8 2.0 2.3 2.7 ns
1.8 2.1 2.5 2.8 ns
2.0 2.2 2.5 3.0 ns
1.8 2.1 2.4 2.8 ns
2.0 2.2 2.5 3.0 ns
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 2.1 2.4 2.8 3.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 2.3 2.7 3.1 3.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 1.3 1.5 1.7 2.0 ns
Note:
1. Delays based on 35 pF loading, except t
28 v3.1
ENZL
and t
ENZH
. For t
ENZL
and t
the loading is 5 pF.
ENZH
Page 29

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16P Timing Characteristics
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions, V
= 4.75V, V
CCR
CCA,VCCI
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
C-Cell Propagation Delays
t
PD
Internal Array Module 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
Predicted Routing Delays
t
DC
t
FC
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RD3
t
RD4
t
RD8
t
RD12
FO=1 Routing Delay, Direct
Connect
FO=1 Routing Delay, Fast Connect 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
1
2
0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 ns
R-Cell Timing
t
RCO
t
CLR
t
PRESET
t
SUD
t
HD
t
WASYN
Sequential Clock-to-Q 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.4 ns
Asynchronous Clear-to-Q 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Asynchronous Preset-to-Q 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Set-Up 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.8 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Hold 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
Asynchronous Pulse Width 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Input Module Propagation Delays
t
INYH
t
INYL
Predicted Input Routing Delays
t
IRD1
t
IRD2
t
IRD3
t
IRD4
t
IRD8
t
IRD12
Input Data Pad-to-Y HIGH 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Input Data Pad-to-Y LOW 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
2
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.2 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 1.9 2.2 2.5 2.9 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
Notes:
1. For dual-module macros, use tPD + t
RD1
+ t
PDn
, t
RCO
+ t
RD1
+ t
PDn
or t
PD1
+ t
RD1
+ t
, whichever is appropriate.
SUD
2. Routing delays are for typical designs across worst-case operating conditions. These parameters should be used for estimating device
performance. Post-route timing analysis or simulation is required to determine actual worst-case performance. Post-route timing is
based on actual routing delay measurements performed on the device prior to shipment.
v3.1 29
Page 30

A54SX16P Timing Characteristics (continued)
54SX Family FPGAs
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions, V
= 4.75V, V
CCR
CCA,VCCI
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
Dedicated (Hard-Wired) Array Clock Network
t
HCKH
t
HCKL
t
HPWH
t
HPWL
t
HCKSW
t
HP
f
HMAX
Input LOW to HIGH
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
1.2 1.4 1.5 1.8 ns
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.9 ns
Minimum Pulse Width HIGH 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Minimum Pulse Width LOW 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Maximum Skew 0.2 0.2 0.3 0.3 ns
Minimum Period 2.7 3.1 3.6 4.2 ns
Maximum Frequency 350 320 280 240 MHz
Routed Array Clock Networks
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RPWH
t
RPWL
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
Input LOW to HIGH (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
1.6 1.8 2.1 2.5 ns
1.8 2.0 2.3 2.7 ns
1.8 2.1 2.5 2.8 ns
2.0 2.2 2.5 3.0 ns
1.8 2.1 2.4 2.8 ns
2.0 2.2 2.5 3.0 ns
Min. Pulse Width HIGH 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Min. Pulse Width LOW 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Maximum Skew (Light Load) 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.7 ns
Maximum Skew (50% Load) 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Maximum Skew (100% Load) 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
TTL Output Module Timing
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 2.4 2.8 3.1 3.7 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 2.3 2.9 3.2 3.8 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 3.0 3.4 3.9 4.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 3.3 3.8 4.3 5.0 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 2.3 2.7 3.0 3.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 2.8 3.2 3.7 4.3 ns
TTL/PCI Output Module Timing
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 1.5 1.7 2.0 2.3 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 1.9 2.2 2.4 2.9 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 2.3 2.6 3.0 3.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.3 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 2.7 3.1 3.5 4.1 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 2.9 3.3 3.7 4.4 ns
30 v3.1
Page 31

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX16P Timing Characteristics (continued)
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions V
= 3.0V, V
CCR
CCA
, V
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
CCI
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
PCI Output Module Timing
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 1.8 2.0 2.3 2.7 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 1.7 2.0 2.2 2.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 0.8 1.0 1.1 1.3 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 1.2 1.2 1.5 1.8 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 1.0 1.1 1.3 1.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.7 ns
1
TTL Output Module Timing
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 2.1 2.5 2.8 3.3 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 2.0 2.3 2.6 3.1 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 2.5 2.9 3.2 3.8 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 3.0 3.5 3.9 4.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 2.3 2.7 3.1 3.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 2.9 3.3 3.7 4.4 ns
Note:
1. Delays based on 10 pF loading.
v3.1 31
Page 32

A54SX32 Timing Characteristics
54SX Family FPGAs
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions, V
= 4.75V, V
CCR
CCA,VCCI
= 3.0V, TJ = 70°C)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
C-Cell Propagation Delays
t
PD
Internal Array Module 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 ns
Predicted Routing Delays
t
DC
t
FC
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RD3
t
RD4
t
RD8
t
RD12
FO=1 Routing Delay, Direct Connect 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 ns
FO=1 Routing Delay, Fast Connect 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 2.7 3.1 3.5 4.1 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 4.0 4.7 5.3 6.2 ns
1
2
R-Cell Timing
t
RCO
t
CLR
t
PRESET
t
SUD
t
HD
t
WASYN
Sequential Clock-to-Q 0.8 1.1 1.3 1.4 ns
Asynchronous Clear-to-Q 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Asynchronous Preset-to-Q 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Set-Up 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 ns
Flip-Flop Data Input Hold 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 ns
Asynchronous Pulse Width 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Input Module Propagation Delays
t
INYH
t
INYL
Predicted Input Routing Delays
t
IRD1
t
IRD2
t
IRD3
t
IRD4
t
IRD8
t
IRD12
Input Data Pad-to-Y HIGH 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Input Data Pad-to-Y LOW 1.5 1.7 1 .9 2.2 ns
2
FO=1 Routing Delay 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
FO=2 Routing Delay 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 ns
FO=3 Routing Delay 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 ns
FO=4 Routing Delay 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
FO=8 Routing Delay 2.7 3.1 3.5 4.1 ns
FO=12 Routing Delay 4.0 4.7 5.3 6.2 ns
Notes:
1. For dual-module macros, use tPD + t
RD1
+ t
PDn
, t
RCO
+ t
RD1
+ t
PDn
or t
PD1
+ t
RD1
+ t
, whichever is appropriate.
SUD
2. Routing delays are for typical designs across worst-case operating conditions. These parameters should be used for estimating device
performance. Post-route timing analysis or simulation is required to determine actual worst-case performance. Post-route timing is
based on actual routing delay measurements performed on the device prior to shipment.
32 v3.1
Page 33

54SX Family FPGAs
A54SX32 Timing Characteristics (continued)
(Worst-Case Commercial Conditions)
‘–3’ Speed ‘–2’ Speed ‘–1’ Speed ‘Std’ Speed
Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Units
Dedicated (Hard-Wired) Array Clock Network
t
HCKH
Input LOW to HIGH
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HCKL
Input HIGH to LOW
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
t
HPWH
t
HPWL
t
HCKSW
t
HP
f
HMAX
Minimum Pulse Width HIGH 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Minimum Pulse Width LOW 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.1 ns
Maximum Skew 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.5 ns
Minimum Period 2.7 3.1 3.6 4.2 ns
Maximum Frequency 350 320 280 240 MHz
Routed Array Clock Networks
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RCKH
t
RCKL
t
RPWH
t
RPWL
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
t
RCKSW
TTL Output Module Timing
Input LOW to HIGH (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (Light Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (50% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input LOW to HIGH (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Input HIGH to LOW (100% Load)
(Pad to R-Cell Input)
Min. Pulse Width HIGH 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Min. Pulse Width LOW 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.2 ns
Maximum Skew (Light Load) 0.85 0.98 1.1 1.3 ns
Maximum Skew (50% Load) 1.23 1.4 1 .6 1.9 ns
Maximum Skew (100% Load) 1.30 1.5 1.7 2.0 ns
1
1.9 2.1 2.4 2.8 ns
1.9 2.1 2.4 2.8 ns
2.4 2.7 3.0 3.5 ns
2.4 2.7 3.1 3.6 ns
2.7 3.0 3.5 4.1 ns
2.7 3.1 3.6 4.2 ns
2.7 3.1 3.5 4.1 ns
2.8 3.2 3.6 4.3 ns
t
DLH
t
DHL
t
ENZL
t
ENZH
t
ENLZ
t
ENHZ
Data-to-Pad LOW to HIGH 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Data-to-Pad HIGH to LOW 1.6 1.9 2.1 2.5 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to L 2.1 2.4 2.8 3.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, Z to H 2.3 2.7 3.1 3.6 ns
Enable-to-Pad, L to Z 1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 ns
Enable-to-Pad, H to Z 1.3 1.5 1.7 2.0 ns
Note:
1. Delays based on 35pF loading, except t
ENZL
and t
ENZH
. For t
and t
ENZL
v3.1 33
the loading is 5pF.
ENZH
Page 34

Pin Description
54SX Family FPGAs
CLKA/B Clock A and B
These pins are 3.3V/5.0V PCI/TTL clock inputs for clock
distribution networks. The clock input is buffered prior to
clocking the R-cells. If not used, this pin must be set LOW or
HIGH on the board. It must not be left floating. (For
A54SX72A, these clocks can be configured as bidirectional.)
GND Ground
LOW supply voltage.
HCLK Dedicate d (Hard-wired)
Array Clock
This pin is the 3.3V/5.0V PCI/TTL clock input for sequential
modules. This input is directly wired to each R-cell and
offers clock speeds independent of the number of R-cells
being driven. If not used, this pin must be set LOW or HIGH
on the board. It must not be left floating.
I/O Input/Output
The I/O pin functions as an input, output, tristate, or
bidirectional buffer. Based on certain configurations, input
and output levels are compatible with standard TTL, LVTTL,
3.3V PCI or 5.0V PCI specifications. Unused I/O pins are
automatically tristated by the Designer Series software.
NC No Connection
This pin is not connected to circuitry within the device.
PRA, I/O Probe A
The Probe A pin is used to output data from any
user-defined design node within the device. This
independent diagnostic pin can be used in conjunction with
the Probe B pin to allow real-time diagnostic output of any
signal path within the device. The Probe A pin can be used
as a user-defined I/O when veri ficatio n has b een c omplete d.
The pin’s probe capabilities can be permanently disabled to
protect programmed design confidentiality.
PRB, I/O Probe B
The Probe B pin is used to output data from any node wi thin
the device. This diagnostic pin can be used in conjunction
with the Probe A pin to allow real-time diagnostic output of
any signal path within the device. The Probe B pin can be
used as a user-defined I/O when verification has been
completed. The pin’s probe capabilities can be permanently
disabled to protect programmed design confidentiality.
TCK Test Clock
Test clock input for diagnostic probe and device
programming. In flexible mode, TCK bec omes active when
the TMS pin is set LOW (refer to Table 2 on page 8). This pin
functions as an I/O when the boundary scan state machine
reaches the “logic reset” state.
TDI Test Data Input
Serial input for boundary scan testing and diagnostic probe.
In flexible mode, TDI is active when the TMS pin is set LOW
(refer to Table 2 on page 8). This pin functions as an I/O
when the boundary scan state machine reaches the “logic
reset” state.
TDO Test Data Output
Serial output for boundary scan testing. In flexible mode,
TDO is active when the TMS pin is set LOW (refer to Table 2
on page 8). This pin functions as an I/O when the boundary
scan state machine reaches the “logic reset” state.
TMS Test Mode Select
The TMS pin controls the use of the IEEE 1149.1 Boundary
Scan pins (TCK, TDI, TDO). In flexible mode when the TMS
pin is set LOW, the TCK, TDI, and TDO pins are boundary
scan pins (refer to Table 2 on page 8). Once the boundary
scan pins are in test mode, they will remain in that mode
until the internal boundary scan state machine reaches the
“logic reset” state. At this point, the boundary scan pins will
be released and will function as regular I/O pins. The “logic
reset” state is reached 5 TCK cycles after the TMS pin is set
HIGH. In dedicated test mode, TMS functions as specified in
the IEEE 1149.1 specifications.
V
CCI
Supply Voltage
Supply voltage for I/Os. See Table 1 on page 8.
V
CCA
Supply Voltage
Supply voltage for Array. See Table 1 on page 8.
V
CCR
Supply Voltage
Supply voltage for input tolerance (required for internal
biasing) See Table 1 on page 8.
34 v3.1
Page 35

54SX Family FPGAs
Package Pin Assignments
84-Pin PLCC (Top View)
184
84-Pin
PLCC
v3.1 35
Page 36

84-Pin PLCC Package
Pin
Number
1V
2GND 44 I/O
3V
4 PRA, I/O 46 I/O
5I/O 47I/O
6I/O 48I/O
7V
8I/O 50I/O
9I/O 51I/O
10 I/O 52 TDO, I/O
1 1 TCK, I/O 53 I/O
12 TDI, I/O 54 I/O
13 I/O 55 I/O
14 I/O 56 I/O
15 I/O 57 I/O
16 TMS 58 I/O
17 I/O 59 V
18 I/O 60 V
19 I/O 61 GND
20 I/O 62 I/O
21 I/O 63 I/O
22 I/O 64 I/O
23 I/O 65 I/O
24 I/O 66 I/O
25 I/O 67 I/O
26 I/O 68 V
27 GND 69 GND
28 V
29 I/O 71 I/O
30 I/O 72 I/O
31 I/O 73 I/O
32 I/O 74 I/O
33 I/O 75 I/O
34 I/O 76 I/O
35 I/O 77 I/O
36 I/O 78 I/O
37 I/O 79 I/O
38 I/O 80 I/O
39 I/O 81 I/O
40 PRB, I/O 82 I/O
41 V
42 GND 84 CLKB
A54SX08
Function
CCR
CCA
CCI
CCI
CCA
54SX Family FPGAs
Pin
Number
43 V
45 HCLK
49 I/O
70 I/O
83 CLKA
A54SX08
Function
CCR
CCA
CCI
CCA
36 v3.1
Page 37

54SX Family FPGAs
Package Pin Assignments (continued)
208-Pin PQFP (Top View)
208
1
208-Pin PQFP
v3.1 37
Page 38

54SX Family FPGAs
208-Pin PQFP
Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
1 GND GND GND 54 I/O I/O I/O
2 TDI, I/O TDI, I/O TDI, I/O 55 I/O I/O I/O
3 I/O I/O I/O 56 I/O I/O I/O
4 NC I/O I/O 57 I/O I/O I/O
5 I/O I/O I/O 58 I/O I/O I/O
6 NC I/O I/O 59 I/O I/O I/O
7 I/O I/O I/O 60 V
CCI
V
CCI
8 I/O I/O I/O 61 NC I/O I/O
9 I/O I/O I/O 62 I/O I/O I/O
10 I/O I/O I/O 63 I/O I/O I/O
11 TMS TMS TMS 64 NC I/O I/O
12 V
CCI
V
CCI
V
CCI
65* I/O I/O NC*
13 I/O I/O I/O 66 I/O I/O I/O
14 NC I/O I/O 67 NC I/O I/O
15 I/O I/O I/O 68 I/O I/O I/O
16 I/O I/O I/O 69 I/O I/O I/O
17 NC I/O I/O 70 NC I/O I/O
18 I/O I/O I/O 71 I/O I/O I/O
19 I/O I/O I/O 72 I/O I/O I/O
20 NC I/O I/O 73 NC I/O I/O
21 I/O I/O I/O 74 I/O I/O I/O
22 I/O I/O I/O 75 NC I/O I/O
23 NC I/O I /O 76 PRB, I/O PRB, I/O PRB, I/O
24 I/O I/O I/O 77 GND GND GND
25 V
CCR
V
CCR
V
CCR
78 V
CCA
V
CCA
26 GND GND GND 79 GND GND GND
27 V
CCA
V
CCA
V
CCA
80 V
CCR
V
CCR
28 GND GND GND 81 I/O I/O I/O
29 I/O I/O I/O 82 HCLK HCLK HCLK
30 I/O I/O I/O 83 I/O I/O I/O
31 NC I/O I/O 84 I/O I/O I/O
32 I/O I/O I/O 85 NC I/O I/O
33 I/O I/O I/O 86 I/O I/O I/O
34 I/O I/O I/O 87 I/O I/O I/O
35 NC I/O I/O 88 NC I/O I/O
36 I/O I/O I/O 89 I/O I/O I/O
37 I/O I/O I/O 90 I/O I/O I/O
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
I/O I/O I/O 91 NC I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 92 I/O I/O I/O
V
V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
93 I/O I/O I/O
94 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 95 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 96 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 97 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 98 V
CCI
V
CCI
I/O I/O I/O 99 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 100 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 101 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 102 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 103 TDO, I/O TDO, I/O TDO, I/O
I/O I/O I/O 104 I/O I/O I/O
GND GND GND 105 GND GND GND
I/O I/O I/O 106 NC I/O I/O
* Please note that Pin 65 in the A54SX32—PQ208 is a no connect (NC).
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
38 v3.1
Page 39

54SX Family FPGAs
208-Pin PQFP (Continued)
A54SX16,
Pin Number
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
A54SX08
Function
I/O I/O I/O 158 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 159 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 160 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 161 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 162 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 163 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 164 V
V
CCA
V
CCI
NC I/O I/O 167 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 168 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 169 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 170 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 171 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 172 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 173 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 174 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 175 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 176 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 177 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 178 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 179 I/O I/O I/O
GND GND GND 180 CLKA CLKA CLKA
V
CCA
GND GND GND 182 V
V
CCR
I/O I/O I/O 184 V
I/O I/O I/O 185 GND GND GND
NC I/O I/O 186 PRA, I/O PRA, I/O PRA, I/O
I/O I/O I/O 187 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 188 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 189 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 190 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 191 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 192 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 193 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 194 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 195 NC I/O I/O
V
CCA
GND GND GND 197 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 198 NC I/O I/O
V
CCI
I/O I/O I/O 200 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 201 V
I/O I/O I/O 202 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 203 NC I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 204 I/O I/O I/O
I/O I/O I/O 205 NC I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 206 I/O I/O I/O
NC I/O I/O 207 I/O I/O I/O
GND GND GND 208 TCK, I/O TCK, I/O TCK, I/O
A54SX16P
Function
V
CCA
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCA
V
CCI
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
V
CCA
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCA
V
CCI
* Please note that Pin 65 in the A54SX32—PQ208 is a no connect (NC).
A54SX08
Function
CCI
A54SX16P
Function
V
CCI
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
165 I/O I/O I/O
166 I/O I/O I/O
181 CLKB CLKB CLKB
A54SX16,
CCR
V
CCR
V
CCR
183 GND GND GND
CCA
V
CCA
V
CCA
196 I/O I/O I/O
199 I/O I/O I/O
CCI
V
CCI
V
CCI
v3.1 39
Page 40

Package Pin Assignments (continued)
144-Pin TQFP (Top View)
144
1
54SX Family FPGAs
144-Pin
TQFP
40 v3.1
Page 41

54SX Family FPGAs
144-Pin TQFP
Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16P
Function
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16P
Function
1 GND GND GND 41 I/O I/O I/O
2 T DI, I/O TDI, I/O TDI, I/O 42 I/O I/O I/O
3 I/O I/O I/O 43 I/O I/O I/O
4 I/O I/O I/O 44 V
CCI
V
CCI
5 I/O I/O I/O 45 I/O I/O I/O
6 I/O I/O I/O 46 I/O I/O I/O
7 I/O I/O I/O 47 I/O I/O I/O
8 I/O I/O I/O 48 I/O I/O I/O
9 TMS TMS TMS 49 I/O I/O I/O
10 V
CCI
V
CCI
V
CCI
50 I/O I/O I/O
11 GND GND GND 51 I/O I/O I/O
12 I/O I/O I/O 52 I/O I/O I/O
13 I/O I/O I/O 53 I/O I/O I/O
14 I/O I/O I/O 5 4 PRB, I/O PRB, I/O PRB, I/O
15 I/O I/O I/O 55 I/O I/O I/O
16 I/O I/O I/O 56 V
CCA
V
CCA
17 I/O I/O I/O 57 GND GND GND
18 I/O I/O I/O 58 V
19 V
20 V
CCR
CCA
V
V
CCR
CCA
V
V
CCR
CCA
59 I/O I/O I/O
60 HCLK HCLK HCLK
CCR
V
CCR
21 I/O I/O I/O 61 I/O I/O I/O
22 I/O I/O I/O 62 I/O I/O I/O
23 I/O I/O I/O 63 I/O I/O I/O
24 I/O I/O I/O 64 I/O I/O I/O
25 I/O I/O I/O 65 I/O I/O I/O
26 I/O I/O I/O 66 I/O I/O I/O
27 I/O I/O I/O 67 I/O I/O I/O
28 GND GND GND 68 V
29 V
30 V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
69 I/O I/O I/O
70 I/O I/O I/O
CCI
V
CCI
31 I/O I/O I/O 71 TDO, I/O TDO , I/O TDO, I/O
32 I/O I/O I/O 72 I/O I/O I/O
33 I/O I/O I/O 73 GND GND GND
34 I/O I/O I/O 74 I/O I/O I/O
35 I/O I/O I/O 75 I/O I/O I/O
36 GND GND GND 76 I/O I/O I/O
37 I/O I/O I/O 77 I/O I/O I/O
38 I/O I/O I/O 78 I/O I/O I/O
39 I/O I/O I/O 79 V
40 I/O I/O I/O 80 V
CCA
CCI
V
V
CCA
CCI
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCI
v3.1 41
Page 42

144-Pin TQFP (Continued)
54SX Family FPGAs
Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16P
Function
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16P
Function
81 GND GND GND 113 I/O I/O I/O
82 I/O I/O I/O 114 I/O I/O I/O
83 I/O I/O I/O 115 V
CCI
V
CCI
84 I/O I/O I/O 116 I/O I/O I/O
85 I/O I/O I/O 117 I/O I/O I/O
86 I/O I/O I/O 118 I/O I/O I/O
87 I/O I/O I/O 119 I/O I/O I/O
88 I/O I/O I/O 120 I/O I/O I/O
89 V
90 V
CCA
CCR
V
V
CCA
CCR
V
V
CCA
CCR
121 I/O I/O I/O
122 I/O I/O I/O
91 I/O I/O I/O 123 I/O I/O I/O
92 I/O I/O I/O 124 I/O I/O I/O
93 I/O I/O I/O 125 CLKA CLKA CLKA
94 I/O I/O I/O 126 CLKB CLKB CLKB
95 I/O I/O I/O 127 V
CCR
V
CCR
96 I/O I/O I/O 128 GND GND GND
97 I/O I/O I/O 129 V
98 V
CCA
V
CCA
V
CCA
130 I/O I/O I/O
CCA
V
CCA
99 GND GND GND 131 PRA, I/O PRA, I/O PRA, I/O
100 I/O I/O I/O 132 I/O I/O I/O
101 GND GND GND 133 I/O I/O I/O
102 V
CCI
V
CCI
V
CCI
134 I/O I/O I/O
103 I/O I/O I/O 135 I/O I/O I/O
104 I/O I/O I/O 136 I/O I/O I/O
105 I/O I/O I/O 137 I/O I/O I/O
106 I/O I/O I/O 138 I/O I/O I/O
107 I/O I/O I/O 139 I/O I/O I/O
108 I/O I/O I/O 140 V
CCI
V
CCI
109 GND GND GND 141 I/O I/O I/O
110 I/O I/O I/O 142 I/O I/O I/O
111 I/O I/O I/O 143 I/O I/O I/O
112 I/O I/O I/O 144 TCK, I/O TCK, I/O TCK, I/O
113 I/O I/O I/O
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
V
CCR
V
CCA
V
CCI
42 v3.1
Page 43

54SX Family FPGAs
Package Pin Assignments (continued)
176-Pin TQFP (Top View)
176
1
176-Pin
TQFP
v3.1 43
Page 44

54SX Family FPGAs
176-Pin TQFP
Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
1 GND GND GND 45 I/O I/O I/O
2 T DI, I/O TDI, I/O TDI, I/O 46 I/O I/O I/O
3 NC I/O I/O 47 I/O I/O I/O
4 I/O I/O I/O 48 I/O I/O I/O
5 I/O I/O I/O 49 I/O I/O I/O
6 I/O I/O I/O 50 I/O I/O I/O
7 I/O I/O I/O 51 I/O I/O I/O
8 I/O I/O I/O 52 V
CCI
V
CCI
9 I/O I/O I/O 53 I/O I/O I/O
10 TMS TMS TMS 54 NC I/O I/O
11 V
CCI
V
CCI
V
CCI
55 I/O I/O I/O
12 NC I/O I/O 56 I/O I/O I/O
13 I/O I/O I/O 57 NC I/O I/O
14 I/O I/O I/O 58 I/O I/O I/O
15 I/O I/O I/O 59 I/O I/O I/O
16 I/O I/O I/O 60 I/O I/O I/O
17 I/O I/O I/O 61 I/O I/O I/O
18 I/O I/O I/O 62 I/O I/O I/O
19 I/O I/O I/O 63 I/O I/O I/O
20 I/O I/O I/O 64 PRB, I/O PRB, I/O PRB, I/O
21 GND GND GND 65 GND GND GND
22 V
CCA
23 GND GND GND 67 V
V
CCA
V
CCA
66 V
CCA
CCR
V
V
CCA
CCR
24 I/O I/O I/O 68 I/O I/O I/O
25 I/O I/O I/O 69 HCLK HCLK HCLK
26 I/O I/O I/O 70 I/O I/O I/O
27 I/O I/O I/O 71 I/O I/O I/O
28 I/O I/O I/O 72 I/O I/O I/O
29 I/O I/O I/O 73 I/O I/O I/O
30 I/O I/O I/O 74 I/O I/O I/O
31 I/O I/O I/O 75 I/O I/O I/O
32 V
33 V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
V
V
CCI
CCA
76 I/O I/O I/O
77 I/O I/O I/O
34 I/O I/O I/O 78 I/O I/O I/O
35 I/O I/O I/O 79 NC I/O I/O
36 I/O I/O I/O 80 I/O I/O I/O
37 I/O I/O I/O 81 NC I/O I/O
38 I/O I/O I/O 82 V
CCI
V
CCI
39 I/O I/O I/O 83 I/O I/O I/O
40 NC I/O I/O 84 I/O I/O I/O
41 I/O I/O I/O 85 I/O I/O I/O
42 NC I/O I/O 86 I/O I/O I/O
43 I/O I/O I/O 87 TDO, I/O TDO , I/O TDO, I/O
44 GND GND GND 88 I/O I/O I/O
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCR
V
CCI
44 v3.1
Page 45

54SX Family FPGAs
176-Pin TQFP (Continued)
Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX08
Function
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function
89 GND GND GND 133 GND GND GND
90 NC I/O I/O 134 I/O I/O I/O
91 NC I/O I/O 135 I/O I/O I/O
92 I/O I/O I/O 136 I/O I/O I/O
93 I/O I/O I/O 137 I/O I/O I/O
94 I/O I/O I/O 138 I/O I/O I/O
95 I/O I/O I/O 139 I/O I/O I/O
96 I/O I/O I/O 140 V
CCI
V
CCI
97 I/O I/O I/O 141 I/O I/O I/O
98 V
99 V
CCA
CCI
V
V
CCA
CCI
V
V
CCA
CCI
142 I/O I/O I/O
143 I/O I/O I/O
100 I/O I/O I/O 144 I/O I/O I/O
101 I/O I/O I/O 145 I/O I/O I/O
102 I/O I/O I/O 146 I/O I/O I/O
103 I/O I/O I/O 147 I/O I/O I/O
104 I/O I/O I/O 148 I/O I/O I/O
105 I/O I/O I/O 149 I/O I/O I/O
106 I/O I/O I/O 150 I/O I/O I/O
107 I/O I/O I/O 151 I/O I/O I/O
108 GND GND GND 152 CLKA CLKA CLKA
109 V
CCA
110 GND GND GND 154 V
V
CCA
V
CCA
153 CLKB CLKB CLKB
CCR
V
CCR
111 I/O I/O I/O 155 GND GND GND
112 I/O I/O I/O 156 V
CCA
V
CCA
113 I/O I/O I/O 157 PRA, I/O PRA, I/O PRA, I/O
114 I/O I/O I/O 158 I/O I/O I/O
115 I/O I/O I/O 159 I/O I/O I/O
116 I/O I/O I/O 160 I/O I/O I/O
117 I/O I/O I/O 161 I/O I/O I/O
118 NC I/O I/O 162 I/O I/O I/O
119 I/O I/O I/O 163 I/O I/O I/O
120 NC I/O I/O 164 I/O I/O I/O
121 NC I/O I/O 165 I/O I/O I/O
122 V
CCA
V
CCA
V
CCA
166 I/O I/O I/O
123 GND GND GND 167 I/O I/O I/O
124 V
CCI
125 I/O I/O I/O 169 V
V
CCI
V
CCI
168 NC I/O I/O
CCI
V
CCI
126 I/O I/O I/O 170 I/O I/O I/O
127 I/O I/O I/O 171 NC I/O I/O
128 I/O I/O I/O 172 NC I/O I/O
129 I/O I/O I/O 173 NC I/O I/O
130 I/O I/O I/O 174 I/O I/O I/O
131 NC I/O I/O 175 I/O I/O I/O
132 NC I/O I/O 176 TCK, I/O TCK, I/O TCK, I/O
A54SX32
Function
V
CCI
V
CCR
V
CCA
V
CCI
v3.1 45
Page 46

Package Pin Assignments (continued)
100-Pin VQFP (Top View)
100
1
54SX Family FPGAs
100-Pin
VQFP
46 v3.1
Page 47

54SX Family FPGAs
100-VQFP
Pin Number
1 GND GND 51 GND GND
2 TDI, I/O TDI, I/O 52 I/O I/O
3 I/O I/O 53 I/O I/O
4 I/O I/O 54 I/O I/O
5 I/O I/O 55 I/O I/O
6 I/O I/O 56 I/O I/O
7TMSTMS 57V
8V
9 GND GND 59 I/O I/O
10 I/O I/O 60 I/O I/O
11 I/O I/O 61 I/O I/O
12 I/O I/O 62 I/O I/O
13 I/O I/O 63 I/O I/O
14 I/O I/O 64 I/O I/O
15 I/O I/O 65 I/O I/O
16 I/O I/O 66 I/O I/O
17 I/O I/O 67 V
18 I/O I/O 68 GND GND
19 I/O I/O 69 GND GND
20 V
21 I/O I/O 71 I/O I/O
22 I/O I/O 72 I/O I/O
23 I/O I/O 73 I/O I/O
24 I/O I/O 74 I/O I/O
25 I/O I/O 75 I/O I/O
26 I/O I/O 76 I/O I/O
27 I/O I/O 77 I/O I/O
28 I/O I/O 78 I/O I/O
29 I/O I/O 79 I/O I/O
30 I/O I/O 80 I/O I/O
31 I/O I/O 81 I/O I/O
32 I/O I/O 82 V
33 I/O I/O 83 I/O I/O
34 PRB, I/O PRB, I/O 84 I/O I/O
35 V
36 GND GND 86 I/O I/O
37 V
38 I/O I/O 88 CLKB CLKB
39 HCLK HCLK 89 V
40 I/O I/O 90 V
41 I/O I/O 91 GND GND
42 I/O I/O 92 PRA, I/O PRA, I/O
43 I/O I/O 93 I/O I/O
44 V
45 I/O I/O 95 I/O I/O
46 I/O I/O 96 I/O I/O
47 I/O I/O 97 I/O I/O
48 I/O I/O 98 I/O I/O
49 TDO, I/O TDO, I/O 99 I/O I/O
50 I/O I/O 100 TCK, I/O TCK, I/O
A54SX08
Function
CCI
CCI
CCA
CCR
CCI
A54SX16,
A54SX16P
Function Pin Number
V
V
V
V
V
CCI
CCI
CCA
CCR
CCI
58 V
70 I/O I/O
85 I/O I/O
87 CLKA CLKA
94 I/O I/O
A54SX08
Function
CCA
CCI
CCA
CCI
CCR
CCA
A54SX16
A54SX16P
Function
V
CCA
V
CCI
V
CCA
V
CCI
V
CCR
V
CCA
v3.1 47
Page 48

Package Pin Assignments (continued)
313-Pin PBGA (Top View)
54SX Family FPGAs
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
1
23456789101112131415
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
1
2345678910111213141516171819202122232425
48 v3.1
Page 49

54SX Family FPGAs
313-Pin PBGA
Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A1 GND AC15 I/O C5 NC F20 I/O
A3 NC AC17 I/O C7 I/O F22 I/O
A5 I/O AC19 I/O C9 I/O F24 I/O
A7 I/O AC21 I/O C11 I/O G1 I/O
A9 I/O AC23 I/O C13 V
CCI
G3 TMS
A11 I/O AC25 NC C15 I/O G5 I/O
A13 V
CCR
A15 I/O AD4 I/O C19 V
A17 I/O AD6 V
AD2 GND C17 I/O G7 I/O
G9 V
CCI
CCI
C21 I/O G11 I/O
A19 I/O AD8 I/O C23 I/O G13 CLKB
A21 I/O AD10 I/O C25 NC G15 I/O
A23 NC AD12 PRB, I/O D2 I/O G17 I/O
A25 GND AD14 I/O D4 NC G19 I/O
AA1 I/O AD16 I/O D6 I/O G21 I/O
AA3 I/O AD18 I/O D8 I/O G23 I/O
AA5 NC AD20 I/O D10 I/O G25 I/O
AA7 I/O AD22 NC D12 I/O H2 I/O
AA9 NC AD24 I/O D14 I/O H4 I/O
AA11 I/O AE1 NC D16 I/O H6 I/O
AA13 I/O AE3 I/O D18 I/O H8 I/O
AA15 I/O AE5 I/O D20 I/O H10 I/O
AA17 I/O AE7 I/O D22 I/O H12 PRA, I/O
AA19 I/O AE9 I/O D24 NC H14 I/O
AA21 I/O AE11 I/O E1 I/O H16 I/O
AA23 NC AE13 V
CCA
E3 NC H18 NC
AA25 I/O AE15 I/O E5 I/O H20 I/O
AB2 NC AE17 I/O E7 I/O H22 V
AB4 NC AE19 I/O E9 I/O H24 I/O
AB6 I/O AE21 I/O E11 I/O J1 I/O
AB8 I/O AE23 TDO, I/O E13 V
CCA
J3 I/O
AB10 I/O AE25 GND E15 I/O J5 I/O
AB12 I/O B2 TCK, I/O E17 I/O J7 NC
AB14 I/O B4 I/O E19 I/O J9 I/O
AB16 I/O B6 I/O E21 I/O J11 I/O
AB18 V
CCI
B8 I/O E23 I/O J13 CLKA
AB20 NC B10 I/O E25 I/O J15 I/O
AB22 I/O B12 I/O F2 I/O J17 I/O
AB24 I/O B14 I/O F4 I/O J19 I/O
AC1 I/O B16 I/O F6 NC J21 GND
AC3 I/O B18 I/O F8 I/O J23 I/O
AC5 I/O B20 I/O F10 NC J25 I/O
AC7 I/O B22 I/O F12 I/O K2 I/O
AC9 I/O B24 I/O F14 I/O K4 I/O
AC11 I/O C1 TDI, I/O F16 NC K6 I/O
AC13 V
CCR
C3 I/O F18 I/O K8 V
A54SX32
Function
CCI
CCI
CCI
v3.1 49
Page 50

54SX Family FPGAs
313-Pin PBGA (Continued)
Pin Number
Function Pin Number
K10 I/O N3 V
K12 I/O N5 V
A54SX32
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
CCA
CCR
R21 I/O V18 I/O
R23 I/O V20 I/O
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
K14 I/O N7 I/O R25 I/O V22 V
K16 I/O N9 V
CCI
T2 I/O V24 V
K18 I/O N11 GND T4 I/O W1 I/O
K20 V
CCA
N13 GND T6 I/O W3 I/O
K22 I/O N15 GND T8 I/O W5 I/O
K24 I/O N17 I/O T10 I/O W7 NC
L1 I/O N19 I/O T12 I/O W9 I/O
L3 I/O N21 I/O T14 HCLK W11 I/O
L5 I/O N23 V
L7 I/O N25 V
CCR
CCA
T16 I/O W13 V
T18 I/O W15 I /O
L9 I/O P2 I/O T20 I/O W17 I/O
L11 I/O P4 I/O T22 I/O W19 I/O
L13 GND P6 I/O T24 I/O W21 I/O
L15 I/O P8 I/O U1 I/O W23 I/O
L17 I/O P10 I/O U3 I/O W25 I/O
L19 I/O P12 GND U5 V
CCI
Y2 I/O
L21 I/O P14 GND U7 I/O Y4 I/O
L23 I/O P16 I/O U9 I/O Y6 I/O
L25 I/O P18 I/O U15 I/O Y8 I/O
M2 I/O P20 NC U17 I/O Y10 I/O
M4 I/O P22 I/O U19 I/O Y12 I/O
M6 I/O P24 I/O U21 I/O Y14 I/O
M8 I/O R1 I/O U23 I/O Y16 I/O
M10 I/O R3 I/O U25 I/O Y18 I/O
M12 GND R5 I/O V2 V
CCA
Y20 NC
M14 GND R7 I/O V4 I/O Y22 I/O
M16 V
CCI
R9 I/O V6 I/O Y24 NC
M18 I/O R11 I/O V8 I/O
M20 I/O R13 GND V10 I/O
M22 I/O R15 I/O V12 I/O
M24 I/O R17 I/O V14 I/O
N1 I/O R19 I/O V16 NC
A54SX32
Function
CCA
CCI
CCI
50 v3.1
Page 51

54SX Family FPGAs
Package Pin Assignments (continued)
329-Pin PBGA (Top View)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
2322212019181716151410 11 12 13987654321
v3.1 51
Page 52

54SX Family FPGAs
329-Pin PBGA
Pin Number
Function Pin Number
A1 GND AA23 V
A54SX32
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
CCI
AC22 V
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
CCI
C21 V
A2 GND AB1 I/O AC23 GND C22 GND
A3 V
CCI
AB2 GND B1 V
CCI
C23 NC
A4 NC AB3 I/O B2 GND D1 I/O
A5 I/O AB4 I/O B3 I/O D2 I/O
A6 I/O AB5 I/O B4 I/O D3 I/O
A7 V
CCI
AB6 I/O B5 I/O D4 TCK, I/O
A8 NC AB7 I/O B6 I/O D5 I/O
A9 I/O AB8 I/O B7 I/O D6 I/O
A10 I/O AB9 I/O B8 I/O D7 I/O
A11 I/O AB10 I/O B9 I/O D8 I/O
A12 I/O AB11 PRB, I/O B10 I/O D9 I/O
A13 CLKB AB12 I/O B11 I/O D10 I/O
A14 I/O AB13 HCLK B12 PRA, I/O D11 V
A15 I/O AB14 I/O B13 CLKA D12 V
A16 I/O AB15 I/O B14 I/O D13 I/O
A17 I/O AB16 I/O B15 I/O D14 I/O
A18 I/O AB17 I/O B16 I/O D15 I/O
A19 I/O AB18 I/O B17 I/O D16 I/O
A20 I/O AB19 I/O B18 I/O D17 I/O
A21 NC AB20 I/O B19 I/O D18 I/O
A22 V
CCI
AB21 I/O B20 I/O D19 I/O
A23 GND AB22 GND B21 I/O D20 I/O
AA1 V
CCI
AA2 I/O AC1 GND B23 V
AA3 GND AC2 V
AB23 I/O B22 GND D21 I/O
D22 I/O
CCI
CCI
C1 NC D23 I/O
AA4 I/O AC3 NC C2 TDI, I/O E1 V
AA5 I/O AC4 I/O C3 GND E2 I/O
AA6 I/O AC5 I/O C4 I/O E3 I/O
AA7 I/O AC6 I/O C5 I/O E4 I/O
AA8 I/O AC7 I/O C6 I/O E20 I/O
AA9 I/O AC8 I/O C7 I/O E21 I/O
AA10 I/O AC9 V
CCI
C8 I/O E22 I/O
AA11 I/O AC10 I/O C9 I/O E23 I/O
AA12 I/O AC11 I/O C10 I/O F1 I/O
AA13 I/O AC12 I/O C11 I/O F2 TMS
AA14 I/O AC13 I/O C12 I/O F3 I/O
AA15 I/O AC14 I/O C13 I/O F4 I/O
AA16 I/O AC15 NC C14 I/O F20 I/O
AA17 I/O AC16 I/O C15 I/O F21 I/O
AA18 I/O AC17 I/O C16 I/O F22 I/O
AA19 I/O AC18 I/O C17 I/O F23 I/O
AA20 TDO, I/O AC19 I/O C18 I/O G1 I/O
AA21 V
CCI
AC20 I/O C19 I/O G 2 I/O
AA22 I/O AC21 NC C20 I/O G3 I/O
A54SX32
Function
CCI
CCA
CCR
CCI
52 v3.1
Page 53

54SX Family FPGAs
329-Pin PBGA
Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
A54SX32
Function Pin Number
G4 I/O L22 I/O R20 I/O Y10 I/O
G20 I/O L23 NC R21 I/O Y11 I/O
G21 I/O M1 I/O R22 I/O Y12 V
G22 I/O M2 I/O R23 I/O Y13 V
G23 GND M3 I/O T1 I/O Y14 I/O
H1 I/O M4 V
CCA
T2 I/O Y15 I/O
H2 I/O M10 GND T3 I/O Y16 I/O
H3 I/O M11 GND T4 I/O Y17 I/O
H4 I/O M12 GND T20 I/O Y18 I/O
H20 V
CCA
M13 GND T21 I/O Y19 I/O
H21 I/O M14 GND T22 I/O Y20 GND
H22 I/O M20 V
CCA
T23 I/O Y21 I/O
H23 I/O M21 I/O U1 I/O Y22 I/O
J1 NC M22 I/O U2 I/O Y23 I/O
J2 I/O M23 V
CCI
U3 V
CCA
J3 I/O N1 I/O U4 I/O
J4 I/O N2 I/O U20 I/O
J20 I/O N3 I/O U21 V
CCA
J21 I/O N4 I/O U22 I/O
J22 I/O N10 GND U23 I/O
J23 I/O N11 GND V1 V
CCI
K1 I/O N12 GND V2 I/O
K2 I/O N13 GND V3 I/O
K3 I/O N14 GND V4 I/O
K4 I/O N20 NC V20 I/O
K10 GND N21 I/O V21 I/O
K1 1 GND N22 I/O V22 I/O
K12 GND N23 I/O V23 I/O
K13 GND P1 I/O W1 I/O
K14 GND P2 I/O W2 I/O
K20 I/O P3 I/O W3 I/O
K21 I/O P4 I/O W4 I/O
K22 I/O P10 GND W20 I/O
K23 I/O P11 GND W21 I/O
L1 I/O P12 GND W22 I/O
L2 I/O P13 GND W23 NC
L3 I/O P14 GND Y1 NC
L4 V
CCR
P20 I/O Y2 I/O
L10 GND P21 I/O Y3 I/O
L1 1 GND P22 I/O Y4 GND
L12 GND P23 I/O Y5 I/O
L13 GND R1 I/O Y6 I/O
L14 GND R2 I/O Y7 I/O
L20 V
CCR
R3 I/O Y8 I/O
L21 I/O R4 I/O Y9 I/O
A54SX32
Function
CCA
CCR
v3.1 53
Page 54

Package Pin Assignments (Continued)
54SX Family FPGAs
144-Pin FBGA (Top View)
1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
2
4
3
6
5
8
7
9
10 11
12
H
J
K
L
M
54 v3.1
Page 55

54SX Family FPGAs
144-Pin FBGA
Pin Number
A1 I/O E1 I/O J1 I/O
A2 I/O E2 I/O J2 I/O
A3 I/O E3 I/O J3 I/O
A4 I/O E4 I/O J4 I/O
A5 V
A6 GND E6 V
A7 CLKA E7 V
A8 I/O E8 V
A9 I/O E9 V
A10 I/O E10 I/O J10 I/O
A11 I/O E11 GND J11 I/O
A12 I/O E12 I/O J12 V
B1 I/O F1 I/O K1 I/O
B2 GND F2 I/O K2 I/O
B3 I/O F3 V
B4 I/O F4 I/O K4 I/O
B5 I/O F5 GND K5 I/O
B6 I/O F6 GND K6 I/O
B7 CLKB F7 GND K7 GND
B8 I/O F8 V
B9 I/O F9 I/O K9 I/O
B10 I/O F10 GND K10 GND
B11 GND F11 I/O K11 I/O
B12 I/O F12 I/O K12 I/O
C1 I/O G1 I/O L1 GND
C2 I/O G2 GND L2 I/O
C3 TCK, I/O G3 I/O L3 I/O
C4 I/O G4 I/O L4 I/O
C5 I/O G5 GND L5 I/O
C6 PRA, I/O G6 GND L6 I/O
C7 I/O G7 GND L7 HCLK
C8 I/O G8 V
C9 I/O G9 I/O L9 I/O
C10 I/O G10 I/O L10 I/O
C11 I/O G11 I/O L11 I/O
C12 I/O G12 I/O L12 I/O
D1 I/O H1 I/O M1 I/O
D2 V
D3 TDI, I/O H3 I/O M3 I/O
D4 I/O H4 I/O M4 I/O
D5 I/O H5 V
D6 I/O H6 V
D7 I/O H7 V
D8 I/O H8 V
D9 I/O H9 V
D10 I/O H10 I/O M10 I/O
D1 1 I/O H11 I/O M11 TDO, I/O
D12 I/O H12 V
A54SX08
Function Pin Number
CCA
CCI
E5 TMS J5 I/O
H2 I/O M2 I/O
A54SX08
Function Pin Number
CCI
CCI
CCI
CCA
CCR
CCI
CCI
CCA
CCA
CCI
CCI
CCA
CCR
J6 PRB, I/O
J7 I/O
J8 I/O
J9 I/O
K3 I/O
K8 I/O
L8 I/O
M5 I/O
M6 I/O
M7 V
M8 I/O
M9 I/O
M12 I/O
A54SX08
Function
CCA
CCA
v3.1 55
Page 56

54SX Family FPGAs
List of Changes
The following table lists critical changes that were made in the current version of the document.
Previous version Changes in current version (v3.1) Page
v3.0.1
The storage temperature in the “Absolute Maximum Ratings1” table on page 10 was
updated.
Table 1 on page 8 was updated. page 8
page 10
Datasheet Categories
In order to provide the latest information to designers, some datasheets are published before data has been fully
characterized. Datasheets are designated as “Product Brief,” “Advanced,” “Production.” The definition of these categories
are as follows:
Product Brief
The product brief is a modified version of an advanced datasheet containing general product information. This brief
summarizes specific device and family information for unreleased products.
Advanced
This datasheet version contains initial estimated information based on simulation, other products, devices, or speed grades.
This information can be used as estimates but not for production.
Unmarked (production)
This datasheet version contains information that is considered to be final.
56 v3.1
Page 57

Actel and the Actel logo are registered trademarks of Actel Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their owners.
http://www.actel.com
Actel Corporation
955 East Arques Avenue
Sunnyvale, California 94086
USA
Tel: (408) 739-1010
Fax: (408) 739-1540
Actel Europe Ltd.
Dunlop House, Riverside Way
Camberley, Surrey GU15 3YL
United Kingdom
Tel:
+44 (0)1276 401450
Fax:
+44 (0)1276 401490
Actel Japan
EXOS Ebisu Bldg. 4F
1-24-14 Ebisu Shibuya-ku
Tokyo 150 Japan
Tel: +81 03-3445-7671
Fax: +81 03-3445-7668
Actel Hong Kong
39th Floor
One Pacific Place
88 Queensway
Admiralty, Hong Kong
Tel: 852-22735712
572137-4/6.03
 Loading...
Loading...