Page 1

DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
December 1990
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74HC/HCT160
Presettable synchronous BCD
decade counter; asynchronous
reset
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
Page 2
December 1990 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
FEATURES
• Synchronous counting and loading
• Two count enable inputs for n-bit cascading
• Positive-edge triggered clock
• Asynchronous reset
• Output capability: standard
• ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT160 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT160 are synchronous presettable decade
counters which feature an internal look-ahead carry and
can be used for high-speed counting.
Synchronous operation is provided by having all flip-flops
clocked simultaneously on the positive-going edge of the
clock (CP).
The outputs (Q
0
to Q3) of the counters may be preset to a
HIGH or LOW level. A LOW level at the parallel enable
input (PE) disables the counting action and causes the
data at the data inputs (D0 to D3) to be loaded into the
counter on the positive-going edge of the clock (providing
that the set-up and hold time requirements forPE are met).
Preset takes place regardless of the levels at count enable
inputs (CEP and CET).
A LOW level at the master reset input (MR) sets all four
outputs of the flip-flops (Q0 to Q3) to LOW level regardless
of the levels at CP, PE, CET and CEP inputs (thus
providing an asynchronous clear function).
The look-ahead carry simplifies serial cascading of the
counters. Both count enable inputs (CEP and CET) must
be HIGH to count. The CET input is fed forward to enable
the terminal count output (TC). The TC output thus
enabled will produce a HIGH output pulse of a duration
approximately equal to a HIGH level output of Q0. This
pulse can be used to enable the next cascaded stage.
The maximum clock frequency for the cascaded counters
is determined by the CP to TC propagation delay and CEP
to CP set-up time, according to the following formula:
f
max
=
1
t
P max()
CP to TC()+tSU(CEP to CP)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; tr=tf= 6 ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
t
PHL
propagation delay
CP to Q
n
CP to TC
MR to Q
n
MR to TC
CET to TC
CL=15pF;
VCC=5V 19
21
21
21
14
21
24
23
26
14
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
t
PLH
propagation delay
CP to Q
n
CP to TC
CET to TC
19
21
14
21
20
7
ns
ns
ns
f
max
maximum clock
frequency
61 31 MHz
C
I
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
C
PD
power dissipation
capacitance per
package
notes 1 and 2
39 34 pF
Notes
1. CPD is used to determine the
dynamic power dissipation
(PD in µW):
PD=CPD× V
CC
2
× fi+
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo)
where:
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) = sum of
outputs
CL= output load capacitance in
pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is
VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is
VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
Page 3
December 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
ORDERING INFORMATION
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”
.
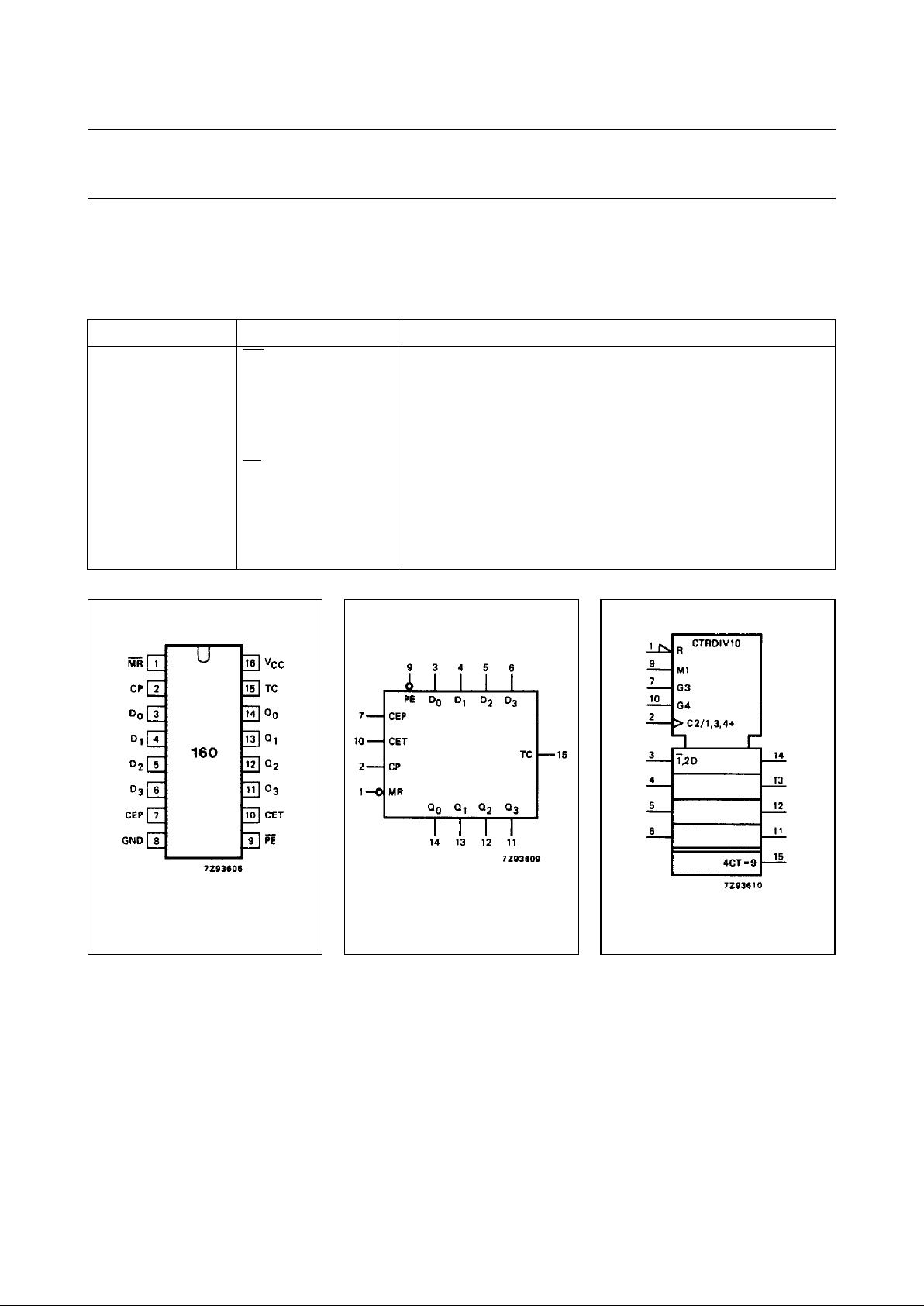
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1
MR asynchronous master reset (active LOW)
2 CP clock input (LOW-to-HIGH, edge-triggered)
3, 4, 5, 6 D
0
to D
3
data inputs
7 CEP count enable input
8 GND ground (0 V)
9
PE parallel enable input (active LOW)
10 CET count enable carry input
14, 13, 12, 11 Q
0
to Q
3
flip-flop outputs
15 TC terminal count output
16 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol. Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
Page 4

December 1990 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
FUNCTION TABLE
Notes
1. The TC output is HIGH when CET is HIGH and the counter is at terminal count (HLLH).
H = HIGH voltage level
h = HIGH voltage level one set-up time prior to the LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
L = LOW voltage level
I = LOW voltage level one set-up time prior to the LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
q = lower case letters indicate the state of the referenced output one set-up time prior to the LOW-to-HIGH CP
transition
X = don’t care
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
OPERATING MODE
INPUTS OUTPUTS
MR CP CEP CET PE D
n
Q
n
TC
reset (clear) L XXXXXL L
parallel load H
H
↑
↑
X
X
X
X
I
I
I
h
L
H
L
(1)
count H ↑ hhhXcount
(1)
hold H X I X h X q
n
(1)
(do nothing) H X X I h X q
n
L
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
Page 5

December 1990 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
Fig.5 State diagram.
Fig.6 Typical timing sequence: reset outputs to zero;
preset to BCD seven; count to eight, nine, zero,
one, two and three; inhibit.
Fig.7 Logic diagram.
Page 6

December 1990 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HC
For the DC characteristics see
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications”
.
Output capability: standard
ICC category: MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HC
GND = 0 V; t
r=tf
= 6 ns; CL= 50 pF
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HC
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min. typ. max. min. max. min. max.
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
propagation delay
CP to Q
n
61
22
18
185
37
31
230
46
39
280
56
48
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 8
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
propagation delay
CP to TC
69
25
20
215
43
31
270
54
46
325
65
55
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 8
t
PHL
propagation delay
MR to Q
n
69
25
20
210
42
36
265
53
45
315
63
54
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 9
t
PHL
propagation delay
MR to TC
69
25
20
220
44
37
275
55
47
330
66
56
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 9
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
propagation delay
CET to TC
47
17
14
150
30
26
190
38
33
225
45
38
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 10
t
THL
/ t
TLH
output transition time 19
7
6
75
15
13
95
19
16
110
22
19
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Figs 8 and 10
t
W
clock pulse width
HIGH or LOW
80
16
14
22
8
6
100
20
17
120
24
20
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 8
t
W
master reset pulse width
LOW
80
16
14
28
10
8
100
20
17
120
24
20
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 9
t
rem
removal time
MR to CP
100
20
17
30
11
9
125
25
21
150
30
26
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 9
t
su
set-up time
Dn to CP
80
16
14
22
8
6
100
20
17
120
24
20
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 11
t
su
set-up time
PE to CP
135
27
23
41
15
12
170
34
29
205
41
35
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 11
Page 7

December 1990 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
t
su
set-up time
CEP, CET to CP
200
40
34
63
23
18
250
50
43
300
60
51
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 12
t
h
hold time
Dn to CP
0
0
0
−17
−6
−5
0
0
0
0
0
0
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Figs 11 and 12
t
h
hold time
PE to CP
0
0
0
−41
−15
−12
0
0
0
0
0
0
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Figs 11 and 12
t
h
hold time
CEP, CET to CP
0
0
0
−58
−21
−17
0
0
0
0
0
0
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Figs 11 and 12
f
max
maximum clock pulse
frequency
6.0
30
35
18
55
66
4.8
24
28
4.0
20
24
MHz 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig. 8
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HC
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min. typ. max. min. max. min. max.
Page 8

December 1990 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HCT
For the DC characteristics see
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications”
.
Output capability: standard
ICC category: MSI
Note to HCT types
The value of additional quiescent supply current (∆I
CC
) for unit load of 1 is given in the family specifications.
To determine ∆ICC per input, multiply this value by the unit load coefficient shown in the table below.
INPUT UNIT LOAD COEFFICIENT
MR 0.95
CP 0.80
CEP 0.25
D
n
0.25
CET 1.05
PT 0.30
Page 9

December 1990 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous BCD decade
counter; asynchronous reset
74HC/HCT160
AC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HCT
GND = 0 V; t
r=tf
= 6 ns; CL= 50 pF
PACKAGE OUTLINES
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines”
.
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HCT
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min. typ. max. min. max. min. max.
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
propagation delay
CP to Q
n
25 43 54 65 ns 4.5 Fig. 8
t
PHL
propagation delay
CP to TC
28 48 60 72 ns 4.5 Fig. 8
t
PLH
propagation delay
CP to TC
23 39 49 59 ns 4.5 Fig. 8
t
PHL
propagation delay
MR to Q
n
27 50 63 75 ns 4.5 Fig. 9
t
PHL
propagation delay
MR to TC
30 50 63 75 ns 4.5 Fig. 9
t
PHL
propagation delay
CET to TC
17 35 44 53 ns 4.5 Fig. 10
t
PLH
propagation delay
CET to TC
9 17 21 26 ns 4.5 Fig. 10
t
THL
/ t
TLH
output transition time 7 15 19 22 ns 4.5 Figs 8 and 10
t
W
clock pulse width
HIGH or LOW
16 8 20 24 ns 4.5 Fig. 8
t
W
master reset pulse width
LOW
20 11 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig. 9
t
rem
removal time
MR to CP
20 9 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig. 9
t
su
set-up time
Dn to CP
18 10 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig. 11
t
su
set-up time
PE to CP
30 18 44 53 ns 4.5 Fig. 11
t
su
set-up time
CEP, CET to CP
50 30 63 75 ns 4.5 Fig. 12
t
h
hold time
Dn to CP
0 −8 0 0 ns 4.5 Figs 11 and 12
t
h
hold time
PE to CP
0 −13 0 0 ns 4.5 Figs 11 and 12
t
h
hold time
CEP, CET to CP
0 −21 0 0 ns 4.5 Figs 11 and 12
f
max
maximum clock pulse
frequency
16 28 13 11 MHz 4.5 Fig. 8
 Loading...
Loading...