Page 1

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of April 1988
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
December 1990
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74HC/HCT221
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
Page 2
December 1990 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
FEATURES
• Pulse width variance is typically less than ±5%
• Pin-out identical to “123”
• Overriding reset terminates output pulse
• nB inputs have hysteresis for improved noise immunity
• Output capability: standard (except for nR
EXT/CEXT
)
• ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT221 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT221 are dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrators. Each multivibrator features an active
LOW-going edge input (n
A) and an active HIGH-going
edge input (nB), either of which can be used as an enable
input.
Pulse triggering occurs at a particular voltage level and is
not directly related to the transition time of the input pulse.
Schmitt-trigger input circuitry for the nB inputs allow
jitter-free triggering from inputs with slow transition rates,
providing the circuit with excellent noise immunity.
Once triggered, the outputs (nQ, nQ) are independent of
further transitions of nA and nB inputs and are a function
of the timing components. The output pulses can be
terminated by the overriding active LOW reset inputs
(nRD). Input pulses may be of any duration relative to the
output pulse.
Pulse width stability is achieved through internal
compensation and is virtually independent of VCC and
temperature. In most applications pulse stability will only
be limited by the accuracy of the external timing
components.
The output pulse width is defined by the following
relationship:
tW=C
EXTREXTIn2
tW= 0.7C
EXTREXT
Pin assignments for the “221” are identical to those of the
“123” so that the “221” can be substituted for those
products in systems not using the retrigger by merely
changing the value of R
EXT
and/or C
EXT
.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; tr=tf= 6 ns
Notes
1. C
PD
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PD in µW):
PD=CPD× V
CC
2
× fi+∑(CL× V
CC
2
× fo) + 0.33 × C
EXT
× V
CC
2
× fo+ D × 28 × VCCwhere:
fi= input frequency in MHz; fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
C
EXT
= timing capacitance in pF; CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V; D = duty factor in %
2. For HC the condition is VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
propagation delay C
L
= 15 pF; VCC=5 V;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ; C
EXT
= 0 pF
t
PHL
nA, nB, nRD to nQ, nQ 2932ns
t
PLH
nA, nB, nRD to nQ, nQ 3536ns
C
I
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
C
PD
power dissipation capacitance per package notes 1 and 2 90 96 pF
Page 3
December 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
ORDERING INFORMATION
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”
.
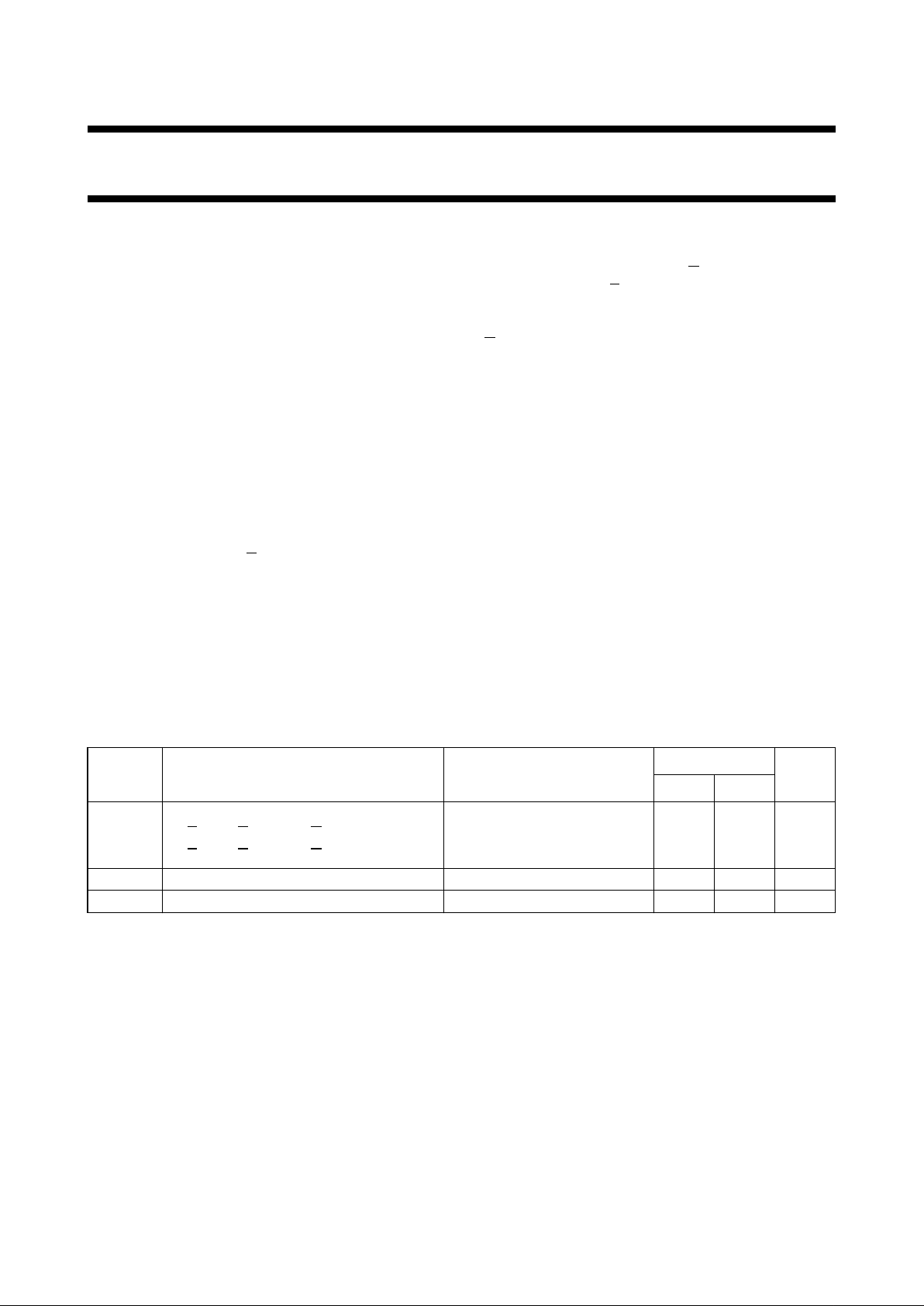
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1, 9 1
A, 2A trigger inputs (negative-edge triggered)
2, 10 1B, 2B trigger inputs (positive-edge triggered)
3, 11 1
RD, 2R
D
direct reset inputs (active LOW)
4, 12 1
Q, 2Q outputs (active LOW)
72R
EXT/CEXT
external resistor/capacitor connection
8 GND ground (0 V)
13, 5 1Q, 2Q outputs (active HIGH)
14, 6 1C
EXT
, 2C
EXT
external capacitor connection
15 1R
EXT/CEXT
external resistor/capacitor connection
16 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol. Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
Page 4
December 1990 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
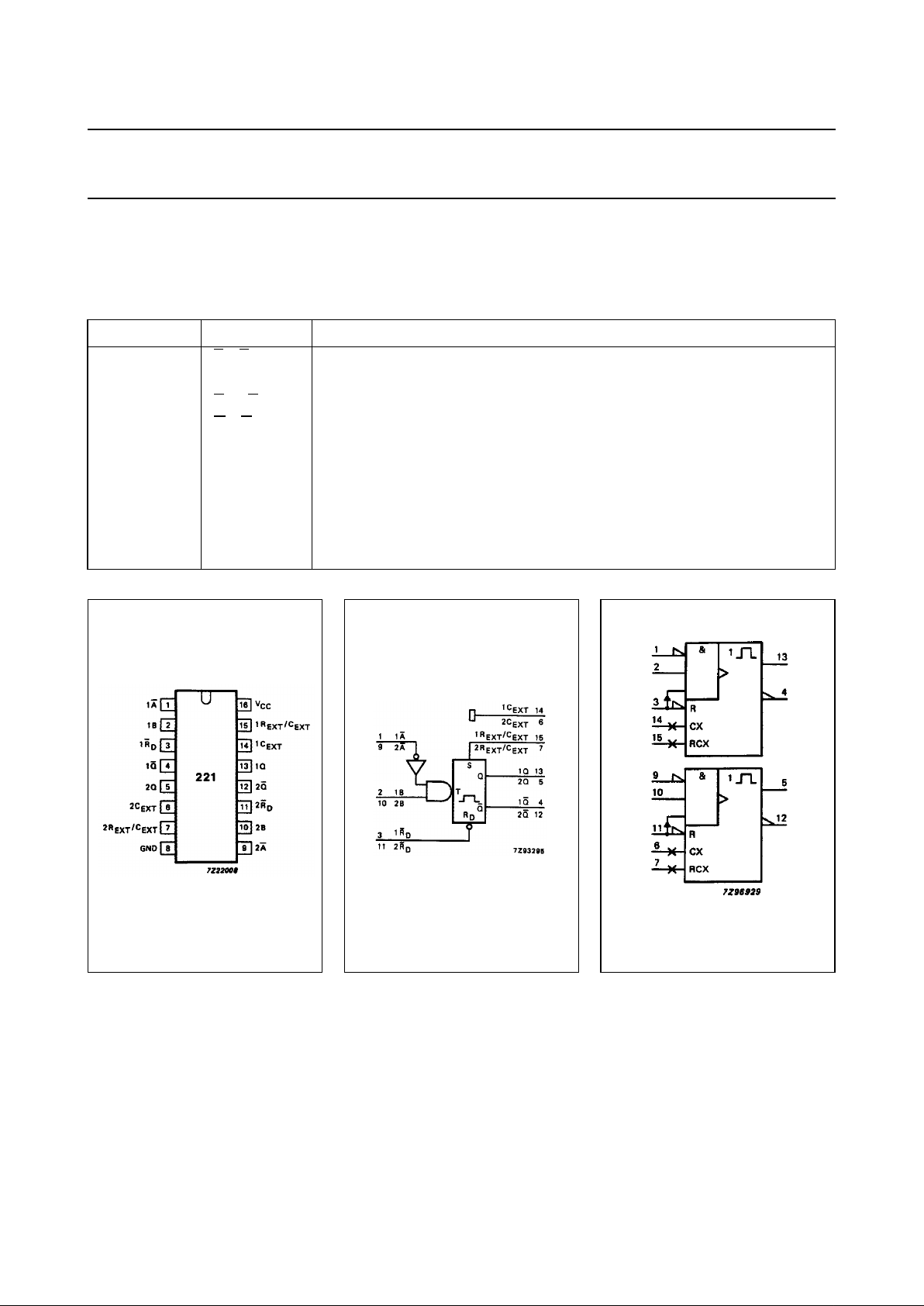
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
FUNCTION TABLE
Notes
1. H = HIGH voltage level
L = LOW voltage level
X = don’t care
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH level
↓ = HIGH-to-LOW level
= one HIGH-level output pulse
= one LOW-level output pulse
2. If the monostable was triggered before this condition
was established the pulse will continue as
programmed.
3. For this combination the reset input must be LOW and
the following sequence must be used:
pin 1 (or 9) must be set HIGH or pin 2 (or 10) set LOW;
then pin 1 (or 9) must be LOW and pin 2 (or 10) set
HIGH. Now the reset input goes from LOW-to-HIGH
and the device will be triggered.
INPUTS OUTPUTS
nR
D
nAnBnQnQ
LXXLH
XHXL
(2)
H
(2)
XXLL
(2)
H
(2)
HL↑
H↓H
↑LH
(3) (3)
Page 5

December 1990 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
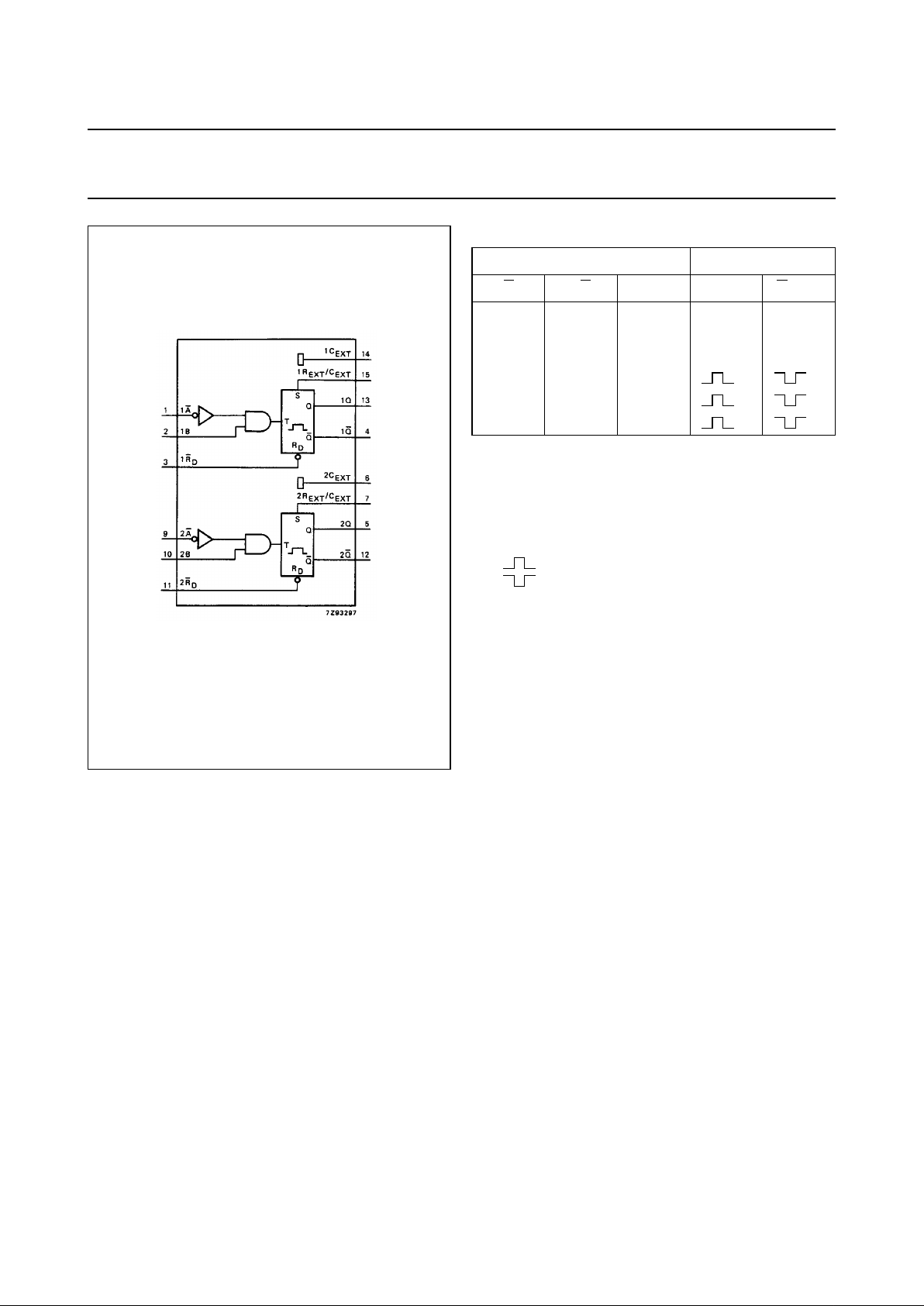
Note
It is recommended to ground pins 6 (2C
EXT
) and 14 (1C
EXT
) externally to pin 8 (GND).
Fig.5 Logic diagram.
Fig.6 Timing component connections.
Page 6

December 1990 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HC
For the DC characteristics see
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications”
.
Output capability: standard (except for nR
EXT/CEXT
)
ICC category: MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HC
GND = 0 V; t
r=tf
= 6 ns; CL= 50 pF
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HC
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min typ max. min max. min. max.
t
PLH
propagation delay (trigger)
nA, nB to nQ
72
26
21
220
44
37
275
55
47
330
66
56
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PLH
propagation delay (trigger)
nRD to nQ
80
29
23
245
49
42
305
61
52
370
74
63
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (trigger)
nA, nB to nQ
58
21
17
180
36
31
225
45
38
270
54
46
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (trigger)
nRD to nQ
63
23
18
195
39
33
245
49
42
295
59
50
ns 2.0
4.5
6,0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PLH
propagation delay (reset)
nRD to nQ
66
24
19
200
40
34
250
50
43
300
60
51
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.11
t
PLH
propagation delay (reset)
nRD to nQ
58
21
17
180
36
31
225
45
38
270
54
46
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.11
t
THL
/
t
TLH
output transition time 19
7
6
75
15
13
95
19
16
110
22
19
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig.10
t
W
trigger pulse width
nA = LOW
75
15
13
25
9
7
95
19
16
110
22
19
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig.7
t
W
trigger pulse width
nB = HIGH
90
18
15
30
11
9
115
23
20
135
27
23
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig.7
t
W
trigger pulse width
nRD= LOW
75
15
13
25
9
7
95
19
16
110
22
19
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig.8
t
W
output pulse width
nQ = LOW
nQ = HIGH
630 700 770 602 798 595 805 µs 5.0 C
EXT
= 100 nF;
R
EXT
= 10 kΩ;
Fig.10
Page 7

December 1990 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
t
W
output pulse width
nQ or nQ
140 −− ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 28 nF;
R
EXT
=2 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
W
output pulse width
nQ or nQ
1.5 −− µs 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 1 nF;
R
EXT
=2 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
W
output pulse width
nQ or nQ
7 −− µs 2.0
4.5
6.0
C
EXT
= 1 nF;
R
EXT
= 10 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
W
pulse width match
between circuits
in the package
± 2 −− % 4.5
to
5.5
C
EXT
= 1000 pF;
R
EXT
= 10 kΩ
t
rem
removal time
nRD to nA
or nB
100
20
17
30
11
9
125
25
21
150
30
26
ns 2.0
4.5
6.0
Fig.9
R
EXT
external timing resistor 10
2
1000
1000−−
−
−
kΩ 2.0
5.0
Fig.12
Fig.13
C
EXT
external timing capacitor no limits pF 2.0
5.0
Fig.12
Fig.13
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HC
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min typ max. min max. min. max.
Page 8

December 1990 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HCT
For the DC characteristics see
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications”
.
Output capability: standard (except for nR
EXT/CEXT
)
ICC category: MSI
Note to HCT types
The value of additional quiescent supply current (∆I
CC
) for a unit load of 1 is given in the family specifications.
To determine ∆ICC per input, multiply this value by the unit load coefficient shown in the table below.
INPUT UNIT LOAD COEFFICIENT
nB 0.30
n
A 0.50
n
R
D
0.50
Page 9

December 1990 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
AC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HCT
GND = 0 V; t
r=tf
= 6 ns; CL= 50 pF
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HCT
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min typ max min max. min. max.
t
PLH
propagation delay (trigger)
nA, nRD to nQ
30 50 63 75 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PLH
propagation delay (trigger)
nB to nQ
24 42 53 63 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (trigger)
nA to nQ
26 44 55 66 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (trigger)
nB to nQ
21 35 44 53 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (trigger)
nRD to nQ
26 43 54 65 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
PHL
propagation delay (reset)
nRD to nQ
26 43 54 65 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.11
t
PLH
propagation delay (reset)
nRD to nQ
31 51 64 77 ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 0 pF;
R
EXT
=5 kΩ;
Fig.11
t
THL
/ t
TLH
output transition time 7 15 19 22 ns 4.5 Fig.10
t
W
trigger pulse width
nA = LOW
20 13 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig.10
t
W
trigger pulse width
nB = HIGH
20 13 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig.10
t
W
pulse width
nRD= LOW
22 13 28 33 ns 4.5 Fig.8
t
W
output pulse width
nQ = LOW
nQ = HIGH
630 700 770 602 798 595 805 µs 5.0 C
EXT
= 100 nF;
R
EXT
= 10 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
W
trigger pulse width
nQ or nQ
140 −− ns 4.5 C
EXT
= 28 pF;
R
EXT
=2 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
W
trigger pulse width
nQ or nQ
1.5 −− µs 4.5 C
EXT
= 1 nF;
R
EXT
= 2 kΩ;
Fig.10
Page 10

December 1990 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
t
W
trigger pulse width
nQ or nQ
7 −− µs 4.5 C
EXT
= 1 nF;
R
EXT
= 10 kΩ;
Fig.10
t
rem
removal time
nRD to nA or nB
20 12 25 30 ns 4.5 Fig.9
R
EXT
external timing resistor 2 1000 −− kΩ5.0 Fig.13
C
EXT
external timing capacitor no limits pF 5.0 Fig.13
SYMBOL PARAMETER
T
amb
(°C)
UNIT
TEST CONDITIONS
74HCT
V
CC
(V)
WAVEFORMS
+25 −40 to +85 −40 to +125
min typ max min max. min. max.
Page 11

December 1990 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
AC WAVEFORMS
Fig.7 Output pulse control; nRD= HIGH.
Fig.8 Output pulse control using reset input nRD;
nA = LOW.
Fig.9 Waveforms showing the removal times;
nRD to nA or nB.
(1) HC : VM=VM= 50%; VI= GND to VCC.
HCT : V
M=VM
= 1.3 V; VI= GND to 3 V.
Fig.10 Waveforms showing the triggering of One
Shot by input nA or input nB for one period
(tW) and minimum pulse widths of the trigger
inputs nA and nB.
(1) HC : VM=VM= 50%; VI= GND to VCC.
HCT : V
M=VM
= 1.3 V; VI= GND to 3 V.
Fig.11 Waveforms showing the reset to nQ and nQ
output propagation delays.
(1) HC : VM=VM= 50%; VI= GND to VCC.
HCT : V
M=VM
= 1.3 V; VI= GND to 3 V.
Page 12

December 1990 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
Fig.12 HC typical output pulse width as a function of timing capacitance (VCC = 2 V).
Page 13

December 1990 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
Fig.13 HC/HCT typical output pulse width as a function of timing capacitance (VCC= 4.5 V).
Page 14

December 1990 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
Fig.14 HC typical output pulse width as a function of timing capacitance (VCC= 6 V).
Page 15

December 1990 15
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Dual non-retriggerable monostable
multivibrator with reset
74HC/HCT221
Fig.15 Typical output pulse width as a function of
temperature; CX= 0.1 µF; RX=10KΩ;
VCC=5V.
Fig.16 k factor as a function of supply voltage;
RX=10KΩ;T
amb
=25°C.
Power-down consideration
A large capacitor (CX) may cause problems when
powering-down the monostable due to the energy stored
in this capacitor. When a system containing this device is
powered-down or a rapid decrease of VCC to zero occurs,
the monostable may substain damage, due to the
capacitor discharging through the input protection diodes.
To avoid this possibility, use a damping diode (DX)
preferably a germanium or Schottky type diode able to
withstand large current surges and connect as shown in
Fig.17.
Fig.17 Power-down protection circuit.
PACKAGE OUTLINES
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines”
.
 Loading...
Loading...