Datasheet 74ACTQ16374SSCX, 74ACTQ16374SSC, 74ACTQ16374MTDX, 74ACTQ16374MTD, 74ACTQ16374CW Datasheet (Fairchild Semiconductor)
Page 1
© 1999 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation DS010935 www.fairchildsemi.com
June 1991
Revised November 1999
74ACTQ16374 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs
74ACTQ16374
16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs
General Description
The ACTQ16374 contains sixteen non-inverting D-type flipflops with 3-STATE outputs and is intended for bus oriented
applications. The device is byte controlled. A buffered clock
(CP) and Output Enable (OE) are common to each byte
and can be shorted together for full 16-bit operation.
The ACTQ16245 utilizes Fairchild Quiet Series technology to guarantee quiet output switching and improved
dynamic threshold perf ormance. FACT Quiet Series fe atures GTO output control for superior performance.
Features
■ Utilizes Fairchild FACT Quiet Series technology
■ Guaranteed simultaneous switching noise level and
dynamic threshold performan ce
■ Guaranteed pin-to-pin output skew
■ Buffered Positive edge-triggered clock
■ Separate control logic for each byte
■ 16-bit version of the ACTQ374
■ Outputs source/sink 24 mA
■ Additional specs for Multiple Output Switching
■ Output loadings specs for both 50 pF and 250 pF loads
Ordering Code:
Device also available in Tape and Reel. Specify by appending s uffix let te r “X” to the ordering code.
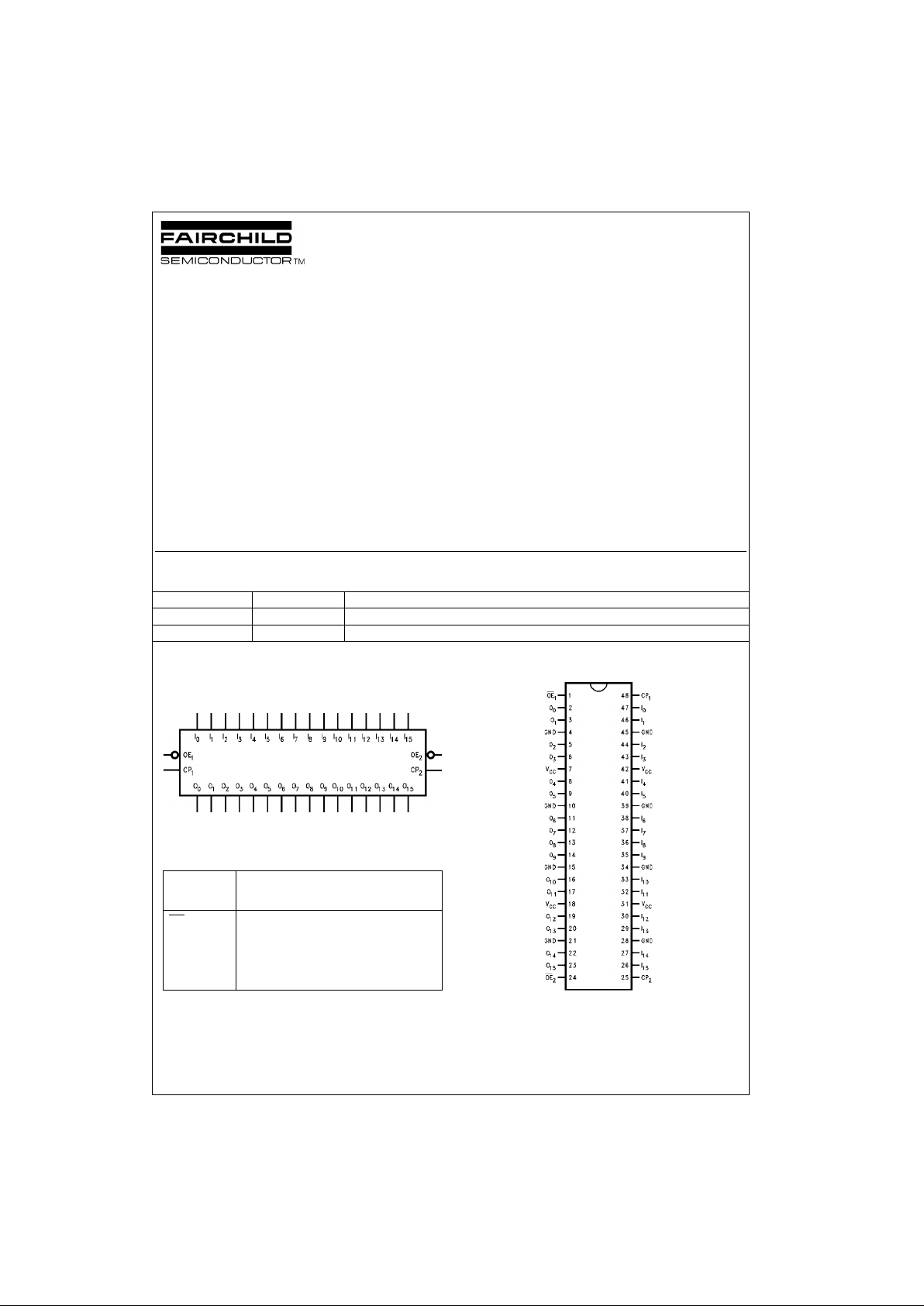
Logic Symbol
Pin Descriptions
Connection Diagram
FACT, FACT Quiet Series and GTO are trademarks of Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation.
Order Number Package Number Package Description
74ACTQ16374SSC MS48A 48-Lead Small Shrink Outline Package (SSOP), JEDEC MO-118, 0.300” Wide
74ACTQ16374MTD MTD48 48-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP), JEDEC MO-153, 6.1mm Wide
Pin
Description
Names
OE
n
Output Enable Input (Active LOW)
CP
n
Clock Pulse Input
I
0–I15
Inputs
O
0–O15
Outputs
Page 2
www.fairchildsemi.com 2
74ACTQ16374
Functional Description
The ACTQ16374 consists of sixteen edge-triggered flipflops with individua l D-type inputs and 3-STATE true outputs. The device is byt e co ntro l led wi th e ach byte fun ction ing identically, but independ ent of the other. The control
pins can be shor ted tog eth er to ob tai n fu ll 16-bit operation.
Each byte has a buffered clock and buffered Output Enable
common to all flip-flo ps within that byte. The description
which follows applies to each byte. Each flip-flop will store
the state of their individual D inputs that meet the setup and
hold time requirem ents on the LOW-to-HIG H Clock (CP
n
)
transition. With the Output Ena ble (OE
n
) LOW, the con-
tents of the flip-flops a re available at the outputs. When
OE
n
is HIGH, the outputs go to the high imped ance state.
Operation of the OE
n
input does not affect the st ate of the
flip-flops.
Tr uth Tables
H = HIGH Voltage Level
L = LOW Voltage Level
X= Immaterial
Z = HIGH Impedance
= LOW-to-HIGH Transition
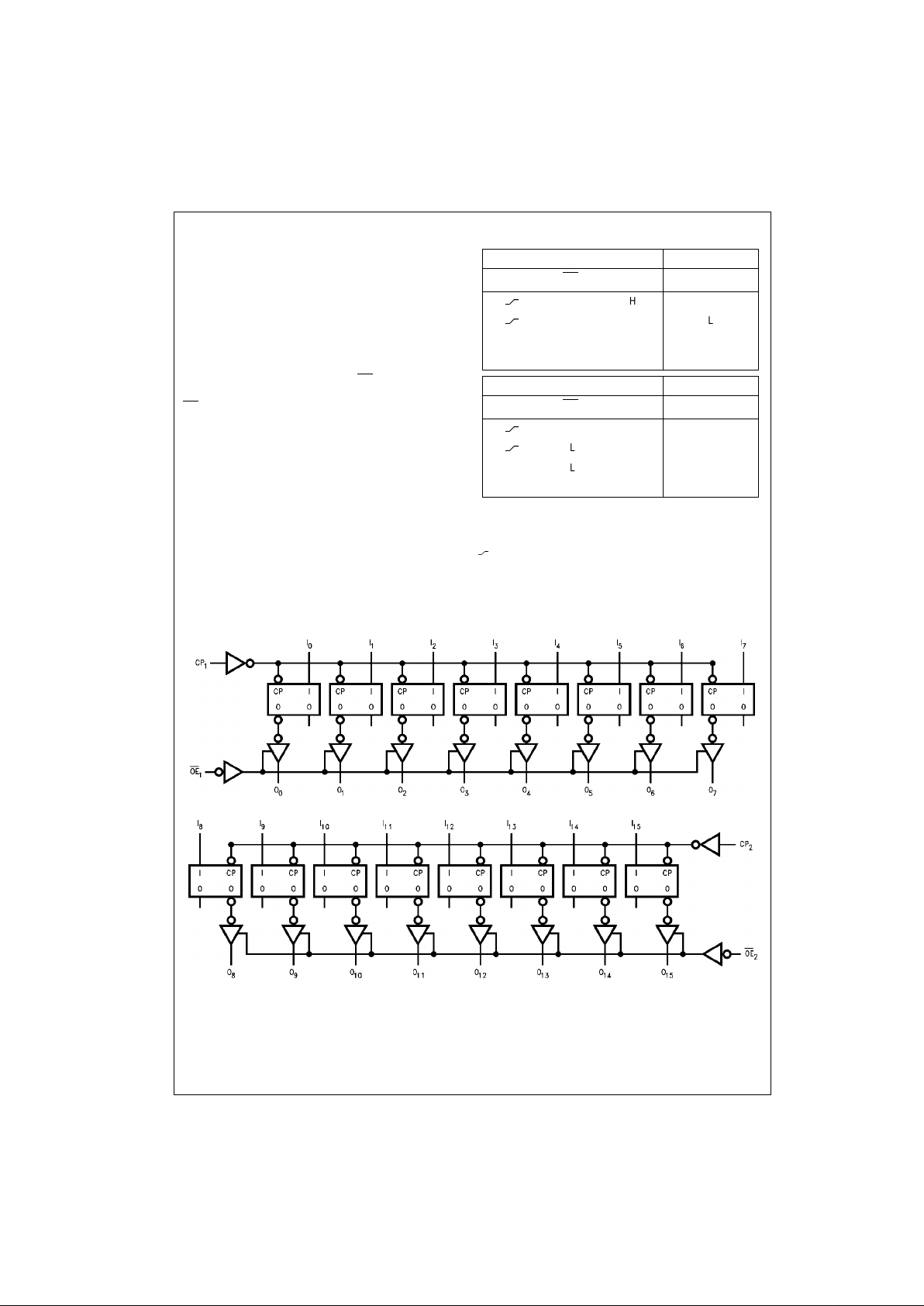
Logic Diagrams
Byte 1 (0:7)
Byte 2 (8:15)
Inputs Outputs
CP
1
OE
1
I0–I
7
O0–O
7
LH H
LL L
L L X (Previous)
XHX Z
Inputs Outputs
CP
2
OE
2
I8–I
15
O8–O
15
LH H
LL L
L L X (Previous)
XHX Z
Page 3
3 www.fairchildsemi.com
74ACTQ16374
Absolute Maximum Ratings(Note 1) Recommended Operating
Conditions
Note 1: Absolute max imum ratings are t hose values bey ond which damage
to the device may occu r. The databook spe cificatio ns shou ld be met, wit hout exception to ensure that the system design is reliable over its power
supply, temperature, and output/input loading variables. Fairchild does not
recommend operation of FACT circuits outside dat abook specifications.
DC Electrical Characteristics
Note 2: All outputs loaded; thresholds associated with output under test.
Note 3: Maximum test duration 2.0 ms; one output loaded at a time.
Note 4: Worst case package.
Note 5: Maximum number of outputs that can switch simultaneously is n. (n − 1) out puts are switched LOW and one output held LOW.
Note 6: Maximum number of outputs that can switch simultaneously is n. (n − 1) out puts are switched HIGH and one output held HIGH.
Note 7: Maximum number of data inputs (n) switching. (n − 1) input switching 0V to 3V (ACTQ). Input under test switching 3V to threshold (V
ILD
).
Supply Voltage (VCC) −0.5V to +7.0V
DC Input Diode Current (I
IK
)
V
I
= −0.5V −20 mA
V
I
= VCC + 0.5V +20 mA
DC Output Diode Current (I
OK
)
V
O
= −0.5V −20 mA
V
O
= VCC + 0.5V +20 mA
DC Output Voltage (V
O
) −0.5V to VCC + 0.5V
DC Output Source/Sink Current (I
O
) ±50 mA
DC V
CC
or Ground Current
per Output Pin ± 50 mA
Storage Temperature −65°C to +150°C
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) 4.5V to 5.5V
Input Voltage (V
I
)0V to V
CC
Output Voltage (VO)0V to V
CC
Operating Temperature (TA) −40°C to +85°C
Minimum Input Edge Rate (∆V/∆t) 125 mV/ns
V
IN
from 0.8V to 2.0V
V
CC
@ 4.5V, 5.5V
Symbol Parameter
V
CC
TA = +25°CTA = −40°C to +85°C
Units Conditions
(V) Typ Guaranteed Limits
V
IH
Minimum HIGH 4.5 1.5 2.0 2.0
V
V
OUT
= 0.1V
Input Voltage 5.5 1.5 2.0 2.0 or VCC − 0.1V
V
IL
Maximum LOW 4.5 1.5 0.8 0.8
V
V
OUT
= 0.1V
Input Voltage 5.5 1.5 0.8 0.8 or VCC − 0.1V
V
OH
Minimum HIGH 4.5 4.49 4.4 4.4
VI
OUT
= −50 µA
Output Voltage 5.5 5.49 5.4 5.4
VIN = VIL or V
IH
4.5 3.86 3.76 V IOH = −24 mA
5.5 4.86 4.76 IOH = −24 mA (Note 2)
V
OL
Maximum LOW 4.5 0.001 0.1 0.1
VI
OUT
= 50 µA
Output Voltage 5.5 0.001 0.1 0.1
VIN = VIL or V
IH
4.5 0.36 0.44 V IOL = 24 mA
5.5 0.36 0.44 I
OL
= 24 mA (Note 2)
I
OZ
Maximum 3-STATE
5.5 ± 0.5 ± 5.0 µA
VI = VIL, V
IH
Leakage Current VO = VCC, GND
I
IN
Maximum Input Leakage Current 5.5 ± 0.1 ± 1.0 µAVI = VCC, GND
I
CCT
Maximum ICC/Input 5.5 0.6 1.5 mA VI = VCC − 2.1V
I
CC
Maximum Quiescent Supply Current 5.5 8.0 80.0 µAVIN = VCC or GND
I
OLD
Minimum Dynamic
5.5
75 mA V
OLD
= 1.65V Max
I
OHD
Output Current (Note 3) −75 mA V
OHD
= 3.85V Min
V
OLP
Quiet Output Maximum
5.0 0.5 0.8 V
Figure 1, Figure 2
Dynamic V
OL
(Note 5)(Note 6)
V
OLV
Quiet Output
5.0 −0.5 −1.0 V
Figure 1, Figure 2
Minimum Dynamic V
OL
(Note 5)(Note 6)
V
OHP
Maximum Overshoot 5.0 VOH + 1.0 VOH + 1.5 V Figure 1, Figure 2
(Note 4)(Note 6)
V
OHV
Minimum VCC Droop 5.0 VOH − 1.0 VOH − 1.8 V Figure 1, Figure 2
(Note 4)(Note 6)
V
IHD
Minimum HIGH Dynamic Input Voltage Level 5.0 1.7 2.0 V (Note 4)(Note 7)
V
ILD
Maximum LOW Dynamic Input Voltage Level 5.0 1.2 0.8 V (Note 4)(Note 7)
Page 4

www.fairchildsemi.com 4
74ACTQ16374
AC Electrical Characteristics
Note 8: Voltage Range 5.0 is 5.0V ± 0.5V.
AC Operating Requirements
Note 9: Voltage Range 5.0 is 5.0V ± 0.5V.
V
CC
TA = +25°CT
A
= −40°C to +85°C
Symbol Parameter (V)
C
L
= 50 pF CL = 50 pF
Units
(Note 8) Min Typ Max Min Max
f
MAX
Maximum Clock Frequency 5.0 71 67 MHz
t
PLH
Propagation Delay 5.0 3.1 5.3 7.9 3.1 8.4
ns
t
PHL
CP to O
n
3.0 5.1 7.3 3.0 7.8
t
PZH
Output Enable Time 5.0 2.5 4.7 7.4 2.5 7.9
ns
t
PZL
3.0 5.4 8.0 2.0 8.5
t
PHZ
Output Disable Time 5.0 2.1 5.1 7.9 2.1 8.2
ns
t
PLZ
2.0 4.8 7.4 2.0 7.9
V
CC
TA = +25°CT
A
= −40°C to +85°C
Symbol Parameter (V)
C
L
= 50 pF CL = 50 pF
Units
(Note 9) Typ Guar ant eed Lim its
t
S
Setup Time, HIGH or LOW
5.0 0.7 3.0 3.0 ns
Input to Clock
t
H
Hold Time, HIGH or LOW
5.0 0.8 1.0 1.0 ns
Input to Clock
t
W
CP Pulse Width,
5.0 1.5 5.0 5.0 ns
HIGH or LOW
Page 5

5 www.fairchildsemi.com
74ACTQ16374
Extended AC Electrical Characteristics
Note 10: This specification is guaranteed but not tested. The limits apply to propagation delays for all paths described switching in phase
(i.e., all LOW-to-HIGH, HIGH-to-LOW, etc.).
Note 11: This specification is guaranteed but not tested. The limits represent propagation delays with 250 pF load capacitors in place of the 50 pF load
capacitors in the standard AC load. This specification pertains to single output switching only.
Note 12: Skew is def ined as the absolu te valu e of the differ ence be tween the actu al propag ation de lays f or any tw o separ ate outpu ts of the sam e devi ce.
The specification appli es t o an y ou tput s sw itchi ng HIGH -to -LO W (t
OSHL
), LOW-to-HIGH (t
OSLH
), or any combination switching LOW-to-HIGH and/or HIGH-
to-LOW (t
OST
).
Note 13: 3-STATE delays are load dominate d and have been excluded from the datasheet.
Note 14: The Output D is able Time is dominated by the RC network (500Ω, 250 pF ) on the output and has bee n excluded from the data s heet.
Capacitance
TA = −40°C to +85°C
C
L
= 50 pF TA = −40°C to +85°C
Symbol Parameter 16 Outputs Switching
C
L
= 250 pF
Units
(Note 10) (Note 11)
Min Typ Max Min Max
t
PLH
Propagation Delay 4.7 13.3 6.6 16.3
ns
t
PHL
Data to Output 4.6 11.4 6.4 15.5
t
PZH
Output Enable Time 3.5 10.4
(Note 13) ns
t
PZL
3.8 10.9
t
PHZ
Output Disable Time 3.4 8.5
(Note 14) ns
t
PLZ
3.1 8.1
t
OSHL
Pin to Pin Skew
1.3 ns
(Note 12) HL Data to Output
t
OSLH
Pin to Pin Skew
2.1 ns
(Note 12) LH Data to Output
t
OST
Pin to Pin Skew
4.0 ns
(Note 12) LH/HL Data to Output
Symbol Parameter Typ Units Conditions
C
IN
Input Capacitance 4.5 pF VCC = 5.0V
C
PD
Power Dissipation Capacitance 30 pF VCC = 5.0V
Page 6

www.fairchildsemi.com 6
74ACTQ16374
FACT Noise Characteristics
The setup of a noise characteristics measurement is critical
to the accuracy and repeatability of the tests. The following
is a brief description of the setup used to measure the
noise characteristics of FACT.
Equipment:
Hewlett Packard Model 8180A Word Generator
PC-163A Test Fixture
Tektronics Model 7854 Oscilloscope
Procedure:
1. Verify Test Fixture Loading: Standard Load 50 pF,
500Ω.
2. Deskew the HFS gener ator so that no two channels
have greater than 150 ps skew between them. This
requires that the oscilloscope be deskewed first. It is
important to deskew the HFS generator channels
before testing. This will ensure that the outputs sw itch
simultaneously.
3. Terminate all inputs and outputs to ensure pro per load ing of the outputs a nd that the input levels a re at the
correct voltage.
4. Set the HFS generato r to togg le all bu t one out put at a
frequency of 1 MHz. Greater frequencies will increase
DUT heating and effect the results of the measurement.
5. Set the HFS generator input levels at 0V LOW and 3V
HIGH for ACT devices and 0V LOW and 5V HIGH for
AC devices. Verify levels with an oscilloscope.
V
OHV
and V
OLP
are measured with respect to ground reference.
Input pulses have the following characteristics: f = 1MHz, t
r
= 3ns,
t
f
= 3ns, skew < 150 ps.
FIGURE 1. Quiet Output Noise Voltage Waveforms
V
OLP/VOLV
and V
OHP/VOHV
:
• Determine the quiet output pin that demonstrates the
greatest noise levels. The worst case pin will usually be
the furthest from the gr ound pin. Monitor th e o utp ut voltages using a 50Ω coaxi al cable p lugg ed into a standa rd
SMB type connector on the te st fixture. Do not use an
active FET probe.
• Measure V
OLP
and V
OLV
on the quiet output du ring the
worst case transition for active and enable. Measure
V
OHP
and V
OHV
on the quiet output during the worst
case active and enable transition.
• Verify that the GND reference recorded on the oscilloscope has not drifted to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of the measurements.
V
ILD
and V
IHD
:
• Monitor one of the switching outputs using a 50Ω coaxial
cable plugged into a standard SMB type connec tor on
the test fixture. Do not use an active FET probe.
• First increase the inp ut LOW voltage level, V
IL
, until the
output begins to oscillate or step out a min of 2 ns. Oscillation is defined as noi se on the output LOW l evel that
exceeds V
IL
limits, or on output HIGH levels that exceed
V
IH
limits. The input LOW voltage level at which oscilla-
tion occurs is defined as V
ILD
.
• Next decrease the input HIGH voltag e level on the, V
IH
,
until the output begins to oscillate or steps out a min of 2
ns. Oscillation is defined as noise on the output LOW
level that exceeds V
IL
limits, or on output HIGH levels
that exceed V
IH
limits. The input HIGH voltage level at
which oscillation occurs is defined as V
IHD
.
• Verify that the GND reference recorded on the oscilloscope has not drifted to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of the measurements.
FIGURE 2. Simultaneous Switching Test Circuit
Page 7

7 www.fairchildsemi.com
74ACTQ16374
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
48-Lead Small Shrink Outline Package (SSOP), JEDEC MO-118, 0.300” Wi d e
Package Num b er MS48A
Page 8

www.fairchildsemi.com 8
74ACTQ16374 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
48-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP), JEDEC MO-153, 6.1mm Wide
Package Number MTD48
Fairchild does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitr y described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and
Fairchild reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
FAIRCHILD’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF FAIRCHILD
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or syste ms
which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the
body, or (b) support or sustain life, and (c) whose failure
to perform when properly used in accordance with
instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant inju ry to the
user.
2. A critical component in any compon ent of a lif e supp ort
device or system whose failure t o perform can be reasonably expected to ca use the failure of the life supp ort
device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
www.fairchildsemi.com
 Loading...
Loading...