
DATA CONNECT ENTERPRISE
IG202T and IGV23 Modem
User’s Manual
Document Number 520-01005-001 Rev. A

DATA CONNECT
Contents
Contents .................................................................................................................. iii
Figures..................................................................................................................... iv
Chapter 1 Introduction ............................................................................................ 5
Features ...................................................................................................................... 6
Applications .................................................................................................................7
Chapter 2 Installation .............................................................................................. 8
Unpacking Your Hardware .......................................................................................... 8
Additional Items You Need to Complete Your Installation........................................... 8
Hardware Overview..................................................................................................... 9
Front View ................................................................................................................... 9
Back View.................................................................................................................... 9
Rack-Mount View ...................................................................................................... 10
Installation Summary................................................................................................. 10
Configuring the Modem ............................................................................................. 11
Setting the DIP Switches...........................................................................................13
SW1-1 Auto RTS .............................................................................................. 14
SW1-2 RTS-CTS Delay (Bell 202 Mode Only) .................................................14
SW1-3 Transmit Carrier Control ....................................................................... 14
SW1-4 – Soft Carrier Control............................................................................... 15
SW1-5 Anti-streaming ......................................................................................15
SW1-6 2-Wire or 4-Wire Operation ..................................................................15
SW1-7 Transmitter Termination Impedance..................................................... 15
SW1-8 Receiver Termination Impedance......................................................... 16
JP1 Transmit Level...........................................................................................16
JP2 RS-232 or RS-485 Serial Interface (Standalone Only)............................. 17
For Rack-Mount Plug-in Modules ........................................................................ 17
Connecting to a Transmission Line ........................................................................... 18
Connecting to a Voltage Source................................................................................ 19
Connecting to an RS-232 Device .............................................................................. 20
Connecting to an RS-485 Device .............................................................................. 20
LEDs.......................................................................................................................... 21
Loopback Control Switch........................................................................................... 21
Problem Solving ........................................................................................................ 23
iii User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Contents
Figures
Figure 1-1. Point-to-Point Network Using the IG202T/V23 Modem ........................................ 7
Figure 1-2. Multipoint Polling Network Using the IG202T/V23 Modem................................... 7
Figure 2-1. Front View of the IG202T/V23 Modem ................................................................. 9
Figure 2-2. Back View of IG202T Modem ............................................................................. 10
Figure 2-3. Rack-Mount Module for the IG202T-RM Modem Board ..................................... 10
Figure 2-4. IG202T & IGV23 Stand-alone Modem Board ..................................................... 12
Figure 2-5. IG202T & IGV23 -mount Modem Board .............................................................13
Figure 2-7. Pin Locations on the Modem’s RJ-11C Jack ...................................................... 20
Figure 2-8. Loopback Diagnostic Modes............................................................................... 22
Figure 2-9. Back-to-Back Connection to a Second Modem .................................................. 25
iv User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

DATA CONNECT ENTERPRISE
Chapter 1
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing Data Connect IG202T and IGV23 leased line modem,
the finest industrial-grade modem available. This manual will cover both the standalone
IG202T, a Bell 202 compatible, and the standalone IGV23, an ITU-V23 compatible modems.
The Data Connect
wire, full-du
The modem is designed utilizing the stand FSK modulation technology to achieve high
performance and low cost.
The IG202T/V23 modem is ideally suited for multi-point communication systems that require
fast response time, short training time, and low throughput delay.
This User’s Guide describes the IG202T/V23 (AC-powered) and IG202T-DC/V23-DC (DCpowered) stand-alone modems, as well as the rack-mount IG202T-RM plug-in module for
the Motorola/UDS RM16M. This manual is designed to get your modem “up and running” as
quickly as possible. It contains all the information you need to configure and install your
modem. It also contains troubleshooting information in the unlikely event you encounter a
problem with your modem.
plex or 2-wire, half-duplex operation over a voice-band leased line or private line.
IG202T/V23 modem is a 0 to1200 bps modem designed for 4-
5 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Introduction
Features
The IG202T/V23 modem is specifically designed for harsh environments typically associated
in utility substations and industrial facilities. Though functionally similar to commercial
modems, the IG202T/V23 provides the following unique features that make it well suited for
utility and industrial applications.
y Packaged in a rugged, compact enclosure for industrial applications.
y Leased-line interface protected with heavy-duty surge protection devices.
y Built-in hardware watchdog timer for software lock-up prevention without
requiring human intervention, making it ideal for unmanned locations.
y Works within an extended temperature range of -40ºC to +85ºC.
y Designed with coupling transformers for high-voltage isolation and common
mode noise rejection in industrial and commercial environments.
y Operate over voice-band conditioned or unconditioned leased-line and pilot
wires.
y Accepts power from a wide range of AC and DC power supplies:
– IG202T/V23: 90 to 265 VAC or 100 to 400 VDC
– IG202T/V23-DC: 10 to 60 VDC
– IG202T/V23-RM: Plug-in module for the Motorola/UDS RM16M modem nest
y Standard industrial connectors for data, analog, and power interfaces allow
reliable interconnection to other industrial equipment.
y Asynchronous data rates 0-1200 bps.
y Easily accessible DIP switches for user configuration and option selection.
y DB9-F connector for RS-232/V.24 interface, and RJ-11 for RS-485.
y Local analog, local digital, and remote digital loopback diagnostics.
6 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
Introduction
Applications
The IG202T/V23 modem is designed for point-to-point and multipoint data communications.
Figure 1-1 shows a typical point-to-point configuration using the IG202T modem and Figure
1-2 shows a typical multipoint configuration using the IG202T modem.
Modem
Workstation
Modem
Remote Terminal
Figure 1-1. Point-to-Point Network Using the IG202T/V23 Modem
Modem
Modem
Workstation
Modem
Modem
Modem
Remote Terminal
Modem
Remote Terminal
Figure 1-2. Multipoint Polling Network Using the IG202T/V23 Modem
There are a number of factors that can affect the modem’s operation and performance.
These include:
y Modem speed (i.e. bit error rate, transmission line distance)
y 2-wire or 4-wire configuration
y Transmission line characteristics, noise, and line impairments
y Transmission cable length (pilot wire)
y Network configuration (point-to-point or multipoint)
7 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

DATA CONNECT ENTERPRISE
Chapter 2
Installation
This chapter describes how to configure and install the modem to maximize the performance
and to match with your Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) or Remote Terminal Unit (RTU).
Unpacking Your Hardware
Your package should include:
y At least one of the following IG202T or IGV23 modems:
– Model IG202T or IGV23 for 90 to 265 VAC
Model IG202T-DC or IGV23-DC for 10 to 60 VDC
–
or 100 to 400 VDC
– Model IG202T-RM or IGV23-RM for RM16M plug-in module
y A switching power supply module for 90-265VAC input (model IG202T or IGV23
only)
y A leased-line cable with optional earth ground conductor (for stand-alone units
only)
y A DC power cable (model IG202T-DC or IGV23 modem only)
y This User’s Manual or CD-ROM
If your package contents are damaged or missing, contact your place of purchase.
Additional Items You Need to Complete Your Installation
To complete your installation and operate your modem, you need these additional items:
y Two- or four-wire transmission line or leased line
y A DB-9 data cable for your RS-232 interface Data Terminal Equipment (DTE)
port, or a RJ-11C data cable for your RS-485 DTE.
y Power supply that provides either:
– 90 to 265 Volts AC, 50 to 60 Hz, single phase or 100 to 400 VDC (if you have
the model IG202T/V23 modem), or
– 10 to 60 Volts DC (if you have the model IG202T-DC modem)
8 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
– For the IG202T-RM, consult the documentation for your Motorola/UDS
RM16M
Hardware Overview
Front View
Figure 2-1 shows the front view of the IG202T/V23 stand-alone modem. Starting from the
left side, this view shows:
y A set of eight LEDs for modem interface status (see Table 2-4 on page 21)
y A loopback control push-button switch (see Loopback Control Switch on page 21)
Figure 2-1. Front View of the IG202T/V23 Modem
Back View
Figure 2-2 shows the back view of the IG202T stand-alone modem. Starting from the left
side, this view shows:
y A 4-wire/2-wire configuration block labeled LEASED LINE
y An RJ-11 modular jack labeled RS-485 for connecting the modem to an RS-485
RTU
y A female, 9-pin RS-232 connector labeled RS-232 for connecting the modem to a
standard DTE (RTU)
y A power connector labeled 10-48V DC
9 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
Figure 2-2. Back View of IG202T Modem
Rack-Mount View
Figure 2-3 shows the rack-mount plug-in module.
Figure 2-3. Rack-Mount Module for the IG202T-RM Modem Board
Installation Summary
This section describes the steps for installing the modem.
10 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
NOTE:
It is important to follow the steps below to configure the modem’s DIP
switches to match your DTE/RTU interface requirement and the transmission
line characteristics. If you are not certain about your system’s parameters or
the leased-line configuration, please contact your network administrator for
assistance.
1. Configure the modem using the DIP switches and jumpers. See pages 13 .
2. Connect to a transmission line. See page 18.
3. Connect to a voltage source. See page 19.
4. Connect a DTE device. See page 20.
Configuring the Modem
You configure the modem using the 8-position DIP switch and two sets of configuration
jumpers on the printed circuit board of the modem labeled S1, JP1 and JP2.
Configuration DIP switches S1 for the stand-alone and rack-mount modems are identical.
Their descriptions in this user’s manual apply to both modem versions. Configuration jumper
JP1 for the standalone and rack-mount modem card is used to select transmit output level.
It is important to follow the steps described below, in the order shown, to ensure that you
configure your modem properly using the modem DIP switches:
1. Use DIP switch 1 (S1) to configure the modem for your host DTE interface and
network topology. Using S1, you select the modem’s serial port to match your
host computer or RTU devices, and other DTE specific operating parameters.
2. Use Jumper (JP1) to select the modem’s transmitter output level to match your
specific leased line conditions. The JP2 is used only in the standalone modem for
selecting either RS-232 or RS-485 interface.
3. After you change the DIP switch settings, recycle power to the modem to have
the settings take effect.
NOTE:
The DIP switch settings will not take effect until you recycle power to the
modem.
To access the configuration DIP switches and jumpers on the stand-alone modem:
1. Ground yourself to discharge any ESD, which might cause damage to the
sensitive devices on the modem board.
2. Use a small Philips screw driver to remove the two screws at the bottom of the
enclosure and remove the top cover. The location of the DIP switches and
jumpers for the stand-alone modem are shown in Figure 2-4. For DIP switches
and jumpers on the rack-mount plug-in module, see Figure 2-5.
11 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
3. Replace the top cover after the configuration is completed.
Configuration Switch
(SW1)
D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13
Configuration Jumpers
JP1 & JP2
JP2
5
6
1
2
J4
J3 J1
SW1
U5
U1
OFF
1
8
J2
T1
D14
JP1
1
2
S3
U2
78
T2
Figure 2-4. IG202T & IGV23 Stand-alone Modem Board
12 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
Configuration DIP Switches
y
a
l
r
r
e
e
e
m
D
e
z
z
1
3
2
i
a
i
l
g
l
l
l
l
S
e
1
2
a
n
a
r
e
e
e
T
t
u
a
u
n
n
v
v
v
C
S
q
q
R
e
e
e
o
o
-
-
i
i
i
E
E
L
L
L
t
t
t
S
v
p
p
n
T
x
c
x
x
x
x
O
R
O
A
R
T
T
Data Rate 1
Data Rate 2
Data Rate 3
D2 D1D3D4D5D6D7D8D9
Char Length
S1 S2
U3
U4
S3
U2
R
Auto RTS
Tx Carrier
4W/2W
Tx Impedance
RDLB Disable
Factory only
T
T
10
U8
U1
U5
10
11
U10
U12
U6
U14
Y1
Y2
U9
U7
2
J1
1
13 14
D27 D25
GT4 GT3
U21
U22
JP1
U17
U15
U15
U18
for Receiver Termination
E3
J2
600 ohmHigh-Z
31
D11 D10
Configuration Jumper
U19
F1
T1
F2
F3
T2
GT2 GT1
F4
E2
E1
Figure 2-5. IG202T & IGV23 -mount Modem Board
Setting the DIP Switches
SW1 is a 8-position DIP switches used to configure all the options and features of the
modem. Table 2-3 shows the setting of the switches.
NOTE:
Switches SW1 are toggle switches. To configure the switches, use a small
sharp pin to firmly press down on one end to open or to close each switch.
Never leave any switch in half open and half close. Press down on the side of
the switch labeled OPEN is referring to as OFF condition. When the switch is
CLOSED, it is in the ON state.
Table 2-1. Modem Switch Settings
DIP Switches
SW1-1: Auto RTS
SW1-2: RTS-CTS Delay (Bell 202 mode only)
SW1-3: Transmit Carrier Control
SW1-4: Soft Carrier (Bell 202 mode only)
SW1-5: Anti-streaming
SW1-6: 2- or 4-wire leased line
SW1-7: Transmitter Termination
SW1-8: Receiver Termination
Switch Settings
ON OFF (Default)
DIP Switch S1
Enable Disable
33 ms
10.0 ms (Bell 202T)
33 ms (V.23 mode)
Constant ON Controlled by RTS
Enable Disable
Enable (30 seconds) Disable
2-wire half duplex 4-wire full duplex
Controlled by RTS 600 ohms
600 ohms High (approx 20K)
13 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
SW1-1 Auto RTS
y SW1-1 ON = Enable Auto RTS
y SW1-1 OFF = Disable Auto RTS (default)
For data terminals that do not provide hardware Request To Send (RTS), set switch SW1-1
to ON to enable auto RTS mode. In this mode, TXD is detected at the modem and an
internal RTS signal is turned ON. After training completes, the TXD is transmitted to the
remote modem. The transmitter turns itself off if no TXD is detected after a pre-determined
length of idle time.
SW1-2 RTS-CTS Delay (Bell 202 Mode Only)
y SW1-2 ON = 33.0 ms delay
y SW1-2 OFF = 10.0 ms delay (default)
Switches SW1-2 determines the duration of the RTS-CTS delay in Bell 202 mode. For V23
mode, the RTS-CTS delay is fixed at 33 ms.
SW1-3 Transmit Carrier Control
y SW1-3 ON = Constant carrier
y SW1-3 OFF = Controlled by RTS (default)
Switch SW1-3 selects either constant or switched carrier. Constant carrier allows DTEs,
such as asynchronous terminals or RTUs, to operate with modems, without requiring an
input RTS signal. If you enable constant carrier (switch SW1-3 = ON), the modem forces the
transmit carrier active and the RTS-CTS delay is shortened to less than 0.5 ms.
You can use constant carrier in 4-wire point-to-point, or at the master unit of multi-point
network applications to reduce modem training time.
In switched-carrier mode (switch SW1-3 = OFF), the RTS-CTS delay is determined by SW12 setting.
14 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
SW1-4 – Soft Carrier Control
x SW1-4 ON = Soft Carrier is enabled
x SW1-4 OFF = Soft Carrier is disabled
In Bell 202T mode, when soft carrier mode is enabled, a carrier frequency of 900 Hz is
transmitted at the end of a transmission in order to turn off the carrier detect (CD) at the
receiving modem. This feature is only use for the Bell 202T modems.
SW1-5 Anti-streaming
x SW1-5 ON = Anti-streaming is active
x SW1-5 OFF = Anti-stream is inactive (default)
Typically, anti-streaming is used in multi-point applications to prevent a malfunctioning slave
data terminal or RTU from occupying the line indefinitely. When anti-streaming is active, the
modem can transmit data for a maximum of 30 seconds before the transmitter turns off
automatically. The modem then looks for an ON-to-OFF RTS transition before proceeding
with normal operation.
SW1-6 2-Wire or 4-Wire Operation
y SW1-6 ON = 2-Wire, Half-Duplex Mode
y SW1-6 OFF = 4-Wire, Full-Duplex Mode (default)
Switch SW1-6 configures the modem for either 4-wire full-duplex or 2-wire half-duplex
operation.
SW1-7 Transmitter Termination Impedance
y SW1-7 ON = Switched by RTS
y SW1-7 OFF = 600 : (default)
Switch SW1-7 is used for multi-point configuration networks. When multiple modems are
connected on the same metallic circuit:
y The transmitter termination should be of high impedance if the modem is not
transmitting in order not put a load on the line.
y The transmitter is only terminated with 600 ohms when RTS is asserted.
15 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
This configuration should be used for all slave modems to prevent the transmitting modem
from being unnecessarily burdened. To select this configuration, set switch S1-7 ON for the
slave modems.
If you use the modem with transmission lines that are transformer-coupled or with an
impedance-isolated network (such as a transformer bridge), set switch S1-7 OFF for proper
operation.
SW1-8 Receiver Termination Impedance
y SW1-8 ON = 600 : (default)
y SW1-8 OFF = Modem receiver is in high input impedance (20K ohms)
Switch SW1-8 is used for multi-point configuration networks. When multiple modems are
connected on the same metallic circuit:
In a point to multipoint network configuration, all except one of the slave modem’s receiver
termination should be set to high impedance if the modems’ receivers are connected by the
same circuit such that it will not load down the receiver signals. Only one receiving modem
should be set to terminated at 600 ohms
The master modem’s receiver is always terminated with 600 ohms
JP1 Transmit Level
JP1-1 through JP1-8 adjust the modem’s transmit level. Table 2-3 2-2 shows the transmit
levels you can select using a 2-position shunt to connect 2 pins from JP1.
Table 2-2. Transmit Levels
Transmit Level JP1 Jumper Settings
0 dBm Pin 1 to Pin 2
4 dBm
8 dBm
12 dBm
.
Pin 3 to Pin 4
Pin 5 to Pin 6
Pin 7 to Pin 8
16 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
JP2 RS-232 or RS-485 Serial Interface (Standalone Only)
JP2, a 6-pin header, is used to select the communication port for the modem. You may
select to use either the RS-232 or RS-485 port. Only one type of interface is supported by
the modem. Table 2-33 shows the two jumpers must be placed to make the selection.
Table 2-3. RS-232 or RS485 Select
RS-232/ V.24 Interface RS485/RS422 Interface
JP2: Pin 1 to Pin 3
Pin 2 to Pin 4
JP2: Pin 3 to Pin 5
Pin 4 to Pin 6
.
For Rack-Mount Plug-in Modules
Jumper block JP2 is not needed as the Rack will only support RS-232/V24 only.
17 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
Connecting to a Transmission Line
The modem has a transmission line interface (RS-11C) that can be configured for 2- or 4wire analog connection, where in 4- wire connection, one pair (Tx-A and Tx-B) is used to
transmit data and the other pair (Rx-A and Rx-B) is used to receive data. The transmit pair
and receive pair are non-polarized. Table 2-44 shows the pin numbers and corresponding
signals for the modem. Error! Reference source not found. shows the transmission line
interface.
NOTE:
For communication to occur, the Rx line of one modem must connect to the Tx
line of the other modem. The modem’s Tx/Rx pair are non-polarized.
NOTE:
The modem does not support leased-line operation with DC shielding current.
Leased-line connector pin assignments for the rack-mount module can be
found in the documentation for your Motorola/UDS RM16M.
Table 2-4. Transmission Line Connector Pin Assignments
This Pin Number… Corresponds to This Signal…
1 Not Uesd
Rx
Tx (Tx/Rx)
Tx (Tx/Rx)
Rx
NOTE:
2
3
4
5
6 Not Used
When 2-wire half duplex is used, the center pair must be used for both
transmit and receive.
18 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
Pin #6 Pin #1

Installation
Connecting to a Voltage Source
The back panel of the modem provides a 2-position screw terminal power interface
connector. For your convenience, the DC voltage of the input power is non-polarized. To
meet your specific application, the modems can be powered from the following power
sources:
y Model IG202T (with AC-DC power converter): 90 to 265 Volts AC, 50 to 60 Hz,
single phase or 100 to 400 VDC. The output of the converter is a 12 VDC source
that will power the modem.
y Model IG202T-DC (DC version): 10 to 60 Volts DC. The model IG202T-DC
comes with a power cord for making this connection.
Figure 2-2 on page 10 shows the connection to the Model IG202T’s power interface shows
the connection to the Model IG202T-DC’s power interface.
WARNING:
Before you connect a voltage source, observe the following power supply
voltage guidelines. Otherwise, you will void your warranty if the wrong voltage
is applied.
y Be sure the voltage source is within the permitted ranges shown
above. Otherwise, your modem and any attached devices may be
damaged.
y Customer-supplied cables must be suitable for the site
environmental conditions.
y Screw terminals on the power interface accept 24 to 16 AWG.
However, surge protection is effective only if there is a solidly
earthed ground connection greater than 18 AWG.
y Be sure the power source is not controlled by a wall switch, which
can be inadvertently turned off, shutting off power to the modem.
19 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
Installation
Connecting to an RS-232 Device
The modem back panel provides a female, 9-pin RS-232 connector that accepts an attached
RS-232 device (see Figure 2-2 on page 10). This connector accepts a standard connection
to a DTE (RTU) that conforms to the pin assignments shown under “RS-232 (DTE)
Interface” on page 26.
Connecting to an RS-485 Device
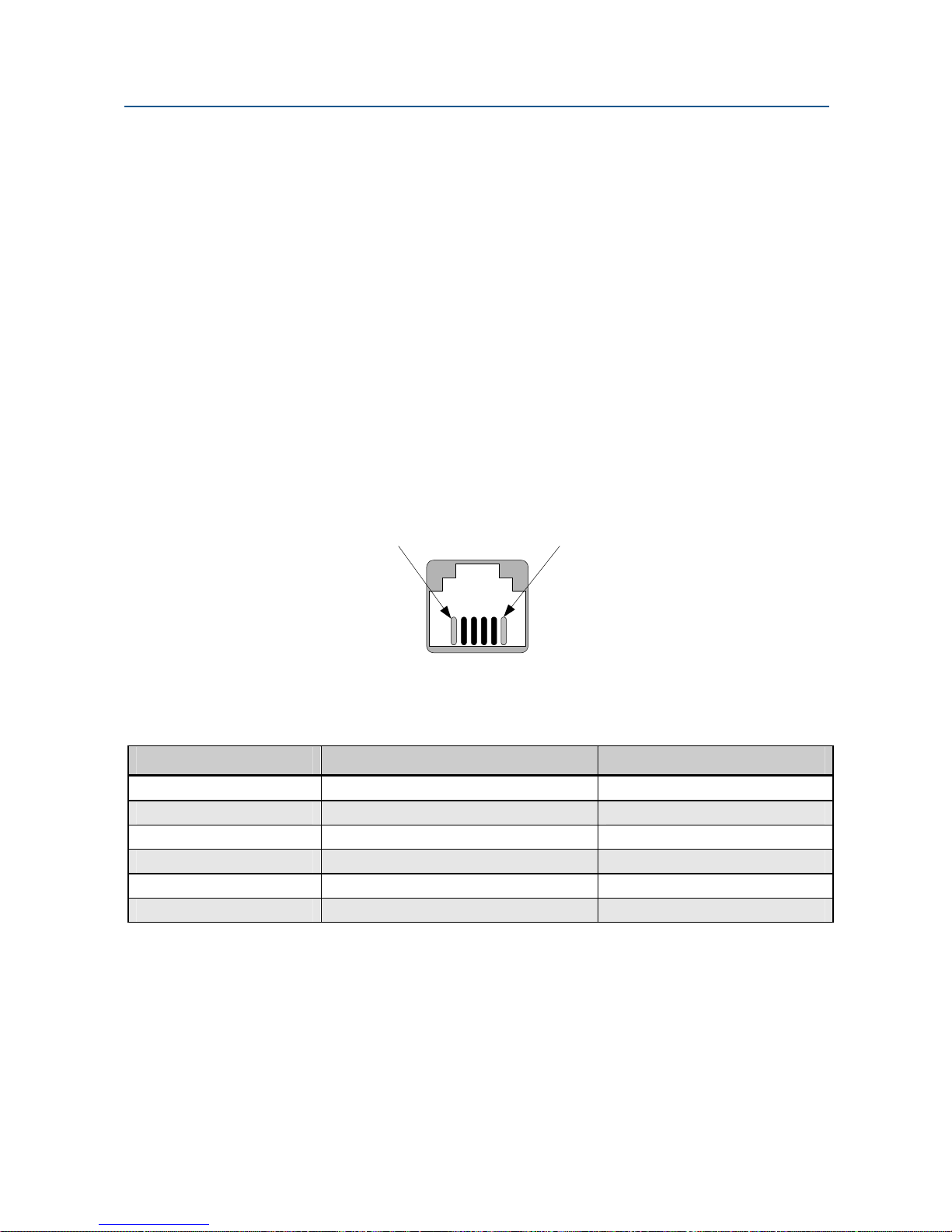
The modem rear panel provide an RJ-11C module jack connector for a 4-pin RS-485 or RS422 interface in the event that your DTE or RTU does not support the RS-232 interface (see
Figure 2-2 on page 10 and Figure 2-6).
The pin assignments for the RS-485 interface are listed in Table 2-3.
Pin #6 Pin #1
Figure 2-6. Pin Locations on the Modem’s RJ-11C Jack
Table 2-3. RJ-11C Modular Jack Pin Assignments
RJ-11 Pin Number… Corresponds to Signal Name Modem Input or Output
1 Not Used NA
2 RxD+ Output
3 RxD- Output
4 TxD+ Input
5 TxD- Input
6 Not Used NA
20 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
LEDs
The front panel of the modem provides the LEDs shown in Table 2-3.
Table 2-4. Modem LEDs
LED Color Description
RTS Yellow Request To Send
CTS Yellow Clear To Send
TD Yellow Transmit Data
RD Yellow Receive Data
CD Yellow Carrier Detect
MR Yellow Modem Ready
ALB Red* Local Analog Loopback
DLB Red* Local Digital Loopback
* When the modem is in remote loopback (V.54 Loop 2), both the ALB and DLB LEDs go ON.
Loopback Control Switch
The front panel of the modem has a push button for initiating the following loopback
diagnostic tests:
y Local digital loopback started by pressing the button one time. The DLB LED
should be ON. When a DTE is connected to the RS-232 port of the modem, the
transmit data is loop back to the DTE as receive data. This test will verify the
modem’s RS-232 interface along with the cable attached.
y Local analog loopback started by pressing the button two times. The ALB LED
should be ON. When a DTE is connected to the RS-232 port of the modem, the
transmit data is loop back to the DTE as receive data. This test will verify the
modem transmitter, receiver, and its RS-232 interface along with the connecting
cable.
y Remote digital loopback Press the local modem’s diagnostics test button three
times. Both the ALB and DLB LEDs should be ON. In this mode, the modem is
performing a loop back to the remote modem (V.54 loop 2 configuration). The
This test will verify both modems’ transmitters, receivers, and the leased line
21 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

Installation
Figure 2-7 shows these three loopback diagnostics.
HOST
HOST
HOST
Transmitter
Leased Line
Receiver
Receiver
Transmitter
Local (Host) Analog Loop Back
Transmitter
Leased Line
Receiver
Receiver
Transmitter
Local (Host) Digital Loop Back
Transmitter
Leased Line
Receiver
Receiver
Transmitter
Remote (RTU) Digital Loop Back
Figure 2-7. Loopback Diagnostic Modes
RTU
RTU
RTU
22 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

DATA CONNECT ENTERPRISE
Appendix A
Troubleshooting
In the event you encounter a problem using your Data Connect Enterprise modem, refer to
the troubleshooting information in this appendix.
IMPORTANT:
If you encounter a problem with your modem, be sure the switches on the
modem are set to the appropriate positions (see Table 2-1 on page 13). If
a switch is halfway between an on and off setting, the modem will not
operate properly.
Problem Solving
Table A-1 offers troubleshooting solutions for modem problems.
Table A-1 Problem Solving
If… Perform These Procedures…
No LEDs are ON at the front
panel
Modem does not respond to the
attached DTE and the all LEDs
are off.
Modem does not receive data,
and the DCD and RxD LEDs are
off.
The RTS, CTS, and TxD LEDs
do not blink.
Check the power supply source. Be sure the input power to the
modem’s power connector is between 10 to 60VDC
Check the connecting RS-232 or RS-485 cable between the DTE and
the modem. The MR LED (Modem Ready) on the front panel should
be ON when the modem is idle.
Check the DIP switches of both modems to make sure that the same
data rate and operating parameters are identical on both modems.
The receive line pair may be disconnected from the modem. Make
sure the transmission line connection to the modem is accurate and
secure.
The receive signal level may be below the CD threshold. Set switch
S1-5 ON to see whether configuring the modem for a 43 dBm
threshold resolves the problem.
If this problem remains unresolved, perform a local ALB loopback
test to determine if the modem’s receiver is functioning correctly.
The attached terminal or DTE may not be sending data to the
modem. Verify that data is being transmitted. If data is being
transmitted, make sure the RS-232 cable is sound and securely
connected to the modem and terminal or DTE.
23 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem

DATA CONNECT ENTERPRISE
General Specifications
Appendix B
Specifications
Data rate:
Data format:
DTE interface:
Line conditions:
Operating modes:
Modulation:
RTS-CTS Delay:
Receiver dynamic range:
Operating temperature:
Power supply:
0-1200 bps
Transparent to DTE
EIA RS-232/V.24, or RS-485 compatible
TELCO voice band 4- or 2-wire leased line, conditioned or unconditioned
lines. Private metallic circuits
2-wire half-duplex or 4-wire full-duplex
FSK, Bell 202T or V.23 compatible
x Mark = 1200 Hz (1300 Hz, V.23)
x Space = 2200 Hz (2100 Hz, V.23)
x Soft Carrier = 900 Hz (Bell 202T only)
10 or 33 ms (Bell 202T)
33 ms (V.23)
0 to –43 dBm
-40qC to +85qC
Wide range switching power supply:
x IG202T (AC version): 90 to 265 Volts AC, 50/60 Hz, single phase or
90 to 400 VDC
x IG202T-DC (DC version):10 to 60 Volts DC
Surge protection:
Carrier control:
Carrier loss recovery:
Auto RTS:
Anti-streaming:
Mechanical Specifications
Enclosure:
Dimensions:
24 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
Leased line, up to 15KV
Constant or switched, DIP switch selectable
Automatically
Support DTE without hardware RTS
30-second timer to prevent transmitter lock-up network
ABS with removable top cover
4.1” wide x 4.9” long x 1.40” high
Specifications
Weight:
Interface connectors
Leased Line:
Data Terminal Equipment:
0.5 lbs without AC to DC power converter module
4-position RJ-11C modular Jack
DB-9 female connector (for RS-232)
RJ-11C module jack (for RS-485)
Interface Connector Pin Assignments
Table B-1. Leased Line RJ-11C Pin Assignments
This Pin Number… Corresponds to This Signal…
1 Not Uesd
2
3
4
5
6 Not Used
Rx
Tx (Tx/Rx)
Tx (Tx/Rx)
Rx
NOTE:
When 2-wire half-duplex is used, the TX pair must be used for both transmit
and receive.
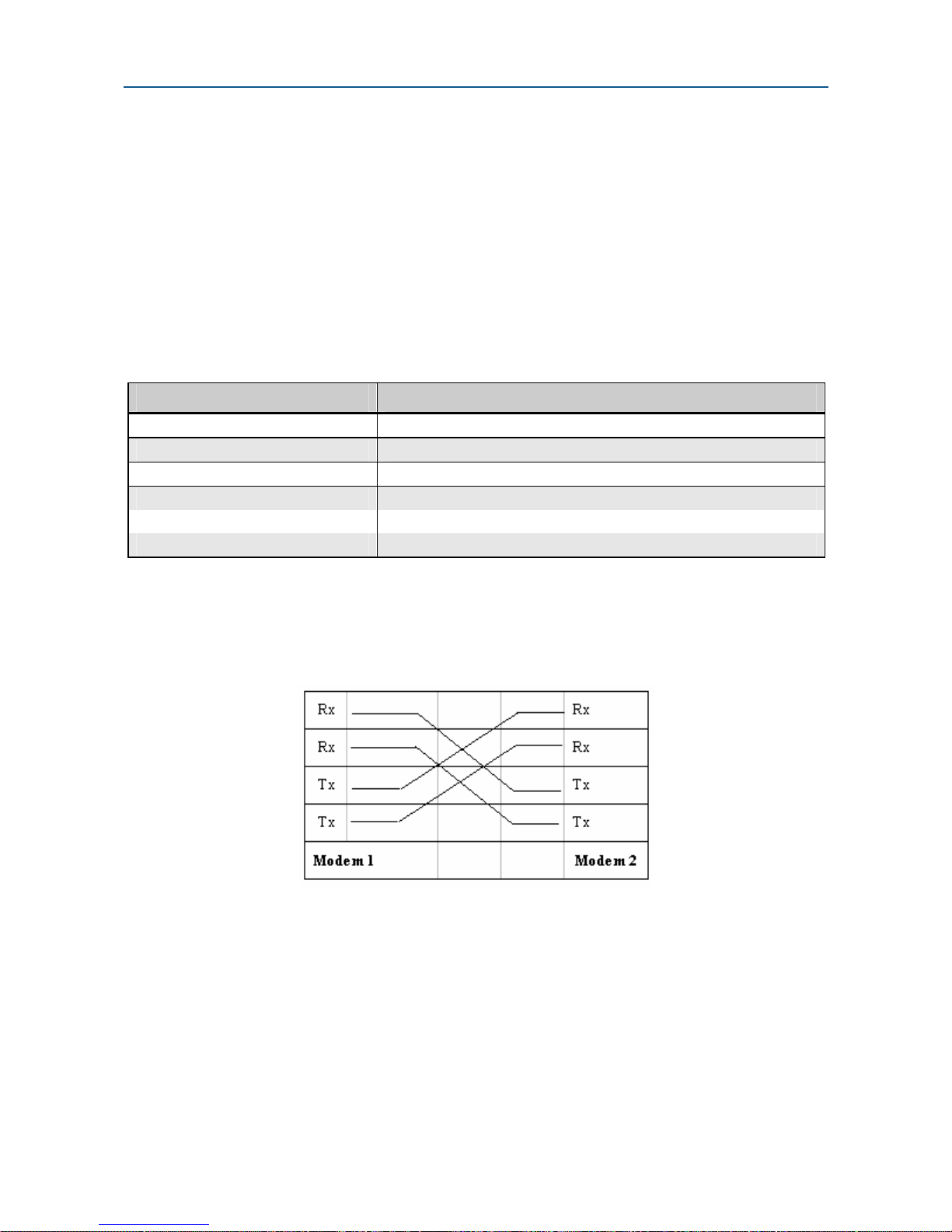
Figure 2-8. Back-to-Back Connection to a Second Modem
25 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
Specifications
RS-232 (DTE) Interface
Table B-2. RS-232 (DTE) Interface
Signal Name Modem Input/Output DB-9 Pin Description
DCD Output 1 Data Carrier Detected
RXD Output 2 Receive Data
TXD Input 3 Transmit Data
SG
DSR Output 6 Data Set Ready
RTS Input 7 Request To Send
CTS Output 8 Clear To Send
5 Signal Ground
(Modem Ready)
RS-485 (DTE) Interface
Table B-3. RS-485 (DTE) Interface
RJ-11 Pin Number… Corresponds to Signal Name Modem Input or Output
1 Not Used NA
2 RxD+ Output
3 RxD- Output
4 TxD+ Input
5 TxD- Input
6 Not Used NA
Environmental Specifications
Operating temperature:
Storage temperature:
Operating humidity:
Line isolation:
Surge protection:
-40 to + 85
-40 to +125
5 to 95 %, non-condensing
3750 V RMS
Leased line up to 15K VA
o
C
o
C
26 User’s Manual - SM202T/SMV23 Modem
 Loading...
Loading...