
01234
5
47
12890
1
49122134
2134141


Classified as Public
VACON SYSTEM INTERFACE APPLICATION
MANUAL
INDEX
Document code: DPD01975A
Software code: APFIFF40V100
Date: 16.12.2020
1. System interface Application - introduction ............................................................................................ 6
1.1 General .................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.2 Basic Features ....................................................................................................................................... 7
1.3 Condition Based Monitoring ................................................................................................................. 8
1.3.1 Introduction to Condition-based Monitoring ................................................................................... 8
1.3.2 Condition-based monitoring stages ................................................................................................ 10
1.4 Acronyms ............................................................................................................................................ 12
3. Version parameter compatibility issues ................................................................................................ 13
4. Control I/O ............................................................................................................................................ 14
5. “Terminal To Function” (TTF) programming principle ............................................................................ 15
5.1 Defining an input/output for a certain function on keypad ................................................................ 15
5.2 Defining a terminal for a certain function with NCDrive programming tool ...................................... 16
5.3 Defining unused inputs/outputs ......................................................................................................... 17
6. System interface Application – Monitoring Values ................................................................................ 18
6.1 Monitoring values (Control keypad: menu M1) .................................................................................. 19
6.1.1 Monitoring Values .......................................................................................................................... 19
6.1.2 Monitoring values 2 ........................................................................................................................ 20
6.1.3 FieldBus Monitoring values ............................................................................................................ 21
6.1.4 Master/Follower Monitoring values .............................................................................................. 22
6.1.5 PI Control Monitoring values .......................................................................................................... 22
6.1.6 Speed reference Chain .................................................................................................................... 22
6.1.7 Torque Reference Chain ................................................................................................................. 22
6.1.8 SM Excitation .................................................................................................................................. 23
6.1.9 Functional Safety Monitoring ......................................................................................................... 23
6.1.10 Condition Based Monitoring ...................................................................................................... 24
6.2 Monitoring values description ............................................................................................................ 26
6.2.1 Monitoring values ........................................................................................................................... 26
6.2.2 Monitoring values 2 ........................................................................................................................ 29
6.2.3 FieldBus Monitoring values ............................................................................................................ 34
6.2.4 Master / Follower ........................................................................................................................... 41
6.2.5 PI Control monitoring ..................................................................................................................... 45
6.2.6 Speed Reference Chain ................................................................................................................... 46
6.2.7 Torque Reference Chain ................................................................................................................. 47
6.2.8 SM Excitation Monitor .................................................................................................................... 47
6.2.9 Functional Safety Monitoring ......................................................................................................... 48
6.2.10 Condition Based Monitoring ...................................................................................................... 54
7. SIA-II Application – Parameter List ........................................................................................................ 57
7.1 Basic parameters ................................................................................................................................. 57
7.2 Reference Handling ............................................................................................................................. 58

2 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
7.2.1 Basic Settings .................................................................................................................................. 58
7.2.2 Constant Reference ........................................................................................................................ 58
7.2.3 Torque Reference ........................................................................................................................... 59
7.2.4 Torque Reference OL Settings ........................................................................................................ 59
7.2.5 Prohibit Speed parameters ............................................................................................................. 60
7.2.6 Motor Potentiometer ..................................................................................................................... 60
7.2.7 Adjust Reference............................................................................................................................. 60
7.2.8 Follower .......................................................................................................................................... 60
7.3 Ramp Control ...................................................................................................................................... 62
7.3.1 Basic Settings .................................................................................................................................. 62
7.3.2 Quick Stop ....................................................................................................................................... 62
7.3.3 Ramp Control Options .................................................................................................................... 63
7.4 Input Signals ........................................................................................................................................ 63
7.4.1 Basic Settings .................................................................................................................................. 63
7.4.2 Digital inputs ................................................................................................................................... 64
7.4.3 Analogue input 1 ............................................................................................................................. 65
7.4.4 Analogue input 2 ............................................................................................................................. 65
7.4.5 Analogue input 3 ............................................................................................................................. 65
7.4.6 Analogue input 4 ............................................................................................................................. 66
7.4.7 Options ........................................................................................................................................... 66
7.5 Output Signals ..................................................................................................................................... 67
7.5.1 Digital output signals ...................................................................................................................... 67
7.5.2 Analogue output 1 .......................................................................................................................... 67
7.5.3 Analogue output 2 .......................................................................................................................... 68
7.5.4 Analogue output 3 .......................................................................................................................... 69
7.5.5 Analogue output 4 .......................................................................................................................... 69
7.5.6 Delayed digital output 1 ................................................................................................................. 70
7.5.7 Delayed digital output 2 ................................................................................................................. 70
7.6 Limit Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 71
7.6.1 Current handling ............................................................................................................................. 71
7.6.2 Power Handling ............................................................................................................................... 71
7.6.3 Torque Handling ............................................................................................................................. 71
7.6.4 Speed Handling ............................................................................................................................... 71
7.6.5 DC-Link Handling ............................................................................................................................. 72
7.7 Flux and DC Current handling ............................................................................................................. 73
7.7.1 Flux and DC Current handling OL Settings ...................................................................................... 73
7.7.2 Flux and DC Current handling CL Settings ....................................................................................... 73
7.8 Motor Control ..................................................................................................................................... 74
7.8.1 Motor Control Basic Settings .......................................................................................................... 74
7.8.2 Open Loop....................................................................................................................................... 74
7.8.3 Closed Loop Control Settings .......................................................................................................... 75
7.8.4 PMSM Control settings ................................................................................................................... 76
7.8.5 Stabilators ....................................................................................................................................... 77
7.8.6 Tuning parameters .......................................................................................................................... 78
7.8.7 Identification parameters ............................................................................................................... 79
7.8.8 Fine tuning parameters................................................................................................................... 80
7.8.9 SM Excitation .................................................................................................................................. 80
7.9 Speed Control ...................................................................................................................................... 82
7.9.1 Speed Control CL Settings ............................................................................................................... 82
7.9.2 Speed Control Basic settings ........................................................................................................... 82
7.9.3 Speed Control OL Settings .............................................................................................................. 82
7.10 Drive Control ....................................................................................................................................... 83
7.11 Master Follower Control Parameters .................................................................................................. 83
7.12 Protections .......................................................................................................................................... 84
7.12.1 General settings.......................................................................................................................... 84
7.12.2 Temperature sensor protections ................................................................................................ 84
7.12.3 Stall Protection ........................................................................................................................... 85
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 3
Classified as Public
7.12.4 Speed error monitoring .............................................................................................................. 85
7.12.5 Motor thermal protections ........................................................................................................ 85
7.12.6 Living Zero monitoring (i.e. 4 mA fault) ...................................................................................... 86
7.12.7 Underload protection ................................................................................................................. 86
7.12.8 Earth Fault protection ................................................................................................................ 86
7.12.9 Cooling protection ...................................................................................................................... 86
7.12.10 Fieldbus protection .................................................................................................................... 86
7.12.11 Master Follower ......................................................................................................................... 87
7.12.12 Mechanical Brake ....................................................................................................................... 88
7.12.13 External Fault .............................................................................................................................. 88
7.12.14 Encoder fault .............................................................................................................................. 88
7.12.15 Signal Monitoring Function ........................................................................................................ 88
7.12.16 Options ....................................................................................................................................... 88
7.13 Fieldbus parameters ........................................................................................................................... 89
7.14 ID Functions ........................................................................................................................................ 91
7.14.1 Value Control .............................................................................................................................. 91
7.14.2 DIN ID Control 1 .......................................................................................................................... 91
7.14.3 DIN ID Control 2 .......................................................................................................................... 91
7.14.4 DIN ID Control 3 .......................................................................................................................... 91
7.14.5 ID Controlled Digital Output ....................................................................................................... 92
7.15 Brake Control ...................................................................................................................................... 93
7.16 Auto Reset parameters ....................................................................................................................... 94
7.17 PI Control Parameters ......................................................................................................................... 94
7.18 Functional Safety ................................................................................................................................. 95
7.19 Condition Based Monitoring ............................................................................................................... 96
7.19.1 Stator Winding............................................................................................................................ 97
7.19.2 Vibration ..................................................................................................................................... 99
7.19.3 Load .......................................................................................................................................... 100
7.20 Keypad control (Control keypad: Menu M3) .................................................................................... 101
7.21 System menu (Control keypad: Menu M6) ....................................................................................... 101
7.22 Expander boards (Control keypad: Menu M7) .................................................................................. 101
8. SIA-II Application - Description of parameters ..................................................................................... 102
8.1 Basic Parameters ............................................................................................................................... 102
8.2 Reference Handling ............................................................................................... 110
8.2.1 Basic Parameters .......................................................................................................................... 112
8.2.2 Constant Reference ...................................................................................................................... 121
8.2.3 Torque Reference ......................................................................................................................... 123
8.2.4 Prohibited speed ........................................................................................................................... 129
8.2.5 Motor potentiometer ................................................................................................................... 130
8.2.6 Adjust Reference........................................................................................................................... 132
8.2.7 Follower Reference ....................................................................................................................... 134
8.3 Ramp control ..................................................................................................................................... 137
8.3.1 Jogging function ............................................................................................................................ 139
8.3.2 Quick Stop ..................................................................................................................................... 141
8.3.3 Ramp Options ............................................................................................................................... 146
8.4 Input signals ...................................................................................................................................... 148
8.4.1 Basic Settings ................................................................................................................................ 148
8.4.2 Digital inputs ................................................................................................................................. 150
8.4.3 Analogue Input 1 & 2 .................................................................................................................... 156
8.4.4 Analogue input 3 & 4 .................................................................................................................... 161
8.4.5 Inversion control ........................................................................................................................... 164
8.5 Output signals ................................................................................................................................... 165
8.5.1 Digital output signals .................................................................................................................... 165
8.5.2 Analogue outputs 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 ................................................................................................... 170
8.5.3 Delayed Digital Output 1 & 2 ........................................................................................................ 174
8.6 Limit settings ..................................................................................................................................... 177
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

4 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
8.6.1 Current limit handling ................................................................................................................... 177
8.6.2 Power limit handling ..................................................................................................................... 178
8.6.3 Torque limit handling .................................................................................................................... 179
8.6.4 Speed limit handling ..................................................................................................................... 182
8.6.5 DC Link handling ........................................................................................................................... 184
8.6.6 Limit options ................................................................................................................................. 186
8.7 DC current and magnetization handling ........................................................................................... 188
8.7.1 Open loop settings ........................................................................................................................ 188
8.7.2 Closed loop settings ...................................................................................................................... 192
8.8 Motor Control ................................................................................................................................... 193
8.8.1 Open Loop..................................................................................................................................... 198
8.8.2 Close Loop Settings ....................................................................................................................... 202
8.8.3 Permanent magnet synchronous motor settings ......................................................................... 204
8.8.4 Stabilization settings ..................................................................................................................... 210
8.8.5 Tuning settings ............................................................................................................................. 213
8.8.6 Identification settings .................................................................................................................. 215
8.8.7 Fine tuning parameters................................................................................................................. 216
8.8.8 Synchronous machine control ...................................................................................................... 217
8.9 Speed Control settings ...................................................................................................................... 219
8.9.1 Closed Loop Speed Control Settings ............................................................................................. 219
8.9.2 Speed controller tuning for different speed areas ....................................................................... 221
8.9.3 Speed controller gain with different loads ................................................................................... 222
8.9.4 Open Loop Settings ....................................................................................................................... 227
8.10 Drive Control ..................................................................................................................................... 228
8.11 Master Follower ................................................................................................................................ 232
8.11.1 Master Follower: Standard system .......................................................................................... 232
8.11.2 Master Follower: DriveSynch system ....................................................................................... 233
8.11.3 Master follower configuration ................................................................................................. 235
8.12 Protections ........................................................................................................................................ 237
8.12.1 General settings........................................................................................................................ 237
8.12.2 PT-100....................................................................................................................................... 239
8.12.3 Stall protection ......................................................................................................................... 241
8.12.4 Speed Error ............................................................................................................................... 243
8.12.5 Motor Protection ...................................................................................................................... 244
8.12.6 4mA Protection ........................................................................................................................ 247
8.12.7 Underload protection ............................................................................................................... 248
8.12.8 Earth Fault ................................................................................................................................ 250
8.12.9 Cooling protection .................................................................................................................... 251
8.12.10 Fieldbus communication .......................................................................................................... 252
8.12.11 Master Follower communication ............................................................................................. 253
8.12.12 Brake monitoring function ....................................................................................................... 254
8.12.13 External Fault function ............................................................................................................. 255
8.12.14 Encoder fault ............................................................................................................................ 256
8.12.15 Signal Monitoring Function ...................................................................................................... 256
8.13 Fieldbus settings ................................................................................................................................ 258
8.13.1 General settings........................................................................................................................ 258
8.14 ID Functions ...................................................................................................................................... 261
8.14.1 Value Control ............................................................................................................................ 261
8.14.2 DIN ID Control........................................................................................................................... 263
8.14.3 ID-controlled DO ....................................................................................................................... 264
8.15 Brake Control .................................................................................................................................... 265
8.15.1 Run away load protection ........................................................................................................ 268
8.15.2 Closed Loop settings ................................................................................................................. 269
8.15.3 Functions .................................................................................................................................. 269
8.16 Auto Fault Reset ................................................................................................................................ 270
8.17 PI Control........................................................................................................................................... 273
8.18 Functional Safety ............................................................................................................................... 275
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 5
Classified as Public
8.19 Condition Based Monitoring ............................................................................................................. 276
8.19.1 Baseline Settings....................................................................................................................... 276
8.19.2 Stator Winding.......................................................................................................................... 278
8.19.3 Vibration ................................................................................................................................... 278
8.19.4 Threshold Value ........................................................................................................................ 279
8.19.5 Limits ........................................................................................................................................ 280
8.19.6 Counters ................................................................................................................................... 282
8.20 Keypad control parameters ............................................................................................................... 283
9. Status and control word in detail ........................................................................................................ 284
9.1 Combination 1, ProfiDrive Standard with Profibus option board .................................................. 285
9.1.1 Control Word Combination 1, ProfiDrive Standard with profibus option board ....................... 285
9.1.2 Status Word Combination 1, ProfiDrive Standard with profibus option board ......................... 285
9.2 Combination 2, ByPass ProfiDrive .................................................................................................. 286
9.2.1 State Diagram ............................................................................................................................... 286
9.2.2 State Machine ............................................................................................................................... 287
9.2.3 FB Control Word ........................................................................................................................... 288
9.2.4 FB Status Word ............................................................................................................................. 291
9.3 Combination 3, ByPass Standard.................................................................................................... 294
9.3.1 FB Control Word Combination 3, ByPass Standard ................................................................... 294
9.3.2 FB Status Word Combination 3, ByPass Standard ..................................................................... 294
9.4 Aux Control Word ............................................................................................................................. 295
9.5 Aux Status Word ............................................................................................................................... 296
9.6 Status Word (Application) ................................................................................................................. 298
10. Identification function for permanent magnet synchronous motor ................................................ 299
10.1 Zero position identification with absolute encoder. ......................................................................... 299
10.2 Start position with incremental encoder without Z-pulse input. ...................................................... 299
10.3 Identification with incremental encoder with Z-pulse input. ........................................................... 300
11. Monitoring Signal for different purposes ........................................................................................ 301
11.1 Signals for basic monitoring .............................................................................................................. 301
11.2 Firmware Reference Chain ................................................................................................................ 302
11.2.1 Reference chain before ramp generator. ................................................................................. 302
11.2.2 Reference chain after ramp generator. .................................................................................... 302
11.2.3 Speed Controller ....................................................................................................................... 303
11.2.4 Acceleration Compensation ..................................................................................................... 303
11.2.5 Torque Reference Chain ........................................................................................................... 303
12. Data Logger Trigger Word ............................................................................................................... 304
13. Problem solving............................................................................................................................... 305
14. Fault codes ...................................................................................................................................... 306
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
6 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
1. SYSTEM INTERFACE APPLICATION - INTRODUCTION
Software APFIFF40, System Interface application
The System Interface Application is typically used in coordinated drives with overriding
control system. The recommended interface to control System Interface application is a
fieldbus. Communication through hardwired analogue and digital inputs is also well
supported.
1.1 General
This application is not backwards compatible. Please read the application change note or
chapter 2 Version parameter compatibility issues in this application manual to see what needs
to be noted when updating the application. See also the updated parameter description in
NCDrive when commissioning.
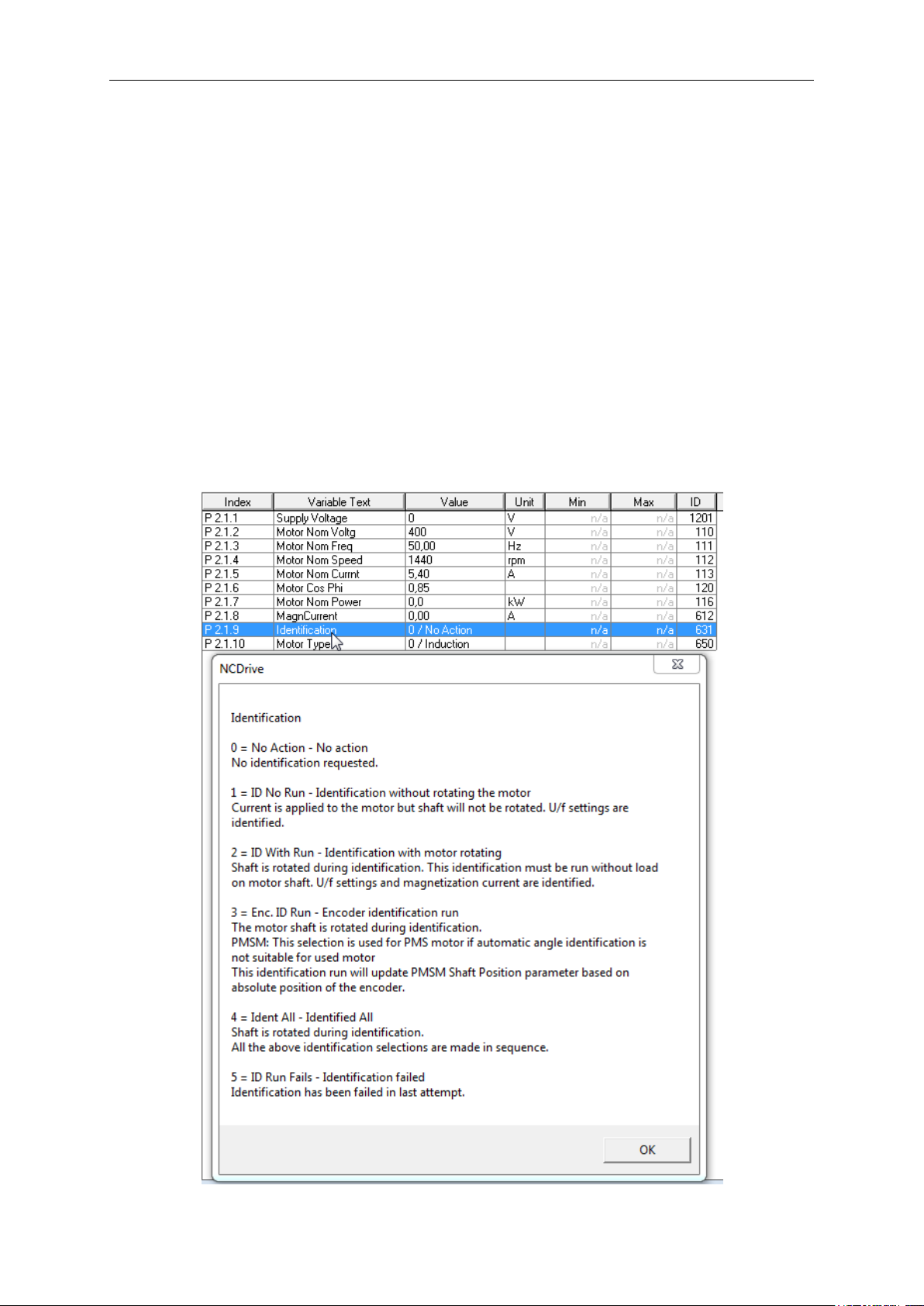
Help is available in NCDrive through selecting “Variable Text” and pressing “F1”.
Below an example from Identification parameter help text from the NCDrive.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 7
Classified as Public
1.2 Basic Features
The System Interface application provides a wide range of parameters for controlling
induction motors and permanent magnet motors. It can be used for various kinds of different
processes where wide flexibility of I/O signals is needed.
The main focus has been how drive can be controlled over Fieldbus. A flexible ID control
possibility takes the application suitability to different process to a new level, allowing any
input or actual value to be connected to any parameter with a scaling factor.
Additional functions:
• Joystick input dead zone
• Master Follower function for steering propeller and double winding motors
• Different torque limits for motoring and generating side
• Cooling monitor input from heat exchange unit with selectable response.
• Brake monitoring input and actual current monitor for immediate brake close.
• Separate speed control tuning for different speeds and loads
• Jogging function with two different references
• Possibility to connect FB Process data to any parameter and some monitoring values
• Analogue input 3 and 4 can control any parameter by ID number.
• Support for four analogue output
• Support for two PT100 board
• Condition Based Monitoring (license)
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

8 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
N O T I C E
ISO10816 standard provides guidance for evaluating vibration severity for
machines operating within 10-200 Hz of frequency range. The standard shall be
complied with before commissioning of vibration monitoring function.
1.3 Condition Based Monitoring
NXP offers Condition Based Monitoring to identify motor faults at an early stage. Stator
Winding, Vibration and Load Monitoring is supported in this application.
The Condition
Based Monitoring is license protected. Users need to buy a license key from a Danfoss
supplier to make the Condition Based Monitoring effective.
1.3.1 Introduction to Condition-based Monitoring
Benefits of installing the condition-based monitoring firmware are as follows:
• Reduces unexpected downtime
• Optimizes drive or motor working conditions
• Eliminates unexpected halts in production
Condition-based monitoring enables to regularly check the condition and performance of the
machine when the drive is in service and detects mechanical, motor, or application failures in
advance. Corrective actions can be performed before the process or application is impacted.
Fault or warnings are triggered in the drive to notify customers or service technicians. Some
of the corrective actions include replacement of faulty motors or bearings and ensuring the
motor is running within optimal conditions.
Following are the monitoring capabilities introduced:
• Motor stator winding monitoring: During monitoring, inter-turn short circuit or
unbalance in the motor winding is detected in advance. Damages caused by motor stator
winding isolation occurs over a period of time. When more winding turns are impacted, the
overcurrent protection is activated due to extensive heating and stops the motor.
• Vibration monitoring: With the help of external sensors, the drive can monitor vibration
levels in a motor. Vibrations affect motor control and can lead to motor failure. During
monitoring, early detection of motor misalignment is detected and wear and tear of
mechanical parts are identified earlier.
• Load envelope: Mechanical load of an application is monitored by comparing current load
curve with expected load curve based on data gathered during commissioning. During
monitoring, overload and under-load deviations which occur in applications are detected.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 9
Classified as Public
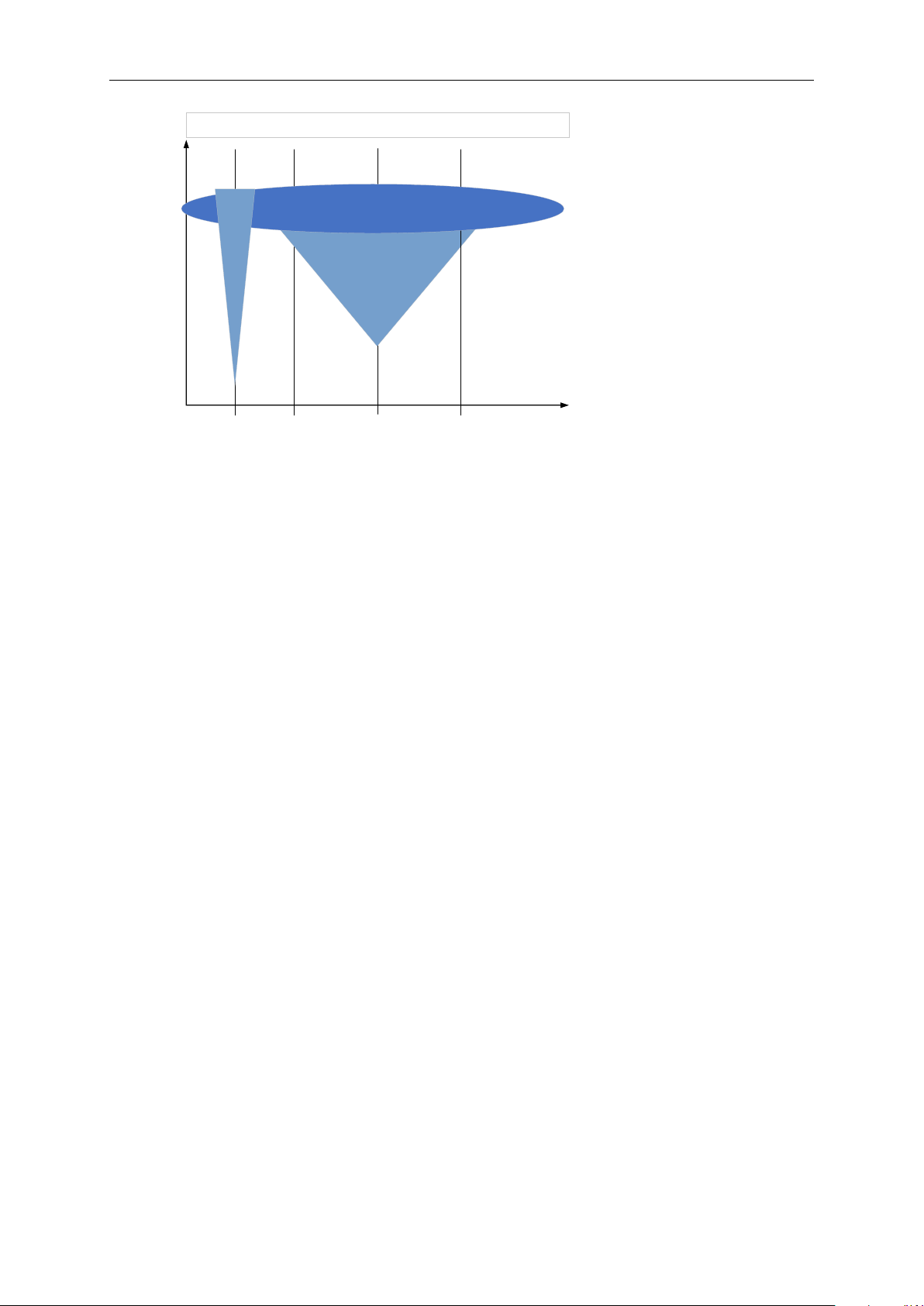
Fault types
Fault severity
Electrc motor faults,
e.g. windings
Mech motor faults,
e.g. bearings
Vibration level (RMS)
monitoring
Mechanic fault e.g.
Shaft misalignment
Application specific
fault e.g. Clogged
pump
Sensitivity of detection methods (qualitative)
Load monitoring
Stator winding fault detection
To begin condition-based monitoring a baseline must be generated. During this activity, the
system captures motor stator winding speed points for each baseline. The user can define the
duration, minimum and maximum speed for baseline generation. During baseline generation,
10 speed points are captured. The first and last speed point is captured based on the defined
minimum and maximum speed respectively.
When speed points are not captured properly, baseline generation fails, then a new baseline
has to be generated.
The baseline serves as a reference for threshold limits. Using parameters, the user can select
the type of baseline measurement.
• Baseline Run: The drive controls the motor speed and monitors required values to derive a
baseline. The drive creates a speed profile for baseline measurement. The drive interrupts the
application during baseline run to operate on the speed profile created for baseline
measurement. The duration for baseline calculation can be specified. Baseline measurements
can copy to other drive or return to same drive after factory reset.
• Manual Run: “Manual” means that the measurement points can be directly configured
manually by the user through modified parameters. Manual run can be made before or after
baseline run.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
10 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
Threshold
Calculation
Baseline
Computation
Monitoring
• Manual
• Baseline Run
• Warnings &
Alarm/Fault
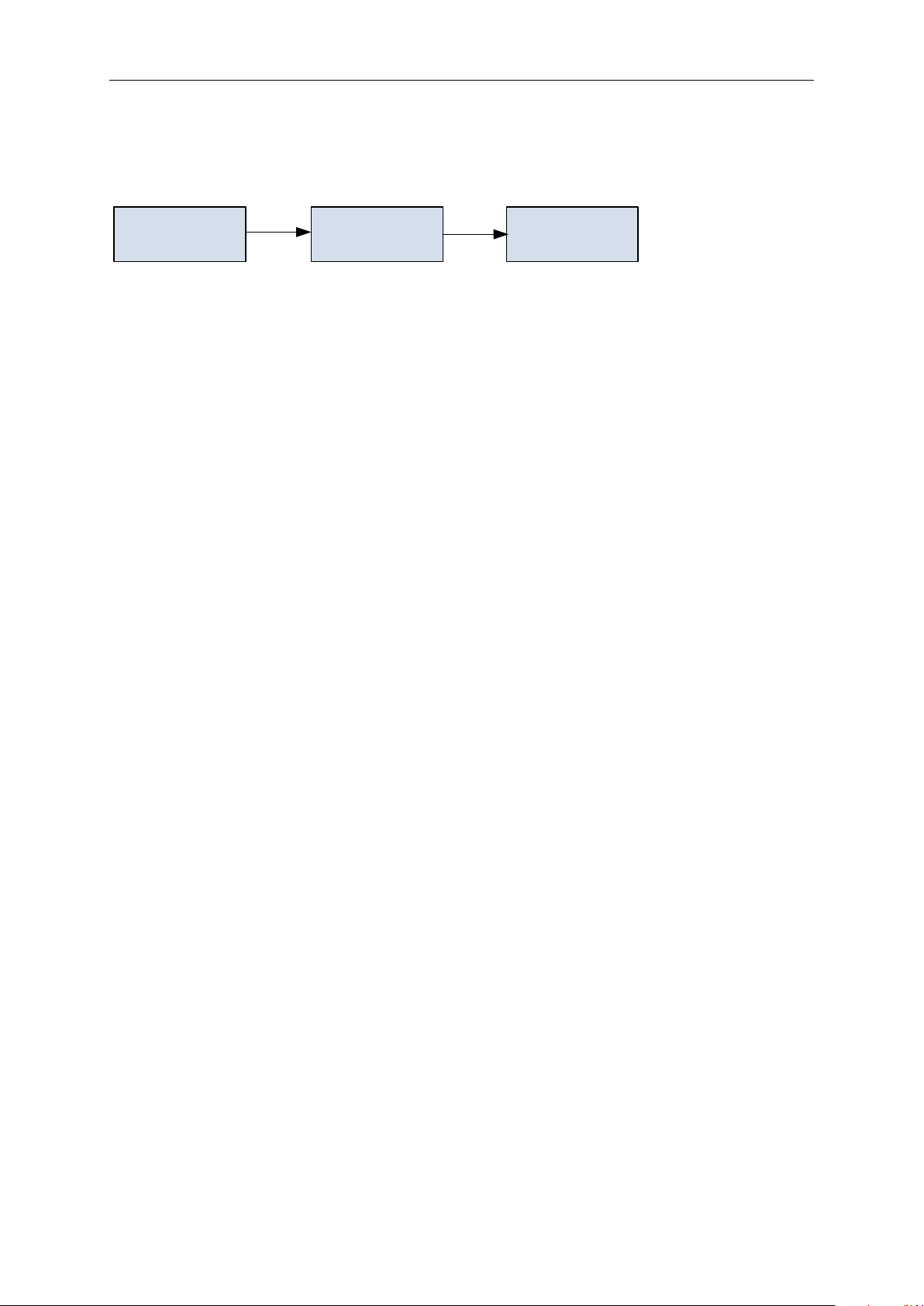
1.3.2 Condition-based monitoring stages
Different stages of condition-based monitoring are as shown
Baseline Computation: During the initial stage, baselines for different types of conditionbased monitoring are computed, based on the type of baseline mode selected by the user.
Threshold Calculation: Once the baseline is computed, the thresholds for warnings (stage 1
and stage 2) and alarm/fault are computed based on the warning or alarm/fault mode. The
threshold and mode are set via parameters.
Monitoring: After the thresholds are calculated, condition-based monitoring begins.
Alarm/fault and warnings are triggered during deviations to notify customers.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 11
Classified as Public
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

12 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
1.4 Acronyms
AC = Alternating Current
AI = Analogue Input
AIO = All-In-One Applications
AM = Asynchronous Motor
ASIC = Application Specific Integrated Circuit
CBM = Condition Based Monitoring
CL = Closed Loop
DC = Direct Current
DI = Digital Input
DO = Digital Output
DS = DriveSynch
FB = Field Bus
FFT = Function To Terminal
FW = Firmware
FWP = Field Weakening Point
FWPV = Field Weakening Point Voltage
GE = Greater or Egual
HW = Hardware
I/f = Current / Frequency
Id = Magnetization Current
IGBT = Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
INV = Inversion
Iq = Torque Producing Current
LT = Less Than
MF = Master-Follower
OL = Open Loop
PID = Proportional Integral Derivative
PM = Permanent Magnet
PMSM = Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
PU = Per Unit
RO = Relay Output
RS = Reset Set
SB = System Bus
Sep.Ex SM = Separatelly Excitated Synchronous Motor
SM = Synchronous Machine
SPC = Speed Control
SQS = Sfe Quick Stop
SR = Set Reset
SRM = Synchronous Reluctance Motor
SS1 = Safe Stop 1
STO = Safe Torque Off
SW = Software
TC = Torque Control
TC = Time Constant
TTF = Terminal To Function
U/f = Voltage / Frequency
UV = Under Voltage
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 13
Classified as Public
3. VERSION PARAMETER COMPATIBILITY ISSUES
Latest released and previous versions from below link
http://drivesliterature.danfoss.com/performCachedSearch.action
Update Note 1: This application parameters are not kept backwards compatible if new
features or improvements would be difficult to implement by doing so. Read this change note
and chapter “Compatibility issues in parameters between versions” from manual before
updating the application.
Update Note 2: It’s recommended to use compare function for parameter changes when
updating application, especially in cases when version number change is considerably high.
Application is constantly developed; this includes changing parameter default values, and if
parameters are directly downloaded to drive improved default values may be lost.
APFIFF10 vs. APFIFF40
- APFIFF40 SIA application is needed to consider as a new application when making
commissioning. Old version parameters file should not be downloaded directly to the
drive. Recommended action is to change parameters by using compare function of
NCDrive.
Notable changes:
- DO1, DO2 and DO3 control is now in main control word instead of Aux Control Word.
- Emergency stop is now Quick stop function and operation is redesigned.
APFIFF40 V037
- Reference selection 19 Fast Speed reference is not available anymore. Combined
with reference selection 9 FB Speed Reference. See updated restrictions from
Control Slot Selector parameter.
- Reference selection 11 Fast Torque reference is not available anymore. Combined
with reference selection 8 FB Torque Reference. See updated restriction from
Control Slot Selector parameter.
APFIFF40 V051
- P2.14.5.1 “ID.Bit Free DO” was same with parameter as P2.5.6.6 “ID.Bit Free DO”,
fixed. P2.14.5.1 “ID.Bit Free DO” ID number is now ID1217
APFIFF40 V059
- F84 Speed Protection is by default Fault by Coasting, Limit is 120 rpm.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
14 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
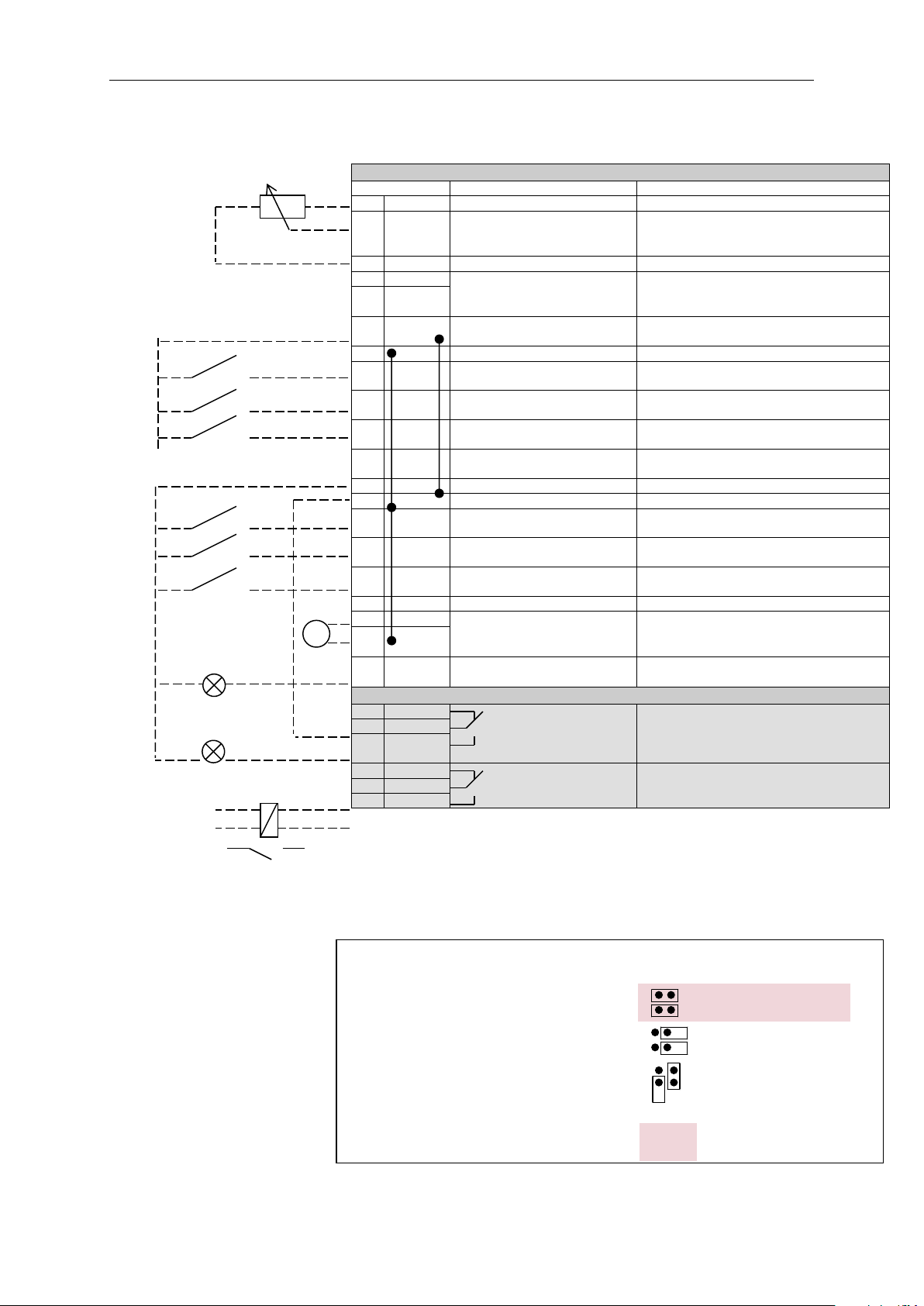
NXOPTA1
Terminal
Signal
Description
1
+10V
ref
Reference voltage output
Voltage for potentiometer, etc.
2
AI1+
Analogue input 1.
Range 0-10V, Ri = 200k
Range 0-20 mA Ri = 250
Analogue input 1 reference.
Input range selected by jumpers.
Default range: Voltage 0 – 10 V
3
AI1-
I/O Ground
Ground for reference and controls
4
AI2+
Analogue input 2.
Range 0-10V, Ri = 200k
Range 0-20 mA Ri = 250
Analogue input 2 reference
Input range selected by jumpers.
Default range: Current 0 – 20 mA
5
AI2-
6
+24V
Control voltage output
Voltage for switches, etc. max 0.1 A
7
GND
I/O ground
Ground for reference and controls
8
DIN1
Start forward
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact closed = start forward
Programmable start logic P2.4.1.1
9
DIN2
Start reverse
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact closed = start reverse
Programmable logic P2.4.1.1
10
DIN3
Fault reset
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact open = no fault
Contact closed = fault
11
CMA
Common for DIN 1—DIN 3
Connect to GND or +24V
12
+24V
Control voltage output
Voltage for switches (see #6)
13
GND
I/O ground
Ground for reference and controls
14
DIN4
Run Enable
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact closed = Run Enabled
Contact open = Run Disabled
15
DIN5
Main Switch Ack.
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact closed = Switch is closed.
Contact open= Switch is open.
16
DIN6
Controlled Stop
Programmable G2.2.7
Contact open= Quick Stop Active. Contact
closed = Quick stop not active.
17
CMB
Common for DIN4—DIN6
Connect to GND or +24V
18
AOA1+
Analogue output 1
Programmable P2.3.1.2
Output range selected by jumpers.
Range 0—20 mA. RL, max. 500
Range 0—10 V. RL > 1k
19
AOA1-
20
DOA1
Digital output
Programmable
Open collector, I50mA, U48 VDC
NXOPTA2
21
RO1
Relay output 1
Programmable G2.3.3
Switching capacity
24 Vdc / 8 A
250 Vac / 8 A
125 Vdc / 0.4 A
22
RO1
23
RO1
24
RO2
Relay output 2
Programmable G2.3.3
Programmable
No function defined at default
25
RO2
26
RO2
Jumper block X3 :
CMA a nd CMB g rounding
CMB c o nnected to G ND
CMA c o nnec ted to G ND
CMB isolated from G N D
CMA iso lated fro m G ND
CMB a nd CMA
internally c o nnec te d tog ether,
isolated from G N D
= Factory d efault
220
VAC
Reference potentiometer,
1…10 k
mA
4. CONTROL I/O
Note: See Users Manual, chapter Control Connections, for hardware specification and
configuration.
Table 4-1. System Interface application default I/O configuration and
connection example.
Note: See jumper selections below.
More information in Vacon NX
User's Manual, Chapter 6.2.2.2.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 15
Classified as Public
READY
I/Oterm
DigOUT:B.1
AI Ref Faul/Warn
READY
I/Oterm
DigOUT:0.0
READY
I/Oterm
DigOUT:0.0
READY
I/Oterm
DigOUT:B.1
enter
AI Ref Faul/Warn AI Ref Faul/Warn AI Ref Faul/Warn
5. “TERMINAL TO FUNCTION” (TTF) PROGRAMMING PRINCIPLE
The programming principle of the input and output signals in the Multipurpose Control
Application NXP as well as in the Pump and Fan Control Application (and partly in the
other applications) is different compared to the conventional method used in other Vacon NX
applications.
In the conventional programming method, Function to Terminal Programming Method
(FTT), you have a fixed input or output that you define a certain function for. The
applications mentioned above, however, use the Terminal to Function Programming method
(TTF) in which the programming process is carried out the other way round: Functions
appear as parameters which the operator defines a certain input/output for. See Warning on
page 16.
5.1 Defining an input/output for a certain function on keypad
Connecting a certain input or output with a certain function (parameter) is done by giving the
parameter an appropriate value. The value is formed of the Board slot on the Vacon NX
control board (see Vacon NX User's Manual, Chapter 6.2) and the respective signal number,
see below.
Function name
Slot Terminal number
Terminal type
Example: You want to connect the digital output function Reference fault/warning
(parameter 2.3.3.7) to the digital output DO1 on the basic board NXOPTA1 (see Vacon NX
User's Manual, Chapter 6.2).
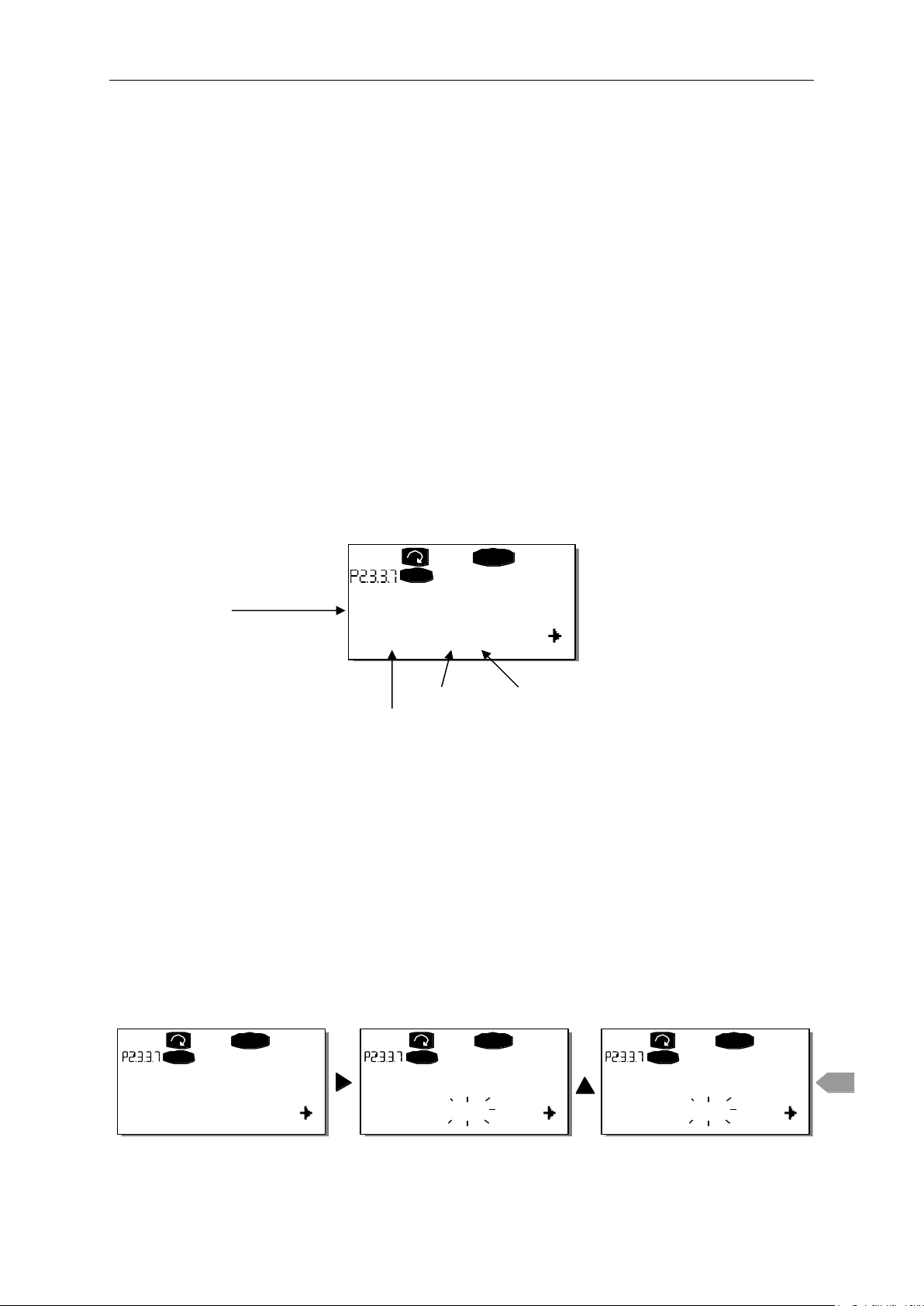
First find the parameter 2.3.3.7 on the keypad. Press the Menu button right once to enter the
edit mode. On the value line, you will see the terminal type on the left (DigIN, DigOUT,
An.IN, An.OUT) and on the right, the present input/output the function is connected to (B.3,
A.2 etc.), or if not connected, a value (0.#).
When the value is blinking, hold down the Browser button up or down to find the desired
board slot and signal number. The program will scroll the board slots starting from 0 and
proceeding from A to E and the I/O selection from 1 to 10.
Once you have set the desired value, press the Enter button once to confirm the change.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
16 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Classified as Public
Be ABSOLUTELY sure not to connect two functions to one and
same output in order to avoid function overruns and to ensure
flawless operation.
!
WARNING
Note: The inputs, unlike the outputs, cannot be changed in RUN state.
5.2 Defining a terminal for a certain function with NCDrive programming tool
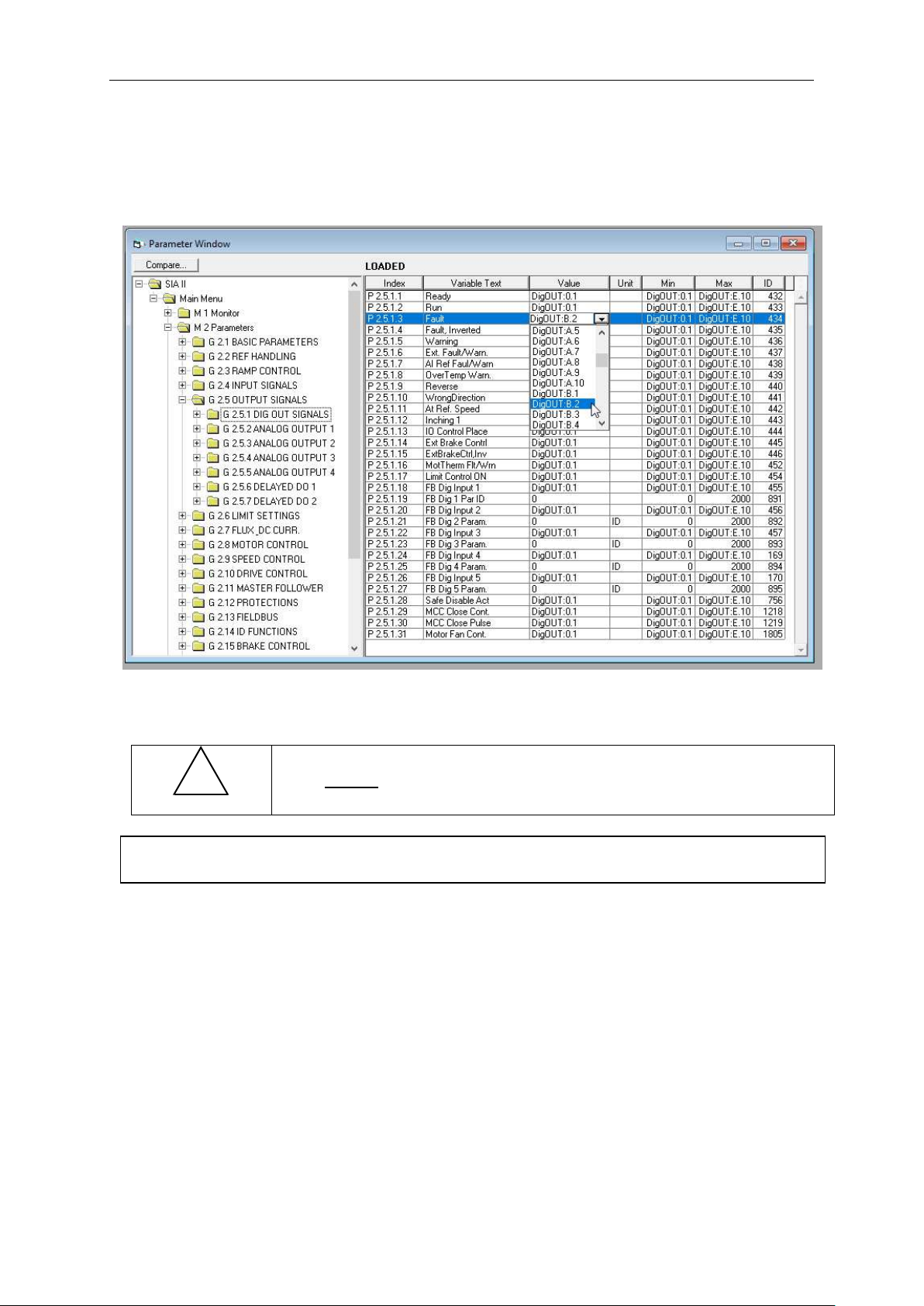
If you use the NCDrive Programming Tool for parametrizing you will have to establish the
connection between the function and input/output in the same way as with the control panel.
Just pick the address code from the drop-down menu in the Value column (see the Figure
below).
Figure 5-1. Screenshot of NCDrive programming tool; Entering the address code
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 17
Classified as Public
5.3 Defining unused inputs/outputs
All unused inputs and outputs must be given the board slot value 0 and the value 1 also for
the terminal number. The value 0.1 is also the default value for most of the functions.
However, if you want to use the values of a digital input signal for e.g. testing purposes
only, you can set the board slot value to 0 and the terminal number to any number between
2…10 to place the input to a TRUE state. In other words, the value 1 corresponds to 'open
contact' and values 2 to 10 to 'closed contact'.
In case of analogue inputs, giving the value 1 for the terminal number corresponds to 0%
signal level, value 2 corresponds to 20%, value 3 to 30% and so on. Giving value 10 for the
terminal number corresponds to 100% signal level.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
18 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
6. SYSTEM INTERFACE APPLICATION – MONITORING VALUES
On the next pages you will find the lists of parameters within the respective parameter
groups. The parameter descriptions are given on pages 102 to 269. Parameter description
includes more than is available in this application see parameter list what is available.
Column explanations:
Code = Location indication on the keypad; Shows the operator the present
parameter number
Parameter = Name of parameter
Min = Minimum value of parameter
Max = Maximum value of parameter
Unit = Unit of parameter value; Given if available
Default = Value preset by factory
Cust = Customer’s own setting
ID = ID number of the parameter
_____ = On parameter code: Parameter value can only be changed after the FC has
been stopped.
_____ = Apply the Terminal to Function method (TTF) to these parameters (see
chapter 5)
_____ = Monitoring value is possible to control from fieldbus by ID number
The manual presents signals that are not normally visible for monitoring. i.e. is not a
parameter or standard monitoring signal. These signals are presented with [Letter]. e.g.
[FW]MotorRegulatorStatus
[V] Normal monitoring signal
[P] Normal parameter in application.
[FW] Firmware signal, Can be monitored with NCDrive when signal type is selected
Firmware
[A] Application signal, can be monitored with NCDrive when signal type is selected
Application.
[R] Reference type parameter on keypad.
[F] Function. Signal is received as a output of function.
[DI] Digital input signal.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 19
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Unit
Form
ID
Description
V1.1
Output frequency
Hz
#,##
1
Output frequency to motor
V1.2
Frequency reference
Hz
#,##
25
Frequency reference to motor control
V1.3
Motor speed
rpm # 2
Motor speed in rpm
V1.4
Motor current
A
Varies
3
1 s linear filtering. Format changes
depending on unit size.
V1.5
Motor torque
%
Varies
4
In % of Motor nominal torque. Format
changes depending in Torque Scale
parameter
V1.6
Shaft Power
%
#.#
5
Format changes depending in Torque Scale
parameter
V1.7
Motor voltage
V
#,#
6
Calculated motor voltage
V1.8
DC link voltage
V # 7
Measured DC voltage, filtered.
V1.9
Unit temperature
C
# 8 Heatsink temperature
V1.10
Motor temperature
varies
#,#
9
Calculated motor temperature
V1.11
Analogue input 1
%
#,##
13
AI1, unfiltered.
V1.12
Analogue input 2
%
#,##
14
AI2, unfiltered.
V1.13
Analogue input 3
%
#,##
27
AI3, unfiltered.
V1.14
Analogue input 4
%
#,##
28
AI4, unfiltered.
V1.15
Analogue Out 1
%
#,##
26
AO1
V1.16
Analogue Out 2
%
#,##
31
AO2
V1.17
Analogue Out 3
%
#,##
32
AO3
V1.18
Analogue Out 4
%
#,##
1526
V1.19
DIN1, DIN2, DIN3
15
Digital input statuses
V1.20
DIN4, DIN5, DIN6
16
Digital input statuses
V1.21
Torque reference
%
18
Used Torque Reference. Format changes
depending in Torque Scale parameter
V1.22
PT-100 Temperature
Cº
#,#
42
Highest temperature of OPTB8 board. 4 s
filtering.
G1.23
Multimonitoring items
Displays three selectable monitoring values
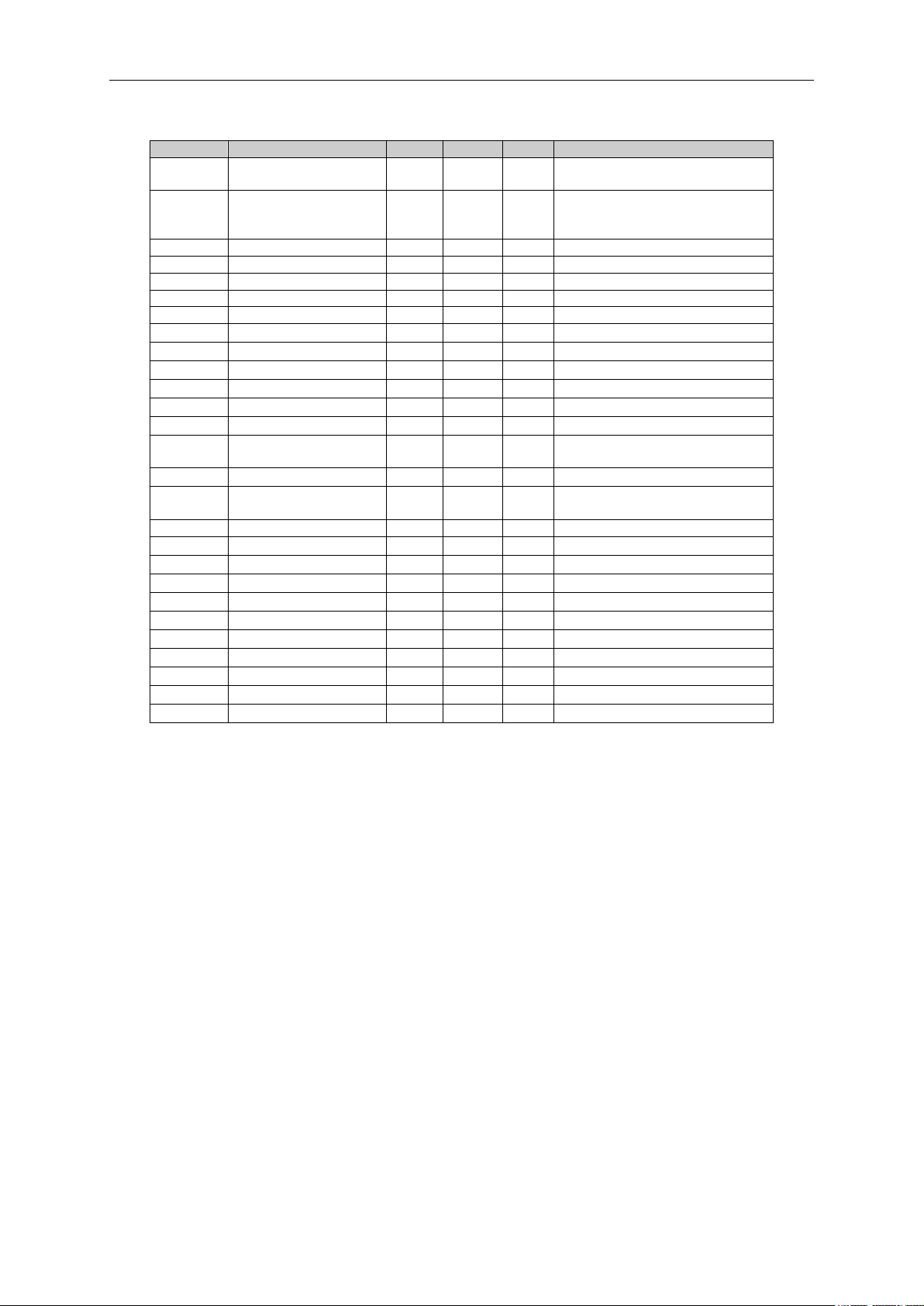
6.1 Monitoring values (Control keypad: menu M1)
6.1.1 Monitoring Values
The monitoring values are the actual values of parameters and signals as well as statuses and
measurements.
Table 6-1. Monitoring values
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
20 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Unit
Form
ID
Description
V1.24.1
Current
A
Varies
1113
Unfiltered motor current. Format
changes depending on unit size.
V1.24.2
Torque
%
Varies
1125
Unfiltered motor torque. Format
changes depending in Torque Scale
parameter
V1.24.3
DC Voltage
V # 44
Unfiltered DC link voltage
V1.24.4
Application Status Word
43
V1.24.5
Shaft Frequency
Hz
#,##
96
Filtered used for speed control
V1.24.6
Encoder 1 Frequency
Hz
#,##
1164
Unfiltered, directly from encoder
V1.24.7
Output Power
kw 1508
Unfiltered electrical power
V1.24.8
Measured temperature 1
Cº
#,#
50
4 s filtering.
V1.24.9
Measured temperature 2
Cº
#,#
51
4 s filtering.
V1.24.10
Measured temperature 3
Cº
#,#
52
4 s filtering.
V1.24.11
Measured temperature 4
Cº
#,#
69
4 s filtering.
V1.24.12
Measured temperature 5
Cº
#,#
70
4 s filtering.
V1.24.13
Measured temperature 6
Cº
#,#
71
4 s filtering.
V1.24.14
ABS Encoder
Revolutions
r
#
55
V1.24.15
ABS Encoder Position
#
54
V1.24.16
Final Frequency
Reference
Hz
#,##
1845
V1.24.17
Step response
Hz
#,###
1846
V1.24.18
CosPhiiActual
#,###
68 V1.24.19
Flux Current
%
#,#
72 V1.24.20
ID Run Status
49 V1.24.21
Rotor Flux
%
#,#
1158 V1.24.22
Step Frequency
Hz
#,##
1871 V1.24.23
Ident fail
98 V1.24.24
Limit & Requlators
77 V1.24.25
Non Ready Cause
#
1608 V1.24.26
Prevent MC Ready
#
1609 V1.24.27
Serial Number Key
1997
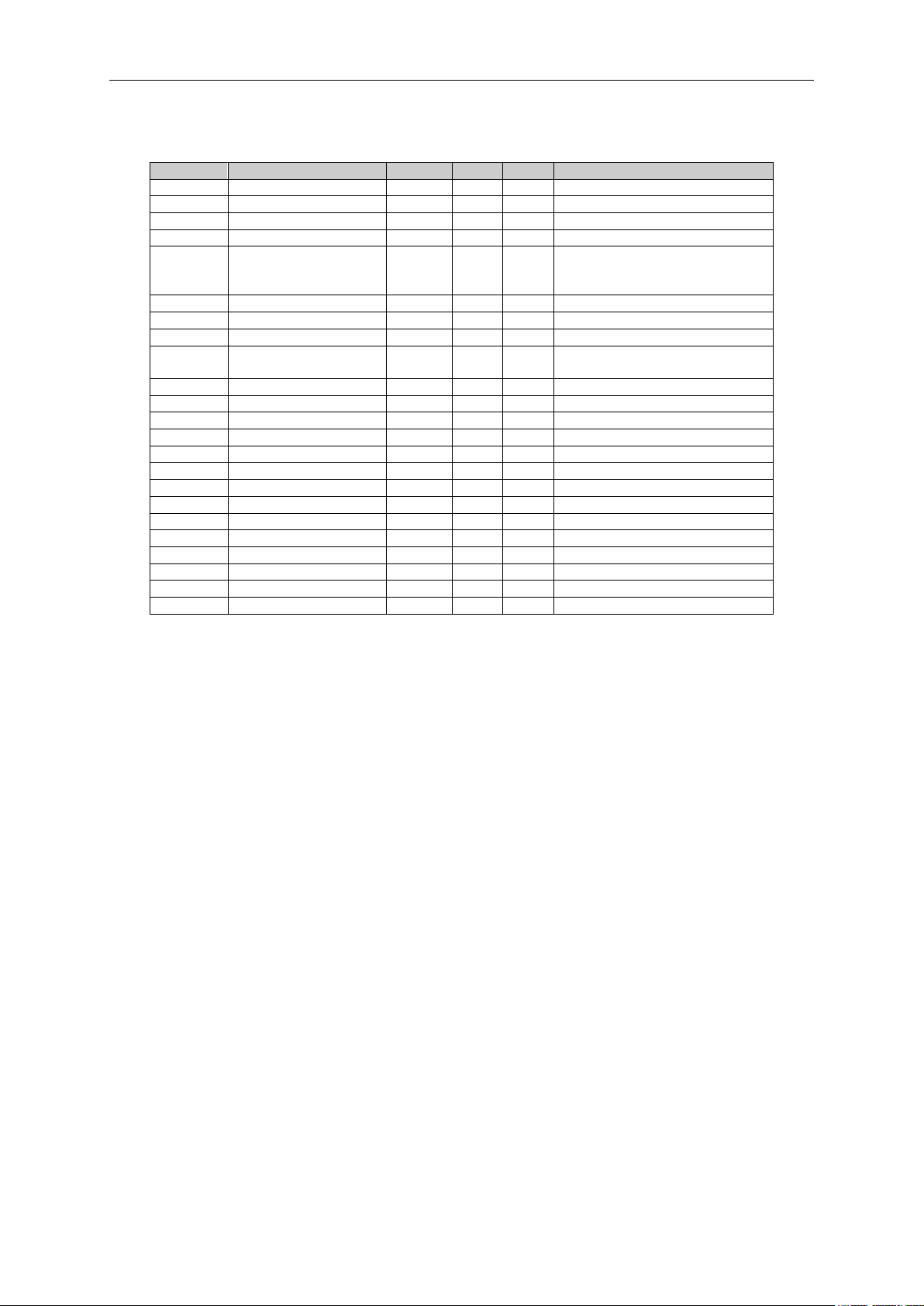
6.1.2 Monitoring values 2
Table 6-2. Monitoring values 2
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 21
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.25.1
FB Control Word
1160
V1.25.2
FB Speed Reference
875
V1.25.3
FB Status Word
65 V1.25.4
FB Actual speed
865
V1.25.5
FB Torque Reference
% 1140
Default Control of FB PD 1. Format
changes depending in Torque Scale
parameter
V1.25.6
FB Limit Scaling
%
#,##
46
Default Control of FB PD 2
V1.25.7
FB Adjust Reference
%
#,##
47
Default Control of FB PD 3
V1.25.8
FB Analog Output
%
#,##
48
Default Control of FB PD 4
V1.25.9
FB Motor Current
A
#,#
45
Motor current (drive independent)
given with one decimal point
V1.25.10
Fault Word 1
1172
V1.25.11
Fault Word 2
1173 V1.25.12
Warning Word 1
1174 V1.25.13
AuxStatusWord
1163 V1.25.14
Last Active Fault
# 37
V1.25.15
AuxControlWord
1161
V1.25.16
Din Status Word
56 V1.25.17
Din Status Word 2
57 V1.25.18
MC Status
64 V1.25.19
Last Active Warning
# 74
V1.25.20
Shaft Rounds
r # 1170
V1.25.21
Shaft Angle
Dec
#
1169
V1.25.22
Fault Word 10
1202
V1.25.23
Warning Word 10
1269
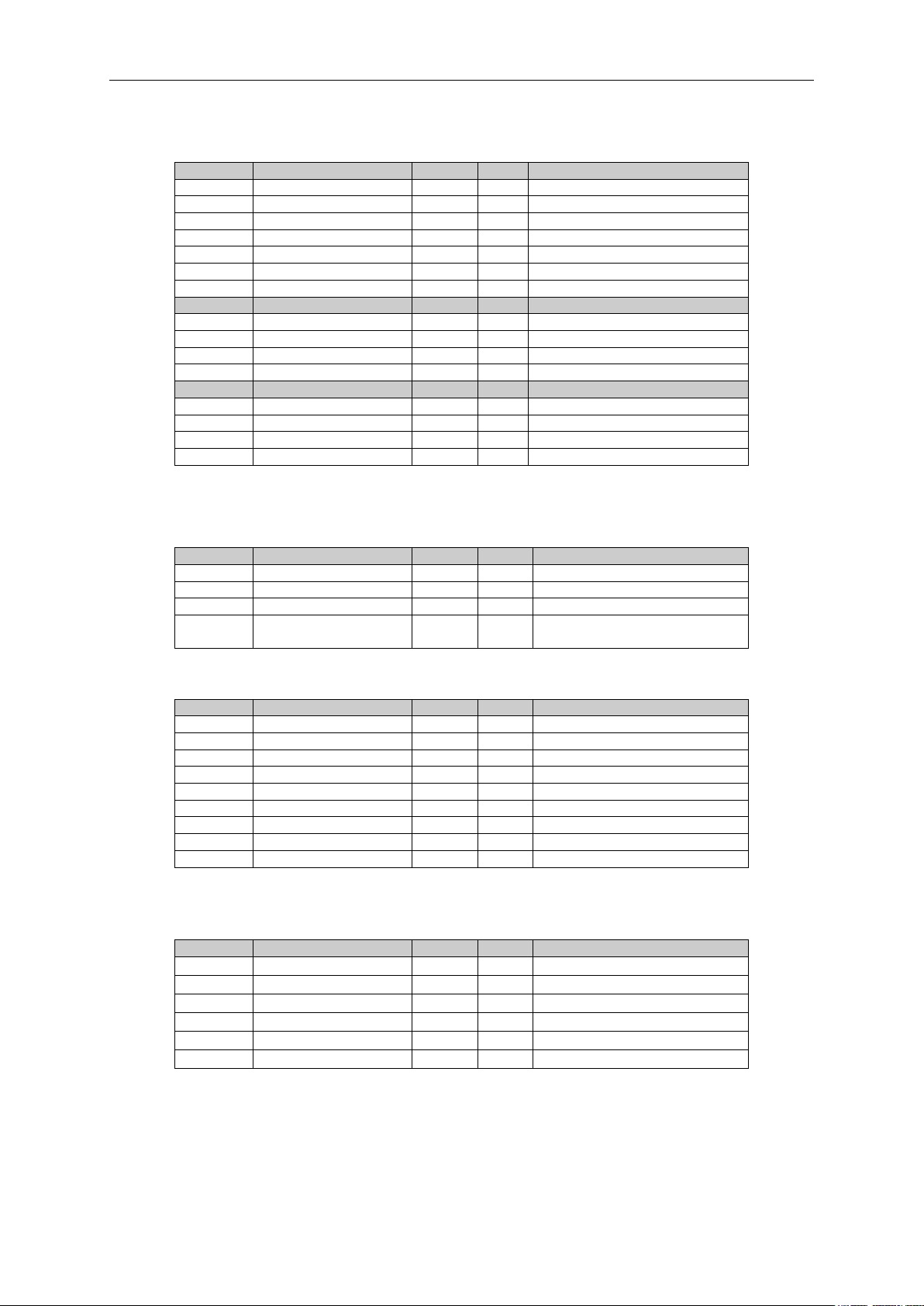
6.1.3 FieldBus Monitoring values
Table 6-3. FieldBus Monitoring values
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
22 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.26.1
SB SystemStatus
1601
V1.26.2
Total Current
A
80
Sum current of all drives (DS)
V1.26.3
Master CW
A
93
Control Word of Master Drive
V1.26.4
Master Freq. Ref
Hz
1842 V1.26.5
Master Ramp Out
Hz
1843 V1.26.6
Master Torque Ref
%
1139
V1.26.7
Master SPC Out
%
1844
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.26.8.1
Motor Current D1
A
1616
V1.26.8.2
Motor Current D2
A
1605
V1.26.8.3
Motor Current D3
A
1606
V1.26.9.4
Motor Current D4
A
1607
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.26.9.1
Status Word D1
1615
V1.26.9.2
Status Word D2
1602
V1.26.9.3
Status Word D3
1603
V1.26.9.4
Status Word D4
1604
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.27.1
PI Reference
20
Used PI Reference
V1.27.2
PI Actual Value
21
PI Actual value
V1.27.3
PI Output
23
PI Output before scaling
V1.27.4
PI Output Scaled
1807
Scaled PI Output
This is used for ID connection
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.28.1
Speed Ref 1
rpm
1126 V1.28.2
Speed Ref 2
rpm
1127
V1.28.3
Speed Ref Actual
rpm
1128
V1.28.4
Speed Ref Ramp Out
rpm
1129 V1.28.5
Speed Ref Step
rpm
1121 V1.28.6
Speed Ref Final
rpm
1131 V1.28.7
Speed Ref Error
rpm
1132
V1.28.8
Speed Drooping
rpm
1147
V1.28.9
Speed Measured
rpm
1124
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.29.1
Torque Reference
%
18 V1.29.2
Torque Ref. 3
%
1144 V1.29.3
Torque Ref Final
%
1145 V1.29.4
Speed Control Out
%
1134 V1.29.5
Accell Compensation
%
1146 V1.29.6
Torque Ref. Actual
%
1180
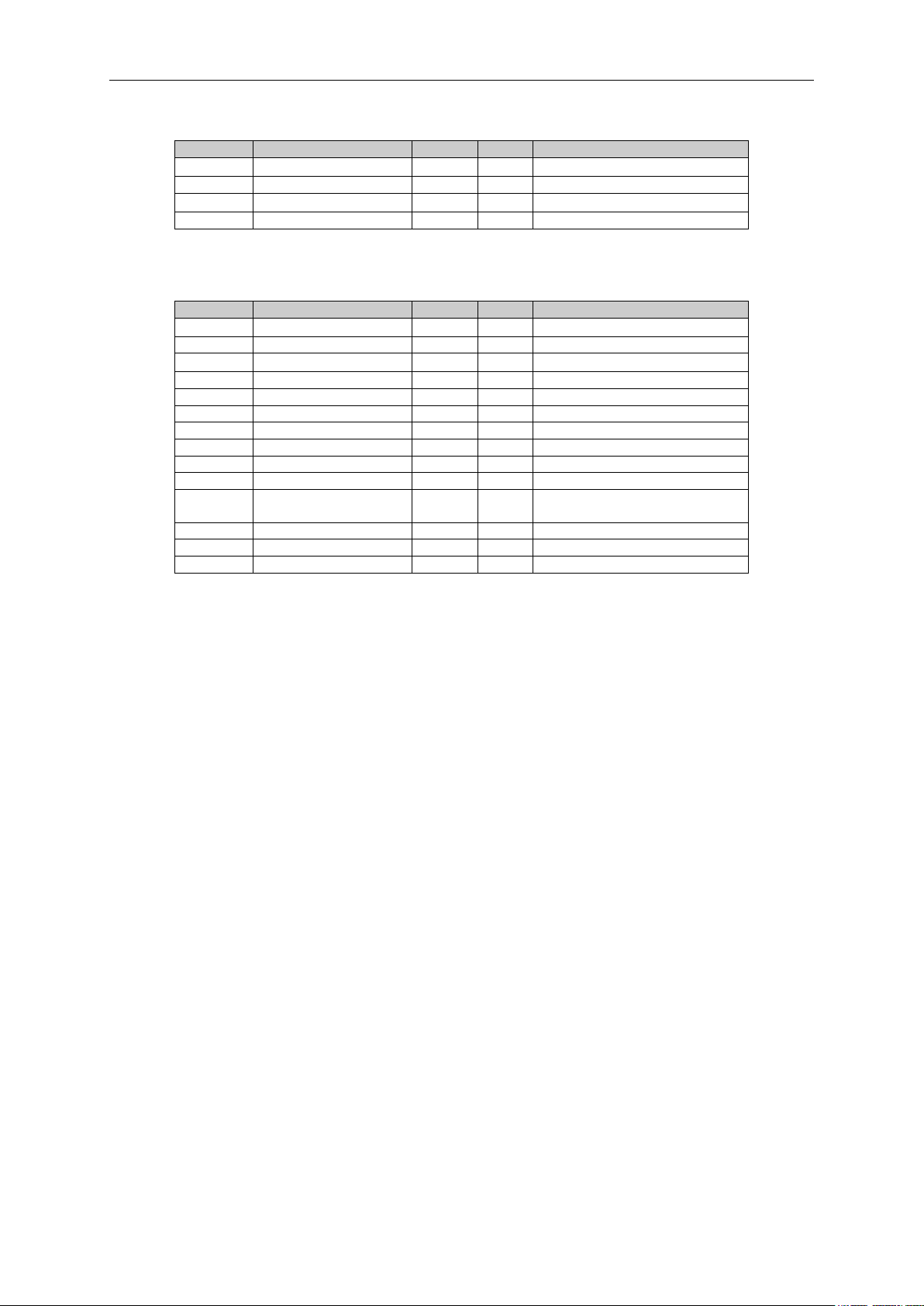
6.1.4 Master/Follower Monitoring values
Table 6-4. Master/Follower Monitoring values
6.1.5 PI Control Monitoring values
6.1.6 Speed reference Chain
6.1.7 Torque Reference Chain
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 23
Classified as Public
Code
Signal
Unit
ID
Description
V1.30.1
Magnetization Reference
%
1767
V1.30.2
Magn Ref AO
%
1768
V1.30.3
Magnetization Actual
%
1816
V1.30.4
Magn Act AI
%
1817
Code
Signal
Unit
ID
Description
V1.31.1
Safety App Status
1653
V1.31.2
Integrity Level
1640
V1.31.3
Acknowledge Mode
1641
V1.31.4
Safety Encoder Speed
rpm
1642 V1.31.5
Ramp Selection
1643 V1.31.6
Function Reached
1644
V1.31.7
Request DIN
1645
V1.31.8
Request PLC
1646 V1.31.9
Function In Use
1647
V1.31.10
Safety Status Word
1648
V1.31.11
Safety General Status
Word
1649
V1.31.12
Safety Status
1650
V1.31.13
Safety Zero Speed
1651
V1.31.14
SBC Speed
rpm
1652
6.1.8 SM Excitation
6.1.9 Functional Safety Monitoring
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
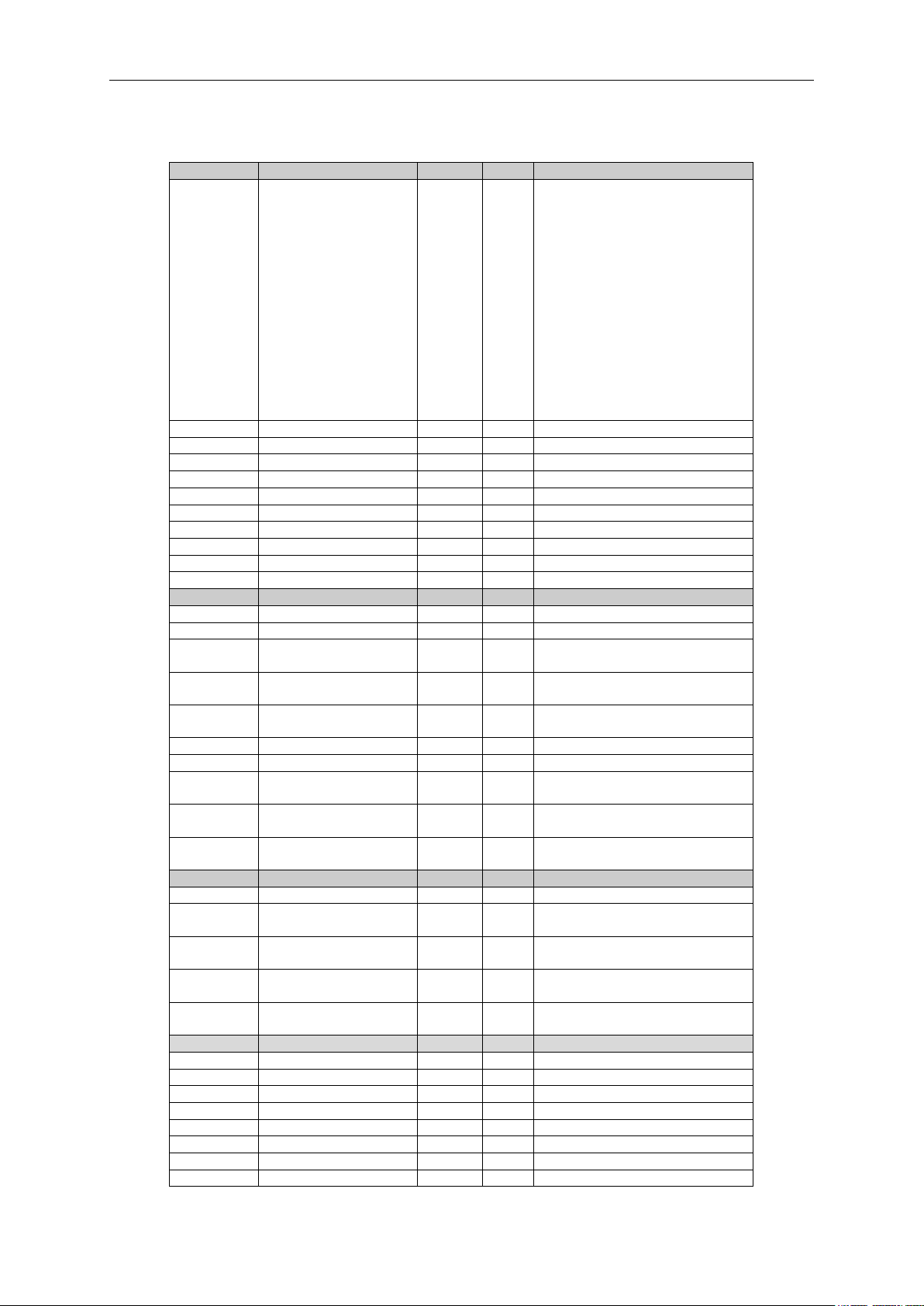
24 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.32.1.1
Baseline Status
3622
0=Not Started
1=Running
2=Running 10%
3=Running 20%
4=Running 30%
5=Running 40%
6=Running 50%
7=Running 60%
8=Running 70%
9=Running 80%
10=Running 90%
11=Completed
12=Run Failed
13=Manual Before Baseline
14=Manual After Baseline
V1.32.1.2
Baseline Data 1
Hz or %
3601 V1.32.1.3
Baseline Data 2
Hz or %
3602 V1.32.1.4
Baseline Data 3
Hz or %
3603 V1.32.1.5
Baseline Data 4
Hz or %
3604
V1.32.1.6
Baseline Data 5
Hz or %
3605
V1.32.1.7
Baseline Data 6
Hz or %
3606 V1.32.1.8
Baseline Data 7
Hz or %
3607 V1.32.1.9
Baseline Data 8
Hz or %
3608 V1.32.1.10
Baseline Data 9
Hz or %
3609
V1.32.1.11
Baseline Data 10
Hz or %
3610
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.32.2.1
Current Unbalance
%
3617
V1.32.2.2
Current Threshold Value
%
3620
V1.32.2.3
Current Warning S1
High
%
3611
V1.32.2.4
Current Warning S2
High
%
3612 V.1.32.2.5
Current Alarm/Fault
High
%
3613
V1.32.2.6
Voltage Unbalance
%
3618
V1.32.2.7
Voltage Threshold Value
%
3621
V1.32.2.8
Voltage Warning S1
High
%
3614 V1.32.2.9
Voltage Warning S2
High
%
3615
V.1.32.2.10
Voltage Alarm/Fault
High
%
3616
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.32.3.1
Vibration
%
3623
V1.32.3.2
Vibration Threshold
Value
%
3624
V1.32.3.3
Vibration Warning S1
High
%
3625
V1.32.3.4
Vibration Warning S2
High
%
3626 V.1.32.3.5
Vibration Alarm/Fault
High
%
3627
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V1.32.4.1
Motor Torque
%
4 V1.32.4.2
Load Threshold Value
%
3628
V1.32.4.3
Load Warning S1 High
%
3639
V1.32.4.4
Load Warning S2 High
%
3630
V.1.32.4.5
Load Alarm/Fault High
%
3631
V1.32.4.6
Load Warning S1 Low
%
3632
V1.32.4.7
Load Warning S2 Low
%
3633
V.1.32.4.8
Load Alarm/Fault Low
%
3634
6.1.10 Condition Based Monitoring
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
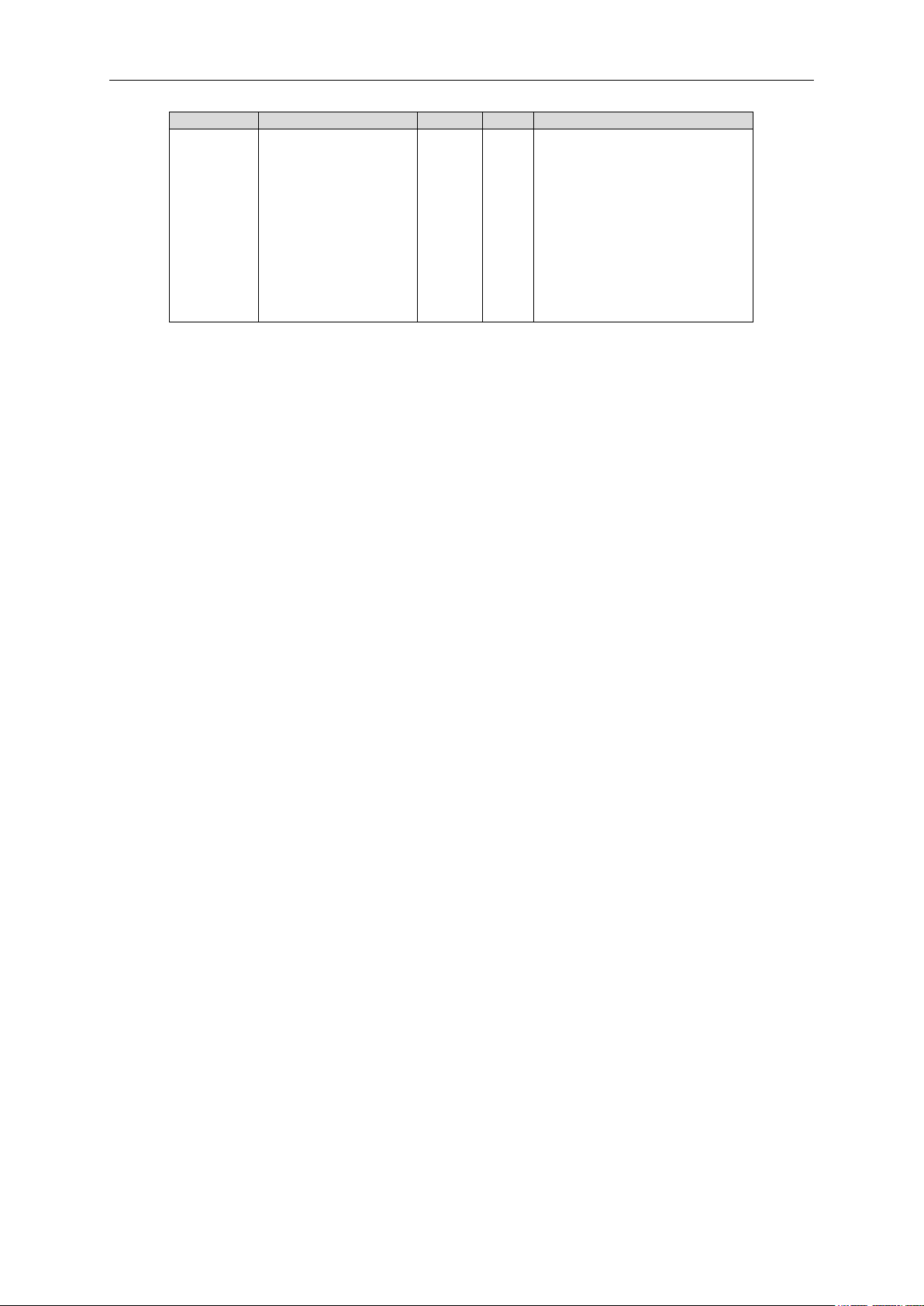
apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 25
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Unit
ID
Description
V.1.32.5
Condition Based Status
3619
B0= Stator current warning S1
B1= Stator voltage warning S1
B2= Vibration warning S1
B3= Load warning S1
B5= Stator current warning S2
B6= Stator voltage warning S2
B7= Vibration warning S2
B8= Load warning S2
B10= Stator current alarm/fault
B11= Stator voltage alarm/fault
B12= Vibration alarm/fault
B13= Load alarm/fault
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
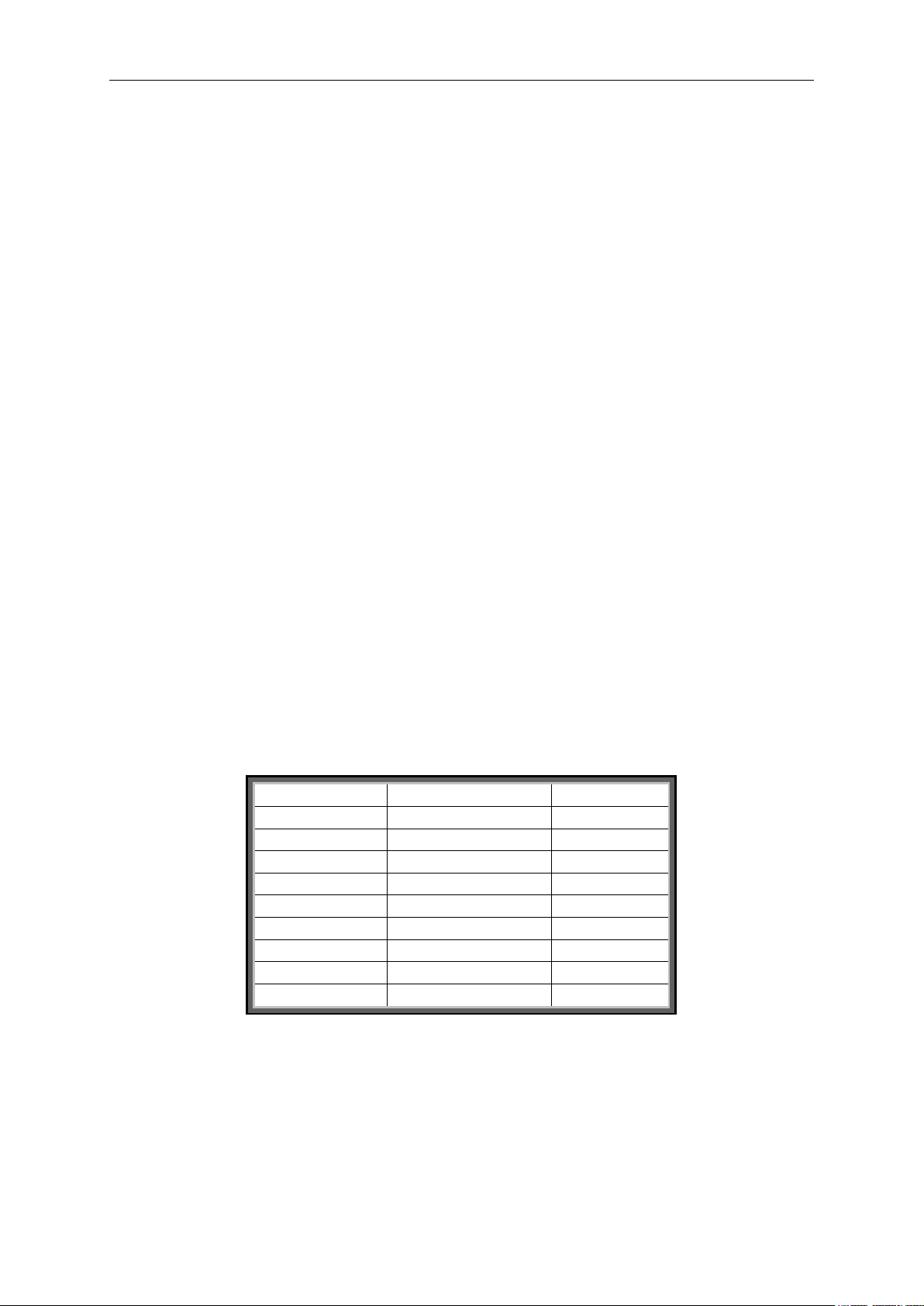
26 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Voltage
Size
Scale
208 – 240 Vac
NX0001 – NX0011
100 – 0,01A
208 – 240 Vac
NX0012 – NX0420
10 – 0,1A
208 – 240 Vac
NX0530
1 – 1A
380 – 500 Vac
NX0003 – NX0007
100 – 0,01A
380 – 500 Vac
NX0009 – NX0300
10 – 0,1A
380 – 500 Vac
NX0385 – NX2643
1 – 1A
525 – 690 Vac
NX0004 – NX0013
100 – 0,01A
525 – 690 Vac
NX0018 – NX0261
10 – 0,1A
525 – 690 Vac
NX0325 – NX1500
1 – 1A
6.2 Monitoring values description
6.2.1 Monitoring values
V1.1 Output frequency [#,## Hz] ID1
Output frequency to motor, updated at 10 ms time level.
V1.2 Frequency reference [#,## Hz] ID 25
Frequency reference to motor control, after speed share function. updates at 1
ms time level.
V1.3 Motor speed [# rpm] ID 2
Motor speed in rpm
V1.4 Motor current [Unit size dependent A] ID 3
Open loop:
1 s linear filtering.
Closed Loop:
32 ms filtering
Drive Synch Operation Master drive
This value is the total current of the system divided by number of drives in the
system (SbLastID). SbLastId cannot be changed; it needs to be set according to
how many drives are linked with system bus.
Drive Synch Operation Follower drive
This value is the current of the drive’s own power unit.
Current scaling in different size of units
Note: ID45, usually in Process data OUT 3 is scaled to be with one decimal
always.
V1.5 Shaft Power [Torque Scale Dependent %] ID 5
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 27
Classified as Public
Calculated motor power
V1.6 Motor torque [Torque Scale Dependent %] ID 4
In % of Motor nominal torque
Open loop
1 s linear filtering
Closed Loop
32 ms filtering
Drive Synch Operation Follower drive
This value is the torque of the drive’s own power unit related to set motor
nominal current.
V1.7 Motor voltage [#,# V] ID 6
Calculated motor voltage
V1.8 DC link voltage [# V] ID 7
Measured DC voltage, filtered.
V1.9 Unit temperature
C ID 8
Heatsink temperature
V1.10 Motor temperature % or °C ID 9
Calculated motor temperature. 105 % is tripping limit if response is fault.
Motor temperature is calculated in Celsius when motor nom temp rise parameter
(ID 1922) is activated.
T[°C] = MotorTemperature[%]*MotorNomTempRise[°C]/100% + Tamb[°C]
V1.11 Analogue input 1 [#,## %] ID 13
V1.12 Analogue input 2 [ #,## %] ID 14
Unfiltered analogue input level.
0 % = 0 mA / 0 V, -100 % = -10 V, 100 % = 20 mA / 10 V.
Monitoring scaling is determined by the option board parameter.
V1.13 Analogue input 3 [#,## %] ID 27
V1.14 Analogue input 4 [#,## %] ID 28
It is possible to adjust this input value from fieldbus when the input terminal
selection is 0.1. This way it is possible to adjust the free analogue input from
fieldbus and have all analogue input functions available for fieldbus process
data.
V1.15 Analogue Out 1 [#,## %] ID 26
V1.16 Analogue Out 2 [#,## %] ID 31
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

28 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
DIN1/DIN2/DIN3 status
DIN4/DIN5/DIN6 status
b0
DIN3
DIN6
b1
DIN2
DIN5
b2
DIN1
DIN4
V1.17 Analogue Out 3 [#,## %] ID 32
V1.18 Analogue Out 4 [#,## %] ID 1526
Analogue Output value 0 % = 0 mA / 0 V, 100 % = 20 mA / 10 V
V1.19 DIN1, DIN2, DIN3 ID 15
V1.20 DIN4, DIN5, DIN6 ID 16
V1.21 Torque reference % ID 18
Torque reference value before load share.
V1.22 PT-100 Temperature Cº ID 42 [#,#]
Highest temperature of OPTB8 board. 4 s filtering.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 29
Classified as Public
Application Status Word ID43
FALSE
TRUE
b0
Flux not ready
Flux ready (>90 %)
b1
Not in Ready state
Ready
b2
Not Running
Running
b3
No Fault
Fault
b4
Direction Forward
Direction Reverse
b5
Emergency Stop Active
Emergency Stop NOT Active
b6
Run Disabled
Run Enable
b7
No Warning
Warning
b8
b9
b10
b11
No DC Brake
DC Brake is active
b12
No Run Request
Run Request
b13
No Limit Controls Active
Limit control Active
b14
External Brake Control OFF
External Brake Control ON
b15
6.2.2 Monitoring values 2
V1.24.1 Current A ID 1113
Unfiltered motor current, recommended signal for NCDrive monitoring.
Drive Synch Operation Master drive
This value is the total current of the system divided by number of drives in the
system (SbLastID). SbLastId cannot be changed; it needs to be set according to
how many drives are linked with system bus.
Drive Synch Operation Follower drive
This value is current of drive own power unit.
V1.24.2 Torque % ID 1125
Unfiltered motor torque, recommended signal for NCDrive monitoring.
V1.24.3 DC Voltage V ID 44
Unfiltered DC link voltage, recommended signal for NCDrive monitoring.
V1.24.4 Application Status Word ID 43 “Status Word”
Application Status Word combines different drive statuses to one data word.
Recommended signal for NCDrive monitoring.
V1.24.5 Shaft Frequency Hz ID96
V1.24.6 Encoder 1 Frequency Hz ID 1164
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Filtered Encoder frequency, used for speed control
Unfiltered encoder frequency, directly from encoder.

30 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
V1.24.7 Output Power kw ID 1508
Unfiltered electrical drive output power.
V1.24.8 Measured temperature 1 Cº ID 50
V1.24.9 Measured temperature 2 Cº ID 51
V1.24.10 Measured temperature 3 Cº ID 52
V1.24.11 Measured temperature 4 Cº ID 69
V1.24.12 Measured temperature 5 Cº ID 70
V1.24.13 Measured temperature 6 Cº ID 71
Separate measurement from two PT100 board. The signal has 4 s filtering time.
V1.24.14 ABS Encoder Revolutions ID55
Absolute encoder revolution information.
V1.24.15 ABS Encoder Position ID54
Absolute encoder position within one rotation. See encoder manual for scaling.
V1.24.16 Final Frequency Reference Hz ID 1845
Final reference to speed controller. After ramp generator and after Speed Step
function, used for closed loop speed tuning when used together with Encoder 1
frequency.
V1.24.17 Step response Hz ID 1846
Frequency error. Compares ramp output to actual encoder frequency with 0,001
Hz accuracy. Can be used for speed control tuning in closed loop control.
V1.24.18 CosPhiiActual ID 68
Estimated Cos Phii.
V1.24.19 Flux Current % ID 72
Flux current part of the total current. 100 % = Motor Nominal Current.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 31
Classified as Public
ID Run Status ID49
Bit
0
Rs identification, programmable U/f curve
1 Tr/Lm identification at stand still
2 Magnetization current identification run
3 Saturation curve identification run
4 PMSM encoder zero-position identification run
5 Magnetization current default initialisation
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
V1.24.20 ID Run Status ID49
When bit is zero identification has not been done.
V1.24.21 Rotor Flux ID1158
Calculated Rotor Flux
V1.24.22 Step Frequency ID1871
Frequency reference from NCDrive when making the speed controller tuning.
Used together with Step Response monitoring variable.
V1.24.23 Ident Failure Code [Ident Fail. Code] ID 98
Failure code for failed identification:
1 = Current measurement offset
2 = Identification current level
3 = Acceleration time too long
4 = Identification frequency reference not reached
5 = Too low or high magnetization current
6 = Flux curve outside expected levels
7 = PMSM, Encoder zero position
8 = Too low maximum frequency limit
9 = PMSM, encoder zero pulse not found.
10 = Ls Identification timeout
11 = Ls Identification current
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

32 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Limit & Requlators ID77
Signal
b0
Motoring Current Limit
b1
Generator Current Limit
b2
Motoring Torque Limit
b3
Generator Torque Limit
b4
Over Voltage Requlator
b5
Under Voltage Regulator
b6
Positive Speed Controller Limit
b7
Negative Speed Controller Limit
b8
Positive Iq Limit
b9
Negative Iq Limit
b10
b11
b12
b13
b14
b15
Non Ready Cause ID1608
Signal
b0
Fault is Active
b1
Prevent MC Ready is set
b2
Charge switch is open
b3
DC Voltage not OK
b4
Power unit state not OK
b5
Start-up Wizard is active
b6
Run Enable is not set
b7
Ready state prevented by STO
b8
b9
b10
b11
b12
b13
b14
b15
V1.24.24 Limits and Regulators ID77
V1.24.25 Non Ready Cause ID 1608
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 33
Classified as Public
Prevent MC Ready ID1609
Signal
b0
Endat option board (OPTBB, OPTBE) communication is not
initialized after power-up.
b1
Drive sync master has wrong modulator or 1000ms task parameters
are not initialized
b2
Drive sync follower delay is active
b3
Drive sync failure in sw modulator double period mode
b4
Charge switch delay is active
b5
AFE fast run disable through ENC C1 is active
b6
100ms task not executed
b7 b8
b9
b10 b11 b12 b13 b14
b15
V1.24.26 Prevent MC Ready ID 1609
V1.24.27 Serial Number Key ID 1997
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

34 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Bit
Description
Value = 0
Value = 1
0
OFF
ON, Reset after Fault or b1 and b2
1
Coasting Stop
ON, On normal operation: Keep TRUE
2
Quick Stop
ON, On normal operation: Keep TRUE
3
STOP REQUEST
RUN REQUST
4
Force ramp to Zero
Enable Ramp,
5
Freeze Ramp
Enable Ramp,
6
Force Ref to Zero
Enable Ramp,
7
No Action
FAULT RESET (0 -> 1)
8
No Action
Jogging 1
9
No Action
Jogging 2
10
Disable Profibus control
Enable Profibus control
11
Watchdog pulse (Fieldbus
DIN1=OFF)
Watchdog pulse (Fieldbus DIN1=ON)
12
Fieldbus DIN2=OFF
Fieldbus DIN2=ON
13
Fieldbus DIN3=OFF
Fieldbus DIN3=ON
14
Fieldbus DIN4=OFF
Fieldbus DIN4=ON
15
For internal use: FB Fault
FB Communication fault. Always zero with fast
profibus mode.
6.2.3 FieldBus Monitoring values
V1.25.1 FB Control Word ID1160
Control word used in bypass mode. See P2.13.22 and option board ByPass.
V1.25.2 FB Speed Reference ID 875
Speed reference from fieldbus
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 35
Classified as Public
Bit
Description
Value = 0
Value = 1
0
Not ready to switch on
Ready to switch on
1
Not ready to operate
Ready to operate
2
Not Running
Running
3
No Fault
Fault
4
Coast stop Active
Coast stop not active
5
Quick stop active
Quick stop not active
6
Switch not inhibited
Switch on inhibit
7
No Warning
Warning
8
Speed error
Speed At Reference
9
No FB Control request
FB Control Active
10
Fout < P2.6.4.5 Above Speed Lim
Fout > P2.6.4.5 Above Speed Lim
11
SW ID.BIT Selection 1
Updated at 100 ms time level
12
SW ID.BIT Selection 2
Updated at 100 ms time level
13
SW ID.BIT Selection 3
Updated at 100 ms time level
14
SW ID.BIT Selection 4
Updated at 100 ms time level
15
Fieldbus DIN1=OFF
Fieldbus DIN1=ON (Watchdog pulse)
V1.25.3 FB Status Word ID65
PROFIdrive type status word. Generated in the application level.
Selected by P2.13.17 GSW, to be used. When needed with profibus board,
operation mode needs to be set to ByPass in option board and with P2.13.19
ProfiBus Mode select: 2 / ProfiDrive.
V1.25.4 FB Actual Speed ID 865
Actual speed of the drive. Scaled with process speed and FB Reference Scale
parametes.
V1.25.5 FB Torque Reference % ID 1140
Torque reference value from fieldbus
Default Control of FB PD 1
V1.25.6 FB Limit Scaling % ID 46
Limit scaling input value from fieldbus.
Default Control of FB PD 2.
V1.25.7 FB Adjust Reference % ID 47
Reference adjustment value from fieldbus.
Default Control of FB PD 3.
V1.25.8 FB Analog Output % ID 48
Fieldbus value to control analogue output.
Default Control of FB PD 4.
V1.25.9 FB Motor Current A ID 45
Motor current (drive independent) given with one decimal point.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

36 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Fault Word 1 ID1172
Bit
Fault(s)
B0
F1 Over current, F31 IGBT, F41 IGBT
B1
F2 Over Voltage
B2
F9 Under Voltage
B3
F15 Motor Stalled
B4
F3 Earth Fault
B5
F17 Motor Underload
B6
F14 Unit Over Temperature
B7
F16 Motor Temperature, F29 Thermistor,
B8
F10 Input line fault
B9 B10 B11
F52 Keypad or F52 PC communication fault
B12
F53 FieldBus fault
B13
F59 System Bus fault
B14
F54 Slot Communication fault
B15
F50 4mA fault
Fault Word 2 ID1173
Bit
Fault(s)
B0
F11 Output phase
B1
F5 Charge Switch
B2
F43 Encoder Fault
B3 B4 B5
B6
F51 External fault
B7
F12 Brake Chopper
B8
B9
F31 IGBT, F41 IGBT
B10
F58 Brake Fault
B11
F60 Cooling Failure
B12
B13
F8 System Fault
B14
F64 Main Switch
B15
V1.25.10 Fault Word 1 ID 1172
Different faults are collected to two words that can be read from fieldbus or with
NCDrive PC software.
V1.25.11 Fault Word 2 ID 1173
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 37
Classified as Public
Warning Word 1 ID1174
Bit
Warning(s)
B0
W15 Motor Stalled
B1
W16 Motor Over Temperature, W29 Thermistor
B2
W17 Motor Under Load
B3
W10 Input Phase Loss
B4
W11 Output Phase Loss
B5
W30 Safe Torque Off
B6 B7
B8
W14 Unit Over Temperature
B9
W50 4 mA warning
B10
W59 Motor Fan
B11
W63 Quick Stop
B12
W62 Run Disabled
B13
Inching Enabled, no warning indication
B14
W58 Brake Warning
B15
W52 Keypad or W52 PC Communication
Aux Status Word ID1163
Function
Comment
b0
Data Logger triggered
Reserved
b1
Window control active and speed outside of
widow
b2
Motoring or Generator side limits active
b3
Under or over voltage regulator
b4
Reversing
b5
IO Control active
b6
Reserved
b7
Brake Open Command
b8
DC Ready, Pulse
Pulse
b9
Charge SW State
b10
Drive in torque control mode
b11
Speed zero
b12
Reserved
Reserved
b13
Reserved
Reserved
b14
Reserved
Reserved
b15
Reserved
Reserved
V1.25.12 Warning Word 1 ID 1174
V1.25.13 AuxStatusWord ID 1163
V1.25.14 Fault History ID 37
Fault number of the last active fault.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

38 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Aux Control Word ID1161
Function
Comment
b0
Reserved
Reserved
b1
Reserved
Reserved
b2
Bypass ramp
Reserved
b3
Force reference from I/O Ref 2
Reference is taken from I/O Reference 2
b4
Reserved
Reserved
b5
Reserved
Reserved
b6
Reserved
Reserved
b7
Ext brake is forced open
Command to open external brake
unconditionally
b8
Force Ramp Out to zero
Reserved
b9
Reset encoder position
b10
Reserved
Reserved
b11
Reserved
Reserved
b12
Reserved
Reserved
b13
Reserved
Reserved
b14
Reserved
Reserved
b15
Reserved
Quick Stop Acknowledge
DIN StatusWord 1
DIN StatusWord 2
b0
DIN: A.1
DIN: C.5
b1
DIN: A.2
DIN: C.6
b2
DIN: A.3
DIN: D.1
b3
DIN: A.4
DIN: D.2
b4
DIN: A.5
DIN: D.3
b5
DIN: A.6
DIN: D.4
b6
DIN: B.1
DIN: D.5
b7
DIN: B.2
DIN: D.6
b8
DIN: B.3
DIN: E.1
b9
DIN: B.4
DIN: E.2
b10
DIN: B.5
DIN: E.3
b11
DIN: B.6
DIN: E.4
b12
DIN: C.1
DIN: E.5
b13
DIN: C.2
DIN: E.6
b14
DIN: C.3
b15
DIN: C.4
V1.25.15 AuxControlWord ID 1161
V1.25.16 Din Status Word ID 56
V1.25.17 Din Status Word 2 ID 57
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 39
Classified as Public
Motor Control Status Word
FALSE
TRUE
b0
Not in Ready state
Ready
b1
Not Running
Running
b2
Direction Clockwise
Counter clockwise
b3
No Fault
Fault
b4
No Warning
Warning
b5 At reference speed
b6 At Zero Speed
b7 Flux Ready
b8 TC Speed Limiter Active
b9
Encoder Direction
Counter clockwise
b10 Under Voltage Fast stop
b11
No DC brake
DC Brake is active
b12
b13 Restart delay active
b14
b15
V1.25.18 MC Status ID 64
This is the value that is also send to fieldbus on those fieldbus that do not use
own state machine.
V1.25.19 Warning ID 74
Last active warning.
V1.25.20 Shaft Rounds ID 1170
Rounds information from incremental encoder. The value is reset when 24 Vdc is
removed from the drive.
V1.25.21 Shaft Angle ID 1169
Angle information from incremental encoder. The value is reset when 24 Vdc is
removed from the drive.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

40 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Fault Word 10 ID1202
Bit
Warning(s)
B0
W61 Speed Error
B1
B2 B3 B4
W56 PT100 Warning
B5 B6
B7
B8
B9 B10 B11 B12 B13 B14
B15
Warning Word 10 ID1269
Bit
Warning(s)
B0
W61 Speed Error
B1 B2 B3 B4
W56 or W65 PT100 Warning
B5 B6 B7 B8 B9
B10 B11
B12
B13 B14
B15
V1.25.22 Fault Word 10 ID1202
V1.25.23 Warning Word 10 ID1269
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 41
Classified as Public
System Bus Status Word ID1601
FALSE
TRUE
b0 Drive 1 in synch
b1 Drive 1 Ready
b2 Drive 1 Running
b3 Drive 1 Fault
b4 Drive 2 in synch
b5 Drive 2 Ready
b6 Drive 2 Running
b7 Drive 2 Fault
b8 Drive 3 in synch
b9 Drive 3 Ready
b10 Drive 3 Running
b11 Drive 3 Fault
b12 Drive 4 in synch
b13 Drive 4 Ready
b14 Drive 4 Running
b15 Drive 4 Fault
6.2.4 Master / Follower
V1.26.1 SB SystemStatus ID 1601
D1: Status of all (max 4) drives status in system bus.
D2, D3 and D4: Drive own status B0-B3
V1.26.2 Total Current A ID 80
D1: This value is the current of whole drive synch system.
D2, D3 and D4:This value is the sum current of the drive’s own power unit and
that of the drives with smaller system bus identification number starting from
master drive.
If D2 Master: This value is the current of whole drive synch system.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

42 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Master Control Word
Standard Master Follower
Drive Sync operation
b0
Ready Status
b1
Run Enable Command
b2
Final Run Request
b3
Fault Reset
Fault Reset
b4
Running
Running
b5
Fault active
b6
External Brake Control
External Brake Control
b7
Communication WD
Communication WD
b8
Ramp Hold Command
b9
Data logger trig Command
Data logger trig Command
b10
Master in Ramp Stop
b11
Master in Start Delay
b12
Force Ramp out to zero
b13
Emergency Stop Active
b14
Disable MF Diagnostic
Disable MF Diagnostic
b15
Freeze Reference
V1.26.3 Master Control Word ID93
Master Drive Control Word. Master Sending, Follower receiving.
V1.26.4 Master Freq Ref Hz ID1842
Reference before ramp generator. When drive is in follower mode this is
reference send by master drive. If master or a single drive this is the drive own
reference before ramp generator
V1.26.5 Master Ramp Out Hz ID1843
Final frequency reference, after the ramp generator but before speed controller.
When drive is in follower mode this is the reference send by master drive, used
when drive is a ramp follower. If master or a single drive this is the drive own
reference after ramp generator but before speed controller.
V1.26.6 Master Torque Ref % ID1139
Final torque reference after speed controller and torque reference chain. When
drive is in follower mode this is reference send by master drive. If master or a
single drive this is the drive own.
V1.26.7 Master SPC Out % ID1844
Speed Controller output. When drive is in follower mode this is reference send by
master drive. If master or a single drive this is drive own reference.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 43
Classified as Public
V1.26.8.1 Motor Current D1 A ID 1616
D1, D2, D3 and D4: This value is the current of drive own power unit.
V1.26.8.2 Motor Current D2 A ID 1605
D1:This value is the current of drive number two power unit.
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
V1.26.8.3 Motor Current D3 A ID 1606
D1:This value is the current of drive number three power unit.
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
V1.26.8.4 Motor Current D4 A ID 1607
D1: This value is the current of drive number four power unit.
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

44 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Follower Drive status word
FALSE
TRUE
b0
Flux not ready
Flux ready (>90 %)
b1
Not in Ready state
Ready
b2
Not Running
Running
b3
No Fault
Fault
b4 ChargeSwState
b5
b6
Run Disabled
Run Enable
b7
No Warning
Warning
b8
b9
b10 SB Communication OK
b11
No DC Brake
DC Brake is active
b12
No Run Request
Run Request
b13
No Limit Controls Active
Limit control Active
b14
External Brake Control OFF
External Brake Control ON
b15 Heard Beat
V1.26.9.1 Status Word D1 ID 1615
D1: Status Word for D1 without B15
D2,D3 and D4: Status Word that is send to D1.
V1.26.9.2 Status Word D2 ID 1602
D1: D2 Status Word
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
V1.26.9.3 Status Word D3 ID 1603
D1: D3 Status Word
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
V1.26.9.4 Status Word D4 ID 1604
D1: D4 Status Word
D2,D3 and D4: Not updated.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 45
Classified as Public
6.2.5 PI Control monitoring
This PI control uses ID numbers for input and output signal. See detail in PI Control chapter.
V1.27.1 PI Reference ID20
Used PI Reference, reference is selected by ID number.
V1.27.2 PI Actual Value ID21
PI Actual value. Actual input is selected by ID number.
V1.27.3 PI Output ID23
PI Output before scaling. This value uses PI Out High and Low for limiting.
V1.27.3 PI Output Scaled ID1807
Scaled PI Output.
This is used for ID connection. Scaling function is used to scale value more
suitable for connected signal. e.g. when output is connected to torque limit actual
value need to be -1000 ...+1000 (-100,0 %..+100,0 %) But PI Out High and Low
can be from -30000...+30000 to have more accurate PI control.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

46 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
6.2.6 Speed Reference Chain
Monitoring points for speed reference chain in actual order
V1.28.1 Speed Ref 1 rpm ID1126
Speed reference after reference selector, before speed share.
V1.28.2 Speed Ref 2 rpm ID 1127
Speed reference after speed share, before interpolator and filtering
V1.28.3 Speed Ref Actual rpm ID 1128
Speed reference input for ramp controller.
V1.28.4 Speed Ref Ramp Out rpm ID 1129
Speed reference output from ramp controller.
V1.28.5 Speed Ref Step rpm ID 1121
Speed step scaled to rpm.
V1.28.6 Speed Ref Final rpm ID 1131
Speed reference for speed controller.
V1.28.7 Speed Ref Error rpm ID 1132
Speed error, used for speed controller tuning with Speed Ref Step.
V1.28.8 Speed Drooping rpm ID 1147
Rpm value of the drooping function.
V1.28.9 Speed Measured rpm ID 1124
Unfiltered actual speed, directly from encoder.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 47
Classified as Public
6.2.7 Torque Reference Chain
Monitoring points for torque reference chain in actual order
V1.29.1 Torque Reference % ID18
Torque reference after reference selector, before load share.
V1.29.2 Torque Ref. 3 % ID 1144
Torque reference after load share, before filtering and interpolator.
V1.29.3 Torque Ref Final % ID 1145
Final torque reference from torque reference chain.
V1.29.4 Speed Control Out % ID 1134
Torque reference from speed controller.
V1.29.5 Acceleration Compensation % ID 1146
Torque reference from acceleration compensation.
V1.29.6 Torque Ref. Actual % ID 1180
Final torque reference from speed control and torque control. Also includes
torque step and acceleration compensation factors.
6.2.8 SM Excitation Monitor
V1.30.1 Magnetization Reference % 1767
Excitation reference 100 % = No load magnetization.
V1.30.2 Magn Ref AO % 1768
Magnetization reference in analogue output scale. 100 % = 20 mA.
V1.30.3 Magnetization Actual % 1816
Actual Excitation 100 % = No load magnetization
V1.30.4 Magn Act AI % ID1817
Magnetization actual in analogue input scale. 100 % = 20 mA.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

48 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
FALSE
TRUE
b0
Drive ack not accepted
Advanced safety option board will accept ack
from drive
b1
Drive reset not accepted
Advanced safety option board will accept reset
from drive
b2
b3
b4
b5
b6
b7
b8
b9
b10
b11
b12
b13
b14
b15
6.2.9 Functional Safety Monitoring
V1.31.1 Safety App Status ID1653
V1.31.2 Integrity Level ID1640
Safety integrity level (SIL) of drive. Considers presence of OPTAF, control board
version and power unit topology.
Possible values: 0 (no safety), 2 (SIL2), 3 (SIL3). *)
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 49
Classified as Public
FALSE
TRUE
b0
B0 = Start up (STO active)
[ACK-STO-Boot]
b1
B1 = STO [ACK-STO]
b2
B2 = SS1 [ACK-SS1]
b3
B3 = SS2 [ACK-SS2]
b4
B4 = SQS [ACK-SQS]
b5
B5 = SLS [ACK-SLS]
b6
B6 = SSR [ACK-SSR]
b7
B7 = SMS [ACK-SMS]
b8
B8 = SSM [ACK-SSM]
b9
B9 = SAR [ACK-SAR]
b10
B10 = SDI [ACK-SDI]
b11
b12
b13
b14
b15
V1.31.3 Acknowledge Mode ID1641
Bits indicate whether specific safety functions are acknowledged automatically
by advanced safety option board or require acknowledge from outside.
0 = automatic, 1 = manual
V1.31.4 Safety Encoder Speed ID1642
Encoder speed in RPM reported by advanced safety option board.
V1.31.5 Ramp Selection ID1643
B1,B0 = SLS ramp
B3,B2 = SSR ramp
00 = none, 01 = ramp 1, 10 = ramp 2. *)
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

50 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
FALSE
TRUE
b0
STO
b1
SS1 b2
SS2 b3
SQS b4
SSR b5
SLS1
b6
SLS2
b7
SLS3
b8
SDI+
b9
SDI-
b10
SSM
b11
SMS
b12
SAR
b13
SOS b14
SBC b15
FALSE
TRUE
b0
STO b1
SS1 b2
SS2 b3
SQS b4
SSR
b5
SLS1
b6
SLS2
b7
SLS3
b8
SDI+
b9
SDI-
b10
SSM
b11
SMS
b12
SAR b13
b14
b15
V1.31.6 Function Reached ID1644
Advanced safety option board -> Control board safety function status word. For
active functions, indicates if a safety function is reached
V1.31.7 Request DIN ID1645
Advanced safety option board -> Control board safety function request word.
Indicates if a function is requested by Digital input of the advanced safety option
board.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 51
Classified as Public
FALSE
TRUE
b0
STO
b1
SS1 b2
SS2 b3
SQS b4
SSR b5
SLS1
b6
SLS2
b7
SLS3
b8
SDI+
b9
SDI-
b10
SSM
b11
SMS
b12
SAR
b13
b14
b15
FALSE
TRUE
b0
STO
b1
SS1 b2
SS2 b3
SQS b4
SOS b5
SBC b6
SLS b7
SSR b8
SMS
b9
SSM
b10
SAR
b11
SDI b12
b13
b14
b15
V1.31.8 Request PLC ID1646
Advanced safety option board -> Control board safety function request word.
Indicates if a function is requested by safe PLC.
V1.31.9 Function In Use ID1647
Indicates which safety functions have been enabled by configuration
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

52 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
FALSE
TRUE
b0
STO
b1
SS1 b2
SS2 b3
SQS b4
SSR b5
SLS1
b6
SLS2
b7
SLS3
b8
SDI+
b9
SDI-
b10
SSM
b11
SMS
b12
SAR
b13
b14
b15
FALSE
TRUE
b0
DIN1
b1
DIN2
b2
SIN3
b3
SIN4
b4
DOUT1
b5
DOUT2
b6
SSM_Above_Max_Limit
b7
SSM_Below_Max_Limit
b8
Acknowledge_Requested_DIN
b9
Acknowledge_Requested_PLC
b10
Acknowledge_Requested_Drive
b11
SS1_Ramp_Select
b12
SS2_Ramp_Select
b13
Reset_Requested_DIN
b14
Reset_Requested_PLC
b15
Reset_Requested_Drive
V1.31.10 Safety Status Word ID1648
Advanced safety option board -> Control board safety function status word.
Indicates if a safety function is active (being executed). 1 = active, 0 = not active
V1.31.11 Safety General Status Word ID1649
Indicates states of the advanced safety option board input & outputs.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 53
Classified as Public
FALSE
TRUE
b0
StoAtexBoardDetected
b1
StoLinesActivated
b2
StoFault
b3
StoConfigureError
b4
StoDiagnosticFault
b5
StoThermistorActivated
b6
StoThermistorFaultActive
b7
StoThermistorDiagnosticFault
b8
StoThermistorShortCircuitFault
b9
StoChannel1State
b10
StoChannel2State
b11
StartUpPreventActivated
b12
b13
b14
b15
V1.31.12 Safety Status ID1650
V1.31.13 Safety Zero Speed ID1651
Speed value the advanced safety option board uses for determining motor
stoppage.
V1.31.14 SBC Speed rpm ID1652
Indicates the speed the brake is intended to be activated.
If SBC Order = 1 (SBC activated after STO/SOS), SBC will be activated at SBC
Speed or after SBC t1.
If SBC Order = 0 (SBC activated before STO/SOS), SBC Speed is neglected.
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

54 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Baseline Status ID 3622
0
Not Started
1
Running
2
Running 10%
3
Running 20%
4
Running 30%
5
Running 40%
6
Running 50%
7
Running 60%
8
Running 70%
9
Running 80%
10
Running 90%
11
Completed
12
Run Failed
13
Manual run before baseline run completed
14
Manual run after baseline run completed
15
6.2.10 Condition Based Monitoring
V1.32.1.1 Baseline Status ID 3622
Monitoring points for the baseline data. The baseline data is chosen using the baseline data
selector ID 3509.
V1.32.1.2 Baseline Data 1 Hz or % ID 3601
V1.32.1.3 Baseline Data 2 Hz or % ID 3602
V1.32.1.4 Baseline Data 3 Hz or % ID 3603
V1.32.1.5 Baseline Data 4 Hz or % ID 3604
V1.32.1.6 Baseline Data 5 Hz or % ID 3605
V1.32.1.7 Baseline Data 6 Hz or % ID 3606
V1.32.1.8 Baseline Data 7 Hz or % ID 3607
V1.32.1.9 Baseline Data 8 Hz or % ID 3608
V1.32.1.10 Baseline Data 9 Hz or % ID 3609
V1.32.1.11 Baseline Data 10 Hz or % ID 3610
V1.32.2.1 Current Unbalance % ID 3617
Current unbalance value in the stator winding monitoring
V1.32.2.2 Current Threshold Value % ID 3620
Current threshold value after interpolating
V1.32.2.3 Current Warning S1 High % ID 3611
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 55
Classified as Public
The warning S1 high threshold value
V1.32.2.4 Current Warning S2 High % ID 3612
The warning S2 high threshold value
V1.32.2.5 Current Alarm/Fault High % ID 3613
The alarm/fault high threshold value
V1.32.2.6 Voltage Unbalance % ID 3618
Voltage unbalance value in the stator winding monitoring
V1.32.2.7 Voltage Threshold Value % ID 3621
Voltage threshold value after interpolating
V1.32.2.8 Voltage Warning S1 High % ID 3614
The warning S1 high threshold value
V1.32.2.9 Voltage Warning S2 High % ID 3615
The warning S2 high threshold value
V1.32.2.10 Voltage Alarm/Fault High % ID 3616
The alarm/fault high threshold value
V1.32.3.1 Vibration % ID 3623
Vibration value in the condition based monitoring
V1.32.3.2 Vibration Threshold Value % ID 3624
Vibration threshold value after interpolating
V1.32.3.3 Vibration Warning S1 High % ID 3625
The warning S1 high threshold value
V1.32.3.4 Vibration Warning S2 High % ID 3626
The warning S2 high threshold value
V1.32.3.5 Vibration Alarm/Fault High % ID 3627
The alarm/fault high threshold value
V1.32.4.1 Motor Torque % ID 4
In % of Motor nominal torque
V1.32.4.2 Load Threshold Value % ID 3628
Load threshold value after interpolating
V1.32.4.3 Load Warning S1 High % ID 3619
The warning S1 high threshold value
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

56 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Condition Based Status ID 3619
Bit
B0
Stator Winding Current Warning S1
B1
Stator Winding Voltage Warning S1
B2
Vibration Warning S1
B3
Load Warning S1
B4
B5
Stator Winding Current Warning S2
B6
Stator Winding Voltage Warning S2
B7
Vibration Warning S2
B8
Load Warning S2
B9 B10
Stator Winding Current Alarm/Fault
B11
Stator Winding Voltage Alarm/Fault
B12
Vibration Warning Alarm/Fault
B13
Load Warning Alarm/Fault
B14 B15
V1.32.4.4 Load Warning S2 High % ID 3630
The warning S2 high threshold value
V1.32.4.5 Vibration Alarm/Fault High % ID 3631
The alarm/fault high threshold value
V1.32.4.6 Load Warning S1 Low % ID 3632
The warning S1 low threshold value
V1.32.4.7 Load Warning S2 Low % ID 3633
The warning S2 low threshold value
V1.32.4.8 Load Alarm/Fault Low % ID 3634
The alarm/fault low threshold value
V1.32.5 Condition Based Status ID 3619
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 57
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.1.1
Supply Voltage
Varies
Varies V 0
1201
0 = Drive internal logic
P2.1.2
Motor nominal voltage
20
690
V
NX2: 230V
NX5: 400V
NX6: 690V
110
Check the rating plate of the
motor. Note also used
connection Delta/Star
P2.1.3
Motor nominal
frequency
4,00
320,00
Hz
50,00
111
Check the rating plate of the
motor
P2.1.4
Motor nominal speed
5
20 000
rpm
1440
112
The default applies for a 4pole motor and a nominal
size frequency converter.
P2.1.5
Motor nominal
current
0,1 x IH
2 x IH A IH
113
Check the rating plate of the
motor.
P2.1.6
Motor cos
0,30
1,00 0,85
120
Check the rating plate of the
motor
P2.1.7
Motor Nominal
Power
0,0
3200,0
kW
0,0
116
Check the rating plate of the
motor
P2.1.8
Magnetizing current
0,00
100,00 A 0,00
612
0,00 A = Drive uses
estimated value from motor
name plate values
P2.1.9
Identification
0
11 0 631
0=No action
1=Identification w/o run
2=Identification with run
3=Encoder ID Run
4=Ident All
5=Absolute encoder, locked
rotor
6=U/f and Magnetization
7=DTC Identification
NOTE: Set motor control
mode to Freq Control before
identification!
P2.1.10
Motor type
0 4
0 650
0=Induction Motor
1=PMS Motor
2=Sep.Ex SM
3=Reserved
4=SRM
7. SIA-II APPLICATION – PARAMETER LIST
7.1 Basic parameters
Table 7-1. Basic parameters G2.1
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

58 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.1
Process Speed
0,0
6000,0
rpm
1500,0
1203 P2.2.2
FB Ref Scale
0
32000
20000
899
P2.2.3
Torque Scale
0 1
0
1247
0=100,0 %
1=100,00 %
P2.2.4
I/O Reference
0
18 0 117
0=AI1
1=AI2
2=AI1+AI2
3=AI1-AI2
4=AI2-AI1
5=AI1xAI2
6=AI1 Joystick
7=AI2 Joystick
8=Keypad
9=Fieldbus
10=Motor potentiometer
11=AI1, AI2 minimum
12=AI1, AI2 maximum
13=Process Speed
14=AI1/AI2 selection
15=Encoder 1
16=Encoder 2
17=Master Ref
18=Master Ramp
P2.2.5
Keypad reference
selector
0 9 8
121
See par.2.2.4
P2.2.6
Fieldbus control
reference
0 9 9
122
See par.2.2.4
P2.2.7
I/O Reference 2
0
16 1 131
See ID117 & ID422
P2.2.8
Speed Share
-300,00
300,00
%
100,00
1241 P2.2.9
Load Share
0,0
500,0 % 100,0
1248
P2.2.10
Minimum Speed
0
1500
rpm 0
101
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.11.1
Inching speed
reference
0
32000
rpm
150
124
P2.2.11.2
Jogging Reference 1
-32000
32000
rpm
-60
1239
P2.2.11.3
Jogging Reference 2
-32000
32000
rpm
60
1240
P2.2.11.4
Preset speed 1
0.00
320.00
Hz
10.00
105
Multi-step speed 1
P2.2.11.5
Preset speed 2
0.00
320.00
Hz
15.00
106
Multi-step speed 2
P2.2.11.6
Preset speed 3
0.00
320.00
Hz
20.00
126
Multi-step speed 3
P2.2.11.7
Preset speed 4
0.00
320.00
Hz
25.00
127
Multi-step speed 4
P2.2.11.8
Preset speed 5
0.00
320.00
Hz
30.00
128
Multi-step speed 5
P2.2.11.9
Preset speed 6
0.00
320.00
Hz
40.00
129
Multi-step speed 6
P2.2.11.10
Preset speed 7
0.00
320.00
Hz
50.00
130
Multi-step speed 7
7.2 Reference Handling
7.2.1 Basic Settings
7.2.2 Constant Reference
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 59
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.12.1
Torque reference
selection
0
10 0 641
0=Not used
1=AI1
2=AI2
3=AI3
4=AI4
5=AI1 joystick (-10 – 10 V)
6=AI2 joystick (-10 – 10 V)
7=Torque reference from
keypad, R3.5
8=FB Torque Reference
9=Master Torque
10=Master SPC
P2.2.12.2
Torque reference
max.
–300,0
300,0 % 100 642
P2.2.12.3
Torque reference
min.
–300,0
300,0 % 0,0 643
P2.2.12.4
Torque reference
filtering time
0
32000
ms
0 1244
P2.2.12.5
Torque Reference
Dead Zone
0,0
300,0 % 0,00
1246
P2.2.12.6
Torque Reference
Hysteresis
-300,0
300,0 % 0,0
1245
P2.2.12.7
Window negative
0
5000
rpm
2,00
1305 P2.2.12.8
Window positive
0
5000
rpm
2,00
1304 P2.2.12.9
Window negative off
0
P2.2.12.7
rpm
0,00
1307
P2.2.12.10
Window positive off
0
P2.2.12.8
rpm
0,00
1306
P2.2.12.11
Torque Ref Ramp
Time
0
30000
ms
0 1249
P2.2.12.12
Torque step
-100,0
100,0 % 0,0
1253
P2.2.12.13
Torque Reference
Add
-100,0
100,0 % 0,0
1264
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
2.2.12.14.1
Open loop torque
control minimum
speed
0,00
32000
rpm
100
636
2.2.12.14.2
Open loop torque
controller
P gain
0
32000 150
639
2.2.12.14.3
Open loop torque
controller
I gain
0
32000 10 640
7.2.3 Torque Reference
7.2.4 Torque Reference OL Settings
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

60 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.13.1
Prohibit Speed range 1
low limit
-100
32000
rpm
0,00
509
0=Not used
P2.2.13.2
Prohibit Speed range 1
high limit
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
510
0=Not used
P2.2.13.3
Ramp time factor
0,1
10,0 x 1,0
518
Multiplier of the currently
Selected ramp time between
prohibit speed limits.
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.14.1
Motor potentiometer
ramp rate
0,10
200,00
Hz/s
1,00
331
Ramp rate for motor potentio
meter
P2.2.14.2
Motor potentiometer
reference memory reset
0 2 1
367
0=No reset
1=Reset in stop state
2=Reset in powered down
P2.2.14.3
Motor potentiometer
reference copy
0 2 0
366
0=No copy
1=Copy Reference
2=Copy output frequency
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.2.15.1
Adjust input
0 5 0
493
0=Not used
1=AI1
2=AI2
3=AI3
4=AI4
5=Fieldbus
P2.2.15.2
Adjust minimum
0,0
100,0 % 0,0
494
Adjust limit to decrease ref.
P2.2.15.3
Adjust maximum
0,0
100,0 % 0,0
495
Adjust limit to increase ref.
P2.2.15.4
Speed Step
-20000
20000 0
1252
Same scaling as in Fieldbus
reference.
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
7.2.5 Prohibit Speed parameters
Table 7-2. Prohibit Speed (G2.2.12)
7.2.6 Motor Potentiometer
Table 7-3. Motor potentiomer (G2.2.13)
7.2.7 Adjust Reference
7.2.8 Follower
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 61
Classified as Public
P2.2.16.1
Follower Speed
Reference Select
0
18 17
1081
0=AI1
1=AI2
2=AI1+AI2
3=AI1-AI2
4=AI2-AI1
5=AI1xAI2
6=AI1 Joystick
7=AI2 Joystick
8=Keypad
9=Fieldbus
10=Motor potentiometer
11=AI1, AI2 minimum
12=AI1, AI2 maximum
13=Process Speed
14=AI1/AI2 selection
15=Encoder 1
16=Encoder 2
17=Master Reference
18=Master Ramp Out
P2.2.16.2
Follower Torque
Reference Select
0
10 10
1083
0=Not used
1=AI1
2=AI2
3=AI3
4=AI4
5=AI1 joystick (-10 – 10 V)
6=AI2 joystick (-10 – 10 V)
7=Torque reference from
keypad, R3.5
8=FB Torque Reference
9=Master Torque
10=Master SPC
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

62 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.3.1
Start function
0 1
0 505
0=Ramp
1=Flying start
P2.3.2
Stop function
0 1
0 506
0=Coasting
1=Ramp
P2.3.3
Acceleration time 1
0,0
3270,0 s 3,0
103
zero speed to Process Speed
P2.3.4
Deceleration time 1
0,0
3270,0 s 3,0
104
Process Speed to zero speed
P2.3.5
Ramp 1 shape
0
100 % 2 500
0=Linear
>0=S-curve ramp time
P2.3.6
Acceleration time 2
0,0
3270,0 s 10,0
502
P2.3.7
Deceleration time 2
0,0
3270,0 s 10,0
503
P2.3.8
Ramp 2 shape
0
100 % 4 501
0=Linear
>0=S-curve ramp time
P2.3.9
Jogging Inc Ramp
0, 1
320,0 s 1,0
1257
P2.3.10
Jogging Dec Ramp
0,1
320,0 s 1,0
1258
P2.3.11
Jogging Ramp Shape
0
100 % 0
1259
P2.3.12
Jogging Stop Function
0 1
0
1810
0=Coasting
1=Ramp
P2.3.13
Disable Speed Ramp
1815
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.3.13.1
Quick Stop Mode
0 5
0
1276
0=Coasting
1= Ramp
2=Fast Stop
3= Power/Torque Stop
4= Power/Torque and SPC
limit stop
5=Ramp stop with
Power/Torque and SPC
limits.
P2.3.13.2
Quick Stop Ramp
Time
0,1
3200,0 s 5,0
1256
P2.3.13.3
Quick Stop Power
Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1293
P2.3.13.4
Quick Stop Torque
Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1294
P2.3.13.5
IO Quick Stop
Delay
0,00
320,00 s 0,00
1254
P2.3.13.6
Quick stop
acknowledge time
0,00
10,00 s 0,00
1263
P2.3.13.7
Quick Stop
Monitoring
0 3
0
1759
7.3 Ramp Control
7.3.1 Basic Settings
7.3.2 Quick Stop
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 63
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.3.14.1
Ramp: Skip S2
0 1
0
1900
0=No
1= Yes
P2.3.14.2
CL Ramp Follower
Encoder speed
0 1
0
1902
0=No
1= Yes
P2.3.14.3
RampIn
Interpolator TC
0
200
ms
20
1184
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.1.1
Start/Stop logic selection
0 7 5
300
Start signal
1
(Default:
DIN1)
Start signal
2
(Default:
DIN2)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Start fwd
Start/Stop
Start/Stop
Start pulse
Start
Start fwd*
Start*/Stop
Start*/Stop
Start rvs
Reverse
Run enable
Stop pulse
Mot.Pot UP
Start rvs*
Reverse
Run Enable
* = Rising edge required to start
7.3.3 Ramp Control Options
7.4 Input Signals
7.4.1 Basic Settings
Table 7-4. Input signals: basic settings, G2.2.1
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

64 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.2.1
Start signal 1
0.1
A.1 403
Forward, See ID300
P2.4.2.2
Start signal 2
0.1
A.2 404
Reverse. See ID300
P2.4.2.3
Run enable
0.1
0.2 407
Motor start enabled (cc)
P2.4.2.4
Reverse
0.1
0.1 412
Direction forward (oc)
Direction reverse (cc)
P2.4.2.5
Motor potentiometer reference
DOWN
0.1
0.1 417
Mot.pot. reference decreases (cc)
P2.4.2.6
Motor potentiometer reference
UP
0.1
0.1 418
Mot.pot. reference increases (cc)
P2.4.2.7
Fault reset
0.1
0.1 414
All faults reset (cc)
P2.4.2.8
External fault 1
0.1
0.1 405
Ext. fault displayed
P2.4.2.9
External fault 2
0.1
0.2 406
Ext. fault displayed
P2.4.2.10
Acc/Dec time selection
0.1
0.1 408
Acc/Dec time 1 (oc)
Acc/Dec time 2 (cc)
P2.4.2.11
Acc/Dec prohibit
0.1
0.1 415
Acc/Dec prohibited (cc)
P2.4.2.12
DC braking
0.1
0.1 416
DC braking active (cc)
P2.4.2.13
Inching speed
0.1
0.1 413
Inching speed selected for reference
(cc)
P2.4.2.14
IO reference 1 / 2 selection
0.1
0.1 422
IO reference selection:14 ID117
P2.4.2.15
Control from I/O terminal
0.1
0.1 409
Force control place to I/O terminal
(cc)
P2.4.2.16
Control from keypad
0.1
0.1 410
Force control place to keypad (cc)
P2.4.2.17
Control from fieldbus
0.1
0.1 411
Force control place to fieldbus (cc)
P2.4.2.18
Parameter set 1/set 2 selection
0.1
0.1 496
Closed cont.=Set 2 is used
Open cont.=Set 1 is used
P2.4.2.19
External Brake Acknowledge
0.1
0.2 1210
Monitoring signal from mechanical
brake
P2.4.2.20
Cooling Monitor
0.1
0.2 750
Used when water cooled unit
P2.4.2.21
Enable Jogging
0.1
0.1 532
Enables Jogging function
P2.4.2.22
Jogging 1
0.1
0.1 531
Jogging reference 1
This will start the drive.
P2.4.2.23
Jogging 2
0.1
0.1 532
Jogging reference 2
This will start the drive.
P2.4.2.24
Reset Position
0.1
0.1 1090
P2.4.2.25
Quick Stop
0.1
A.6 1213
P2.4.2.26
Input Switch Acknowledge
0.1
A.5 1209
P2.4.2.27
Max Speed 2
0.1
0.1 1511 P2.4.2.28
PI Activations
0.1
0.1 1804 P2.4.2.29
Motor Fan Acknowledge
0.1
0.1 1211 P2.4.2.30
Disable Positive Speed
0.1
0.2 1813
P2.4.2.31
Disable Negative Speed
0.1
0.2 1814
P2.4.2.32
Preset speed 1
0.1
0.1 419
See preset speeds in basing parameter
group G2.2.11
P2.4.2.33
Preset speed 2
0.1
0.1 420
P2.4.2.34
Preset speed 3
0.1
0.1 421
cc = closing contact
oc = opening contact
7.4.2 Digital inputs
Table 7-5. Digital input signals, G2.2.4
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 65
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.3.1
AI1 signal selection
0.1
E.10 A.1
377
Slot . Board input No.
P2.4.3.2
AI1 filter time
0,000
32,000
s
0,000
324
0=No filtering
P2.4.3.3
AI1 signal range
0 3
0
320
0=0…100%*
1=20…100%* 4 mA Fault
2= -10V…+10V*
3= Custom range*
P2.4.3.4
AI1 custom minimum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
0,00
321
Custom Range:
Minimum input
P2.4.3.5
AI1 custom maximum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
100,00
322
Custom Range:
Maximum input
P2.4.3.6
AI1 reference scaling,
minimum value
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
303
Selects the speed that
corresponds to the min.
reference signal
P2.4.3.7
AI1 reference scaling,
maximum value
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
304
Selects the speed that
corresponds to the max.
reference signal
P2.4.3.8
AI1 joystick Dead Zone
0,00
20,00
%
0,00
384
Dead Zone for joystick input
P2.4.3.9
AI1 sleep limit
0,00
100,00
%
0,00
385
Drive goest to stop if input
is below this limit for this
time.
P2.4.3.10
AI1 sleep delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
386
P2.4.3.11
AI1 joystick offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
165
Press enter for 1s to set
offset
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.4.1
AI2 signal selection
0.1
E.10 A.2
388
Slot . Board input No.
P2.4.4.2
AI2 filter time
0,000
32,000
s
0,000
329
0=No filtering
P2.4.4.3
AI2 signal range
0 3
1
325
0=0…100%*
1=20…100%* 4 mA Fault
2= -10V…+10V*
3= Custom range*
P2.4.4.4
AI2 custom minimum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
0,00
326
Custom Range:
Minimum input
P2.4.4.5
AI2 custom maximum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
100,00
327
Custom Range:
Maximum input
P2.4.4.6
AI2 reference scaling,
minimum value
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
393
Selects the speed that
corresponds to the min.
reference signal
P2.4.4.7
AI2 reference scaling,
maximum value
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
394
Selects the speed that
corresponds to the max.
reference signal
P2.4.4.8
AI2 joystick Dead
Zone
0,00
20,00
%
0,00
395
Dead Zone for joystick input
P2.4.4.9
AI2 sleep limit
0,00
100,00
%
0,00
396
Drive goest to stop if input
is below this limit for this
time.
P2.4.4.10
AI2 sleep delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
397
P2.4.4.11
AI2 joystick offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
166
Press enter for 1s to set
offset
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
*Remember to place jumpers of block X2 accordingly. See
NX User's Manual, chapter 6.2.2.2
7.4.3 Analogue input 1
Table 7-6. Analogue input 1 parameters, G2.2.2
7.4.4 Analogue input 2
Table 7-7. Analogue input 2 parameters, G2.2.3
7.4.5 Analogue input 3
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

66 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
P2.4.5.1
AI3 signal selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
141
Slot . Board input No.
If 0.1 ID27 can be
controlled from FB
P2.4.5.2
AI3 filter time
0,000
32,000
s
0,000
142
0=No filtering
P2.4.5.3
AI3 custom minimum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
0,00
144
Custom range always
active.
P2.4.5.4
AI3 custom maximum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
100,00
145
Custom range always
active.
P2.4.5.5
AI3 signal inversion
0 1
0 151
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.4.5.6
AI3 reference scaling,
minimum value
-32000
32000 0
1037
Selects the value that
corresponds to the min.
reference signal
P2.4.5.7
AI3 reference scaling,
maximum value
-32000
32000 0
1038
Selects the value that
corresponds to the max.
reference signal
P2.4.5.8
AI3 Controlled ID
0
10000 0
1509
Select parameter that you
want to control by ID
number.
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.6.1
AI4 signal selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
152
Slot . Board input No.
If 0.1 ID28 can be
controlled from FB
P2.4.6.2
AI4 filter time
0,000
32,000
s
0,000
153
0=No filtering
P2.4.6.3
AI4 custom minimum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
0,00
155
Custom range always
active.
P2.4.6.4
AI4 custom maximum
setting
-160,00
160,00
%
100,00
156
Custom range always
active.
P2.4.6.5
AI4 signal inversion
0 1
0 162
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.4.6.6
AI3 reference scaling,
minimum value
-32000
-32000 0
1039
Selects the value that
corresponds to the min.
reference signal
P2.4.6.7
AI3 reference scaling,
maximum value
-32000
32000 0
1040
Selects the value that
corresponds to the max.
reference signal
P2.4.6.8
AI4 Controlled ID
0
10000 0
1510
Select parameter that you
want to control by ID
number.
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.4.7.1
Input signal inversion
Control
0
65535 1091
**Remember to place jumpers of block X2 accordingly. See
NX User's Manual, chapter 6.2.2.2
Table 7-8. Analogue input 3 parameters, G2.2.4
7.4.6 Analogue input 4
Table 7-9. Analogue input 4 parameters, G2.2.5
7.4.7 Options
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 67
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.1.1
Ready
0.1
0.1
432
Ready to Run
P2.5.1.2
Run
0.1
0.1
433
Running
P2.5.1.3
Fault
0.1
0.1
434
Drive in fault state
P2.5.1.4
Inverted fault
0.1
0.1
435
Drive not in fault state
P2.5.1.5
Warning
0.1
0.1
436
Warning active
P2.5.1.6
External fault
0.1
0.1
437
External fault active
P2.5.1.7
Reference fault/warning
0.1
0.1
438
4 mA fault active
P2.5.1.8
Over temperature warning
0.1
0.1
439
Drive over temperature active
P2.5.1.9
Reverse
0.1
0.1
440
Output speed < 0 rpm
P2.5.1.10
Unrequested direction
0.1
0.1
441
Reference <> Speed
P2.5.1.11
At speed
0.1
0.1
442
Reference = Speed
P2.5.1.12
Inching speed
0.1
0.1
443
Inching speed command
active
P2.5.1.13
External control place
0.1
0.1
444
IO control active
P2.5.1.14
External brake control
0.1
0.1
445
See explanations on page
Error! Bookmark not
defined..
P2.5.1.15
External brake control,
inverted
0.1
0.1
446
P2.5.1.16
Motor thermal protection
0.1
0.1
452
Thermistor fault or warning
P2.5.1.17
Motor regulator activation
0.1
0.1
454
One of limit controller is
active
P2.5.1.18
Fieldbus digital input 1
0.1
0.1
455
FB CW B11
P2.5.1.19
FB Dig 1 Parameter
ID0
ID0
891
Select parameter to control
P2.5.1.20
Fieldbus digital input 2
0.1
0.1
456
FB CW B12
P2.5.1.21
FB Dig 2 Parameter
ID0
ID0
892
Select parameter to control
P2.5.1.22
Fieldbus digital input 3
0.1
0.1
457
FB CW B13
P2.5.1.23
FB Dig 3 Parameter
ID0
ID0
893
Select parameter to control
P2.5.1.24
Fieldbus digital input 4
0.1
0.1
169
FB CW B14
P2.5.1.25
FB Dig 4 Parameter
ID0
ID0
894
Select parameter to control
P2.5.1.26
Fieldbus digital input 5
0.1
0.1
170
FB CW B15
P2.5.1.27
FB Dig 5 Parameter
ID0
ID0
895
Select parameter to control
P2.5.1.28
Safe Disable Active
0.1
0.1
756
P2.5.1.29
MCC Close Cont
0.1
0.1
1218
P2.5.1.30
MCC Close Pulse
0.1
0.1
1219
P2.5.1.31
Motor Fan Control
0.1
0.1
1805
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.2.1
Analogue output 1
signal selection
0.1
E.10 A.1
464
TTF programming
See chapter 3.1 and 3.2
P2.5.2.2
Analogue output 1
function
0
18 0
307
0=Not used (4 mA / 2 V)
1=Output freq. (0—f
max
)
2=Freq. reference (0—f
max
)
3=Motor speed (0—Motor
nominal speed)
4=Motor current (0—I
nMotor
)
5=Motor torque (0—T
nMotor
)
6=Motor power (0—P
nMotor
)
7=Motor voltage (0-U
nMotor
)
8=DC-link volt (0—1000V)
9=AI1
10=AI2
7.5 Output Signals
7.5.1 Digital output signals
7.5.2 Analogue output 1
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

68 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
11=Output freq. (f
min
- f
max
)
12=-2xTorque…+2xTorque
13=-2xPower…+2xPower
14=PT100 temperature
15=FB Analog Output
16= -2xSpeed…+2xSpeed
17= Encoder speed (0—
Motor nominal speed)
18=Unit Temperature
P2.5.2.3
Analogue output 1 filter
time
0,00
10,00
s
1,00
308
0=No filtering
P2.5.2.4
Analogue output 1
inversion
0 1 0
309
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.5.2.5
Analogue output 1
minimum
0 1 0
310
0=0 mA (0 %)
1=4 mA (20 %)
P2.5.2.6
Analogue output 1
scale
10
1000 % 100
311
P2.5.2.7
Analogue output 1
offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
375
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.3.1
Analogue output 2
signal selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
471
TTF programming
See chapter 3.1 and 3.2
P2.5.3.2
Analogue output 2
function
0
18 0
472
See P2.5.2.2
P2.5.3.3
Analogue output 2 filter
time
0,00
10,00
s
1,00
473
0=No filtering
P2.5.3.4
Analogue output 2
inversion
0 1 0
474
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.5.3.5
Analogue output 2
minimum
0 1 0
475
0=0 mA (0 %)
1=4 mA (20 %)
P2.5.3.6
Analogue output 2
scale
10
1000 % 100
476
P2.5.3.7
Analogue output 2
offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
477
Table 7-10. Analogue output 1 parameters, G2.3.5
7.5.3 Analogue output 2
Table 7-11. Analogue output 2 parameters, G2.3.6
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 69
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.4.1
Analogue output 3
signal selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
478
TTF programming
See chapter 3.1 and 3.2
P2.5.4.2
Analogue output 3
function
0
18 0
479
See P2.5.2.2
P2.5.4.3
Analogue output 3 filter
time
0,00
10,00
s
1,00
480
0=No filtering
P2.5.4.4
Analogue output 3
inversion
0 1 0
481
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.5.4.5
Analogue output 3
minimum
0 1 0
482
0=0 mA (0 %)
1=4 mA (20 %)
P2.5.4.6
Analogue output 3
scale
10
1000 % 100
483
P2.5.4.7
Analogue output 3
offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
484
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.5.1
Analogue output 4
signal selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
1527
TTF programming
See chapter 3.1 and 3.2
P2.5.5.2
Analogue output 4
function
0
18 0
1520
See P2.5.2.2
P2.5.5.3
Analogue output 4 filter
time
0,00
10,00
s
1,00
1521
0=No filtering
P2.5.5.4
Analogue output 4
inversion
0 1 0
1522
0=Not inverted
1=Inverted
P2.5.5.5
Analogue output 4
minimum
0 1 0
1523
0=0 mA (0 %)
1=4 mA (20 %)
P2.5.5.6
Analogue output 4
scale
10
1000 % 100
1525
P2.5.5.7
Analogue output 4
offset
-100,00
100,00
%
0,00
1524
7.5.4 Analogue output 3
Table 7-12. Analogue output 3 parameters, G2.3.7
7.5.5 Analogue output 4
Table 7-13. Analogue output 4 parameters, G2.3.8
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

70 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.6.1
Digital output 1 signal
selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
486
Posibility to invert by
ID1091 INV Commands
P2.5.6.2
Digital output 1
function
0
28 1
312
0=Not used
1=Ready
2=Run
3=Fault
4=Fault inverted
5=FC overheat warning
6=Ext. fault or warning
7=Ref. fault or warning
8=Warning
9=Reverse
10=Jogging or inching
11=At speed
12=Mot. regulator active
13=Not used
14= Not used
15= Not used
16= Not used
17=External brake control
18=I/O control place act.
19= Not used
20=Reference inverted
21=Ext. brake control
inverted
22=Therm. fault or warn.
23= Not used
24=Fieldbus input data 1
25=Fieldbus input data 2
26=Fieldbus input data 3
27=Warning Set Reset
28=ID.Bit Select
P2.5.6.3
Digital output 1 on
delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
487
0,00 = On delay not in use
P2.5.6.4
Digital output 1 off
delay
0,00
320,00
s
0.00
488
0,00 = Off delay not in use
P2.5.6.5
Invert delayed DO1
0 1 0
1587
0=No
1=Yes
P2.5.6.6
ID.Bit Free DO
0,00
2000,15
0,00
1216
P2.5.6.7
DDO1 Feed Back
0.1
E.10 0.1
1326
P2.5.6.8
Feed Back Delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
1808
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.5.7.1
Digital output 2 signal
selection
0.1
E.10 0.1
489
Possibility to invert by
ID1091 INV Commands
P2.5.7.2
Digital output 2
function
0
28 0
490
See P2.5.6.2
P2.5.7.3
Digital output 2 on
delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
491
0,00 = On delay not in use
P2.5.7.4
Digital output 2 off
delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
492
0,00 = Off delay not in use
P2.5.7.5
Invert delayed DO2
1588
0=No
1=Yes
P2.5.7.6
ID.Bit Free DO
0,00
2000,15
0,00
1385
P2.5.7.7
DDO2 Feed Back
0.1
E.10 0.1
1277
P2.5.7.8
Feed Back Delay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
1809
7.5.6 Delayed digital output 1
Table 7-14. Delayed digital output 1 parameters, G2.3.1
7.5.7 Delayed digital output 2
Table 7-15. Delayed digital output 2 parameters, G2.3.2
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 71
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.1.1
Current limit
0
2 x IH A IL 107
Limit will lower frequency
P2.6.1.2
Current Limit Kp
1
32000 1451
P2.6.1.3
Current Limit Ki
1
32000 1452
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.2.1
Power Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1722
General power limit
P2.6.2.2
Generator Power Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1290
P2.6.2.3
Motoring Power Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1289
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.3.1
Torque Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
609
General maximum limit
P2.6.3.2
Motoring Torque Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1287
Motoring side torque limit
P2.6.3.3
Generator Torque Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1288
Generator side torque limit
P2.6.3.4
Pull Out Slip Limit
0,0
3270,0
%
500,0
1291
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.3.5.1
Torque limit control P-
gain
0,0
32000 3000
610
P2.6.3.5.2
Torque limit control
I-gain
0,0
32000 200
611
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.3.6.1
SPC Out Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1382
P2.6.3.6.2
SPC Pos Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
646
P2.6.3.6.3
SPC Neg Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
645
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.4.1
Negative speed limit
-30000
P2.6.4.2
rpm
0 1286
Alternative limit for negative
direction
P2.6.4.2
Positive speed limit
P2.6.4.1
30000
rpm
1500
1285
Alternative limit for positive
direction
P2.6.4.3
Zero speed limit
0
30000
rpm
5 1283
P2.6.4.4
Max speed 2
0
320,00
Hz
750
1512
Maximum speed limit that is
activated by digital input.
P2.6.4.5
Above Speed Lim
0
32000
rpm
1500
1251
Will set FB SW B10
7.6 Limit Settings
7.6.1 Current handling
7.6.2 Power Handling
7.6.3 Torque Handling
7.6.3.1 Torque Handling OL Settings
7.6.3.2 Torque Handling CL Settings
7.6.4 Speed Handling
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

72 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.5.1
Overvoltage controller
0 2
1 607
0=Not used
1=Used (no ramping)
2=Used (ramping)
P2.6.5.2
Over Voltage
Reference selector
0 2
1
1262
0=High Voltage
1=Normal Voltage
2=BrakeChopperLevel
P2.6.5.3
Over Voltage Kp
0
32765 2000
1468
P2.6.5.4
Over Voltage Ki
0
32765 50
1409
P2.6.5.5
Over Voltage Kp Add
0
32765 2000
1425
P2.6.5.6
Brake chopper
0 4
0 504
0=Disabled
1=Used when running
2=External brake chopper
3=Used when stopped/running
4=Used when running (no
testing)
P2.6.5.7
Brake Chopper Level
0
1267
V
Varies
1267
500 V unit: 567 Vdc
6690 V unit: 836 Vdc
P2.6.5.8
Brake Resistor Torque
Limit
0,0
300,0 % 300,0
1268
P2.6.5.9
Undervoltage controller
0 2
1 608
0=Not used
1=Used (no ramping)
2=Used (ramping to zero)
P2.6.5.10
Under Voltage Kp
0
32765 4000
1415
P2.6.5.11
Under Voltage Ki
0
32765 400
1416
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.5.12.1
Over voltage
reference
513
1210
V
Varies
1528
P2.6.5.12.2
Over voltage
motoring side torque
limit
0,0
300,0 % 10,0
1623
Maximum motoring torque
when over voltage controller is
active.
P2.6.5.12.3
Under Voltage Ref
425
931 V Varies
1567
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.6.6.1
Limit Total Current In
Closed Loop
0 1
0
1901
0=No
1=Yes
7.6.5 DC-Link Handling
7.6.5.1 DC-Link Handling CL Settings
7.6.5.2 Limit Settings Options
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 73
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.7.1.1
DC braking current
0,00
IL A 0,00
507
P2.7.1.2
DC braking time
at start
0,00
600,00 s 0,00
516
0=DC brake is off at start
P2.7.1.3
DC braking time
at stop
0,00
600,00 s 0,00
508
0=DC brake is off at stop
P2.7.1.4
Speed to start DC
braking during
ramp stop
0
1000
rpm
1 515
P2.7.1.5
Scaling of DC-braking
current
0 5
0 400
Scaling from 0 to ID507
0=Not used
1=AI1
2=AI2
3=AI3
4=AI4
5=FB Limit Scaling
P2.7.1.6
DC-Brake Current in
Stop
0,00
IL A Varies
1080
P2.7.1.7
Flux brake
0 1
0 520
0=Off
1=On
P2.7.1.8
Flux braking current
0,00
IL A IH 519
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.7.2.1
Magnetizing current at
start
0
IL A 0,00
627
P2.7.2.2
Magnetizing time at start
0,0
600,0 s 0,0
628
P2.7.2.3
Flux Reference
0,0
500,0 % 100,0
1250
P2.7.2.4
Flux Off Delay
-1
32000 s 0
1402
-1=forever
P2.7.2.5
Stop State Flux
0,0
150,0 % 100,0
1401
7.7 Flux and DC Current handling
7.7.1 Flux and DC Current handling OL Settings
7.7.2 Flux and DC Current handling CL Settings
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

74 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.1
Motor control mode
0 4
0 600
0=Frequency control
1=Speed control
2=Speed/Torque control
3=Closed loop speed ctrl
4=Closed loop Speed/torque
ctrl
P2.8.2
Torque Select
1 5
1
1278
1=Speed Control
2=Torque
3=Min
4=Max
5=Window
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.3.1
U/f optimisation
0 1
0 109
0=Not used
1=Automatic torque boost
P2.8.3.2
U/f ratio selection
0 3
0 108
0=Linear
1=Squared
2=Programmable
3=Linear with flux optim.
P2.8.3.3
Field weakening point
4,00
320,00
Hz
50,00
602
P2.8.3.4
Voltage at field
weakening point
10,00 200,00
%
100,00
603
n% x U
nmot
P2.8.3.5
U/f curve midpoint
frequency
0,00
P2.6.4
Hz
50,00
604 P2.8.3.6
U/f curve midpoint
voltage
0,00
100,00
%
100,00
605
n% x U
nmot
Parameter max. value = P2.6.5
P2.8.3.7
Output voltage at zero
frequency
0,00
40,00 % 0,00
606
n% x U
nmot
P2.8.4.8
I/f Start
0 1
0 534
0=Disabled
1=Enabled
P2.8.4.9
I/f Current
0.0
150.0 % 50.0
1693
P2.8.4.10
I/f Control Limit
0.0
300.0 % 10.0
1790
P2.8.3.11
MakeFluxTime
0
32000
ms
200
660
7.8 Motor Control
7.8.1 Motor Control Basic Settings
7.8.2 Open Loop
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 75
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.4.1
Current control
P gain
0,00
100,00
%
40,00
617 P2.8.4.2
Current control
I Time
0,0
3200,0
ms
1,5
657
P2.8.4.3
Encoder Selection
0 1
0
1595
0=Encoder Input 1
1=Encoder Input 2
P2.8.4.4
Motor Temperature
Compensation mode
0 2
0
1426
0=Not used
1=Internal
2=Measured Temperature
P2.8.4.5
Slip adjust
0
500 % 75
619 P2.8.4.6
Slip Adjust Cold
0
500 % 75
1183
P2.8.4.7
SC Torque Chain Select
0
65535 0
1557
Default 96 after identification.
P2.8.4.8
TC Speed Limit Select
0
65535 0
1568
P2.8.4.9
TCDunDampGain
0,00
100,00 % 0,00
1576
P2.8.4.10
TCDynDampTC
0
32000
ms 0
1577
7.8.3 Closed Loop Control Settings
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

76 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.5.1
PMSM Shaft
Position
0
65535 0
649
P2.8.5.2
Start Angle
Identification mode
0
10 0
1691
0=Automatic
1=Forced
2=After Power Up
3=Disabled
P2.8.5.3
Start Angle
Identification DC
Current
0,0
150,0 % 0,0
1756
P2.8.5.4
Polarity Pulse
Current
-10,0
200,0 % 0,0
1566
P2.8.5.5
Start Angle ID Time
0
32000
ms
0
1755
P2.8.5.6
I/f Current
0,0
150,0 % 50,0
1693
P2.8.5.7
I/f Control Limit
0,0
300,0 % 10,0
1790
P2.8.5.8
Flux Current Kp
0
32000
5000
651
P2.8.5.9
Flux Current Ti
0
1000 25
652
P2.8.5.10
External Id
Reference
-150,0
150,0 % 0,0
1730
P2.8.5.11
Enable Rs
Identification
0 1
1
654
0=No
1=Yes
P2.8.5.12
Lsd Voltage Drop
-32000
32000 0
1757
P2.8.5.13
Lsq Voltage Drop
-32000
32000 0
1758
P2.8.6.14
EncIDCurrent
0.0
150.0 % 90.0
1734 P2.8.6.15
Polarity ID Mode
0 1
1737
P2.8.6.16
Polarity Pulse
Length
0
1000
ms
200
1742 P2.8.6.17
Polarity Detection
Angle
0.0
360.0
Deg
1.5
1748
P2.8.6.18
Angle
Identification
Mode
0 2
1749
P2.8.6.19
Current Control
Kp d
0
32000 %
1761
P2.8.6.20
Voltage Margin
0.0
120.0 %
1759
P2.8.6.21
Encoder ID Run
Mode
0 2 0
680
P2.8.6.22
Start Angle Offset
-360,0
360,0
Dec
0,0
696 P2.8.6.23
VoltageCorr. Kp
0,000
32,000
0,100
1783
P2.8.6.24
VoltageCorr. Ki
0
32000
5000
1784
7.8.4 PMSM Control settings
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 77
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.6.1
Torque Stabilator
Damping
0
1000 800
1413
With PMSM use 980
P2.8.6.2
Torque Stabilator Gain
0
1000 100
1412
P2.8.6.3
Torque Stabilator Gain
in FWP
0
1000 50
1414
P2.8.6.4
Torque Stabilator Limit
0
1500 150
1720
P2.8.6.5
Flux Circle Stabilator
Gain
0
32767
10000
1550
P2.8.6.6
Flux Stabilator Gain
0
32000 500
1797
P2.8.6.7
Flux Circle Stabilator
TC
0
32700 900
1551
P2.8.6.8
Voltage Stabilator TC
0
1000 900
1552
P2.8.6.9
Voltage Stabilator Gain
0
100,0 % 10,0
1738
P2.8.6.10
Voltage Stabilator
Limit
0
320,00
Hz
1,50
1553
7.8.5 Stabilators
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

78 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.7.1
Fly Start Options
0
65535 0 1610
P2.8.7.2
MC Options
0
65535 0 1740
P2.8.7.3
Resonance Damping
Select
0
11 0 1760
0=Not in Use
1=BandPass (Speed)
2=BandStop+BandPass.
(Speed)
11=BandPass (Iq Actual)
P2.8.7.4
Damping Frequency
0,0
450,0
Hz
0,0
1763 P2.8.7.5
Damping Gain
0
32000 0 1764 P2.8.8.6
Damping Phase
0
360 0,00
1765
P2.8.7.7
Damping Activation
Frequency
0
320,00 % 0 1770
P2.8.7.8
Damping Filter Time
Constant
0
32700 105
1771
P2.8.7.9
Over Modulation Limit
50
120 % 105
1515
If you have sini filter in use set
this to 101 %
P2.8.7.10
Modulator Index Limit
0
200 % 100
655
P2.8.7.11
DC Voltage Filter
0,0
500,0
Hz
0,0
1591
P2.8.7.12
Process Frequency
0,00
320,00
Hz
0,00
1811
Keep zero if Process Speed is
used
P2.8.7.13
GearRatioMultipl
0
32000 1 1558
P2.8.7.14
GearRatioDivider
0
32000 1 1559
7.8.6 Tuning parameters
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 79
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.8.1
Flux 10 %
0
2500 % 10
1355
P2.8.8.2
Flux 20 %
0
2500 % 20
1356
P2.8.8.3
Flux 30 %
0
2500 % 30
1357
P2.8.8.4
Flux 40 %
0
2500 % 40
1358
P2.8.8.5
Flux 50 %
0
2500 % 50
1359
P2.8.8.6
Flux 60 %
0
2500 % 60
1360
P2.8.8.7
Flux 70 %
0
2500 % 70
1361
P2.8.8.8
Flux 80 %
0
2500 % 80
1362
P2.8.8.9
Flux 90 %
0
2500 % 90
1363
P2.8.8.10
Flux 100 %
0
2500 % 100
1364
P2.8.8.11
Flux 110 %
0
2500 % 110
1365
P2.8.8.12
Flux 120 %
0
2500 % 120
1366
P2.8.8.13
Flux 130 %
0
2500 % 130
1367
P2.8.8.14
Flux 140 %
0
2500 % 140
1368
P2.8.8.15
Flux 150 %
0
2500 % 150
1369
P2.8.8.16
Rs voltage drop
0
30000
Varies
662
Used for torque calculation
in open loop
P2.8.8.17
Ir add zero point
voltage
0
30000
Varies
664
P2.8.8.18
Ir add generator
scale
0
30000
Varies
665
P2.8.8.19
Ir add motoring
scale
0
30000
Varies
667
P2.8.8.20
Ls Voltage Dropp
0
3000 0
673
P2.8.8.21
Motor BEM
Voltage
0,00
320,00 % 0
674
P2.8.8.22
Iu Offset
-32000
32000 0
668
P2.8.8.23
Iv Offset
-32000
32000 0
669
P2.8.8.24
Iw Offset
-32000
32000 0
670
P2.8.8.25
Estimator Kp
0
32000 400
1781
P2.8.8.26
Estimator Ki
0
32000
1782
P2.8.8.27
Voltage Drop
0
2000 671
P2.8.8.28
ID Run Current
Kp
695
P2.8.8.29
DeadTimeComp.
1751
P2.8.8.30
DeadTieContCur
L
1752
7.8.7 Identification parameters
Table 7-16. Identification parameters, G2.6.4
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

80 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P 2.8.9.1
DeadTHWCompDisab
1750
P 2.8.9.2
CurrMeasFCompTC
1554 P 2.8.9.3
CurrLimOptions
1702 P 2.8.9.4
AdConvStartShift
1701 P 2.8.9.5
DCVoltageBalGain
1519
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.10.1
No Load
Magnetization Current
0,0
3200 A 0,0
1966
P2.8.10.2
Magnetization Current
Limit
0,0
3200 A 0,0
1973
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.10.3.1
Magnetization
Reference offset
-100,0
100,0 % 0,0
1872
P2.8.10.3.2
CosPhii Kp
0,0
3200,0
%
50,0
1975 P2.8.10.3.3
CosPhii Ti
0,0
3200,0
ms
50,0
1976 P2.8.10.3.4
Flux Control Kp
0,0
3000,0
%
400,0
1772
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.10.4.1
Magnetization
Reference AO
0.1
E.10
AnOUT
0.1
1963
P2.8.10.4.2
20 mA Reference
0,0
500,0
%
330,0
1971
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.10.5.1
Magnetization Actual
AI
0.1
E.10
AnIN
0.1
1964
P2.8.10.5.2
Magn AI Nom Level
0
320 % 44,25
1974
P2.8.10.5.3
20 mA Actual
0,0
3200,0 A 0,0
1965
P2.8.10.5.4
Magn Act AI Filt TC
0
1000
Ms 5
1972
7.8.8 Fine tuning parameters
These parameters are for special cases.
7.8.9 SM Excitation
7.8.9.1 SM Tuning
7.8.9.2 SM Reference AO
7.8.9.3 SM Actual AI
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 81
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.8.10.6.1
MgnReadyToStart
0.1
E.10
DigIN:0.1
1956
P2.8.10.6.2
MgnReadyForLoad
0.1
E.10
DigIN:0.1
1957 P2.8.10.6.3
StartMgnSystem
0.1
E.10
DigOUT:0.1
1958 P2.8.10.6.4
StartMagnetizatn
0.1
E.10
DigOUT:0.1
1959
7.8.9.4 SM Magn DO / DI
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

82 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.9.1.1
Speed control P gain
0
1000 30
613
P2.9.1.2
Speed control I time
-3200,0
32000
ms
100
614
Negative value uses 0,1 ms
format instead of 1 ms
P2.9.1.3
0-speed time at start
0
32000
ms
100
615
P2.9.1.4
0-speed time at stop
0
32000
ms
100
616
P2.9.1.5
SPC f1 Point
0,00
320,00
Hz
0,00
1301
P2.9.1.6
SPC f0 Point
0,00
320,00
Hz
0,00
1300
P2.9.1.7
SPC Kp f0
0
1000 % 100
1299
P2.9.1.8
SPC Kp FWP
0
1000 % 100
1298
P2.9.1.9
SPC Torque
minimum
0
400,0 % 0,0
1296 P2.9.1.10
SPC Torque
minimum Kp
0
1000 % 100
1295
P2.9.1.11
SPC Kp TC Torque
0
1000
ms 0
1297
P2.9.1.12
Acceleration
compensation
0,00
300,00 s 0,00
626
P2.9.1.13
Speed Error Filter TC
0
1000
ms 0
1311 P2.9.1.14
Encoder filter time
0
1000
ms 0
618
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.9.2
Load drooping
0,00
100,00 % 0,00
620
P2.9.3
Load Drooping Time
0
32000
ms 0
656
For dynamic changes
P2.9.4
Load Drooping Removal
0 2
0
1534
0=Normal
1= At zero Freq Lim
2=Linear zero to Fnom
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.9.5.1
Speed controller
P gain (open loop)
0
32767 3000
637
P2.9.5.1
Speed controller
I gain (open loop)
0
32767 300
638
7.9 Speed Control
7.9.1 Speed Control CL Settings
7.9.2 Speed Control Basic settings
7.9.3 Speed Control OL Settings
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 83
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.10.1
Switching frequency
1,0
Varies
kHz
Varies
601
P2.10.2
Modulator Type
0 3 0
1516
P2.10.3
Control Options
0
65535 64
1084
P2.10.4
Control Options 2
0
65535 0
1798
P2.10.5
Advanced Options 1
0
65535 0
1560
P2.10.6
Advanced Options 2
0
65535 0
1561
P2.10.7
Advanced Options 4
0
65535 0
1563
P2.10.8
Advanced Options 5
0
65535 0
1564
P2.10.9
Advanced Options 6
0
65535 0
1565
P2.10.10
Advanced Options 7
0
65535 0
1589
P2.10.11
Restart Delay
0
65535
s
Varies
1424
P2.10.12
Reverse VW Phases
0 1 0
1062
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.11.1
Master Follower
Mode
0 4
0
1324
0=Not Used
1=Master
2=Follower
3=Drive Synch Master
4=Drive Synch Follower
P2.11.2
Follower Stop
Function
0 2
2
1089
0=Coasting
1=Ramping
2=As Master
P2.11.3
Follower phase shift
0,0
360,0
Dec
0,0
1518
Phase shift between
multiple wind motors.
7.10 Drive Control
7.11 Master Follower Control Parameters
Table 7-17. Master Follower Control parameters, G2.5
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

84 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.1.1
Input phase supervision
0 3
0 730
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.1.2
Response to
undervoltage fault
0 1
0 727
0=Fault stored in history
1=Fault not stored
P2.12.1.3
Output phase supervision
0 3
2 702
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.1.4
Response to slot fault
0 3
2 734
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.1.5
Safe Disable Response
0 2
1 755
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.1.6
Keypad and PC
Communication fault
mode
1 2
2
1329
1=Warning (Stopping)
2=Fault,
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.2.1
No. of PT100 inputs
0 5
0 739
0=Not used (ID Write)
1=PT100 input 1
2= PT100 input 1 & 2
3= PT100 input 1 & 2 & 3
4= PT100 input 2 & 3
5= PT100 input 3
P2.12.2.2
Response to PT100
fault
0 3
2 740
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.2.3
PT100 warning limit
–30,0
200,0
Cº
120,0
741
P2.12.2.4
PT100 fault limit
–30,0
200,0
Cº
130,0
742
P2.12.2.5
No. of PT100 2
inputs
0 5
0 743
See ID739
P2.12.2.6
PT100 warning limit
–30,0
200,0
Cº
120,0
745 P2.12.2.7
PT100 fault limit
–30,0
200,0
Cº
130,0
746
P2.12.2.8
PT100 AI In
0 6
0
1222
0=Not used
1=AI1 1 Sensor
2= AI1 2 Sensor
3= AI1 3 Sensor
4= AI2 1 Sensor
5= AI2 2 Sensor
6= AI2 3 Sensor
P2.12.2.9
KTY AI In
0 6
0
1224
0=Not used
1=AI1 1 Sensor
2= AI1 2 Sensor
3= AI1 3 Sensor
4= AI2 1 Sensor
5= AI2 2 Sensor
6= AI2 3 Sensor
2.12.2.10.1
Channel 1B Warn
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
764 2.12.2.10.2
Channel 1B Fault
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
765
2.12.2.10.3
Channel 1C Warn
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
768 2.12.2.10.4
Channel 1C Fault
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
769 2.12.2.10.5
Channel 2B Warn
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
770
7.12 Protections
7.12.1 General settings
7.12.2 Temperature sensor protections
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 85
Classified as Public
2.12.2.10.6
Channel 2B Fault
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
771
2.12.2.10.7
Channel 2C Warn
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
772
2.12.2.10.8
Channel 2C Fault
-30,0
200,0
Cº
0,0
773
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.3.1
Stall protection
0 3
0 709
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.3.2
Stall current
0,1
2 x IH A IH 710
P2.12.3.3
Stall RPM limit
1,0
P2.1.2
Hz
25,0
712
P2.12.3.4
Stall time limit
1,00
120,00
s
15,00
711
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.4.1
Speed Error Mode
0 3
0 752
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault, stop
3=Fault, stop by coasting
P2.12.4.2
Speed Error Limit
0,0
100,0 % 5,0
753 P2.12.4.3
Speed Fault Delay
0,00
100,00 S 0,1
754
P2.12.4.4
Over Speed Fault
Response
0 2
2
1812
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault, stop by coasting
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.5.1
Thermal protection of the
motor
0 3
2 704
P2.12.5.2
Motor ambient
temperature factor
–
100,0
100,0 % 0,0
705 P2.12.5.3
Motor cooling factor at
zero speed
0,0
150,0 % 40,0
706 P2.12.5.4
Motor thermal time
constant
1
200
min
45
707
P2.12.5.5
Motor duty cycle
0
100 % 100
708
P2.12.5.6
Response to thermistor
fault
0 3
2 732
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.5.7
Motor Fan Off Delay
0
32000 s 0
1320
P2.12.5.8
MotorNomTempRise
0
300.0
Cº 0
1922
7.12.3 Stall Protection
7.12.4 Speed error monitoring
7.12.5 Motor thermal protections
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

86 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.6.1
Response to 4mA
reference fault
0 5
0 700
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Warning+Previous speed
3=Wrng+Preset speed
4=Fault,stop
5=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.6.2
4mA reference fault
speed
0
1500
rpm
0 728
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.7.1
Underload protection
0 3
0 713
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.7.2
Field weakening area
load
10,0
150,0 % 50,0
714
P2.12.7.3
Zero speed load
5,0
150,0 % 10,0
715
P2.12.7.4
Underload protection
time limit
2,00
600,00
s
20,00
716
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.8.1
Earth fault protection
0 3
2 703
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.8.2
Eart fault current limit
0,0
100,0 % 50,0
1333
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.9.1
Cooling Fault
Response
1 2
2 762
1=Warning
2= Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.9.2
Cooling Fault delay
0,00
7,00 s 2,00
751
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.10.1
Fieldbus
Communication
response
0 3
2 733
0=No Action
1=Warning
2= Fault
3= Fault,stop by coasting
4=Warning; Prev speed
5=Quick Stop
P2.12.10.2
FB Fault Delay
0,00
60,00 s 0,50
1850
Delay to fault when FB
Response is 4
P2.12.10.3
FB Watchdog Delay
0,00
30,00 s 0,00
1354
Delay when WD pulse is
missing. 0,00 s = Disabled
7.12.6 Living Zero monitoring (i.e. 4 mA fault)
7.12.7 Underload protection
7.12.8 Earth Fault protection
7.12.9 Cooling protection
7.12.10 Fieldbus protection
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 87
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.11.1
System Bus Fault
0 3
1
1082
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.11.2
System Bus Fault
Delay
0,00
320,00 s 3,00
1352
P2.12.11.3
Follower Fault
0 3
0
1536
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.11.4
Drive Synch Follower
fault
0 2
2
1531
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
7.12.11 Master Follower
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

88 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.12.1
Brake Fault Action
1 3
1
1316
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.12.2
Brake Fault Delay
0,00
320,00 s 0,20
1317
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.13.1
Response to external
fault 1
0 3
2 701
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
P2.12.13.2
Response to external
fault 2
0 3
2 747
0=No response
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Fault,stop by coasting
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.14.1
Encoder fault mode
1 3
2
1353
1=Warning
2=Fault,stop
3=Warning, Change to Open
Loop
P2.12.14.2
Iq Fault Limit
0
300 % 100
1800
P2.12.14.3
Fast Hz Limit
0,00
320,00
Hz
10,00
1801
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.15.1
Monitored ID
0
10000 0
1431
P2.12.15.2
Monitored Level
0 1
0
1432
0=High Level
1=Low Level
P2.12.15.3
Warning Level
-32000
32000 0
1433
P2.12.15.4
Fault Level
-32000
32000 0
1437
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.12.16
Disable Stop Lock
0 1 0
1086
P2.12.17
Reset Datalogger
0 4
0
1857
0 = Auto
1 = Reset to Auto
2 = SW Default
3 = Auto Fast
4 = No Change
7.12.12 Mechanical Brake
7.12.13 External Fault
7.12.14 Encoder fault
7.12.15 Signal Monitoring Function
7.12.16 Options
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 89
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.13.1
Fieldbus process
data out 1 selection
0
10000 1 852
Choose monitoring data with
parameter ID
Def: Output Frequency
P2.13.2
Fieldbus process
data out 2 selection
0
10000 2 853
Def: Motor Speed
P2.13.3
Fieldbus process
data out 3 selection
0
10000 3 854
Def: Motor Current to FB
P2.13.4
Fieldbus process
data out 4 selection
0
10000 4 855
Def: Motor Torque
P2.13.5
Fieldbus process
data out 5 selection
0
10000 5 856
Def: Motor Power
P2.13.6
Fieldbus process
data out 6 selection
0
10000 6 857
Def: Motor Voltage
P2.13.7
Fieldbus process
data out 7 selection
0
10000 7 858
Def: DC-Link Voltage
P2.13.8
Fieldbus process
data out 8 selection
0
10000 37
859
Def: Last Active Fault
P2.13.9
Fieldbus process
data out 9 selection
0
10000 0 558
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.10
Fieldbus process
data out 10 selection
0
10000 0 559
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.11
Fieldbus process
data out 11 selection
0
10000 0 560
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.12
Fieldbus process
data out 12 selection
0
10000 0 561
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.13
Fieldbus process
data out 13 selection
0
10000 0 562
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.14
Fieldbus process
data out 14 selection
0
10000 0 563
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.15
Fieldbus process
data out 15 selection
0
10000 0 564
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.16
Fieldbus process
data out 16 selection
0
10000 0 565
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.17
Fieldbus process
data in 1 selection
0
10000 1140
876
Choose controlled data with
parameter ID.
Def: FB Torque Reference
P2.13.18
Fieldbus process
data in 2 selection
0
10000 46
877
Def: FB Limit Scaling
P2.13.19
Fieldbus process
data in 3 selection
0
10000 47
878
Def: FB Adjust Reference
P2.13.20
Fieldbus process
data in 4 selection
0
10000 48
879
Def: FB Analogue Output.
P2.13.21
Fieldbus process
data in 5 selection
0
10000 0 880
Choose controlled data with
parameter ID
P2.13.22
Fieldbus process
data in 6 selection
0
10000 0 881
Choose controlled data with
parameter ID
P2.13.23
Fieldbus process
data in 7 selection
0
10000 0 882
Choose controlled data with
parameter ID
P2.13.24
Fieldbus process
data in 8 selection
0
10000 0 883
Choose controlled data with
parameter ID
P2.13.25
Fieldbus process
data in 9 selection
0
10000 0 550
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.26
Fieldbus process
data in 10 selection
0
10000 0 551
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.27
Fieldbus process
data in 11 selection
0
10000 0 552
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.28
Fieldbus process
data in 12 selection
0
10000 0 553
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.29
Fieldbus process
data in 13 selection
0
10000 0 554
Visible with correct hardware
and software
7.13 Fieldbus parameters
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

90 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
P2.13.30
Fieldbus process
data in 14 selection
0
10000 0 555
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.31
Fieldbus process
data in 15 selection
0
10000 0 556
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.32
Fieldbus process
data in 16 selection
0
10000 0 557
Visible with correct hardware
and software
P2.13.33
General Status Word
ID
0
10000 67
897
Choose monitoring data in
General Status Word
P2.13.34
Control Slot Selector
0 9
0
1440
0=All
4=Slot D
5=Slot E
6=Slot D Fast
7=Slot E Fast
8=Slot D 16 Data
9=Slot E 16 Data
P2.13.35
State Machine
0 2
2 896
0 = Echo
1 = Standard
2 = ProfiDrive
P2.13.36
FB Reference Filter
TC
0
32000
ms
0 863 P2.13.37
Enable FB
Monitoring
0 1
0
1629
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
P2.13.38
SW ID.Bit 11
selection
0
2000,00 0
1625 P2.13.39
SW ID.Bit 12
selection
0
2000,00 0
1626
P2.13.40
SW ID.Bit 13
selection
0
2000,00 0
1627 P2.13.41
SW ID.Bit 14
selection
0
2000,00 0
1628
Table 7-18. Fieldbus parameters
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 91
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.14.1.1
Control Input Signal ID
0
10000
ID 0
1580
P2.14.1.2
Control Input Off Limit
-32000
32000 0
1581
P2.14.1.3
Control Input On Limit
-32000
32000 0
1582
P2.14.1.4
Control Output Off
Value
-32000
32000 0
1583
P2.14.1.5
Control Output On
Value
-32000
32000 0
1584
P2.14.1.6
Control Output Signal
ID
0
10000
ID
0
1585
P2.14.1.7
Control Mode
0 5
0
1586
0=SR ABS
1=Scale ABS
2=Scale INV ABS
3=SR
4=Scale
5=Scale INV
P2.14.1.8
Control Output Filtering
rime
0,000
32,000 s 0,000
1721
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.14.2.1
ID Control DIN
0.1
E.10
0.1
1570
Slot . Board input No.
P2.14.2.2
Controlled ID
0
10000
ID
0 1571
Select ID that is controlled
by digital input
P2.14.2.3
False value
-32000
32000 0 1572
Value when DI is low
P2.14.2.4
True value
-32000
32000 0 1573
Value when DI is high
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.14.3.1
ID Control DIN
0.1
E.10
0.1
1590
Slot . Board input No.
P2.14.3.2
Controlled ID
0
10000
ID
0 1575
Select ID that is controlled
by digital input
P2.14.3.3
False value
-32000
32000 0 1592
Value when DI is low
P2.14.3.4
True value
-32000
32000 0 1593
Value when DI is high
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.14.4.1
ID Control DIN
0.1
E.10
0.1
1578
Slot . Board input No.
P2.14.4.2
Controlled ID
0
10000
ID
0 1579
Select ID that is controlled
by digital input
P2.14.4.3
False value
-32000
32000 0 1594
Value when DI is low
P2.14.4.4
True value
-32000
32000 0 1596
Value when DI is high
7.14 ID Functions
7.14.1 Value Control
Table 7-19. Power reference input signal selection, G2.2.8
7.14.2 DIN ID Control 1
Table 7-20. DIN ID Control parameters, G2.2.8
7.14.3 DIN ID Control 2
Table 7-21. DIN ID Control parameters, G2.2.8
7.14.4 DIN ID Control 3
Table 7-22. DIN ID Control parameters, G2.2.8
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

92 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.14.5.1
ID.Bit Free DO
0,00
2000,15
0,00
1217
P2.14.5.2
Free DO Sel
0,1
E.10 0,1
1574
7.14.5 ID Controlled Digital Output
Table 7-23. ID Controlled Digital Output parameters, G2.14.5
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 93
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.15.1
BrakeMechDelay
0,00
320,00
s
0,00
1544
Time that is required to
open the brake
P2.15.2
Brake OFF FreqLim
Open Loop
0,00
32000
rpm
1,50
1535
Opening limit and
maximum reference limit
when brake is closed.
P2.15.3
Brake OFF RPM Lim
Closed Loop
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
1555
Opening limit and
maximum reference limit
when brake is closed.
P2.15.4
Brake ON RPM Lim
+
0,00
32000
rpm
1,00
1539
Close frequency from
positive direction
P2.15.5
Brake ON RPM Lim
-
0,00
32000
rpm
1,50
1540
Close frequency from
negative direction
P2.15.6
Brake On/Off Current
Limit
0,00
320,00
A
0,00
1085
Brake is closed
immediately if current goes
below this value.
P2.15.7
Generator Torque
limit increase speed
level
0,00
32000
rpm
0,00
1547
Function disabled when
zero. Point where
Generator torque limit stars
to increase.
P2.15.8
Generator Torque
limit increase
maximum speed limit
0,00
32000
rpm
100,00
1548
Point where torque value
of ID1549 is added to base
generator torque limit.
P2.15.9
Generator Torque
limit increase
maximum addition
0,0
300,0
%
300,0
1549
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.15.10.1
Start-up torque
0 3
0 621
0=Not used
1=Torque memory
2=Torque reference
3=Start-up torque fwd/rev
4=Start-up torque Ref
P2.15.10.2
Start-up torque FWD
–300,0
300,0 s 0,0
633
P2.15.10.3
Start-up torque REV
–300,0
300,0 s 0,0
634
P2.15.10.4
Start Up Torque Time
-1
10000
ms
-1
1371
-1 = Automatic
P2.15.10.5
Start Up Torque Ref
-300,0
300,0 % 0,0
1375
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.15.11.1
Stop Torque Release
Time
0
500
ms
0
1858
7.15 Brake Control
Table 7-24. Brake control parameters, G2.15.8
7.15.1.1 Brake Control Start up torque for CL
7.15.1.2 Functions
Table 7-25. Functions parameters, G2.15.14
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

94 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.16.1
Wait time
0,10
10,00 s 0,50
717
P2.16.2
Trial time
0,00
60,00 s 0,10
718
P2.16.3
Start function
0 2
2
719
0=Ramp
1=Flying start
2=According to Start
Function
P2.16.4
Number of tries after
undervoltage trip
0
10 0
720
P2.16.5
Number of tries after
overvoltage trip
0
10 0
721 P2.16.6
Number of tries after
overcurrent trip
0 3
0
722
P2.16.7
Number of tries after
reference trip
0
10 0
723
P2.16.8
Number of tries after
motor temperature fault
trip
0
10 0
726
P2.16.9
Number of tries after
external fault trip
0
10 0
725
P2.16.10
Number of tries after
underload fault trip
0
10 0
738
P2.16.11
Fault Simulation
0
65535 0
1569
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Step
Default
ID
Note
P2.17.1
PI controller gain
0,0
1000,0
% 100,0
118
P2.17.2
PI controller I-time
0,00
320,00
s 1,00
119
P2.17.3
PI Reference
-32000
32000
0
167
P2.17.4
PI controller
reference signal
ID
0
10000
167
332
Default P2.17.3
P2.17.5
PI Actual value ID
0
10000
0
333
P2.17.6
PI Controller output
ID
0
10000
0
1802
P2.17.7
PI Controller Scale
-32000
32000
1
340
>= 1 = No inversion
<=-1 = Inverted
0 = Illegal value
P2.17.8
PI Low limit
-32000
32000
359 P2.17.9
PI High limit
-32000
32000
% 10000
360
P2.17.10
PI Controller
Output scale
-3200,0
3200,0
% 100,0
1803
P2.17.11
PI Stop state value
-32000
32000
0
1806
7.16 Auto Reset parameters
Table 7-26. Auto reset parameters, G2.16
7.17 PI Control Parameters
Table 27. PI Controller parameters, G2.17
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 95
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.18.1
SQS Reaction
0 1 1
545
0=No Action
1=Quick Stop
P2.18.2
SS1 Reaction
0 1 1
542
0=No Action
1=Stop
2=Quick Stop
P2.18.3
SS2 Reaction
0 1 1
546
0=No Action
1=Zero Speed
2=Quick Stop
P2.18.4
SDI Reaction
0 1 1
544
0=No Action
1=Disable Dir
P2.18.5
SLS Reaction
0 1 1
543
0=No Action
1=Limit Reference
P2.18.6
SSR Reaction
0 1 1
547
0=No Action
1= Limit Reference
P2.18.7
Safety Options
0
65535 2 548
7.18 Functional Safety
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

96 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.1
Condition Based
Monitoring Fault
Mode
0 2 1
3540
0=No response
1=Warnings
2=Fault + Warnings
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.2.1
Baseline Start
0 1 0
3501
0=No Action
1=Baseline Run
P2.19.2.2
Baseline Min Freq
0
320,00
Hz 0
3502
P2.19.2.3
Baseline Max Freq
0
320,00
Hz
50,00
3503
P2.19.2.4
Baseline Run
Duration
30
7200 s 120
3504
P2.19.2.5
Modified Array
0
16 0
3506
0=Freq Points
1=Current Max Steady
2=Current Min Steady
3=Current Mean Steady
4=Current Std Steady
5= Voltage Max Steady
6= Voltage Min Steady
7= Voltage Mean Steady
8= Voltage Std Steady
9=Vibration Max Ramp
10= Vibration Min Ramp
11= Vibration Mean Ramp
12= Vibration Std Ramp
13= Load Max Steady
14= Load Min Steady
15= Load Mean Steady
16= Load Std Steady
P2.19.2.6
Modified Point
0 9 0
3507
P2.19.2.7
Modified Value
-300,00
320,00
Hz or
%
0
3508
P2.19.2.8
Modified Activation
0 1
0
3505
0=No Action
1=Set Modified Value
P2.19.2.9
Baseline Data
Selector
0
16 0
3509
0=Freq Points
1=Current Max Steady
2=Current Min Steady
3=Current Mean Steady
4=Current Std Steady
5= Voltage Max Steady
6= Voltage Min Steady
7= Voltage Mean Steady
8= Voltage Std Steady
9=Vibration Max Ramp
10= Vibration Min Ramp
11= Vibration Mean Ramp
12= Vibration Std Ramp
13= Load Max Steady
14= Load Min Steady
15= Load Mean Steady
16= Load Std Steady
7.19 Condition Based Monitoring
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

apfiff40 SIA II VACON® • 97
Classified as Public
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.1
Line Frequency
0
100,00
Hz
50,00
1913
P2.19.3.2
Line Frequency
Hysteresis
0
10,00
Hz
1,00
1914
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.3.1
Mean Factor
-10
10 1
3511
P2.19.3.3.2
Min Factor
-10
10 0
3512
P2.19.3.3.3
Max Factor
-10
10 0
3513
P2.19.3.3.4
Std Factor
-10
10 0
3514
P2.19.3.3.5
Interpolation Type
0 1 1
3515
0=Constant
1=Linear
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.4.1
Warning S1 Mode
0 2 0
3516
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.4.2
Warning S1 High
0
100,0 % 0
3517
P2.19.3.4.3
Warning S1 Delay
0
3600 s 0
3518
P2.19.3.4.4
Warning S2 Mode
0 2 0
3519
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.4.5
Warning S2 High
0
100,0 % 0
3720
P2.19.3.4.6
Warning S2 Delay
0
3600 s 0
3721
P2.19.3.4.7
Alarm/fault Mode
0 2 0
3522
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.4.8
Alarm/fault High
0
100,0 % 0
3523
P2.19.3.4.9
Alarm/fault Delay
0
3600 s 0
3524
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.5.1
Warning S1 Counter
0
3600 s 0
3541
P2.19.3.5.2
Warning S2 Counter
0
3600 s 0
3542
P2.19.3.5.3
Alarm/fault Counter
0
3600 s 0
3543
P2.19.3.5.4
Stop Counter Delay
0
320 s 0
3549
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.6.1
Mean Factor
-10
10 1
3526
P2.19.3.6.2
Min Factor
-10
10 0
3527
P2.19.3.6.3
Max Factor
-10
10 0
3528
P2.19.3.6.4
Std Factor
-10
10 0
3529
P2.19.3.6.5
Interpolation Type
0 1 1
3530
0=Constant
1=Linear
7.19.1 Stator Winding
7.19.1.1 Current Unbalance Threshold Value
7.19.1.2 Current Unbalance Limits
7.19.1.3 Current Unbalance Counters
7.19.1.4 Voltage Unbalance Threshold Value
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/

98 • VACON® apfiff40 SIA II
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.7.1
Warning S1 Mode
0 2 0
3531
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.7.2
Warning S1 High
0
100,0 % 0
3532
P2.19.3.7.3
Warning S1 Delay
0
3600 s 0
3533
P2.19.3.7.4
Warning S2 Mode
0 2 0
3534
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.7.5
Warning S2 High
0
100,0 % 0
3535
P2.19.3.7.6
Warning S2 Delay
0
3600 s 0
3536
P2.19.3.7.7
Alarm/fault Mode
0 2 0
3537
0=Abs. value
1=Baseline offset
2=Baseline factor
P2.19.3.7.8
Alarm/fault High
0
100,0 % 0
3538
P2.19.3.7.9
Alarm/fault Delay
0
3600 s 0
3539
Code
Parameter
Min
Max
Unit
Default
Cust
ID
Note
P2.19.3.8.1
Warning S1 Counter
0
3600 s 0
3546
P2.19.3.8.2
Warning S2 Counter
0
3600 s 0
3547
P2.19.3.8.3
Alarm/fault Counter
0
3600 s 0
3548
P2.19.3.8.4
Stop Counter Delay
0
320 s 0
3549
7.19.1.5 Voltage Unbalance Limits
7.19.1.6 Voltage Unbalance Counters
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
 Loading...
Loading...