Page 1
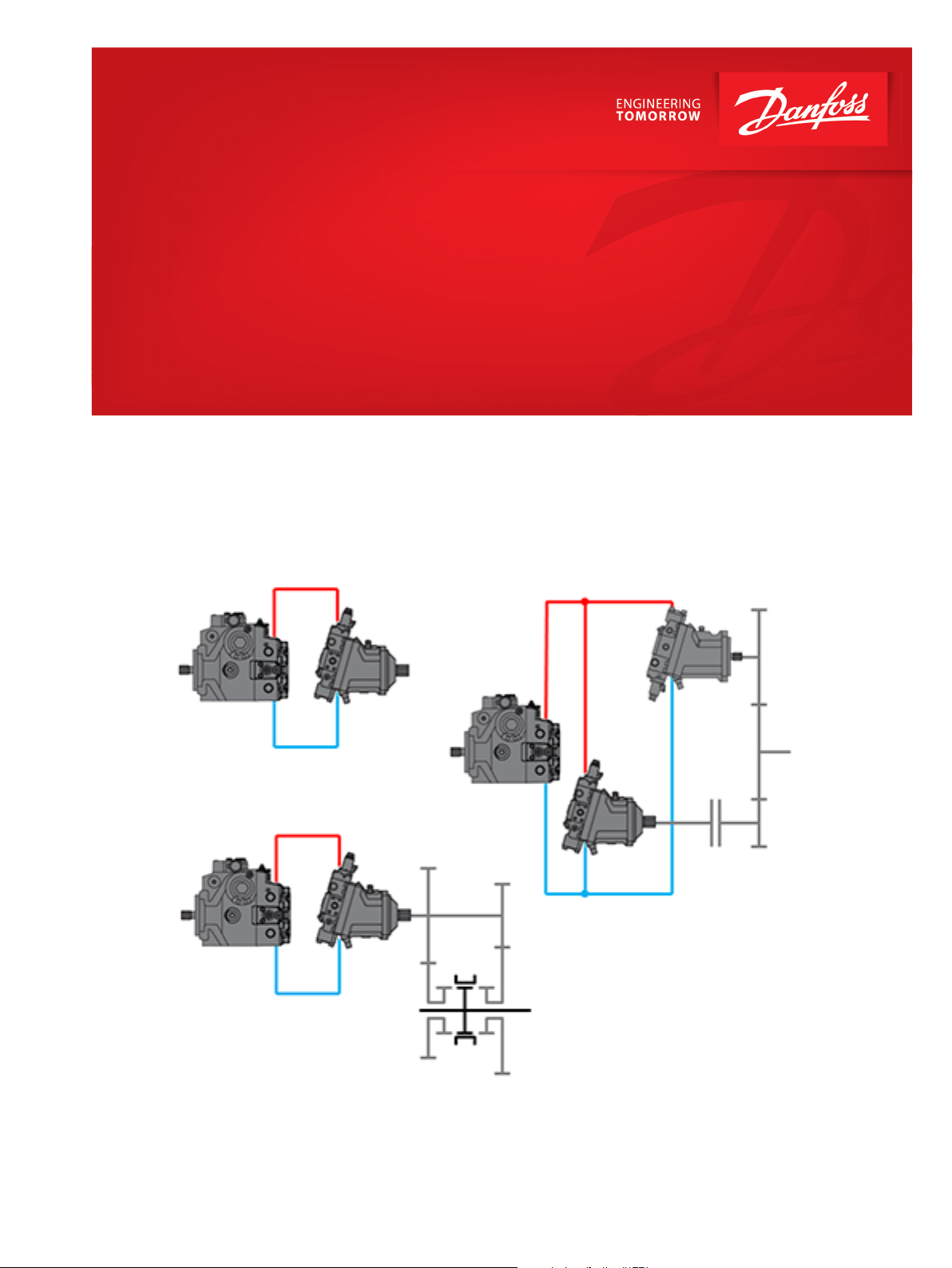
System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Automotive Control PC-AC
www.danfoss.com
Page 2

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
July 2020 Added PC-AC SP content 0201
March 2019 First edition 0101
2 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 3

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Contents
Basic information
Propel controller system overview.............................................................................................................................................4
Functional safety
Standards.............................................................................................................................................................................................5
PC-AC
Basic functions...................................................................................................................................................................................6
Advanced functions.........................................................................................................................................................................6
PC-AC SP
Basic functions...................................................................................................................................................................................7
Advanced functions.........................................................................................................................................................................7
System design....................................................................................................................................................................................9
PC-AC 2MT
Basic functions................................................................................................................................................................................ 10
Advanced functions......................................................................................................................................................................11
System design.................................................................................................................................................................................12
Functions
Function overview.........................................................................................................................................................................14
Propel functions............................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Protections
Engine control and protection..................................................................................................................................................18
Gearbox control and protection...............................................................................................................................................19
Auxiliary functions
Propel controller
Controller specification................................................................................................................................................................21
General dimensions...................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Pin assignments..............................................................................................................................................................................23
Mode Types.................................................................................................................................................................................14
Automotive Transport Mode................................................................................................................................................15
Non-Automotive Work Mode (FCMD)...............................................................................................................................15
ECO fuel saving mode.............................................................................................................................................................15
Mode transition control..........................................................................................................................................................15
Start Protection......................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Quick stop in automotive mode......................................................................................................................................... 16
State and direction change...................................................................................................................................................16
Hydromotor overspeed protection....................................................................................................................................16
Electronic Pressure Limiter (ePL).........................................................................................................................................16
Electronic pressure compensator over ride (ePCOR)...................................................................................................16
Load limiter.................................................................................................................................................................................16
Hydraulic-System overheat protection............................................................................................................................ 17
Vehicle constant-speed-drive (CSD).................................................................................................................................. 17
Cruise control.............................................................................................................................................................................17
Filter on drive pedal.................................................................................................................................................................17
Vehicle speed dependent ramps........................................................................................................................................17
Semi-Automatic calibration function................................................................................................................................17
1939-CAN engine interface...................................................................................................................................................18
CAN user interface....................................................................................................................................................................18
Engine speed control.............................................................................................................................................................. 18
Engine anti-stall protection.................................................................................................................................................. 18
All range engine overspeed..................................................................................................................................................18
All range engine overspeed with retarder.......................................................................................................................18
Cold start protection............................................................................................................................................................... 18
Gearbox control........................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Shift monitoring control........................................................................................................................................................ 19
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 3
Page 4
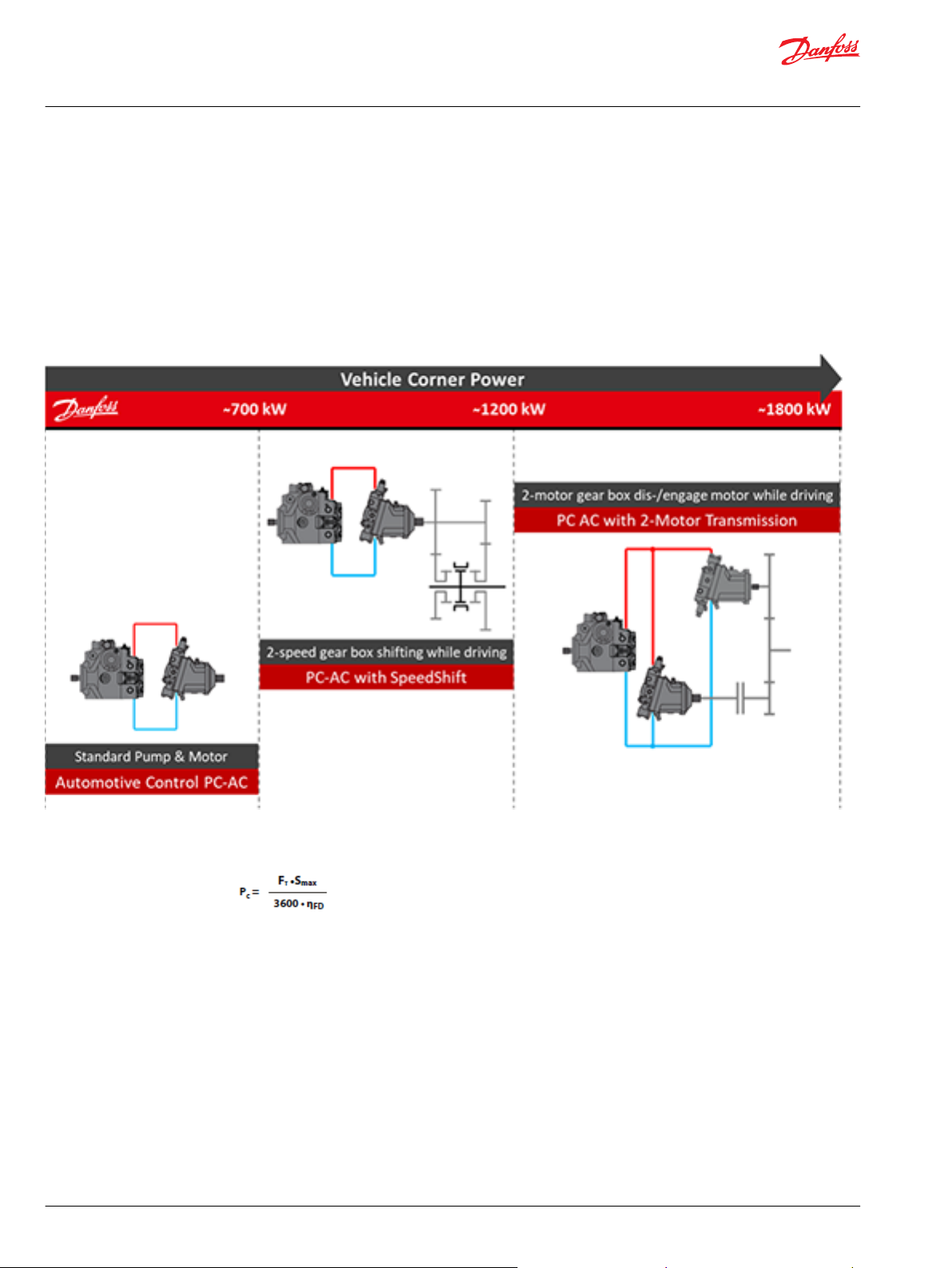
System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Basic information
The Propel Controller Solutions are designed to support single path hydrostatic transmissions systems.
Danfoss offers several solutions for the propel system to cover vehicle corner power ranges up to 1800
kW. All of these propel system solutions combining proven hardware like PLUS+1® Safety Controller and
H1 hydraulic pumps and motors with reliable software developed according to current safety standards.
With the pre-installed application software and easily changeable control parameters, it is possible to
tailor the vehicle's driving behavior to the individual requirements of the customer.
Propel controller system overview
Definition of vehicle corner power
Where:
P
c
S
max
Corner Power (kW)
max Vehicle Speed (km/h)
ղFD Final drive efficiency (-)
4 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 5

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Functional safety
The Propel Controller Software is designed to control a single-path transmission system consisting of one
pump and one (or two) hydrostatic motor(s). The propel controller and the application software needs to
fulfill the safety requirements according to machine directive (2006/42/EC).
PLUS+1® PC controllers are advanced elements of the PLUS+1® family of mobile machine management
products. The design of this general purpose safety controller includes features required for sophisticated
machine control strategies. It is equally suited for use in safety related or general machine control
applications.
These controllers have dual processors with the secondary processor having access to all controller
inputs and supervisory control of outputs. These controllers support smart digital inputs. Current
measurement capability has been added to some multifunction inputs. Device outputs can be
individually controlled by the secondary processor.
The Safety Manual of the propel controller solutions (available by request from your local Danfoss
representative) is intended to guide the system integrator concerning functional safety. The document
describes a possible implementation of the needed safety functions.
Standards
Type A Standards
Cover aspects applicable to all types of machines
•
IEC 61508 functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems
Type B Standards
Cover particular safety and ergonomic aspects of machinery
•
ISO 15998 Controller for earth moving machinery
•
EN ISO 13849-1:2015 Safety of machinery- Safety-related parts of control systems- Parts 1 & 2
•
ISO 25119 Agriculture machinery (former EN 16590)
Type C Standards
Machine safety standards dealing with detailed safety requirements for a particular machine or group of
machines
•
ISO 20474-2017, former DIN/EN 474 Earth moving machinery
•
EN 1459-1:2017 Rough-terrain trucks – Safety requirements and verification – Part 1: Variable-reach
trucks
•
EN 4254:2013 Agricultural machinery – Safety – Part 1: General requirements
•
EU 167/2013 Agricultural and Forestry vehicles (Tractor directive)
•
EU 1322/2014
‒
EU 68/2015
‒
EU 96/2015
‒
EU 208/2015
‒
EU 1788/2016
‒
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 5
Page 6

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC
The propel controller application PC-AC is designed to control a single-path hydrostatic transmission
system consisting of one pump and one motor. The hydrostatic pump is equipped with two proportional
valves.
In the PC-AC system the hydrostatic pump can be controlled in pressure dependent (NFPE) or pressure
independent (EDC) pump control mode.
The PC-AC system is optimized for use with a hydrostatic motor equipped with a proportional (PROP)
valve to control pressure or motor displacement.
The Danfoss patented Flow Controller Motor Displacement (FCMD) allows the software to change the
control command according to the system flow. Which brings advantages in controllability, engine
power utilization and system load dependency.
Parking brake valve, reverse motion buzzer, forward/reverse lamp indicator, a retarder valve and a
stabilizer valve can be controlled by additional digital outputs.
The PC-AC system can read several analog, digital, and frequency signals representing operator input,
system demands, and machine status inputs.
The CAN Communication Interface is used for diagnosis purposes and for information exchanging with
other controllers such as engines, other Danfoss power solutions or customer controllers.
Basic functions
Advanced functions
The PC-AC commands the basic vehicle driving behavior and performance (i.e. acceleration, deceleration,
and vehicle speed). The operator selects the driving mode, driving direction, and basic transmission set
point command via throttle or creep/drive pedal. An additional input, the inch pedal command, can be
used to override the basic transmission command.
A number of advanced features can be independently activated and configured depending on the
installed application software package. Below is a list of the primary advanced functions:
•
Engine and motor over-speed protection
•
Engine anti-stall
•
Constant speed control
•
ECO fuel saving mode
•
Vehicle speed limitation and flow limiter
•
Intelligent operator presence detection
•
Electronic swash plate control
•
Temperature compensation and overheat-protection
•
Maximum motor torque at vehicle start
•
Engine speed dependent retarder control
•
Cruise control
•
User defined I/Os
6 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 7

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC SP
The PC-AC SP system is dedicated for use with one hydromotor which is mounted on a two speed
syncronizer gearbox. A syncroniser allows gear change while driving (SpeedShift).
The SpeedShift function will control and monitor the two speed gearbox. The hydrostatic components
are controlled according the requirements to perform a fast and smooth gear change.
A proportional controlled hydromotor with 0° and de-energized minimum displacement is required for
SpeedShift. The 0° position of the hydromotor is monitored with a MBS 1250 pressure sensor in port M4
(min. servo chamber).
The gear stage is not linked to a system mode; a gear change is possible for all 4 system modes. It can be
automatically or manually triggered. The software will ensure a gear change is only applied if it is possible
and safe (dependent on vehicle speed, acceleration/deceleration, and temperature).
The CAN Communication Interface is used for diagnosis purposes and information exchanging with other
controllers such as engines and other Danfoss power solutions or customer controllers.
Basic functions
The PC-AC SP offers the same basic function like the PC-AC. It controls basic vehicle driving behavior and
performance (i.e. acceleration, deceleration, and vehicle speed). Additional it controls the two speed
gearbox. The operator selects the driving mode, driving direction, driving gear and the transmission set
point via throttle or creep/drive pedal.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Four system modes, selectable by the driver for different drive behavior
Independent pump/hydromotor profiling and ramping for each system mode
Independent pump/hydromotor profiles in first and second gear operation
Electric drive pedal
Electronic inching
Load dependent pump displacement control (automotive)
Proportional hydromotor displacement control by flow (FCMD)
User defined I/Os
Advanced functions
Protection and safety functions
•
Safety controlled vehicle start protection
•
Operator presence detection
•
Software based pressure protection
•
Hydraulic system overheat and low temperature protection
•
Hydromotor overspeed protection
•
SIL2 compliant
Performance functions
•
ECO fuel saving mode
•
Vehicle speed limitation
•
Dynamic brake light, automatic park brake, reverse buzzer and vehicle speed controlled output
functions
•
Advanced CAN J1939 interface
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 7
Page 8

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC SP
Engine control and protection
•
•
•
Gearbox control and protection
•
•
•
•
•
CAN J1939 engine interface
Engine speed control via drive pedal with safety controlled monitoring function
Engine over speed and cold start protection
Approved by gearbox manufacturer
Shift valve control (automatic or manual triggered)
Gear detection
Measure hydromotor M4 pressure for 0° detection (with start up and plausibility check)
Fault management
8 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 9

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC SP
System design
System Overview of Danfoss Components
H1P Pump with load dependent NFPE control Electronic pressure limitation by
software (without hydraulic pressure limiter valve)
Optional: Control Cut Off (CCO), Swash angle sensor
Technical Information document number: BC152886483968.
Electric proportional control (M1/CA control without BPD)
Electronic load limitation by software (without hydraulic PCOR)
De-energized min. displacement
Without Speed Sensor
Technical Information document number: BC152886483576.
User manual Safety Controller PC AC SpeedShift
Technical Information document number: BC152986484387.
Pressure sensors MBS 1250
Data sheet document number: AI152886480966.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 9
Page 10

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC 2MT
The propel controller application PC-AC 2MT is designed to control a single-path hydrostatic transmission
system consisting of one hydrostatic pump, two hydromotors and the gearbox control. The hydrostatic
pump is equipped with two proportional valves.
In the PC-AC 2MT application the hydrostatic pump can be controlled in pressure dependent (NFPE)
pump control mode.
The PC-AC 2MT system is optimized for use with two hydromotor which are mounted on a gearbox with
different ratios to the gearbox output shaft. At slow vehicle speeds (e.g. up to 14 kph) the machine is
operated with both hydromotors (high tractive force due to two motors engaged and high ratio of
hydromotor M2). At a certain vehicle speed the rated speed capacity of the gearbox and/or hydromotor
M2 are reached. At this condition the gearbox control allows the hydromotor M2 to be switched off
(jump from x%-displacement to ZERO displacement) and the hydromotor M2 is mechanically
disconnected from the gearbox. The disengagement and engagement of hydromotor M2 is actuated on
the fly without loss of tractive force while shifting. After the hydromotor M2 is disconnected the vehicle
operates up to final vehicle speed (e.g. 40 kph) just with hydromotor M1.
Proportional valves are used on the hydromotor controls. The Danfoss patented Flow Controller Motor
Displacement (FCMD) allows the software to change the control command according to the system flow
which brings advantages in controllability, engine power utilization and system load dependency.
Parking brake valve, reverse motion buzzer, forward/reverse lamp indicator can be controlled by
additional digital outputs.
The PC-AC system can read several analog, digital, and frequency signals representing operator input,
system demands, and machine status inputs.
The CAN Communication Interface is used for diagnosis purposes and for information exchanging with
other controllers such as engines, other Danfoss Power Solutions or customer controllers.
Basic functions
The PC-AC 2MT commands the basic vehicle driving behavior and performance (i.e. acceleration,
deceleration, and vehicle speed). The operator selects the driving mode, driving direction, and basic
transmission set point command via throttle or creep/drive pedal. An additional input, the inch pedal
command, can be used to override the basic transmission command.
Four system modes, selectable by the driver for different drive behavior
•
Independent pump/motor profiling and ramping for each system mode
•
Independent motor profiles in one motor and two motor operation
•
Electric drive pedal
•
Electronic inching
•
Load dependent pump displacement control (automotive)
•
Proportional hydromotor displacement control by flow (FCMD)
•
User defined I/Os
•
10 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 11

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC 2MT
Advanced functions
Protection and safety functions
•
•
•
•
•
•
Performance functions
•
•
•
•
Safety controlled vehicle start protection
Operator presence detection
Software based pressure protection
Hydraulic system overheat and low temperature protection
Hydromotor overspeed protection
SIL2 compliant
ECO fuel saving mode
Vehicle speed limitation
Dynamic brake light, automatic park brake, reverse buzzer and vehicle speed controlled output
functions
Advanced CAN J1939 interface
Engine control and protection
•
CAN J1939 engine interface
•
Engine speed control via drive pedal with safety controlled monitoring function
•
Engine over speed and cold start protection
Gearbox control and protection
•
Approved by gearbox manufacturer
•
Clutch control
•
Slip detection
•
Fault manager
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 11
Page 12

H1B Motor 1
H1B
Motor 2
Shift valve
CAN-Bus
Forward
Reverse
Diesel Engine
Two Motor
Transmission
Gearbox
Engine ECU
Safety
Controller
H1 Pump
MBS 1250
F/N/R Inch pedal Drive pedal
System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC 2MT
System design
System Overview of Danfoss Components
H1P Pump with load dependent NFPE control Electronic pressure limitation by
software (without hydraulic pressure limiter valve)
Optional: Control Cut Off (CCO), Swash angle sensor
Technical Information document number: BC152886483968.
H1 Bent Axis Motor 1 (always engaged)
Electric proportional control (L1/L2 control)
De-energized max. displacement
Electronic pressure limitation by software (without hydraulic PCOR)
Technical Information document number: BC152886483576.
H1 Bent Axis Motor 2 (can be disconnected)
Electric proportional control (M1/M2 control)
De-energized min. displacement
Electronic pressure limitation by software (without hydraulic PCOR)
Technical Information document number: BC152886483576.
Safety Controller PC AC 2MT
Technical Information document number: BC152986484387.
12 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 13

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
PC-AC 2MT
Pressure sensors MBS 1250
Data sheet document number: AI152886480966.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 13
Page 14

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Functions
The available functions for the individual software solution can be found in the table below. A more
detailed description of the individual function can be found on the following pages.
Function overview
Function PC-AC PC-AC SP PC-AC 2MT
Automotive Transport Mode (FCMD) x x x
Non-automotive Work Mode (FCMD) x x x
ECO fuel saving mode x x x
Mode Transition Control x x x
Start Protection x x x
Quick stop in Automotive Mode x x x
State and Direct Change x x x
Hydromotor Overspeed Protection x x x
Load limiter x x x
ePCOR - - x
ePL - - x
Hydraulic-System Overheat Protection x x x
Vehicle Constant-Speed-Drive (CSD) x x x
Vehicle-Speed-Limitation x x x
Cruise Control x x Filter for drive pedal x x x
Vehicle speed depending Ramps x x x
Semi-Auto Calibration Function x x x
J1939-CAN User Interface x x x
CAN User Interface (e.g. Error Messages,
calibration start)
Status and Error LED x x x
Engine Speed Control x x x
Engine Anti-stall Protection x x x
All range Engine Overspeed x x x
Engine Over Speed Protection with Retarder x x Optional
Cold Start Protection x x x
Brake light x x x
Automatic Park Brake Control x x x
Gearbox Control - x x
Shift Monitoring - x x
x x x
Propel functions
In the following the control functions are described. Not all of the functions are available for all software
solutions. The available functions for the individual software solution can be found in table on previous
page.
Mode Types
The application software provides different hydrostatic propel methods, defined as mode types, which
can be set individually by parameter.
14 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 15

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Functions
Automotive Transport Mode
Proportional pump and hydromotor displacement control. The setpoint of the pump drive curves is given
by the engine rpm. The engine rpm is commanded by a drive pedal.
The hydromotor setpoint is calculated from the actual pump flow (FCMD - Flow Controlled Motor
Displacement). The pump flow is calculated from the displacement of the hydromotor (detected by the
control current) and the hydromotor rpm.
•
•
•
•
Non-Automotive Work Mode (FCMD)
Proportional pump and hydromotor displacement control. The setpoint of the drive curves is given by a
pedal command independent of the engine rpm. The engine rpm is commanded by a hand throttle to
mainly fulfill the requirements of the work hydraulic.
The hydromotor setpoint is calculated from the actual pump flow (FCMD - Flow Controlled Motor
Displacement). The pump flow is calculated from the displacement of the hydromotor (detected by the
control current) and the hydromotor rpm.
•
•
•
•
•
•
Drive pedal controls vehicle speed
Load dependent mode
Brake/inch signal reduce vehicle speed
Coast down when release the drive pedal
Drive pedal controls vehicle speed
Engine speed is set separately according requirement of work functions
Load independent mode
Brake/inch signal reduce vehicle speed
Vehicle speed limitation by the drive pedal (no roll down the hill)
Antistall protect the engine from overloading
ECO fuel saving mode
The ECO fuel saving mode is designed for the Automotive Transport Mode (FCMD). It needs a CAN
controlled Engine (TSC1 & EEC1), an electric drive pedal and a larger pump displacement. The ECO Mode
function reduces the engine rpm setpoint (TSC1) automatically when a vehicle speed is reached for a
defined time. This will reduce the fuel consumption and noise emission. The pump displacement will be
increased to keep the vehicle speed on the same level with a reduced engine rpm. The ECO mode is
automatically switched off, if the vehicle slows down or the driver releases the electric drive pedal. If the
engine is overloaded (EEC1) the “Engine Speed Command” will be increased.
The ECO Mode is available in all Automotive Transport Modes and can enabled individually in each ofthe
four Modes.
Mode transition control
This function allows configuration of an application specific System Mode transition. The System Mode
The propel controller can exchange information with the engine via the CAN J1939 protocol (TSC1
change condition can be dependent on multiple factors including actual FNR direction, drive pedal
message or Kubota protocol). All CAN messages can be individually activated and designated for usage.
Input, and ground speed. The following functions and standard messages are provided: The vehicle
driving direction change can be configured on vehicle speed.
When a momentary FNR switch logic is configured, the driving direction change request is rejected if the
vehicle speed is above a predefined speed.
Start Protection
The Safety Controlled Vehicle Start Protection prevents commanded, unexpected, or otherwise
dangerous machine propel movement after initial power on the engine. The Start Protection is
monitoring the following signals.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 15
Page 16

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Functions
•
•
•
•
•
If all conditions are fulfilled the Start Protection will switch OFF and the vehicle can drive.
Quick stop in automotive mode
When operating the vehicle in Automotive Transport Mode the propel controller will use the engine rpm
as the setpoint. The electric drive pedal position (out of the deadband) is used as an enable signal. The
driver must press the drive pedal and the engine rpm must rise to move the vehicle. If the driver release
the drive pedal fully (drive pedal return into the deadband), the pump current will decrease with an
adjustable ramp to a defined value. The vehicle will decelerate much faster compared to the today’s
behavior.
If the driver release the drive pedal to a minimum value (drive pedal signal is over the deadband), the
pump current will follow the drive curve as today. The vehicle will decelerate “normal”.
State and direction change
After a direction change request by the FNR switch, the system state will wait until the vehicle speed is
lower than the “Vehicle Speed for State Change” before it will switch to Neutral or the other direction.
Engine rpm
Battery voltage
Error status
Inch calibration
FNR in Neutral
Hydromotor overspeed protection
The Hydromotor Overspeed Protection prevents the hydromotor(s) from over speeding by either
decreasing pump displacement or increasing hydromotor displacement. The hydromotor rpm speed
limit, is user defined and valid in all four System Modes when activated
Electronic Pressure Limiter (ePL)
The electronic pressure limitater prevents the pump from over pressure. When the system pressure
exceeds the ePL pressure setting (set by parameter) the pump is being stroked towards min
displacement to maintain the pressure in the system. The system pressure information is provided by
MBS1250 pressure sensor located in the system pressure lines.
Electronic pressure compensator over ride (ePCOR)
The electronic Pressure Compensator Over Ride prevents the motor from over pressure. When the system
pressure exceeds the ePCOR pressure setting (set by parameter) the motor is being stroked towards max
displacement to maintain the pressure in the system. The system pressure information is provided by
MBS1250 pressure sensor located in the system pressure lines. Dependent on the available engine power
different features might be required:
•
Engine power higher than hydrostatic system can utilize → ePCOR required
•
Engine power less than hydrostatic system can utilize → Load Limiter required
Load limiter
The Load Limiter allows the system to utilize maximum available engine power. The commanded engine
rpm (TSC1) is compared with the measured engine rpm (EEC1). If the engine is drooped, the engine Load
Limiter function will increase the hydrostatic motor displacement to maintain a certain engine droop
level set by parameter. It works with CAN controlled engines.
Dependent on the available engine power different features might be required:
16 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 17

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Functions
•
•
Hydraulic-System overheat protection
An external temperature sensor, in the hydromotor PPU sensor, will measure the hydraulic oil
temperature. The function protects the complete hydrostatic system by reducing the pump flow (by
pump command) at extreme high temperatures according to user defined temperature curve.
Vehicle constant-speed-drive (CSD)
The CSD function will allows driving with a constant vehicle speed, independent of the load. If the actual
vehicle speed differs from the commanded speed, the CSD function will adjust the pump and
hydromotor command to compensate the speed difference. The speed set-point usually comes from an
electric drive pedal. For the feedback a hydromotor or vehicle speed sensor is required.
Cruise control
The Cruise Control will keep the vehicle speed constant during driving. The driver can release the drive
pedal if Cruise Control is enabled.
When the vehicle is driving the required speed, within the defined range, the driver press the “Set”
button, the vehicle speed is captured (frozen). The driver can release the drive pedal. A signal light will
show “Cruise Control switched on”. The software will keep the vehicle speed constant by adjusting the
setpoint.
An actuation of the drive pedal above the captured value (higher wins) will accelerate the vehicle. If the
drive pedal is released again, the vehicle speed will return to the captured value.
The cruise control signal light is still on.
The cruise control is switched off, if the inch pedal is pressed (more to a defined level), the FNR is
switched to neutral, the seat switch (door switch) is operated, the “Stop” button is pressed or the mode is
changed. The cruise control signal light is switched off.
To resume the stored vehicle speed again, the driver has to press the drive pedal and the “Resume”
button.
If cruise control is switched on, the driver can increase the vehicle speed by pressing the “Set” button. The
speed step and trigger time can be set by parameter. To decrease the vehicle speed, the driver can press
the button “Resume”.
Engine power higher than hydrostatic system can utilize → ePCOR required
Engine power less than hydrostatic system can utilize → Load Limiter required
Filter on drive pedal
When driving over a field or other rough terrain, the vehicle is shaking and the driver has no chance to
keep the electric drive pedal constant in one position. The filter function for the drive pedal is able to
filter this short movement. The Filter can configure individually in each Mode.
Vehicle speed dependent ramps
The time ramps for the pump and hydromotor must different depending on the vehicle speed. A vehicle
speed dependent multiplier will adjust the ramp times.
Semi-Automatic calibration function
All hydraulic components like hydromotors having tolerances. Even during lifetime they will change their
control behavior. The semi automatic calibration routine for the hydrostatic motors can be started by
service tool or CAN message. A pump calibration is due to NFPE pump not required.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 17
Page 18

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Protections
Engine control and protection
1939-CAN engine interface
The propel controller can exchange information with the engine via the CAN J1939 protocol (TSC1
message . All CAN messages can be individually activated and designated for usage. The following
functions and standard messages are provided:
•
•
•
•
•
CAN user interface
The propel controller can exchange information with external divices via DM1 and DM2 CAN messages. A
easy realisation to display error messages or the start of calibration routines is possible.
Engine speed control
An electric drive pedal with redundant input can be connected to the AC Control. The Engine Speed
setpoint is transmitted via CAN TSC1 to the engine controller.
Engine speed control (TSC1) via redundant drive pedal
Engine Anti-Stall protection
Engine Overspeed protection during inching
Engine Overspeed protection with Retarder function
Cold start protection
Engine anti-stall protection
The Engine Antistall protection prevents the engine from being stalled due to overload. The commanded
engine rpm (TSC1) is compared with the measured engine rpm (EEC1). If the engine is drooped, the
engine Antistall function will reduce the hydrostatic propel command to reduce the engine load and the
vehicle speed.
The engine Antistall function can be individually enabled for each system mode and is configurable. It
works with CAN controlled engines.
All range engine overspeed
The engine rpm is monitored in all driving situations, independent of the FNR position, seat switch
(enable), SAFE or LIMITED state. If the engine is in overspeed, a system mode change is blocked. The
overspeed protection is only active if the vehicle is moving.
When the system detects an overspeed situation, the pump will swivel out. That will limit the
deceleration of the vehicle. The driver must use the service brake to reduce the vehicle speed.
The rpm range for the overspeed detection can define by parameter. Time ramps for activation and
deactivation of the function are available.
Optional the Hydromotor (only proportional Control) is commanded to a smaller displacement. With a
larger pump and smaller Hydromotor displacement the deceleration of the vehicle will be lower. The
driver has to use the service brake.
All range engine overspeed with retarder
The engine rpm dependent Retarder Control toggles a digital output when the actual engine rpm
exceeds a user defined level. The Retarder can activate a valve of the work hydraulic to give load to
engine and prevent an over speeding.
Cold start protection
A temperature sensor measures the system temperature. If the temperature is lower than a user defined
level, the engine rpm command (TSC1) is limited until the system is warmed up to protect the engine and
the hydraulic system.
18 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 19

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Protections
Gearbox control and protection
Gearbox control
The gearbox control provides the function to actuate the shift gearbox. It actuates the shift valve and
controls the hydrostatic components according to the individual gearbox supplier specification.
Shift monitoring control
The shift monitoring control monitors the shifting process based on sensor information. It also continues
to monitor operation condition outside the shifting process.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 19
Page 20

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Auxiliary functions
Automatic park brake control
The park brake logic supports "negative brakes".
Brake applied = output is switched on
Brake released = output switched off
The conditions for the automatic park brake control are:
•
•
•
•
Delay times for park brake application and release are individually configurable.
The park brake is connected in closed loop, that means a short circuit or broken connection will detected
and lead into a SAFE state error.
Brake light
The digital brake light output is switched on if the inch/brake pedal command exceeds a user defined
value or the calculated deceleration is too high (measured by the hydromotor rpm sensor). This even
applies the brake light if the vehicle decelerates by the hydrostatic system. There will be an on/off delay
to avoid flickering of the brake lights.
Software machine state in STOP mode
Actual pump valve current below user defined value
Actual inch pedal command exceeds user defined value.
Actual vehicle speed is lower than an user defined value
Reverse buzzer
The reverse buzzer is switched on if the FNR is set to reverse.
Vehicle speed dependent outpost speed
The retarder control (Engine-Speed-Dependent Output) is switched on if the actual engine rpm exceeds a
user defined level. It can be used to enable a retarder to increase the braking capability of the system. It
can also be used to provide a signal to the boom damping system or the all wheel steering.
Error handling
The control system can detect failures which leads to different type of error modes. The safe state will
stop the machine. A limited state will reduce the machine performance and will provide information to
the driver. This can be done directly by acoustical signal, or indirectly via display by visual indication
triggered by a CAN DM1 or DM2 message.
20 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 21

System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Propel controller
Controller specification
Dual Processor Primary Flash: 1 MB; RAM: 128 kB
Rated supply voltage 12 V system 9-16 V
Rated supply voltage 24 V system 18-36 V
Digital and PWM outputs 3000 mA
Sensor supply (internal) 5 V / 500 mA
Ambient temperature -40 to 85°C
IP rating with attached connectors IP69k
EMC immunity 150 V/m
Vibration and shock tested IEC60068
Input (24 user defined inputs)
Input Function
7 x digital FNR (direction selection), temperature switch gearbox, park brake switch, park brake
10 x analog Inch pedal, drive pedal, hydrostatic oil temperature, operator presence, engine speed
4 x frequency Hydro-motor rpm
3 x frequency For customized function (option dependent)
Secondary Flash: 512 kB; RAM: 64 kB
feedback, clutch pressure feedback, pin not used
setpoint, pressure sensors, system mode switches
Output (14 user defined outputs)
Output Function
4 x PWM Pump and hydro-motor displacement control
2 x PWM For customized function (option dependent)
8 x digital Dynamic brake light, park brake, reverse buzzer, retarder control (optional), status LED,
clutch valve, low side switches pump and motor
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 21
Page 22

114.4 [4.50]
159.7 [6.29]
25.2 [1.0]
143.3 [5.64]
97.0
[3.82]
35.0 [1.38]
144.5 [5.69]
ysa1473441044006
C
C
System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Propel controller
General dimensions
Dimensions in mm [in]
Caution
PCB damage may occur. All device power supply + pins must be connected to battery +.
Caution
This device is not field serviceable. Opening the device housing will void the warranty.
* The Propel Controller is suitable as a safety-related part of a control system up to SIL 2 when used per
Danfoss requirements and the machine is so certified by an appropriate notified body or certifying
authority.
Use care when wiring mating connector. Pinouts listed are for device pins.
22 | © Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
Page 23

2198B
1 2 3 4 5
11 12 13 14 15
2524232221
3534333231
4544434241
6 7 8 9 10
16 17 18 19 20
3029282726
4039383736
5049484746
System Description
Propel Controller Solutions
Propel controller
Pin assignments
Pin connector
Pin Controller function Pin Controller function
C1-P1 Power ground - C1-P26 DIN/AIN/FreqIN
C1-P2 Power supply + C1-P27 DIN/AIN/FreqIN
C1-P3 CAN0 + C1-P28 DIN/AIN/FreqIN
C1-P4 CAN0 - C1-P29 DIN/AIN/FreqIN
C1-P5 DIN/AIN/CAN shield C1-P30 DIN/AIN/FreqIN
C1-P6 DIN/AIN/SnsrPwr1.6Vdc C1-P31 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN
C1-P7 DIN/AIN/SnsrPwr3.3Vdc C1-P32 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN
C1-P8 3-12Vdc SnsrPwr + C1-P33 DOUT
C1-P9 SnsrPwr - (sensor ground) C1-P34 DOUT
C1-P10 DIN/AIN C1-P35 DOUT
C1-P11 DIN/AIN C1-P36 DOUT
C1-P12 DIN/AIN C1-P37 DOUT
C1-P13 DIN/AIN C1-P38 DOUT
C1-P14 DIN/AIN C1-P39 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P15 DIN/AIN C1-P40 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P16 DIN/AIN C1-P41 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P17 DIN/AIN C1-P42 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P18 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN C1-P43 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P19 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN C1-P44 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P20 CAN1 + C1-P45 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P21 CAN1 - C1-P46 PWMOUT/CrntOUT/DOUT
C1-P22 DIN/AIN/CAN shield C1-P47 Power supply +
C1-P23 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN C1-P48 Power supply +
C1-P24 DIN/AIN/ResIN/CrntIN C1-P49 Power supply +
C1-P25 DIN/AIN/FreqIN C1-P50 Power supply +
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201 | 23
Page 24

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions (US) Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions Trading
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 2080 6201
Products we offer:
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
DCV directional control
•
valves
Electric converters
•
Electric machines
•
Electric motors
•
Gear motors
•
Gear pumps
•
Hydrostatic motors
•
Hydrostatic pumps
•
Orbital motors
•
PLUS+1® controllers
•
PLUS+1® displays
•
PLUS+1® joysticks and
•
pedals
PLUS+1® operator
•
interfaces
PLUS+1® sensors
•
PLUS+1® software
•
PLUS+1® software services,
•
support and training
Position controls and
•
sensors
PVG proportional valves
•
Steering components and
•
systems
Telematics
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electric components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market as well as the
marine sector. Building on our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with you to
ensure exceptional performance for a broad range of applications. We help you and other
customers around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles
and vessels to market faster.
Danfoss Power Solutions – your strongest partner in mobile hydraulics and mobile
electrification.
Go to www.danfoss.com for further product information.
We offer you expert worldwide support for ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also
provide you with comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
©
Danfoss | July 2020 AB298174786006en-000201
 Loading...
Loading...