Page 1
Instructions
Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller
PCVP DN 100-250, PN 16/25
English Page2
Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung
Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler
PCVP DN 100-250, PN 16/25
Deutsch Seite 16
© Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B | 1
Page 2

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
Table of Contents
1 Safety Notes ......................................................3
2 Definition of Application ............................3
3 Description .........................................................4
3.1 Construction ........................................................4
3.2 Mode of Operation ...........................................4
4 Technical Data ..................................................4
5 Scope of Delivery ................................... 5
6 Assembly ................................................ 6
6.1 Prior to Assembly ...............................................6
6.2 Installation Position, Installation Place ......6
6.3 When Installaling observe .............................. 6
6.4 Impulse Tube Installation ................................6
6.5 Insulation ..............................................................6
6.6 Installation Scheme ........................................... 7
6.7 Assembly Drawings, Dimensions ................ 8
7 Start-up ................................................. 10
7.1 Required static Pressure, Pressure
Difference .......................................................... 10
7.2 Leak and Pressure Test ................................... 10
7.3 Filling the System ............................................ 10
7.4 Start-up ................................................................ 10
7.5 Putting out of Operation .............................. 10
7.6 Adjustment of the Differential
Pressure ...............................................................11
7.7 Sealing .................................................................11
7.8 Function Test .....................................................12
8 Trouble Shooting ................................ 12
9 Replacement of Valve, Actuator,
Trims ..................................................... 13
9.1 Dismounting and Mounting
Actuator Valve ...................................................13
9.2 Replacement of Trim Valve VFG 2 ..............14
9.3 Dismounting, Mounting
Actuator AVP .....................................................14
9.4 Replacement of Trim Valve AVP ..................15
2 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 3

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
1 Safety Notes
MAINTENANCE
FREE
Prior to assembly and
commissioning to avoid injury
of persons and damages of the
devices, it is absolutely
necessary to carefully read and
observe these instructions.
Necessary assembly, start-up, and maintenance
work must be performed only by qualified,
trained and authorized personnel.
Prior to assembly and maintenance work on the
controller, the system must be:
depressurized,
cooled down,
emptied and
cleaned.
Please comply with the instructions of the
system manufacturer or system operator.
2 Definition of
Application
The controller is used for flow rate limitation of
water for heating, district heating and cooling
systems.
The admissible medium temperatures depend
on the design and comprise 5-150 °C,
5-200 °C.
The technical data on the rating plates determine the use.
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 3
Page 4
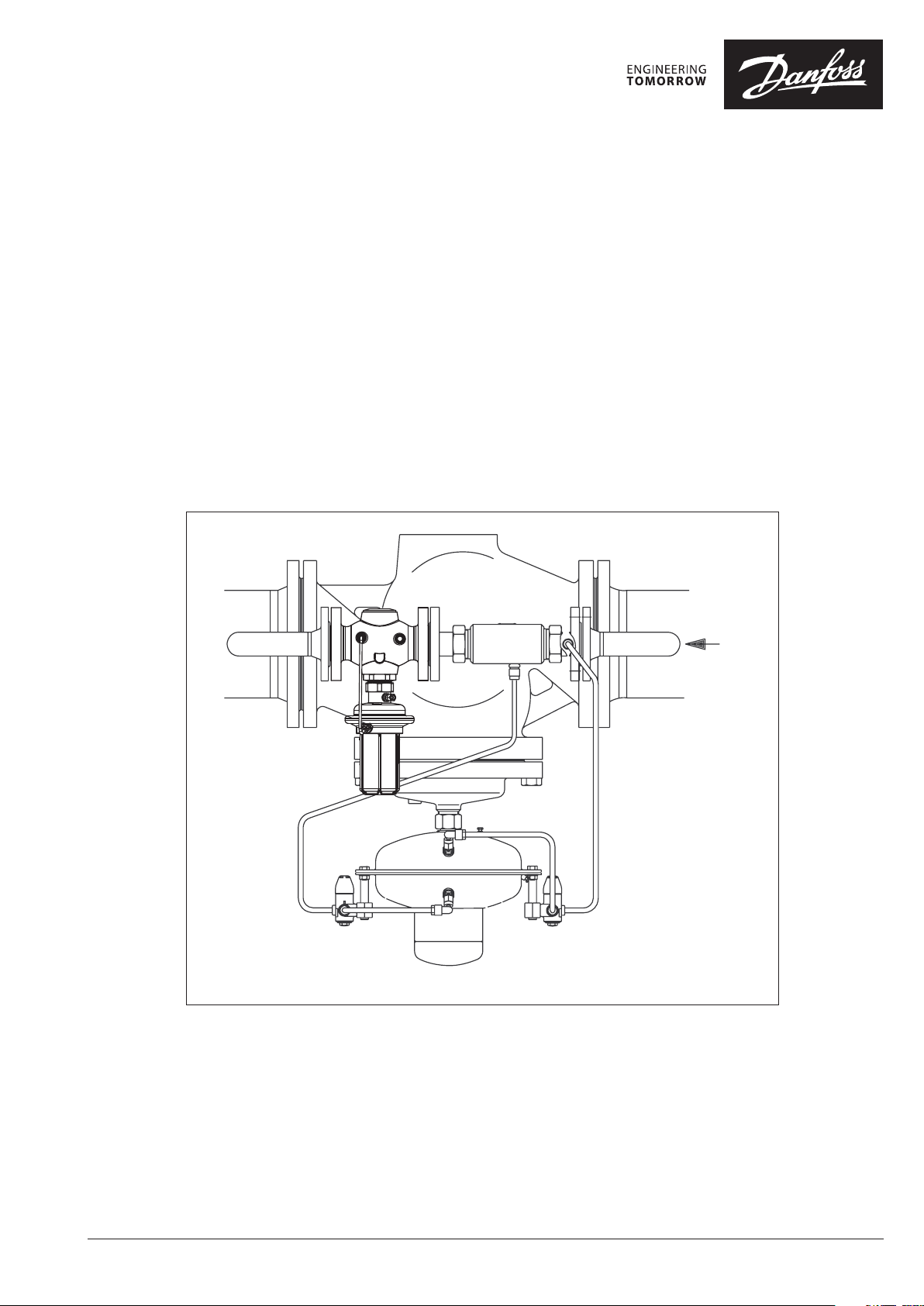
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
Pilot controller AVP
T
only by DN150-250
3 Description
3.1 Construction
hrottling valve
3.2 Mode of Operation
The control unit consists of the PCV-VFG2
valve unit, installed in the main pipe, and the
differential pressure controller AVP installed as
pilot controllers in the bypass. In the bypass line,
a throttle element is installed in front of the pilot
controllers.
The controller keeps the differential pressure
across the corresponding section on a constant
level.
The valve and the pilot valves are pressurebalanced.
The setpoint for the differential pressure is
adjusted by pre-stressing the setpoint spring of
the pilot controller AVP.
The valve unit in the main pipe is opening on
rising pressure. The pilot controllers in the
bypass line are closing on rising pressure.
Throttling element
Valve unit PCV-VFG 2
Throttling valve
In case of small flow rates, the valve in the main
pipe remains closed through the pressure spring
in the actuator of the valve unit. The pressure is
exclusively controlled by the pilot controller.
If the flow rate in the bypass is increased, the
pressure in the throttle element (Venturi nozzle)
decreases.
The reduced pressure acts through an impulse
tube upon the lower chamber of the actuator
of the valve unit. The main valve is thus opened
shock-free and continuously.
If the flow rate is reduced, the pressure in the
throttle element raises and the main valve closes.
This sequential switching guarantees an
operation free of vibrations and a small control
deviation over a wide positioning range.
4 Technical Data Technical data, see rating plates and the PCV
data sheet.
4 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 5
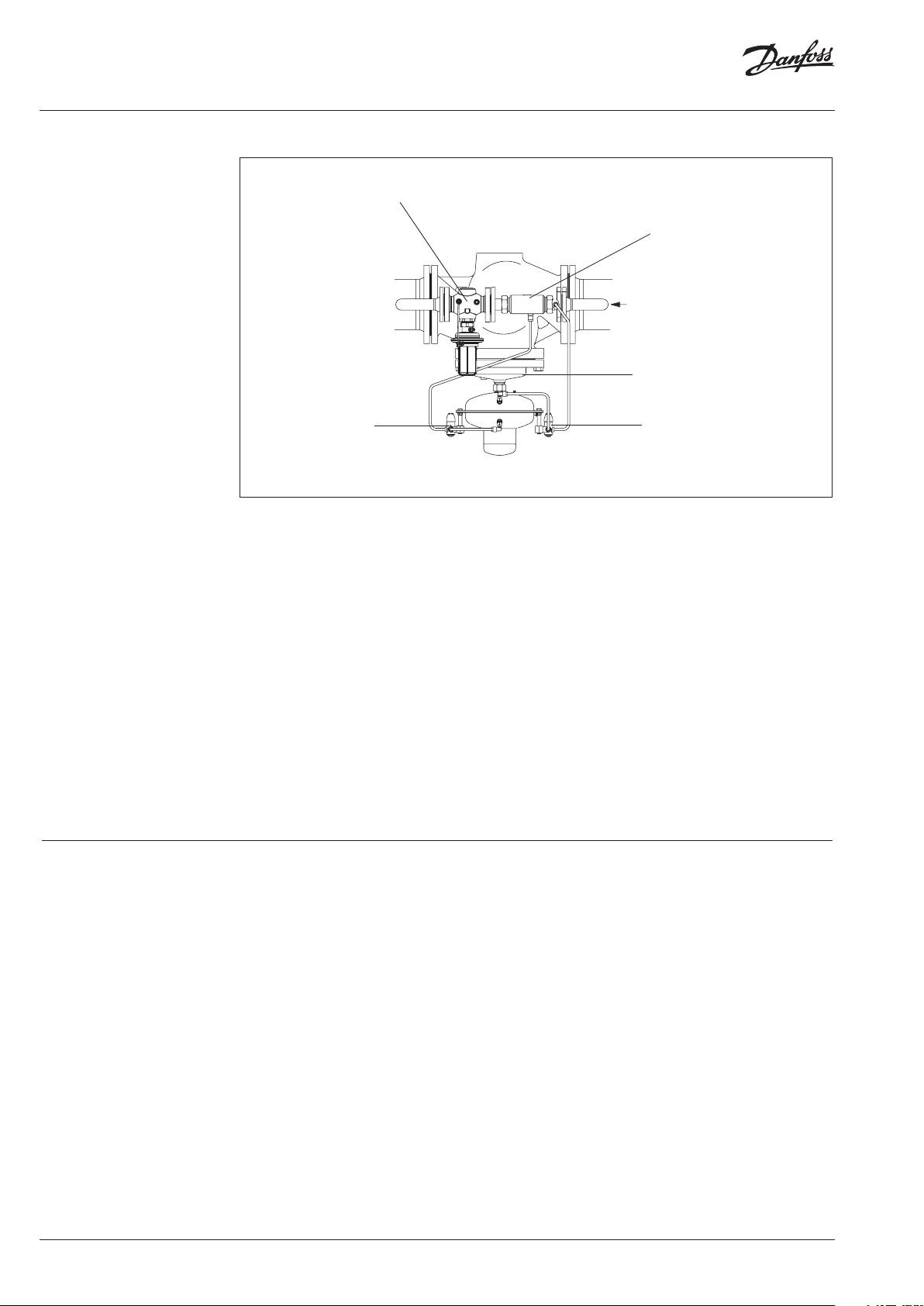
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
5 Scope of Delivery
DN 100-125
Assembly kit valve unit PCV-VFG 2 Pilot controller AVP DN 25
AVP
Throttling element
Cu pipe Ø 6 × 1 × 1500 mm
Cu pipe Ø 10 × 1 × 3000 mm
DN 150-250
Assembly kit valve unit PCV-VFG 21 Pilot controller AVP DN 40
Throttling element
Cu pipe Ø 6 × 1 × 1500 mm
Cu pipe Ø 10 × 1 × 3000 mm
AVP
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 5
Page 6
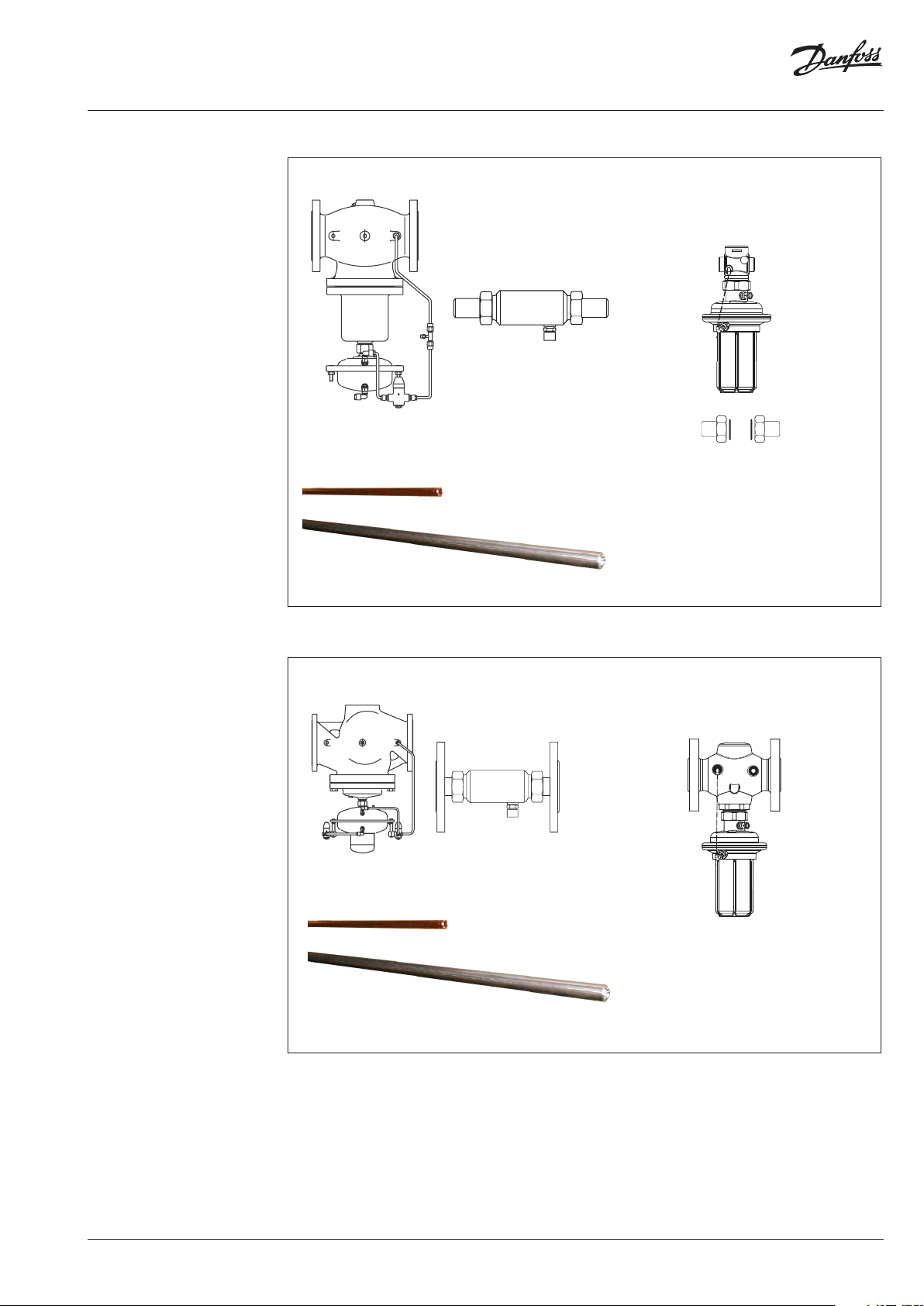
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
6 Assembly 6.1 Prior to Assembly:
Depressurized system before
any assembly work !
CAUTION!
• Clean pipeline system.
• Install strainer in front of the controller.
• Install shut-off units in front of and behind
the controller.
6.2 Installation Position, Installation Place
• Installation is only permitted in horizontal
pipelines with the actuators hanging in a
downward position.
• The controller may be installed in the supply
as well as in the return line.
6.3 When installing:
• Observe direction of flow.
• Design with welded ends:
• Loads on the valve body and the throttle
element by the pipes are not permitted.
6.4 Impulse Tube Installation
See installation scheme, section 6.6.
For CU pipes Ø 10 × 1, insert sockets 1 on both
sides.
1
Care for correct position of the cutting rings 2.
2
pin only
weld
do NOT
weld
6.5 Insulation
The diaphragm actuators must not be insulated
when insulating system parts.
6 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 7
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
V
P
)
lay impulse tube during mounting
V
P
lay impulse tube during mounting
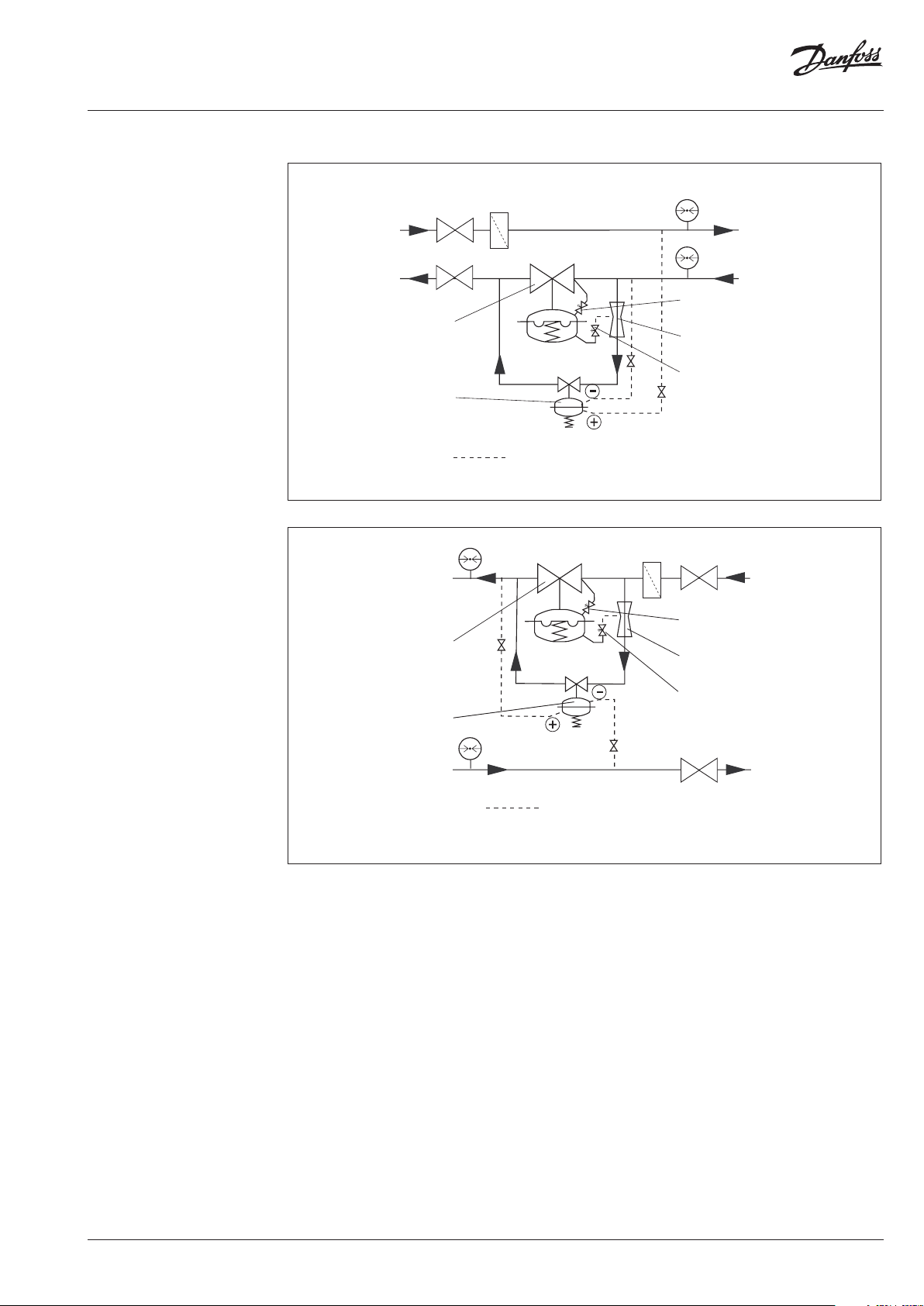
6.6 Installation Scheme
Throttling valve
alve unit PCV - VFG2
ilot controller AVP
Installation in the Return Line
alve unit PCV - VFG2
ilot controller AVP
Throttling element
Throttling valve
(only by DN 150 - 250
Throttling valve
Throttling element
Throttling valve
(only by DN 150 - 250)
Installation in the Supply Line
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 7
Page 8
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
.
CU pipe Ø 6 × 1
to the return flow
these parts are not in the scope of delivery
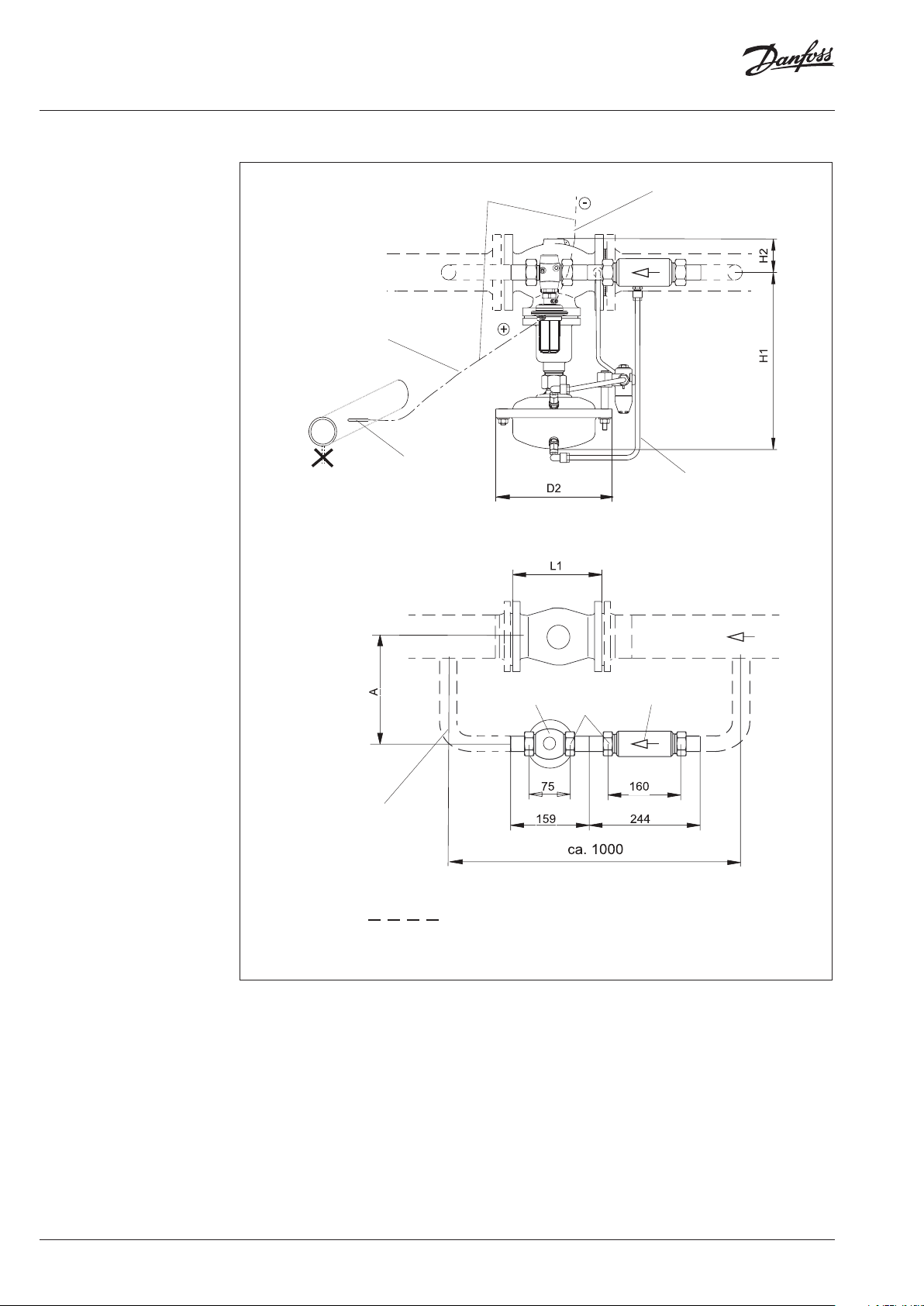
6.7 Assembly Drawings, Dimensions
Lay when assembling.
pp
ly
to the su
Install impulse tubes
laterally because of dirt
flow
Cu pipe Ø 10 × 1
Lay when assembling
DN 100-125
DN 25: pipe Ø 33.7 × 3.2
Material: ST 35.8
(not part of the delivery)
Pilot controller AVP
DN 25 SW 50
Throttling
element
8 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 9
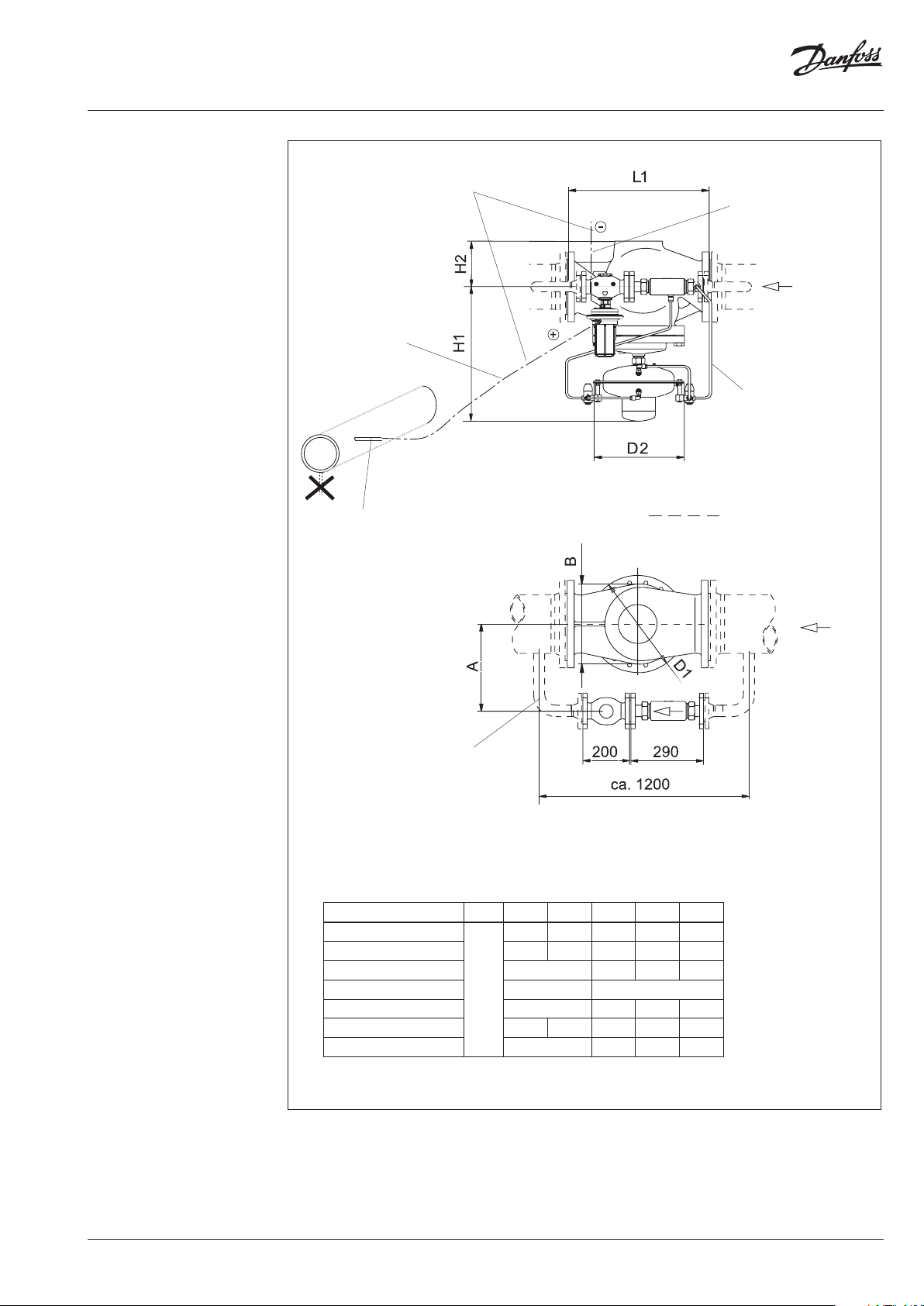
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
CU pipe Ø 6 × 1
Lay when assembling.
to the supply flow
to the return flow
Cu pipe Ø 10 × 1
Lay when assembling.
Install impulse tubes
laterally because of dirt
DN 40: pipe Ø 48.3 × 3.2
Material: ST 35.8
(not part of the delivery)
DN 150-250
Dimensions
Nominal diameter DN 100 125 150 200 250
L1
H1 530 530 619 647 697
H2 - 174 229 254
D2 263 380
D1 250 350 385 500
B 200 210 310 336 412
A ≥ 290 320 350 410
350 400 480 600 730
mm
these parts are
not in the scope of delivery
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 9
Page 10
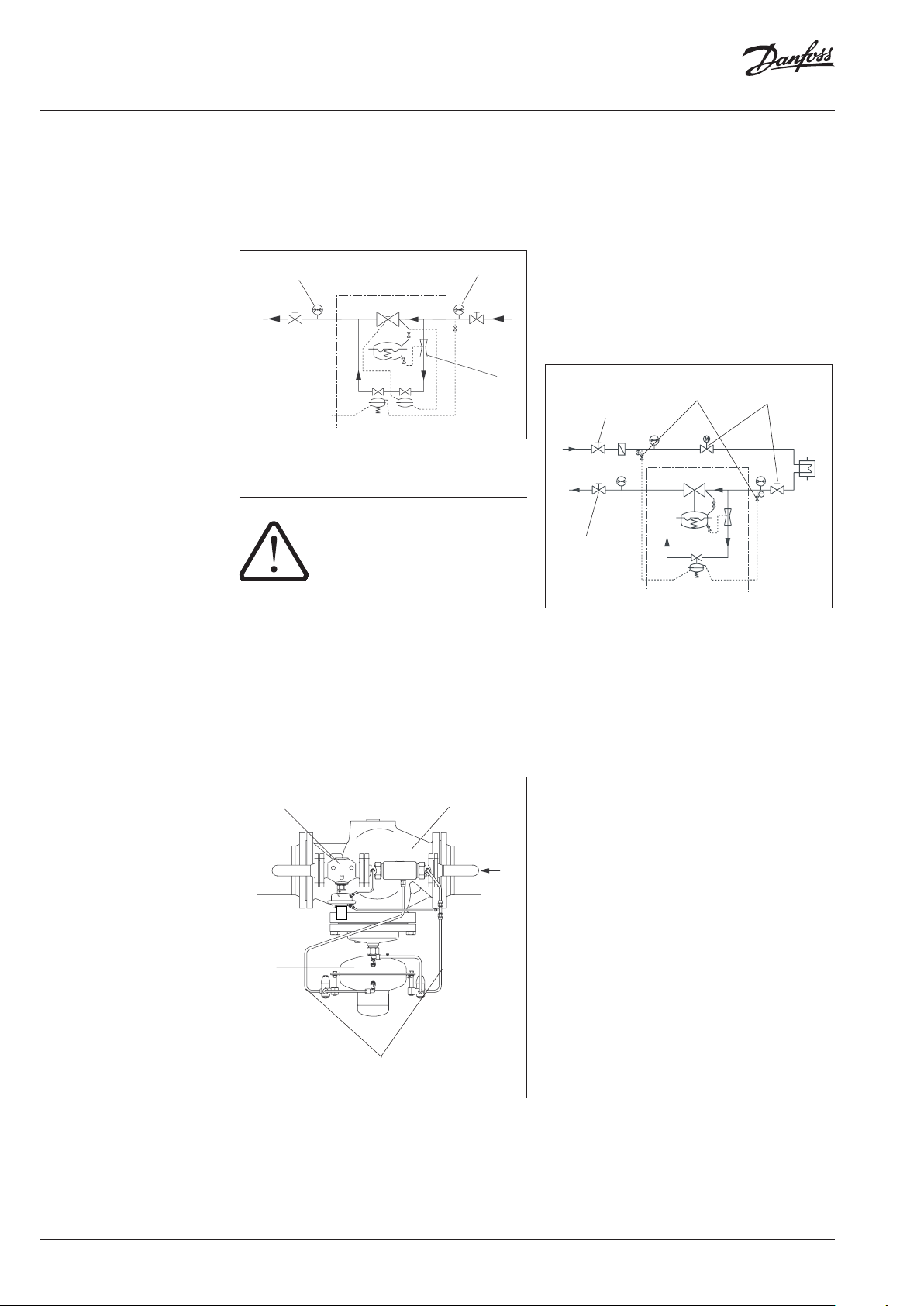
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
5
4
3
67
p2 p1
7 Start-up 7.1 Required Static Pressure
The static pressure p1 in front of the controller
must not fall below 1,5 bar (excess pressure).
Non-observance may lead to cavitation and
damages in the throttling element 1.
7.2 Leak and Pressure Tests
To avoid too high pressures at
the diaphragm actuators, the
following should be observed
prior to any pressure tests:
7.3 Filling the System
Note:
The controller 4 is closed when no pressure is
applied and only opens with a defined flow in the
bypass.
The pilot controller 5 is closing on rising pressure.
1. Open shut-off valves 6 that possibly exist in
the impulse tubes.
2. Open units 7 of the system.
3. Slowly open shut-off units in the supply
flow 8 and the return flow 9.
1
8
9
Actuator of valve unit:
The admissible operating excess pressure in the
actuator 2 is 25 bar 1). For higher pressures, you
must:
• Remove the impulse tubes 3 at the actuator
and close the connections with a stopper.
• Prior to any leak or pressure test, the
instructions in section 7.3 must be complied
with.
7.4 Start-up
During starting-up the filled system, open the
units in the same sequence as described in
section 7.3.
7.5 Putting out of operation
When putting the system out of operation, first
close the shut-off units in the supply flow and
then those of the return flow.
2
10 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
1)
Pre-condi tion: Same pressure on both side s of the diaphragm.
If the pressure lo ad is one-sided, the (+)diaphragm cham ber
may have an excess p ressure of 1 bar in comparison to th e (-)
diaphragm chamber.
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 11

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
1
P1
2
4
p
5
7.6 Adjustment of the Differential Pressure
The setpoint of the differential pressure must
be adjusted at the pilot controller AVP 1. The
setpoint range is indicated on the rating plate of
the actuator.
Procedure
1. Prior to the differential pressure adjustment,
start the system as described in section 7.4.
The differential pressure can also be adjusted
while the bypass 2 is opened.
2. Adjust the flow rate at the unit by which the
differential pressure is controlled.
Adjustment, e.g. at unit 3 or 4 or via bypass 2
to approx. 50 % of the max. flow rate 5.
3. Adjustment of the differential pressure
setpoint by turning the setpoint adjuster 6.
Turning to the right, reduces the setpoint.
Turning to the left, increases the setpoint.
4. Observe pressure indicators 7.
7.7 Sealing
The setpoint adjusters may be sealed.
3
7
PCVP
P2
0 50% V
max
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 11
Page 12

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
7.8 Function Test
Differential pressure
Check the differential pressure on the pressure
indicators by opening and closing a unit in
the corresponding section of the system to be
controlled.
If the differential pressure is exceeded in either
direction, adjust the differential pressure as
described in section 7.6.
8 Trouble Shooting
Fault Possibl e cause Remedy
Controller does
not hold the
differential
pressure on a
constant level
Air in the actuators
1. Loosen impulse tube connections
at the actuators by approx. 1 rotation.
2. Deaerate, Caution hot water !
(move impulse tube until medium
3. Tighten impulse tube connections.
Differential
pressure is
too high
Impulse tubes or impulse tube connections are
dirty or damaged.
Pilot valve AVP does not close:
Valve seat or plug is dirt y or damaged.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Clean impulse tubes and impulse
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Dismount actutor and trim.
Procedure see section 9.4.
3. Clean seat and plug.
4. If damaged, replace trim or valve.
Valve VFG2 does not close:
Valve seat or plug is dirt y or damaged.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Dismount actutor and trim 1).
Procedure, see section 9.2.
3. Clean seat and plug.
4. If damaged, replace trim or valve.
Differential
pressure is too low
Rolling diaphragm in the actuator AVP
(pilot controller) is defective,
i.e. valve AVP does not close.
Valve plug of the pilot valve AVP
does not open:
Valve seat or plug is dirt y or damaged,
trim is dirty.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Replace actuator, see section 9.2.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Dismount actuator and trim.
Procedure, see section 9.4.
3. Clean seat and plug.
4. If damaged, replace trim or valve.
Valve plug of the pilot valve VFG2
does not open:
Valve seat or plug is dirt y or damaged,
trim is dirty.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Dismount actutor and trim 1).
Procedure, see sections 9.1 and 9.2.
3. Clean seat and plug.
4. If damaged, replace trim or valve.
Rolling diaphragm in the actuator of the valve
unit is defective, i.e. valve VFG2 does not open.
1. Remove impulse tube.
2. Loosen union nut SW 46
and remove actuator,
see also section 9.1.
3. Replace actuator.
1)
The trim can be r eplaced by qualified pers onnel up to DN 125.
From DN 150 replacement shou ld be carried out by the Danfoss s ervice personnel.
penetrates).
tube connections and check for free
passage.
12 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 13

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
g
Cone
to the left
9 Replacement of Valve,
Actuator, Trim
9.1 Dismounting and Mounting Actuator and
Valve
Note:
The springs 1 in the actuator are pre-stressed.
Therefore, the actuator must be pushed upwards
to be dismounted. You need a second person to
do this.
Valve unit DN 100 –125
3
SW 46
5
2
1
4
Valve unit DN 150–250
3
SW 46
1
4
Turn
actuator
The stem of the actuator 4 is screwed into the
valve stem 3.
Dismounting
1. Dismount impulse tubes.
2. Completely loosen union nut 1.
The actuator hangs on the screwed-in
stem 4.
Valve stem 3 and the stem of the actuator 4 are
not screwed to eachother.
Dismounting
1. Dismount impulse tubes.
2. Support actuator below or by a second
person as the springs 1 are pre-stressed.
3. Loosen union nut 2.
4. Remove actuator.
Prior to assembly check cone 5 !
5
rease
1. Clean cone prior to mounting.
2. Check O rings for damages, in case of
damages, replace cone (see Spare Parts).
3. Grease cone with high-performance fitting
component: BARRIERTA L55/3 HV
(see Spare Parts).
The actuator weights approx.
20 kg. In addition, an internal
spring package is pre-stressed.
Secure against dropping down
before unscrewing.
3. Screw the stem of the actuators 4 out of the
valve stem 3 by turning the actuator to the
left.
Mounting
1. Place actuator at the valve and push upward
to press the spring package in the actuator
together (second person necessary).
2. Carefully turn actuator to the right.
By this, carefully screw in the stem of the
actuator into the valve stem to its stop.
Then, return the actuator by
approx. 1 rotation (to the left)
3. Align actuator, observe position of the
control lines connections.
4. Tighten union nut 1, torque 100 Nm.
Mounting
1. Place actuator at the valve and push
upwards.
2. Screw on union nut 2.
3. Align actuator, observe position of impulse
tube connections.
4. Tighten union nut 1, max. torque 100 Nm.
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 13
Page 14

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
2
3
1
5
6
9 Replacement of Valve,
Actuator, Trim
9.2 Replacement of Trim Valve VFG2
The trim can be replaced by qualified personnel
up to DN 125. From DN 150 replacement should
be carried out by the Danfoss service personnel.
Removing the trim:
Valves DN 100–125
4
1. Dismount actuator 1 (see section 9.1).
2. Unscrew hexagon head cap screw 2.
3. Remove b onnet 3.
4. Take out trim 4.
Prior to installation:
Clean sealing surfaces 5 and socket 6, grease
sealing surfaces with antiseize graphite
petroleum.
9.3 Dismounting, Mounting Actuator AVP
1
AVP
Dismounting
1. Dismount impulse tubes.
2. Loosen union nut 1.
3. Remove a ctuator.
Mounting
1. Place actuator at the valve and align,
observe position of the impulse tube
connections.
2. Screw on union nut 1 and tighten, torque
100 Nm.
14 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
Installing the trim:
Mounitng is carried out in reverse order.
Torque hexagon head cap screws 2:
DN Torque Wrench
100-125 180 N m SW 30
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 15

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
2
9.4 Replacement of Trim Valve AVP
AVP DN 25 AVP DN 40
2
Dismounting
1. Unscrew actuator (see above).
2. Unscrew trim 2.
DN 25: with pipe tongs, wrap gum strips
around the trim
DN 40: with wrench SW 55
3. Pull out trim.
Mounting
Mounting is carried out in reverse order. Only
tighten with low torque, sealing is made with
O rings.
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 15
Page 16

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Sicherheitshinweise ................................... 17
2 Bestimmungsgemäße
Verwendung ................................................... 17
3 Beschreibung ................................................. 18
3.1 Aufbau .................................................................18
3.2 Wirkungsweise .................................................18
4 Technische Daten ......................................... 18
5 Lieferumfang .................................................19
6 Montage ...........................................................20
6.1 Vor der Montage beachten ......................... 20
6.2 Einbaulage, Einbauort .................................. 20
6.3 Beim Einbau beachten .................................. 20
6.4 Einbau Steuerleitung ..................................... 20
6.5 Isolierung ........................................................... 20
6.6 Einbauschemas ..................................................21
6.7 Montagezeichnungen,
Abmessungen .................................................. 22
7 Inbetriebnahme ............................................24
7.1 Erforderliche(r) statischer Druck,
Druckdifferenz .................................................. 24
7.2 Dichtheitsprüfung / Druckprüfung ......... 24
7.3 Füllung der Anlage ......................................... 24
7.4 Inbetriebnahme .............................................. 24
7.5 Ausserbetriebnahme ..................................... 24
7.6 Differenzdruckeinstellung .......................... 25
7.7 Plombierung .....................................................25
7.8 Funktionsprüfung .......................................... 26
8 Störungshinweise ........................................26
9 Austausch von Ventil, Antrieb,
Innengarnituren ........................................... 27
9.1 Antrieb demontieren, montieren ............. 27
9.2 Austausch der Innengarnitur
Ventil VFG 2 ....................................................... 28
16 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
9.3 Demontage, Montage
Antrieb AVP ....................................................... 28
9.4 Austausch der Innengarnitur
Ventil AVP .......................................................... 28
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 17

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
1 Sicherheitshinweise
MAINTENANCE
FREE
Um Verletzungen an Personen
und Schäden am Gerät zu
vermeiden, ist diese Anleitung
vor der Montage unbedingt zu
beachten.
Montage, Inbetriebnahme und
Wartungsarbeiten dürfen nur von sachkundigen
und autorisierten Personen durchgeführt
werden.
Vor Montage und Wartungsarbeiten am Regler
die Anlage:
drucklos machen,
abkühlen,
entleeren und
reinigen.
Die Vorgaben des Anlagenherstellers und
Anlagenbetreibers sind zu beachten.
2 Bestimmungsgemäße
Verwendung
Der Regler dient der Volumenstrombegrenzung
und Differenzdruckregelung von Wasser für
Heizung, Fernwärmeheizung und Kühlsysteme.
Die zulässigen Mediumstemperaturen sind je
nach Ausführung 5 - 150 °C, 5 - 200 °C.
Die technischen Daten auf den Typenschildern
sind für die Verwendung maßgebend.
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 17
Page 18

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
Pilotregler AVPDrosselelement DE
Drosselventil
nur bei DN150-250
3 Beschreibung
3.1 Aufbau
3.2 Wirkungsweise
Die Regeleinheit besteht aus dem in der
Hauptleitung eingebauten Stellgerät PCV-VFG2
und dem im Bypass als Pilotregler angeordneten
Differenzdruckregler AVP. In der Bypassleitung ist
vor dem Pilotregler ein Drosselement eingebaut.
Der Regler hält den Differenzdruck über der
Anlagenstrecke konstant entsprechend dem
eingestellten Sollwert.
Das Stellventil und das Pilotventil ist
druckentlastet.
Die Sollwerteinstellung des Differenzdruckes
erfolgt über die Vorspannung der Sollwertfeder
des Pilotreglers AVP.
Das Stellgerät in der Hauptleitung ist drucklos
geschlossen. Der Pilotregler in der Bypassleitung
ist drucklos geöffnet.
Hauptleitung
Bypass
Stellgerät PCV-VFG2
Drosselventil
Bei geringen Volumenströmen bleibt das Ventil
in der Hauptleitung durch die Druckfeder
im Antrieb des Stellgerätes geschlossen. Die
Differenzdruckregelung erfolgt ausschließlich
über den Pilotregler.
Erhöht sich der Volumenstrom in der
Bypassleitung, so sinkt der Druck im
Drosselelement (Venturidüse).
Dieser abgesenkte Druck wirkt über eine
Steuerleitung auf die Unterkammer des Antriebs
des Stellgerätes. Das Hauptventil wird dadurch
stoßfrei und stetig geöffnet.
Reduziert sich der Volumenstrom, so steigt der
Druck im Drosselelement an und das Hauptventil
schließt.
Diese Folgeschaltung gewährleistet eine
schwingungsfreie Betriebsweise und eine
geringe Regelabweichung über einen großen
Stellbereich.
4 Technische Daten Technische Daten siehe Typenschilder und
Datenblatt PCV.
18 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 19

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
5 Lieferumfang
DN 100-125
Bausatz Stellgerät PCV-VFG2 Pilotregler DN 25
AVP
Drosselelement
Cu-Rohr Ø 6 × 1 × 1500 mm
Cu-Rohr Ø 10 × 1 × 3000 mm
DN 150-250
Bausatz Stellgerät PCV-VFG2 Pilotregler DN 40
AVP
Drosselelement
Cu-Rohr Ø 6 × 1 × 1500 mm
Cu-Rohr Ø 10 × 1 × 3000 mm
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 19
Page 20

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
6 Montage 6.1 Vor der Montage beachten
Anlage vor der Montage
drucklos machen!
Achtung!
• Rohrleitungssystem reinigen
• Schmutzfänger vor dem Regler einbauen
• Absperrarmaturen vor und nach dem Regler
einbauen
6.2 Einbaulage, Einbauort
• Der Einbau ist nur in waagrechte
Rohrleitung mit nach unten hängenden
Antrieben zulässig.
• Der Regler kann im Vorlauf oder Rücklauf
der Anlage eingebaut werden
6.3 Beim Einbau beachten
• Durchflussrichtung beachten
• Ausführung mit Anschweißenden element
by the pipes are not permitted.
• Belastung der Ventilgehäuse und des
6.4 Einbau Steuerleitung
Siehe Einbauschema Abschnitt 6.6
Bei den CU-Leitungen Ø10 ×1 beidseitig
Einsteckhülsen 1 einfügen.
1
Richtige Lage der Schneidringe 2 beachten
2
nur Heften
Schweißen
nicht
Schweißen
Drosselelementes durch die Rohrleitungen
sind nicht zulässig.
6.5 Isolierung
Bei Isoliermaßnahmen dürfen die
Membranantriebe nicht isoliert werden.
20 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 21

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
Stellgerät PC
P
Steuerleitungen bei Montage verlegen
Stellgerät PC
P
Steuerleitungen bei Montage verlegen
6.6 Installation Scheme
Drosselventil
ilotregler AVP
Einbau im Rücklauf
ilotregler AVP
V - VFG 2
V - VFG 2
Drosselelement
Drosselventil
(nur bei DN 150 - 250)
Drosselventil
Drosselelement
Drosselventil
(nur bei DN 150 - 250)
VI.JA.B3.5B
Einbau im Vorlauf
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 21
Page 22

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
CU-Rohr Ø 6 × 1
Rohrleitung
Vo
6.7 Montagezeichnung, Abmessungen
rlauf
Bei Montage verlegen
zum Vorlauf
Steuerleitungen wegen
Verschmutzung seitlich
anbringen
zum Rücklauf
CU-Rohr Ø 10 × 1
Bei Montage verlegen.
Stellgerät PCV - VFG 2
DN 100-125
Pilotregler AVP
Drosselelement
DN 25 SW 50
22 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 23

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
.
CU-Rohr Ø 6 × 1
Bei Montage verlegen.
zum Vorlauf
Rohrleitung
Vorlauf
Steuerleitungen wegen
Verschmutzung seitlich
anbringen
zum Rücklauf
CU-Rohr Ø 10 × 1
Bei Montage verlegen
gestrichelt dargestellte
Komponenten sind kein
Lieferbestandteil
DN 150-250
DN 40: Rohr Ø 48,3 × 3,2
Werkstoff: ST 35.8
(kein Lieferbestandteil)
Abmessungen
Nennweite DN 100 125 150 200 250
L1
H1 530 530 619 647 697
H2 - 174 229 254
D2 263 380
D1 250 350 385 500
B 200 210 310 336 412
A ≥ 290 320 350 410
350 400 480 600 730
mm
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 23
Page 24

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
p2 p1
5
4
3
67
7 Inbetriebnahme 7.1 Erforderliche(r) statischer Druck,
Druckdifferenz
Für die Funktion ist eine Mindestdruckdifferenz
erforderlich: p1 − p2 ≥ 0,5 bar
Der statische Druck p1 vor dem Regler darf
1, 5 bar (Überdruck) nicht unterschreiten.
Nichtbeachtung kann zu Kavitation und Schäden
im Drosselement 1 führen.
7.2 Dichtheits-, Druckprüfung
Um unzulässig hohe Drücke
an den Membranantrieben
zu vermeiden muß vor
Druckprüfungen folgendes
beachtet werden:
Antrieb Stellgerät:
Der zulässige Betriebsüberdruck im Antrieb 2
beträgt 25 bar 1) . Bei höherem Prüfdruck müssen:
• Die Steuerleitungen 3 am Antrieb entfernt
und die Anschlüsse mit einem Stopfen
verschlossen werden.
• Vor einer Dichtheitsprüfung bzw.
Druckprüfung nach Abschnitt 7.3 vorgehen
7.3 Füllung der Anlage
Hinweis:
Der Stellgerät 4 ist drucklos geschlossen und öffnet
erst bei definiertem Durchfluss im Bypass.
Der Pilotregler 5 ist drucklos geöffnet.
Vorgehensweise
1. Eventuell in den Steuerleitungen vorhandene
Absperrventile 6 öffnen.
2. Armaturen 7 in der Anlage öffnen.
3. Die Absperrarmaturen im Vorlauf 8 und im
Rücklauf 9 langsam öffnen.
1
8
9
7.4 Inbetriebnahme
Bei der Inbetriebnahme der gefüllten Anlage
ist die gleiche Reihenfolge beim Öffnen
der Armaturen zu beachten wie unter 7.3
beschrieben.
7.5 Ausserbetriebnahme
Bei der Ausserbetriebnahme zuerst die
Absperrarmaturen im Vorlauf und dann im
Rücklauf schließen.
24 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
2
1)
Voraussetzung:
gleicher Druck auf beiden Seiten der Membrane. Bei einseitiger
Druckbela stung ist in der (+)-Membrankammer ei n max.
Überdruck ge genüber der (-)-Memb rankammer von 1 bar
zulässig.
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 25

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
1
P1
4
p
0 50% V
5
7.6 Differenzdruckeinstellung
Der Sollwert des Differenzdrucks ist an
dem Pilotregler AVP 1 einzustellen. Der
Sollwertbereich ist auf dem Typschild des
Antriebes angegeben.
Vorgehensweise
1. Vor der Differenzdruckeinstellung
Inbetriebnahme der Anlage nach Abschnitt
7.4 durchführen.
Die Einstellung des Differenzdruckes kann
auch erfolgen, wenn nur ein Bypass 2
geöffnet ist und die Anlage (z. B. Ventile 3
und 4) geschlossen ist.
2. Den Volumenstrom an einer Armatur, über
welche der Differenzdruck zu regeln ist,
einstellen.
Einstellung z.B. an der Armatur 3 oder 4 oder
über einen Bypass 2 auf ca. 50 % 5 des max.
Volumenstroms.
3. Einstellung des Differenzdrucksollwertes
durch Drehung des Sollwertstellers 6.
Rechtsdrehung : Sollwert reduzieren
Linksdrehung: Sollwert erhöhen
4. Die Druckanzeigen 7 sind zu beachten.
7.7 Plombierung
Der Sollwertsteller kann plombiert werden.
3
7
PCVP
2
P2
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 25
Page 26

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
7.8 Funktionsprüfung
Differenzdruck
Durch Öffnen und Schließen einer Armatur
in der zu regelnden Anlagenstrecke ist der
Differenzdruck über die Druckanzeigen zu
überprüfen.
Bei Über- oder Unterschreitung den
Differenzdruck nach Abschnitt 7.6 nachstellen.
8 Störungshinweise
Störung Mögliche Ursache Maßnahme
Regler hält den
Differenzdruck
nicht konstant
Luft in den Antrieben
1. Steuerleitungsanschlüsse an den
Antrieben ca. 1 Umdrehung lösen
2. Entlüften, Achtung Heisswaser!
(Steuerleitung bewegen bis Medium
austritt)
3. Steuerleitungsanschlüsse wieder
anziehen
Steuerleitungen bzw. Steuerleitungsanschlüsse
verschmutzt oder verstopft
1. Steuerleitungen demontieren
2. Steuerleitungen und Anschlüsse
reinigen und Durchgang überprüfen
Differenzdruck
zu hoch
Pilotventil AVP schließt nicht:
Ventilsitz bz w. Kegel verschmut zt oder
beschädigt
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Antrieb und Innengarnitur
demontieren Vorgehensweise siehe
Abschnitt 9.4
3. Sitz und Kegel reinigen
4. Bei Beschädigung Innengarnitur bzw.
Ventil austauschen
Stellventil VFG 2 schließt nicht:
Ventilsitz bz w. Kegel verschmut zt oder
beschädigt
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Antrieb und Innengarnitur
demontieren
Vorgehensweise siehe Abschnitt 9.2
3. Sitz und Kegel reinigen
4. Bei Beschädigung Innengarnitur
bzw. Ventil austauschen
Volumenstrom
zu niedrig
Rollmembrane im Antrieb AVP (Pilotregler)
defekt, d. h. Ventil AVP schließt nicht
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Antrieb austauschen, siehe Abschnitt
9.3
Ventilkegel des Pilotventils AVP öffnet nicht:
Ventilsitz bz w. Kegel verschmut zt
oder beschädigt, Innengarnitur verschmutzt
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Antrieb und Innengarnitur
demontieren Vorgehensweise siehe
Abschnitt 9.4
3. Sitz und Kegel reinigen
4. Bei Beschädigung Innengarnitur bzw.
Ventil austauschen
Ventilkegel des Stellventils VFG2
öffnet nicht:
Ventilsitz bz w. Kegel verschmut zt oder
beschädigt, Innengarnitur verschmutzt
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Antrieb und Innengarnitur
demontieren
Vorgehensweise siehe Abschnitt 9.1
und 9.2
3. Sitz und Kegel reinigen
4. Bei Beschädigung Innengarnitur
bzw. Ventil austauschen
Rollmembrane im Antrieb des Stellgerätes
defekt, d. h. Ventil VFG2 öffnet nicht
1. Steuerleitungen abbauen
2. Überwurfmutter SW 46
lösen und Antrieb abnehmen
siehe auch Abschnitt 9.1
3. Antrieb austauschen
1)
Austausch der In nengarnitur bis DN 125 ist durch sachkund ige Personen möglich. A b DN 150 sollte der
Austausch durch d en Danfoss-Kundendiens t erfolgen.
1)
1)
26 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 27

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
g
Cone
drehen
3
9 Austausch von
Ventil, Antrieb,
Innengarnituren
9.1 Antrieb demontieren, montieren
Hinweis:
Die Federn 1 im Antrieb sind vorgespannt. Deshalb
muss der Antrieb zur Demontage, Montage
hochgedrückt werden. Hierzu ist eine 2. Person
erforderlich.
3
SW 46
5
Stellgerät DN 100 –125
Ventilstange 3 und die Stange des Antriebs 4
sind nicht miteinander verschraubt.
Demontage
1. Steuerleitungen demontieren
2. Antrieb unten abstützen oder durch 2.
Person gegenhalten, da Federn 1
vorgespannt sind
3. Überwur fmutter 2 lösen
4. Antrieb abnehmen
Vor der Montage Konus 5 überprüfen
2
1
4
SW 46
1
4
Antrieb
nach links
DN 150–250
Die Stange des Antriebs 4 ist in die
Ventilstange 3 eingeschraubt.
Demontage
1. Steuerleitungen demontieren
2. Überwur fmut ter 1 ganz lösen
Antrieb bleibt an der eingeschraubten
Stange 4 hängen
Der Antrieb wiegt ca. 20 kg,
zusätzlich ist internes
Federpaket vorgespannt.
Vor dem Herausschrauben
gegen herunterfallen sichern.
3. Durch drehen des Antriebs nach links die
Stange des Antriebs 4 aus der Ventilstange 3
herausschrauben
5
fetten
rease
1. Konus vor der Montage reinigen
2. O-Ringe auf Beschädigung überprüfen, bei
Beschädigung Konus austauschen (siehe
Ersatzteile)
3. Konus fetten mit HochleistungsArmaturenfett: z. B. BARRIERTA L55/3 HV
Montage
1. Antrieb am Ventil ansetzen und
hochdrücken
2. Überwur fmut ter 2 aufschrauben
3. Antrieb ausrichten, Position der
Steuerleitungsanschlüsse beachten
4. Überwur fmut ter 1 anziehen, max.
Anzugsmoment 100 Nm
Konus
Montage
1. Antrieb am Ventil ansetzen und
hochdrücken um Federpaket im
Antrieb zusammenzudrücken (2. Person
erforderlich)
2. Antrieb vorsichtig nach rechts drehen.
Dadurch die Stange des Antriebes in die
Ventilstange vorsichtig bis zum Anschlag
eindrehen.
danach unbedingt den
Antrieb um ca. 1 Umdrehung
zurückdrehen (nach links)
3. Antrieb ausrichten, Position der
Steuerleitungsanschlüsse beachten
4. Überwurfmutter 1 anziehen,
Anzugsmoment 100 Nm
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 27
Page 28

Einbau-, Bedienungsanleitung Hilfsgesteuerter Differenzdruckregler PCVP
2
3
1
5
6
2
9.2 Austausch der Innengarnitur Ventil VFG2
Der Austausch der Innengarnitur bis DN 125
ist durch sachkundige Personen möglich. Ab
DN 150 sollte der Austausch durch den DanfossKundendienst erfolgen.
Innengarnitur ausbauen
Ventile DN 100–125
4
1. Antrieb 1 demontieren (siehe Abschnitt 9.1)
2. Sechskantschraub en 2 herausschrauben
3. Ventilunterteil 3 abnehmen
4. Innengarnitur 4 herausnehmen
Innengarnitur einbauen
Die Montage erfolgt in umgekehrter
Reihenfolge.
Anzugsmoment der Sechskantschrauben 2:
DN Torque Wrench
100-125 18 0 Nm SW 30
9.4 Austausch der Innengarnitur Ventil AVP
AVP DN 25
Vor dem Einbau
Dichtflächen 5 und Buchse 6 reinigen,
Dichtflächen mit Graphitfett fetten
2
9.3 Demontage, Montage Antrieb AVP
AVP DN 40
Demontage
1
Demontage
1. Steuerleitungen demontieren
2. Überwur fmut ter 1 lösen
3. Antrieb abnehmen
Montage
1. Antrieb am Ventil aufsetzen und ausrichten,
Position der Steuerleitungsanschlüsse
beachten
2. Überwur mutter 1 aufschrauben und
anziehen, Anzugsmoment 100 Nm
1. Antrieb abschrauben (siehe oben)
2. Innengarnitur 2 herausschrauben
DN 25: mit Rohrzange, Gummistreifen um
Innengarnitur wickeln
DN 40: mit Schlüssel SW 55
3. Innengarnitur herausziehen
Montage
Die Montage erfolgt in umgekehrter
Reihenfolge. Die Innengarnitur nur mit
niedrigem Anzugsmoment anziehen,
Abdichtung erfolgt mit O-Ringen.
28 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 29

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 29
Page 30

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
30 | © Danfoss | 2016.05
VI.JA.B3.5B
Page 31

Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
VI.JA.B3.5B
© Danfoss | 2016.05 | 31
Page 32

Danf
already on order pro
All trademarks in this material are property of the respec
Instructions Pilot-controlled Differential Pressure Controller PCVP
oss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
vided that such alterations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary eady agreed.
32 | © Danfoss | DHS-SRMT/SI | 2016.05
tive companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
73696670 / VI.JA.B3.5B
 Loading...
Loading...