Page 1

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP Contents
Contents
1 Safety
Safety Note 3
Safety Regulations 3
Warning against Unintended St art 4
2 Introduction
About this Manual 5
Technical Overview 5
Assumptions 5
Hardware 5
Background Knowledge 5
Available Literature 6
ODVA Conformance 6
Abbreviations 6
3 How to Install
The EtherNet/IP Option 7
How to Install Option in Frequency Converter 8
3
5
7
LED Behaviour 9
Topology 10
Network 11
Recommended Design Rules 12
EMC Precautions 13
4 How to Configure
IP Settings 15
Ethernet Link Parameters 16
Configuring the Scanner 17
IP traffic 19
5 How to Control
How to Control 21
I/O Assembly Instances 21
EtherNet/IP Connections 22
Class 1 connection 22
Class 3 connection 23
15
21
Unconnected Messages, UCMM 23
Control Word Profile 23
Change of State, COS 24
Danfoss FC Control Profile 25
Danfoss FC Control Profile
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
25
1
Page 2
Contents MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Status Word according to FC ProfileDrive Profile (STW) 26
ODVA Control Profile 27
Control Word under Instances 20/70 and 21/71 27
Status Word under Instances 20/70 and 21/71 28
Reference Handling 29
Bus Speed Reference Value under Instances 100-101-103/150-151-153 29
Bus Speed Reference Value under Instances 20/70 and 21/71 30
6 Parameters
Parameter Group 8-** 31
Parameter Group 12-** 35
IP Settings 35
Ethernet Link Parameters 36
Process Data 37
EtherNet/IP 38
Other EtherNet Services 39
Advanced EtherNet Settings 40
Parameter List 42
Data Types 44
Data Types Supported by FC 200/FC 300 44
7 Troubleshooting
Step-by-step Troubleshooting 45
Alarm Word and Warning Word 45
8 Appendix
31
45
51
Supported CIP Objects 51
Index
59
2
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 3

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 1 Safety
1Safety
1
1.1.1 Copyright, Limitation of Liability and Revision Rights
This publication contains information proprietary to Danfoss. By accepting and u sing this manual the user agrees that the information contained herein
will be used solely for operating equipment from Danfoss or equipment from other vendors provided that such equipment is intended for communication
with Danfoss equipment over an Ethernet serial communication link. This publication is protected under the Copyright laws of Denmark and most other
countries.
Danfoss does not guarantee that a software program produced according to the guidelines provided in this manual will function properly in every physical,
hardware or software environment.
Although Danfoss has tested and reviewed the documentation within this manual, Danfoss makes no warranty or representation, either express or implied,
with respect to this documentation, including its quality, performance, or fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event shall Danfoss be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use, or the inability to use information
contained in this manual, even if advised of the possibility of such damages. In particular, Danfoss is not responsible for any costs including but not limited
to those incurred as a result of lost profits or revenue, loss o r damage of equipment , loss of compu ter programs, loss of data, the costs t o substitute
these, or any claims by third parties.
Danfoss reserves the right to revise this publication at any time and to make changes in its contents without prior notice or any obligation to notify
previous users of such revisions or changes.
1.1.2 Safety Note
The voltage of the frequency converter is dangerous whenev er connected to mains. Incorrect installation of the motor, frequency
converter or fieldbus may cause damage to the equipment, serious perso nal injury or death. Consequently, the instructions in this
manual, as well as national and local rules and safety regulations, must be complied with.
1.1.3 Safety Regulations
1. The frequency converter must be disconnected from mains if repair work is to be carried out. Check that the mains supply has been disconnected
and that the necessary time has passed before removing motor and mains plugs.
2. The [OFF] key on the LCP of the frequency converter does not disconnect the equipment from mains and is thus not to be used as a safety
switch.
3. Correct protective earthing or grounding of the equipment must be established, the user must be protected against supply voltage, and th e
motor must be protected against overload in accordance with applicable national and local regulations.
4. The earth leakage currents are higher than 3.5 mA.
5. Protection against motor overload is not included in the factory setting. If this function is desired, set par. to data value ETR trip or data value
ETR warning.
NB!
The function is initialised at 1.16 x rated motor current and rated motor frequency. For the North American market; the ETR functions
provide class 20 motor overload protection in accordance with NEC.
6. Do not remove the plugs for the motor and mains supply while the frequency converter is connected to mains. Check that the mains supply has
been disconnected and that the necessary time has passed before removing motor and mains plugs.
7. Please note that the frequency converter has more voltage inputs than L1, L2 and L3, when load sharing (linking of DC intermediate circuit) and
external 24 V DC have been installed. Check that all voltage inputs have been disconnected and that the necessary time has passed before
commencing repair work.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
3
Page 4
1
1 Safety MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
1.1.4 Warning against Unintended Start
1. The motor can be brought to a stop by means of digital commands, bus commands, references or a local stop, while the freq uency converter
is connected to mains. If personal sa fet y considerations make it necessary to ensure that no unintended start occurs, these stop functions are
not sufficient.
2. While parameters are being changed, the motor may start. Consequently, the [OFF] key must always be activated.
3. A motor that has been stopped may start if faults occur in the electronics of the frequency converter , or if a temporary ove rload or a fault in
the supply mains or the motor connection ceases.
Touching the electrical parts may be fatal - even after the equipment has been disconnected from mains.
Also make sure that other voltage inputs have been disconnected, such as external 24 V DC, load sharing (linkage of DC intermediate circuit), as well as
the motor connection for kinetic back up.
Please take note of discharge times and further safety guidelines from the section: “Safety and conformity”, in the respective Design Guide (MG.33.Ax.yy).
4
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 5

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 2 Introduction
2Introduction
2.1.1 About this Manual
First time users can obtain the most essential information for quick installation and set-up in these chapters:
Introduction
How to Install
How to Configure the System
For more detailed information including the full range of set-up options and diagnosis tools please refer to the ch apters:
How to Configure the System
How to Control the FC 200/FC 300
How to Access FC 200/FC 300 Parameters
Parameters
Troubleshooting
Terminology:
In this manual several terms for Ethernet is used.
-EtherNet/IP, is the term used to describe the CIP/ODVA application protocol.
-Ethernet, is a common term u sed to describe the ph y sical layer of the network and does not relate to the application protocol.
2.1.2 Technical Overview
EtherNet/IP™ was introduced in 2001 and today is the most developed, proven and complete industri al Ethernet network solut ion available for manufacturing automation. EtherNet/IP is a member of a family of networks that implements the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP
encompasses a comprehensive suite of messages and services for a variety of manufacturing automati on applications, including control, safety, syn chronization, motion, configuration and information. As a truly media-independent protocol that is su pported by hundred s of vendors from around the
world, CIP provides users with unified communication architecture throughou t the manufacturing enterprise.
™
) at its upper layers. CIP
2
EtherNet/IP provides users with the network tools to deploy standard Ethernet technology for manufacturing applications while ena bling Intern et and
enterprise connectivity.
2.1.3 Assumptions
These operating instructions are under the conditions that the Danfoss EtherNet/IP option is used in conjunction with a Danfoss FC 200/FC 300 frequency
converter, inclusive that the installed controller supports the interfaces described in this document and that all the requirements stipulated in the controller,
as well as the frequency converter, are strictly observed along with all limitations herein.
2.1.4 Hardware
This manual relates to the EtherNet/IP option MCA 121, type no. 130B1119 (un-coated) and 130B1219 (coated).
2.1.5 Background Knowledge
The Danfoss EtherNet/IP Option Card is designed to communicate with any system complying with the CIP EtherNet/IP standard. Familiarity with this
technology is assumed. Issues regarding hardware or software produced by other manufact urers, including commissioning tools, are beyond the scope
of this manual, and are not the responsibility of Danfoss.
For information regarding commissioning tools, or communication to a non-Danfoss node, please consult the appropriate manua ls.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
5
Page 6

2
2 Introduction MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
2.1.6 Available Literature
Available Literature for FC 200/FC 300
- The VLT AutomationDrive Operating Instructions provide the neccessary information for getting the drive up and running.
- The VLT AutomationDrive Design Guide entails all technical information about the drive design and applications including encoder, resolver and
relay options.
- The VLT AutomationDrive Profibus Operating Instructions provide the information required for controlling, monitoring and programming the
drive via a Profibus fieldbus.
- The VLT AutomationDrive Operating Instructions provide the information required for controlling, monitoring and programming the drive via a
DeviceNet fieldbus.
- The VLT AutomationDrive MCT 10 Operating Instructions provide information for installation and use of the software on a PC.
- The VLT AutomationDrive IP21 / Type 1 Instruction pr ovides information for installing the IP21 / Type 1 op t io n .
- The VLT AutomationDrive 24 V DC Backup Instruction provi des information for installing the 24 V DC Backup option.
Danfoss Drives technical literature is also available online at www.danfoss.com/drive s .
2.1.7 ODVA Conformance
The EtherNet/IP option is tested to conform to the ODVA standards, and is certified, towards conformance test level version 3.
2.1.8 Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition
API Actual Packet Interval
CC Control Card
CIP Common Industrial Protocol
CTW Control Word
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
EIP EtherNet/IP
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
I/O Input/Output
IP Internet Protocol
LCP Local Control Panel
LED Light Emitting Diode
LSB Least Significant Bit
MAR Major Reco verable fail
MAU Major Unrecoverable fail
MAV Main Actual Value (actual output)
MSB Most Significant Bit
MRV Main Reference Value
N/A Not applicable
ODVA Open DeviceNet Vendor Association
PC Personal Computer
PLC Programmable Logic Controller
PNU Parameter Number
REF Reference (= MRV)
RTC Real Time Clock
STP Spanning tree Protocol
STW Status Word
6
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 7
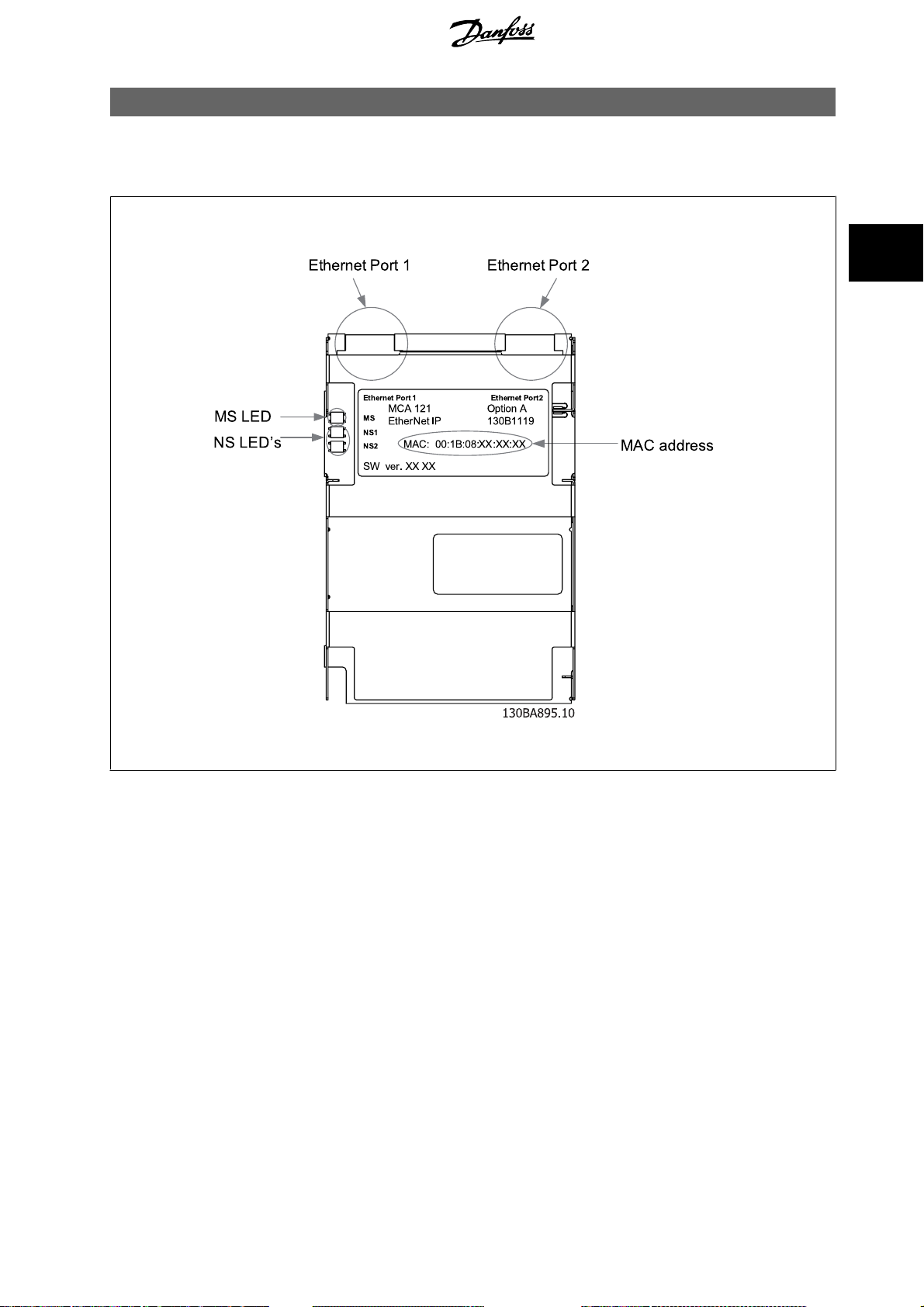
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 3 How to Install
3How to Install
3.1.1 The EtherNet/IP Option
3
/
. .
Illustration 3.1: Overview of the option
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
7
Page 8
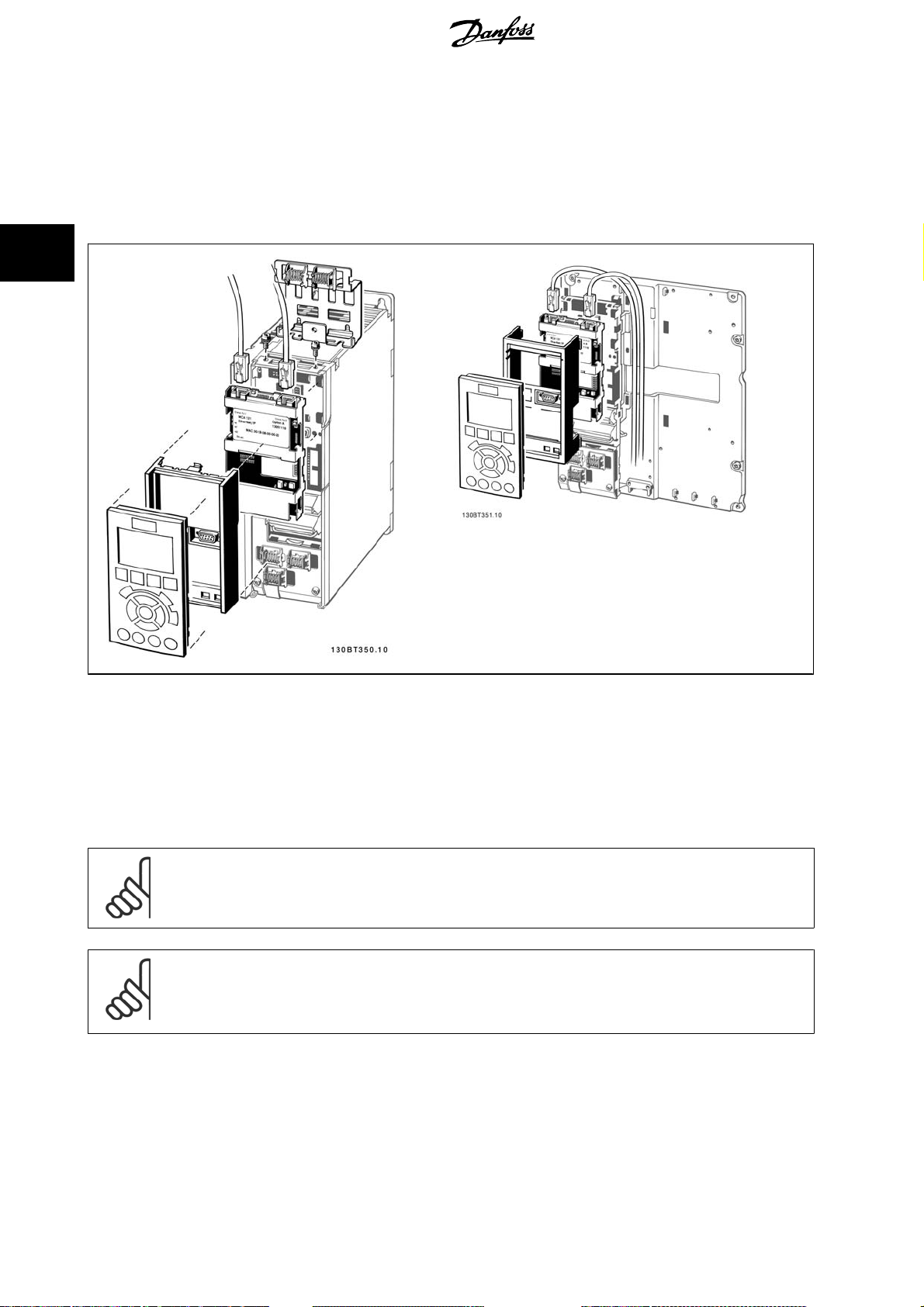
3
3 How to Install MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
3.1.2 How to Install Option in Frequency Converter
Items required for installing a fieldbus option in the frequency converter:
- The fieldbus option
- Fieldbus option adaptor frame for the FC 200/FC 300. This frame is deeper than the standard frame, to allow space for the fieldbus option
beneath
- Strain relief (only for A1 and A2 enclosures)
Instructions:
- Remove LCP panel from the FC 200/FC 300.
- Remove the frame located beneath and discard it.
- Push the option into place. The Ethernet connectors must be facing upwards.
- Remove both knock- ou ts on the fieldbus option adaptor frame.
- Push the fieldbus option adaptor frame for the FC 200/FC 300 into place.
- Replace the LCP and attach cable
NB!
Do not strip the Ethernet cable and ground it via the strain relief-plate! The grounding of screened Ethernet cable is done through the
RJ-45 connector on the opti on.
NB!
After installing the MCA 121 option, be aware of the following parameter settings:
par. 8-01
par.8-02
Control Site
Control Word Source
: [2]
Controlword only
: [3]
Option A
or [0]
Digital and ctrl. word
8
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 9

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 3 How to Install
3.1.3 LED Behaviour
The option has 3 bi-coloured LEDs according to ODVA specifications:
LED Label
MS Module Status
NS1 Network Status Ethernet Port 1
NS2 Network Status Ethernet Port 2
The option LED’s operates according to ODVA specifications.
State LED Description
No power Off The device is un-powered
Device operational Green: Solid green The device is operational
Standby Green: Flashing green The device needs commission ing
Minor fault Red: Flashing red The device has detected a recoverable fault
Major fault Red: Solid red The device has detected an un-reco verable fault
Self test
Table 3.1: MS: Module Status
State LED Description
No IP-address (no power) Off
No connections Green: Flashing green
Connected Green: Solid green
Connection time-out Red: Flashing red One or more CIP connections have timed-out
Duplicate IP Red: Solid red
Self test
Description
Red: Flashing red/
Green:
Red:
Green
green
Flashing red/green The EIP option is in self-test mode
The EIP option is in self-test mode
The device does not have a valid IP-address (or
is un-powered)
There are no established CIP connections to the
device
There is established (at least) one CIP connection to the device
The IP-address assigned to the device is already
in use
3
Table 3.2: NS1 + NS2: Network Status (one per port)
During normal operation the MS and at least one NS LED will show a constant green light.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
9
Page 10
3 How to Install MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
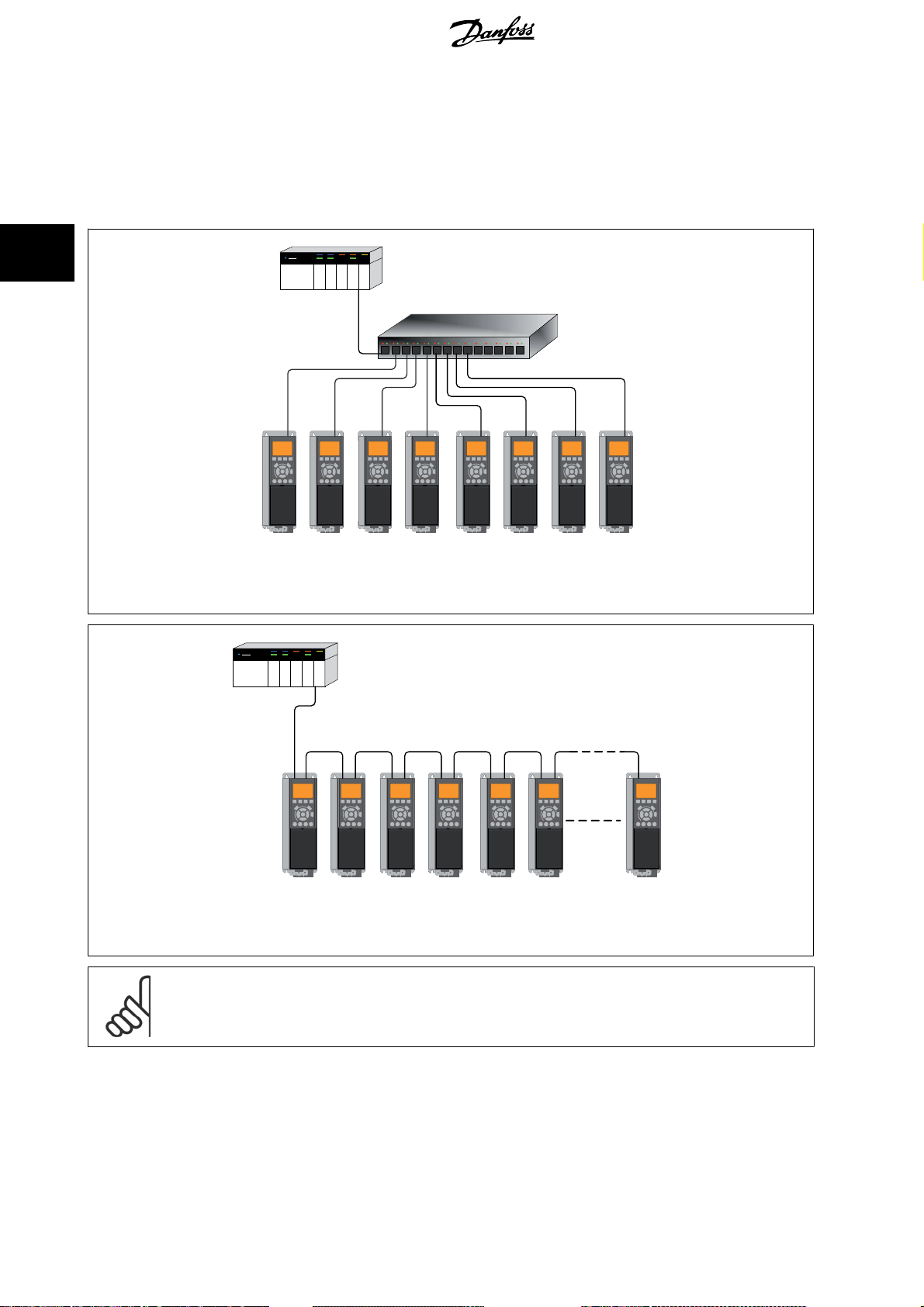
3.1.4 Topology
The MCA 121 features a build-in Ethernet-switch, thus having two Etherne t RJ-45 connectors. This enables the po ssibility for connecting several EtherNet/
IP options in a line topology as an alternative to the typical star-topology.
The two ports are equal, in the sense that they are transparent for the option. If only one connector is used, either port can be used.
3
Illustration 3.2: Star topology
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDriv e
VLT
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDrive
130BA903.10
VLT
AutomationDriv e
Illustration 3.3: Line topology
NB!
For line topology please refer to section: “Recommended design rules” In a line topology all drives must be powered, either by mains
or by their 24 V DC option cards, for the build-in switch to work.
10
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
VLT
AutomationDriv e
130BA904.10
Page 11
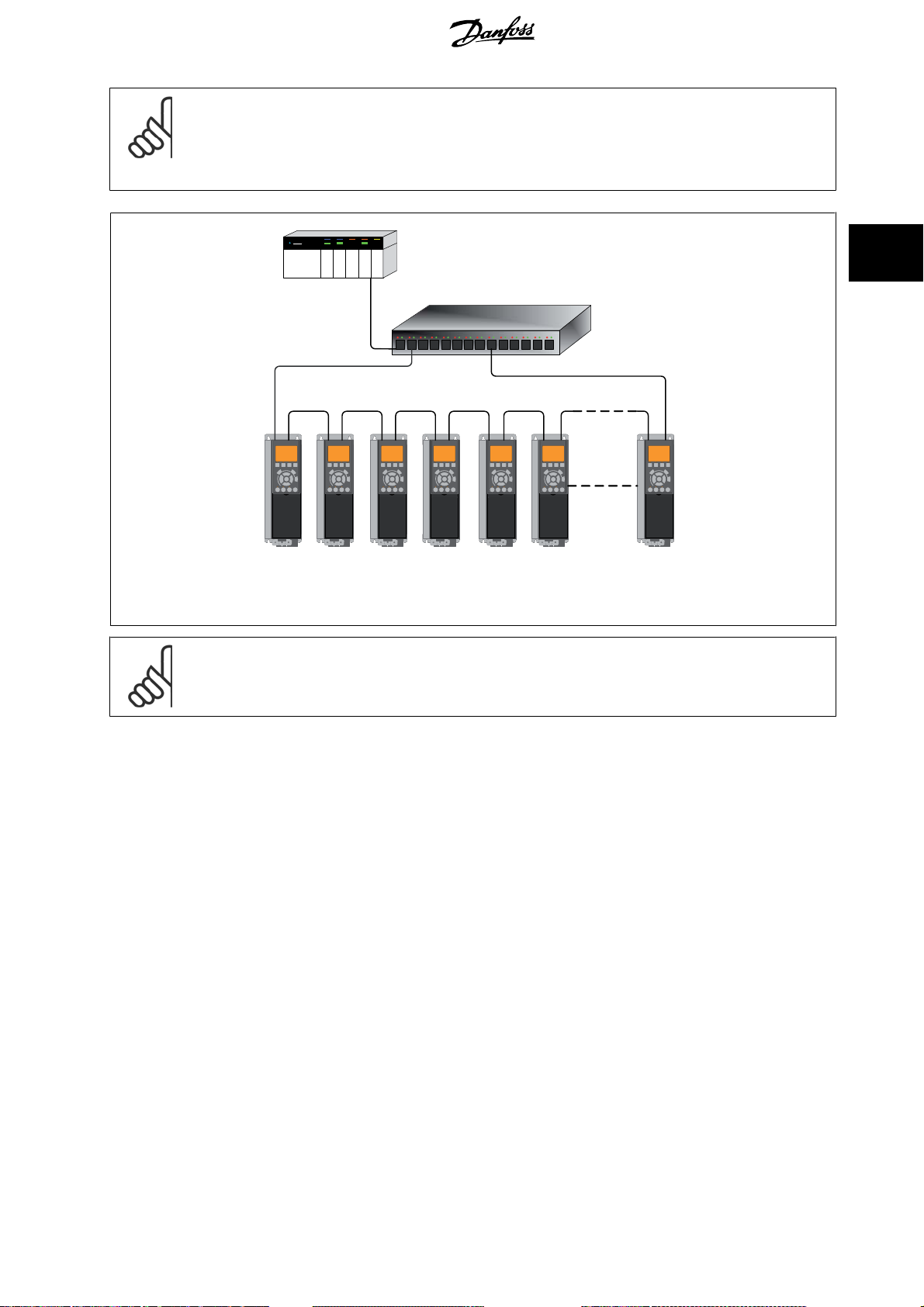
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 3 How to Install
NB!
Please observe that mounting drives of different power-sizes in a line topology may result in unwanted power-off behaviour.
Smaller drives discharge faster than bigge r drives. This c an result in loss of link in the line to pology, w hich may l ead to control word
timeout.
To avoid this, mount the drives with the longest discharge time first in the line topology.
3
VLT
AutomationD riv e
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
½
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
130BA905.10
Illustration 3.4: Ring/redundant line topology
NB!
For this type of topology it is crucial that t he network switch supp orts Spanning Tree Pro tocol (STP) or Rapid Spacing Tree (RSTP),
and that STP is enabled. For more information on Spanning Tree please refer to section
IP traffic
.
3.1.5 Network
It is of high importance that the media chosen for Ethernet data transmission are suitable. Usually CAT 5e and 6 cables are recommended for industrial
applications. Both types of cable are available as Unshielded Twisted Pair and Shielded Twisted Pair. Generally shielded cables are recommended for use
in industrial environments and with frequency converters.
A maximum cable-length of 100 m is allowed between switches.
Optical fibres can be used for gapping longer distances and providing galvanic isolation.
For connecting EtherNet/IP devices both hubs and switches can be used. It is, however, recommended always to use suitable industrial graded Ethernet
IP Traffic
switches. For more information regarding IP-switching, please refer to section:
in this manual.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
11
Page 12

3
3 How to Install MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
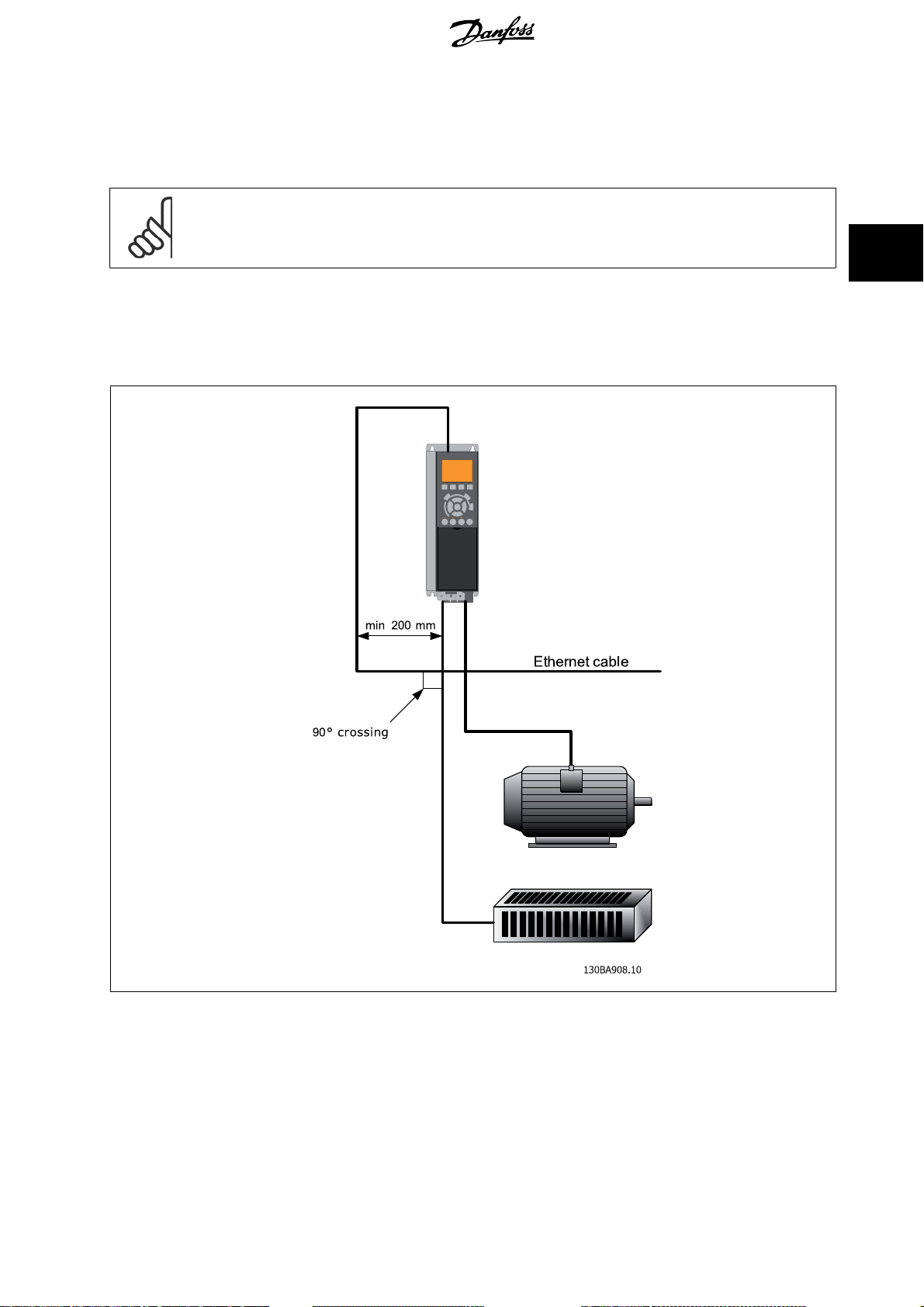
3.1.6 Recommended Design Rules
While designing Ethernet networks special attention and caution must be taken regarding active network components.
While designing a network for line topolo gy it is important to notice that a small delay is added with each every switch in the line.
It is not recommended to connect more than 32 drives in a line at any API. Exceeding the recommended design rules, may result in failing communication.
VLT
VLT
VLT
VLT
VLT
AutomationDrive
AutomationDrive
AutomationDr ive
AutomationDr ive
Max. 32 drives
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDrive
VLT
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDr ive
VLT
AutomationDr ive
12
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 13
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 3 How to Install
3.1.7 EMC Precautions
The following EMC precautions are recommended in order to achieve interference-free operation of the Ethernet network. Additional EMC information is
available in the FC 200/FC 300 series Design Guide.
NB!
Relevant national and lo cal regulations, for example regarding protective earth connection, must be observed.
3
The Ethernet communication cable must be kept away from motor and brake resistor cables to avoid coupling of high frequency noise from one cable to
the other. Normally a distance of 200 mm (8 inches) is sufficient, but maintain ing the greate st possible dista nce between the cables is recommended,
especially where cables run in parallel over long distances. When crossing is unavoidable, the Ethernet cable must cross motor and brake resistor cables
at an angle of 90 degrees.
VLT
Au to mati on D ri v e
.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
13
Page 14
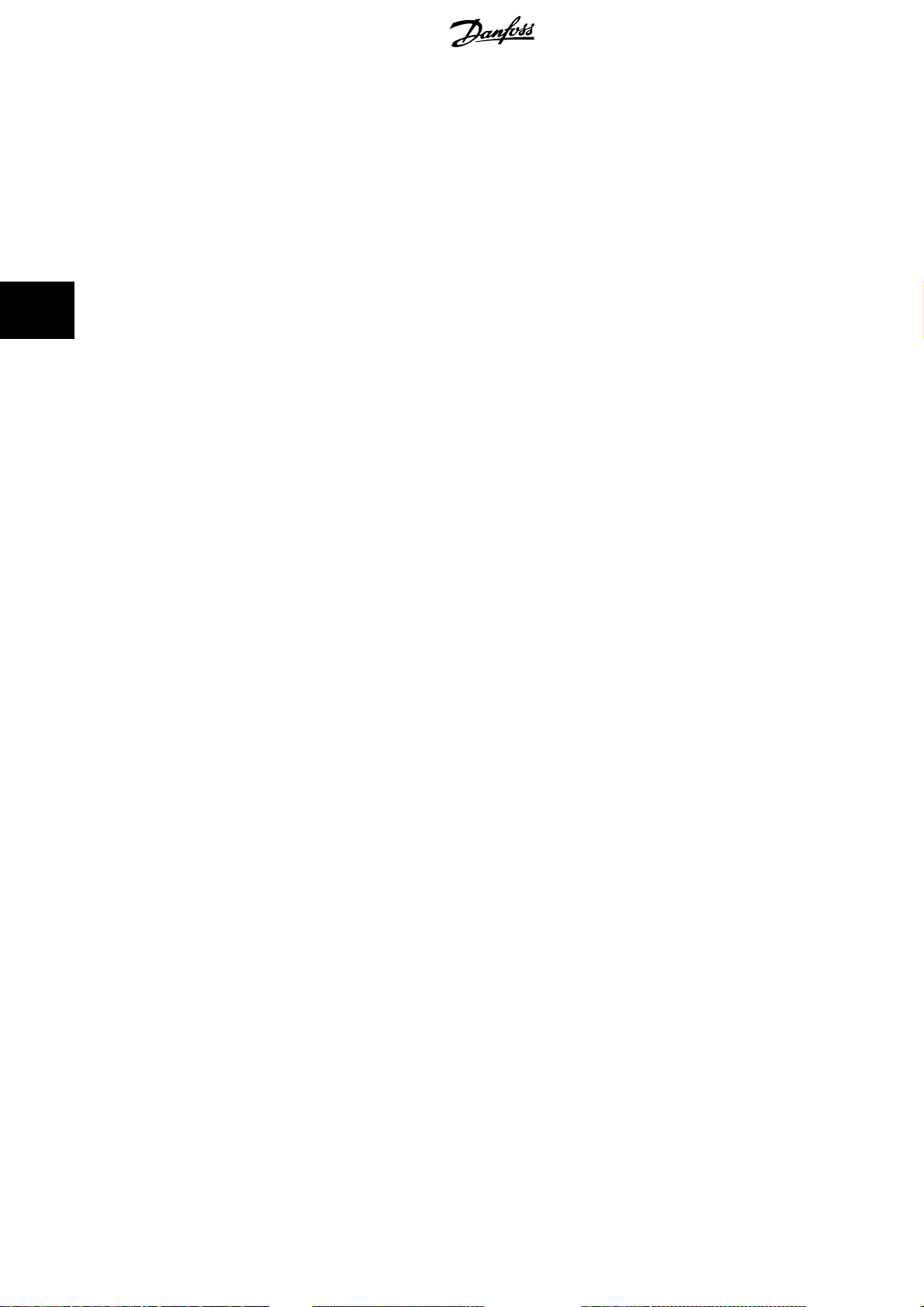
4
4 How to Configure MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
14
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 15

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 4 How to Configure
4 How to Configure
4.1.1 IP Settings
All IP-related parameters are located in parameter group 12-0*:
12-00 IP Address Assignment
12-01 IP Address
12-02 Subnet Mask
12-03 Default Gateway
12-04 DHCP Server
12-05 Lease Expires
12-06 Name Servers
12-07 Domain Name
12-08 Host Name
12-09 Physical Address
The MCA 121 option offers several ways of IP address assignment.
4
Setting up drive with manual assigned IP address:
Par. Name Value
12-00
12-01
12-02
12-03
*= Class C IP address example. Any valid IP address can be entered.
NB!
A power-cycle is necessary after setting the IP parameters manually.
Setting up drive with automatic (BOOTP/DHCP) assigned IP address:
Par. Name Value
12-00
12-01
12-02
12-03
By IP address assigned by DHCP/BOOTP server, the assigned
Server
, the IP address of the found DHCP or BOOTP server is displayed. For DHCP only: The remaining leas e-time ca n be re ad-out in par . 12- 05
Expires
.
Par. 12-09,
DHCP or BOOTP, the physical MAC address is linked with a fixed IP address.
IP Address Assignment
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Physical Address
IP Address Assignment
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
[1] DHCP/[2] BOOTP
Read only
Read only
Read only
IP Address
reads out the MAC address of option, which is al so printed on the label of the option. If using fixed leases together with
and
Subnet Mask
[0] MANUAL
192.168.0.xxx*
255.255.255.0*
optional
can be read out in par. 12-01 and 12-02. In p ar. 12-04
DHCP
Lease
NB!
If no DHCP or BOOTP reply has been received after 4 attempts (e.g. if the DHCP/BOOTP server has been powered off), the option will
fallback to the last good known IP address.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
15
Page 16

4 How to Configure MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
4
Par. 12-03,
Par. 12-06,
Par. 12-07,
Par. 12-08,
Are used with Domain Name Server systems and are a ll optional. If DHCP or BOOTP is select ed as IP a ddress assignment, these pa rameters a re read
only.
Default Gateway
Name Servers
Domain Name
Host Name
NB!
It is only possible to assign valid class A, B and C IP address to the option. The valid ranges are shown in the below table:
Class A 1.0.0.1 - 126.255.255.254
Class B 128.1.0.1 - 191.255.255.254
Class C 192.0.1.1 - 223.255.254.254
is optional and only used in routed networks.
4.1.2 Ethernet Link Parameters
Parameter group 12-1* holds information Ethernet Link information:
12-10 Link Status
12-11 Link Duration
12-12 Auto Negotiation
12-13 Link Speed
12-14 Link Duplex
Please note the Ethernet Link Parameters are unique per port.
Par. 12-10,
Par. 12-10,
Par. 12-11,
Par. 12-12,
duplex mode. In this process, the connected devices first share their capabilities as for these parameters and then choose the fastest transmission mode
they both support.
By default this function is enabled.
Incapability between the connected devices, may lead to decreased commu n ic ation performance.
To prevent this, Auto Negotiation can be disabled.
If par. 12-12 is set to OFF, link speed and duplex mode can be configured manually in par. 12-13 and 12-14.
Par. 12-13,
Par. 12-14,
Half-duplex provides communication in both directions, but only in on e dir ection at a time (not simulta n eously).
Full-duplex allows communication in both directions, and unlike half -duplex, allows for this to happen simu l t aneously.
Link Status
Link Status
Link Duration
Auto Negotiation
Link Speed
Link Duplex
and par. 12-11,
will display Link or No Link according to the status of the present port.
will display the duration of the link on the present port. If the link is broken the counter will be reset.
– is a feature that enables two connected Ethernet devices to choose common transmission parameters, such as speed and
– displays/sets the link speed per port. “Non e” is displayed if no link is present.
– displays/sets the duplex mode per port.
Link Duration
displays information on the link status, per port.
16
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 17
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 4 How to Configure
4.1.3 Configuring the Scanner
EDS file
Danfoss provides a generic English EDS (Electronic Data Sheet) file covering al l v olt age and power sizes, for off-line configu ration.
The EDS file can be downloaded from:
http://www.danfoss.com/BusinessAreas/DrivesSolutions/Softwaredownload/DDFieldbus_Setup_Files.htm
NB!
The current version of the major EtherNet/IP configuration tools does not support EDS-files for EtherNet/IP devices.
Configuring a Rockwell Master
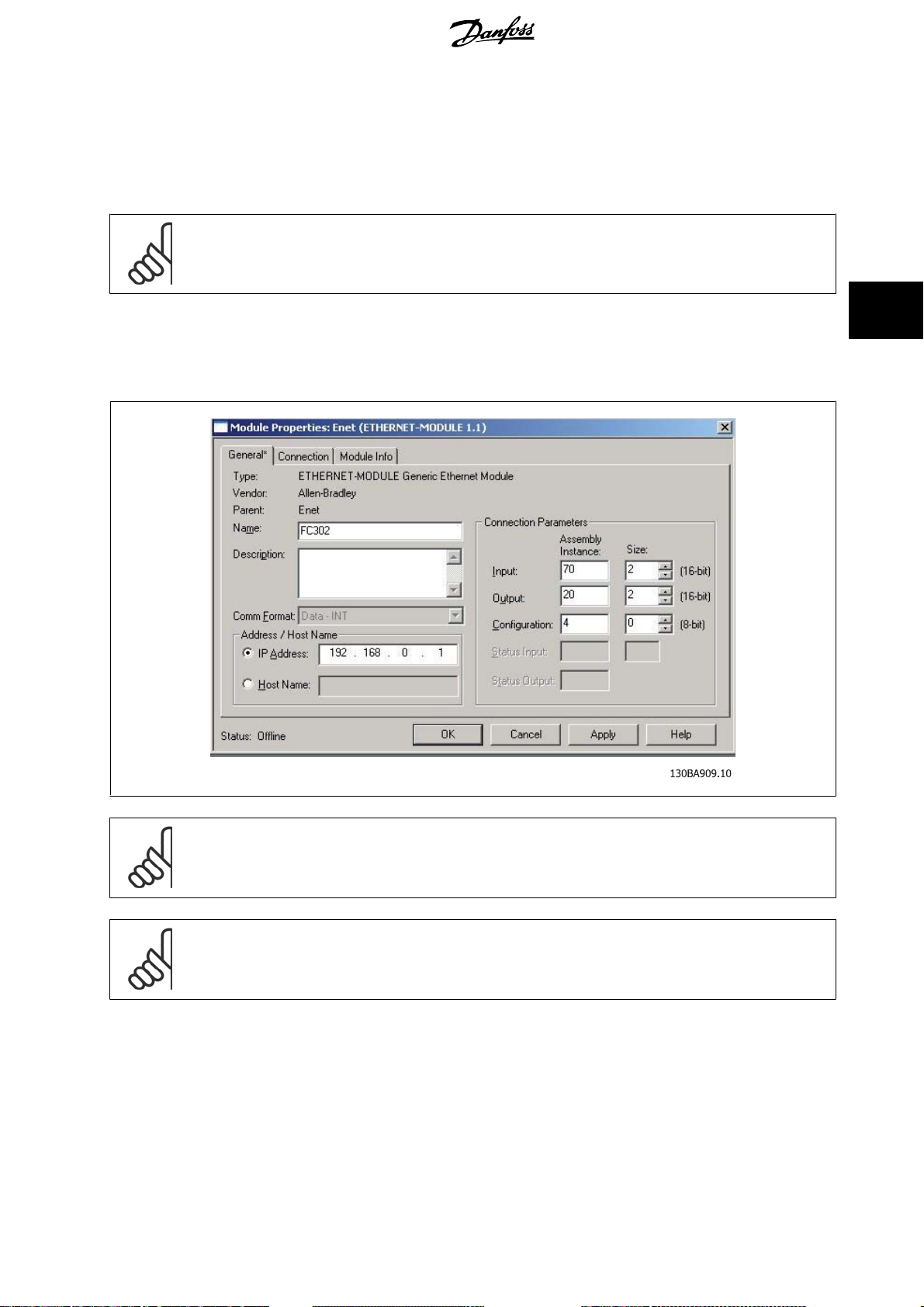
For configuring a FC 200/FC 300 with MCA121 for op eration w ith a Rockwell (Allen-Bradley) Scanner via EtherNet/IP, the FC 200/F C 300 m ust be add ed
Generic Ethernet Module
as a
Under the
General
-tab, enter information about: Name of device, IP Address, Assembly Instance and Data size
.
4
Under the
NB!
Configuration
Under
NB!
Please note that the example shows a 20/70 assembly instance connection. This requires par. 8-10
Other supported connections are shown in section:
Connection
-tab, enter information about: RII and fault conditions.
in the Connection Parameters a “4” must be entered as Assembly Instance.
I/O Assembly Instanced
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
.
Control Profile
to be set to: ODVA.
17
Page 18
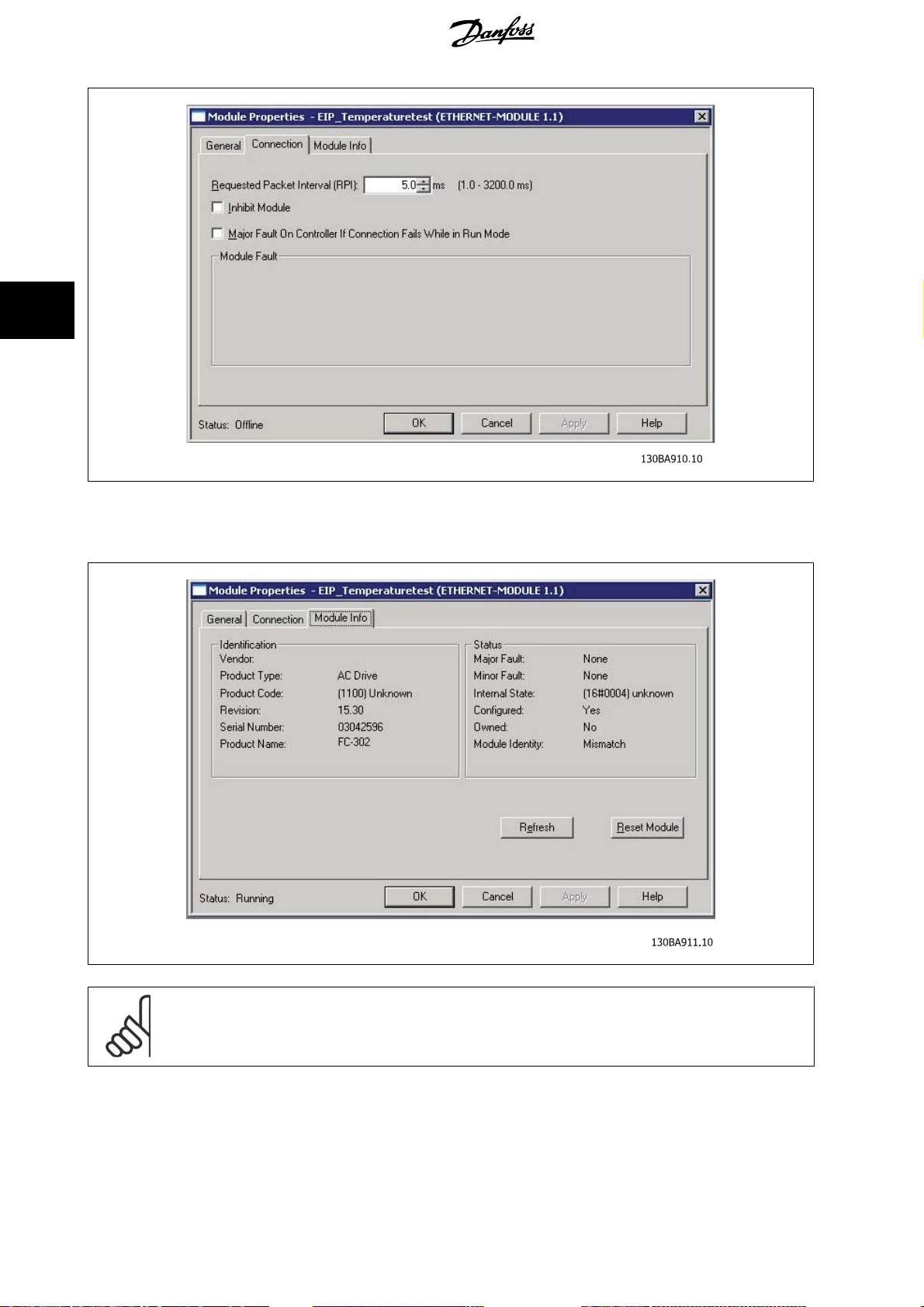
4
4 How to Configure MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
The
Module Info
Reset Module
The
– This tap holds generic information.
– This button will make a simulated Power-cycle of the drive.
18
NB!
For more information on the CIP class 1 Forward Open command, please refer to section:
Control
-chapter.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
EtherNet/IP Connections
under the
How to
Page 19
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 4 How to Configure
4.1.4 IP traffic
The use of Ethernet based network for industrial automation purposes, calls for careful and thorough network design. Especially the use of active ne twork
components like switches and routers requires detailed know-how about the behaviour of IP tr affic.
Some important issues:
Multicast
Multicast traffic; is traffic that is addressed to a number of recipients. Each host processes the received multicast packet to deter mine if it is the targe t
for the packet. If not, the IP package is discarded. This causes an excessive network load of each node in the network since they are flooded with multicast
packages. The nature of EtherNet/IP traffic is that all Originator-to-Target traffic is Unicast (point-to-point) but Target-to-Originator traffic is optional
Multicast. This enables that several listen only -connections can be made to a single host.
In switched networks hosts also have the risk of becoming flooded with multicast traffic. A switch usually forwards traffic by MAC address tables build by
looking into the source address field of all the frames it r e c eives.
A multicast MAC address is never used as a source address for a packet. Such addresses do not appear in the MAC address table, and the switch has no
method for learning them, so it will just forward all multicast traffic to all connected hosts.
IGMP
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is an integrated part of IP. It allows hosts to join or leave a multicast host group. Group membership
information is exchanged between a specific host and the nearest multicast router.
For EtherNet/IP networks it is essential that the switches used, supports IGMP Snooping. IGMP Snooping enables the switch to “listen in" on the IGMP
conversation between hosts and routers. By doing this the switch will recognise which hosts are members of which groups, thus being able to forward
multicast traffic only to the appropriate hosts.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
For an Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can exist between two nodes. Spanning-Tree Protocol is a link management protocol
that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the network.
When loops occur, some switches see stations appear on both sides of it self. This condition confuses the forwarding algorithm and allows for duplicate
frames to be forwarded.
To provide path redundancy, Spanning-Tree Protocol defines a tree that spans all switches in an extended network. Spanning-Tree Protocol forces certain
redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If one network segment in the Spanning-Tree Protocol becomes unreachable, or if Spanning-Tree
Protocol costs change, the spanning-tree algorithm reconfigures the spanning-tree topology and re-establishes the link by activating the standby path.
Spanning-Tree Protocol operation is necessary if the FC 200/FC 300’s are running in a ring/redundant line topology.
4
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
19
Page 20

5
5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
20
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 21

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 5 How to Control
5How to Control
5.1 How to Control
5.1.1 I/O Assembly Instances
I/O Assembly Instances are a number of defined process control objects with defined content comprising control and status information.
Unlike DeviceNet it is possible to run with asymmetrical instances. E.g. 101 /153 = 8 bytes/20 bytes.
It is not possible to mix instances across profiles, e.g. 20/100. Assembly instances must be consistent to the: ODVA or FC profile.
The controlling instance can be read in par. 12- 2 0,
The figure below shows the I/O Assembly Instance options for controlling and monitoring the FC 200/FC 300 drive.
Profile
(par.8-10
ODVA
Control Word
)
Profile
Direction
Originator →Target
Target →Originator
Control Instance
Instances
(decimal)
20 4
21 4
70 4
71 4
100 4
.
Size
(bytes)
Data
5
Originator →Target
FC
Target →Originator
NB!
Use of 32-bit process data.
For configuration of a 2-word (32-bit) parameter read/write, use 2 consecutive arrays in par. 12-21 and 12-22, like [2]+[3], [4]+[5],
[6]+[7] etc. Read/write of 2-word values in arrays like: [3]+[4], [5]+[6], [7]+[8] are not possible.
101 8
103 20
150 4
151 8
153 20
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
21
Page 22

5
5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
5.1.2 EtherNet/IP Connections
The MCA 121 option supports the CIP connections described in the following sections:
5.1.3 Class 1 connection
I/O connection using TCP transport. Maximum one Class 1 connection is supported by the EtherNet/IP option, but several listen only connection can be
established if multicast is selected a s Transport type. This type of connection is use d for c yc lic I/O and Change-Of-State connections. The connection is
established with a Forward Open command, containing the following information:
Transport Type:
Specified for both directions:
- Originator-to-Target / Target-to-Originator.
- Point to Point
- Multicast (Target-to-Originator only)
Data Size:
Specified (in bytes) for both directions: Originator -> Target / Target -> Originator.
The data-size depends on the assembly-instance chosen in:
Destination
.
Instances (decimal) Data Size
Originator →Target Target →Originator
20, 21, 100 70, 71, 150 4 bytes
101 151 8 bytes
103 153 20 bytes
Packet Rate:
Specified (in milliseconds) for both directions: Originator -> Target / Target -> Originator.
Minimum packet rate supported: 1 ms
Production Inhibit Timeout:
Specifies (in milliseconds) the timeout-time for both directions.
Trigger:
Selects the transport trigger type:
- Cyclic (Data is transmitted cyclically as polled I/O)
- Change Of State (Data is transmitted on Change of State only. COS-filters are set-up in par. 12-38 COS Filters)
Connection Points
Specified for both directions: Originator -> Target / Target -> Originator.
Direction Connection Points
Originator →Target 20, 21
Target →Originator 70, 71
Originator →Target 100, 101, 103
Target →Originator 150, 151, 153
(par.8-10
Profile
Control Word Profile
ODVA
FC
)
(decimal)
22
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 23

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 5 How to Control
5.1.4 Class 3 connection
Cyclic connection using UDP transport.
Maximum 6 Class 3 connections are supported.
This type of connection is used for explicit messaging. The connection is established with a Forward Open command, containing the following information:
Connection Name:
Given name for the connection
Message Parameters
- Service Code
- Class
- Instance
- Attribute
- Member
- Request Data
5.1.5 Unconnected Messages, UCMM
5
Non-cyclic (single) connection using TCP transport.
This type of connection is used for explicit messaging. The connection is established on-the-fly and does not require any Forward Open command.
Message Parameters
- Service Code
- Class
- Instance
- Attribute
- Member
- Request Data
Please refer to section Appendix for information on accessing CIP objects explicitly.
5.1.6 Control Word Profile
The Control profile is selected in par.8-10
- ODVA; gives access to the ODVA specific profiles and assembly instances: 20, 21, 70 and 71
- FC; enables the Danfoss profile and assembly instances: 100, 101, 103, 150, 151 and 153
For more information on the different profiles, please refer to the subsequent sections.
NB!
Change of control profile
It is only possible to change the Control profile while the drive is stopped. Control word and reference will not be recalculated to match
the selected profile, but are kept at the last good known value.
Control Word Profile
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
23
Page 24

5
5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
5.1.7 Change of State, COS
The event controlled operation mode is used to minimize network traffic. Messages a re transmitted only if a defined state or value has changed. The
condition for triggering a COS message, is determined by the insertion of COS-filters (par. 12-38), for each bit in the different PCD-words.
The filter acts like a logical AND-function: If a bit in the filter is set to “1”, the COS-function triggers when there is a change to the corresponding bit for
the PCD-word.
Parameter 12-38 can be used to fil ter out und esir ed events for COS. If a filter bit is set to 0, the corresponding I/0 Instance bit will be unable to produce
a COS message. By default, all bits in the COS filters are set to 0.
In order to signal that the connection has not been interrupted, or the device is not powered off, a Heartbeat Message is transmitted wit hin a specified
time interval (Hea r tbeat Interval). Thi s interval is defined in Attribute Heartbeat Time of the c onnection object, Class 0x01.
To prevent the device from producing heavy netwo rk traffic when a value changes frequently, a Production Inhibit Time is defined in par. 12-37 . This
parameter defines the minimum time between two COS messages. If par. 12-37 is set to 0, the Production Inhibit Timer is disabled.
The figure below shows the different PCD’s and their corresponding filter parameters.
24
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 25

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 5 How to Control
5.2 Danfoss FC Control Profile
5.2.1 Danfoss FC Control Profile
Control Word according to FC ProfileDrive Profile. Instances 100, 101,
103/150, 151, 153
→
Illustration 5.1: (par.8-10
Bit Bit value = 0 Bit value = 1
00 Reference value External selection LSB
01 Reference value External selection MSB
02 DC brake Ramp
03
Coasting No coasting
04 Quick stop Ramp
05 Hold output frequency Use ramp
06 Ramp stop Start
07
No function Reset
08 No function Jog
09 Ramp 1 Ramp 2
10 Data invalid Data valid
11
No function Relay 01 active
12 No function Relay 04 active
13 Parameter set-up Selection LSB
14 Parameter set-up Selection MSB
15 No function Reverse
Explanation of Control Bits
Bits 00/01
Bits 00 and 01 are used to choose between the four reference values,
which are pre-programmed in par. 3-10
the following table:
Programmed
ref. value
1 3-10 [0] 0 0
2 3-10 [1] 0 1
3 3-10 [2] 1 0
4 3-10 [3] 1 1
Parameter Bit 01 Bit 00
Control Word Profile
Preset Reference
= FC profile)
according to
NB!
In par. 8-56
is made to define how Bit 00/01 gates with the corresponding function on the digital inputs.
Bit 02, DC brake:
Bit 02 = ‘0’ leads to DC braking and stop. Braking cu rrent and durati on
are set in par. 2-01
02 = ‘1’ leads to ramping, par. 3-41
Bit 03, Coasting:
Bit 03 = ‘0’ causes the frequency converter to immediately "let go" of the
motor (the output transistors are "shut off"), so that it coasts to a standstill.
Bit 03 = ‘1’ enables the frequency converter to start the motor if the other
starting conditions have been fulfilled.
Bit 04, Quick stop:
Bit 04 = ‘0’ causes a stop, in wh ich th e mot or sp eed is ra mped do wn to
stop via par. 3-81
Bit 05, Hold output frequency:
Bit 05 = ‘0’ causes the present output frequency (in Hz) to freeze. The
frozen output frequency can then be changed only by means of the digital
inputs (par. 5-10
Input
) programmed to
DC Brake Current
NB!
In par. 8-50
fine how Bit 03 gates with the corresponding function
on a digital input.
Quick Stop Ramp Time
Terminal 18 Digital Input
NB!
If Freeze output is active, the frequency converter can
only be stopped by the following:
Preset Reference Select
and par. 2-02
Ramp 1 Ramp up Time
Coasting Select
.
to par. 5-15
Speed up
and
Speed down
• Bit 03 Coasting stop
•Bit 02 DC braking
• Digital input (par. 5-10
to par. 5-15
Input
programmed to
DC braking, Coasting stop
select a selection
DC Braking Time
a selection is made to de-
. Bit
Terminal 33 Digital
.
Terminal 18 Digital
Terminal 33 Digital Input
or
Reset and coasting stop
5
)
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
25
Page 26

5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
5
Bit 06, Ramp stop/start:
Bit 06 = ‘0’ causes a stop, in which the motor speed is ramped down to
stop via the selected
quency converter to start the motor, if the other starting conditions have
been fulfilled.
Bit 07, Reset:
Bit 07 = ‘0’ no reset. Bit 07 = ‘1’ resets a trip. Reset is activated on the
leading edge of the signal, i.e. when changing fr om logic ‘0’ to logic ‘1’.
Bit 08, Jog:
Bit 08 = ‘1’ causes the output frequency to be determined by
par. 3-19
Bit 09, Selection of ramp 1/2:
Bit 09 = ‘0’ means that ramp 1 is active (par. 3-40
par. 3-47
ramp 2 (par. 3-50
Jog Speed [RPM]
Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Decel. Start
Decel. Start
Bit 10, Data not valid/Data valid:
This bit tells the frequency converter whether the control word is to be
used or ignored. Bit 10 = ‘0’ causes the control word to be ignored, Bit
10 = ‘1’ causes the control word to be used. The control word is always
contained in the telegram, regardless of which type of telegram is used,
so this function is useful for ‘turning off’ the control word when not required for updating or reading parameters.
ramp down
NB!
In par. 8-53
to define how Bit 06 Ramp stop/start gates with the
corresponding function on a digital input.
parameter. Bit 06 = ‘1’ permits the fre-
Start Select
.
Start select a selection is made
Ramp 1 Type
). Bit 09 = ‘1’ means that
Ramp 2 Type
) is active.
to par. 3-57
Ramp 2 S-ramp Ratio at
to
Bit 11, Relay 01:
Bit 11 = ‘0’ Relay not activated. Bit 11 = ‘1’ Relay 01 activated, provided
Control word bit 11
Bit 12, Relay 02:
Bit 12 = ‘0’ Relay 02 has not been activated. Bit 12 = ‘1’ Relay 02 has
been activated, provided
par. 5-40
Bit 13/14, Selection of set-up:
Bits 13 and 14 are used to select one of four menu set-ups according to
the following table:
Set-up
The function is only possible when
par. 0-10
Bit 15 Reverse:
Bit 15 = ‘0’ causes no reversing. Bit 15 = ‘1’ causes reversing. Note: In
the factory setting reversing is set to
lect
. Bit 15 causes reversing only when
or
Logic OR
has been chosen in par. 5-40
Control word bit 12
Function Relay
1 0 0
20 1
3 1 0
41 1
Active Set-up
.
Bit 14 Bit 13
.
NB!
In par. 8-55
how Bit 13/14 gates with the corresponding function
on the digital inputs.
Set-up Select
digital
Function Relay
has been chosen in
Multi-Set-ups
a selection is made to define
in par.8-54
.
is selected in
Reversing Se-
Ser. communication, Logic AND
is selected.
5.2.2 Status Word according to FC ProfileDrive Profile (STW)
→
Illustration 5.2: (par.8-10
Control Word Profile
)
Bit Bit value = 0 Bit value = 1
00 Control not ready Control ready
01 Drive not ready Drive ready
02 Coasting Enable
03 No error Trip
04 No error Error (no trip)
05 Reserved 06 No error Trip lock
07 No warning Warning
08 Speed ≠ reference Speed = reference
09 Local operation Bus control
10 Out of frequency limit Frequenc y limi t ok
11 No operation In operation
12 Drive ok Stopped, auto start
13 Voltage ok Voltage exceeded
14 Torque ok Tor que exceed ed
15 Thermal ok Thermal exceeded
26
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 27

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 5 How to Control
Explanation of the Status Bits
Bit 00, Control ready:
Bit 00 = ‘0’ means that the frequency converter has tripped. Bit 00 = ‘1’
means that the frequency converter controls are ready, but that the power component is not necessarily receiving any power supply (in the event
of external 24 V supply to controls).
Bit 01, Drive ready:
Bit 01 = ‘1’. The frequency converter is ready for operation.
Bit 02, Coasting stop:
Bit 02 = ‘0’. The frequency converter has released the motor. Bit 02 =
‘1’. The frequency converter can start the motor when a start command
is given.
Bit 03, No error/Trip:
Bit 03 = ‘0’ means that the frequency converter is not in fault mode. Bit
03 = ‘1’ means that the frequency converter is tripped, and that a reset
signal is required to re-establish operation.
Bit 04, No error/Error (no trip):
Bit 04 = ‘0’ means that the frequency converter is not in fault mode. Bit
04 = ‘1’ means that there is a frequency converter error but no trip.
Bit 05, Reserved:
Bit 05 is not used in the status word.
Bit 06, No error / Trip lock:
Bit 06 = ‘0’ means that the frequency converter is not in fault mode. Bit
06 = ‘1’ means that the frequency converter is tripped, and locked.
Bit 07, No warning/Warning:
Bit 07 = ‘0’ means that there are no warnings. Bit 07 = ‘1’ means that a
warning has occurred.
Bit 08, Speed≠ reference/Speed = reference:
Bit 08 = ‘0’ means that the motor is running, but that the present speed
is different from the preset speed reference. For example, this might occur while the speed is being ramped up/down during start/stop. Bit 08 =
‘1’ means that the present motor speed matches the preset speed reference.
Bit 09, Local operation/Bus control:
Bit 09 = ‘0’ means that [STOP/RESET] is activated on the control unit, or
that Local control in par. 3-13
to control the frequency converter via serial communication. Bit 09 = ‘1’
means that it is possible to control the frequency converter via the fieldbus/ serial communication.
Bit 10, Out of frequency limit:
Bit 10 = ‘0’, if the output frequency has reached the value in
par. 4-11
Limit [RPM]
defined limits.
Bit 11, No operation/In operation :
Bit 11 = ‘0’ means that the motor is not running. Bit 11 = ‘1’ means that
the frequency converter has a start signal or that the output frequency is
greater than 0 Hz.
Bit 12, Drive OK/Stopped, auto start:
Bit 12 = ‘0’ means that there is no temporary over temperature on the
inverter. Bit 12 = ‘1’ means that the inverter has stopped because of over
temperature, but that the unit has not tripped and will resume operation
once the over temperature stops.
Bit 13, Voltage OK/Voltage exceeded:
Bit 13 = ‘0’ means that there are no voltage warnings. Bit 13 = ‘1’ means
that the DC voltage in the frequency converter’s intermediate circuit is
too low or too high.
Bit 14, Torque OK/Torque limit exceeded:
Bit 14 = ‘0’ means that the motor current is lower than the torque limit
selected in par. 4-16 and 4-17 Torque limit. Bit 14 = ‘1’ means that the
torque limit in par. 4-16 and 4-17 Torque limit has been exceeded. The
nominal torque can be read in par. 16-16
Bit 15, Thermal OK/limit exceeded:
Bit 15 = ‘0’ means that the timers for both motor thermal protection and
VLT thermal protection, have not exceeded 100%. Bit 15 = ‘1’ means that
one of the limits has exceeded 100%.
Motor Speed Low Limit [RPM]
. Bit 10 = ‘1’ means that the output frequency is within the
Reference Site
or par. 4-13
is selected. It is not possible
Motor Speed High
Torque [Nm]
.
5
5.3 ODVA Control Profile
5.3.1 Control Word under Instances 20/70 and 21/71
Set par.8-10
The control word in Instances 20 and 21 is defined as follows:
Control Word Profile
→
to ODVA.
00 Stop Run Fwd Stop Run Fwd
01 - - Stop Run Rev
02
03 - - - 04
05 - - - Net Ctrl
06
07-15 - - - -
NB!
Bits 00 and 02 in Instance 20 are identical with bits 00
and 02 in the more extensive Instance 21.
Bit
Instance 20 Instance 21
Bit = 0 Bit =1 Bit = 0 Bit =1
No function Fault reset No function Fault reset
----
--- Net Ref
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
27
Page 28

5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
5
Explanation of the Bits:
Bit 0, Run Fwd:
Bit 0 = "0" means that the VLT frequency converter has a stop command.
Bit 0 = "1" leads to a start command and the VLT frequency converter
will start to run the motor clockwise.
Bit 1, Run Rev:
Bit 1 = "0" leads to a stop of the motor. Bit 1 = "1" leads to a start of the
motor.
Bit 2, Fault Reset:
Bit 2 = "0" means that there is no trip reset. Bit 2 = "1" means that a trip
is reset.
Bit 3, No function:
Bit 3 has no function.
Bit 4, No function:
Bit 4 has no function.
Bit 5, Net Control:
Bit 5 = "0" means that the drive is controlled from the standard inputs.
Bit 5 = "1" means that EIP controls the drive.
Bit 6, Net Reference:
Bit 6 = "0" Reference is from the standard inputs. Bit 6 = "1" Reference
is from EIP.
5.3.2 Status Word under Instances 20/70 and 21/71
The status word in Instances 70 and 71 is defined as follows:
→
NB!
Bits 00 and 02 in Instance 70 are identical with bits 00
and 02 in the more extensive Instance 71.
Bit
00 No Fault Fault No Fault Fault
01 - - - Warning
02
03 - - - Running 2 Rev.
04
05 - - - Ctrl from Net
06
07 - - - At ref.
08-15
Explanation of the Bits:
Bit 0, Fault:
Bit 0 = "0" means that there is no fault in the frequency converter. Bit 0
= "1" means that there is a fault in the frequency converter.
Instance 70 Instance 71
Bit = 0 Bit =1 Bit = 0 Bit =1
- Running 1
Fwd
-- -Ready
-- -Ref. from Net
-- State Attribute
- Running 1 Fwd
Bit 1, Warning:
Bit 0 = "0" means that there is no unusual situation. Bit 0 = "1" means
that an abnormal condition has occurred.
Bit 2, Running 1:
Bit 2 = "0" means that the drive is not in one of these states or that Run
1 is not set. Bit 2 = "1" means that the drive state attribute is enabled or
stopping, or that Fault-Stop and bit 0 (Run 1) of the control word are set
at the same time.
Bit 3, Running 2:
Bit 3 = "0" means that the drive is in neither of these states or that Run
2 is not set. Bit 3 = "1" means that the drive state attribute is enabled or
stopping, or that fault-stop and bit 0 (Run 2) of the control word are set
at the same time.
Bit 4, Ready:
Bit 4 = "0" means that the state attribute is in another state. Bit 4 = "1"
means that the state attribute is ready, enabled or stopping.
Bit 5, Control from net:
Bit 5 = "0" means that the drive is controlled from the standard inputs.
Bit 5 = "1" means that EIP has control (start, stop, reverse) of the drive.
Bit 6, Ref from net:
Bit 6 = "0" means that the reference comes from inputs to the drive. Bit
6 = "1" means that the reference comes from EIP.
Bit 7, At reference:
Bit 7 = "0" means that the motor is running, but that the present speed
is different from the preset speed reference, i.e. the speed is being ramped up/down during start/stop. Bit 7 = "1" means that the drive and
reference speeds are equal.
Bit 8 - 15, State attribute:
(Instance 71 only) Represents the state attribute of the drive, as indicated
in the following table:
NB!
Please note that changes will affect parameters 8-50
to 8-56.
NB!
Please note that changes will affect par. 3-15
ence Resource 1
For the Speed reference, see section
to par. 3-17
Reference Resource 3
Bus speed refer-
ence value under Instances 20/70 and 21/71
Refer-
.
.
28
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 29
MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 5 How to Control
Bit Number Meaning
8 (Vendor specific)
9Start up
10 Not ready
11 Ready
12 Enabled
13 Stopping
14 Fault stop
15 Faulted
For more detail of the actual output speed, see the section
speed under Instances 20/70 and 21/71
.
Actual output
5.4 Reference Handling
5.4.1 Bus Speed Reference Value under Instances 100-101-103/150-151-153
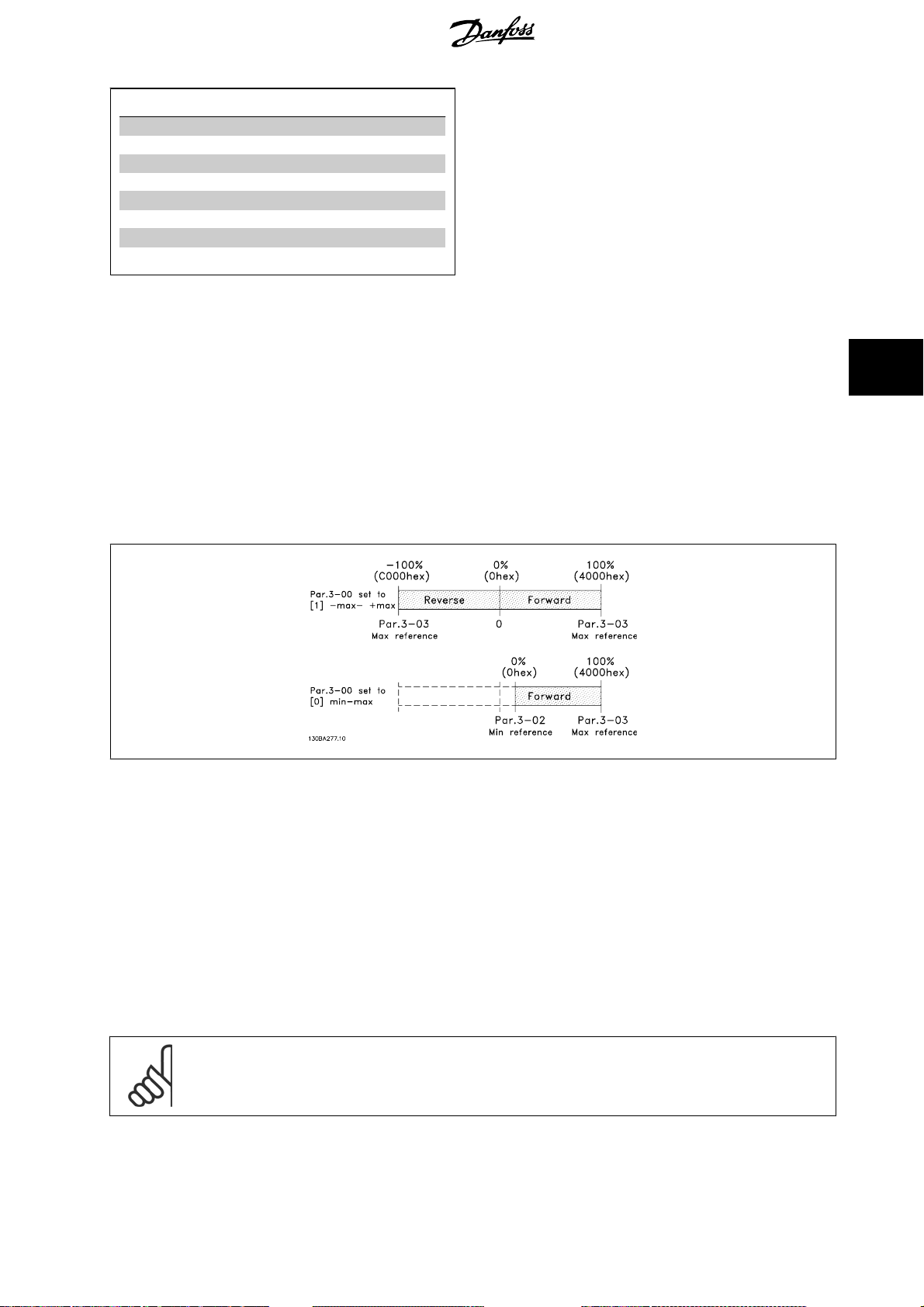
In FC-Profile (par. 8-10 = [0] FC profile) the reference is scaled as a normalized relative value in percent. The value is transmitted in hexadeci mal:
0% = 0hex
100% = 4000hex
-100% = C000hex
Depending of the setting of par. 3-00
Reference Range
, the reference is scaled from – Max. to + Max. or from Min. to Max.
5
The actual reference [Ref. %] in the VLT frequency convert er depends on the settings in the following para mete rs:
Par. 1-23
Par. 1-25
Par. 3-02
Par. 3-03
All references provided to the frequency converter are added to the total reference value. If a reference is to be controlled by the fieldbus onl y, ensure
that all other reference inputs are zero.
This means that digital and analogue input terminals should not be used for reference signals. The default setting (0%) should be maintained for preset
references in par. 3-10
MAV is scaled in the same way as the reference.
Motor Frequency
Motor Nominal Speed
Minimum Refer e nce
Maximum Reference
Preset Reference
NB!
If the bus speed reference is negative, and the control word contains a run reverse signal, the drive will run clockwise (- - is +).
.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
29
Page 30

5 How to Control MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
5.4.2 Bus Speed Reference Value under Instances 20/70 and 21/71
5
→
The speed reference value should be transmitted to the VLT frequency converter in the form of a 16-bit word. The value is transmitted directly in RPM.
30
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 31

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
6 Parameters
6.1 Parameter Group 8-**
8-01 Control Site
Option: Function:
The setting in this parameter overrides the settings in par.8-50
Reference Select
[0] * Digital an d c t rl.word Control by using both digital input and control word.
[1] Digital only Control by using digital inputs only.
[2] Controlword only Control by using control word only.
.
8-02 Control Word Source
Select the source of the control word: one of two serial interfaces or four installed options. During initial power-up, the frequency converter automatically
sets this parameter to
change in the configuration, sets par.8-02
is installed after initial power-up, the setting of par.8-02
67
Option Changed
This parameter cannot be adjusted while the motor is running.
.
Option A
[3] if it detects a valid fieldbus option installed in slot A. If the option is removed, the frequency converter detects a
Control Word Source
back to default setting
Control Word Source
FC
RS485, and the frequency converter then trips. If an option
will not change but the frequency converter will trip and display: Alarm
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] FC RS485
[2] FC USB
[3] * Option A
[4] Option B
[5] Option C0
[6] Option C1
Coasting Select
to par.8-56
Preset
6
8-03 Control Word Timeout Time
Range: Function:
1.0 s* [0.1 - 18000.0 s] Enter the maxi mum time expected to pass between the reception of two co nsecutive telegrams. If
this time is exceeded, it indicates that the serial communication has stopped. The function selected
in par.8-04
by a valid control word.
Control Word Timeout Function
will then be carried out. The time-out counter is triggered
8-04 Control Word Timeout Function
Select the time-ou t function. The time-out function activates when the control word fails to be updated within the time period specified in par.
8-03
Control Word Timeout Time
.
Option: Function:
[0] * Off Resumes control via serial bus (Fieldbus or standard) using the most recent control word.
[1] Freeze output Freezes output frequency until communication resumes.
[2] Stop Stops with auto restart when communication resumes.
[3] Jogging Runs the motor at JOG frequency until communication resumes.
[4] Max. speed Runs the motor at maximum frequency until communication resumes.
[5] Stop and trip Stops the motor, then resets the frequency converter in order to restart: via the fieldbus, via the
reset button on the LCP or via a digital input.
[7] Select setup 1 Changes the set-up upon reestablishment of communication follo wing a con trol word t ime-out. I f
communication resumes causing the time-out situation to disappear, par.8-05
End-of-Timeout
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
31
Page 32

6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Function
defines whether to resume the set-up used before the time-out or to retain the set-up
endorsed by the time-out function.
6
[8] Select setup 2 See [7]
[9] Select setup 3 See [7]
[10] Select setup 4 See [7]
NB!
The following configuration is required in order to change the set-up after a time-out:
Set par. 0-10
Active Set-up
to [9]
Select setup 1
Select setup 1
Select setup 1
Multi set-up
and select the relevant link in par. 0-12
8-05 End-of-Timeout Function
Option: Function:
Select the action after receiving a valid control word following a time-out. This parameter is active
only when par. 8-04
[0] Hold set-up Retains the set-up selected in par. 8-04
par. 8-06
Reset Control Timeout
[1] * Resume set-up Resumes the set-up active prior to the time-out.
Control Timeout Function
Control Timeout Function
toggles. Then the frequency converter resumes its original set-up.
8-06 Reset Control Word Timeout
This parameter is active only when
Hold set-up
[0] has been selected in par.8-05
End-of-Timeout Function
Option: Function:
[0] * Do not reset Retains the set-u p specified in par.8-04
time-out.
Control Word Timeout Function
This Set-up Linked to
is set to [Set-up 1-4].
.
.
and displays a warning, until
, following a contr ol word
[1] Do reset Returns the frequency converter to the original set-up follow ing a con trol wo rd tim e-out. The f re-
quency converter performs the reset and then immediately reverts to the
Do not reset
[0] setting
8-10 Control Word Profile
Select the interpretation of the control and status words corresponding to the installed fieldbus. Only the selections valid for the fieldbus installed in
slot A will be visible in the LCP display.
For guidelines in selection of
For additional guidelines in the selection of
the installed fieldbus.
FC profile
[0] and
PROFIdrive profile
PROFIdrive profile
[1] please refer to the
[1],
ODVA
[5] and
Serial communication via RS 485 Interface
CANopen DSP 402
[7], please refer to the Operating Instructions for
section.
Option: Function:
[0] * FC profile
[5] ODVA
8-13 Configurable Status Word STW
Option: Function:
This parameter enables configuration of bits 12 – 15 in the status word.
[0] No function
[1] * Profile Default Function corresponds to the profile default selected in par. 8-10
[2] Alarm 68 Only Only set in case of an Alarm 68.
[3] Trip excl Alarm 68 S et in case of a tr ip, except if the trip is executed by an Alarm 68.
[16] T37 DI status The bit indicates the status of terminal 37.
“0” indicates T37 is low (safe stop)
“1” indicates T37 is high (normal)
Control Profile
.
32
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 33

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
8-14 Configurable Control Word CTW
Option: Function:
Selection of control word bit 10 if it is active low or active high
[0] None
[1] * Profile default
[2] CTW Valid, active low
8-50 Coasting Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the coasting function via the terminals (digital input) and/or via the bus.
[0] Digital input
[1] Bus Activates Sta rt command via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
[2] Logic AND Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port, AND additionally via one of the
digital inputs.
[3] * Logic OR Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port OR via one of the digital inputs.
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
6
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
33
Page 34

6
6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
8-51 Quick Stop Select
Select control of the Quick Stop function via the terminals (digital input) and/or via the bus.
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input
[1] Bus
[2] Logic AND
[3] * Logic OR
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
8-52 DC Brake Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the DC brake via the terminals (digital input) and/or via the fieldbus.
[0] Digital input
[1] Bus Activates Start command via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
[2] Logic AND Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port, AND additionally via one of the
digital inputs.
[3] * Logic OR Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port OR via one of the digital inputs.
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
8-53 Start Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the frequency converter start function via the terminals (digital input) and/or via
the fieldbus.
[0] Digital input Activates Start command via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activates Start command via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
[2] Logic AND Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port, AND additionally via one of the
digital inputs.
[3] * Logic OR Activates Start command via the fieldbus/serial communication port OR via one of the digital inputs.
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
8-54 Reversing Select
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input Select control of the frequency converter reverse function via the terminals (digital input) and/or
via the fieldbus.
[1] Bus Activates the Reverse command via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
[2] Logic AND Activates the Reverse command via the fieldbus/serial communication port, AND additiona lly via
one of the digital inputs.
34
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 35

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
[3] * Logic OR Activates the Reverse command via the fieldbus/serial communication port OR via one of the digital
inputs.
NB!
This parameter is only active when par. 8-01
8-55 Set-up Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the frequency converter set-up selection via the terminals (digital input) and/or via
the fieldbus.
[0] Digital input Activates the set-up selection via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activates the set-up selection via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
[2] Logic AND Activates the set-up se le ctio n via t h e fie ldbus /serial com muni cati on por t, A ND a ddit ional ly vi a on e
of the digital inputs.
[3] * Logic OR Activate the set-up selection via the fieldbus/serial comm unication port OR via one of the digital
inputs.
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
6
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
8-56 Preset Reference Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the frequency converter Preset Reference selection via the terminals (digital input)
and/or via the fieldbus.
[0] Digital input Activates Preset Reference selection via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activates Preset Reference selection via the serial communication port or fieldbus option.
[2] Logic AND Activates Preset Reference selectio n via the fieldbus/seria l communication po rt, AND additiona lly
via one of the digital inputs.
[3] * Logic OR Activates the Preset Reference selection via the f ieldbus/seria l commu nication po rt OR via one of
the digital inputs.
NB!
This parameter is active only when par.8-01
Control Site
is set to [0]
Digital and control word
.
6.2 Parameter Group 12-**
6.2.1 IP Settings
12-00 IP Address Assignment
Option: Function:
Selects the IP Address assignment method.
[0] * Manual IP-address can be set in par. 12-01 IP Address.
[1] DHCP IP-address is assigned via DHCP server.
[2] BOOTP IP-address is assigned via BOOTP server.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
35
Page 36

6
6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
12-01 IP Address
Range: Function:
[000.000.000.000 -
255.255.255.255]
12-02 Subnet Mask
Range: Function:
[000.000.000.000 -
255.255.255.255]
12-03 Default Gateway
Range: Function:
[000.000.000.000 –
255.255.255.255]
12-04 DHCP Server
Range: Function:
[000.000.000.000 –
255.255.255.255]
Configure the IP address of the option. Read-only if par. 12-00 set to DHCP or BOOTP.
Configure the IP subnet mask of the option. Read-only if par. 12-00 set to DHCP or BOOTP.
Configure the IP default gateway of the option. Read-only if par. 12-00 set to DHCP or BOOTP.
Read only. Displays the IP address of the found DHCP or BOOTP server.
NB!
A power-cycle is necessary after setting the IP parameters manually.
12-05 Lease Expires
Range: Function:
[dd:hh:mm:ss] Read only. Displays the lea s e-time left for the current DHCP-assigned IP address.
12-06 Name Servers
Option: Function:
IP addresses of Domain Name Servers. Can be automatically assigned when using DHCP.
[0] Primary DNS
[1] Secondary DNS
12-07 Domain Name
Range: Function:
Blank [0-19 characters] Domain name of the attached network. Can be automatically assigned when using DHCP.
12-08 Host Name
Range: Function:
Blank [0-19 characters] Logical (given) name of option.
12-09 Physical Address
Range: Function:
[00:1B:08:00:00:00 – 00:1B:
08:FF:FF:FF]
Read only Displays the Physical (MAC) address of the option.
6.2.2 Ethernet Link Parameters
12-1* Ethernet Link Parameters
Option: Function:
Applies for whole parameter group.
36
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 37

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
[0] Port 1
[1] Port 2
12-10 Link Status
Option: Function:
Read only. Displays the link status of the Ethernet ports.
[0] No link
[1] Link
12-11 Link Duration
Option: Function:
Link Duration Port 1 (dd:hh:mm:ss) Read only. Displays the duration of the present link on each port in dd:hh:mm:ss.
12-12 Auto Negotiation
Option: Function:
Configures Auto Negotiation of Ethernet link parameters, for each port: ON or OFF.
[0] Off
[1] On
Link Speed
12-13 Link Speed
Option: Function:
Forces the link speed for each port in 10 or 100 Mbps. If par. 12-12 is set to: ON, this parameter is
read only and displays the actual link speed. “None” is displayed if no link is present.
[0] * None
[1] 10 Mbps
[2] 100 Mbps
and
Link Duplex
can be configured in par. 12-13 and 12-14.
6
12-14 Link Duplex
Option: Function:
Forces the duplex for each port to Full or Half duplex. If par. 12-12 is set to: ON, this parameter is
read only.
[0] Half duplex
[1] * Full duplex
6.2.3 Process Data
12-20 Control Instance
Range: Function:
[None, 20, 21, 100, 101, 103] Read only. Displays the originator-to-target connecti on point. If no CIP connection is present “None”
is displayed.
12-21 Process Data Config Write
Range: Function:
[[0 - 9] PCD read 0 - 9] Configuration of readable process data.
NB!
For configuration of 2-word (32-bit) parameter read/write, use 2 consecutive arrays in par. 12-21 and 12-22.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
37
Page 38

6
6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
12-22 Process Data Config Read
Range: Function:
[[0 - 9] PCD read 0 - 9] Configuration of readable process data.
12-28 Store Data Values
Option: Function:
This parameter activates a function that stores all parameter values in the non-volatile memory
(EEPROM) thus retaining parameter values at power-down.
The parameter returns to “Off”.
[0] * Off The store function is inactive.
[1] Store All set-ups All parameter value will be stored in the non-volatile memory, in all four setups.
12-29 Store Always
Option: Function:
Activates function that will always store received parameter data in non-volatile memory (EEPROM).
[0] * Off
[1] On
6.2.4 EtherNet/IP
12-30 Warning Parameter
Range: Function:
[0000 – FFFF hex] Read only. Displays the EtherNet/IP specific 16-bit Status-word.
Bit
0 Owned
1Not used
2 Configured
3Not used
4 Not used
5Not used
6 Not used
7Not used
8 Minor recoverable fault
9 Minor unrecoverable fault
10 Major recoverable fault
11 Major unrecoverable fault
12 Not used
13 Not used
14 Not used
15 Not used
12-31 Net Reference
Option: Function:
Read only. Displays the reference source in Instance 21/71.
[0] * Off Reference fro m t he network is not active.
[1] On Reference from the network is active.
Description
12-32 Net Control
Option: Function:
Read only. Displays the control source in Instance 21/71.
[0] * Off Control via the network is not active.
38
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 39

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
[1] On Control via the network is active
12-33 CIP Revision
Option: Function:
Read only. Displays the CIP-version of the option software.
[0] Major version (00 - 99)
[1] Minor version (00 - 99)
12-34 CIP Product Code
Range: Function:
1100 (FC
302) 1110
(FC 301)*
12-37 COS Inhibit Timer
Range: Function:
12-38 COS Filters
Range: Function:
[0 – 9999] Read only. Displays the CIP product code.
[0 – 65.535 ms] Read only Change-Of-State inhibit timer. If the option is configured for COS operation, this inhibit
timer can be configured in the Forward Open telegram to prevent that continuously changing PCD
data generates extensive network traffic. The inhibit time is in milliseconds, 0 = disabled.
[[0 - 9] Filter 0 – 9 (0000 FFFFhex)]
Change-Of-State PCD filters. Sets up a filter mask for each word of process data when operating in
COS-mode. Single bits in the PCD’s can be filtered in/out.
6
6.2.5 Other EtherNet Services
12-80 FTP Server
Option: Function:
[0] * Disable Disables the built-in FTP server.
[1] Enable Enables the built-in FTP server.
12-81 HTTP Server
Option: Function:
[0] * Disable Disables the build-in HTTP (web) server.
[1] Enable Enables the build-in HTTP (web) server.
12-82 SMTP Service
Option: Function:
[0] * Disable Disables the SMTP (e-mail) service on the option.
[1] Enable Enables the SMTP (e-mail) service on the option.
12-89 Transparent Socket Channel Port
Range: Function:
0* [0 – 9999] Configures the TCP port-number for the transparent socket channel. This enables FC-telegrams to
be sent transparently on Ethernet via TCP. Default value is 4000, 0 means disabled.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
39
Page 40

6
6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
6.2.6 Advanced EtherNet Settings
12-90 Cable Diagnostics
Option: Function:
Enables/disables advanced Cable diagnosis function. If enabled, the distance to cable errors can be
read out in par. 12-93. The parameter resumes to the default setting of Disable after the diagnostics
have finished.
[0] * Disable
[1] Enable
NB!
The cable diagnostics function will only be issued on ports where there is no link (see par. 12-10,
12-91 Auto Cross-Over
Option: Function:
[0] Disable Disables the auto cross-over function.
[1] * Enable Enables the auto cross-over function.
Link Status
)
NB!
Disabling of the auto cross-over function will require crossed Ethernet cables for daisy-chaining the options.
12-92 IGMP Snooping
Option: Function:
This prevents flooding of the Ethernet protocol stack by only forwarding multicast packets to ports
that are a member of the multicast group
[0] Disable Disables the IGMP snooping function.
[1] * Enable Enables the IGMP snooping function.
12-93 Cable Error Length
Option: Function:
If Cable Diagnostics is enabled in par. 12-90 , the built-in switch is able via Tim e Domain Reflec-
tometry (TDR). This is a measurement technique which detects common cabling problems such as
open circuits, short circuits and impedance mismatches or breaks in transmission cables. The dis-
tance from the option to the error is displayed in meters with an accuracy of +/- 2m. The value 0
means no errors detected.
[0] Error length Port 1 (0 – 200m)
[1] Error length Port 2 (0 – 200m)
12-94 Broadcast Storm Protection
Option: Function:
The built-in switch is capable of p rotecting the switch system from receiving too many broadcast
packages, which can use up network resources. The value indicates a percentage of the total band-
width that is allowed for broadcast messages.
Example:
The “OFF” means that the filter is disabled –a ll broadcast messages will be passed th rough. The
value “0%” means that no broadcast messages will be passed through. A value of “10%” means
that 10% of the total bandwidth is allowed for broadcast messages, if the amount of broadcast
messages increases above the 10% threshold, they will be blocked.
[0] Protection Value Port 1 (*Off – 2 0%)
40
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 41

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
[1] Protection Value Port 2 (*Off – 20%)
12-95 Broadcast Storm Filter
Option: Function:
Applies to par. 12-94; if the Broadcast Storm Protection should also include Multicast telegrams.
[0] Broadcast only
[1] Broadcast & Multicast
12-98 Interface Counters
Option: Function:
Read only. Advanced Interface counters, from build-in switch, can be used for low-level trouble-
shooting, The parameter shows a sum of port 1 + port 2.
[0] In Octets
[1] In Unicast Packets
[2] In Non-Unicast Packets
[3] In Discards
[4] In Errors
[5] In Unknown Protocols
[6] Out Octets
[7] Out Unicast Packets
[8] Out Non-Unicast Packets
[9] Out Discards
[10] Out Errors
6
12-99 Media Counters
Option: Function:
Read only. Advanced Interface counters, from build-in switch, can be used for low-level trouble-
shooting, The parameter shows a sum of port 1 + port 2.
[0] Alignment Errors
[1] FCS Errors
[2] Single Collisions
[3] Multiple Collisions
[4] SQE Test Errors
[5] Deferred Errors
[6] Late Collisions
[7] Excessive Collisions
[8] MAC Transmit Errors
[9] Carrier Sense Errors
[10] Frame Too Long
[11] MAC Receive Errors
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
41
Page 42

6
6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
6.3 Parameter List
Type
Conver-
sion index
eration
Change during op-
only
Parameter description Default value 4-set-up FC 302
Par. No.
42
Diagnosis Trigger [0] Disable 2 set-ups TRUE - Uint8
#
8-0* General Settings
8-01 Control Site [0] Digital and ctrl.word All set-ups TRUE - Uint 8
8-02 Control Word Source null All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-04 Control Word Timeout Function null 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-06 Reset Control Word Timeout [0] Do not reset All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-03 Control Word Timeout Time 1.0 s 1 set-up TRUE -1 Uint32
8-05 End-of-Timeout Function [1] Resume set-up 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-07
Configurable Control Word CTW [1] Profile default All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-1* Ctrl. Word Settings
8-10 Control Word Profile [0] FC profile All set-ups TRUE - Uint 8
8-13 Configurable Status Word STW [1] Profile default All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-3* FC Port Settings
8-30 Protocol [0] FC 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-31 Address 1 N/A 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
8-14
8-32 FC Port Baud Rate null 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
Max Inter-Char Delay SR 1 set-up TRUE -5 Uint16
8-33 Parity / Stop Bits [0] Even Parity, 1 Stop Bit 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-36 Max Response Delay SR 1 set-up TRUE -3 Uint16
8-4* FC MC protocol set
8-40 Telegram selection [1] Standard telegram 1 2 set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-5* Digital/Bus
8-50 Coasting Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-35 Minimum Response Delay 10 ms All set-ups TRUE -3 Uint16
8-37
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
8-51 Quick Stop Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-52 DC Brake Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-53 Start Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Preset Reference Sele ct [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-55 Set-up Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-8* FC Port Diagnostics
8-80 Bus Message Count 0 N/A All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint32
8-54 Reversing Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-81 Bus Error Count 0 N/A All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint32
8-56
8-82 Slave Messages Rcvd 0 N/A All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint32
8-83 Slave Error Count 0 N/A All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint32
8-9* Bus Jog
8-90 Bus Jog 1 Speed 100 RPM All set-ups TRUE 67 Uint16
8-91 Bus Jog 2 Speed 200 RPM All set-ups TRUE 67 Uint16
Page 43

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 6 Parameters
6
IP Address Assignment 0.0.0.0 0 - 255 - Unsigned 8 -
Parameter Number Parameter Description Default Value Range Conversion Index Data Type Array
12-0* IP Settings
12-00
12-01 IP Address 0.0.0.0 0 – 255 - Oct. string 4 -
12-03 Default Gateway 0.0.0.0 0 - 255 - Oct. string 4 -
12-05 Lease Expires 00:00:00:00 - - Time diff. w/date -
12-07 Domain Name - max. 19 ch. - Visible string 48 -
12-09 Physical Address 00:1B:08:00:00:00 - - Visible string 17 -
12-1* EtherNet Link Parameters
12-10 Link Status No Link [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 [0-1]
12-11 Link Duration 00:00:00:00 - - Time diff. w/date [0-1]
12-12 Auto Negotiation On [1] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 [0-1]
12-14 Link Duplex Full Duplex [1] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 [0-1]
12-2* Process Data
12-20 Control Instance None 20 - 103 - Unsigned 8 -
12-21 Process Data Config Write - - - Unsigned 16 [0-9]
12-22 Process Data Config Read - - - Unsigned 16 [0-9]
12-29 Store Always Off [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-3* EtherNet/IP
12-30 Warning Parameter 0000 hex 0000–FFFF - Unsigned 16 -
12-31 Net Control Off [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-32 Net Reference Off [0] [0 - 1] - Unsign ed 8 -
12-34 CIP Product Code 0 9999 - Unsigned 16 [0-1]
12-38 COS Filters 0000 0000 - FFFF - Unsigned 16 [0-9]
12-8* Other EtherNet Services
12-80 FTP Server Disable [0] [0 – 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-82 SMTP Service Disable [0] [0 – 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-9* Advanced EtherNet Settings
12-90 Cable Diagnostics Disable [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-91 Auto Cross-Over Enable [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-93 Cable Error Length 0 0 - 200 0 Unsigned 16 [0-1]
12-95 Broadcast Storm Filter Enable [1] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 [0-1]
12-02 Subnet Mask 0.0.0.0 0 – 255 - Oct. string 4 -
12-04 DHCP Server 0.0.0.0 0 - 255 - Oct. string 4 -
12-06 Name Servers 0.0.0.0 0 - 255 - Oct. string 4 -
12-08 Host Name - max. 19 ch. - Visible string 48 -
12-13 Link Speed None [0] [0 - 2] - Unsigned 8 [0-1]
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
12-28 Store Data Values Off [0] [0 – 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-33 CIP Revision 00 0 – 99 - Unsigned 16 [0-1]
12-81 HTTP Server Disable [0] [0 – 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-37 COS Inhibit Timer 0 0 - 65535 0 Unsigned 16 -
12-89 Transp. Socket Channel Port Disable [0] [0 – 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-92 IGMP Snooping Enable [0] [0 - 1] - Unsigned 8 -
12-94 Broadcast Storm Protection 0 Off – 20% - Unsigned 16 [0-1]
12-99 Media Counters 0 0 - 65535 - Unsigned 16 [0-11]
12-98 Interface Counters 0 0 - 65535 - Unsigned 16 [0-10]
43
Page 44

6 Parameters MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
6.4 Data Types
6.4.1 Data Types Supported by FC 200/FC 300
Conversion Index
This number to the left refers to a conversion figure on th e right to be used when writing or reading parameters.
6
Conversion Index
67 1/60
6 1000000
5 100000
4 10000
3 1000
2100
1 10
01
-1 0.1
-2 0.01
-3 0.001
-4 0.0001
-5 0.00001
-6 0.000001
Conversion Factor
44
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 45

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 7 Troubleshooting
7 Troubleshooting
7.1.1 Step-by-step Troubleshooting
Check: LEDs
The option contains two LEDs to indicate the state of the device and the network. During normal operation the MS and at least one NS LED will show a
constant green light.
State LED Description
Standby Green: Flashing green The device needs commissioning
Device operational Green: Solid green The device is operational
Major recoverable fault Flashing red The device has detected a recoverable fault (MAR)
Major unrecoverable fault Red: Solid red The device has detected a un-recoverable fault (MAU)
Self test
Table 7.1: MS: Module Status
State LED Description
No connections Green: Flashing green There are no established any CIP connections to the
Connected Green: Solid green There is established (at least) one CIP connection to the
Connection time-out Red: Flashing red One or more CIP connections has timed-out
Duplicate IP Red: Solid red The IP-address assigned to the device is already in use
Self test
Red:
Green:
Red:
Green
Flashing red/green The EIP option is in self-test mode
7
device
device
Flashing red/green The EIP option is in self-test mode
Table 7.2: NS1 + NS2: Network Status (one per port)
Check: Link Status
The status of the Ethernet link cannot be directly identified by means of the LEDs, if no CIP connection is established.
Use par. 12-10,
Use par. 12-11,
The parameter will show the duration of the present link, and preset to 00:00:00:00 if the link is broken.
Check: Cabling
In rare cases of cabling mis-configuration, the option might show the presents of a link, but no communication is running. Exchange the cable in doubt.
Check: IP Address
Verify that the option has a valid IP address (please refer to section: IP Settings) in par. 12-01,
Address NS LEDs will light steady red. If the option is set up for BOOTP or DHCP, verify that a BOOTP or DHCP server is connected in par. 12-04,
Server
Link Status
Link Duration
. If no server is connected, the parameter will show: 000.000.000.000.
to verify presents of the link.
to verify that the link is steady present.
IP Address
. If the option has identified a duplicate IP
DHCP
7.1.2 Alarm Word and Warning Word
Alarm word and warning word are shown in the display in Hex format. If there is more than one warning or alarm, a sum of all warnings or alarms will
be shown. Warning word and alarm word are displayed in par. 16-90 to 16-95. For more information on the individual alarms and warnings, please refer
to: FC 200/FC 300 Design Guide.
NB!
Please note that the availability of the individual alarms and warnings are dependent on the drive type: /FC 200/FC 300 series.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
45
Page 46

7 Troubleshooting MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Warning and Alarm Messages
There is a clear distinction between alarms and warnings. In the event of an alarm, the frequency converter will enter a fault condition. After the cause
for the alarm has been cleared, the master must acknowledge the alarm message in order to start operation of the frequency converter again. A warning,
on the other hand, may appear when a warning condition arises, then disappear when conditions return to normal without interfering with the process.
Warnings
All warnings within the frequency converter are represented by a single bit within a warning word . A warning word is a lways an action paramete r. Bit
status FALSE [0] means no warning, while bit status TRUE [1] means warning. Each bit status has a corresponding text string message. In addition to
the warning word message the master will also be notified via a change in the status word.
Alarms
Following an alarm message the frequency converter will enter a fault condition. Only after the fault has been rectified and the master has acknowledged
the alarm message by a bit in the Control Word, can the VLT resume operation. All alarms within the VLT are represented by a single bit within an alarm
word. An alarm word is always an action parameter. Bit status FALSE [0] means no alarm, while bit status TRUE [1] means alarm. In CIP, Alarms are
divided in to two categories:
- Major Recoverable Faults
- Major Unrecoverable Faults
Please refer to the following sections for a classification of the specific faults.
7
Bit (Hex)
00000001 Brake check 00000002 Power card over temperature MAR
00000004 Earth fault MAU
00000008 Ctrl. card over temperature 00000010 Control word timeout MAR
00000020 Torque limit MAU
00000040 Over current MAR
00000080 Motor thermistor over temp. MAR
00000100 Motor ETR over temperature MAR
00000200 Inverter overloaded MAR
00000400 DC link under voltage MAR
00000800 DC link over voltage MAR
00001000 Short circuit MAU
00002000 Inrush fault MAR
00004000 Mains phase loss MAU
00008000 AMA not OK MAR
00010000 Live zero error MAR
00020000 Internal fault MAU
00040000 Brake overload MAU
00080000 Motor phase U is missing MAU
00100000 Motor phase V is missing MAU
00200000 Motor phase W is missing MAU
00400000 Fieldbus fault MAR
00800000 24V supply fault MAU
01000000 Mains failure MAR
02000000 1.8V supply fault MAU
04000000 Brake resistor short circuit MAR
08000000 Brake chopper fault MAR
10000000 Option change 20000000 Drive initialized 40000000 Safe Stop MAR
80000000 Mech. Brake low -
Alarm word (Par. 16-90) CIP Classification
MAR = Major Recoverable Fault
MAU = Major Unrecoverable Fault
46
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 47

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 7 Troubleshooting
Bit (Hex) Al arm word 2 (Par 16-91)
00000001 Service Trip, Read/Write
00000002 Reserved
00000004 Service Trip, Typecode/Sparepart
00000008 Reserved
00000010 Reserved
00000020 No Flow
00000040 Dry Pump
00000080 End of Curve
00000100 Broken Belt
00000200 Discharge high
00000400 Start failed
00000800 Speed limit
00001000 Reserved
00002000 Reserved
00004000 Reserved
00008000 Reserved
00010000 Reserved
00020000 KTY error
00040000 Fans error
00080000 ECB error
00100000 Reserved
00200000 Reserved
00400000 Reserved
00800000 Reserved
01000000 Reserved
02000000 Reserved
04000000 Reserved
08000000 Reserved
10000000 Reserved
20000000 Reserved
40000000 PTC thermistor
80000000 Dangerous failure
Bit (Hex) Warning word (Par. 16-92)
00000001 Brake check
00000002 Power card over temperature
00000004 Earth fault
00000008 Control card over temperature
00000010 Control word timeout
00000020 Over current
00000040 Torque limit
00000080 Motor thermistor over temp.
00000100 Motor ETR over temperature
00000200 Inverter overloaded
00000400 DC link under voltage
00000800 DC link over voltage
00001000 DC link voltage low
00002000 DC link voltage high
00004000 Mains phase loss
00008000 No motor
00010000 Live zero error
00020000 10V low
00040000 Brake resistor power limit
00080000 Brake resistor short circuit
00100000 Brake chopper fault
00200000 Speed limit
00400000 Fieldbus comm. fault
00800000 24V supply fault
01000000 Mains failure
02000000 Current limit
04000000 Low temperature
08000000 Voltage limit
10000000 Encoder loss
20000000 Output frequency limit
40000000 Safe stop
80000000 Extended status word
7
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
47
Page 48

7 Troubleshooting MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
7
Bit (Hex) Warning word 2 (Par. 16-93)
00000001 Start Delayed
00000002 Stop Delayed
00000004 Clock Failure
00000008 Firemode was active
00000010 Reserved
00000020 No Flow
00000040 Dry Pump
00000080 End of Curve
00000100 Broken Belt
00000200 Discharge high
00000400 Reserved
00000800 Reserved
00001000 Reserved
00002000 Reserved
00004000 Reserved
00008000 Reserved
00010000 Reserved
00020000 KTY warning
00040000 Fans warning
00080000 ECB warning
00100000 Reserved
00200000 Reserved
00400000 Reserved
00800000 Reserved
01000000 Reserved
02000000 Reserved
04000000 Reserved
08000000 Reserved
10000000 Reserved
20000000 Reserved
40000000 PTC thermistor
80000000 Reserved
Bit (Hex) Extended status word (Par.
16-94) FC 200 only !!
00000001 Ramping
00000002 AMA Running
00000004 Start CW/CCW
00000008 Slow Down
00000010 Catch Up
00000020 Feedback high
00000040 Feedback low
00000080 Output current high
00000100 Output current low
00000200 Output frequency high
00000400 Output frequency low
00000800 Brake check OK
00001000 Braking max
00002000 Braking
00004000 Out of speed range
00008000 OVC active
00010000 AC brake
00020000 Password Timelock
00040000 Password Protection
00080000 Reference high
00100000 Reference low
00200000 Local Ref./Remote Ref.
00400000 Reserved
00800000 Reserved
01000000 Reserved
02000000 Reserved
04000000 Reserved
08000000 Reserved
10000000 Reserved
20000000 Reserved
40000000 Reserved
80000000 Reserved
48
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 49

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 7 Troubleshooting
Bit (Hex) Extended status word 2 (Par. 16-95)
FC 200 only !!
00000001 Off
00000002 Hand/Auto
00000004 PROFIbus OFF1 active
00000008 PROFIbus OFF2 active
00000010 PROFIbus OFF3 active
00000020 Relay 123 active
00000040 Start Prevented
00000080 Control ready
00000100 Drive ready
00000200 Quick Stop
00000400 DC Brake
00000800 Stop
00001000 Stand By
00002000 Freeze Output Request
00004000 Freeze Output
00008000 Jog Request
00010000 Jog
00020000 Start Request
00040000 Start
00080000 Start Applied
00100000 Start Delay
00200000 Sleep
00400000 Sleep Boost
00800000 Running
01000000 Bypass
02000000 Fire Mode
04000000 Reserved
08000000 Reserved
10000000 Reserved
20000000 Reserved
40000000 Reserved
80000000 Reserved
7
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
49
Page 50

8 Appendix MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
8
50
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 51

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 8 Appendix
8 Appendix
8.1.1 Supported CIP Objects
As in all implementations of CIP, EtherNet/IP sha res the common Object Model. Objects are a common method to describe the specific application
implemented in a device.
Data is structured in Classes, Instances and Attributes:
A class is a group of objects with the same structure. These groups of objects within a class are called instances. Every instance provides the same
data elements calle d attributes. Each class provides services to access data or to change the state of an object.
Class ID 0x01 Identity Object
Attribute
1 Get Vendor UINT (97) Danfoss Drives vendor code
2 Get Device Type UINT (2) AC Drive
3 Get Product Code UINT Value of par. 12-34
4 Get Revision Struct Value of par. 12-33
5 Get Status WORD EIP status word (par. 12-30)
6 Get Seria l Numbe r UDINT Serial number
7 Get Product Name String Value of par. 15-40 (e.g. “FC 302”)
8 Get State UINT 0 = Non-existent
9 Get Conf. consistency value UINT
Table 8.1: Instance Attributes
Class ID 0x04 Assembly Objects
Instance
20 Set ODVA basic speed control Ou tput 2 Words
21 Set ODVA extended speed control Output 2 Words
70 Get ODVA basic speed control In put 2 Words
71 Get ODVA extended speed control Input 2 Words
100 Set Danfoss Basic Control Output 2 Words
101 Set Danf oss Extended Contro l Out put 4 Words
103 Set Danf oss Extended Control Output 10 Words
150 Get Danfoss Basic Control Input 2 Words
151 Get Danfoss Extended Control Input 4 Words
153 Get Danfoss Extended Control Input 10 Words
Access Name Data type Description
1 = Device Self Testing
2 = Standby
3 = Operational
4 = Major Recoverable Fault
5 = Major Unrecoverable Fault
6-254 = Reserved
255 = Default for Get Attribute All
Access Name Size Description
8
Table 8.2: Instance Attributes
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
51
Page 52

8 Appendix MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Class ID 0x06 Connection Manager
8
Attribute
1 Get Open Requests UINT Number of Forward Open requests received
2 Get Open Format Rejects UINT Number of Forward Open requests rejected due to bad format
3 Get Open Resource Rejects UINT Number of Forward Open requests rejected due to lack of resources
4 Get Open Other Rejects UINT Number of Forward Open requests rejected due to other reasons
5 Get Close Requests UINT Number of Forward Close requests received
6 Get Close Format Req uests UINT Number of Forward Close requests rejected due to bad format
7 Get Close Other Requests UINT Number of Forwar d Close requests r ejecte d due to ot her reasons
8 Get Connection Timeouts UINT Number of connection timeouts
9 Get Connection Entry List Struct of: NumCon-
Table 8.3: Instance Attributes
Class ID 0x28 Motor Data Object
Attribute
1 Get Number of Attributes supported USINT - 7
2 Get List of attributes supported Array of USINT - 3,6,7,8,9,12,15
3 Get/Set Motor Typ e USINT 1-10 3: PM sync. motor (FC 302 only)
6 Get/Set Rated Current UINT 1-24 Unit: 100 mA
7 Get/Set Rated Voltage UINT 1-22 Unit : Volt
8 Get/Set Rated Power UDINT 1-20 Unit: Watt
9 Get/Set Rated Frequency UINT 1-23 Unit: Hertz
12 Get/Set Pole Count UINT 1-39 Number of poles in motor
15 Get/Set Base Speed UINT 1-25 Unit: RPM
Access Name Data Type Description
INT Number of connection entries ConnOpenBits ARRAY of BOOL List
nEntries
Access Name Data Type Parameter Description
of connection data
7: Squirrel cage induction motor
Table 8.4: Instance Attributes
NB!
Class ID 0x28 is only available if ODVA profile is selected in par.8-10
Class ID 0x29 Control Supervisor Object
Attribute
1 Get Number of Attributes supported USINT 12
2 Get List of supported Attributes Array of USINT 3,4,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,1 1 ,12,13,15
3 Get/Set Run 1 (forward) Boolean FC CTW Bit 6 = Run1 XOR Run2
4 Get/Set Run 2 (reverse) Boolean FC CTW Bit 6 = Run1 XOR Run2
5 Get/Set Network Control Boolean Parameter 12-32 value written from option
6 Get State USINT The state of the CIP state-machine
7 Get Running 1 Boolean Run1 AND bit 11 in FC STW
8 Get Running 2 Boolean Run2 AND bit 11 in FC STW
9 Get Ready Boolean STATE_ENABLED or STATE_STOPPING or
10 Get Faulted Boolean Bit 3 in FC STW
11 Get Warning Boolean Bit 7 in FC STW
12 Get/Set Fault reset Boolean Bit 7 in FC CTW
13 Get Fault Code UINT Mapping of par. 16-90
15 Get Control from net Boolean Parameter 12-31 value written from option
Access Name Data Type Description
Control Word Profile
FC CTW Bit15 = 0
FC CTW Bit15 = 1
STATE_FAULT_STOP from state-machine
fault codes
.
Alarm Word
to CIP specific
Table 8.5: Instance Attributes
52
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 53

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 8 Appendix
CIP Malfunction
Code
0 No alarm 0000 0000 No fault 0 unused 0000 0001 No fault 4210 Drive over temperature 0000 0002 Excessive Device Temperature mar
2240 Earth fault 0000 0004 Short to earth mau
0 unused 0000 0008 No fault 8100 Controlword timeout 0000 0010 Communication mir
2310 Overcurrent 0000 0020 Continuous Overcurrent mau
8302 Torque limit 0000 0040 Torque limiting mar
4310 Motor thermistor 0000 0080 Excess Drive Temperature mar
4310 Motor ETR over temp 0000 0100 Excess Drive Temperature mar
2311 Inverter overloaded 0000 0200 Current inside the device, No. 1 mar
3220 DC Link undervoltage 0000 0400 Undervoltage inside the Device mar
3210 DC Link overvoltage 0000 0800 Overvoltage inside the device mar
2130 Short circuiting 0000 1000 Short Circuit mau
2213 Inrush fault 0000 2000 Overcurr. marduring startup
3130 Mains phase loss 0000 4000 Phase Failure mau
5210 AMT fail 0000 8000 Measurement Circuit mir
1000 Live zero fault 0001 0000 General fault mar
6100 Internal fault 0002 0000 Internal software fault mau
7110 Brake resistor power limit 0004 0000 Brake Chopper mau
3300 Motor phase U missing 0008 0000 Output voltage mau
3300 Motor phase V missing 0010 0000 Output voltage mau
3300 Motor phase W missing 0020 0000 Output voltage mau
8100 Fieldbus Comm. fault 0040 0000 Communication mir
5112 24V supply fault 0080 0000 +24V Power supply mau
3100 Mains failure 0100 0000 Mains Voltage mar
5110 1,8V supply fault 0200 0000 Low voltage power supp. mau
7110 Brake resist. short circ. 0400 0000 Brake chopper mar
7110 Brake chopper fault 0800 0000 Brake chopper mar
0 unused 1000 0000 No fault 0 unused 2000 0000 No fault 0 unused 4000 0000 No fault 0 unused 8000 0000 No fault -
Meaning VLT-Code Alarmword CIP Malfunction Meaning CIP Classification
8
Table 8.6: Attribute 13 “Fault Code”
Mir = Minor Recoverable
Mar = Major Recoverable
Mau = Major Unrecoverable
Service Code
0Eh Get_Attribute_Single Returns contents of specified attribute
10h Set_Attribute_Single Sets the contents of specified attribute
05h Reset Resets drive to it’s start-up state.
Table 8.7: Services supported
NB!
Class ID 0x29 is only available if ODVA profile is sele c t ed i n par.8-10
Service Name Service Description
Control Word Profile
.
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
53
Page 54

8 Appendix MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Class ID 0x2A AC/DC Drive Object
8
Attribute
1 Get Number of Attributes Supported USINT 12
2 Get List of Attributes Supported USINT 3,4,6,7,8,18,19,20,21,22,28,29
3 Get At Reference Boolean Bit 8 of FC STW
4 Get/Set Network Reference Boolean value written to parameter "Net Reference"
6 Get/Set Drive Mode USINT Mapping of values from parameter 1-00
7 Get Actual Speed INT See Attribute 22
8 Get/Set Reference Speed INT See Attribute 22
18 Get/Set Acceleration Time UINT Scaled with Attribute 28 and written to par. 3-41
19 Get/Set Deceleration time UINT Scaled with Attribute 28 and written to par. 3-42
20 Get/Set Low Speed Limit UINT Scaled with Attr ibute 22 and written to par. 4-11
21 Get/Set High Speed Limit UINT Scaled with Attribute 22 and written to par. 4-13
22 Get/Set Speed Scale SINT Forms the "Speed Reference" and "Main Actual Value" for
28 Get/Set Time Scale SINT Scaling factor for all time attributes
29 Get Ref From Net Boolean val ue of parameter "Net Reference"
Table 8.8: Instance Attributes
Value of Attribute 6
0 Vendor specific Remaining values not listed below ?
1 Open loop speed ctr. 0 Speed open loop
2 Closed loop speed ctr. 1 Speed closed loop
3Torque ControlNA NA
4 Process Control NA NA
5 Position Control NA NA
Access Rule Information about Data Type Contents
the Drive together with Attribute 7 and 8
ODVA Text Value of par. 1-00 FC Text
Table 8.9: Attribute 6 “Drive Mode”
NB!
Class ID 0x2A is only available if ODVA profile is selected in par.8-10
Class ID 0xF5 Interface Object
Attribute
1 Get Status DWORD Interface status 2 Get Configuration Capa bi li ty DWORD Interface capa bil ity flags 3 Get/Set Configuration Control DWORD Interface control flags -
4Get
5 Get/Set
6 Get/Set Host Name STRING Host name 12-08
Access Rule Name Data Type Description of Attribute Parameter
Physical Link Object STRUCT of: Path to physical link object Path size UINT Size of Path Path Padded EPATH Logical segments identifying the physical link
Interface Configuration STRUCT of: TCP/IP network interface configuration. IP Address UDINT The device’s IP address. 12-01
Network Mask UDINT The device’s network mask. 12-02
Gateway Address UDINT Default gateway address 12-03
Name Server UDINT Primary name server 12-06 [0]
Name Server 2 UDINT Secondary name server 12-06[1]
Domain Name STRING Default domain name 12-07
Control Word Profile
object
.
In Drive
-
Table 8.10: Instance Attributes
54
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 55

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 8 Appendix
Class ID 0xF6 Link Object
Three instances of the Link Object are implemented:
- Instance 1 and 2 relates to the physical Por t 1 and 2 of the option.
- Instance 3 relates to the internal interface of the option, after the build-in switch.
Access
At-
Rule
trib-
ute
1 Get Interface Spe ed UDINT Interface speed in Mbps (e.g., 0, 10, 100, 1000, etc.) 12-13
2 Get Interface Flags DWORD Interface status flags 3 Get Physical Address ARRAY of 6 USINTs MAC layer address 12-09
4Get
5
Get
6 Set Interface Control STRUCT of: Configuration for physical interface -
7 Get Interface Label SHORT_STRING Human readable identification 8 Get Link List Size USINT Number of members in Link List 9 Get Link List ARRAY OF UINT Link List between internal and all according external interfaces -
Name Data Type Description of Attribute Parameter
in drive
Interface Counters STRUCT of
In Octets UDINT Octets received on the interface 12-98 [0]
In Ucast Packets UDINT Unicast packets received on the interface 12-98[1]
In NUcast Packets UDINT Non-unicast packets received on the interface 12-98[2]
In Discards UDINT Inbound packets received on the interf ace b ut discarded 12-98[3]
In Errors UDINT Inbound packets that contain errors (does not include In Discards) 12-98 [4]
In Unknown Protos UDINT Inbound packets with unknown protocol 12-98[5]
Out Octets UDINT Octets sent on the interface 12-98[6]
Out Ucast Packets UDINT Unicast packets sent on the interface 12-98[7]
Out NUcast Packets UDINT Non-unicast packets sent on the interface 12-98[8]
Out Discards UDINT Outbound packets discarded 12-98[9]
Out Errors UDINT Outbound packets that contain errors 12-98[10]
Media Counters STRUCT of: Media-specific counters
Alignment Errors UDINT Frames received that are not an integral number of octets in length 12-99[0]
FCS Errors UDINT Frames received that do not pass the FCS check 12-99[1]
Single Collisions UDINT Successfully transmitted frames which experienced exactly one colli-
sion
Multiple Collisions UDINT Successfully transmitted frames which experienced more than one col-
lision
SQE Test Errors UDINT Number of times SQE test error message is generated 12-99[4]
Deferred Transmissions
Late Collisions UDINT Number of times a collision is detected later than 512 bit times into the
Excessive Collisions UDINT Frames for which transmission fails due to excessive collisions 12-99[7]
MAC Transmit Errors UDINT Frames for which transmission fails due to an internal MAC sub layer
Carrier Sense Errors UDINT Times that the carrier sense condition was lost or never asserted when
Frame Too Long UDINT Frames received that exceed the maximum permitted frame size 12-99[10]
MAC Receive Errors UDINT Frames for which reception on an interface fails due to an internal MAC
Control Bits WORD Interface Control Bits Forced Interface
Speed
UDINT Frames for which first transmission attempt is delayed because the
medium is busy
transmission of a packet
transmit error
attempting to transmit a frame
sub layer receive error
UINT Speed at which the interface shall be forced to operate Speed in Mbps
(10, 100, 1000, etc.)
12-99[2]
12-99[3]
12-99[5]
12-99[6]
12-99[8]
12-99[9]
12-99[11]
-
8
Table 8.11: Instance Attributes
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
55
Page 56

8 Appendix MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Service Code Supported Service Name Description of Service
Class Instance
01h Yes Yes Get_Attribute_All Returns a predefined listing of this objects attributes
0Eh Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the specified attribute.
10h - Yes Set_Attribute_Single Modifies a single attribute.
43h - Yes Get_and_Clear Gets then clears the specified attribute (Interface Coun-
ters or Media Counters).
Table 8.12: Services supported
Class ID 0x0F Parameter Object
8
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT revision of object 01
2 Get Max Instance UINT max instance number variable
3 Get Number of instances UINT amount of instances variable
8 Get Parameter Class Descriptor WORD Parameter description 0x03
9 Get Configuration Assembly Instance UINT instance number of the configuration assembly 0
10 Get/Set Native Language USINT Language ID for all character array accesses variable
Table 8.13: Class attributes
Attribute
1 Set/Get Parameter Value data type described in Attr. 5 actual value of parameter Value of parameter from
2 Get Link path size USINT Size of link path variable
3 Get Link path ARRAY: CIP path of parameter’s origin variable
4 Get Descriptor WORD Description of parameter See Standard
5 Get Data Type EPATH Data type code 6 Get Data size USINT Number of bytes in parameter value variable
7 Get Parameter name string SHORT STRING human readable text string representing
8 Get Units string SHORT STRING human readable text string representing
9 Get Help String SHORT STRING human readable text string representing
10 Get min value data type described in Attr. 5 Generic min valid value Parameter Attribute From
11 Get max value data type described in Attr. 5 Generic max valid value Parameter Attribute From
12 Get default value data type described in Attr. 5 Generic parameter’s default value Parameter Attribute From
13 Get Scaling multiplier UINT multiplier for scaling factor 1
14 Get Scaling divisor UINT divisor for scaling factor 1
15 Get Scaling base UINT base for scaling formula 0
16 Get Scaling offset INT offset for scaling formula 0
17 Get Multiplier l in k UINT parameter instance of multiplier source 0
18 Get divisor link UINT parameter instance of divisor source 0
19 Get base link UINT parameter instance of base source 0
20 Get offset link UINT parameter instance of offset source 0
21 Get decimal precision USINT specifies parameter value format variable
Access Rule Name Data Type Description of Attribute Contents
Access
Rule
Name Data type Description Value
drive
Segment type/port BYTE
Segment Address path
Parameter Attribute From
parameter name
parameter unit
short online help.
drive
Parameter Attribute From
drive
Parameter Attribute From
drive
drive
drive
drive
Table 8.14: Instance attributes
56
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 57

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP 8 Appendix
Service Code Supported Service Name Description of Service
Class Instance
0Eh Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single returns contents of specified attribute
01h Yes Yes Get_Attributes_All returns predefined listing of object attributes
10h No Yes Set_Attribute_Single modifies attribute
4Bh No Yes Get_Enum_String reads enumerated strings from parameter instance
Table 8.15: Services supported
Class ID 0x10 Parameter Group Object
Attribute
1 Get Group Name String SHORT_STRING represents group name Name of Group from Drive
2 Get Number of group members UINT amount of parameters in group value of n
3 Get 1st group parameter (000-099) UINT instance number of Parameter Object variable
4 Get 2nd group parameter (100-199) UINT instance number of Parameter Object variable
… Get … UINT … variable
n+2 Get nth group parameter UINT instance number of Parameter Object variable
Table 8.16: Instance Attributes
Class ID 0x64 – 0xC7 Danfoss Objects
The CIP Class ID 100 to 199 (0x64 to 0xC7) gives access to all drive parameters.
100 0-01 - 0-99
101 1-00 – 1-99
102 2-00 – 2-99
103 3-00 – 3-99
104 4-00 – 4-99
105 5-00 – 5-99
106 6-00 – 6-99
107 7-00 – 7-99
108 8-00 – 8-99
109 9-00 – 9-99
110 10-00 – 10-99
111 11-00 – 11-99
……
199 99-00 – 99-99
Access
Rule
Name Data Type Description Contents
Class (decimal)
Danfoss Parameter range
8
The class Instance and Attribute acts in the following way:
- 100 added to the parameter group = the value for the class.
- 100 added to the remaining parameter number = the value for the instance.
- 100 added to the array index of the parameter = the value for the attribute
Examples: (fictitious parameters)
- Parameter 0-01 [index 0] = Class 100; Instance 101; Attribute 100
- Parameter 1-00 [index 0] = Class 101; Instance 100; Attribute 100 - Parameter 2-59[index 0] = Class 102; Instance 159; Attribute 100
- Parameter 5-34[index 3] = Class 105; Instance 134; Attribute 103
- Parameter 6-54 [index 9] = Class 106; Instance 154; Attribute 109
- Parameter 10-01 [index 0] = Class 110; Instance 101; Attribute 100
All values in decimal.
All parameters are accessed in the Active setup (par. 0-10
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Active Set-up
)
57
Page 58

8 Appendix MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
Service Code Supported Service Name Description of Service
Class Instance
0Eh Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single returns contents of specified attribute
10h No Yes Set_Attribute_Single modifies attribute
4Bh No Yes Get_Att_Scattered returns specified parameter values
4Ch No Yes Set_Att_Scattered sets specified parameter values
Table 8.17: Services supported
8
58
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 59

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP Index
Index
A
Abbreviations 6
Ac/dc Drive Object 54
Alarm Word 45
Assembly Instances 23
Assembly Instances 21
Assembly Objects 51
Assumptions 5
B
Background Knowledge 5
C
Cabling 40
Cabling 45
Change-of-state 22, 39
Cip Objects 23
Cip Objects 51
Class 1 Connection 22
Class 3 Connection 23
Coasting Select 8-50 33
Configurable Control Word Ctw 8-14 33
Configurable Status Word Stw 8-13 32
Configuration 5, 17, 21, 31, 32
Configuration 6, 37, 38
Configuration Assembly Instance 56
Configuration Capability 54
Control Site 8-01 31
Control Supervisor Object 52
Control Word Profile 8-10 32
Control Word Source 8-02 31
Control Word Timeout Function 8-04 31
Control Word Timeout Time 8-03 31
Conversion Index 43, 44
D
Data Type 51, 56
Data Type 43, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57
Data Types 44
Dc Backup 6
Dc Brake Select 8-52 34
Devicenet 6
Drive Profile 25, 26
E
Eds 17
Emc Precautions 13
End-of-timeout Function 8-05 32
Ethernet 13, 16, 17, 19, 36, 37, 39, 40, 45
Ethernet 43
Ethernet/ip 5, 17, 18, 19, 22, 38, 51
F
Fc Profile 21, 29, 32
Fc Profile 25, 26
Forward Open 18, 22, 23, 39, 52
H
Hardware 3, 5
Hardware 5
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
59
Page 60

Index MCA 121 EtherNet/IP
I
I/o 6, 21, 22
Identity Object 51
Igmp 19, 40
Igmp Snooping 43
Installation 3, 5, 6
Installation 7
Interface Object 54
Ip Settings 15, 43, 45
Ip Traffic 19
Ip21 / Type 1 6
L
Led 6, 9
Leds 45
Link Object 54, 55
Literature 6
M
Master 46
Master 17
Motor Data Object 52
Multicast 22
Multicast 19, 41
N
Network 5, 11, 13, 19, 24, 36, 38, 39, 40, 45, 54
Network 9, 11, 52, 54
O
Object Model 51
Objects 57
Odva Conformance 6
Odva Profile 52, 53, 54
Overview 7
P
Parameter Group Object 57
Parameter Object 56, 57
Parameters 4, 15, 16, 57
Parameters 16, 17, 23
Preset Reference Select 8-56 35
Profibus 6
Q
Quick Stop Select 8-51 34
R
Reference 23, 25, 26, 27, 28
Reference 6, 25, 28, 29, 30, 38, 48, 54
References 4
Reset Control Word Timeout 8-06 32
Reversing Select 8-54 34
S
Safety 3
Set-up Select 8-55 35
Spanning Tree 6
Spanning Tree 11, 19
Start Select 8-53 34
60
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 61

MCA 121 EtherNet/IP Index
T
Topology 10, 12, 19
Topology 10
Troubleshooting 45
U
Unconnected Messages 23
W
Warning Word 47, 48
Warning Word 45
MG.90.J2.02 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
61
 Loading...
Loading...