Page 1

Data sheet
Filter solutions for
Danfoss high-pressure pumps and
energy recovery devices
hpp.danfoss.com
Page 2
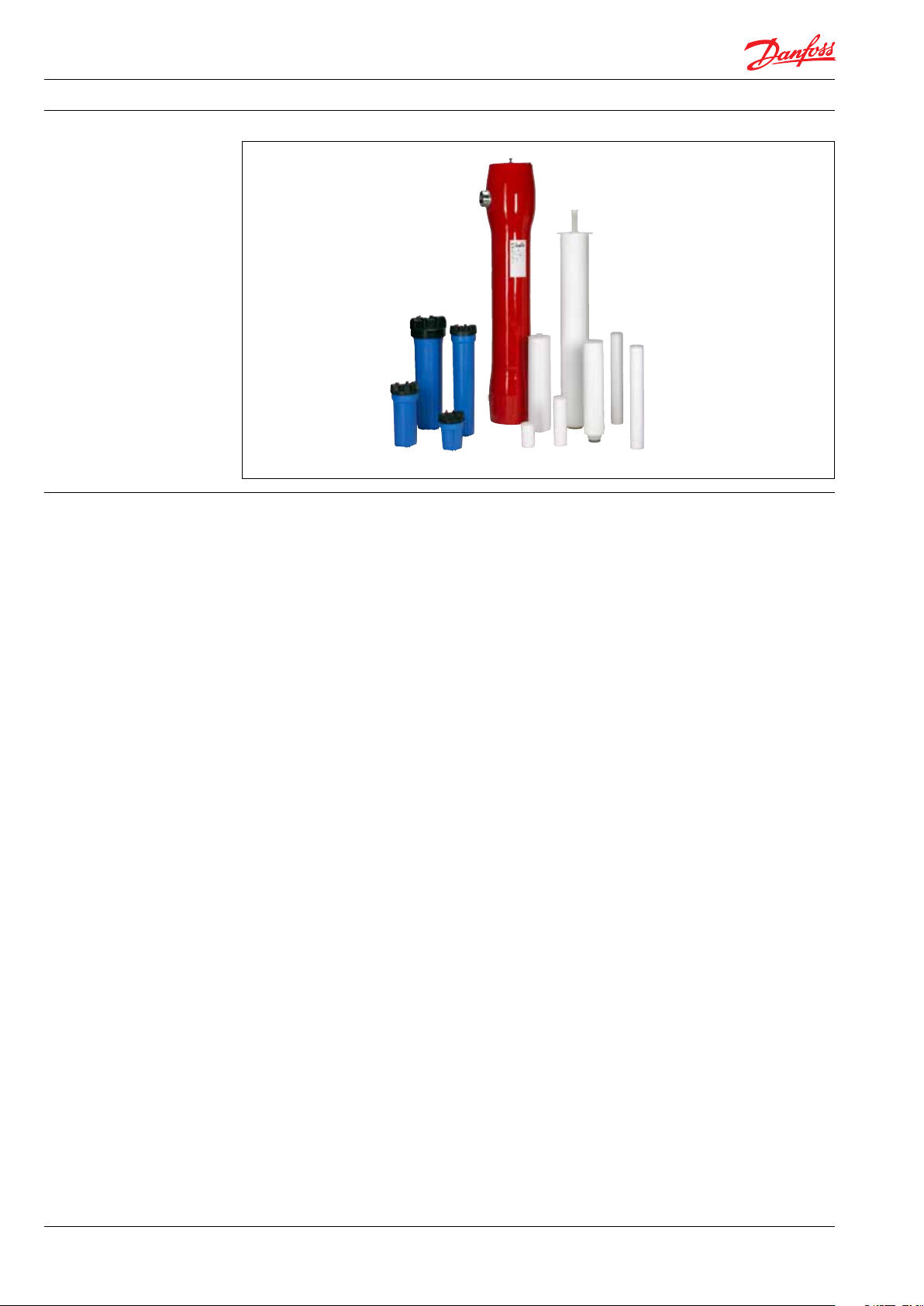
Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
1. Introduction
1.1 Cartridge filters
Cartridge filters are widely used in industrial and
domestic applications for removal of suspended
solids in water. The variety of cartridges available
and the confusing methods of ratings, however,
make selection of cartridges difficult for consumers. It becomes important for users,
therefore, to understand cartridge filters, how
they work, and how manufacturers rate them.
1.2 Filtration
Filtration is a process of removing unwanted
solids from fluids by passing the fluid through a
form of sieving material that retains the solids,
but allows the fluid to pass through. Filtration
efficiency is, therefore, the percentage of solid
retention by the sieve. It is this “sieve” that we
refer to as the filter medium, or simply the filter.
A contaminant is generally referred to as the
material that is to be removed from the fluid, and
the clean fluid is called the
filtrate. In today’s market, manufacturers use
three types of ratings to evaluate filters: nominal
rating, absolute rating and beta ratio.
1.3 Nominal filter rating
A nominal filter rating is an arbitrary value
determined by the filter manufacturer, based
upon removal of some percentage of all particles
of a given size or larger.
- The rating is typical based on a weight percent
(etc. 60 -95%)
- The 5-40% that pass through are NOT defined
by the manufacturer (normally much larger
particles pass through).
- The rating is based on a weight analysis test.
- There is a high risk of channelling when a filter
medium has some oversized pores or a wide
pore-sized distribution.
- There is a high risk of bypass when
cartridge-to-housing seal is ineffective.
1.4 Absolute filter rating
The absolute rating or cut-off point of a filter
refers to the diameter of the largest hard
spherical particle, normally expressed in
micrometres (µm), which will pass through the
filter under specified test conditions.
- The filter is tested under a specific
international well known test method (modified OSU-F2 single-pass filter test system).
- The rating is based on a particle measuring
test.
- The filter is reproducible.
- Higher ∆P does not result in particle
unloading.
- The filter can withstand flow pulsations as well
as viscosity and temperature changes.
- There is no risk of channelling due to the high
quality of the filter media.
- Absolute filtration means that the fluid is
filtered both horizontally and vertically. In
comparison, an inferior nominal type of filter
will allow particles which are more than 10
µ in length to pass the filter, as it only filters
the fluid according to the diameter of the
particles.
- It is NOT possible to reproduce the filter.
- Particle unloading is rising when the ∆P across
the filter increases
2
AI317041322125en-000201 | 03.2021
Page 3
Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
2. Requirements
2.1 Filtration requirement
To achive warrenty and assure the service intervals stated from Danfoss, the PAH, PAHT, APP
pumps require water with no particles larger than
10 micron (10 µ). Thus a 10 µ absolute filter with a
Beta value > 5000 must be used.
- 10 µ means that particles of 10 µ or larger in
size will be caught by the filter.
β-value of filter Filter efficiency
2 50.00% 50,000
4 75.00% 25,000
10 90.00% 10,000
20 95.00% 5,000
40 97. 50 % 2,500
100 99.00% 1,000
200 99.50% 500
-
The Beta value > 5000 refers to the efficiency
of the filter. A filter with a Beta value of > 5000
catches 99.98% of the particles being 10 µ or
larger. This means if there are 100,000 particles
in the fluid (10 µ or larger), only 20 of them
would pass through that filter. Other types of
filters on the market have a Beta value > 10
(90% efficiency), and these filters would allow
10,000 of the 100,000 particles to pass through
the filter.
Number of particles downstream for each
100,000 particles upstream
500 99.80% 200
1,000 99.90% 100
2,000 99.95% 50
5,000 99.98% 20
10,000 99.99% 10
2.2 Filter types
Pleated polypropylene filter elements use the
very latest gradient density micro-fibre media
technology to provide a combination of excellent
absolute micron ratings, high flow rates, and high
dirt-holding capacity.
2.3 Features
- The absolute particle retention provides
excellent protection of the pump and the rest
of the system.
- Compatibility with a broad range of process
chemicals allows use in most applications.
- High flow rate and long service life ensure
minimum downtime of the system.
- High dirt-holding capacity.
- Filter element is easily exchanged.
2.4 Applications
The Danfoss filters can be used in a wide range of
demanding applications such as:
- General water filtration
- RO/DI water filtration
- We recommend CIP cycles in the range of 3-10
PH
AI317041322125en-000201 | 03.2021
3
Page 4
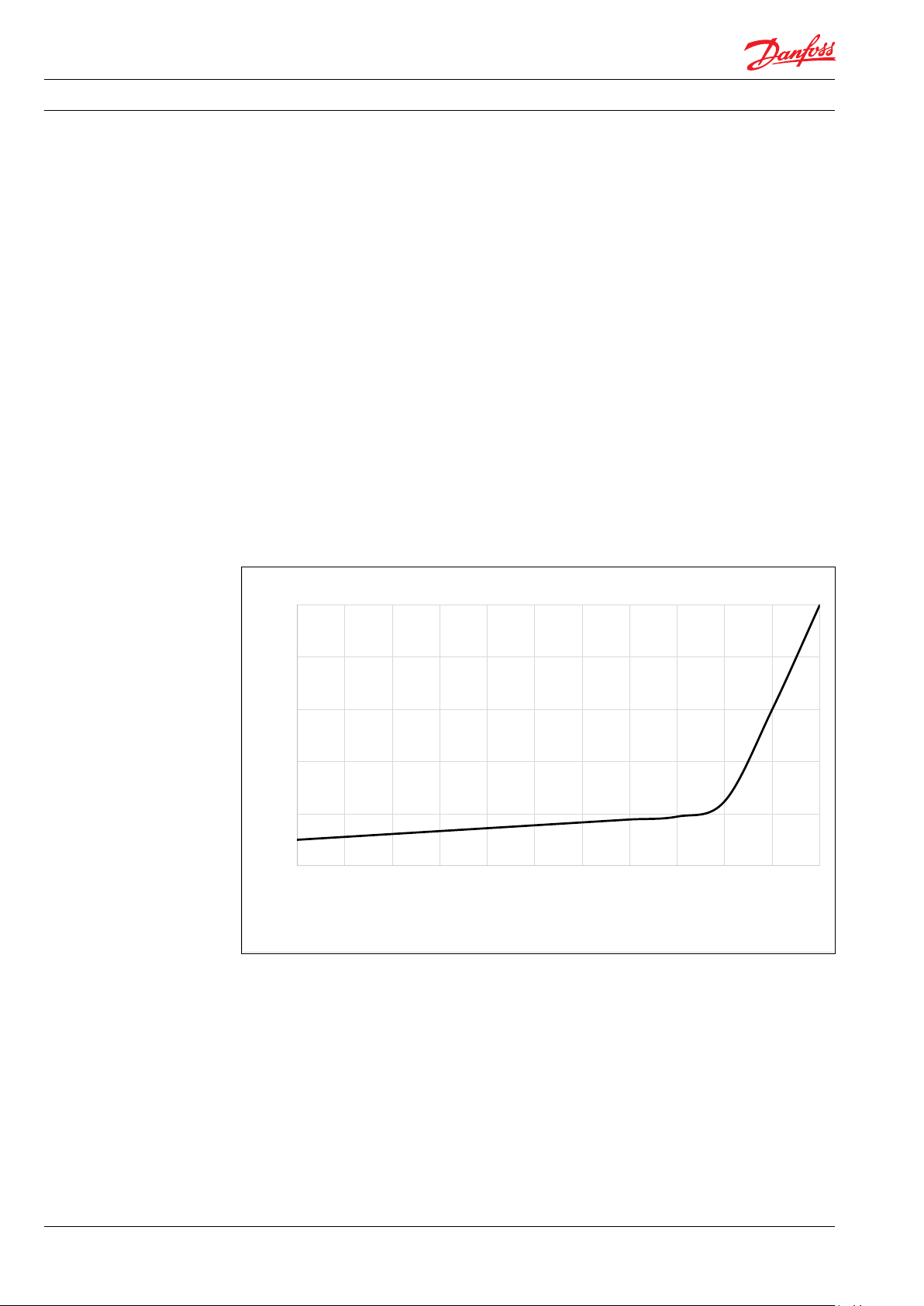
Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
0
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Pressure drop Bar
Time [%]
Typically filter life
Cartridge Pressure Drop
2.5 Right filter choice
There are 2 factors to consider in order to choose
the right filter:
a) The flow through the filter
b) Amount of dirt in the fluid (E.g. SDI).
If the fluid is relatively clean (low SDI), the filter
choice can be based on the pump size as this will
indicate the flow through the filter.
If the fluid is relatively dirty with small particles, a
larger filter size should be chosen to increase the
dirt-holding capacity. For instance, for a flow of
60 l/min fluid containing many small particles a
filter for a flow up to 170 l/min should be chosen.
If the fluid is relatively dirty with larger particles,
a cheaper and less efficient pre-filter should be
placed in front of the main filter. This will ensure
a long life of the more expensive main filter, as
most of the larger dirt particles will be caught in
the cheaper pre-filter.
The prefilter may be of the type ”Nominal filter”.
4
AI317041322125en-000201 | 03.2021
Page 5

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
3. Technical data
3.1 Absolute filters
The Danfoss filter product range includes different types of main filter elements, all fulfilling the
minimum requirement of 10 µ absolute with a Beta value > 5000.
One filter element end has an O-ring seal, and the other end has a closed cap, which has a different
design depending on the specific filter type.
Type 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Type 6 Type 7
Single O-ring located Two O-rings located externally Two O-rings located externally
inside element, on element on element
other end flat closed other end with spear
Filter element Typ e 1 Typ e 2 Typ e 3
Element length
Filtration level
(Beta > 5000)
127 mm
(5”)
10 µ abs 10 µ abs 5 µ abs
254 mm
(10”)
508 mm
(20”)
Max flow (l/min) 15 30 60
3
Max flow (m
/h) 0.9 1.8 3.6
Max flow (gpm) 4 7.9 15.6
Element inner diameter
Element outer diameter
Effective surface
Max differential pressure
at 24 °C (75 °F)
Max operating
temperature
Materials
Element
End caps
Seals
27 mm
(1.06”)
70 mm
(2.75” )
2
0.28 m
(3 sq.ft.)
4 barg
(58 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
Buna-N Buna-N Buna-N
27 mm
(1.06”)
70 mm
(2.75” )
0.55 m
(6 sq.ft.)
4 barg
(58 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
27 mm
(1.06”)
70 mm
(2.75” )
2
1.1 m
(12 sq.ft.)
4 barg
(58 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
2
Net weight
Max. differential pressure before
replacement of filter
0.21 kg
(0.46 lb)
2 barg
(29 psig)
0.27 kg
(0.6 lb)
2 barg
(29 psig)
0.47 kg
(1.0 lb)
2 barg
(29 psig)
Code number 180Z0037 180X5225 180Z0 019
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
5
Page 6

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
Filter element Typ e 4 Type 5 Type 6 Ty pe 7
Element length
Filtration level
(Beta > 5000)
508 mm
(20”)
10 µ abs 10 µ abs 10 µ abs 10 µ abs
508 mm
(20”)
508 mm
(20”)
1020 mm
(40” )
Max flow (l/min) 60 170 170 1000
Max flow (m3/h) 3.6 10.2 10.2 60
Max flow (gpm) 15.6 44.9 44.9 264
Element inner diameter
Element outer diameter
Effective surface
Max differential pressure
at 24 °C (75 °F)
Max operating
temperature
Materials
Element
End caps
Seals
27 mm
(1.06”)
70 mm
(2.75” )
2
1.1 m
(12 sq.ft.)
4 barg
(58 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
Buna-N Buna-N Buna-N Silicone
46 mm
(1.8”)
115 m m
(4.5” )
2.45 m
(26 sq.ft.)
3 barg
(43.5psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
46 mm
(1.8”)
102 mm
(4”)
2
1.8 m²
(19 sq. ft.)
3 barg
(43.5 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
65 mm
(2.56”)
153 mm
(6”)
10 m²
(107.6 sq.ft.)
4 barg
(58 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
1)
1)
1)
Net weight
Max. differential pressure before
replacement of filter
0.48 kg
(1.1 l b)
2 barg
(29 psig)
1.35 kg
(3.0 lb)
2 barg
(29 psig)
0.97 kg
(2.1 l b)
2 barg
(29 psig)
4.0 kg
(8.8 lb)
1.5 barg
(22 psig)
Code number 180Z0006 180Z0285 180Z0083 180Z0653
1
) Recommended max. flow if the fluid is relatively clean and pre-filtered with a hig quality
filter, rated less than 5 µ and efficiency of min.
95%. If fluid is not relatively clean a max. flow
of 36 m³/h is recommended.
3.2 Replacement of filter element
At max. differential pressure, the filter element has reached its dirt capacity.
6
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
Page 7

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
3.3 Housings
Housing
5”
Blue
10”
Blue
20”
Blue
20”
Big blue
40”
Red
Max flow (l/min) 15 30 60 170 1000
3
Max flow (m
/h) 0.9 1.8 3.6 10.2 60
Max. flow (gpm) 4 7.9 15.6 44.9 264
Housing length
Housing diameter
Max pressure at
45 °C (113 °F)
Max operating
temperature
184 mm
(7.24” )
115 m m
(4.52”)
8.6 barg
125 (psig)
45 °C
(113 °F )
311 mm
(12.24” )
130 mm
(5 .11” )
8.6 barg
125 (psig)
45 °C
(113 °F )
568 mm
(22.36”)
130 mm
(5 .11” )
8.6 barg
125 (psig)
45 °C
(113 °F )
600 mm
(23.62”)
183 m m
(7.20 ”)
6.2 barg
(90 psig)
45 °C
(113 °F )
138 4 mm
(54.48”)
270 mm
(10.62”)
16 barg
(232 psig)
60 °C
(140 °F
Vent ¼” BSP
Inlet ½” BSP ¾” BSP ¾” BSP 1½” BSP
3” Vic. Cut
groove
Connections
Outlet ½” BSP ¾” BSP ¾” BSP 1½” BSP
Drain
3” Vic. Cut
groove
1” Vic. Cut
groove
Volume 37 l.
GRP (Glass
Housing Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
reinforced
polypropylene)
Materials
Accessories
recommended
Net weight
Caps
Reinforced
polypropylene
O-ring Buna-N Buna-N Buna-N Buna-N
Victaulic
fittings
0.7 kg
(1.54 lb)
Reinforced
polypropylene
Filter
spanner
(Code no.
180N0785)
1.4 kg
(3.1 lb)
Reinforced
polypropylene
Filter
spanner
(Code no.
180N0785)
2.1 kg
(4.6 lb)
Reinforced
polypropylene
Filter
spanner
(Code no.
180 N1438)
4.1 kg
(9 lb)
Polypropylene
Silicone
PTFE
Acetal
For vertical
mount: Legs
for housing
(180Z0652)
46 kg
(101 lb)
Code number 180Z0281 180X5224 180Z0213 180Z0082 180Z0651
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
7
Page 8

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
3.4 Pre-filtration (nominal filters)
Danfoss offers two different pre-filtration solutions that can be used in addition to the main-
Polypropylene fibre melt blown design with poly
core (90% efficiency) provides optimum sediment
filtering capacity.
filters (and NOT instead of the main filters).
Typ e A Type B
Max flow (l/min) 30 85
Max flow (m³/h) 1.8 5.1
Max flow (gpm) 7.9 22.5
Filtration level
Element length
Element outer diameter
Element inner diameter
Max differential pressure
at 24 °C (75 °F)
Max operating
temperature
Element Polypropylene Polypropylene
3 µ Nominal
Graded density structure
508 mm
(20”)
64 mm
(2.5”)
26 mm
(1.02”)
3.4 barg
(50 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
3 µ Nominal
Graded density structure
508 mm
(20”)
116 mm
(4.5” )
28 mm
(1.10”)
3.4 barg
(50 psig)
50 °C
(122 ° F)
Materials
Code number 180Z0396 180Z0081
Core Polypropylene Polypropylene
Seal None None
3.5 Right pre-filter choice
The 4.5” pre-filter (180Z0081) with a large
graded density structure is a better pre-filter
but more expensive.
If the flow demand is very low, a less expensive
pre-filter (180Z0396) is a good alternative.
3.6 Replacement of filter element
At a differential pressure of 1.5 barg (22 psig)
filter element has reached its dirt capacity.
Typ e A
3.7 Cross reference tabel
Housing
Element
180Z0213
(20” blue housing)
180Z0082
(20” big blue housing)
180Z0396 180Z0081
X
X
Typ e B
NOTE
Pre-filter elements and filter housings are
ordered separately.
8
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
Page 9

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
4. Dimensions
F
10”
/64")
E
20”
Blue
56 mm
(2 1/5”)
133 mm
(5 1/4")
58 mm
(2 1/4”)
ø5,7
15
/64")
(
568 mm
(22 3/8")
A
D
C
B
5”
Blue
A
B
C
D
E
39 mm
1
/2")
(1
120 mm
3
/4")
(4
32 mm
1
/4")
(1
ø4,2
11
/64")
(
184 mm
1
/4")
(7
Blue
56 mm
(2 1/5")
133 mm
(5 1/4")
58 mm
(2 1/4")
ø5,7
15
(
311 mm
(12 ¼")
F ½" BSP ¾" BSP ¾" BSP 1½" BSP
20”
Big blue
77 mm
(3")
185 m m
(7 ¼")
77 mm
(3")
ø7, 7
5
/16")
(
600 mm
(23 5/8")
Code number 180Z0281 180X5224 180Z0213 180Z0082
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
9
Page 10

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
4.1 Vertical mount
4.2 Horizontal mount
10
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
Page 11

Data sheet | Filter solutions for Danfoss high-pressure pumps
5. Accessories
6. Cross reference table
7. Pressure drop total
Element + housing
Filter spanner
Code no. 180N1488 180N0785 18 0N0785 18 0N1438
Element
Housing
180Z0281
(5” blue housing)
180X5224
(10” blue housing)
180Z0213
(20” blue housing)
180Z0082
(20” big blue housing)
180Z0651
(40” red housing)
Element /
Housing
180Z0037 (Type 1)
180Z0281
(5” blue housing)
180X5225 (Type 2)
180X5224
(10” blue housing)
180Z0019 (Type 3)
180Z0213
(20” blue housing)
180Z0006 (Type 4)
180Z0213
(20” blue housing)
180Z0285 (Type 5)
180Z0082
(20” big blue housing)
180Z0653 (Type 7)
180Z0651
(40” red housing”
5”
Blue
180Z0037
(Type 1)
Flow
180X5225
(Typ e 2)
X
15 l/m in 30 l/min 60 l/min 150 l/m in 666 l/min 1000 l/min
0.250 barg
(3.6 psig)
0.105 barg
(1.5 psig)
X
0.190 barg
(2.8 psig)
0.125 barg
(1.8 psig)
0.125 barg
(1.8 psig)
10”
Blue
180Z0 019
(Typ e 3)
X X
180Z0006
(Typ e 4)
0.340 barg
(4.9 psig)
0.340 barg
(4.9 psig)
0.130 barg
(1.9 psig)
20”
Blue
180Z0285
(Typ e 5)
X
0.390 barg
(5.7 psig)
180Z0083
(Typ e 6)
0.128 barg
(1.8 psig)
20”
Big blue
180Z0653
(Typ e 7)
0.230 barg
(3.6 psig)
X
AI3170 41322125en-000201 | 03.2021
11
Page 12

Danfoss A/S
Hogh Pressure Pumps
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg
Denmark
© Danfoss | DCS (im) | 2021.03
AI317041322125en-000201 | 12
 Loading...
Loading...