Dallas Semiconductor DS2405Z-T-R, DS2405Z, DS2405P-T-R, DS2405P, DS2405-T-R Datasheet
...
1 of 15 102299
FEATURES
§ Open drain PIO pin is controlled by
matching 64-bit, laser-engraved registration
number associated with each device
§ Logic level of open drain output can be
determined over 1-Wire bus for closed-loop
control
§ PIO pin sink capability is greater than 4 mA
at 0.4V
§ Multiple DS2405’s can be identified on a
common 1-Wire bus and be turned on or off
independent of other devices on the bus
§ Unique, factory-lasered and tested 64-bit
registration number (8-bit family code +48bit serial number +8-bit CRC tester) assures
absolute identity because no two parts are
alike
§ Built-in multidrop controller ensures
compatibility with other MicroLAN products
§ Reduces control, address, data, and power to
a single data pin
§ Directly connects to a single port pin of a
microprocessor and communicates at up to
16.3 kbits/s
§ 8-bit family code specifies DS2405
communications requirements to reader
§ 8-bit cyclic redundancy check ensures error-
free selection
§ Zero standby power required
§ Low cost TO-92, SOT-223, or 6-pin TSOC
surface mount package
§ 1-Wire communication operates over a wide
voltage range of 2.8V to 6.0V from -40°C to
+85°C
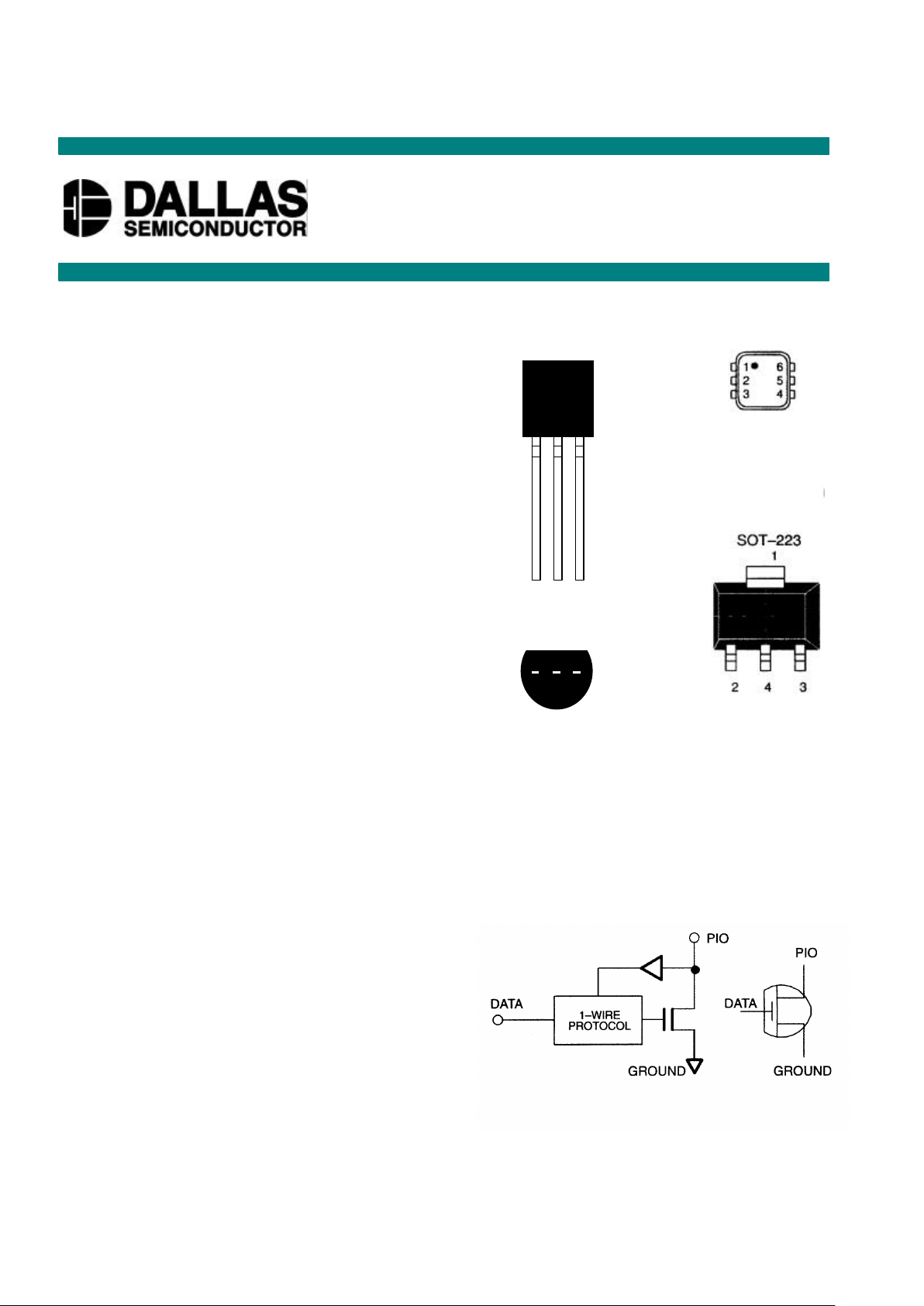
PIN ASSIGNMENT
TSOC PACKAGE
PIN DESCRIPTION TSOC
Pin 1 - Ground Pin 1 - Ground
Pin 2 - Data Pin 2 - Data
Pin 3 - PIO Pin 3 - PIO
Pin 4 - Ground Pin 4-6 -No Connect
DS2405
Addressable Switch
www.dalsemi.com
TOP VIEW
TOP VIEW
3.7 X 4.0 X 1.5
GND
DATA
PIO
NC
NC
NC
BOTTOM VIEW
See Mech.
Drawings Section
TO-92
DS2405
2
3
1 2 3

DS2405
2 of 15 102299
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS2405 TO-92 package
DS2405Z 4-pin SOT-223 package
DS2405P 6-pin TSOC package
DS2405T Tape & Reel version of DS2405
DS2405Y Tape & Reel version of DS2405Z
DS2405V Tape & Reel version of DS2405P
DESCRIPTION
The DS2405 Addressable Switch is an open drain N-channel transistor that can be turned on or off by
matching the 64-bit factory-lasered registration number within each part. The 64-bit number consists of
an 8-bit family code, a unique 48-bit serial number, and an 8-bit cyclic redundancy check.
Communication with the DS2405 follows the standard Dallas Semiconductor 1-Wire protocol and can be
accomplished with a single port pin of a microcontroller. Multiple DS2405 devices can reside on a
common 1-Wire bus creating a MicroLAN. The network controller circuitry is embedded within the chip
including a search algorithm to determine the identity of each DS2405 on the network. The open drain
output (PIO pin) for each DS2405 on the MicroLan can be independently toggled on or off whether there
is one or many devices sharing the same 1-Wire bus. The logic level of the PIO pin for each device on the
MicroLan can also be individually sensed and reported to the bus master.
OVERVIEW
The DS2405 Addressable Switch provides a means for assigning an electronically readable identification
to a particular node or location with additional control capability provided by an open drain N-channel
MOSFET that can be remotely switched and sensed via communication over the 1-Wire bus. The DS2405
contains a factory-lasered registration number that includes a unique 48-bit serial number, an 8-bit CRC,
and an 8-bit family code (05h). The 64-bit ROM portion of the DS2405 not only creates an absolutely
unique electronic identification for the device itself but also is a means to locate and change or obtain the
state of the switch that is associated with the 64-bit ROM. The structure of the 64-bit ROM is shown in
Figure 1. The device derives its power entirely from the 1-Wire bus by storing energy on an internal
capacitor during periods of time when the signal line is high and continues to operate off of this “parasite”
power source during the low times of the 1-Wire line until it returns high to replenish the parasite
(capacitor) supply. The DS2405 uses the standard Dallas Semiconductor 1-Wire protocol for data
transfers, with all data being read and written least significant bit first. Communication to and from the
DS2405 requires a single bidirectional line that is typically the port pin of the microcontroller. The 1Wire bus master (microcontroller) must first issue one of five ROM function commands: 1) Read ROM,
2) Match ROM, 3) Search ROM, 4) Skip ROM, and 5) Active-Only Search ROM. These commands
operate on the 64-bit lasered ROM portion of each device and can singulate a specific device if many are
present on the 1-Wire line as well as indicate to the bus how many and what type of each device is
present. The protocol required for these ROM function commands is described in Figure 4. After a ROM
function command is successfully executed, the open drain output can be toggled or its current status
determined via the 1-Wire bus.
1-WIRE BUS SYSTEM
The 1-Wire bus is a system which has a single bus master and one or more slaves. In all instances, the
DS2405 is a slave device. The bus master is typically a microcontroller. The discussion of this bus system
is broken down into three topics: hardware configuration, transaction sequence, and 1-Wire signaling
(signal type and timing). For a more detailed protocol description, refer to Chapter 4 of the Book of
DS19xx iButton Standards.
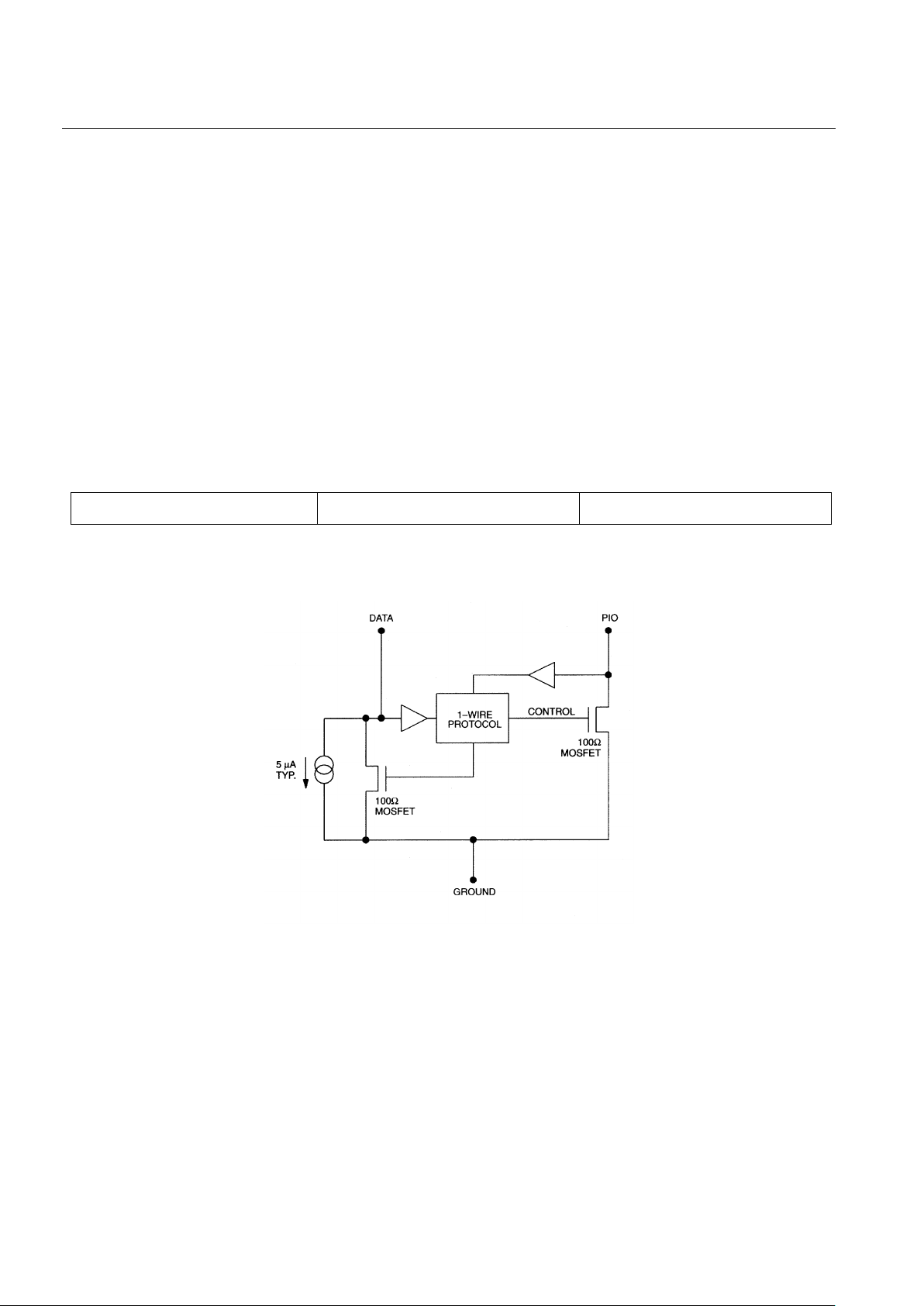
DS2405
3 of 15 102299
Hardware Configuration
The 1-Wire bus has only a single line by definition; it is important that each device on the bus be able to
drive it at the appropriate time. To facilitate this, each device attached to the 1-Wire bus must have an
open drain connection or 3-state outputs. The DS2405 is an open drain part with an internal circuit
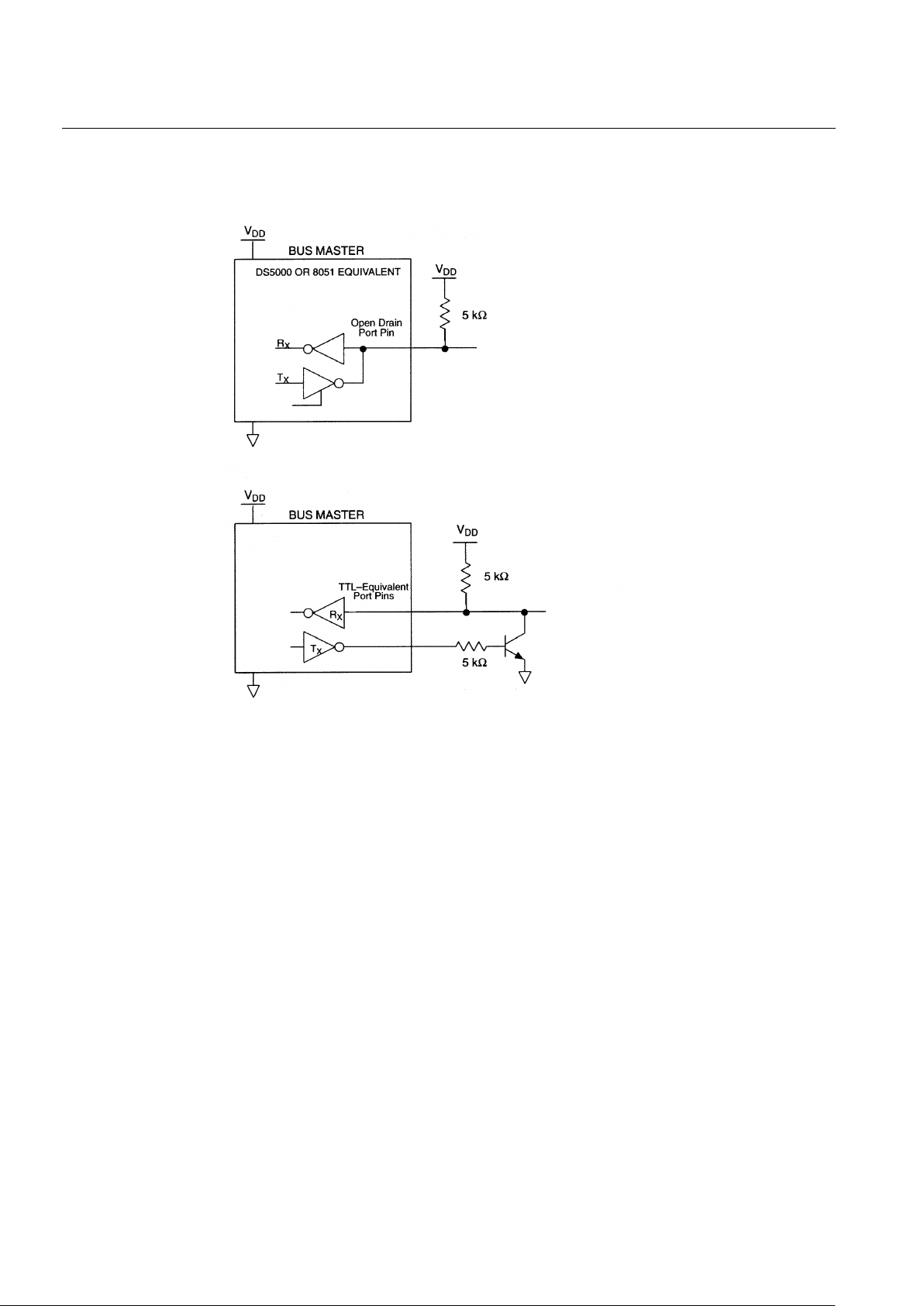
equivalent to that shown in Figure 2. The bus master can be the same equivalent circuit. If a bidirectional
pin is not available, separate output and input pins can be tied together. The bus master requires a pullup
resistor at the master end of the bus, with the bus master circuit equivalent to the one shown in Figure 3.
The value of the pullup resistor should be approximately 5 kΩ for short line lengths. A multidrop bus
consists of a 1-Wire bus with multiple slaves attached. The 1-Wire bus has a maximum data rate of 16.3k
bits per second.
The idle state for the 1-Wire bus is high. If, for any reason, a transaction needs to be suspended, the bus
MUST be left in the idle state if the transaction is to resume. If this does not occur and the bus is left low
for more than 120 µs, one or more of the devices on the bus may be reset. In addition, the state of the PIO
pin for one or more of the DS2405s on the bus may return to its default (off) condition.
DS2405 MEMORY MAP Figure 1
8-Bit CRC Code 48-Bit Serial Number 8-Bit Family Code (05h)
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB LSB
DS2405 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT Figure 2
DS2405
4 of 15 102299
BUS MASTER CIRCUIT Figure 3
A) Open Drain
TRANSACTION SEQUENCE
The sequence for accessing the DS2405 via the 1-Wire port is as follows:
§ Initialization
§ ROM Function Command
§ Read Data
INITIALIZATION
All transactions on the 1-Wire bus begin with an initialization sequence. The initialization sequence
consists of a Reset Pulse transmitted by the bus master followed by a Presence Pulse(s) transmitted by the
slave(s).
The Presence Pulse lets the bus master know that at least one DS2405 is on the bus and is ready to
operate. For more details, see the “1-Wire Signaling” section.
B) Standard TTL
To data connection
of DS2405
To data connection
of DS2405

DS2405
5 of 15 102299
ROM FUNCTION COMMANDS
Once the bus master has detected a presence, it can issue one of five ROM function commands. All ROM
function commands are 8 bits long. A list of these commands follows (refer to flowchart in Figure 4):
Read ROM [33h]
This command allows the bus master to read the DS2405’s 8-bit family code, unique 48-bit serial
number, and 8-bit CRC. This command can be used only if there is a single DS2405 on the bus. If more
than one slave is present on the bus, a data collision will occur when all slaves try to transmit at the same
time (open drain will produce a wired-AND result).
Match ROM [55h]
The Match ROM command, followed by a 64-bit ROM sequence, allows the bus master to address a
specific device on a multidrop bus. All devices that do not match the 64-bit ROM sequence will wait for a
Reset Pulse. The DS2405 that exactly matches the 64-bit ROM sequence will toggle the state of its PIO
pin after the 64th bit of the match is entered. If the open drain N-channel device was off, it will be turned
on and vice versa. After the last bit of the ROM sequence is received from the bus master and the PIO pin
of the selected DS2405 has toggled, additional read time slots issued by the bus master will cause the
DS2405 to output the logic state of its PIO pin onto the 1-Wire bus. If the pulldown is on and the PIO pin
is a logical 0, the DS2405 will respond with read-0 time slots. If the pulldown is off and the PIO pin is a
logical 1 (external pullup is required), the DS2405 will respond with read-1 time slot. Each additional
read time slot issued by the bus master will continue to indicate the state of the PIO pin until a Reset
Pulse is received from the bus master.
Search ROM [F0h]
When a system is initially interrogated, the bus master may not know the number of devices on the 1Wire bus or their 64-bit ROM codes. The Search ROM command allows the bus master to use a process
of elimination to identify the 64-bit ROM codes of all slave devices on the bus. This process of
elimination involves repeated application of a simple three-step procedure where the bus master starts by
reading a bit position in the 64-bit ROM, followed by reading the complement of that bit position, and
finally writing to all the devices still involved in the search the desired logic value for that bit position. An
example is shown below and a flowchart for the search algorithm can be found in the “Book of DS19xx
iButton Standards.”
Four devices are connected to the 1-Wire bus. Their binary ROM contents are:
device 1: xxxxxx10101100
device 2: xxxxxx01010101
device 3: xxxxxx10101111
device 4: xxxxxx10001000
The x’s represent the higher remaining bits. Shown are the lowest 8 bits of the ROM contents. The least
significant bit is to the right in this representation. The search process runs as follows:
1. The master begins the initialization sequence by issuing a Reset Pulse. The devices respond by issuing
Presence Pulses.
2. The master will then issue the Search ROM command on the 1-Wire bus.
 Loading...
Loading...