Dallas Semiconductor DS2154LN, DS2154L Datasheet
r
www.dalsemi.com
100
DS2154
Enhanced E1 Single Chip Transcei ve
FEATURES
Complete E1(CEPT) PCM-30/ISDN-PRI
transceiver functionality
Onboard long- and short-haul line interface for
clock/data recovery and waveshaping
32-bit or 128-bit crystal-less jitter attenuator
Generates line build outs for both 120Ω=and
75Ω=lines
Frames to FAS, CAS, and CRC4 formats
Dual onboard two-frame elastic store slip buffers
that can connect to asynchronous backplanes up to
8.192 MHz
8-bit parallel control port that can be used directly
on either multiplexed or non-multiplexed buses
Extracts and inserts CAS signaling
Detects and generates Remote and AIS alarms
Programmable output clocks for Fractional E1,
H0, and H12 applications
Fully independent transmit and receive
functionality
Full access to both Si and Sa bits aligned with
CRC multiframe
Four separate loopbacks for testing functions
Large counters for bipolar and code violations,
CRC4 codeword errors, FAS errors, and E bits
Pin compatible with DS2152 T1 Enhanced Single-
Chip Transceiver
5V supply; low power CMOS
100-pin 14mm
2
body LQFP package
PACKAGE OUTLINE
1
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS2154L (0°C to 70°C)
DS2154LN (-40°C to +85°C)
DESCRIPTION
The DS2154 Enhanced Single-Chip Transceiver (ESCT) contains all of the necessary functions for
connection to E1 lines. The device is an upward compatible version of the DS2153 Single-Chip
Transceiver. The onboard clock/data recovery circuitry coverts the AMI/HDB3 E1 waveforms to a NRZ
serial stream. The DS2154 automatically adjusts to E1 22AWG (0.6 mm) twisted-pair cables from 0 to
over 2 km in length. The device can generate the necessary G.703 waveshapes for both 75-ohm coax and
120-ohm twisted cables. The onboard jitter attenuator (selectable to either 32 bits or 128 bits) can be
placed in either the transmit or receive data paths. The framer locates the frame and multiframe
boundaries and monitors the data stream for alarms. It is also used for extracting and inserting si gnaling
data, Si, and Sa bit information. The device contains a set of internal registers which the user c an access
to control the operation of the unit. Quick access via the parallel control port allows a single controller to
handle many E1 lines. The device fully meets all of the latest E1 specifications including ITU G.703,
G.704, G.706, G.823, G.932, and I.431 as well as ETS 300 011, 300 233, 300 166, TBR 12 and TBR 13.
1 of 87 112099

DS2154
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.0 INTRODUCTION.............................................................................................................4
New Features................................................................................................................................... 4
Block Diagram................................................................................................................................ 5
Pin List............................................................................................................................................ 7
Pin Description.............................................................................................................................. 10
Register Map................................................................................................................................. 15
2.0 PARALLEL PORT ........................................................................................................20
3.0 CONTROL, ID, AND TEST REGISTERS......................................................................20
SYNC/RESYNC Criteria.............................................................................................................. 22
Framers Loopback......................................................................................................................... 27
Automatic Alarm Generation........................................................................................................ 28
Power-up Sequence....................................................................................................................... 30
Remote Loopback......................................................................................................................... 31
Local Loopback............................................................................................................................. 31
4.0 STATUS AND INFORMATION REGISTERS................................................................32
CRC 4 SYNC Counter.................................................................................................................. 35
Alarm Criteria............................................................................................................................... 36
5.0 ERROR COUNT REGISTERS......................................................................................40
BPV or Code Violation Counter...................................................................................................40
CRC4 Error Counter ..................................................................................................................... 41
E-bit Counter................................................................................................................................. 41
FAS Error Counter........................................................................................................................ 42
6.0 DSO MONITORING FUNCTION...................................................................................43
7.0 SIGNALING OPERATION............................................................................................46
Processor Based Signaling............................................................................................................ 46
Hardware Based Signaling............................................................................................................ 49
8.0 PER-CHANNEL CODE GENERATION........................................................................51
Transmit Side Code Generation.................................................................................................... 51
Receive Side Code Generation ..................................................................................................... 53
9.0 CLOCK BLOCKING REGISTERS................................................................................54
10.0 ELASTIC STORES OPERATION.................................................................................56
11.0 ADDITIONAL (Sa) AND INTERNATIONAL (Si) BIT OPERATION..............................57
Hardware Scheme ......................................................................................................................... 57
Internal Register Scheme Based on Double-Frame...................................................................... 57
Internal Register Scheme Based on CRC4 Multiframe................................................................ 60
2 of 87

DS2154
12.0 LINE INTERFACE FUNCTIONS...................................................................................62
Receive Clock and Data Recovery................................................................................................ 62
Transmit Waveshaping and Line Driving ..................................................................................... 63
Jitter Attenuator............................................................................................................................. 64
13.0 TIMING DIAGRAMS......................................................................................................67
Synchronization Flowchart........................................................................................................... 72
Transmit Data Flow Diagram ....................................................................................................... 73
14.0 CHARACTERISTICS....................................................................................................74
Absolute Maximum Rating........................................................................................................... 74
DC Parameters ..............................................................................................................................74
AC Parameters ..............................................................................................................................75
Timing........................................................................................................................................... 77
Package Description...................................................................................................................... 85
3 of 87
DS2154
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The DS2154 is a super-set version of the popular DS2153 E1 Single-Chip Transceiver offerin g the new
features listed below. All of the original features of the DS2153 have been retained and software created
for the original devices is transferable into the DS2154.
NEW FEATURES SECTION
Option for non-multiplexed bus operation
Crystal-less jitter attenuation
Additional hardware signaling capability including:
Receive signaling reinsertion to a backplane multiframe sync
Availability of signaling in a separate PCM data stream
Signaling freezing
Interrupt generated on change of signaling data
Improved receive sensitivity: 0 dB to -43 dB
Per-channel code insertion in both transmit and receive paths
Expanded access to Sa and Si bits
RCL, RLOS, RRA, and RAIS alarms now interrupt on change of state
8.192 MHz clock synthesizer
Per-channel loopback
Addition of hardware pins to indicate carrier loss and signaling freeze
Line interface function can be completely decoupled from the framer/formatter to
allow:
Interface to optical, HDSL, and other NRZ interfaces
“tap” the transmit and receive bipolar data streams for monitoring purposes
Be able corrupt data and insert framing errors, CRC errors, etc.
Transmit and receive elastic stores now have independent backplane clocks
Ability to monitor one DS0 channel in both the transmit and receive paths
Access to the data streams in between the framer/formatter and the elastic stores
AIS generation in the line interface that is independent of loopbacks
Transmit current limiter to meet the 50 mA short circuit requirement
Option to extend carrier loss criteria to a 1 ms period as per ETS 300 233
Automatic RAI generation to ETS 300 011 specifications
1 and 2
12
7
12
8
11
4
1
8
1
1
1
6
1
1 and 3
12
3
3
4 of 87
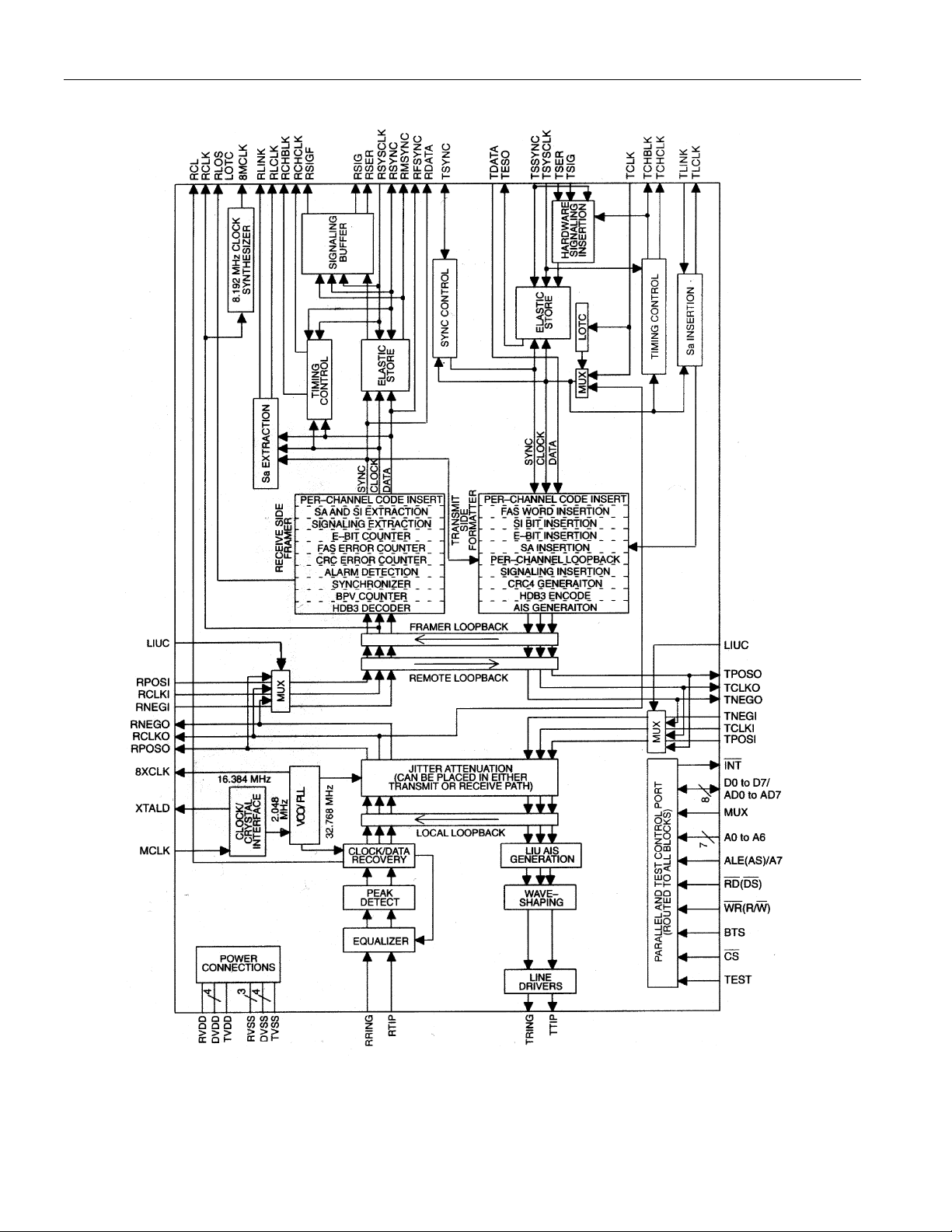
DS2154 ENHANCED E1 SINGLE-CHIP TRANSCEIVER Figure 1-1
DS2154
5 of 87

DS2154
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The analog AMI/HDB3 waveform off of the E1 line is transformer coupled into the RRING and RTIP
pins of the DS2154. The device recovers clock and data from the analog signal and passes it through the
jitter attenuation mux to the receive side framer where the digital serial stream is analyzed to locate the
framing/multiframe pattern. The DS2154 contains an active filter that reconstructs the analog received
signal for the non-linear losses that occur in transmission. The device has a usable receive sensitivit y of 0
dB to -43 dB which allows the device to operate on cables over 2 km in length. The receive side framer
locates the FAS frame and CRC and CAS multiframe boundaries as well as detects incoming alarms
including, carrier loss, loss of synchronization, AIS, and Remote Alarm. If needed, the receive side elastic
store can be enabled in order to absorb the phas e and frequency differences between the recov ered E1
data stream and an asynchronous backplane clock which is provided at the RSYSCLK input. The clock
applied at the RSYSCLK input can be either a 2.048 MHz clock or a 1.544 MHz clock. The RSYSCLK
can also be a bursty clock with speeds up to 8.192 MHz.
The transmit side of the DS2154 is totally independent from the receive side in both the clock
requirements and characteristics. Data off of a backplane can be passed through a transmit side elastic
store if necessary. The transmit formatter will provide the necessary frame/multiframe data overhead for
E1 transmission. Once the data stream has been prepared for transmission, it is sent via the jitter
attenuation mux to the waveshaping and line driver functions. The DS2154 will drive the E1 line from the
TTIP and TRING pins via a coupling transformer. The line driver can handle both 75Ω=and 120Ω=lines
and it has options for high return loss applications. The line driver contains a current limiter that will
restrict the maximum current into a 1Ω=load to less than 50 mA (rms).
READER’S NOTE
This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the E1 operating environment. There are 32 8-bit
timeslots in an E1 systems which are number 0 to 31. Timeslot 0 is transmitted first and received first.
These 32 timeslots are also referred to as channels with a numbering scheme of 1 to 32. Timeslot 0 is
identical to channel 1, timeslot 1 is identical to Channel 2, and so on. Each timeslot (or chann el) is made
up of 8 bits which are numbered 1 to 8. Bit number 1 is the MSB and is transmitted first. Bit number 8 is
the LSB and is transmitted last. Throughout this data sheet, the following abbreviations will be used:
FAS Frame Alignment Signal CRC4 Cyclical Redundancy Check
CAS Channel Associated Signaling CCS Common Channel Signaling
MF Multiframe Sa Additional bits
Si International bits E-bit CRC4 Error bits
6 of 87
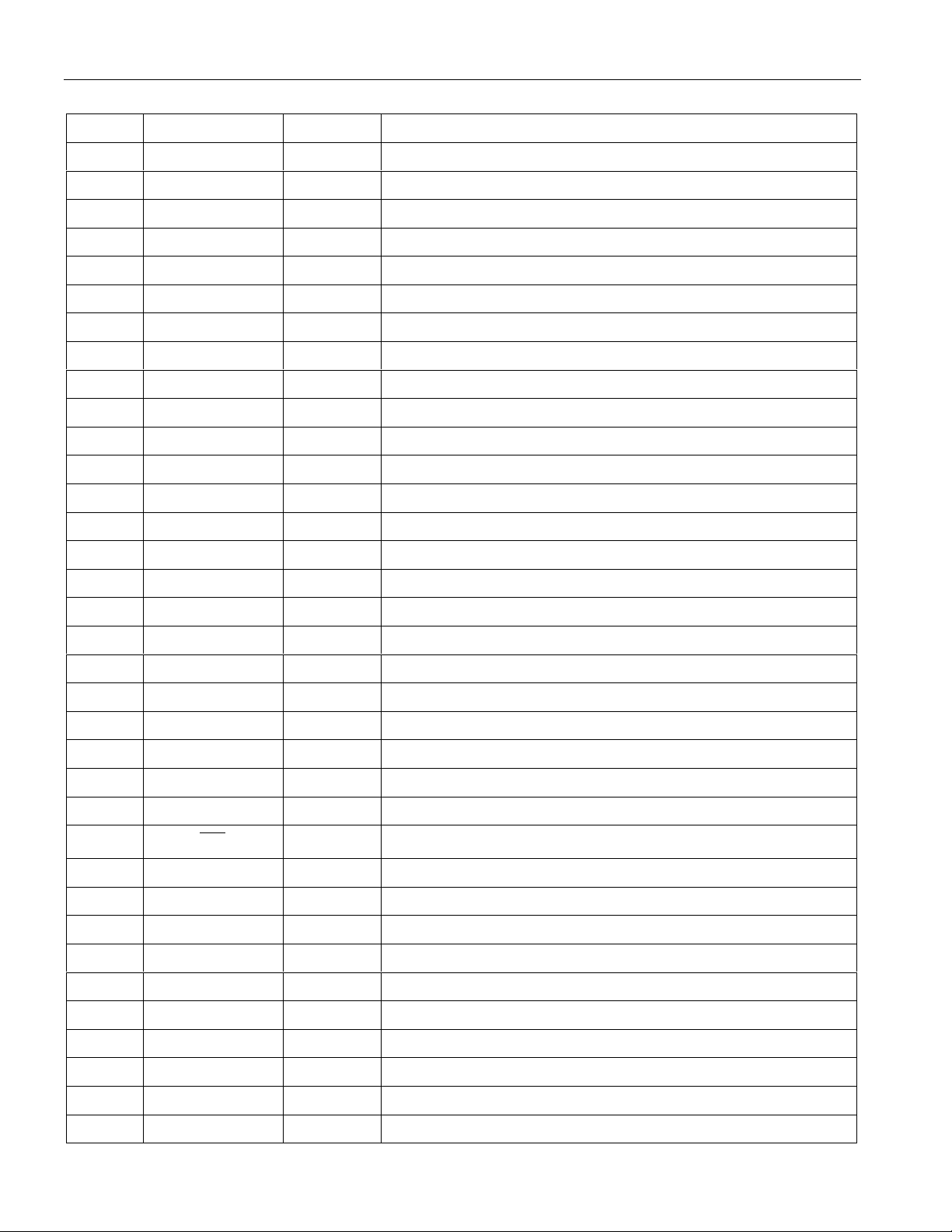
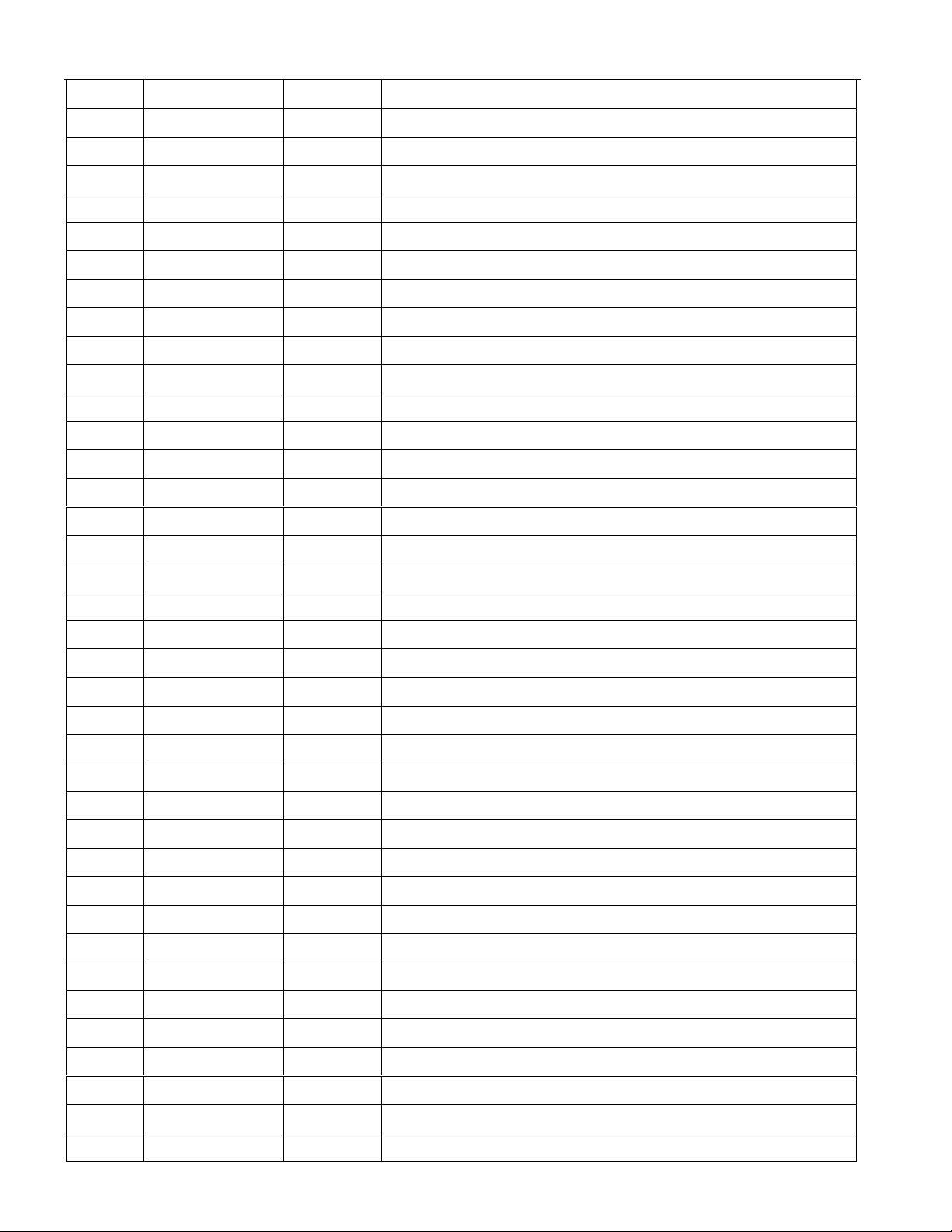
PIN LIST Table 1-1
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
1 RCHBLK O Receive Channel Block.
2 NC - No Connect.
3 8MCLK O 8.192 MHz Clock.
4 NC - No Connect.
5 NC - No Connect.
6 RCL O Receive Carrier Loss.
7 NC - No Connect.
8 NC - No Connect.
9 NC - No Connect.
10 NC - No Connect.
11 BTS I Bus Type Select.
12 LIUC I Line Interface Connect.
13 8XCLK O Eight Times Clock.
DS2154
14 TEST I Test.
15 NC - No Connect.
16 RTIP I Receive Analog Tip Input.
17 RRING I Receive Analog Ring Input.
18 RVDD - Receive Analog Positive Supply
19 RVSS - Receive Analog Signal Ground.
20 RVSS - Receive Analog Signal Ground.
21 MCLK I Master Clock Input.
22 XTALD O Quartz Crystal Driver.
23 NC - No Connect.
24 RVSS - Receive Analog Signal Ground.
25
26 NC - No Connect.
27 NC - No Connect.
28 NC - No Connect.
29 TTIP O Transmit Analog Tip Output.
INT
O Interrupt.
30 TVSS - Transmit Analog Signal Ground.
31 TVDD - Transmit Analog Positive Supply.
32 TRING O Transmit Analog Ring Output.
33 TCHBLK O Transmit Channel Block.
34 TLCLK O Transmit Link Clock.
35 TLINK I Transmit Link Data.
7 of 87
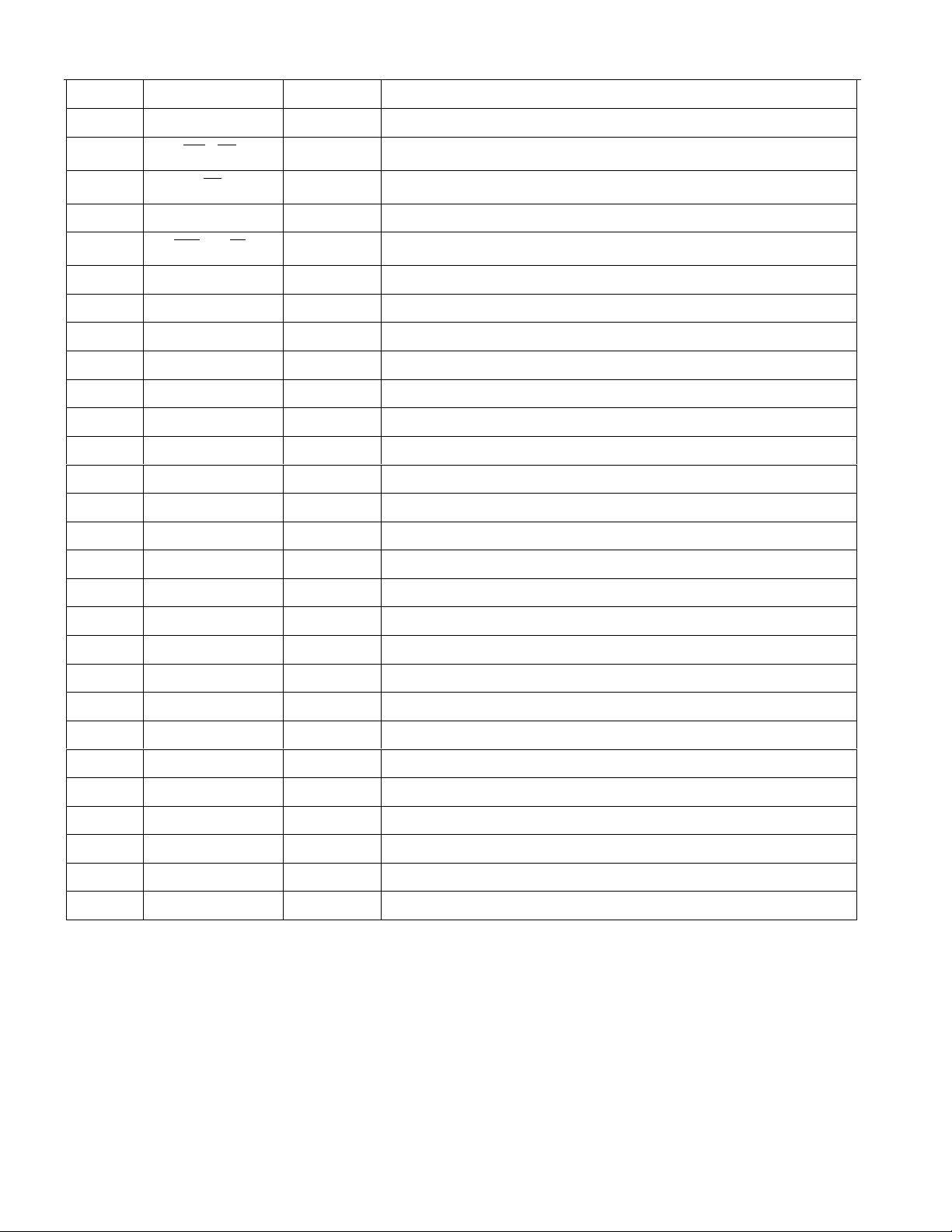
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
36 NC - No Connect.
37 TSYNC I/O Transmit Sync.
38 TPOSI I Transmit Positive Data Input.
39 TNEGI I Transmit Negative Data Input.
40 TCLKI I Transmit Clock Input.
41 TCLKO O Transmit Clock Output.
42 TNEGO O Transmit Negative Data Output.
43 TPOSO O Transmit Positive Data Output.
44 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply.
45 DVSS - Digital Signal Ground.
46 TCLK I Transmit Clock.
47 TSER I Transmit Serial Data.
48 TSIG I Transmit Signaling Input.
49 TESO O Transmit Elastic Store Output.
DS2154
50 TDATA I Transmit Data.
51 TSYSCLK I Transmit System Clock.
52 TSSYNC I Transmit System Sync.
53 TCHCLK O Transmit Channel Clock.
54 NC - No Connect.
55 MUX I Bus Operation.
56 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit 0 / Address/Data Bus Bit 0.
57 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit 1 / Address/Data Bus Bit 1.
58 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2 / Address/Data Bus Bit 2.
59 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3 / Address/Data Bus Bit 3.
60 DVSS - Digital Signal Ground.
61 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply.
62 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit 4 / Address/Data Bus Bit 4.
63 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5 / Address/Data Bus Bit 5.
64 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6 / Address/Data Bus Bit 6.
65 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7 / Address/Data Bus Bit 7.
66 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0.
67 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1.
68 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2.
69 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3.
70 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4.
71 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5.
72 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6.
8 of 87
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
73 A7/ALE I Address Bus Bit 7 / Address Latch Enable.
DS2154
74
75
RD ( DS )
CS
I Read Input (Data Strobe).
I Chip Select.
76 NC - No Connect.
77
WR (R/W )
I Write Input (Read/Write).
78 RLINK O Receive Link Data.
79 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock.
80 DVSS - Digital Signal Ground.
81 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply.
82 RCLK O Receive Clock.
83 DVDD - Digital Positive Supply.
84 DVSS - Digital Signal Ground.
85 RDATA O Receive Data.
86 RPOSI I Receive Positive Data Input.
87 RNEGI I Receive Negative Data Input.
88 RCLKI I Receive Clock Input.
89 RCLKO O Receive Clock Output.
90 RNEGO O Receive Negative Data Output.
91 RPOSO O Receive Positive Data Output.
92 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock.
93 RSIGF O Receive Signaling Freeze Output.
94 RSIG O Receive Signaling Output.
95 RSER O Receive Serial Data.
96 RMSYNC O Receive Multiframe Sync.
97 RFSYNC O Receive Frame S ync.
98 RSYNC I/O Receive Sync.
99 RLOS/LOTC O Receive Loss of Sync / Loss Of Transmit Clock.
100 RSYSCLK I Receive System Clock.
NOTE:
Leave all no connect (NC) pins open circuited.
9 of 87

DS2154
DS2154 PIN DESCRIPTION Table 1-2
TRANSMIT SIDE DIGITAL PINS
Transmit Clock [TCLK]. A 2.048 MHz primary clock. Used to clock data through the transmit side
formatter. Must be present for the parallel control port to operate properly. If not present, the Loss Of
Transmit Clock (LOTC) function can provide a clock.
Transmit Serial Data [TSER]. Transmit NRZ serial data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when
the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit
side elastic store is enabled.
Transmit Channel Clock [TCHCLK]. A 256 kHz clock which pulses high during the LSB of each
channel. Synchronous with TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with
TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial conversion of
channel data.
Transmit Channel Block [TCHBLK]. A user-programmable output that can be forced high or low
during any of the 32 E1 channels. Synchronous with TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is
disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. Useful for
blocking clocks to a serial UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all E1 channels are used
such as Fractional E1, 384 kbps (H0), 768 kbps, 1920 kbps (H12) or ISDN-PRI. Also useful for locating
individual channels in drop-and-insert applications, for external per-channel loopback, and for perchannel conditioning. See Section 9 for details.
Transmit System Clock [TSYSCLK]. 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz clock. Only used when the transmit
side elastic store function is enabled. Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit side
elastic store. Can be burst at rates up to 8.192 MHz.
Transmit Link Clock [TLCLK]. 4 kHz to 20 kHz demand clock (Sa bits) for the TLINK input. See
Section 11 for details.
Transmit Link Data [TLINK]. If enabled, this pin will be sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data
insertion into any combination of the Sa bit positions (Sa4 to Sa8). See Section 11 for details.
Transmit Sync [TSYNC]. A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for the
transmit side. This pin can also be programmed to output either a frame or multiframe pulse. Always
synchronous with TCLK.
Transmit Frame Sync [TSSYNC]. Only used when the transmit side elastic store is enabled. A pulse at
this pin will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. Should be tied low in
applications that do not use the transmit side elastic store. Always synchronous with TSYSCLK.
Transmit Signaling Input [TSIG]. When enabled, this input will be sample signaling bits for insertion
into outgoing PCM E1 data stream. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when the transmit side elastic
store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is
enabled. See Section 13 for timing examples.
Transmit Elastic Store Data Output [TESO]. Updated on the rising edge of TCLK with data out of the
transmit side elastic store whether the elastic store is enabled or not. This pin is normally tied to TDATA.
10 of 87

DS2154
Transmit Data [TDATA]. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK with data to be clocked through the
transmit side formatter. This pin is normally tied to TESO.
Transmit Positive Data Output [TPOSO]. Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data
out of the transmit side formatter. Can be programmed to source NRZ data via the Output Data Format
(TCR1.7) control bit. This pin is normally tied to TPOSI.
Transmit Negative Data Output [TNEGO]. Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar
data out of the transmit side formatter. This pin is normally tied to TNEGI.
Transmit Clock Output [TCLKO]. Buffered clock that is used to clock data through the transmit side
formatter (i.e. either TCLK or RCLKO if Loss Of Transmit Clock is enabled and in effect or RCLKI if
remote loopback is enabled). This pin is normally tied to TCLKI.
Transmit Positive Data Input [TPOSI]. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be
transmitted out onto the E1 line. Can be internally connected to TPOSO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Negative Data Input [TNEGI]. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be
transmitted out onto the E1 line. Can be internally connected to TNEGO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Clock Input [TCLKI]. Line interface transmit clock. Can be internally connected to TCLKO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
RECEIVE SIDE DIGITAL PINS
Receive Link Data [RLINK]. Updated with the full recovered E1 data stream on the rising edge of
RCLK.
Receive Link Clock [RL CLK]. 4 kHz to 20 kHz clock (Sa bits) for the RLINK output. See Section 11
for details.
Receive Clock [RCLK]. 2.048 MHz clock that is used to clock data through the receive side framer.
Receive Channel Clock [RCHCLK]. 256 kHz clock which pulses high during the LSB of each channel.
Synchronous with RCLK when the receive side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK
when the receive side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial conversion of channel data.
Receive Channel Block [RCH BL K]. A user-programmable output that can be forced high or low during
any of the 32 E1 channels. Synchronous with RCLK when the receive side elastic store is disabled.
Synchronous with RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is enabled. Useful for blocking clocks to
a serial UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all E1 chann els are used such as Fr actional
E1, 384k bps service, 768k bps, or ISDN-PRI. Also useful for locatin g individual channels in drop-andinsert applications, for external per-channel loopback, and for per-chann el conditioning. See Section 9 for
details.
Receive Serial Data [RSER]. Received NRZ serial data. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the
receive side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive side
elastic store is enabled.
11 of 87

DS2154
Receive Sync [RSYNC]. An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies either
frame or CAS/CRC multiframe boundaries. If the receive side elastic store is enabled, then this pin can be
enabled to be an input at which a frame or multiframe boundary pulse synchronous with RSYSCLK is
applied.
Receive Frame Sync [RFSYNC ]. An extracted 8 kHz pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which
identifies frame boundaries.
Receive Multiframe Syn c [RMSYNC]. An extracted pulse, one RSYSCLK wide, is output at this pin
which identifies multiframe boundaries. If the receive side elastic store is disabled, then this output will
output multiframe boundaries associated with RCLK.
Receive Data [RDATA]. Updated on the rising edge of RCLK with the data out of the receive side
framer.
Receive System Clock [RSYS CLK]. 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz clock. Only used when the elastic store
function is enabled. Should be tied low in applications that do not use the elastic store. Can be burst at
rates up to 8.192 MHz.
Receive Signaling Ou tput [RSIG]. Outputs signaling bits in a PCM format. Updated on rising edges of
RCLK when the receive side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the rising edges of RSYSCLK when the
receive side elastic store is enabled. See Section 13 for timing examples.
Receive Loss of Sync / Loss of Transmit Clock [RLOS/LOTC]. A dual function output that is
controlled by the TCR2.0 control bit. This pin can be programmed to either toggle high when the
synchronizer is searching for the frame and multiframe or to toggle high if the TCLK pin has not been
toggled for 5 µs.
Receive Carrier Loss [RCL]. Set high when the line interface detects a loss of carrier. [Note: a test
mode exists to allow the DS2154 to detect carrier loss at RPOSI and RNEGI in place of detection at RTIP
and RRING].
Receive Signaling Freeze [RSI GF]. Set high when the signaling data is frozen via either automatic or
manual intervention. Used to alert downstream equipment of the condition.
8 MHz Clock [8MCLK]. 8.192 MHz output clock that is referenced to the clock that is output at the
RCLK pin.
Receive Positive Data Output [R POSO]. Updated on the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data
out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RPOSI.
Receive Negative Data Outpu t [RNEGO]. Update d on the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data
out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RNEGI.
Receive Clock Outpu t [RCLKO]. Buffered recovered clock from the E1 line. This pin is normally tied
to RCLKI.
Receive Positive Data Input [RPOSI]. Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked
through the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied together for a NRZ interface. Can be
internally connected to RPOSO by tying the LIUC pin high.
12 of 87

DS2154
Receive Negative Data Input [RNEGI]. Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked
through the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied together for a NRZ interface. Can be
internally connected to RNEGO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Receive Clock Input [RCLKI]. Clock used to clock data through the receive side framer. This pin is
normally tied to RCLKO. Can be internally connected to RCLKO by tying the LIUC pin high. RCLKI
must be present for the parallel control port to operate properly.
PARALLEL CONTROL PORT PINS
Interrupt [INT]. Flags host controller during conditions and change of conditions defined in the Status
Registers 1 and 2. Active low, open drain output.
3-State Control [Test]. Set high to 3-state all output and I/O pins (including the parallel control port). Set
low for normal operation. Useful in board level testing.
Bus Operation [MUX]. Set low to select non-multiplexed bus operation. Set high to select multiplexed
bus operation.
Data Bus [D0 to D7] or Address/Data Bus [AD0 to AD7]. In non-multiplexed bus operation (MUX=0),
serves as the data bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX=1), serves as a 8-bit multiplexed address /
data bus.
Address Bus [A0 to A6]. In non-multiplexed bus operation (MUX=0), serves as the address bus. In
multiplexed bus operation (MUX=1), these pins are not used and should be tied low.
Bus Type Select [BTS]. Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap low to select Intel bus timing.
This pin controls the function of the RD\(DS), ALE(AS), and WR\(R/W\) pins. If BTS=1, then these pins
assume the function listed in parenthesis ().
Read Input [RD] (Data Strobe [DS ]). RD and DS are active low signals when MUX=11. DS is active
high when MUX = 0. See bus timing diagrams.
Chip Select [CS]. Must be low to read or write to the device. CS is an active low signal.
A7 or Address Latch Enable [ALE] (Address Strobe [AS]). In non-multiplexed bus operation
(MUX=0), serves as the upper address bit. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX=1), serves to demultiplex
the bus on a positive-going edge.
Write Input [WR] (Read/Write [R/W]). WR is an active low signal.
LINE INTERFACE PINS
Master Clock Input [MCLK]. 2.048 MHz (± 50 ppm) clock source with TTL levels is applied at this
pin. This clock is used internally for both clock/data recover y and for jitter attenuation. A quartz crystal
of 2.048 MHz may be applied across MCLK and XTALD instead of the TTL level clock source.
Quartz Crystal Driver [XTALD]. A quartz crystal of 2.048 MHz may be applied across MCLK and
XTALD instead of a TTL level clock source at MCLK. Leave open circuited if a TTL clock source is
applied at MCLK.
13 of 87

DS2154
Eight Times Clock [8XCLK]. 16.384 MHz clock that is frequency locked to the 2.048 MHz clock
provided from the clock/data recovery block (if the jitter attenuator is enabled on the receive side) or from
the TCLKI pin (if the jitter attenuator is enabled on the transmit side). Can be internally disabled via the
TEST2 register if not needed.
Line Interface Connect [LIUC]. Tie low to separate the line interface circuitry from the
framer/formatter circuitry and activate the TPOS I/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEG I/ RCLKI pins. Tie high
to connect the line interface circuitry to the framer/formatter circuitry and deactivate the
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins. When LIUC is tied high, the
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins should be tied low.
Receive Tip and Ring [RTIP and RRING]. Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins
connect via a 1:1 transformer to either the E1 line. See Section 12 for an example.
Transmit Tip and Ring [TTIP and TRING]. Analog line driver outputs. These pins connect via a
1:1.15 or 1:1.36 step-up transformer to the E1 line. See Section 12 for an example.
SUPPLY PINS
Digital Positive Supply [DVDD]. 5.0 volts ± 5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD pins.
Receive Analog Positive Supply [RVDD]. 5.0 volts ± 5%. Should be tied to the DVDD and TVDD pins.
Transmit Analog Positive Supply [TVDD]. 5.0 volts ± 5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and DVDD
pins.
Digital Signal Ground [DVSS]. 0.0 volts. Should be tied to the RVSS and TVSS pins.
Receive Analog Signal Ground [RVSS]. 0.0 volts. Should be tied to the DVSS and TVSS pins.
Transmit Analog Ground [TVSS]. 0.0 volts. Should be tied to the RVSS and DVSS pins.
14 of 87
DS2154
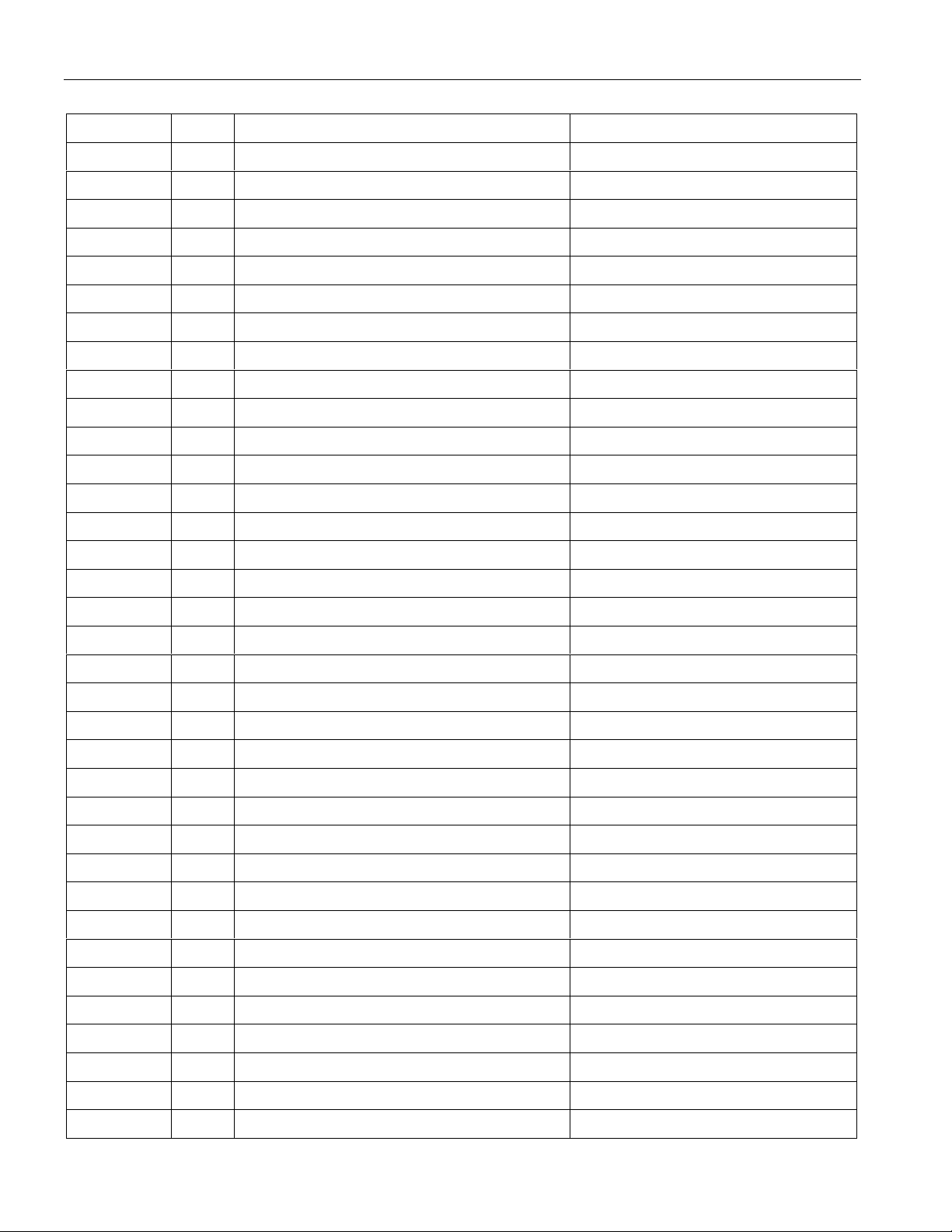
DS2154 REGISTER MAP Table 1-3
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
00 R BPV or Code Violation Count 1. VCR1
01 R BPV or Code Violation Count 2. VCR2
02 R CRC4 Error Count 1 / FAS Error Count 1. CRCCR1
03 R CRC4 Error Count 2. CRCCR2
04 R E-Bit Count 1 / FAS Error Count 2. EBCR1
05 R E-Bit Count 2. EBCR2
06 R/W Status 1. SR1
07 R/W Status 2. SR2
08 R/W Recive Information. RIR
09 - not present. 0A - not present. 0B - not present. 0C - not present. 0D - not present. 0E - not present. 0F R Device ID Register. IDR
10 R/W Receive Control 1. RCR1
11 R/W Receive Control 2. RCR2
12 R/W Transmit Control 1. TCR1
13 R/W Transmit Control 2. TCR2
14 R/W Common Control 1. CCR1
15 R/W Test 1. TEST1 (set to 00h)
16 R/W Interrupt Mask 1. IMR1
17 R/W Interrupt Mask 2. IMR2
18 R/W Line Interface Control. LICR
19 R/W Test 2. TEST2 (set to 00h)
1A R/W Common Control 2. CCR2
1B R/W Common Control 3. CCR3
1C R/W Transmit Sa Bit Control. TSaCR
1D - Not present. 1E R Synchronizer Status. SSR
1F R Receive Non-Align Frame. RNAF
20 R/W Transmit Align Frame. TAF
21 R/W Transmit Non-Align Frame. TNAF
22 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 1. TCBR1
15 of 87
DS2154
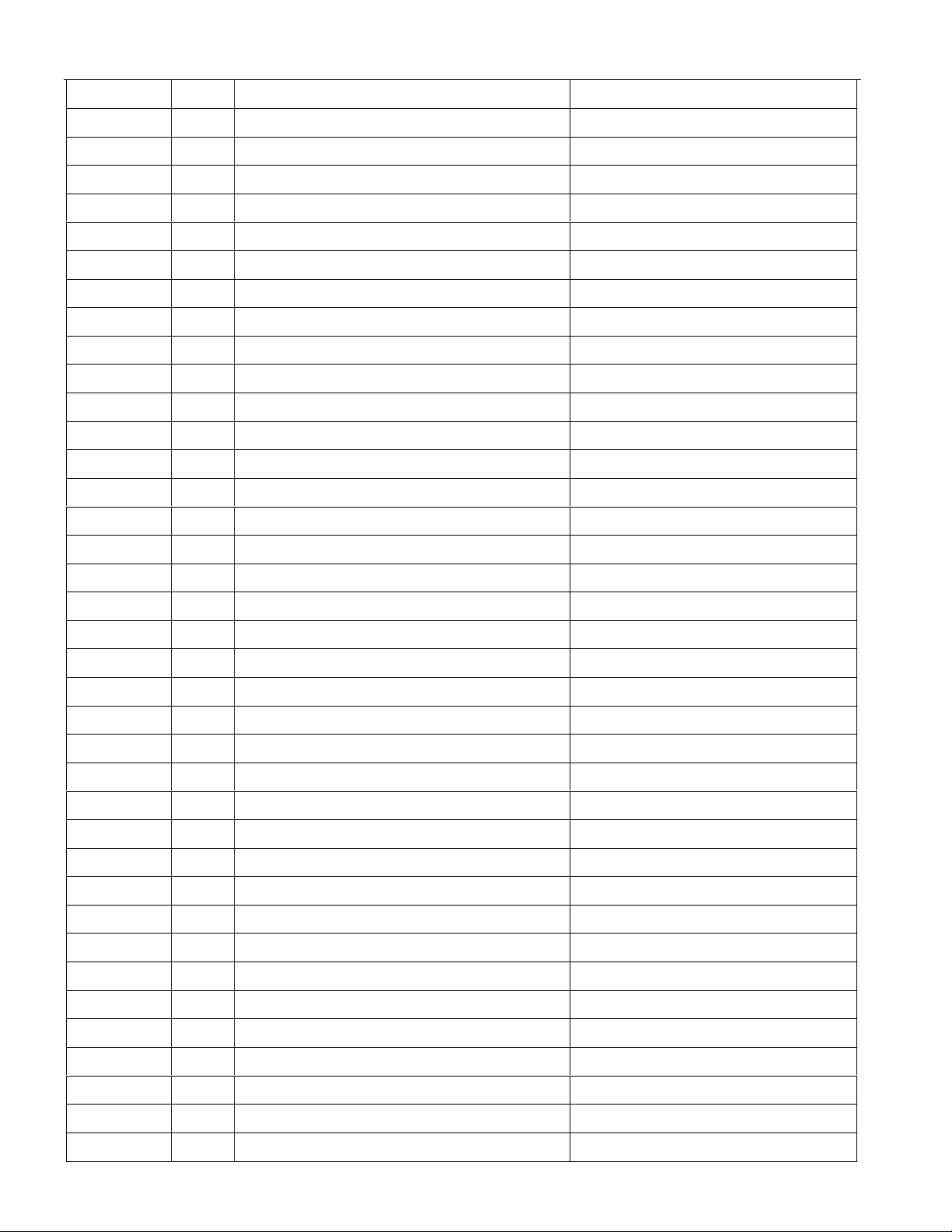
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
23 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 2. TCBR2
24 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 3. TCBR3
25 R/W Transmit Channel Blocking 4. TCBR4
26 R/W Transmit Idle 1. TIR1
27 R/W Transmit Idle 2. TIR2
28 R/W Transmit Idle 3. TIR3
29 R/W Transmit Idle 4. TIR4
2A R/W Transmit Idle Definition. TIDR
2B R/W Receive Channel Blocking 1. RCBR1
2C R/W Receive Channel Blocking 2. RCBR2
2D R/W Receive Channel Blocking 3. RCBR3
2E R/W Receive Channel Blocking 4. RCBR4
2F R Receive Align Frame. RAF
30 R Receive Signaling 1. RS1
31 R Receive Signaling 2. RS2
32 R Receive Signaling 3. RS3
33 R Receive Signaling 4. RS4
34 R Receive Signaling 5. RS5
35 R Receive Signaling 6. RS6
36 R Receive Signaling 7. RS7
37 R Receive Signaling 8. RS8
38 R Receive Signaling 9. RS9
39 R Receive Signaling 10. RS10
3A R Receive Signaling 11. RS11
3B R Receive Signaling 12. RS12
3C R Receive Signaling 13. RS13
3D R Receive Signaling 14. RS14
3E R Receive Signaling 15. RS15
3F R Receive Signaling 16. RS16
40 R/W Transmit Signaling 1. TS1
41 R/W Transmit Signaling 2. TS2
42 R/W Transmit Signaling 3. TS3
43 R/W Transmit Signaling 4. TS4
44 R/W Transmit Signaling 5. TS5
45 R/W Transmit Signaling 6. TS6
46 R/W Transmit Signaling 7. TS7
47 R/W Transmit Signaling 8. TS8
16 of 87
DS2154
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
48 R/W Transmit Signaling 9. TS9
49 R/W Transmit Signaling 10. TS10
4A R/W Transmit Signaling 11. TS11
4B R/W Transmit Signaling 12. TS12
4C R/W Transmit Signaling 13. TS13
4D R/W Transmit Signaling 14. TS14
4E R/W Transmit Signaling 15. TS15
4F R/W Transmit Signaling 16. TS16
50 R/W Transmit Si Bits Align Frame. TSiAF
51 R/W Transmit Si Bits Non-Align Frame. TSiNAF
52 R/W Transmit Remote Alarm Bits. TRA
53 R/W Transmit Sa4 Bits. TSa4
54 R/W Transmit Sa5 Bits. TSa5
55 R/W Transmit Sa6 Bits. TSa6
56 R/W Transmit Sa7 Bits. TSa7
57 R/W Transmit Sa8 Bits. TSa8
58 R Receive Si Bits Align Frame. RSiAF
59 R Receive Si Bits Non-Align Frame. RSiNAF
5A R Receive Remote Alarm Bits. RRA
5B R Receive Sa4 Bits. RSa4
5C R Receive Sa5 Bits. RSa5
5D R Receive Sa6 Bits. RSa6
5E R Receive Sa7 Bits. RSa7
5F R Receive Sa8 Bits. RSa8
60 R/W Transmit Channel 1. TC1
61 R/W Transmit Channel 2. TC2
62 R/W Transmit Channel 3. TC3
63 R/W Transmit Channel 4. TC4
64 R/W Transmit Channel 5. TC5
65 R/W Transmit Channel 6. TC6
66 R/W Transmit Channel 7. TC7
67 R/W Transmit Channel 8. TC8
68 R/W Transmit Channel 9. TC9
69 R/W Transmit Channel 10. TC10
6A R/W Transmit Channel 11. TC11
6B R/W Transmit Channel 12. TC12
6C R/W Transmit Channel 13. TC13
17 of 87
DS2154
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
6D R/W Transmit Channel 14. TC14
6E R/W Transmit Channel 15. TC15
6F R/W Transmit Channel 16. TC16
70 R/W Transmit Channel 17. TC17
71 R/W Transmit Channel 18. TC18
72 R/W Transmit Channel 19. TC19
73 R/W Transmit Channel 20. TC20
74 R/W Transmit Channel 21. TC21
75 R/W Transmit Channel 22. TC22
76 R/W Transmit Channel 23. TC23
77 R/W Transmit Channel 24. TC24
78 R/W Transmit Channel 25. TC25
79 R/W Transmit Channel 26. TC26
7A R/W Transmit Channel 27. TC27
7B R/W Transmit Channel 28. TC28
7C R/W Transmit Channel 29. TC29
7D R/W Transmit Channel 30. TC30
7E R/W Transmit Channel 31. TC31
7F R/W Transmit Channel 32. TC32
80 R/W Receive Channel 1. RC1
81 R/W Receive Channel 2. RC2
82 R/W Receive Channel 3. RC3
83 R/W Receive Channel 4. RC4
84 R/W Receive Channel 5. RC5
85 R/W Receive Channel 6. RC6
86 R/W Receive Channel 7. RC7
87 R/W Receive Channel 8. RC8
88 R/W Receive Channel 9. RC9
89 R/W Receive Channel 10. RC10
8A R/W Receive Channel 11. RC11
8B R/W Receive Channel 12. RC12
8C R/W Receive Channel 13. RC13
8D R/W Receive Channel 14. RC14
8E R/W Receive Channel 15. RC15
8F R/W Receive Channel 16. RC16
90 R/W Receive Channel 17. RC17
91 R/W Receive Channel 18. RC18
18 of 87
DS2154
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
92 R/W Receive Channel 19. RC19
93 R/W Receive Channel 20. RC20
94 R/W Receive Channel 21. RC21
95 R/W Receive Channel 22. RC22
96 R/W Receive Channel 23. RC23
97 R/W Receive Channel 24. RC24
98 R/W Receive Channel 25. RC25
99 R/W Receive Channel 26. RC26
9A R/W Receive Channel 27. RC27
9B R/W Receive Channel 28. RC28
9C R/W Receive Channel 29. RC29
9D R/W Receive Channel 30. RC30
9E R/W Receive Channel 31. RC31
9F R/W Receive Channel 32. RC32
A0 R/W Transmit Channel Control 1. TCC1
A1 R/W Transmit Channel Control 2. TCC2
A2 R/W Transmit Channel Control 3. TCC3
A3 R/W Transmit Channel Control 4. TCC4
A4 R/W Receive Channel Control 1. RCC1
A5 R/W Receive Channel Control 2. RCC2
A6 R/W Receive Channel Control 3. RCC3
A7 R/W Receive Channel Control 4. RCC4
A8 R/W Common Control 4. CCR4
A9 R Transmit DS0 Monitor. TDS0M
AA R/W Common Control 5. CCR5
AB R Receive DS0 Monitor. RDS0M
AC R/W Test 3. TEST3 (set to 00h)
AD R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
AE R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
AF R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
NOTES:
1. Test Registers 1, 2, and 3 are used only by the factory; these registers must be cleared (set to all 0s) on
power-up initialization to insure proper operation.
2. Register banks Bxh, Cxh, Dxh, Exh, and Fxh are not accessible.
19 of 87

DS2154
2.0 PARALLEL PORT
The DS2154 is controlled via either a non-multiplexed (MUX=0) or a multiplexed (MUX=1) bus by an
external microcontroller or microprocessor. The DS2154 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus
timing configurations. If the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola
timing will be selected. All Motorola bus signals are listed in parenthesis (). See the timing diagrams in
the A.C. Electrical Characteristics in Section 14 for more details.
3.0 CONTROL, ID AND TEST REGISTERS
The operation of the DS2154 is configured via a set of nine control registers. Typically, the control
registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the DS2154 has been initialized,
the control registers will only need to be accessed when there is a change in the system configuration.
There are two Receive Control Registers (RCR1 and RCR2), two Transmit Control Registers (TCR1 and
TCR2), and five Common Control Registers (CCR1 to CCR5). Each of the nine registers is described in
this section.
There is a device IDentification Register (IDR) at address 0FH. The MSB of this read-only register is
fixed to a 1, indicating that the DS2154 is present. The pin-for-pin compatible T1 version of the DS2154
also has an ID register at address 0FH and the user can r ead the MSB to determi ne which chip is pres ent
since in the DS2154 the MSB will be set to a 1 and in the DS2152 it will be set to a 0. The lower 4 bits of
the IDR are used to display the die revision of the chip.
The Test Registers at addresses 15, 19, and AC hex are used by the factory in testing the DS2154. On
power-up, the Test Registers should be set to 00 hex in order for the DS2154 to operate properly.
20 of 87
DS2154
IDR: DEVICE IDENTIFICATION REGISTER (Address=0F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
T1E1 0 0 0 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
T1E1 IDR.7
ID3 IDR.3 Chip Revision Bit 3. MSB of a decimal code that represents the
ID2 IDR.1
ID1 IDR.2
ID0 IDR.0 Chip Revision Bit 0. LSB of a decimal code that represents the
T1 or E1 Chip Determination Bit.
0=T1 chip
1=E1 chip
chip revision.
Chip Revision Bit 2.
Chip Revision Bit 1.
chip revision.
RCR1: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=10 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSMF RSM R SIO - - FRC SYNCE RESYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSMF RCR1.7 RSYNC Multiframe Function. Only used if the RSYNC pin is
programmed in the multiframe mode (RCR1.6=1).
0=RSYNC outputs CAS multiframe boundaries
1=RSYNC outputs CRC4 multiframe boundaries
RSM RCR1.6
RSIO RCR1.5 RSYNC I/O Select. (Note: this bit must be set to 0 when
- RCR1.4 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written.
- RCR1.3 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written.
FRC RCR1.2
SYNCE RCR1.1
RESYNC RCR1.0 Resync. When toggled from low to high, a resync is initiated.
RSYNC Mode Select.
0=frame mode (see the timing in Section 13)
1=multiframe mode (see the timing in Section 13)
RCR2.1=0).
0=RSYNC is an output (depends on RCR1.6)
1=RSYNC is an input (only valid if elastic store enabled)
Frame Resync Criteria.
0=resync if FAS received in error 3 consecutive times
1=resync if FAS or bit 2 of non-FAS is received in error 3
consecutive times
Sync Enable.
0=auto resync enabled
1=auto resync disabled
21 of 87
Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
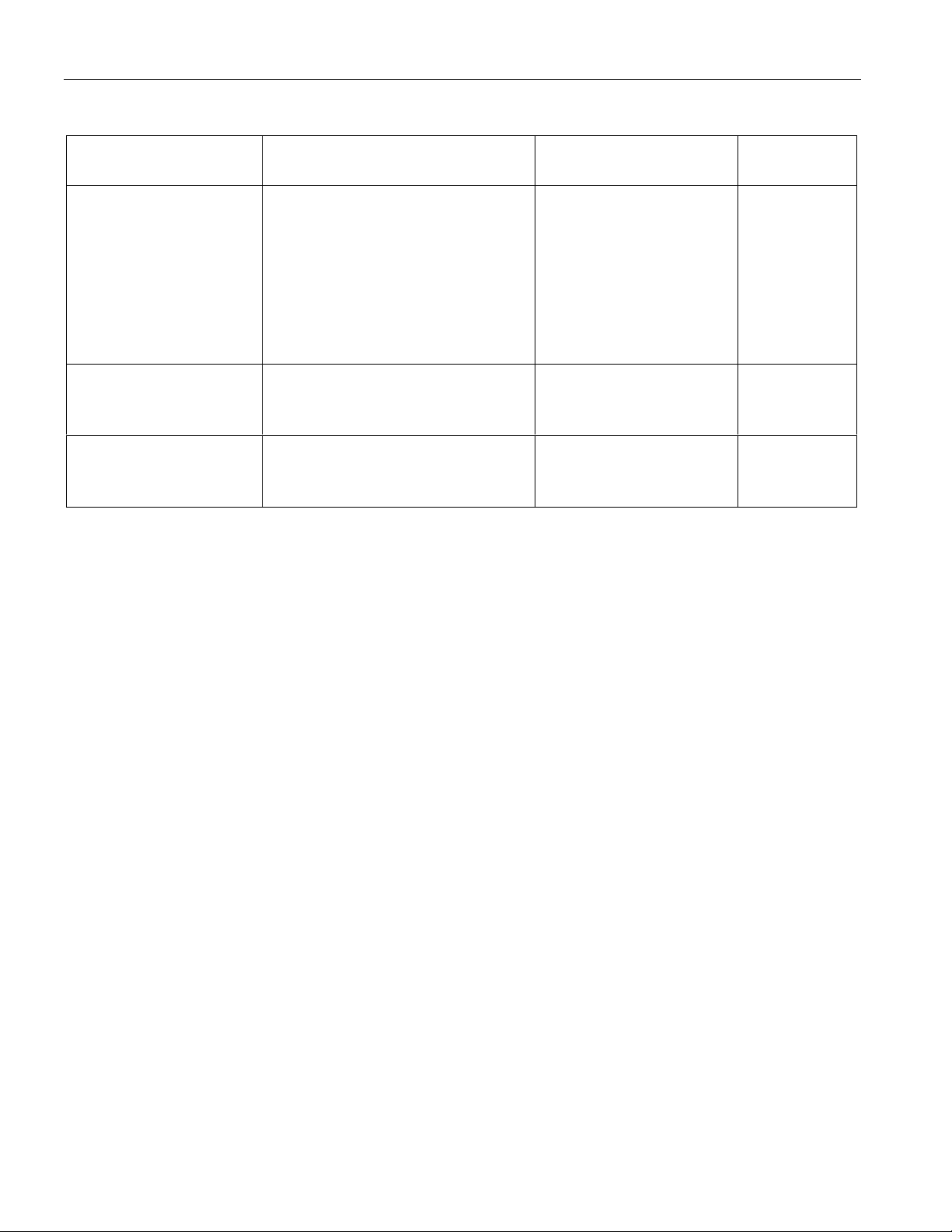
SYNC/RESYNC CRITERIA Table 3-1
FRAME OR MULTI-
FRAME LEVEL SYNC CRITERIA RESYNC CRITERIA ITU SPEC.
DS2154
FAS
CRC4
CAS Valid MF alignment word found
FAS present in frame N and N +
2, and FAS not present in frame
N + 1
Two valid MF alignment words
found within 8 ms
and previous timeslot 16 contains
code other than all 0s
Three consecutive
incorrect FAS received
Alternate (RCR1.2=1)
the above criteria is met
or three consecutive
incorrect bit 2 of nonFAS received
915 or more CRC4 code
words out of 1000
received in error
Two consecutive MF
alignment words
received in error
G.706
4.1.1
4.1.2
G.706
4.2 and 4.3.2
G.732
5.2
22 of 87

DS2154
RCR2: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=11 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S RBCS RESE -
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S RCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to 1 to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa8 bit
position; set to 0 to force RLCLK low during Sa8 bit position.
See Section 13 for timing details.
Sa7S RCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to 1 to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa7 bit
position; set to 0 to force RLCLK low during Sa7 bit position.
See Section 13 for timing details.
Sa6S RCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to 1 to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa6 bit
position; set to 0 to force RLCLK low during Sa6 bit position.
See Section 13 for timing details.
Sa5S RCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to 1 to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa5 bit
position; set to 0 to force RLCLK low during Sa5 bit position.
See Section 13 for timing details.
Sa4S RCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to 1 to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa4 bit
position; set to 0 to force RLCLK low during Sa4 bit position.
See Section 13 for timing details.
RBCS RCR2.2
RESE RCR2.1
- RCR2.0 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written.
Receive Side Backplane Clock Select.
0=if RSYSCLK is 1.544 MHz
1=if RSYSCLK is 2.048 MHz
Receive Side Elastic Store Enable.
0=elastic store is bypassed
1=elastic store is enabled
23 of 87

DS2154
TCR1: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=12 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
ODF TFPT T16S TUA1 TSiS TSA1 TSM TSIO
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ODF TCR1.7
TFPT TCR1.6
T16S TCR1.5
TUA1 TCR1.4
TSiS TCR1.3
Output Data Format.
0=bipolar data at TPOSO and TNEGO
1=NRZ data at TPOSO; TNEGO=0
Transmit Timeslot 0 Pass Through.
0=FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced internally from the
TAF and TNAF registers
1=FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced from TSER
Transmit Timeslot 16 Data Select.
0=sample timeslot 16 at TSER pin
1=source timeslot 16 from TS0 to TS15 registers
Transmit Unframed All 1s.
0=transmit data normally
1=transmit an unframed all 1’s code at TPOSO and TNEGO
Transmit International Bit Select.
0=sample Si bits at TSER pin
1=source Si bits from TAF and TNAF registers (in this mode,
TCR1.6 must be set to 0)
TSA1 TCR1.2
TSM TCR1.1 TSYNC Mode Select.
TSIO TCR1.0
Transmit Signaling All 1s.
0=normal operation
1=force timeslot 16 in every frame to all 1s
0=frame mode (see the timing in Section 13)
1=CAS and CRC4 multiframe mode (see the timing in Section
13)
TSYNC I/O Select.
0=TSYNC is an input
1=TSYNC is an output
NOTE:
See Figure 13-11 for more details about how the Transmit Control Registers affect the operation of the
DS2154.
24 of 87

DS2154
TCR2: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=13 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S ODM AEBE PF
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S TCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa8 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa8 bit. See Section 13 for timing
details.
Sa7S TCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa7 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa7 bit. See Section 13 for timing
details.
Sa6S TCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa6 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa6 bit. See Section 13 for timing
details.
Sa5S TCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa5 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa5 bit. See Section 13 for timing
details.
Sa4S TCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa4 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa4 bit. See Section 13 for timing
details.
ODM TCR2.2
AEBE TCR2.1
PF TCR2.0
Output Data Mode.
0=pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are one full TCLKO period
wide
1=pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are 1/2 TCLKO period wide
Automatic E-Bit Enable.
0=E-bits not automatically set in the transmit direction
1=E-bits automatically set in the transmit direction
Function of RLOS/LOTC Pin.
0=Receive Loss of Sync (RLOS)
1=Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC)
25 of 87

DS2154
CCR1: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=14 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
FLB THDB3 TG802 TCRC4 RSM RHDB3 RG802 RCRC4
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
FLB CCR1.7
THDB3 CCR1.6
TG802 CCR1.5 Transmit G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
TCRC4 CCR1.4
RSM CCR1.3
RHDB3 CCR1.2
Framer Loopback.
0=loopback disabled
1=loopback enabled
Transmit HDB3 Enable.
0=HDB3 disabled
1=HDB3 enabled
0=do not force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
1=force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
Transmit CRC4 Enable.
0=CRC4 disabled
1=CRC4 enabled
Receive Signaling Mode Select.
0=CAS signaling mode
1=CCS signaling mode
Receive HDB3 Enable.
0=HDB3 disabled
1=HDB3 enabled
RG802 CCR1.1 Receive G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
0=do not force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
1=force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
RCRC4 CCR1.0
Receive CRC4 Enable.
0=CRC4 disabled
1=CRC4 enabled
26 of 87

DS2154
FRAMER LOOPBACK
When CCR1.7 is set to a 1, the DS2154 will enter a Framer LoopBack (FLB) mode. See Figure 1-1 for
more details. This loopback is useful in testing and debugging applications. In FLB, the DS2154 will loop
data from the transmit side back to the receive side.
When FLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1. Data will be transmitted as normal at TPOSO and TNEGO.
2. Data input via RPOSI and RNEGI will be ignored.
3. The RCLK output will be replaced with the TCLK input.
CCR2: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=1A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
ECUS VCRFS AAIS ARA RSERC LOTCMC RFF RFE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ECUS CCR2.7 Error Counter Update Select. See Section 5 for details.
0=update error counters once a second
1=update error counters every 62.5 ms (500 frames)
VCRFS CCR2.6 VCR Function Select. See Section 5 for details.
0=count BiPolar Violations (BPVs)
1=count Code Violations (CVs)
AAIS CCR2.5
ARA CCR2.4
RSERC CCR2.3
LOTCMC CCR2.2 Loss of Transmit Clock Mux Control. Determines whether the
RFF CCR2.1 Receive Force Freeze. Freezes receive side signaling at RSIG
Automatic AIS Generation.
0=disabled
1=enabled
Automatic Remote Alarm Generation.
0=disabled
1=enabled
RSER Control.
0=allow RSER to output data as received under all conditions
1=force RSER to 1 under loss of frame alignment conditions
transmit side formatter should switch to the ever-present
RCLKO if the TCLK should fail to transition (see Figure 1-1).
0=do not switch to RCLKO if TCLK stops
1=switch to RCLKO if TCLK stops
(and RSER if CCR3.3=1); will override Receive Freeze Enable
(RFE). See Section 7-2 for details.
0=do not force a freeze event
1=force a freeze event
RFE CCR2.0 Receive Freeze Enable. See Section 7-2 for details.
0=no freezing of receive signaling data will occur
1=allow freezing of receive signaling data at RSIG (and RSER if
CCR3.3=1).
27 of 87
 Loading...
Loading...