dallas semiconductor DS2143, DS2143Q service manual
r
)
(AS)WR(
)
K
K
K
K
R
查询DS2143供应商
www.dalsemi.com
DS2143/DS2143Q
E1 Controlle
FEATURES
E1/ISDN-PRI framing transceiver
Frames to CAS, CCS, and CRC4 formats
Parallel control port
Onboard two frame elastic store slip buffer
Extracts and inserts CAS signaling bits
Programmable output clocks for fractional E1
links, DS0 loopbacks, and drop and insert
applications
Onboard Sa data link support circuitry
FEBE E-Bit detection, counting and
generation
Pin-compatible with DS2141A T1 Controller
5V supply; low power (50 mW) CMOS
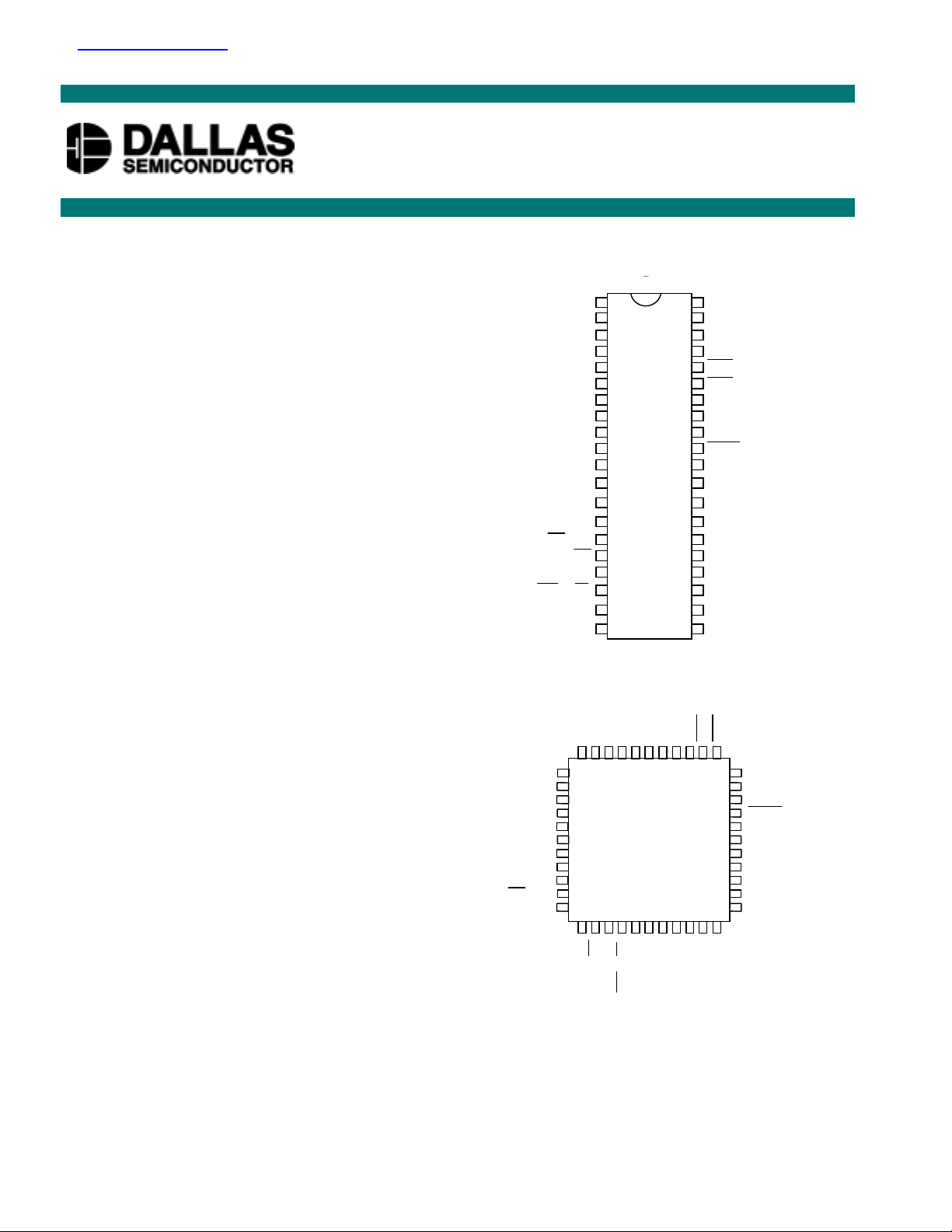
Available in 40-pin DIP and 44-pin PLCC
(DS2143Q)
PIN ASSIGNMENT
TCLK
TSER
TCHCLK
TPOS
TNEG
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
BTS
RD(DS
ALE
R/W
RLINK
VSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
CS
16
17
18
19
20
40-Pin DIP (600-mil)
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
VDD
TSYNC
TLINK
TLCLK
INT1
INT2
RLOS/LOTC
TCHBLK
RCHBLK
LI_CS
LI_CLK
LI_SDI
SYSCLK
RNEG
RPOS
RSYNC
RSER
RCHCLK
RCLK
RLCLK
TLINK
TLCLK
RCL
RCHCL
RSE
INT1
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
RSYNC
INT2
RLOS/LOTC
TCHBLK
RCHBLK
LI_CS
LI_CLK
LI_SDI
NC
NC
SYSCLK
RNEG
RPOS
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
BTS
RD(DS)
NC
TNEG
TPOS
TCHCLK
TSER
TCLK
VDD
TSYNC
6 5 4 3 2 1 44 43 42 4 1 40
7
8
9
10
11
44-PIN PLCC
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 2 5 26 27 28
CS
NC
VSS
RLIN
ALE(AS)
RLCL
WR(R/W)
DESCRIPTION
The DS2143 is a comprehensive, software-driven E1 framer. It is meant to act as a slave or coprocessor to
a microcontroller or microprocessor. Quick access via the parallel control port allows a single micro to
handle many E1 lines. The DS2143 is very flexible and can be configured into numerous orientations via
software. The software orientation of the device allows the user to modify their design to conform to
future E1 specification changes. The controller contains a set of 69 8-bit internal registers which the user
1 of 44 112099

DS2143/DS2143Q
can access. These internal registers are used to configure the device and obtain inform ation from the E1
link. The device fully meets al l of the latest E1 specifications, including CCITT G.704, G.706, and
G.732.
1.0 INTRODUCTION
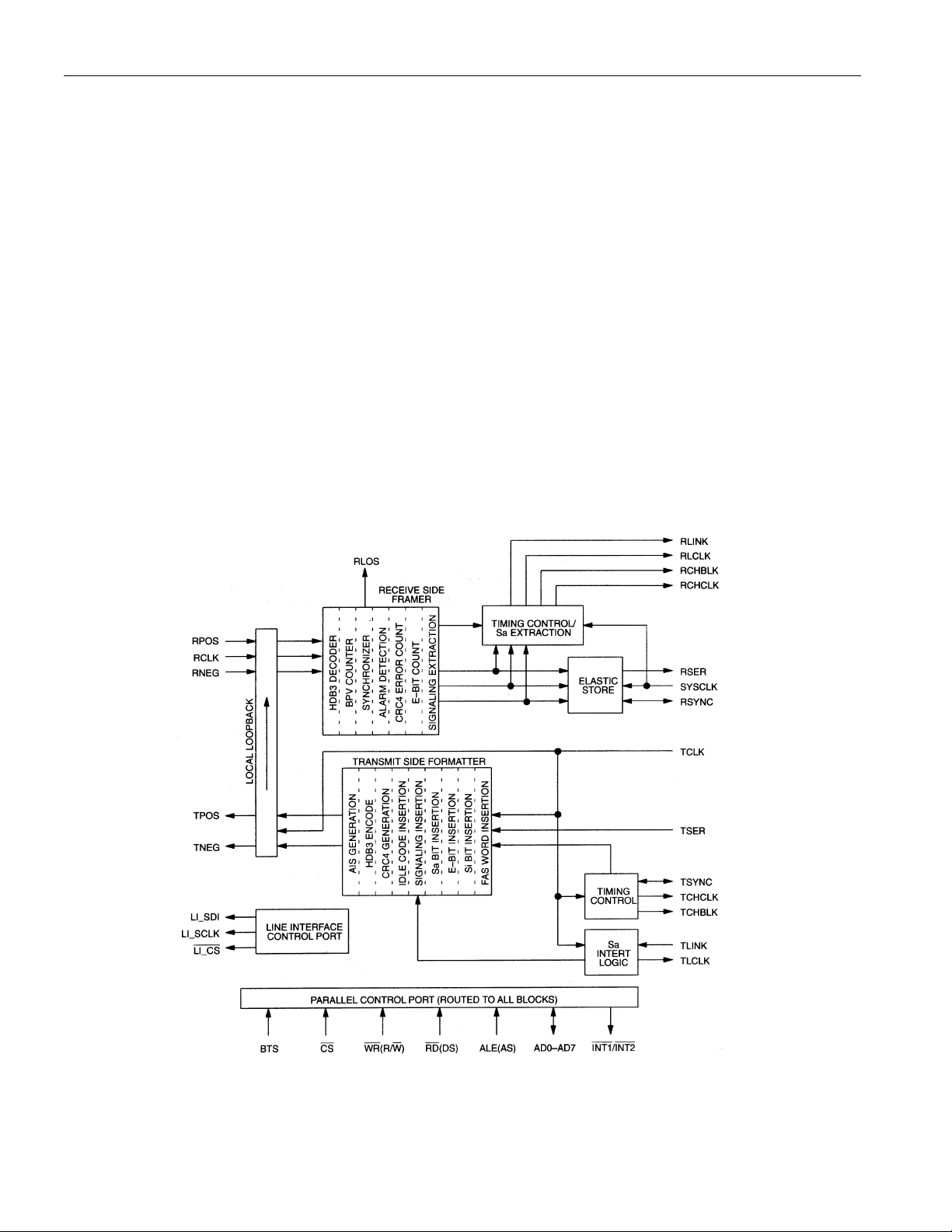
The DS2143 E1 Controller has four main sections: the receive side, the transmit side, the line interface
controller, and the parallel control port. See the Block Diagram. On the receive side, the device will
clock in the serial E1 stream via the RPOS and RNEG pins. The synchronizer will locate the frame and
multiframe patterns and establish their respective positions. This information will be used by the rest of
the receive side circuitry.
The DS2143 is an “off-line” framer, which means that all of the E1 se rial stream that goes into the device
will come out of it unchanged. Once the E1 data has been framed to, the signaling data can be extracted.
The two-frame elastic store can either be enabled or bypassed.
The transmit side clocks in the unframed E1 stream at TSER and add in the framing pattern and the
signaling. The line interface control port will update line interface devices that contain a serial port. The
parallel control port contains a multiplexed address and data structure which can be connected to either a
microcontroller or microprocessor.
Reader’s Note:
This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the E1 operating environment. There are 32 8-bit
timeslots in an E1 systems which are number 0 to 31. Timeslot 0 is transmitted first and received first.
These 32 timeslots are also referred to as channels with a numbering scheme of 1 to 32. Timeslot 0 is
identical to channel 1, timeslot 1 is identical to channel 2, and so on. Each timeslot (or channel) is made
up of 8 bits which are numbered 1 to 8. Bit number 1 is the MSB and is transmitted first. Bit number 8 is
the LSB and is transmitted last. Throughout this data sheet, the following abbreviations will be used:
FAS Frame Alignment Signal
CRC4 Cyclical Redundancy Check
CAS Channel Associated Signaling
CCS Common Channel Signaling
MF Multiframe
Sa Additional bits
Si International bits
E-bit CRC4 Error Bits
2 of 44
DS2143 FEATURES
Parallel control port
Onboard two-frame elastic store
CAS signaling bit extraction and insertion
Fully independent transmit and receive sections
Full alarm detection
Full access to Si and Sa bits
Loss of transmit clock detection
HDB3 coder/decoder
Full transmit transparency
Large error counters
Individual bit-by-bit Sa data link support circuitry
Programmable output clocks
Frame sync generation
Local loopback capability
Automatic CRC4 E-bit support
Loss of receive clock detection
G.802 E1 to T1 mapping support
DS2143 BLOCK DIAGRAM
DS2143/DS2143Q
3 of 44
DS2143/DS2143Q
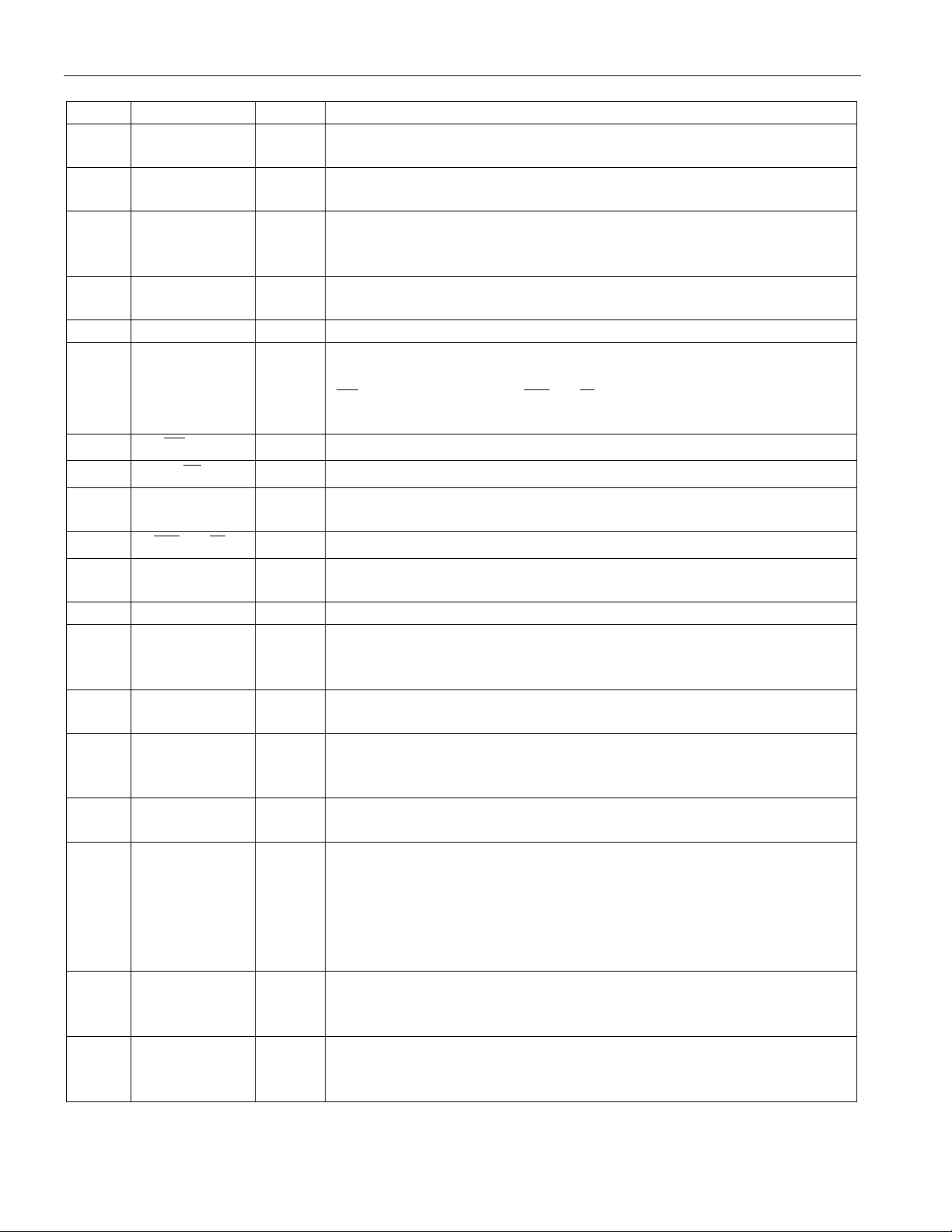
PIN DESCRIPTION Table 1
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
1TCLK ITransmit Clock. 2.048 MHz primary clock. A clock must be
applied at the TCLK pin for the parallel port to operate properly.
2TSER ITransmit Serial Data. Transmit NRZ serial data, sampled on the
falling edge of TCLK.
3TCHCLKOTransmit Channel Clock. 256 kHz clock which pulses high during
the LSB of each channel. Useful for parallel-to-serial conversion of
channel data. See Section 13 for timing details.
4
5
6-13 AD0-AD7 I/O Address/Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
14 BTS I Bus Type Select. Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap
15
16
17 ALE(AS) I Address Latch Enable (Address Strobe). A positive-going edge
18
19 RLINK O Receive Link Data. Outputs Sa bits. See Section 13 for timing
20 V
21 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock. 4 kHz to 20 kHz demand clock for the
22 RCLK I Receive Clock. 2.048 MHz primary clock. A clock must be applied
23 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock. 256 kHz clock which pulses high during
24 RSER O Receive Serial Data. Received NRZ serial data, updated on rising
25 RSYNC I/O Receive Sync. An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this
26
27
28 SYSCLK I System Clock. 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz clock. Only used when
TPOS
TNEG
RD (DS)
CS
WR (R/ W )
SS
RPOS
RNEG
O Transmit Bipolar Data. Updated on rising edge of TCLK. For
optical links, can be programmed to output NRZ data.
low to select Intel bus timing. This pin controls the function of
RD (DS), ALE(AS), and WR (R/W ) pins. If BTS=1, then these pins
assume the function listed in parentheses ().
I
Read Input (Data Strobe).
I Chip Select. Must be low to read or write the port.
serves to demultiplex the bus.
I
Write Input (Read/Write).
details.
- Signal Ground. 0.0 volts.
RLINK output. Controlled by RCR2. See Section 13 for timing
details.
at the RCLK pin for the parallel port to operate properly.
the LSB of each channel. Useful for serial to parallel conversion of
channel data. See Section 13 for timing details.
edges of RCLK.
pin which identifies either frame (RCR1.6=0) or multiframe
boundaries (RCR1.6=1). If the elastic store is enabled via the
RCR2.1, then this pin can be enabled to be an input via RCR1.5 at
which a frame boundary pulse is applied. See Section 13 for timing
details.
I Receive Bipolar Data Inpu ts. Sampled on falling edge of RCLK.
Tie together to receive NRZ data and disable BPV monitoring
circuitry.
the elastic store function is enabled via the RCR2.1. Should be tied
low in applications that do not use the elastic store.
4 of 44
DS2143/DS2143Q
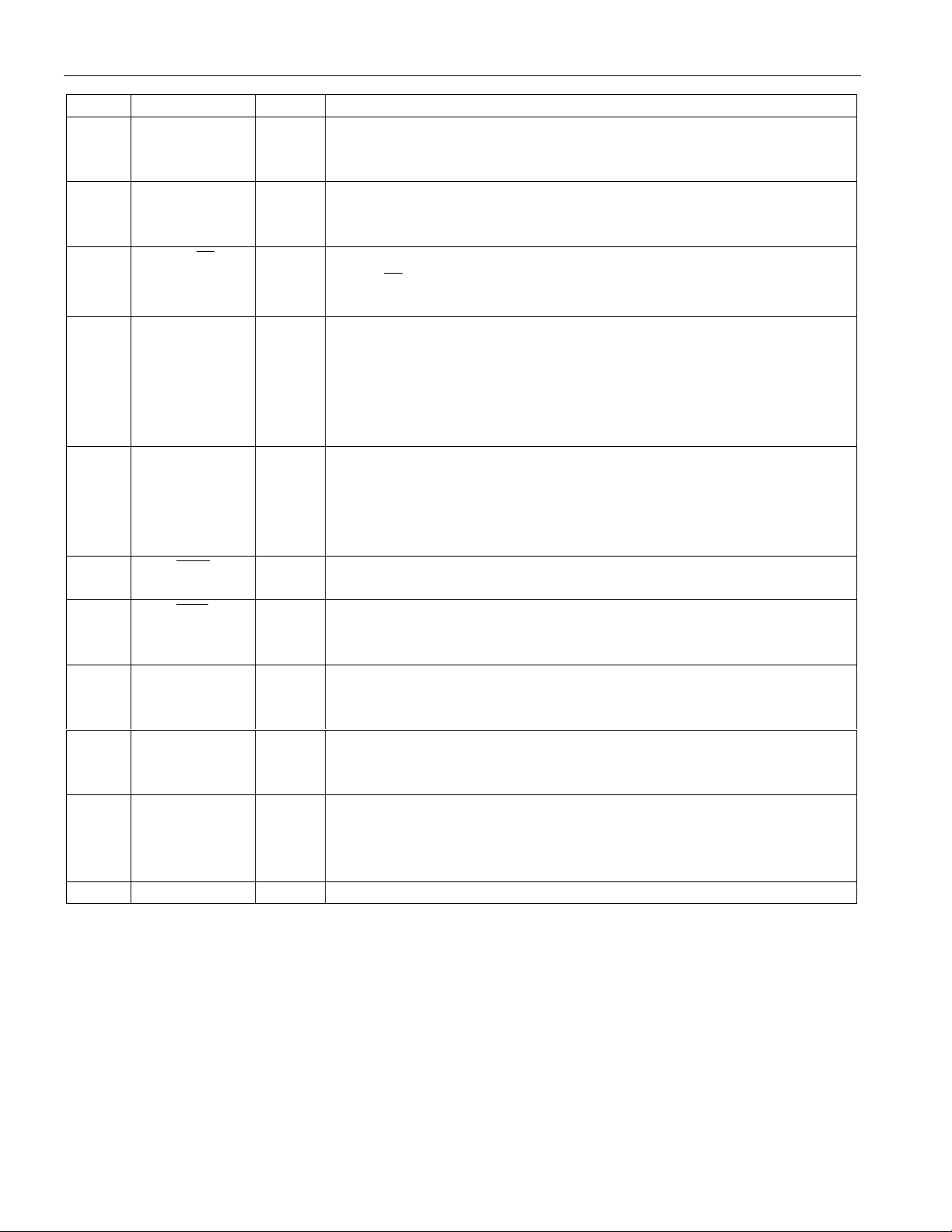
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
29 LI_SDI O Serial Port Data for the Line Interface. Connects directly to the
SDI input pin on the line interface. See Sections 12 and 13 for
timing details.
30 LI_CLK O Serial Port Clock for the Li ne Interface. Connects directly to the
SCLK input pin on the line interface. See Sections 12 and 13 for
timing details.
31
LI_CS
O Serial Port Chip Select for the L ine Interface. Connects directly
to the CS input pin on the line interface. See Sections 12 and 13 for
timing details.
32
33
RCHBLK
TCHBLK
O Receive/Transmit Channel Block. A user programmable output
that can be forced high or low during any of the 32 E1 channels.
Useful for blocking clocks to a serial UART or LAPD controller in
applications where not all E1 channels are used such as Fractional
E1 or ISDN-PRI. Also useful for locating individual channels in
drop-and-insert applications. See Sections 9 and 13 for details.
34 RLOS/LOTC O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock. A dual function
output. If TCR2.0=0, then this pin will toggle high when the
synchronizer is searching for the E1 frame and multiframe. If
TCR2.0=1, then this pin will toggle high if the TCLK pin has not
toggled for 5 µs.
35
INT2
O Receive Alarm Interrupt 2. Fla gs host controller during conditions
defined in Status Register 2. Active low, open drain output.
36
INT1
O Receive Alarm Interrupt 1. Flags host controller during alarm
conditions defined in Status Register 1. Active low, open drain
output.
37 TLCLK O Transmit Link Clock. 4 kHz to 20 kHz demand clock for the
TLINK input. Controlled by TCR2. See Section 13 for timing
details.
38 TLINK I Transmit Link Data. If enabled, this pin will be sampled on the
falling edge of TCLK to insert Sa bits. See Section 13 for timing
details.
39 TSYNC I/O Transmit Sync. A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or
CAS multiframe boundaries for the DS2143. Via TCR1.1, the
DS2143 can be programmed to output either a frame or multiframe
pulse at this pin. See Section 13 for timing details.
40 VDD - Positive Supply. 5.0 volts.
5 of 44
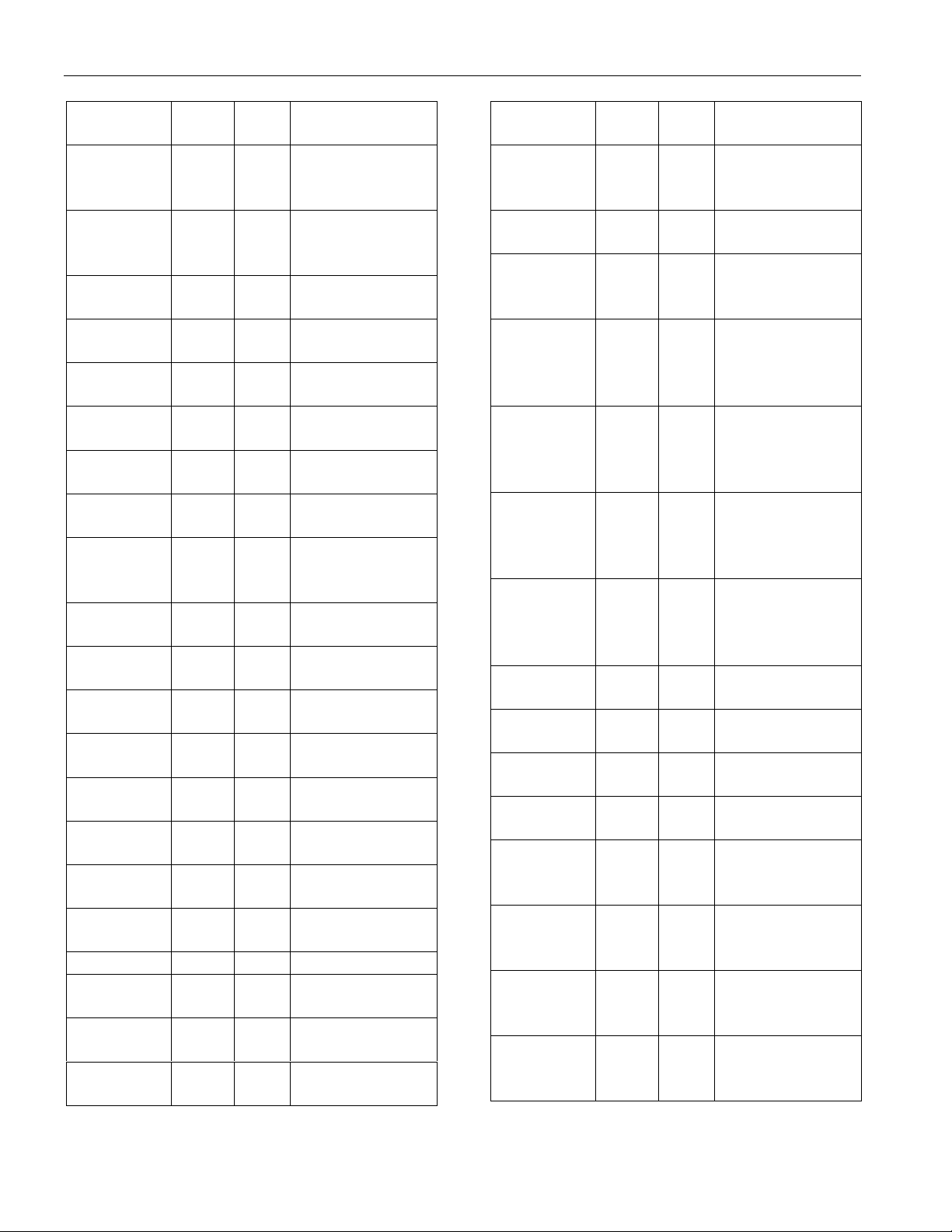
DS2143 REGISTER MAP
ADDRESS
A7 to A0
00000000 00 R Bipolar
00000001 01 R Bipolar
00000010 02 R CRC4 Count
00000011 03 R CRC4 Count
00000100 04 R E-Bit Count
00000101 05 R E-Bit Count
00000110 06 R/W Status Register
00000111 07 R/W Status Register
00001000 08 R/W Receive
00011110 1E R Synchronizer
00010110 16 R/W Interrupt Mask
00010111 17 R/W Interrupt Mask
00010000 10 R/W Receive Control
00010001 11 R/W Receive Control
00010010 12 R/W Transmit Control
00010011 13 R/W Transmit Control
00010100 14 R/W Common
00010101 15 R/W Test Register.
00011000 18 W LI Control
00011001 19 W LI Control
00100000 20 R/W Transmit Align
HEX R/W REGISTER
NAME
Violation Count
Register 1.
Violation Count
Register 2.
Register 1.
Register 2.
Register 1.
Register 2.
1.
2.
Information
Register.
Status Register.
Register 1.
Register 2.
Register 1.
Register 2.
Register 1.
Register 2.
Control Register.
Register Byte 1.
Register Byte 2.
Frame Register.
DS2143/DS2143Q
ADDRESS
A7 to A0
00100001 21 R/W Transmit Non-
00101111 2F R Receive Align
00011111 1F R Receive Non-
00100010 22 R/W Transmit
00100011 23 R/W Transmit
00100100 24 R/W Transmit
00100101 25 R/W Transmit
00100110 26 R/W Transmit Idle
00100111 27 R/W Transmit Idle
00101000 28 R/W Transmit Idle
00101001 29 R/W Transmit Idle
00101010 2A R/W Transmit Idle
00101011 2B R/W Receive Channel
00101100 2C R/W Receive Channel
00101101 2D R/W Receive Channel
HEX R/W REGISTER
NAME
Align Frame
Register.
Frame Register.
Align Frame
Register.
Channel
Blocking
Register 1.
Channel
Blocking
Register 2.
Channel
Blocking
Register 3.
Channel
Blocking
Register 4.
Register 1.
Register 2.
Register 3.
Register 4.
Definition
Register.
Blocking
Register 1.
Blocking
Register 2.
Blocking
Register 3.
6 of 44
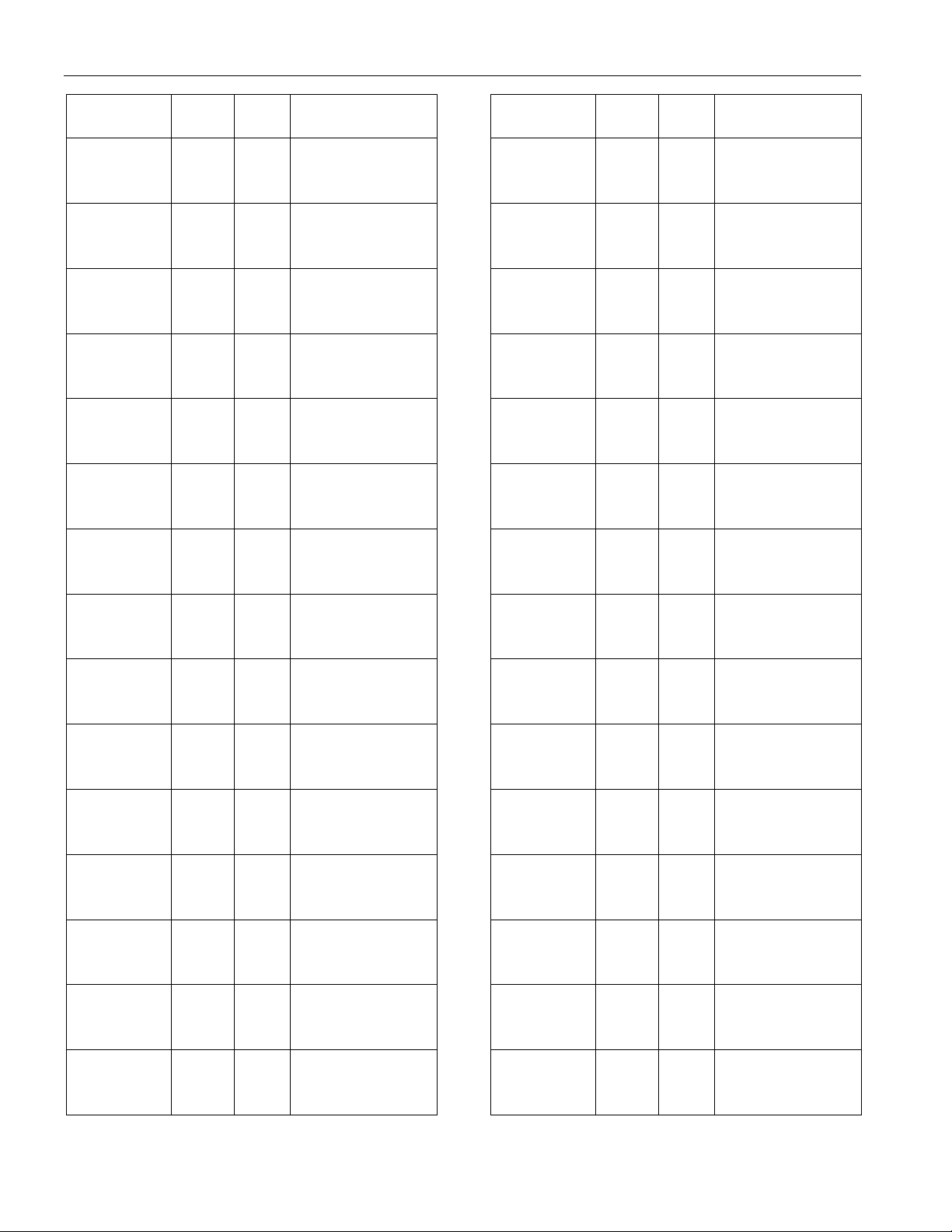
DS2143/DS2143Q
ADDRESS
A7 to A0
HEX R/W REGISTER
NAME
00101110 2E R/W Receive Channel
Blocking
Register 4.
00110000 30 R Receive
Signaling
Register 1.
00110001 31 R Receive
Signaling
Register 2.
00110010 32 R Receive
Signaling
Register 3.
00110011 33 R Receive
Signaling
Register 4.
00110100 34 R Receive
Signaling
Register 5.
00110101 35 R Receive
Signaling
Register 6.
00110110 36 R Receive
Signaling
Register 7.
00110111 37 R Receive
Signaling
Register 8.
00111000 38 R Receive
Signaling
Register 9.
00111001 39 R Receive
Signaling
Register 10.
00111010 3A R Receive
Signaling
Register 11.
00111011 3B R Receive
Signaling
Register 12.
00111100 3C R Receive
Signaling
Register 13.
00111101 3D R Receive
Signaling
Register 14.
ADDRESS
A7 to A0
HEX R/W REGISTER
NAME
00111110 3E R Receive
Signaling
Register 15.
00111111 3F R Receive
Signaling
Register 16.
01000000 40 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 1.
01000001 41 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 2.
01000010 42 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 3.
01000011 43 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 4.
01000100 44 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 5.
01000101 45 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 6.
01000110 46 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 7.
01000111 47 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 8.
01001000 48 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 9.
01001001 49 R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 10.
01001010 4A R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 11.
01001011 4B R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 12.
01001100 4C R/W Transmit
Signaling
Register 13.
7 of 44
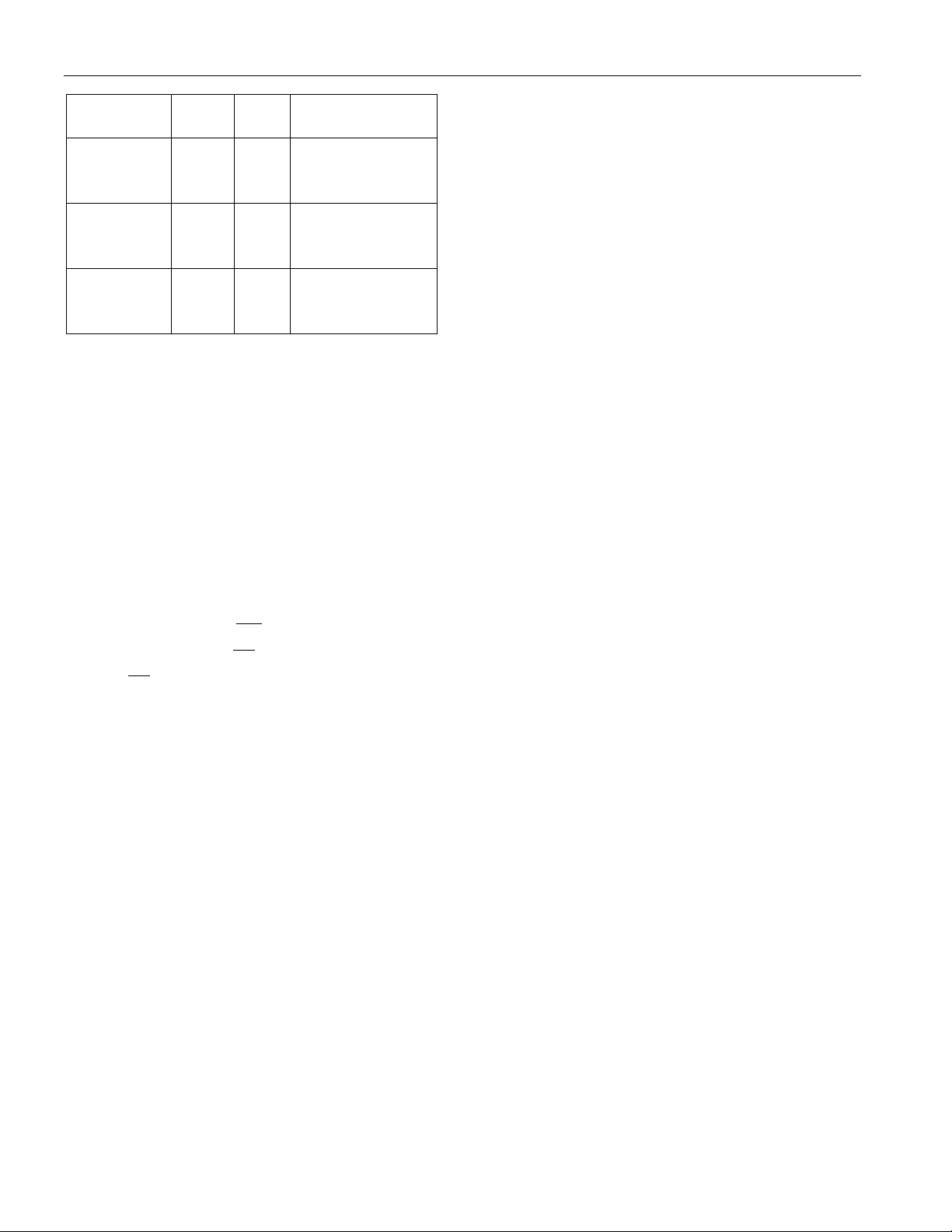
DS2143/DS2143Q
ADDRESS
A7 to A0
01001101 4D R/W Transmit
01001110 4E R/W Transmit
01001111 4F R/W Transmit
Note: All values indicated within the Address
column are hexadecimal.
HEX R/W REGISTER
NAME
Signaling
Register 14.
Signaling
Register 15.
Signaling
Register 16.
2.0 PARALLEL PORT
The DS2143 is controlled via a multiplexed bidirectional address/data bus by an external microcontroller
or microprocessor. The DS2143 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timin g configurations. If
the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola timing will be selected. All
Motorola bus signals are listed in parentheses (). See the timing diagrams in the AC Electrical
Characteristics for more details. The multiplexed bus on the DS2143 saves pins because the address
information and data information share the same signal paths. The addresses are presented to the pins in
the first portion of the bus cycle and data will be transferred on the pins durin g second portion of the bus
cycle. Addresses must be valid prior to the falling edge of ALE(AS), at which time the DS2143 latches
the address from the AD0 to AD7 pins. Valid write data must be present and held stable during the later
portion of the DS or WR pulses. In a read cycle, the DS2143 outputs a byte of data during the latter
portion of the DS or RD pulses. The read cycle is terminated and the bus returns to a high impedance
state as RD transitions high in Intel timing or as DS transitions low in Motorola timing.
3.0 CONTROL AND TEST REGISTERS
The operation of the DS2143 is configured via a set of five registers. T ypically, the control registers are
only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the DS2143 has been initialized, the control
registers will only need to be accessed when there is a chan ge in the s ystem configuration. There are two
Receive Control Registers (RCR1 and RCR2), two Transmit Control Registers (TCR1 and TCR2), and a
Common Control Register (CCR). Each of the five registers is described in this section.
The Test Register at address 15 hex is used by the factory in testing the DS2143. On power-up, the Test
Register should be set to 00 hex in order for the DS2143 to operate properly.
8 of 44

DS2143/DS2143Q
RCR1: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=10 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSMF RSM RSIO - - FRC SYNCE RESYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSMF RCR1.7 RS YNC Multiframe Function. Onl y used if the RSYNC pin is
programmed in the multiframe mode (RCR1.6=1).
0 = RSYNC outputs CAS multiframe boundaries
1 = RSYNC outputs CRC4 multiframe boundaries
RSM RCR1.6 RSYNC Mode Select.
0 = frame mode (see the timing in Section 13)
1 = multiframe mode (see the timing in Section 13)
RSIO RCR1.5 RSYNC I/O Select.
0 = RSYNC is an output (depends on RCR1.6)
1 = RSYNC is an input (only valid if elastic store enabled)
(note: this bit must be set to 0 when RCR2.1=0)
- RCR1.4 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
- RCR1.3 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
FRC RCR1.2 Frame Resync Criteria.
0 = resync if FAS received in error 3 consecutive times
1 = resync if FAS or bit 2 of non-FAS is received in error 3
consecutive times
SYNCE RCR1.1 Sync Enable.
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
RESYNC RCR1.0 Resync. When toggled from low to high, a resync is initiated.
Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
9 of 44
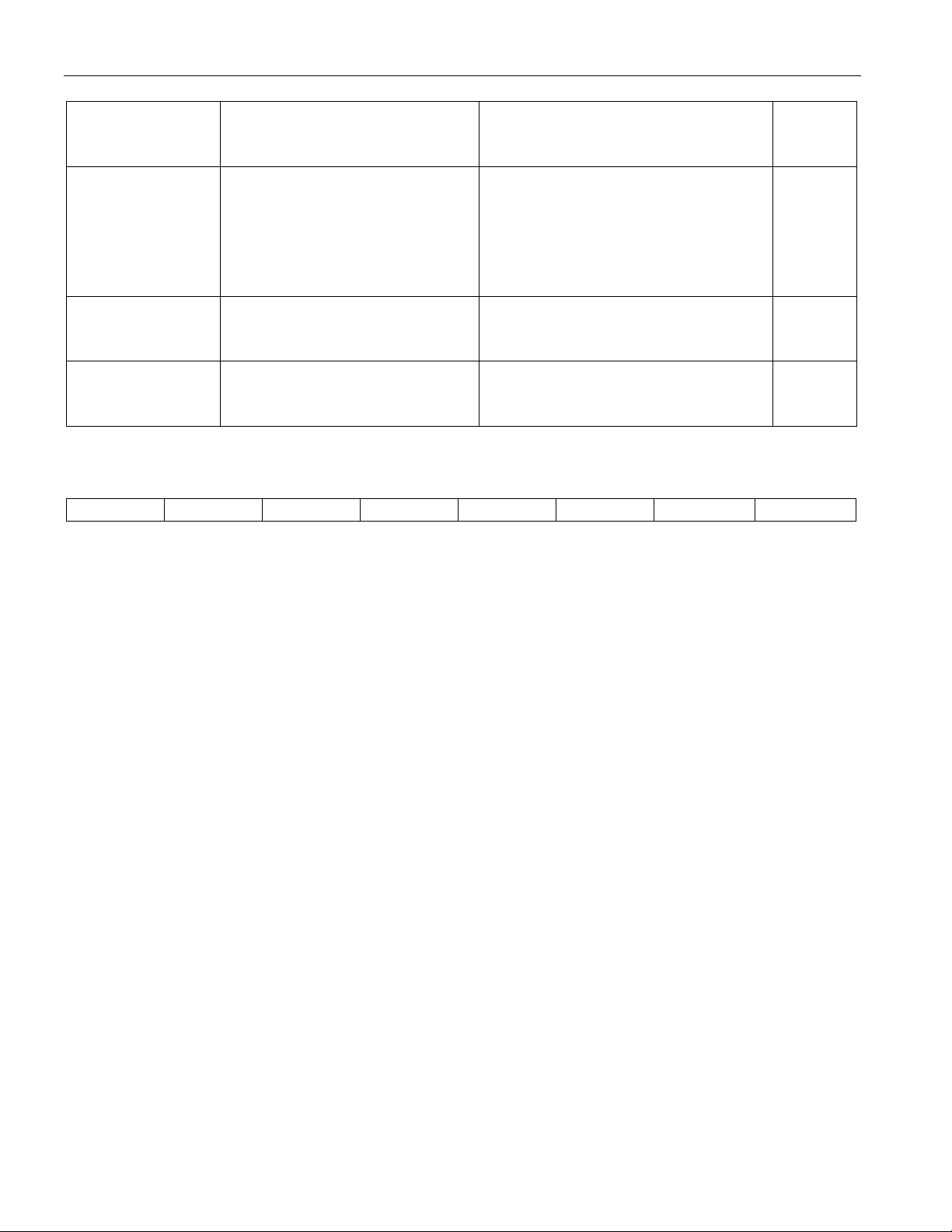
DS2143/DS2143Q
SYNC/RESYNC CRITERIA Table 2
FRAME OR
MULTIFRAME
LEVEL
FAS FAS present in frames N and N
CRC4 Two valid MF alignment words
CAS Valid MF alignment word
SYNC CRITERIA RESYNC CRITERIA
+ 2, and FAS not present in
frame N + 1.
found within 8 ms.
found and previous time slot 16
contains code other than all 0s.
Three consecutive incorrect FAS
received.
Alternate (RCR1.2=1) the above
criteria is met or three consecutive
incorrect bit 2 of non-FAS received.
915 or more CRC4 code words out
of 1000 received in error.
Two consecutive MF alignment
words received in error.
ITU
SPEC.
G.706
4.1.1
4.1.2
G.706
4.2
4.3.2
G.732
5.2
RCR2: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=11 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S SCLKM ESE -
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S RCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to 1 to report the Sa8 bit at the RLINK pin;
set to 0 to not report the Sa8 bit.
Sa7S RCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to 1 to report the Sa7 bit at the RLINK pin;
set to 0 to not report the Sa7 bit.
Sa6S RCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to 1 to report the Sa6 bit at the RLINK pin;
set to 0 to not report the Sa6 bit.
Sa5S RCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to 1 to report the Sa5 bit at the RLINK pin;
set to 0 to not report the Sa5 bit.
Sa4S RCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to 1 to report the Sa4 bit at the RLINK pin;
set to 0 to not report the Sa4 bit.
SCLKM RCR2.2 SYSCLK Mode Select.
0 = if SYSCLK is 1.544 MHz.
1 = if SYSCLK is 2.048 MHz.
ESE RCR2.1 Elastic Store Enable.
0 = elastic store is bypassed.
1 = elastic store is enabled.
- RCR2.0 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
10 of 44

DS2143/DS2143Q
TCR1: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=12 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
ODF TFPT T16S TUA1 TSiS TSA1 TSM TSIO
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ODF TCR1.7 Output Data Format.
0 = bipolar data at TPOS and TNEG.
1 = NRZ data at TPOS; TNEG=0.
TFPT TCR1.6 Transmit Timeslot 0 Pass Through.
0 = FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced internally from the
TAF and TNAF registers.
1 = FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced from TSER.
T16S TCR1.5 Transmit Timeslot 16 Data Select.
0 = sample timeslot 16 at TSER pin.
1 = source timeslot 16 from TS1 to TS16 registers.
TUA1 TCR1.4 Transmit Unframed All 1s.
0 = transmit data normally.
1 = transmit an unframed all 1s code at TPOS and TNEG.
TSiS TCR1.3 Transmit International Bit Select.
0 = sample Si bits at TSER pin.
1 = source Si bits from TAF and TNAF registers (in this mode,
TCR1.6 must be set to 0).
TSA1 TCR1.2 Transmit Signaling All 1s.
0 = normal operation.
1 = force timeslot 16 in every frame to all 1s.
TSM TCR1.1 TSYNC Mode Select.
0 = frame mode (see the timing in Section 13).
1 = CAS and CRC4 multiframe mode (see the timing in Section
13).
TSIO TCR1.0 TSYNC I/O Select.
0 = TSYNC is an input.
1 = TSYNC is an output.
11 of 44

DS2143/DS2143Q
TCR2: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=13 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S - AEBE P34F
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S TCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa8 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa8 bit.
Sa7S TCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa7 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa7 bit.
Sa6S TCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa6 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa6 bit.
Sa5S TCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa5 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa5 bit.
Sa4S TCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to 1 to source the Sa4 bit from the TLINK
pin; set to 0 to not source the Sa4 bit.
- TCR2.2 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
AEBE TCR2.1 Automatic E-Bit Enable.
0 = E-bits not automatically set in the transmit direction.
1 = E-bits automatically set in the transmit direction.
P34F TCR2.0 Function of Pin 34.
0 = Receive Loss of Sync (RLOS).
1 = Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC).
12 of 44

DS2143/DS2143Q
CCR: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER (Address=14 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LLB THDB3 TG802 TCRC4 RSM RHDB3 RG802 RCRC4
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LLB CCR.7 Local Loopback.
0 = loopback disabled.
1 = loopback enabled.
THDB3 CCR.6 Transmit HDB3 Enable.
0 = HDB3 disabled.
1 = HDB3 enabled.
TG802 CCR.5 Transmit G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
0 = do not force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26.
1 = force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26.
TCRC4 CCR.4 Transmit CRC4 Enable.
0 = CRC4 disabled.
1 = CRC4 enabled.
RSM CCR.3 Receive Signaling Mode Select.
0 = CAS signaling mode.
1 = CCS signaling mode.
RHDB3 CCR.2 Receive HDB3 Enable.
0 = HDB3 disabled.
1 = HDB3 enabled.
RG802 CCR.1 Receive G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
0 = do not force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
1 = force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26.
RCRC4 CCR.0 Receive CRC4 Enable.
0 = CRC4 disabled.
1 = CRC4 enabled.
LOCAL LOOPBACK
When CCR.7 is set to a 1, the DS2143 will enter a Local LoopBack (LLB) mode. This loopback is useful
in testing and debugging applications. In LLB, the DS2143 will loop data from the transmit side back to
the receive side. This loopback is synonymous with replacing the RCLK input with the TC LK si gnal, and
the RPOS/RNEG inputs with the TPOS/TNEG outputs. When LLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1. data at RPOS and RNEG will be ignored;
2. all receive side signals will take on timing synchronous with TCLK instead of RCLK;
3. all functions are available.
13 of 44
DS2143/DS2143Q
4.0 STATUS AND INFORMATION REGISTERS
There is a set of four registers that contain information on the current real time status of the DS2143:
Status Register 1 (SR1), Status Register 2 (S R2), Receive Information Register (RIR), and S ynchronizer
Status Register (SSR). When a particular event has occurred (or is occurri ng), the appropriate bit in one
of these three registers will be set to a 1. All of the bits in these registers operate in a latched fashion
(except for the SSR). This means that if an event occu rs and a bit is set to a 1 in an y of the registers, it
will remain set until the user reads that bit. The bit will be cleared when it is read and it will not be set
again until the event has occurred again or if the alarm(s) is still present.
The user will always precede a read of the SR1, SR2, and RIR registers with a write. The byte written to
the register will inform the DS2143 which bits the user wishes to read and have cleared. The user will
write a byte to one of these three registers, with a 1 in the bit positions he or she wishes to read and a 0 in
the bit positions he or she does not wish to obtain the latest information on. When a 1 is written to a bit
location, the read register will be updated with current value and it will be cleared. When a 0 is written to
a bit position, the read register will not be updated and the previous value will be held. A write to the
status and information registers will be immediately followed by a read of the same register. The read
result should be logically AND’ed with the mask byte that was just written and this value should be
written back into the same register to insure that the bit does indeed clear. This second write is ne cessary
because the alarms and events in the status registers occur as ynchronously in respect to their access via
the parallel port. This scheme allows an external microcontroller or microprocessor to individually poll
certain bits without disturbing the other bits in the register. This operation is key in controlling the
DS2143 with higher order software languages.
The SSR register operates differently than the other three. It is a read only register and it reports the status
of the synchronizer in real time. This register is not latched and it is not necessary to prec ede a read of
this register with a write.
The SR1 and SR2 registers have the unique ability to initiate a hardware interrupt via the INT1 and INT2
pins respectively. Each of the alarms and events in the SR1 and SR2 can be eithe r masked or unmasked
from the interrupt pins via the Interrupt Mask Register 1 (IMR1) and Interrupt Mask Register 2 (IMR2)
respectively.
14 of 44
 Loading...
Loading...