Dallas Semiconductor DS1314S-2, DS1314S, DS1314E, DS1314 Datasheet
1 of 11 111999
FEATURES
Converts CMOS SRAM into nonvolatile
memory
Unconditionally write-protects SRAM when
VCC is out of tolerance
Automatically switches to battery backup
supply when VCC power failure occurs
Monitors voltage of a lithium cell and
provides advanced warning of impending
battery failure
Signals low-battery condition on active low
Battery Warning output signal
Automatic V
CC
power-fail detection for 3.0V
or 3.3V power supplies
Space-saving 8-pin DIP and SOIC packages
Optional 16-pin SOIC and 20-pin TSSOP
versions reset processor when power failure
occurs and hold processor in reset during
system power-up
Industrial temperature range of -40°C to
+85°C
PIN ASSIGNMENT
PIN DESCRIPTION
V
CCI
- Power Supply Input
V
CCO
- SRAM Power Supply Output
V
BAT
- Backup Battery Input
CEI - Chip Enable Input
CEO - Chip Enable Output
TOL - V
CC
Tolerance Select
BW - Battery Warning Output
(Open Drain)
RST - Reset Output (Open Drain)
GND - Ground
NC - No Connection
DESCRIPTION
The DS1314 Nonvolatile Controller with Battery Monitor is a CMOS circuit which solves the application
problem of converting CMOS RAM into nonvolatile memory. Incoming power is monitored for an outof-tolerance condition. When such a condition is detected, chip enable is inhibited to accomplish write
protection and the battery is switched on to supply the RAM with uninterrupted power. Special circuitry
uses a low-leakage CMOS process which affords precise voltage detection at extremely low battery
consumption.
DS1314
3V Nonvolatile Controller with Lithium
Battery Monitor
www.dalsemi.com
1
2
3
4
20
19
18
17
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
12
13
14
15
16
NC
V
CCI
RST
NC
NC
BW
NC
CEO
NC
CEI
NC
V
CCO
NC
V
BAT
NC
NC
TOL
NC
NC
GND
DS1314E 20-Pin TSSOP
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
GND
TOL
V
BAT
V
CCO
V
CCI
BW
CEO
CEI
DS1314S-2 8-Pin SOIC
(150-mil)
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
GND
TOL
V
BAT
V
CCO
V
CCI
BW
CEO
CEI
DS1314 8-Pin DIP
(300-mil)
1
2
3
4
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
NC
V
CCO
NC
V
BAT
NC
TOL
NC
GND
NC
V
CCI
RST
NC
BW
CEO
NC
CEI
DS1314S 16-Pin SOIC
(300-mil)
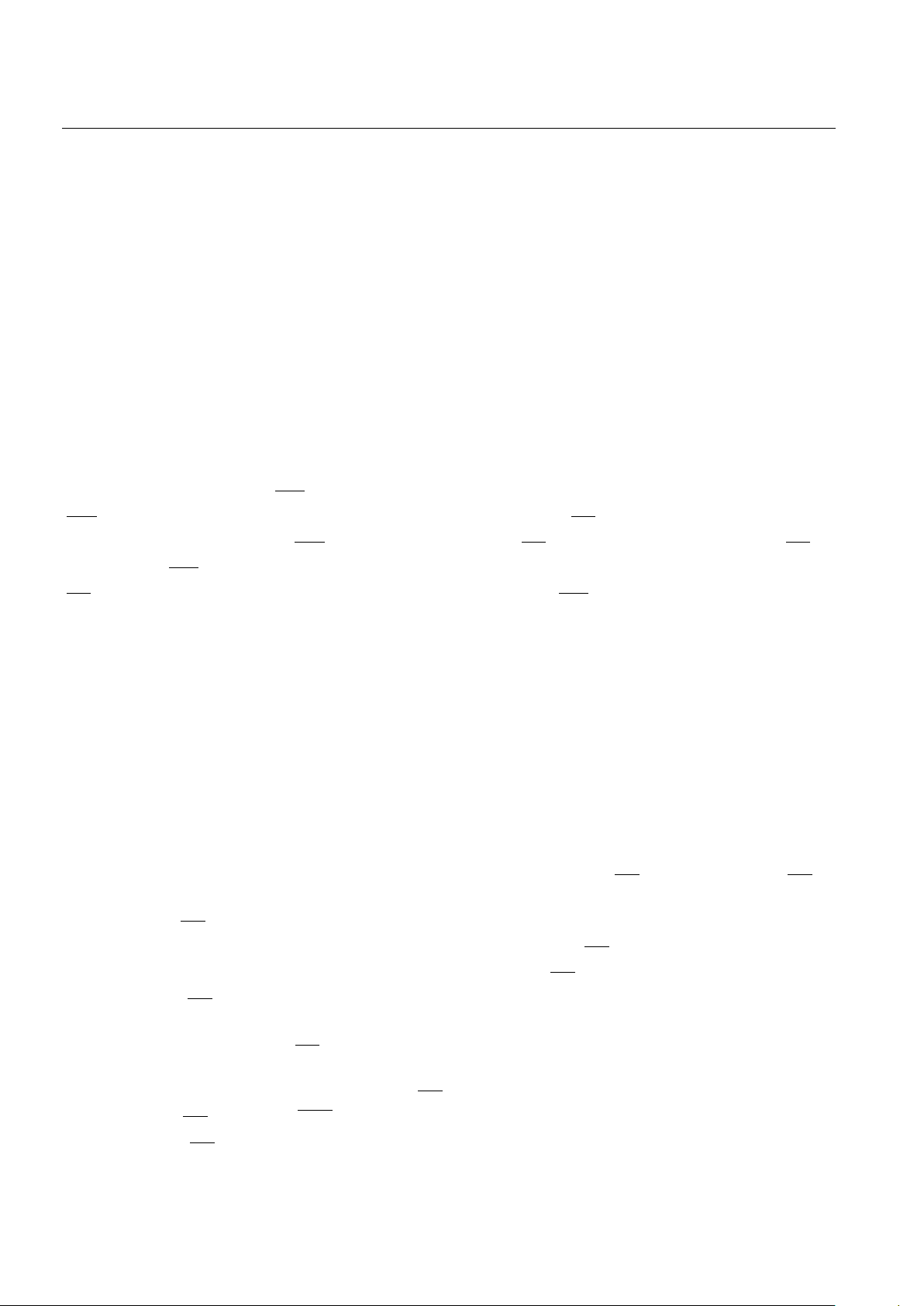
DS1314
2 of 11
In addition to battery-backup support, the DS1314 performs the important function of monitoring the
remaining capacity of the lithium battery and providing a warning before the battery reaches end-of-life.
Because the open-circuit voltage of a lithium backup battery remains relatively constant over the majority
of its life, accurate battery monitoring requires loaded-battery voltage measurement. The DS1314
performs such measurement by periodically comparing the voltage of the battery as it supports an internal
resistive load with a carefully selected reference voltage. If the battery voltage falls below the reference
voltage under such conditions, the battery will soon reach end-of-life. As a result, the Battery Warning
pin is activated to signal the need for battery replacement.
MEMORY BACKUP
The DS1314 performs all the circuit functions required to provide battery-backup for an SRAM. First, the
device provides a switch to direct power from the battery or the system power supply (V
CCI
). Whenever
V
CCI
is less than the switch point VSW and V
CCI
is less than the battery voltage V
BAT
, the battery is
switched in to provide backup power to the SRAM. This switch has voltage drop of less than 0.2 volts.
Second, the DS1314 handles power failure detection and SRAM write protection. V
CCI
is constantly
monitored, and when the supply goes out of tolerance, a precision comparator detects power failure and
inhibits chip enable output ( CEO ) in order to write-protect the SRAM. This is accomplished by holding
CEO to within 0.2 volts of V
CCO
when V
CCI
is out of tolerance. If CEI is (active) low at the time that
power failure is detected, the CEO signal is kept low until CEI is brought high again. Once CEI is
brought high, CEO is taken high and held high until after V
CCI
has returned to its nominal voltage level. If
CEI is not brought high by 1.5 µs after power failure is detected, CEO is forced high at that time. This
specific scheme for delaying write protection for up to 1.5 µs guarantees that any memory access in
progress when power failure occurs will complete properly. Power failure detection occurs at 3.0V
nominal (3.3V supply) when the TOL pin is wired to GND or at 2.7V nominal (3.0V supply) when TOL
is connected to V
CCO
.
BATTERY VOLTAGE MONITORING
The DS1314 automatically performs periodic battery voltage monitoring at a factory-programmed time
interval of 24 hours. Such monitoring begins within t
REC
after V
CCI
rises above V
CCTP
, and is suspended
when power failure occurs.
After each 24-hour period (t
BTCN
) has elapsed, the DS1314 connects V
BAT
to an internal 1.2 MΩ=test
resistor (R
INT
) for one second (t
BTPW
). During this one second, if V
BAT
falls below the factory-
programmed battery voltage trip point (V
BTP
), the battery warning output BW is asserted. While BW is
active battery testing will be performed with period t
BTCW
to detect battery removal and replacement.
Once asserted,
BW remains active until the battery is physically removed and replaced by a fresh cell.
The battery is still re-tested after each V
CC
power-up, however, even if BW was active on power-down. If
the battery is found to be higher than V
BTP
during such testing, BW is deasserted and regular 24-hour
testing resumes.
BW has an open-drain output driver.
Battery replacement following BW activation is normally done with V
CCI
nominal so that SRAM data is
not lost. During battery replacement, the minimum time duration between old battery detachment and
new battery attachment (t
BDBA
) must be met or BW will not deactivate following attachment of the new
battery. Should BW not deactivate for this reason, the new battery can be detached for t
BDBA
and then re-
attached to clear BW .

DS1314
3 of 11
NOTE: The DS1314 cannot constantly monitor an attached battery because such monitoring would
drastically reduce the life of the battery. As a result, the DS1314 only tests the battery for one second out
of every 24 hours and does not monitor the battery in any way between tests. If a good battery (one that
has not been previously flagged with BW ) is removed between battery tests, the DS1314 may not
immediately sense the removal and may not activate BW until the next scheduled battery test. If a battery
is then reattached to the DS1314, the battery may not be tested until the next scheduled test.
NOTE: Battery monitoring is only a useful technique when testing can be done regularly over the entire
life of a lithium battery. Because the DS1314 only performs battery monitoring when VCC is nominal,
systems which are powered-down for excessively long periods can completely drain their lithium cells
without receiving any advanced warning. To prevent such an occurrence, systems using the DS1314
battery monitoring feature should be powered-up periodically (at least once every few months) in order to
perform battery testing. Furthermore, anytime BW is activated on the first battery test after a power-up,
data integrity should be checked via checksum or other technique.
POWER MONITORING
DS1314S and DS1314E varieties have an additional reset pin. These varieties detect out-of-tolerance
power supply conditions and warn a processor-based system of impending power failure. When V
CCI
falls
below the trip point level defined by the TOL pin (V
CCTP
), the V
CCI
comparator activates the reset signal
RST . Reset occurs at 3.0V nominal (3.3V supply) when the TOL pin is connected to GND or at 2.7V
nominal (3.0V supply) when TOL is connected to V
CCO
.
RST also serves as a power-on reset during power-up. After V
CCI
exceeds V
CCTP
, RST will be held active
for 200 ms nominal (t
RPU
). This reset period is sufficiently long to prevent system operation during
power-on transients and to allow t
REC
to expire. RST has an open-drain output driver.
FRESHNESS SEAL MODE
When the battery is first attached to the DS1314 without VCC power applied, the device does not
immediately provide battery-backup power on V
CCO
. Only after V
CCI
exceeds V
CCTP
and later falls below
both VSW and V
BAT
will the DS1314 leave Freshness Seal Mode and provide battery-backup power. This
mode allows a battery to be attached during manufacturing but not used until after the system has been
activated for the first time. As a result, no battery energy is drained during storage and shipping.
DS1314
4 of 11
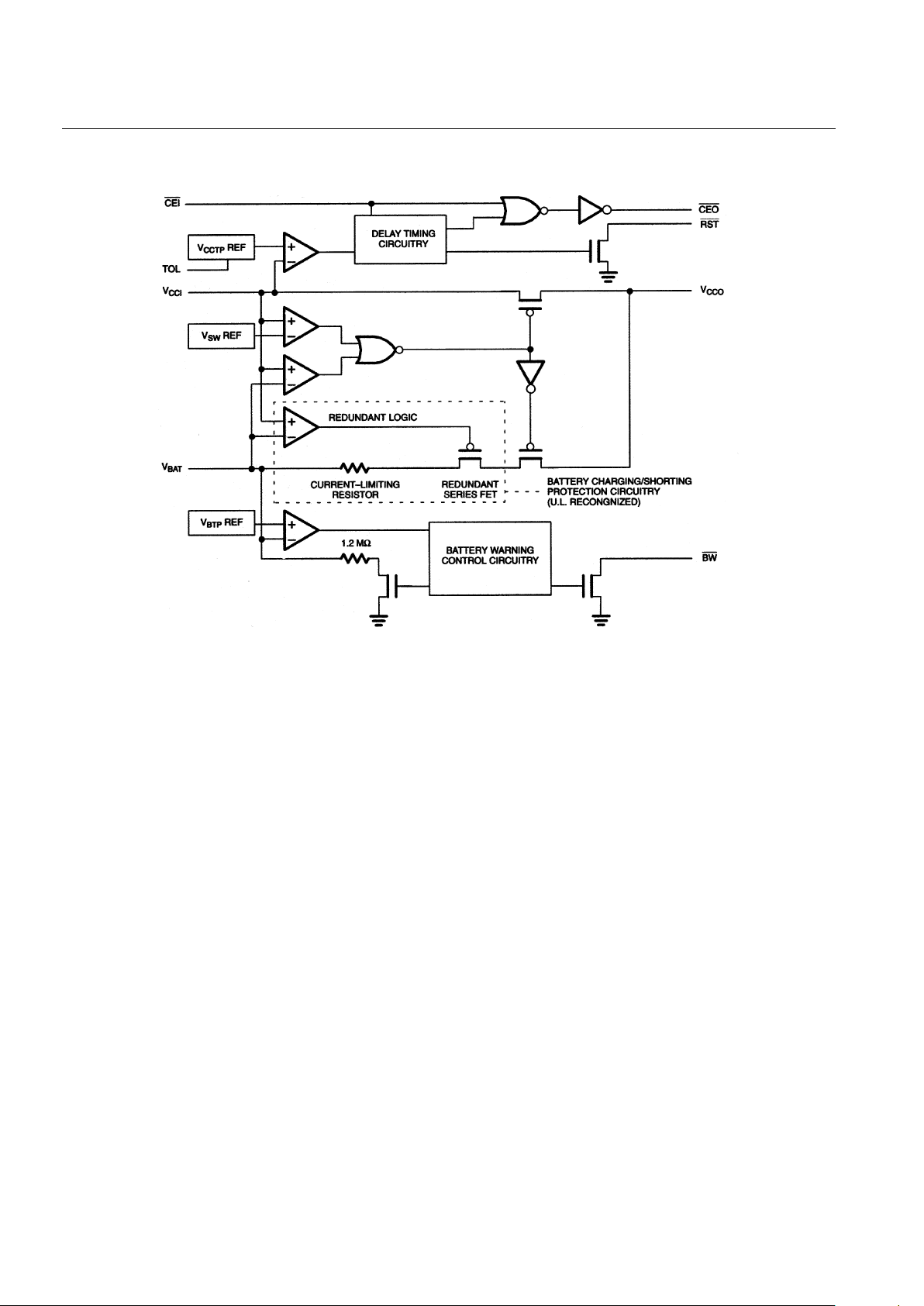
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
 Loading...
Loading...