Dallas Semiconductor DS1239S-5N, DS1239S-5, DS1239S-10, DS1239-5, DS1239-10 Datasheet
1 of 4 111899
FEATURES
Provides necessary control for start up and
shutdown of power supply from keyboard
Holds microprocessor in check during power
transients
Halts and restarts an out-of-control
microprocessor
Monitors push button for external override
Warns microprocessor of an impending power
failure
Converts CMOS SRAM into nonvolatile
memory
Unconditionally write-protects memory when
power supply is out of tolerance
Consumes less than 100 nA of battery current
Controls external power switch for high
current applications
Accurate 10% power supply monitoring
Optional 5% power supply monitoring
designated DS1239-5
Provides orderly shutdown in nonvolatile
microprocessor applications
Supplies necessary control for low-power
“stop mode” in battery operate hand-held
applications
Standard 16-pin DIP or space-saving 16-pin
SOIC
Optional industrial temperature range -40°C
to +85°C
PIN ASSIGNMENT
PIN DESCRIPTION
V
BAT
- +3 Volt Battery Input
V
CCO
- Switched SRAM Supply Output
VCC - +5 Volt Power Supply Input
GND - Ground
PF - Power Fail (Active High)
PF - Power Fail (Active Low)
WC/
SC - Wake-Up Control (Sleep)
PSI - Power Supply Control Input
IN - Early Warning Input
NMI - Non-Maskable Interrupt
ST - Strobe Input
CEO - Chip Enable Output
CEI - Chip Enable Input
PBRST - Pushbutton Reset Input
RST - Reset Output (Active low)
PSO - Power Supply Control Outputs
DESCRIPTION
The DS1239 MicroManager provides all the necessary functions for power supply control and
monitoring, reset control, and memory backup in microprocessor-based systems. Using the DS1239, an
AC power switch is no longer required for microprocessor-based systems. A keyboard control system for
power supply start up and shutdown is provided through the use of the Power Suppl y Control Input and
Output. In other respects, the DS1239 is functionally identical to a DS1236 in the NMOS mode. For a
complete description of the other DS1239 features, refer to the DS1236 data sheet. Pin-out of the
DS1239
MicroManager Chip
www.dalsemi.com
DS1239 16-Pin SOIC (300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings Section
VBAT
VCCO
VCC
PSO
RST
PBRST
1
2
3
16
15
14
GND CEI413
PF
PF
WC/SC
CEO
ST
NMI
5
6
7
12
11
10
PSI IN
89
DS1239 16-Pin DIP (300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings Section
VBAT
VCCO
VCC
PSO
RST
PBRST
1
2
3
16
15
14
GND CEI413
PF
PF
WC/SC
CEO
ST
NMI
5
6
7
12
11
10
PSI IN89
DS1239
2 of 4
DS1239 is identical to the DS1236 with two exceptions. The RC and RST pins have been replaced with
PSI and PSO, respectively. Other pins and functions operate exactly as the DS1236 in NMOS mode.
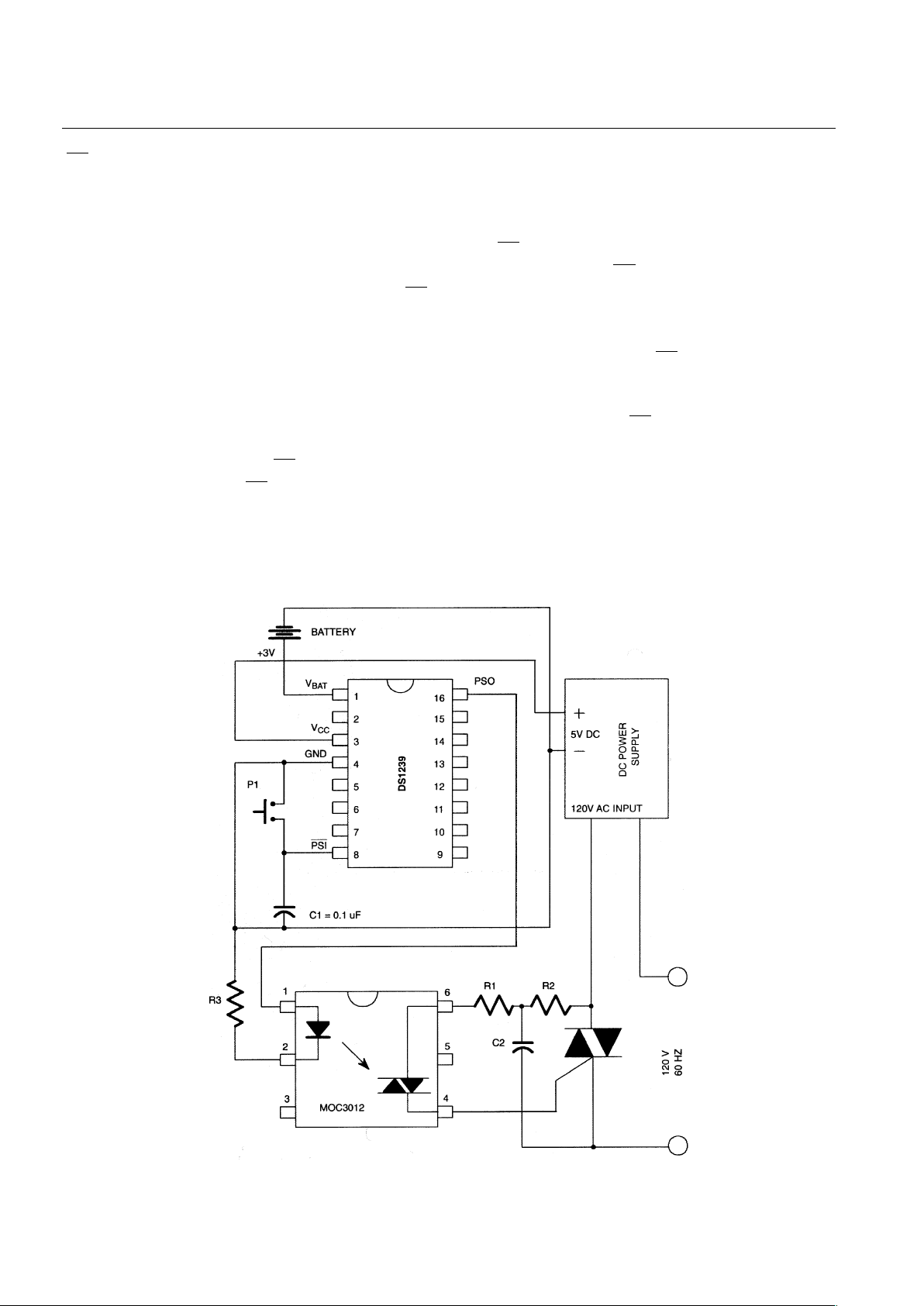
POWER SUPPLY CONTROL
The DS1239 facilitates the power-up and power-down sequencing of a main power supply from a
keyboard or pushbutton. The Power Supply Control Input (
PSI ) and Powe r Supply Control Output (PSO)
are used for this purpose. Prior to establishing a voltage on VCC (+5V), the PSI is internally held at a high
level at all times with the V
BAT
supply. When PSI is forced low via a keypad or other source, the PSO is
connected to the V
BAT
to provide a high level. As shown in Figure 1, this active hi gh signal can be wired
directly to an optically isolated SCR to initiate an AC to DC power-up sequence. This in turn will provide
the supply voltage for VCC. The timing is illustrated in Figure 2. Holding the PSI input low, the PSO
output will supply a connection to the V
BAT
pin until the VCC reaches V
BAT
, or a maximum of 500 ms. If
the supply voltage on VCC rises above the V
BAT
level before the t
PSI
timeout, the PSO pin will remain high
and track the VCC input. If VCC does not rise above V
BAT
before either t
PSI
or PSI is allowed to return to a
high level, the PSO output will return to tristate. Once the PSO output and V
CC
are set at a high level, a
subsequent falling edge on PSI will tristate PSO to initiate a shut down condition. The 10 microamp
current supplied by the
PSI pin allows the use of a 0.1 µF capacitor as a simple pushbutton debounce
circuit. The battery size for this application must be selected to provide the SCR on-current for the power
supply response time and is consequently application-specific.
POWER SUPPLY CONTROL Figure 1
 Loading...
Loading...