Dallas Semiconductor DS1236S-5, DS1236S-10N, DS1236S-10, DS1236N-5, DS1236N-10 Datasheet
...
1 of 19 111899
FEATURES
Holds microprocessor in check during power
transients
Halts and restarts an out-of-control
microprocessor
Monitors pushbutton for external override
Warns microprocessor of an impending power
failure
Converts CMOS SRAM into nonvolatile
memory
Unconditionally write-protects memory when
power supply is out of tolerance
Consumes less than 100 nA of battery current
at 25°C
Controls external power switch for high
current applications
Accurate 10% power supply monitoring
Optional 5% power supply monitoring
designated DS1236-5
Provides orderly shutdown in nonvolatile
microprocessor applications
Supplies necessary control for low-power
“stop mode” in battery operated hand-held
applications
Standard 16-pin DIP or space-saving 16-pin
SOIC
Optional industrial temperature range -40°C
to +85°C
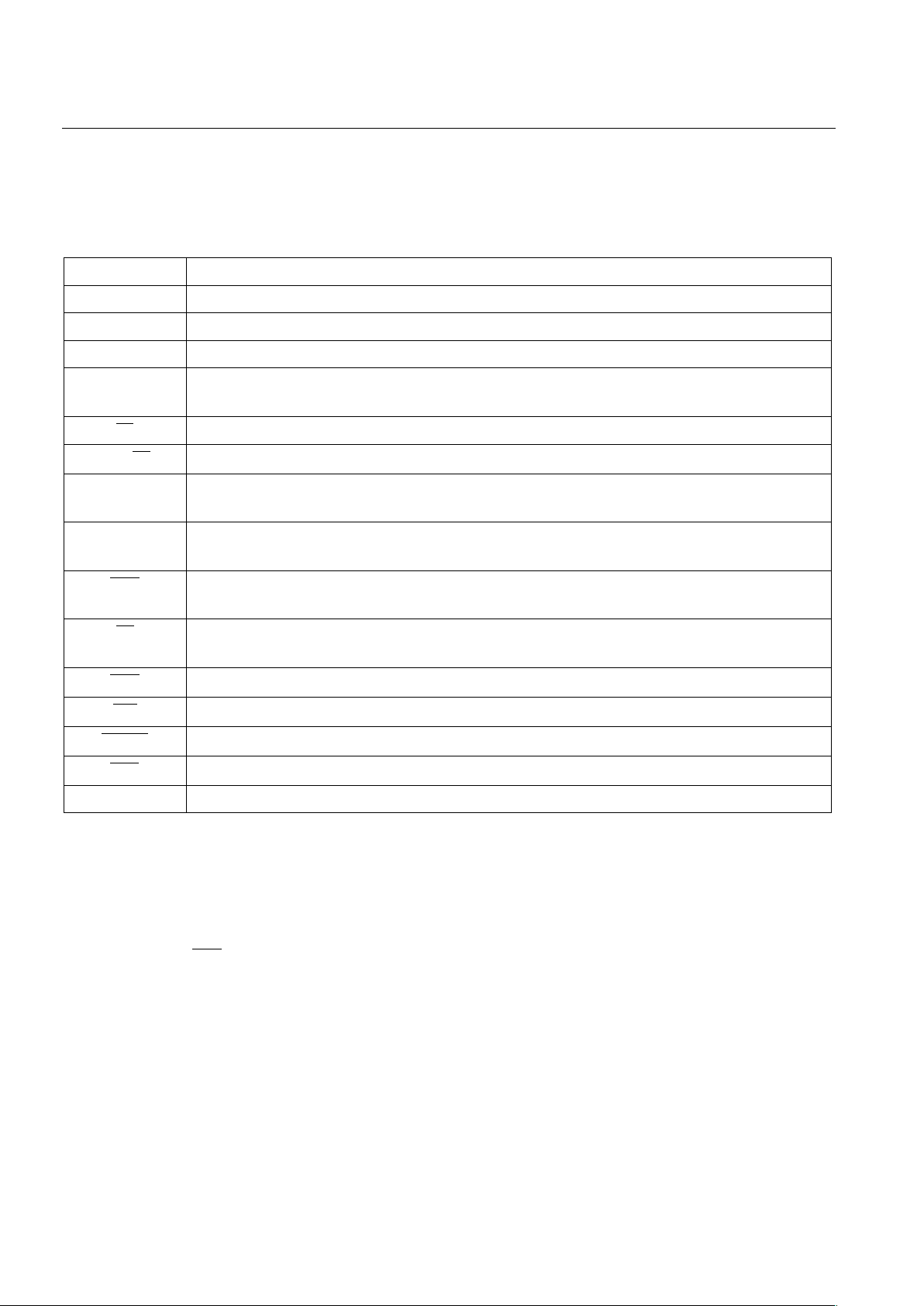
PIN ASSIGNMENT
PIN DESCRIPTION
V
BAT
- +3-Volt Battery Input
V
CCO
- Switched SRAM Supply Output
VCC - +5-Volt Power Supply Input
GND - Ground
PF - Power-Fail (Active High)
PF - Power-Fail (Active Low)
WC/
SC - Wake-Up Control (Sleep)
RC - Reset Control
IN - Early Warning Input
NMI - Non-Maskable Interrupt
ST - Strobe Input
CEO - Chip Enable Output
CEI - Chip Enable Input
PBRST - Pushbutton Reset Input
RST - Reset Output (Active Low)
RST - Reset Output (Active High)
DESCRIPTION
The DS1236 MicroManager Chip provides all the necessary functions for power supply monitoring, res et
control, and memory backup in microprocessor-based systems. A precise internal voltage reference and
comparator circuit monitor power supply status. When an out-of-tolerance condition occurs, the
microprocessor reset and power-fail outputs are forced active, and static RAM control unconditionally
write protects external memory. The DS1236 also provides early warning detection of a user-defined
threshold by driving a non-maskable interrupt. External reset control is provided by a pushbutton reset
DS1236
MicroManager Chip
www.dalsemi.com
16-Pin SOIC (300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings Section
VBAT
VCCO
VCC
RST
RST
PBRST
1
2
3
16
15
14
GND CEI413
PF
PF
WC/SC
CEO
ST
NMI
5
6
7
12
11
10
RCI IN
89
16-Pin DIP (300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings Section
VBAT
VCCO
VCC
RST
RST
PBRST
1
2
3
16
15
14
GND CEI413
PF
PF
WC/SC
CEO
ST
NMI
5
6
7
12
11
10
RC IN89
DS1236
2 of 19
input which is debounced and activates reset outputs. An internal watchdog timer can also force the reset
outputs to the active state if the strobe input is not driven low prior to watchdog timeout. Reset control
and wake-up/sleep control inputs also provide the necessary signals for orderly shutdown and startup in
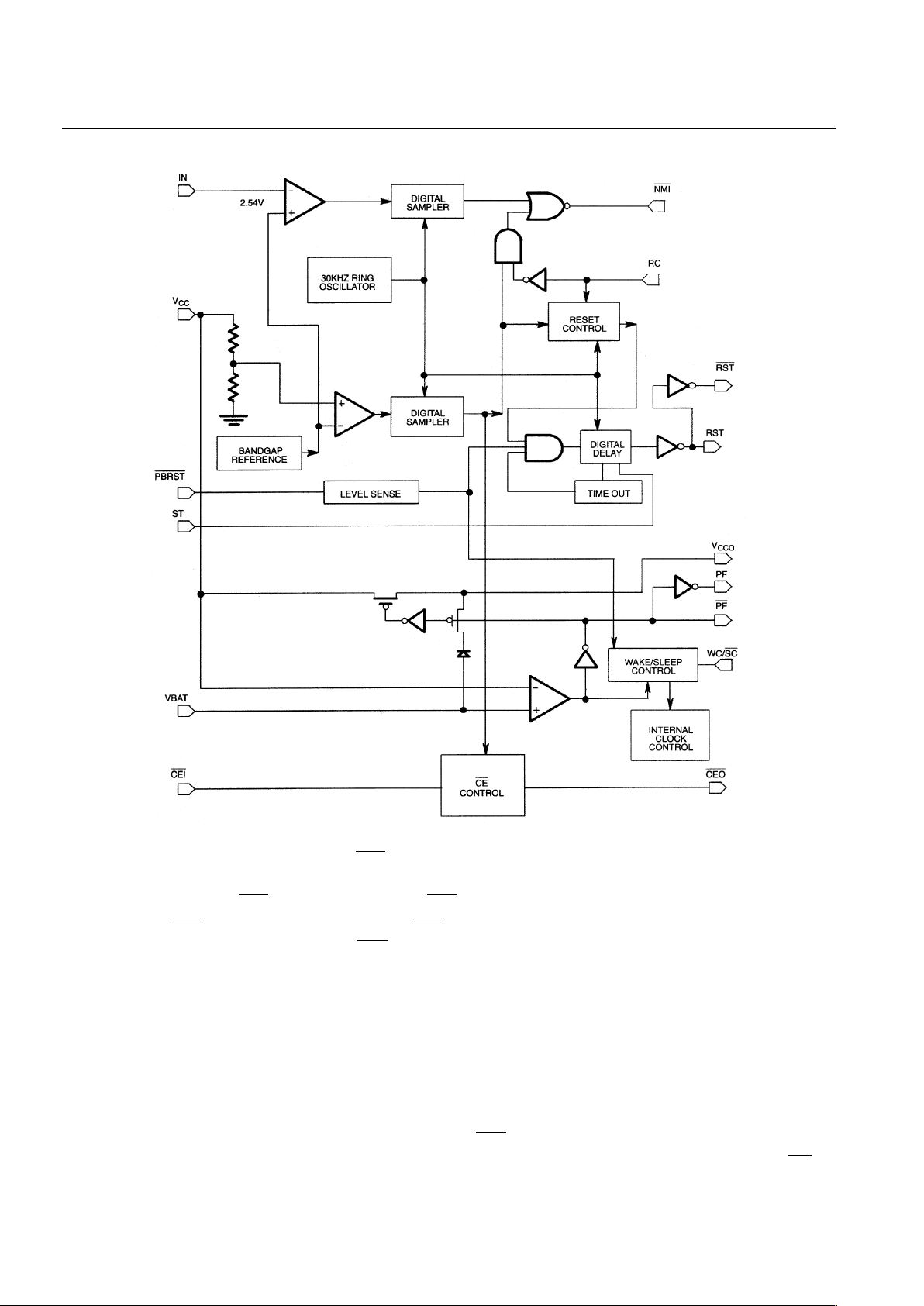
battery backup and battery operated applications. A block diagram of the DS1236 is shown in Figure 1.
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NAME DESCRIPTION
V
BAT
+3V battery input provides nonvolatile operation of control functions.
V
CCO
VCC output for nonvolatile SRAM applications.
V
CC
+5V primary power input.
PF Power-fail indicator, active high, used for external power switching as shown in
Figure 9.
PF
Power-fail indicator, active low.
WC/SC
Wake-up and Sleep control. Invokes low-power mode.
RC
Reset control input. Determines reset output. Normally low for NMOS processors and
high for battery backed CMOS processors.
IN Early warning power-fail input. This voltage sense point can be tied (via resistor
divider) to a user-selected voltage.
NMI
Non-maskable interrupt. Used in conjunction with the IN pin to indicate an impending
power failure.
ST
Strobe input. A high-to-low transition will reset the watchdog timer, indicating that
software is still in control.
CEO
Chip enable output. Used with nonvolatile SRAM applications.
CEI
Chip enable input.
PBRST
Pushbutton reset input.
RST
Active low reset output.
RST Active high reset output.
PROCESSOR MODE
A distinction is often made between CMOS and NMOS processor systems. In a CMOS system, power
consumption may be a concern, and nonvolatile operation is possible by battery backing both the SRAM
and the CMOS processor. All resources would be maintained in the absence of VCC. A power-down reset
is not issued since the low-power mode of most CMOS processors (Stop) is terminated with a Reset. A
pulsed interrupt (
NMI ) is issued to allow the CMOS processor to invoke a sleep mode to save power. For
this case, a power-on reset is desirable to wake up and initialize the processor. The CMOS mode is
invoked by connecting RC to V
CCO
.
An NMOS processor consumes more power, and consequently ma y not be battery backed. In this case, it
is desirable to notify the processor of a power-fail, then keep it in reset during the loss of VCC. This avoids
intermittent or aberrant operation. On power-up, the processor will continue to be reset until V
CC
reaches
an operational level to provide an orderly start. The NMOS mode is invoked by connecting RC to ground.

DS1236
3 of 19
POWER MONITOR
The DS1236 employs a band gap voltage reference and a precision comparator to monitor the 5-volt
supply (VCC) in microprocessor-based systems. When an out-of-tolerance condition occurs, t he RST and
RST outputs are driven to the active state. The V
CC
trip point (V
CCTP
) is set for 10% operation so that the
RST and RST outputs will become active as VCC falls below 4.5 volts (4.37 typical). The V
CCTP
for the
5% operation option (DS1236-5) is set for 4.75 volts (4.62 typical). The RST and RST signals are
excellent for microprocessor reset control, as processing is stopped at the last possible moment of in-
tolerance V
CC
. On power-up, the RST and RST signals are held active for a minimum of 25 ms (100 ms
typical) after V
CCTP
is reached to allow the power supply and microprocessor to stabilize. Note: The
operation described above is obtained with the reset control pin (RC) connected to GND (NMOS mode).
Please review the reset control section for more information.
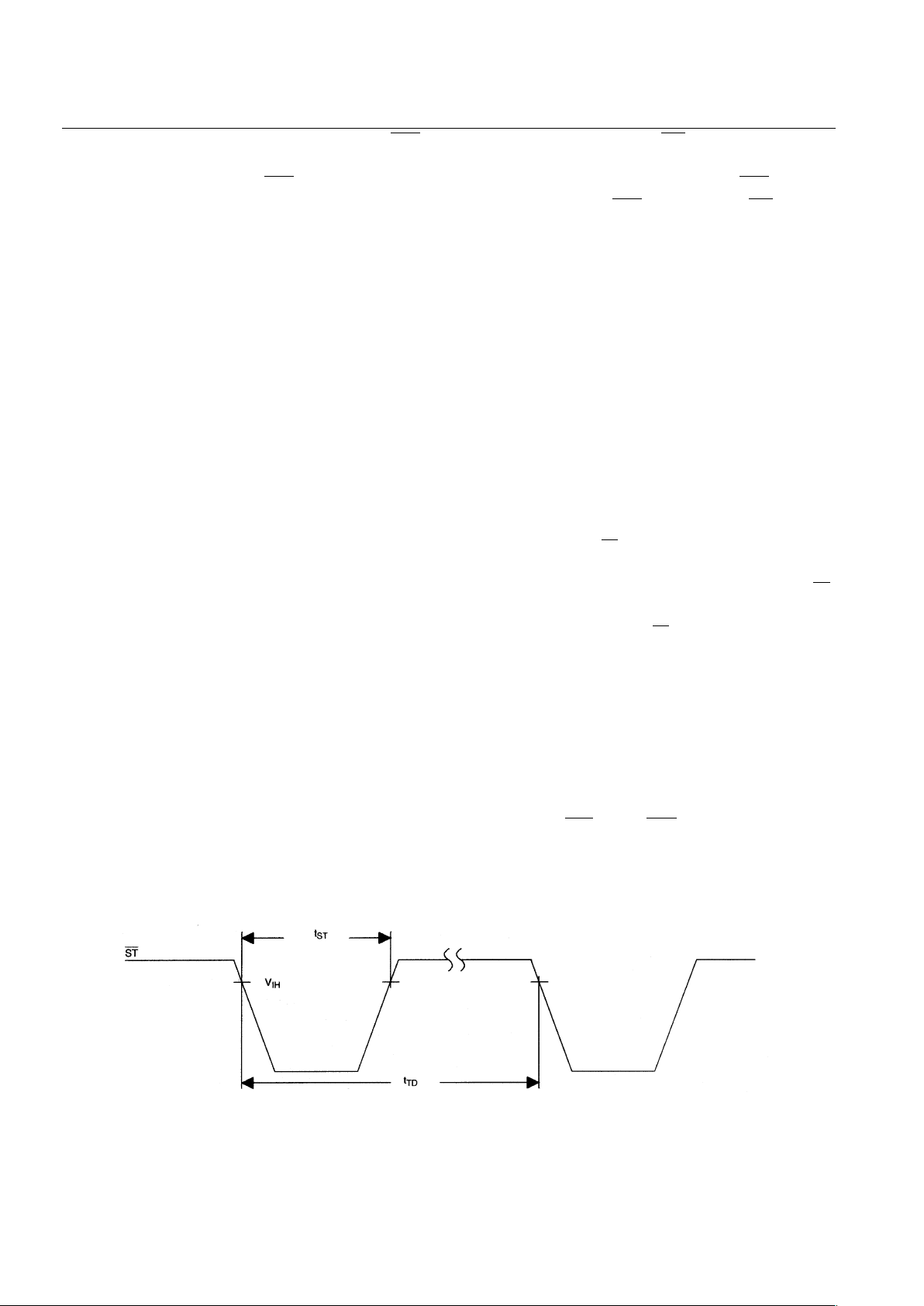
WATCHDOG TIMER
The DS1236 provides a watchdog timer function which forces the RST and RST signals to the active
state when the strobe input (ST ) is not stimulated for a predetermined time period. This time period is 400
ms typically with a maximum time-out of 600 ms. The watchdog time-out period be gins as soon as RST
and RST are inactive. If a high-to-low transition occurs at the ST input prior to time-out, the watchdog
timer is reset and begins to time out again. The ST input timing is shown in Figure 2. To guarantee the
watchdog timer does not time out, a high-to-low transition on ST must occur at or less than 100 ms
(minimum time-out) from a reset. If the watchdog timer is allowed to time out, the RST and RST outputs
are driven to the active state for 25 ms minimum. The ST input can be derived from microprocessor
address, data, and/or control signals. Under normal operating conditions, these signals would routinely
reset the watchdog timer prior to time-out. If the watchdog timer is not required, two methods have been
provided to disable it.
Permanently grounding the IN pin in the CMOS mode (RC=1) will disable the watchdog. In normal
operation with RC=1, the watchdog is disabled as soon as the IN pin is below VTP. With IN grounded, an
NMI output will occur only at power-up, or when the ST pin is strobed. As shown in the Figure 3, a
falling edge on ST will generate an NMI when IN is below VTP. This allows the processor to verify that
power is between VTP and V
CCTP
, as an NMI will be returned immediately after the ST strobe. The
watchdog timer is not affected by the IN pin when in NMOS mode (RC=0).
If the NMI signal is required to monitor supply voltages, the watchdog may also be disabled by leaving
the ST input open. Independent of the state of the RC pin, the watchdog is also disabled as soon as V
CC
falls to V
CCTP
.
PUSHBUTTON RESET
An input pin is provided on the DS1236 for direct connection to a pushbutton. The pushbutton reset input
requires an active low signal. Internally, this input is pulled high by a 10k resistor whenever VCC is
greater than V
BAT
. The PBRST pin is also debounced and timed such that the RST and RST outputs are
driven to the active state for 25 ms minimum. This 25 ms delay begins as the pushbutton is released from
a low level. A typical example of the power monitor, watchdog timer, and pushbutton reset connections
are shown in Figure 4. The PBRST input is disabled whenever the IN pin voltage level is less than V
TP
and the reset control (RC) is tied high (CMOS mode). The PBRST input is also disabled whenever VCC is
below V
BAT
. Timing of the PBRST -generated RST is illustrated in Figure 5.
DS1236
4 of 19
NON-MASKABLE INTERRUPT
The DS1236 generates a non-maskable interrupt NMI for early warning of power failure to a
microprocessor. A precision comparator monitors the voltage level at the IN pin relative to a reference
generated by the internal band gap. The IN pin is a high-impedance input allowing for a user-defined
sense point. An external resistor voltage divider network (Figure 6) is used to interf ace with high voltage
signals. This sense point may be derived from the regulated 5-volt supply or from a higher DC voltage
level closer to the main system power input. Since the IN trip point VTP is 2.54 volts, the proper values
for R1 and R2 can be determined by the equation as shown in Figure 6. Proper operation of the DS1236
requires that the voltage at the IN pin be limited to VIN. Therefore, the maximum allowable voltage at the
supply being monitored (V
MAX
) can also be derived as shown in Figure 6. A simple approach to solving
this equation is to select a value for R2 high enough to keep power consumption low, and solve for R1.
The flexibility of the IN input pin allows for detection of power loss at the earliest point in a power
supply system, maximizing the amount of time for microprocessor shutdown between
NMI and RST or
RST .
When the supply being monitored decays to the voltage sense point, the DS1236 pulses the NMI output
to the active state for a minimum of 200 µs. The NMI power-fail detection circuitry also has built-in time
domain hysteresis. That is, the monitored supply is sampled periodically at a rate determined by an
internal ring oscillator running at approximately 30 kHz (33 µs/cycle). Three consecutive samplings of
out-of-tolerance supply (below V
SENSE
) must occur at the IN pin to a ctivate NMI . Therefore, the supply
must be below the voltage sense point for approximately 100 µs o r the comparator will reset. In this way,
power supply noise is removed from the monitoring function, preventing false trips. During a power-up,
any IN pin levels below VTP are disabled from reaching the NMI pin until VCC rises to V
CCTP
. As a result,
any potential NMI pulse will not be initiated until VCC reaches V
CCTP
.
Removal of an active low level on the NMI pin is controlled by either an internal time-out (when IN pin
is less than VTP) or by the subsequent rise of the IN pin above VTP. The initiation and removal of the NMI
signal during power-up results in an NMI pulse of from 0 µs minimum to 500 µs maximum, depending
on the relative voltage relationship between VCC and the IN pin voltage. As an example, when the IN pin
is tied to ground during power-up, the internal time-out will result in a pulse of 200 µs minimum to 500
µs maximum. In contrast, if the IN pin is tied to V
CCO
during power-up, NMI will not produce a pulse on
power-up. Note that a fast slewing power supply may cause the
NMI to be virtually nonexistent on
power-up. This is of no consequence, however, since an RST will be active.
DS1236
5 of 19
DS1236 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
If the IN pin is connected to V
CCO
, the NMI output will pulse low as VCC decays to V
CCTP
in the NMOS
mode (RC=0). In the CMOS mode (RC=V
CCO
) the power-down of VCC out-of-tolerance at V
CCTP
will not
produce a pulse on the NMI pin. Given that an y NMI pulse has been completed by the time VCC decays
to V
CCTP
, the NMI pin will remain high. The NMI voltage will follow VCC down until VCC decays to
V
BAT
. Once VCC decays to V
BAT
, the NMI pin will either remain at V
OHL
or enter tri-state mode as
determined by the RC pin (see “Reset Control” section).
MEMORY BACKUP
The DS1236 provides all of the necessary functions required to battery back a static RAM. First, a switch
is provided to direct SRAM power from the incoming 5-volt supply (V
CC
) or from an external battery
(V
BAT
), whichever is greater. This switched supply (V
CCO
) can also be used to battery back a CMOS
microprocessor. For more information about nonvolatile processor applications, review the “Reset
Control” and “Wake Control” sections. Second, the same power-fail detection described in the power
monitor section is used to hold the chip enable output (
CEO ) to within 0.3 volts of V
CC
or to within 0.7
volts of V
BAT
. This write protection mechanism occurs as VCC falls below V
CCTP
as specified. If CEI is
DS1236
6 of 19
low at the time power-fail detection occurs, CEO is held in its present state until CEI is returned high, or
the period tCE expires. This delay of write protection until the current memory cycle is completed prevents
the corruption of data. If CEO is in an inactive state at the time of VCC fail detection, CEO will be
unconditionally disabled within tCF. During nominal supply conditions CEO will follow CEI with a
maximum propagation delay of 20 ns. Figure 7 shows a typical nonvolatile SRAM application.
FRESHNESS SEAL
In order to conserve battery capacity during storage and/or shipment of an end system, the DS1236
provides a freshness seal to electrically disconnect the battery. Figure 8 depicts the three pulses below
ground on the IN pin required to invoke the freshness seal. The freshness seal will be disconnected and
normal operation will begin when VCC is cycled and reapplied to a level above V
BAT
.
To prevent negative pulses associated with noise from setting the freshness mode in system applications,
a series diode and resistor can be used to shunt noise to ground. During manuf acturing, the freshness seal
can still be set by holding TP2 at -3 volts while applying the 0 to –3 volts clock to TP1.
POWER SWITCHING
When larger operating currents are required in a battery backed system, the 5-volt supply and battery
supply switches internal to the DS1236 may not be large enough to support the required load through
V
CCO
with a reasonable voltage drop. For these applications, the PF and PF outputs are provided to gate
external power switching devices. As shown in Figure 9, power to the load is switched from VCC to
battery on power-down, and from battery to VCC on power-up. The DS1336 is designed to use the PF
output to switch between V
BAT
and VCC. It provides better leakage and switchover performance than
currently available discrete components. The transition threshold for PF and PF is set to the external
battery voltage V
BAT
, allowing a smooth transition between sources. The load applied to the PF pin from
the external switch will be supplied by the battery. Therefore, if a discrete switch is used, this load should
be taken into consideration when sizing the battery.
RESET CONTROL
As mentioned above, the DS1236 supports two modes of operation. The CMOS mode is used when the
system incorporates a CMOS microprocessor which is battery backed. The NMOS mode is used wh en a
non-battery backed processor is incorporated. The mode is selected b y the RC (Reset Control) pin. The
level of this pin distinguishes timing and level control on RST,
RST , and NMI outputs for volatile
processor operation versus nonvolatile battery backup or battery operated processor applications.
ST/INPUT TIMING Figure 2
 Loading...
Loading...