Dallas Semiconductor DS1232LPu, DS1232LPS, DS1232LP Datasheet
DS1232LP/LPS
Low Power MicroMonitor Chip
DS1232LP/LPS
062698 1/7
FEATURES
• Super low-power version of DS1232
• 50
A
quiescent current
• Halts and restarts an out–of–control microprocessor
• Automatically restarts microprocessor after power
failure
• Monitors pushbutton for external override
• Accurate 5% or 10% microprocessor power supply
monitoring
• 8–pin DIP, 8–pin SOIC or space saving µ–SOP pack-
age available
• Optional 16–pin SOIC package available
• Industrial temperature –40°C to +85°C available, des-
ignated N
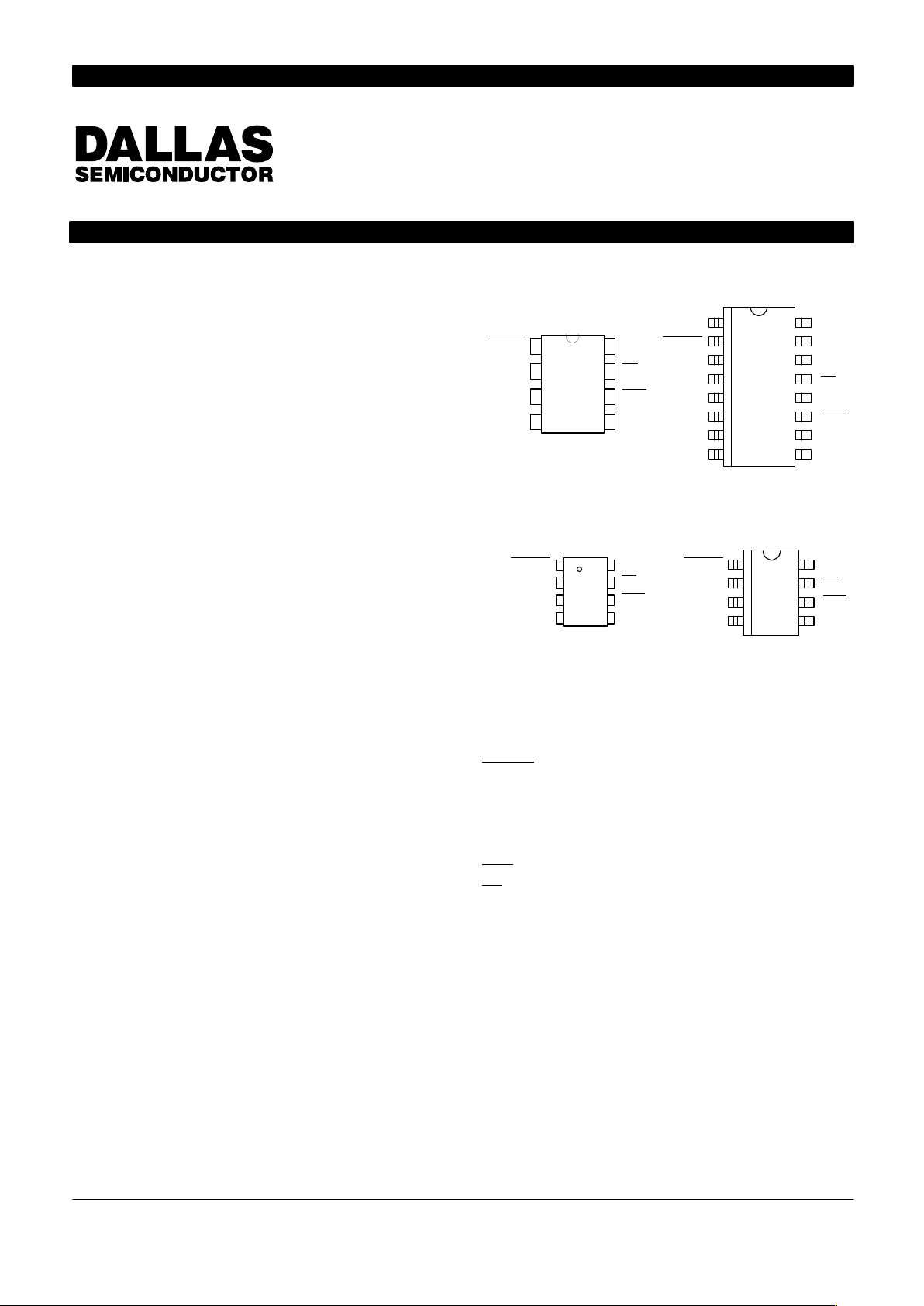
PIN ASSIGNMENT
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V
CC
ST
RST
RST
PBRST
TD
TOL
GND
DS1232LP 8–Pin DIP
(300 Mil)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
DS1232LPS 16–Pin SOIC
(300 Mil)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TD
TOL
GND
PBRST
VCC
ST
RST
RST
DS1232LPS–2 8–Pin
SOIC
(150 Mil)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
NC
PBRST
NC
TD
NC
TOL
NC
GND
NC
VCC
NC
ST
NC
RST
NC
RST
1
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
15
16
DS1232LPµ
(118 MIL µ–SOP)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
V
CC
ST
RST
RST
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
PBRST
TD
TOL
GND
PIN DESCRIPTION
PBRST – Pushbutton Reset Input
TD – Time Delay Set
TOL – Selects 5% or 10% VCC Detect
GND – Ground
RST – Reset Output (Active High)
RST
– Reset Output (Active Low, open drain)
ST – Strobe Input
V
CC
– +5 Volt Power
DESCRIPTION
The DS1232LP/LPS Low Power MicroMonitor Chip
monitors three vital conditions for a microprocessor:
power supply, software execution, and external override. First, a precision temperature–compensated reference and comparator circuit monitors the status of V
CC
.
When an out–of–tolerance condition occurs, an internal
power fail signal is generated which forces reset to the
active state. When V
CC
returns to an in-tolerance condi-
tion, the reset signals are kept in the active state for a
minimum of 250 ms to allow the power supply and processor to stabilize.
The second function the DS1232LP/LPS performs is
pushbutton reset control. The DS1232LP/LPS debounces the pushbutton input and guarantees an active
reset pulse width of 250 ms minimum. The third function
is a watchdog timer. The DS1232LP/LPS has an internal timer that forces the reset signals to the active state if
DS1232LP/LPS
062698 2/7
the strobe input is not driven low prior to time–out. The
watchdog timer function can be set to operate on timeout settings of approximately 150 ms, 600 ms, and 1.2
seconds.
OPERATION – POWER MONITOR
The DS1232LP/LPS detects out–of–tolerance power
supply conditions and warns a processor–based system of impending power failure. When V
CC
falls below a
preset level as defined by TOL, the VCC comparator outputs the signals RST and RST
. When TOL is connected
to ground, the RST and RST
signals become active as
V
CC
falls below 4.75 volts. When TOL is connected to
VCC, the RST and RST signals become active as V
CC
falls below 4.5 volts. The RST and RST are excellent
control signals for a microprocessor, as processing is
stopped at the last possible moments of valid V
CC
. On
power–up, RST and RST
are kept active for a minimum
of 250 ms to allow the power supply and processor to
stabilize.
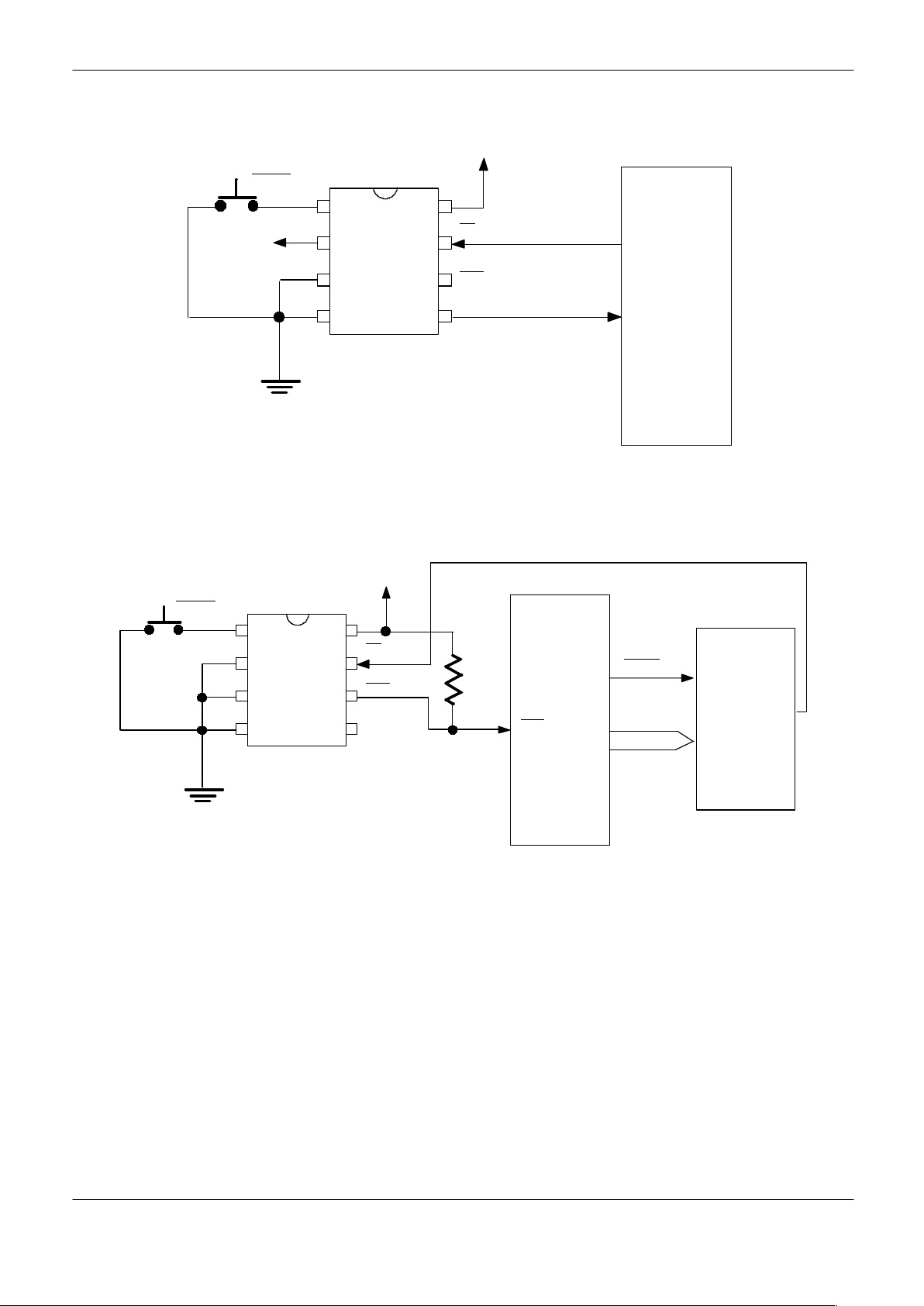
OPERATION – PUSHBUTTON RESET
The DS1232LP/LPS provides an input pin for direct connection to a pushbutton (Figure 1). The pushbutton reset input requires an active low signal. Internally , this input is debounced and timed such that RST and RST
signals of at least 250 ms minimum are generated. The
250 ms delay starts as the pushbutton reset input is released from low level.
OPERATION – WATCHDOG TIMER
The watchdog timer function forces RST and RST signals to the active state when the ST input is not stimulated for a predetermined time period. The time period is
set by the TD input to be typically 150 ms with TD connected to ground, 600 ms with TD left unconnected, and
1.2 seconds with TD connected to V
CC
. The watchdog
timer starts timing out from the set time period as soon
as RST and RST are inactive. If a high–to–low transition
occurs on the ST input pin prior to time–out, the watchdog timer is reset and begins to time–out again. If the
watchdog timer is allowed to time-out, then the RST and
RST
signals are driven to the active state for 250 ms
minimum. The ST
input can be derived from microprocessor address signals, data signals, and/or control signals. When the microprocessor is functioning normally ,
these signals would, as a matter of routine, cause the
watchdog to be reset prior to time–out. To guarantee
that the watchdog timer does not time–out, a high–to–
low transition must occur at or less than the minimum
shown in Table 1. A typical circuit example is shown in
Figure 2.
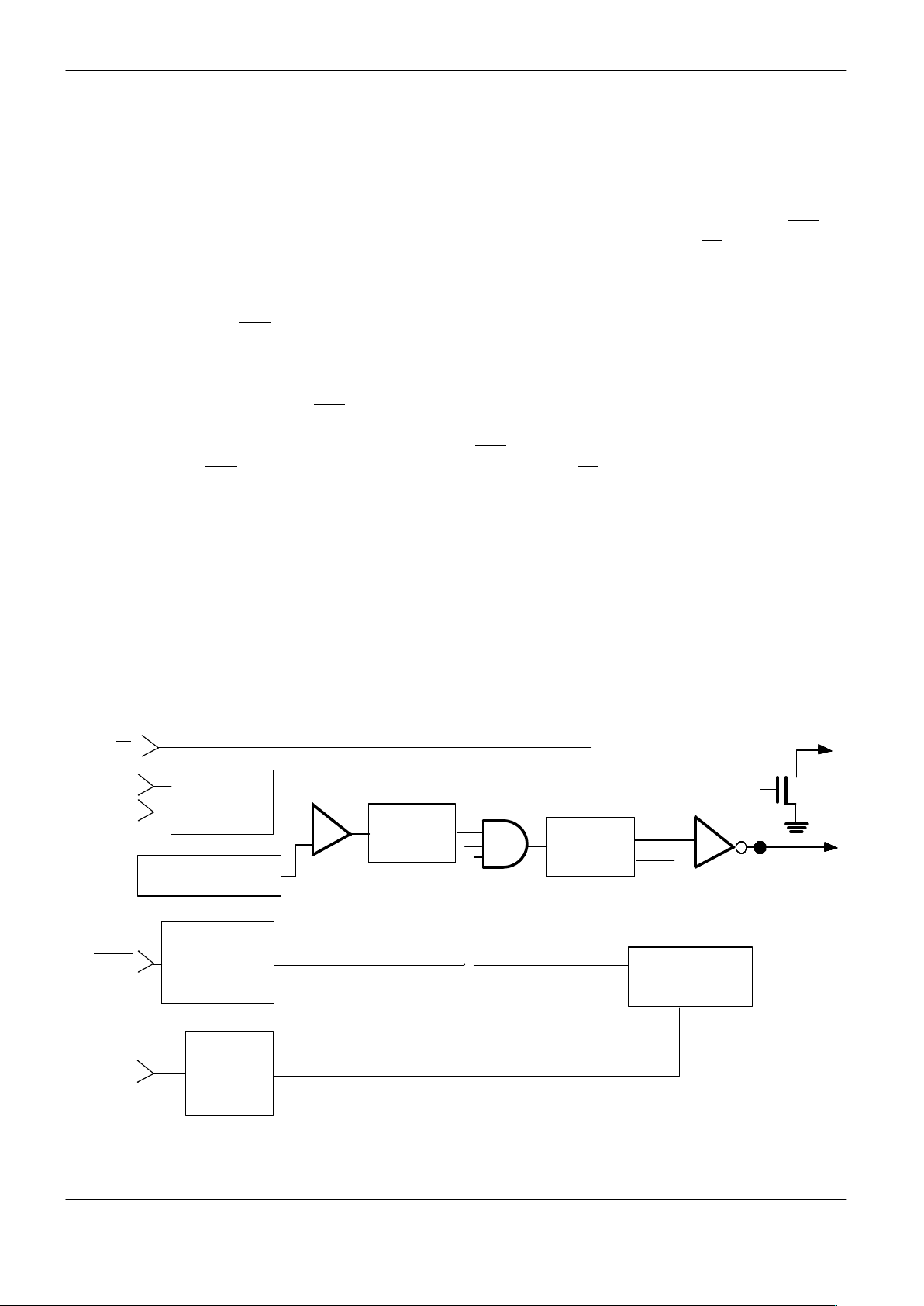
MICROMONITOR BLOCK DIAGRAM
TOL
T.C. REFERENCE
+
–
LEVEL SENSE
VOLTAGE
DIGITAL
DIGITAL
RST
TD
TIME–OUT
RST
ST
PBRST
V
CC
V
CC
TOLERANCE
BIAS
AND
DEBOUNCE
SENSE
COMPARATOR
DELAY
SAMPLER
DS1232LP/LPS
062698 3/7
PUSHBUTTON RESET Figure 1
TD
TOL
GND
RST
ALE
RST
8051
RST
ST
PBRST
V
CC
+5 V
DC
+5 V
DC
P
DS1232
LP/LPS
WATCHDOG TIMER Figure 2
TD
TOL
GND
RST
Z80
ADDRESS
DECODER
10K
RST
ST
PBRST
MREQ
RST
V
CC
+5 V
DC
DS1232
LP/LPS
BUS
 Loading...
Loading...