Dallas Semiconductor DS1222SN, DS1222S, DS1222N, DS1222 Datasheet

1 of 4 111899
FEATURES
Provides bank switching for 16 banks of
memory
Bank switching is software-controlled by a
pattern recognition sequence on four address
inputs
Automatically sets all 16 banks off on
power-up
Bank switching logic allows only one bank on
at a time
Custom recognition patterns are available to
prevent unauthorized access
Full ±10% operating range
Low-power CMOS circuitry
Can be used to expand the address range of
microprocessors and decoders
Optional 16-pin SOIC surface mount package
PIN ASSIGNMENT
PIN DESCRIPTION
AW-A
Z
- Address Inputs
CEI - Chip Enable Input
CEO - Chip Enable Output
NC - No Connection
BS1,BS2, - Bank Select Outputs
BS3,BS4 - Bank Select Outputs
IPF - Power Fail Input
VCC - +5 Volts
GND - Ground
DESCRIPTION
The DS1222 BankSwitch Chip is a CMOS circuit designed to select one of 16 memory banks under
software control. Memory bank switching allows for an increase in memory capacity without additional
address lines. Continuous blocks of memory are enabled by selecting proper memory bank through a
pattern recognition sequence on four address inputs. Custom patterns from Dallas Semiconductor can
provide security through uniqueness and prevent unauthorized access. By combining the DS1222 with
the DS1212 Nonvolatile Controller x16 Chip, up to 16 banks of static RAMs can be selected.
DS1222
BankSwitch Chip
www.dalsemi.com
DS1222 14-Pin DIP
(300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
CEI
V
CC
13
AW
AY
GND
CEO
BS1
BS2
BS3
BS4
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
12
11
10
9
8
PFI
AX
AZ
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
V
CC
CEO
NC
BS1
BS2
BS3
NC
BS4
CEI
NC
PFI
AW
AX
AY
AZ
GND
DS1222S 16-Pin SOIC
(300-mil)
See Mech. Drawings
Section
DS1222
2 of 4
OPERATION - BANK SWITCHING
Initially, on power-up all four bank select outputs are low and the chip enable output (CEO ) is held high.
(Note: the power fail input [ IFP ] must be low prior to power-up to assure proper initialization.) Bank
switching is achieved by matching a predefined pattern stored within the DS1222 with a 16-bit sequence
received on four address inputs. Prior to entering the 16-bit pattern, which sets the bank switch, a read
cycle of 1111 on address inputs AW through AZ should be executed to guarantee that pattern entry starts
with bit 0. Each set of address inputs is clocked into the DS1222 when CEI is driven low. All 16 inputs
must be consecutive read cycles. The first el even cycles must match the exact bit pattern as shown in
Table 1. The last five cycles must match the exact bit pattern as shown for addresses AX, AY, and AZ.
However, address line AW defines the bank number to be enabled as per Table 2.
Switching to a selected bank of memory occurs on the rising edge of
CEI when the last set of bits is input
and a match has been established. After bank selection
CEO always follows CEI with a maximum
propagation delay of 15 ns. The bank selected is determined by the levels set on Bank Select 1 through
Bank Select 4 as per Table 2. These levels are held constant for all memory cycles until a new memory
bank is selected.
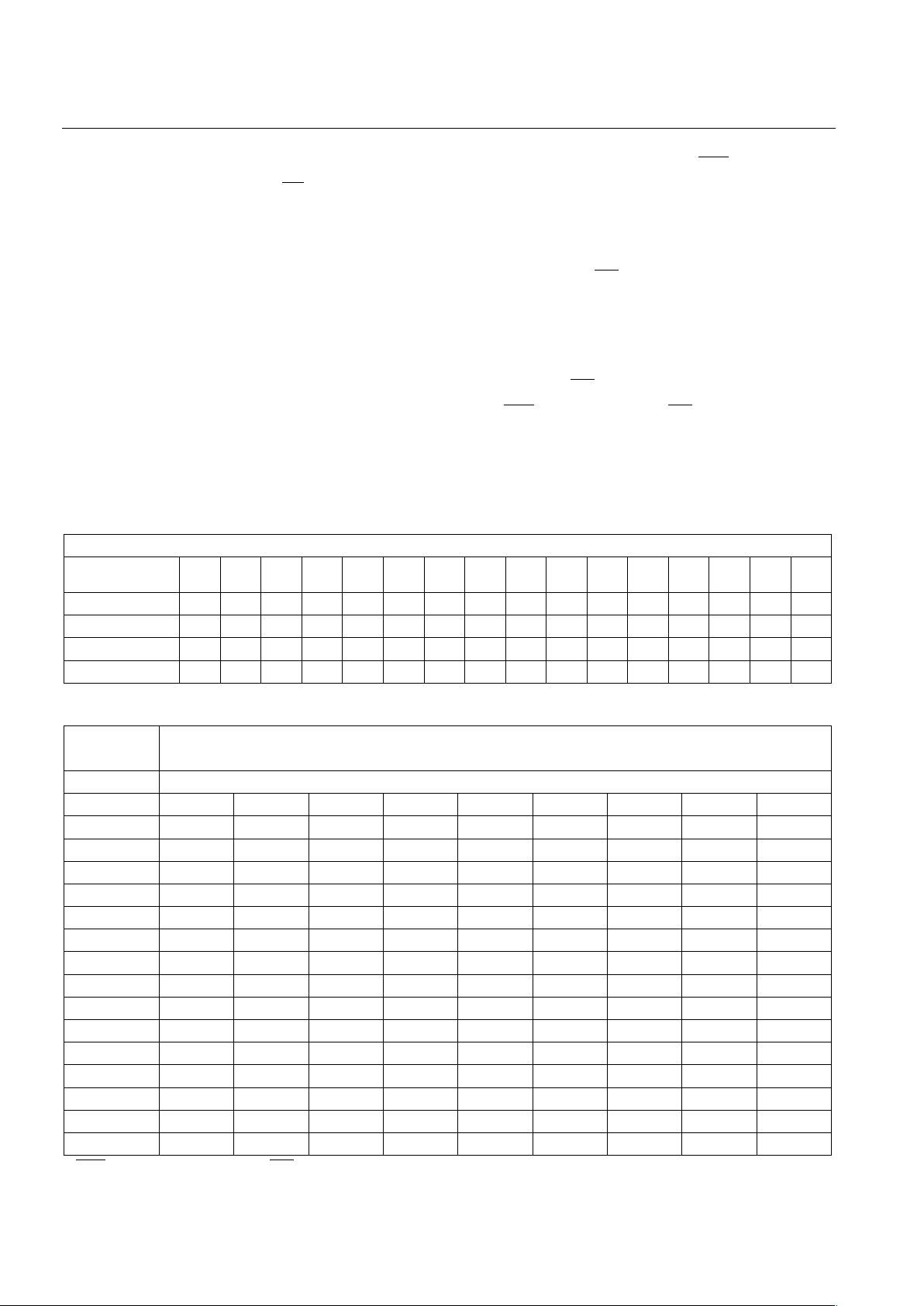
ADDRESS BIT SEQUENCE Table 1
BIT SEQUENCE
ADDRESS
INPUTS 0123456789101112131415
A
W
10100011010xxxxx
A
X
0101110010100011
A
Y
1010001101011100
A
Z
0101110010100011
X See Table 2
BANK SELECT CONTROL Table 2
AW Bit Sequence Outputs
Bank
Selected
11 12 13 14 15 BS1 BS2 BS3 BS4
*Banks Off0 XXXXLowLowLowLow
Bank 010000LowLowLowLow
Bank 110001HighLowLowLow
Bank 210010LowHighLowLow
Bank 310011HighHighLowLow
Bank 410100LowLowHighLow
Bank 510101HighLowHighLow
Bank 610110LowHighHighLow
Bank 7 1 0 1 1 1 High High High Low
Bank 811000LowLowLowHigh
Bank 911001HighLowLowHigh
Bank 1011010LowHighLowHigh
Bank 1111011HighHighLowHigh
Bank 1211100LowLowLowHigh
Bank 13 1 1 1 0 1 High Low High High
Bank 14 1 1 1 1 0 Low High High High
Bank 15 1 1 1 1 1 High High High High
*CEO =VIH independent of CEI
 Loading...
Loading...