Dallas Semiconductor DS1217M3-25, DS1217M2-25, DS1217M1-2-25, DS1217M1-25, DS1217M Datasheet
DS1217M
N
DS1217M
Nonvolatile Read/Write Cartridge
FEATURES
• User-insertable
• Data retention greater than 5 years
• Capacity up to 512K x 8
• Standard bytewide pinout facilitates connection to
JEDEC 28-pin DIP via ribbon cable
• Software-controlled banks maintain 32 x 8 JEDEC
28-pin compatibility
• Multiple cartridges can reside on a common bus
• Automatic write protection circuitry safeguards
against data loss
• Manual switch unconditionally protects data
• Compact size and shape
• Rugged and durable
• Wide operating temperature range of 0°C to 70°C
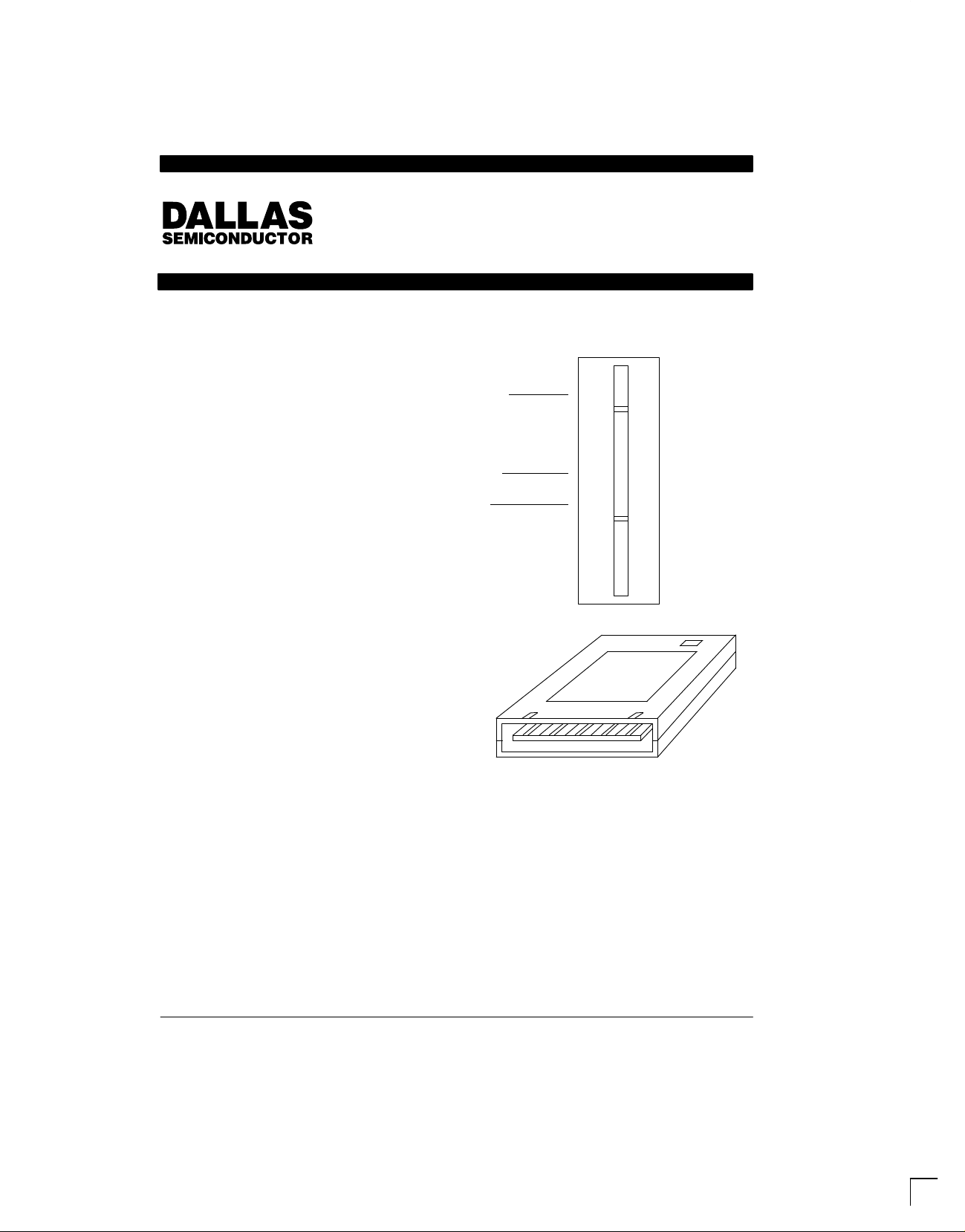
PIN ASSIGNMENT
Name Position Name
Ground
+5 Volts
Write Enable
Address 13
Address 8
Address 9
Address 11
Output Enable
Address 10
Cartridge Enable
Data I/O 7
Data I/O 6
Data I/O 5
Data I/O 4
Data I/O 3
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B8
B9
B10
B11
B12
B13
B14
B15
No Connect
Address 14
Address 12
Address 7
Address 6
Address 5
Address 4
Address 3
Address 2
Address 1
Address 0
Data I/O 0
Data I/O 1
Data I/O 2
Ground
3”
DESCRIPTION
The DS1217M is a nonvolatile RAM designed for portable applications requiring a rugged and durable package. The Nonvolatile Cartridge has memory capacities
from 64K x 8 to 512K x 8. The cartridge is accessed in
continuous 32K byte banks. Bank switching is accomplished under software control by pattern recognition
from the address bus. A card edge connector is required
A1
B1
See Mech. Drawings Section
for connection to a host system. A standard 30-pin connector can be used for direct mount to a printed circuit
board. Alternatively, remote mounting can be accomplished with a ribbon cable terminated with a 28-pin DIP
plug. The remote method can be used to retrofit existing
systems which have JEDEC 28-pin bytewide memory
sites.
030598 1/8

DS1217M
READ MODE
The DS1217M executes a read cycle whenever WE
(write enable) is inactive (high) and CE (cartridge enable) is active (low). The unique address specified by
the address inputs (A0-A14) defines which byte of data
is to be accessed. Valid data will be available to the eight
data I/O pins within t
(access time) after the last ad-
ACC
dress input signal is stable, providing that CE (cartridge
enable) and OE (output enable) access times are also
satisfied. If OE and CE times are not satisfied, then data
access must be measured from the late occurring signal
or OE) and the limiting parameter is either tCO for
(CE
CE or tOE for OE rather than address access. Read
cycles can only occur when V
volts. When V
is less than 4.5 volts, the memory is in-
CC
is greater than 4.5
CC
hibited and all accesses are ignored.
WRITE MODE
The DS1217M is in the write mode whenever both the
WE and CE signals are in the active (low) state after address inputs are stable. The last occurring falling edge
of either CE or WE will determine the start of the write
cycle. The write cycle is terminated by the first rising
edge of either CE
or WE. All address inputs must be
kept valid throughout the write cycle. WE must return to
the high state for a minimum recovery time (t
another cycle can be initiated.The OE
) before
WR
control signal
should be kept inactive (high) during write cycles to
avoid bus contention. However, if the output bus has
been enabled (CE
the outputs in t
can only occur when V
V
is less than 4.5 volts, the memory is write-pro-
CC
and OE active) then WE will disable
from its falling edge. Write cycles
ODW
is greater than 4.5 volts. When
CC
tected.
DATA RETENTION MODE
The Nonvolatile Cartridge provides full functional capability for VCC greater than 4.5 volts and guarantees write
protection for V
tained in the absence of V
port circuitry. The DS1217M constantly monitors V
Should the supply voltage decay , the RAM is automatically write-protected below 4.5 volts. As VCC falls below
approximately 3.0 volts, the power switching circuit connects a lithium energy source to RAM to retain data.
During power-up, when V
3.0 volts, the power switching circuit connects the external VCC to the RAM and disconnects the lithium energy
less than 4.5 volts. Data is main-
CC
without any additional sup-
CC
rises above approximately
CC
CC
source. Normal RAM operation can resume after V
exceeds 4.5 volts.
The DS1217M checks battery status to warn of potential
data loss. Each time that V
power is restored to the
CC
cartridge the battery voltage is checked with a precision
comparator. If the battery supply is less than 2.0 volts,
the second memory cycle is inhibited. Battery status
can, therefore, be determined by performing a read
cycle after power-up to any location in memory, recording that memory location content. A subsequent write
cycle can then be executed to the same memory location, altering data. If the next read cycle fails to verify the
written data, the contents of the memory are questionable.
In many applications, data integrity is paramount. The
cartridge thus has redundant batteries and an internal
isolation switch which provides for the connection of two
batteries. During battery backup time, the battery with
the highest voltage is selected for use. If one battery
fails, the other will automatically take over. The switch
between batteries is transparent to the user. A battery
status warning will occur only if both batteries are less
than 2.0 volts.
BANK SWITCHING
Bank switching is accomplished via address lines A8,
A9, A10, and A11. Initially, on power-up all banks are deselected so that multiple cartridges can reside on a common bus. Bank switching requires that a predefined pattern of 64 bits is matched by sequencing 4 address
inputs (A8 through A11) 16 times while ignoring all other
address inputs. Prior to entering the 64-bit pattern which
will set the band switch, a read cycle of 1111 (address
inputs A8 through A11) must be executed to guarantee
that pattern entry starts with the first set of 3 bits. Each
set of address inputs is entered into the DS1217M by
executing read cycles.The first eleven cycles must
match the exact bit pattern as shown in T able 2. The last
five cycles must match the exact bit pattern for address-
.
es A9, A10, and A11. However, address line 8 defines
which of the 16 banks is to be enabled, or all banks are
deselected, as per T able 3. Switching from one bank to
another occurs as the last of the 16 read cycles is completed. A single bank is selected at any one time. A selected bank will remain active until a new bank is selected, all banks are deselected, or until power is lost.
(See DS1222 BankSwitch Chip data sheet for more detail.)
CC
030598 2/8
DS1217M
REMOTE CONNECTION VIA A RIBBON
CABLE
Existing systems which contain 28-pin bytewide sockets can be retrofitted using a 28-pin DIP plug. The DIP
plug, AMP Part Number 746616-2, can be inserted into
the 28-pin site after the memory is removed. Connection
to the cartridge is accomplished via a 28-pin cable connected to a 30-contact card edge connector, AMP Part
Number 499188-4. The 28-pin ribbon cable must be
right-justified, such that positions A1 and B1 are left disconnected. For applications where the cartridge is installed or removed with power applied, both ground contacts (A1 and B1) on the card edge connector should be
grounded to further enhance data integrity. Access time
push-out may occur as the distance between the cartridge and the driving circuitry is increased.
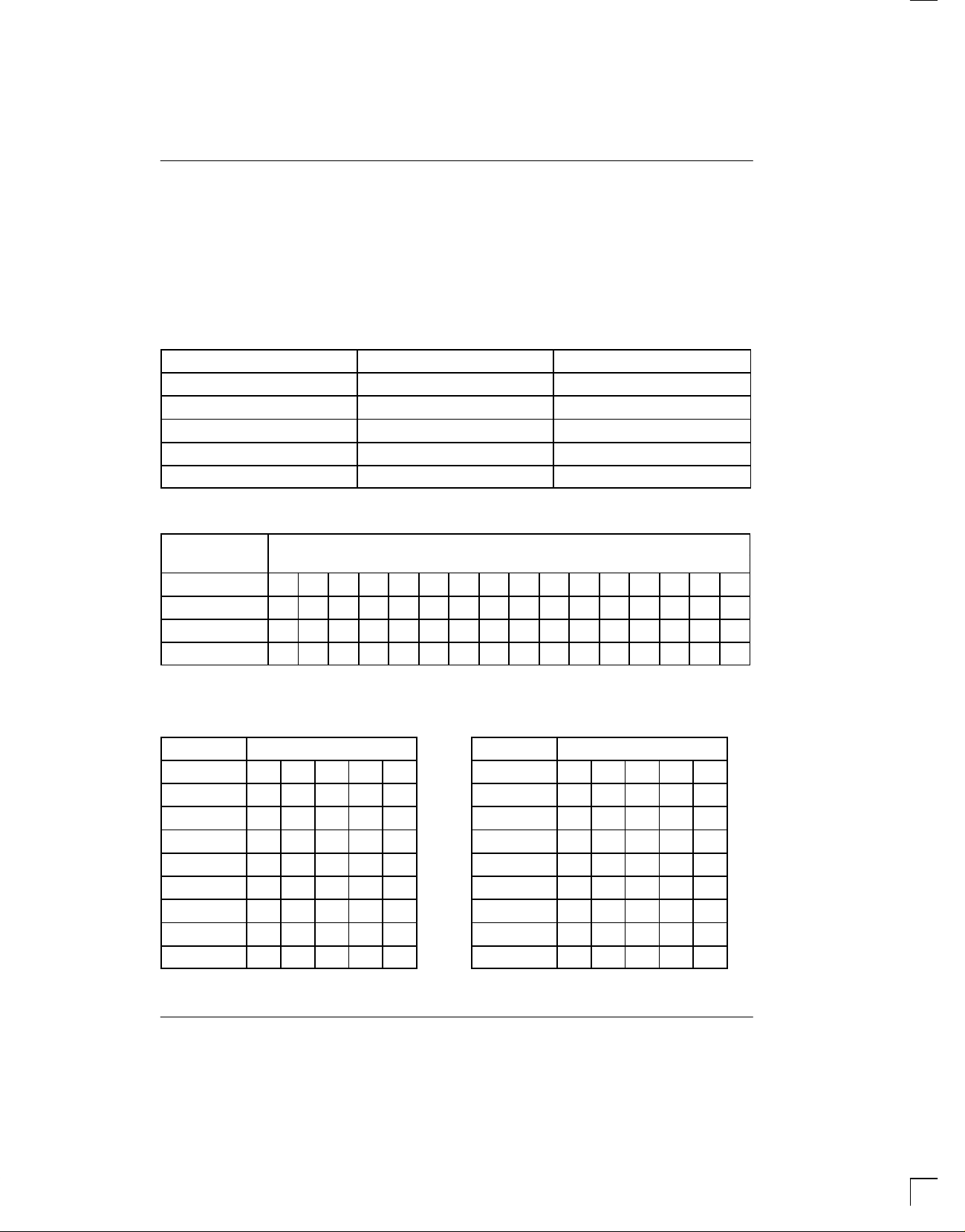
CARTRIDGE NUMBERING Table 1
PART NO. DENSITY NO. OF BANKS
DS1217M 1/2-25 64K x 8 2
DS1217M 1-25 128K x 8 4
DS1217M 2-25 156K x 8 8
DS1217M 3-25 384K x 8 12
DS1217M 4-25 512K x 8 16
ADDRESS INPUT PATTERN Table 2
ADDRESS BIT SEQUENCE
INPUTS 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
A8 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 X X X X X
A9 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
A10 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0
A11 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
X = See Table 3
BANK SELECT TABLE Table 3
BANK A8 BIT SEQUENCE
SELECTED 11 12 13 14 15
BANKS OFF 0 X X X X
BANK 0 1 0 0 0 0
BANK 1 1 0 0 0 1
BANK 2 1 0 0 1 0
BANK 3 1 0 0 1 1
BANK 4 1 0 1 0 0
BANK 5 1 0 1 0 1
BANK 6 1 0 1 1 0
BANK A8 BIT SEQUENCE
BANK 7 1 0 1 1 1
BANK 8 1 1 0 0 0
BANK 9 1 1 0 0 1
BANK 10 1 1 0 1 0
BANK 11 1 1 0 1 1
BANK 12 1 1 1 0 0
BANK 13 1 1 1 0 1
BANK 14 1 1 1 1 0
BANK 15 1 1 1 1 1
030598 3/8
 Loading...
Loading...