Page 1

8-Port Gigabit + 2-Port Gigabit SFP
L2 Managed PoE Switch
User’s Manual
V1.0.0
ZHEJIANG DAHUA VISION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
Page 2

Page 3

Cybersecurity Recommendations
Mandatory actions to be taken towards cybersecurity
1. Change Passwords and Use Strong Passwords:
The number one reason systems get “hacked” is due to having weak or default passwords. It is
recommended to change default passwords immediately and choose a strong password whenever
possible. A strong password should be made up of at least 8 characters and a combination of special
characters, numbers, and upper and lower case letters.
2. Update Firmware
As is standard procedure in the tech-industry, we recommend keeping NVR, DVR, and IP camera
firmware up-to-date to ensure the system is current with the latest security patches and fixes.
“Nice to have” recommendations to improve your network security
1. Change Passwords Regularly
Regularly change the credentials to your devices to help ensure that only authorized users are able to
access the system.
2. Change Default HTTP and TCP Ports:
● Change default HTTP and TCP ports for systems. These are the two ports used to communicate and
to view video feeds remotely.
● These ports can be changed to any set of numbers between 1025-65535. Avoiding the default ports
reduces the risk of outsiders being able to guess which ports you are using.
3. Enable HTTPS/SSL:
Set up an SSL Certificate to enable HTTPS. This will encrypt all communication between your devices
and recorder.
4. Enable IP Filter:
Enabling your IP filter will prevent everyone, except those with specified IP addresses, from accessing
the system.
5. Change ONVIF Password:
On older IP Camera firmware, the ONVIF password does not change when you change the system’s
credentials. You will need to either update the camera’s firmware to the latest revision or manually
change the ONVIF password.
6. Forward Only Ports You Need:
● Only forward the HTTP and TCP ports that you need to use. Do not forward a huge range of numbers
to the device. Do not DMZ the device's IP address.
● You do not need to forward any ports for individual cameras if they are all connected to a recorder on
site; just the NVR is needed.
7. Disable Auto-Login on SmartPSS:
Those using SmartPSS to view their system and on a computer that is used by multiple people should
disable auto-login. This adds a layer of security to prevent users without the appropriate credentials from
accessing the system.
8. Use a Different Username and Password for SmartPSS:
Cybersecurity Recommendations I
Page 4

In the event that your social media, bank, email, etc. account is compromised, you would not want
someone collecting those passwords and trying them out on your video surveillance system. Using a
different username and password for your security system will make it more difficult for someone to
guess their way into your system.
9. Limit Features of Guest Accounts:
If your system is set up for multiple users, ensure that each user only has rights to features and functions
they need to use to perform their job.
10. UPnP:
● UPnP will automatically try to forward ports in your router or modem. Normally this would be a good
thing. However, if your system automatically forwards the ports and you leave the credentials defaulted,
you may end up with unwanted visitors.
● If you manually forwarded the HTTP and TCP ports in your router/modem, this feature should be
turned off regardless. Disabling UPnP is recommended when the function is not used in real
applications.
11. SNMP:
Disable SNMP if you are not using it. If you are using SNMP, you should do so only temporarily, for
tracing and testing purposes only.
12. Multicast:
Multicast is used to share video streams between two recorders. Currently there are no known issues
involving Multicast, but if you are not using this feature, deactivation can enhance your network security.
13. Check the Log:
If you suspect that someone has gained unauthorized access to your system, you can check the system
log. The system log will show you which IP addresses were used to login to your system and what was
accessed.
14. Physically Lock Down the Device:
Ideally, you want to prevent any unauthorized physical access to your system. The best way to achieve
this is to install the recorder in a lockbox, locking server rack, or in a room that is behind a lock and key.
Cybersecurity Recommendations II
Page 5

General
Signal Words
Meaning
Indicates a high potential hazard which, if not avoided, will result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a medium or low potential hazard which, if not avoided,
could result in slight or moderate injury.
Indicates a potential risk which, if not avoided, could result in
property damage, data loss, lower performance, or unpredictable
result.
Provides methods to help you solve a problem or save you time.
Provides additional information as the emphasis and supplement
to the text.
No.
Version
Revision Content
Release Time
1
V1.0.0
First Release.
June 1, 2018
This user’s manual introduces the functions and operations of 8-Port Gigabit + 2-Port Gigabit
SFP L2 Managed PoE Switch devices.
Models
DH-PFS4210-8GT-150
Safety Instructions
The following categorized signal words with defined meaning might appear in the Manual.
Foreword
Revision History
Privacy Protection Notice
As the device user or data controller, you might collect personal data of others' such as face,
fingerprints, car plate number, Email address, phone number, GPS and so on. You need to be
in compliance with the local privacy protection laws and regulations to protect the legitimate
rights and interests of other people by implementing measures include but not limited to:
providing clear and visible identification to inform data subject the existence of surveillance
area and providing related contact.
Foreword III
Page 6

About the Manual
The Manual is for reference only. If there is inconsistency between the Manual and the
actual product, the actual product shall govern.
We are not liable for any loss caused by the operations that do not comply with the Manual.
The Manual would be updated according to the latest laws and regulations of related
regions. For detailed information, see the paper User's Manual, CD-ROM, QR code or our
official website. If there is inconsistency between paper User's Manual and the electronic
version, the electronic version shall prevail.
All the designs and software are subject to change without prior written notice. The product
updates might cause some differences between the actual product and the Manual. Please
contact the customer service for the latest program and supplementary documentation.
There still might be deviation in technical data, functions and operations description, or
errors in print. If there is any doubt or dispute, please refer to our final explanation.
Upgrade the reader software or try other mainstream reader software if the Guide (in PDF
format) cannot be opened.
All trademarks, registered trademarks and the company names in the Manual are the
properties of their respective owners.
Please visit our website, contact the supplier or customer service if there is any problem
occurred when using the device.
If there is any uncertainty or controversy, please refer to our final explanation.
Foreword IV
Page 7

Electrical safety
All installation and operation here should conform to your local electrical safety codes.
The product must be grounded to reduce the risk of electric shock.
We assume no liability or responsibility for all the fires or electrical shock caused by
improper handling or installation.
Transportation security
Heavy stress, violent vibration or water splash are not allowed during transportation, storage
and installation.
Installation
Keep upwards. Handle with care.
Do not apply power to the Device before completing installation.
Do not place objects on the Device.
Qualified engineers needed
All the examination and repair work should be done by the qualified service engineers. We are
not liable for any problems caused by unauthorized modifications or attempted repair.
Important Safeguards and Warnings
Environment
The Device should be installed in a cool, dry place away from conditions such as direct sunlight,
inflammable substances, and explosive substances.
Accessories
Be sure to use all the accessories recommended by manufacturer.
Before installation, please open the package and check all the components are included.
Contact your local retailer ASAP if something is broken in your package.
Battery
Improper battery use might result in fire, explosion, or personal injury.
When replacing the battery, please make sure you are using the same type. Risk of
Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions.
Please make sure to use the same battery model if possible.
We recommend replace battery regularly (such as one-year) to guarantee system time
explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type.
accuracy. Before replacement, please save the system setup, otherwise, you may lose the
data completely.
Important Safeguards and Warnings V
Page 8

Table of Contents
Cybersecurity Recommendations ........................................................................................................... I
Foreword .................................................................................................................................................. III
Important Safeguards and Warnings ..................................................................................................... V
1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Features ........................................................................................................................................ 1
1.3 External Component Description .................................................................................................. 2
1.3.1 Front Panel ......................................................................................................................... 2
1.3.2 Rear Panel .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Package Contents ......................................................................................................................... 4
2 Installation and Connection ................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Installation ..................................................................................................................................... 5
2.1.1 Desktop Installation ............................................................................................................ 5
2.1.2 Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet ................................................................. 5
2.1.3 Power on the Switch ........................................................................................................... 6
2.2 Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch ........................................................................................ 6
2.3 Switch connection to the PD ......................................................................................................... 7
3 Login to the Switch ............................................................................................................................... 8
3.1 Switch to End Node ...................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Login the Switch ............................................................................................................................ 8
4 Switch Configuration .......................................................................................................................... 10
4.1 Quickly Setting ............................................................................................................................ 10
4.2 Port .............................................................................................................................................. 13
4.2.1 Basic config ...................................................................................................................... 13
4.2.2 Port aggregation ............................................................................................................... 15
4.2.3 Port mirroring .................................................................................................................... 16
4.2.4 Port rate-limit .................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.5 Storm control .................................................................................................................... 18
4.2.6 Port isolation ..................................................................................................................... 20
4.2.7 Port information ................................................................................................................ 21
4.3 VLAN ........................................................................................................................................... 22
4.3.1 VLAN Settings .................................................................................................................. 22
4.3.2 Access Port Settings ........................................................................................................ 23
4.3.3 Trunk-port setting .............................................................................................................. 24
4.3.4 Hybrid-port setting ............................................................................................................ 25
4.4 Fault/Safety ................................................................................................................................. 28
4.4.1 Anti attack ......................................................................................................................... 28
4.4.2 Channel detection ............................................................................................................. 33
4.4.3 ACL ................................................................................................................................... 36
4.5 PoE .............................................................................................................................................. 38
4.5.1 PoE Port Config ................................................................................................................ 38
Table of Contents VI
Page 9

4.6 STP ............................................................................................................................................. 39
4.6.1 MSTP region ..................................................................................................................... 40
4.6.2 STP bridge ........................................................................................................................ 41
4.7 DHCP relay ................................................................................................................................. 43
4.7.1 DHCP relay ....................................................................................................................... 44
4.7.2 0ption82 ............................................................................................................................ 44
4.8 QoS ............................................................................................................................................. 46
4.8.1 Queue config .................................................................................................................... 46
4.8.2 Mapping the queue ........................................................................................................... 47
4.9 Addr table .................................................................................................................................... 51
4.9.1 MAC Management ............................................................................................................ 52
4.9.2 MAC Learning and Aging ................................................................................................. 53
4.9.3 MAC Filter ......................................................................................................................... 55
4.10 SNMP ........................................................................................................................................ 55
4.10.2 Snmp config .................................................................................................................... 56
4.10.3 Rmon config .................................................................................................................... 62
4.11 LACP ......................................................................................................................................... 67
4.11.2 Lacp config ..................................................................................................................... 67
4.12 SYSTEM ................................................................................................................................... 70
4.12.2 System config ................................................................................................................. 70
4.12.3 System upgrade .............................................................................................................. 76
4.12.4 Config management ....................................................................................................... 77
4.12.5 Config save ..................................................................................................................... 80
4.12.6 Administrator privileges .................................................................................................. 80
4.12.7 Info collect ....................................................................................................................... 81
Technical Specifications ................................................................................................... 82 Appendix 1
Table of Contents VII
Page 10

Page 11

1.1 Overview
The Switch is a new generation designed for high security and high performance network the
second layer switch. Provides eight 10/100/1000Mbps self-adaption RJ45 port, and two
100/1000Mbps SFP ports, all ports support wire-speed forwarding, can provide you with
larger network flexibility. All ports support Auto MDI/MDIX function. The Switch with a low-cost,
easy-to-use, high performance upgrade your old network to a 1000Mbps Gigabit network.
The Switch supports VLAN ACL based on port, easily implement network monitoring, traffic
regulation, priority tag and traffic control. Support traditional STP/RSTP/MSTP 2 link protection
technology; greatly improve the ability of fault tolerance, redundancy backup to ensure the
stable operation of the network. Support ACL control based on the time, easy control the
access time accurately. Support 802.1x authentication based on the port and MAC, easily set
user access. Perfect QOS strategy and plenty of VLAN function, easy to maintenance and
management, meet the networking and access requirements of small and medium-sized
enterprises, intelligent village, hotel, office network and campus network.
1 Introduction
The Switch all UTP ports support PoE power supply function, support IEEE802.3at standard,
802.3af downward compatibility, power supply equipment for Ethernet, can automatically detect
identification standard of electrical equipment, and through the cable for the power supply.
1.2 Features
Comply with 802.3i, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3x, IEEE 802.3z, IEEE802.1Q ,
IEEE802.1p, IEEE802.3af, IEEE802.3at
Supports PoE power up to 30W for each PoE port, total power up to 140W for all PoE ports
8 x 10/100/1000Mbps Auto MDI/MDI-X Ethernet port
2 x 100/1000Mbps SFP port
8K entry MAC address table of the switch with auto-learning and auto-aging
Supports IEEE802.3x flow control for Full-duplex Mode and backpressure for Half-duplex
Mode
Support Web interface management
supports QoS (quality of service), port mirror, Link aggregation protocol
LED indicators for monitoring Power, System, link/activity/Speed, PoE
Introduction 1
Page 12

1.3 External Component Description
LED
Indicator
Faceplate
Marker
Status
Indication
Power
Indicator
PWR
Off
Power Off
Solid green
Power On
1.3.1 Front Panel
The front panel of the Switch consists of AC power connector, one marker, 1 x Reset button, a
series of LED indicators, 8 x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports, 2 x SFP ports and 1x Console port
as shown as below.
Front panel Figure 1-1
AC Power Connector
Power is supplied through an external AC power adapter. It supports AC 100~240V, 50/60Hz.
Grounding Terminal:
Located on the right side of the power supply connector, use wire grounding to lightning
protection.
Reset button (Reset):
Keep the device powered on and push a paper clip into the hole. Press down the button for 5
seconds to restore the Switch to its original factory default settings.
10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports (1~8):
Designed to connect to the device with a bandwidth of 10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps. Each
has a corresponding Link/Act/Speed and PoE indicator.
SFP ports (9, 10):
Designed to install the SFP module and connect to the device with a bandwidth of 100Mbps or
1000Mbps. Each has a corresponding Link/Act/Speed LED.
Console port (Console):
Designed to connect with the serial port of a computer or terminal for monitoring and
configuring the Switch.
:
LED indicators:
The LED Indicators will allow you to monitor, diagnose and troubleshoot any potential problem
with the Switch, connection or attached devices.
The following chart shows the LED indicators of the Switch along with explanation of each
indicator.
Front panel Table 1-1
Introduction 2
Page 13
LED
Indicator
Faceplate
Marker
Status
Indication
System
indicator
SYS
Off
System not started
Blinking green
System is starting or the system
starts successfully
10/100/10
00
BASE-T
adaptive
Ethernet
port
indicators
(1-8)
Link/Act
/Speed
Off
The port is NOT connected.
Solid green
The port is connected at 1000Mbps.
Solid orange
The port is connected at 100/10Mbps
Blinking
The port is transmitting or receiving
data.
SFP port
indicators
(9-10)
Link/Act
/Speed
Off
The port is NOT connected.
Solid green
The port is connected at 1000Mbps.
Solid orange
The port is connected at 100Mbps
Blinking
The port is transmitting or receiving
data.
PoE
status
indicators
(1-8)
PoE
Off
No PD is connected to the
corresponding port, or no power is
supplied according to the power
limits of the port
Solid orange
A Powered Device is connected to
the port, which supply power
successfully.
Blinking
The PoE power circuit may be in
short or the power current may be
overloaded
1.3.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch contains Heat vent shown as below.
Real panel Figure 1-2
Introduction 3
Heat vent:
The Heat vent is located in the middle position of the rear panel of the switch. It is used for heat
dissipation and ventilation. Do not cover it.
Page 14

1.4 Package Contents
Before installing the Switch, make sure that the following the "packing list" listed OK. If any part
is lost and damaged, please contact your local agent immediately. In addition, make sure that
you have the tools install switches and cables by your hands.
One PoE Web Smart Ethernet Switch
One Installation Component
One AC power cord
One User’s Manual
Introduction 4
Page 15

This part describes how to install your PoE Ethernet Switch and make connections to it. Please
read the following topics and perform the procedures in the order being presented.
2.1 Installation
Please follow the following instructions in avoid of incorrect installation causing device damage
and security threat.
Put the Switch on stable place or desktop in case of falling damage.
Make sure the Switch works in the proper AC input range and matches the voltage labeled
on the Switch.
To keep the Switch free from lightning, do not open the Switch's shell even in power failure.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around the
Switch.
Make sure the cabinet to enough back up the weight of the Switch and its accessories.
2 Installation and Connection
2.1.1 Desktop Installation
Sometimes users are not equipped with the 19-inch standard cabinet. So when installing the
Switch on a desktop, please attach these cushioning rubber feet provided on the bottom at
each corner of the Switch in case of the external vibration. Allow adequate space for ventilation
between the device and the objects around it.
2.1.2 Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet
The Switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-sized, 19-inch rack, which can be placed in a
wiring closet with other equipment. To install the Switch, please follow these steps:
Attach the mounting brackets on the Switch's side panels (one on each side) and Step 1
secure them with the screws provided.
Installation and Connection 5
Page 16
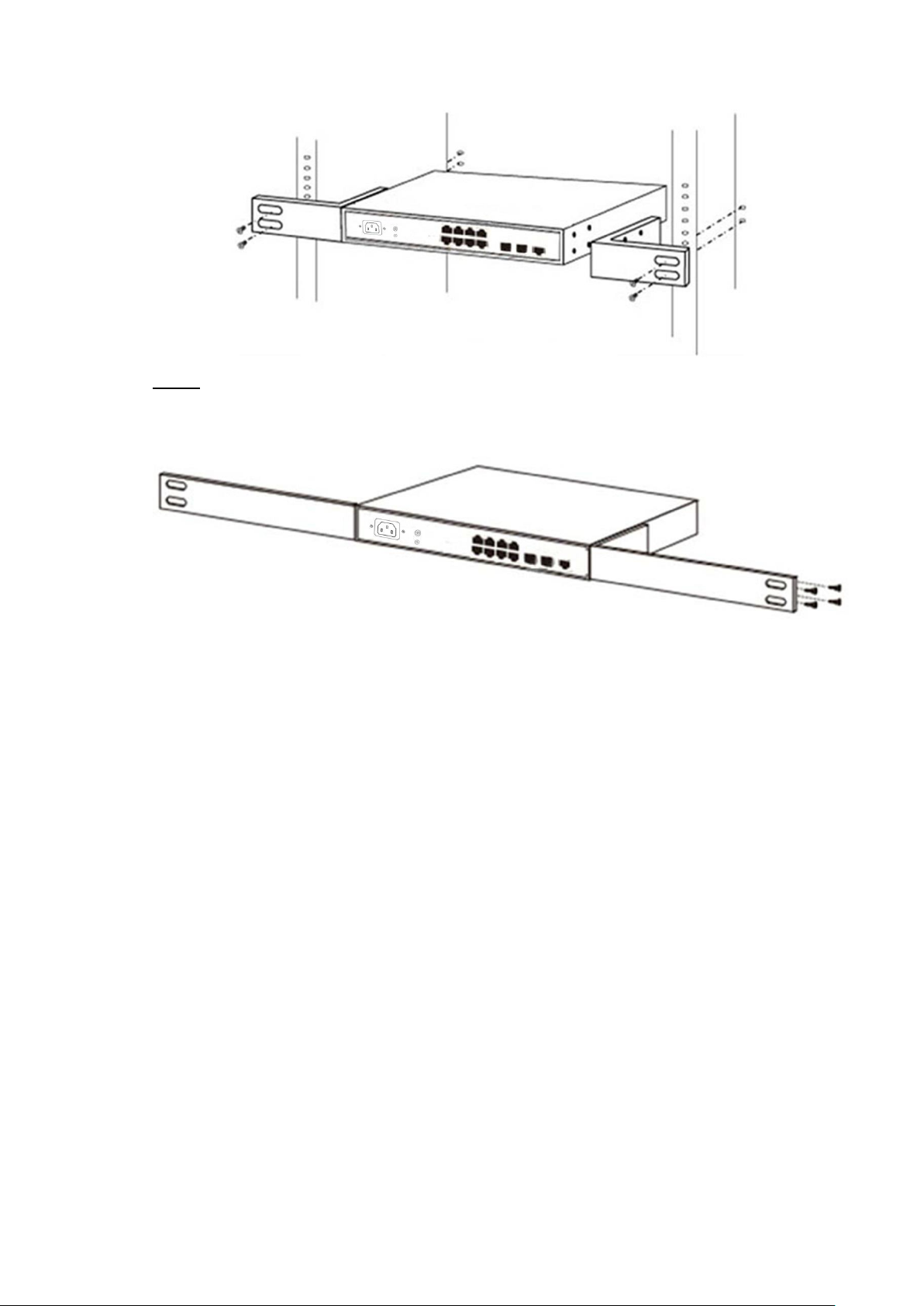
Use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the Switch on the rack and Step 2
tighten it.
Bracket installation Figure 2-1
Rack installation Figure 2-2
2.1.3 Power on the Switch
The Switch is powered on by the AC 100-240V 50/60Hz internal high-performance power
supply. Please follow the next tips to connect:
AC Electrical Outlet:
It is recommended to use single-phase three-wire receptacle with neutral outlet or
multifunctional computer professional receptacle. Please make sure to connect the metal
ground connector to the grounding source on the outlet.
AC Power Cord Connection:
Connect the AC power connector in the back panel of the Switch to external receptacle with the
included power cord, and check the power indicator is ON or not. When it is ON, it indicates the
power connection is OK.
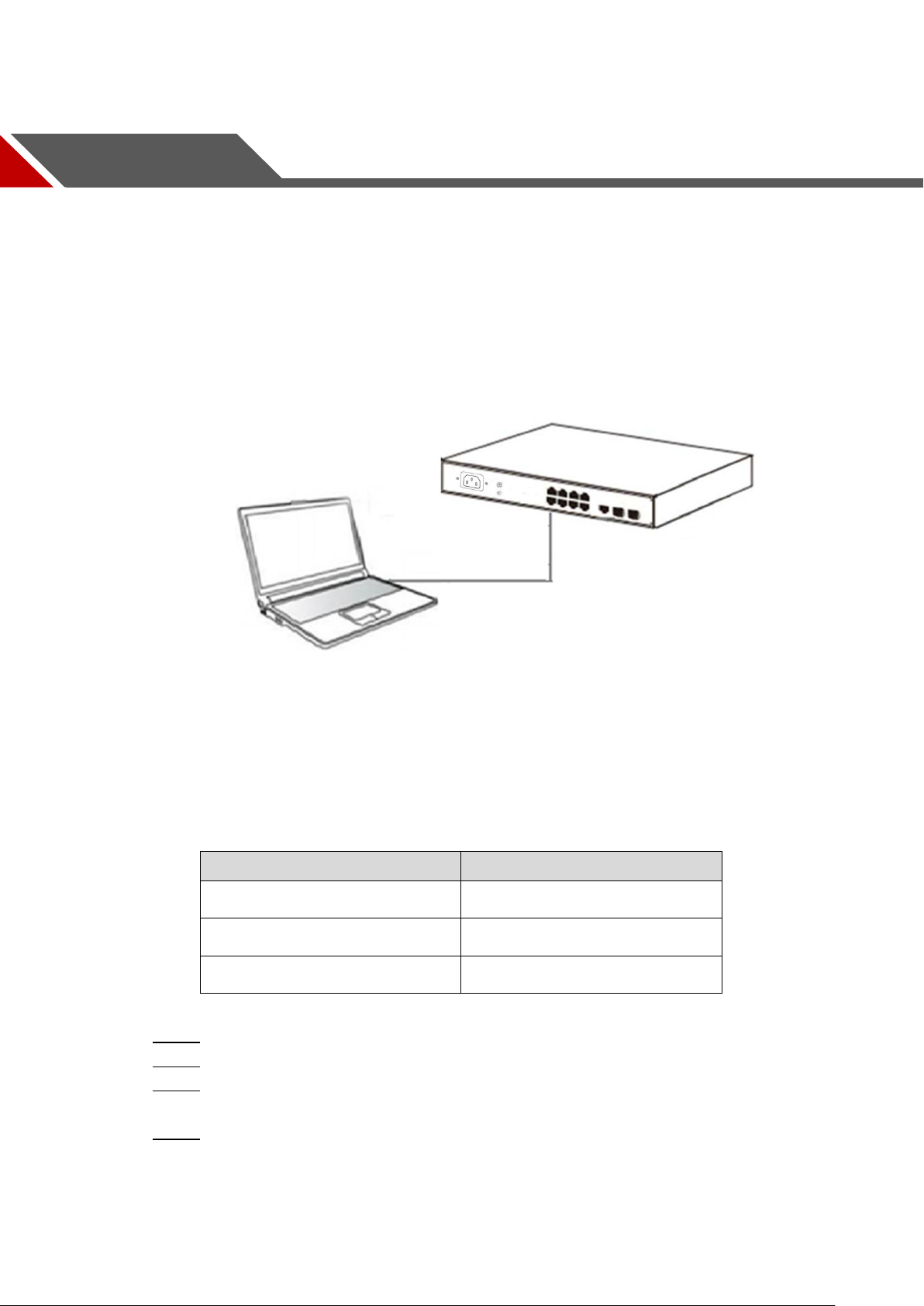
2.2 Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch
Please insert the NIC into the computer, after installing network card driver, please connect one
end of the twisted pair to RJ-45 jack of your computer, the other end will be connected to any
RJ-45 port of the Switch, the distance between Switch and computer is around 100 meters.
Once the connection is OK and the devices are power on normally, the LINK/ACT/Speed status
indicator lights corresponding ports of the Switch.
Installation and Connection 6
Page 17

2.3 Switch connection to the PD
1-8 ports of the Switch have PoE power supply function, the maximum output power up to 30W
each port, it can make PD devices, such as internet phone, network camera, wireless access
point work. You only need to connect the Switch PoE port directly connected to the PD port by
network cable.
Installation and Connection 7
Page 18
3.1 Switch to End Node
Parameter
Default Value
Default IP address
192.168.1.110
Default user name
admin
Default password
admin123
Use standard Cat.5/5e Ethernet cable (UTP/STP) to connect the Switch to end nodes as
described below. Switch ports will automatically adjust to the characteristics (MDI/MDI-X, speed,
duplex) of the device to which is connected.
3 Login to the Switch
Connect PC to switch Figure 3-1
3.2 Login the Switch
As the Switch provides Web-based management login, you can configure your computer’s IP
address manually to log on to the Switch. The default settings of the Switch are shown below.
You can log on to the configuration window of the Switch through following steps:
Connect the Switch with the computer NIC interface. Step 1
Power on the Switch. Step 2
Check whether the IP address of the computer is within this network segment: Step 3
192.168.1.xxx ("xxx" ranges 0~254, except 110), for example, 192.168.1.100.
Open the browser, and enter http://192.168.1.110 and then press "Enter". The Switch Step 4
login window appears, as shown below.
Default value Table 3-1
Login to the Switch 8
Page 19
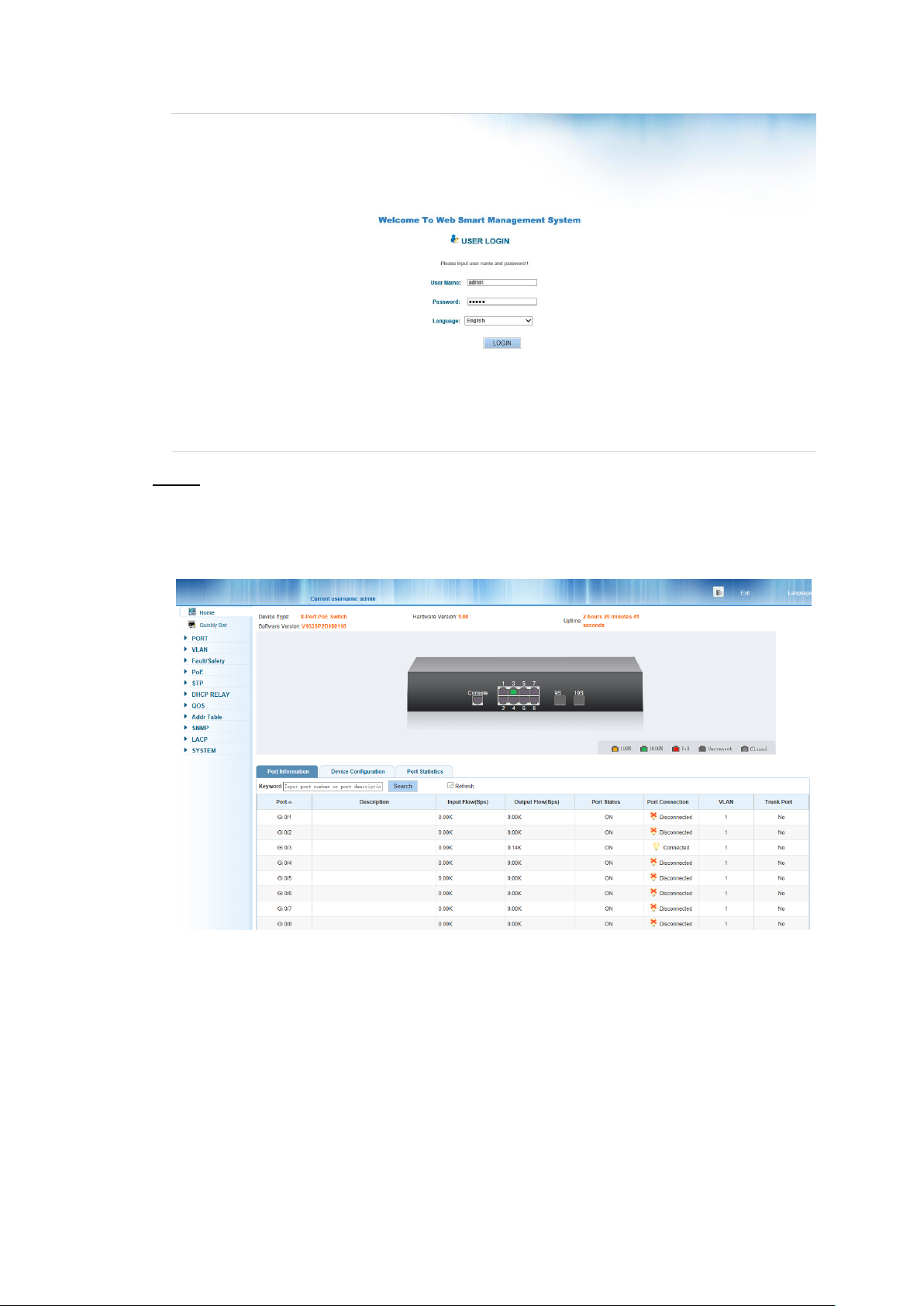
Login windows Figure 3-2
Switching language to English .Enter the Username and Password (The factory default Step 5
Username is admin and Password is admin123), and then click "LOGIN" to log in to
the Switch configuration window.
Switch configuration window Figure 3-3
Login to the Switch 9
Page 20
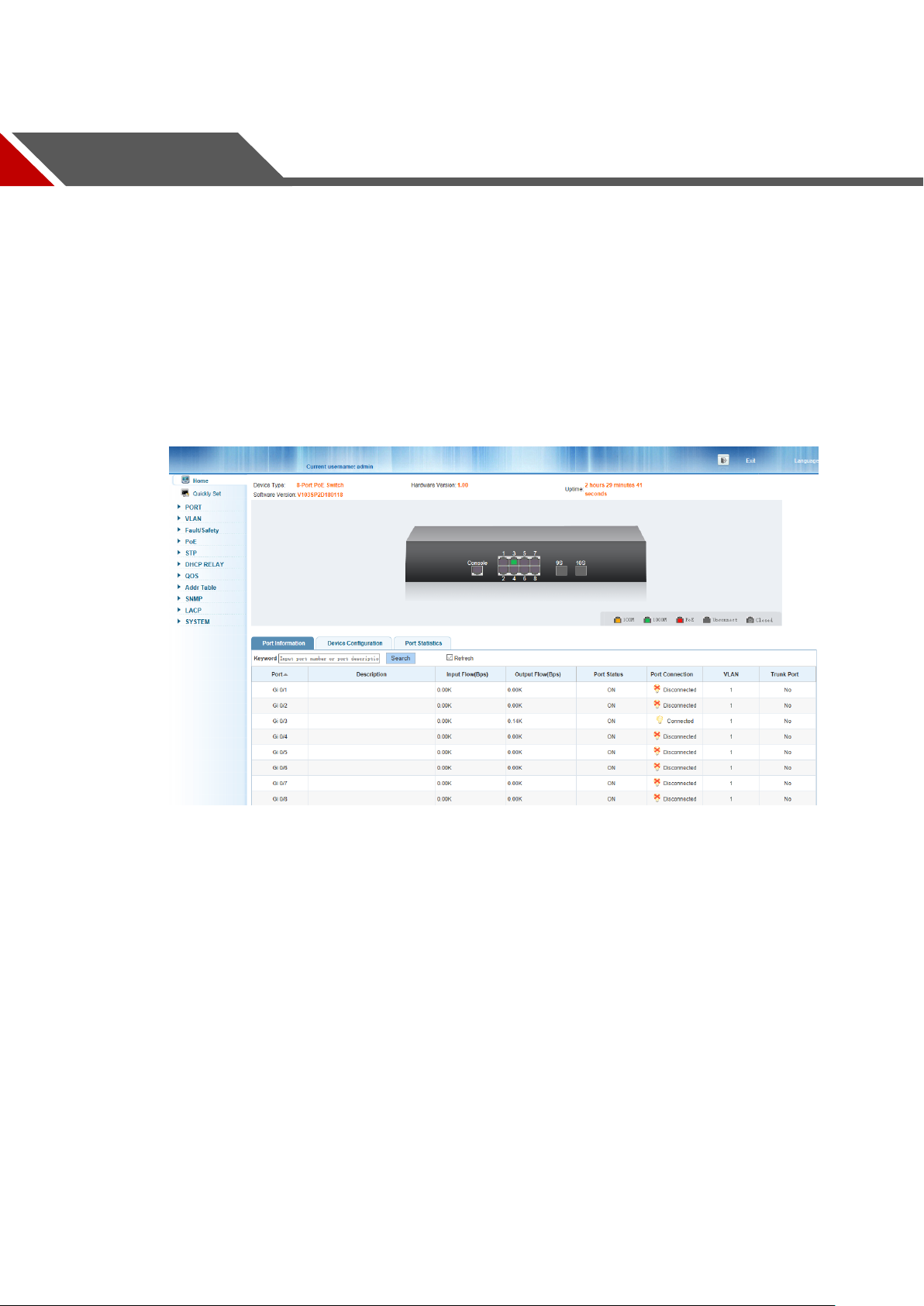
4 Switch Configuration
The Web Smart Ethernet Switch Managed switch software provides rich layer 2 functionality for
switches in your networks. This chapter describes how to use Web-based management
interface(Web UI) to this switch configure managed switch software features.
In the Web UI, the left column shows the configuration menu. Above you can see the
information for switch system, such as memory, software version. The middle shows the
switch’s current link status. Green squares indicate the port link is up, while black squares
indicate the port link is down. Below the switch panel, you can find a common toolbar to provide
useful functions for users. The rest of the screen area displays the configuration settings.
Switch configuration window Figure 4-1
4.1 Quickly Setting
In the navigation bar to select "quickly setting", can create a VLAN in this module, add the port
in the VLAN, set the basic information and modify the switch login password. The following
picture:
Switch Configuration 10
Page 21
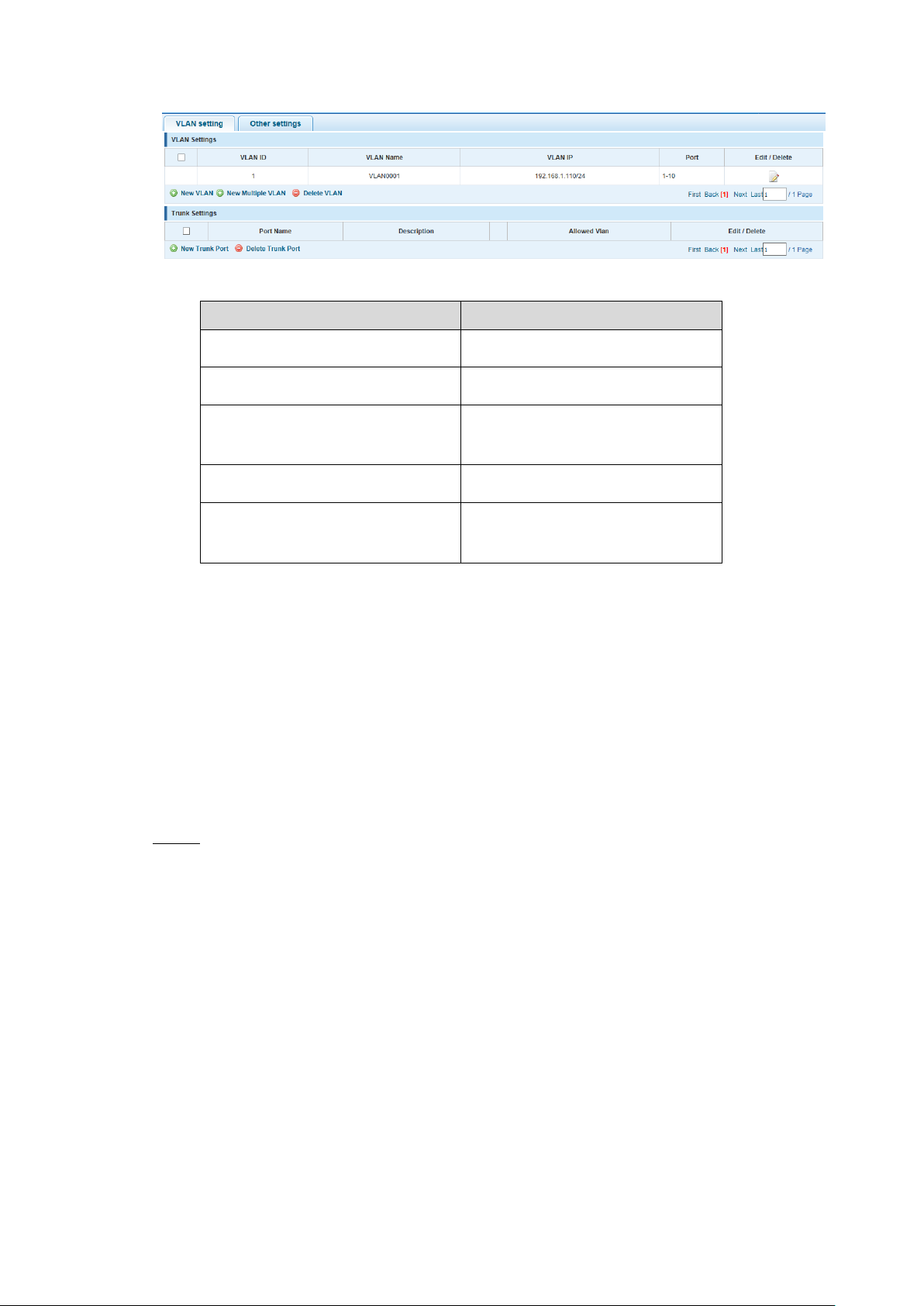
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
VLAN ID
VLAN number
VLAN Name
VLAN mark
VLAN IP
Manage the IP address of the
VLAN
Device Name
Switch name
Management VLAN
Switch’s management in use of
the VLAN
Quickly setting Figure 4-2
【Instructions】
Native VLAN: as a Trunk, the mouth will belong to a Native VLAN. The so-called Native VLAN,
is refers to UNTAG send or receive a message on the interface, is considered belongs to the
VLAN. Obviously, the interface of the default VLAN ID (PVID) in the IEEE 802.1 Q VLAN ID is
the Native VLAN. At the same time, send belong to Native VLAN frame on the Trunk, must
adopt UNTAG way.
Allowed VLAN list: a Trunk can transport the equipment support by default all the VLAN traffic
(1-4094). But, also can by setting the permission VLAN Trunk at the mouth of the list to limit the
flow of some VLAN can't through the Trunk.
【Configuration Example】
VLAN setting: such as create VLAN 2. Sets the port 8 to Trunk , Native VLAN 2. Step 1
Switch Configuration 11
Page 22
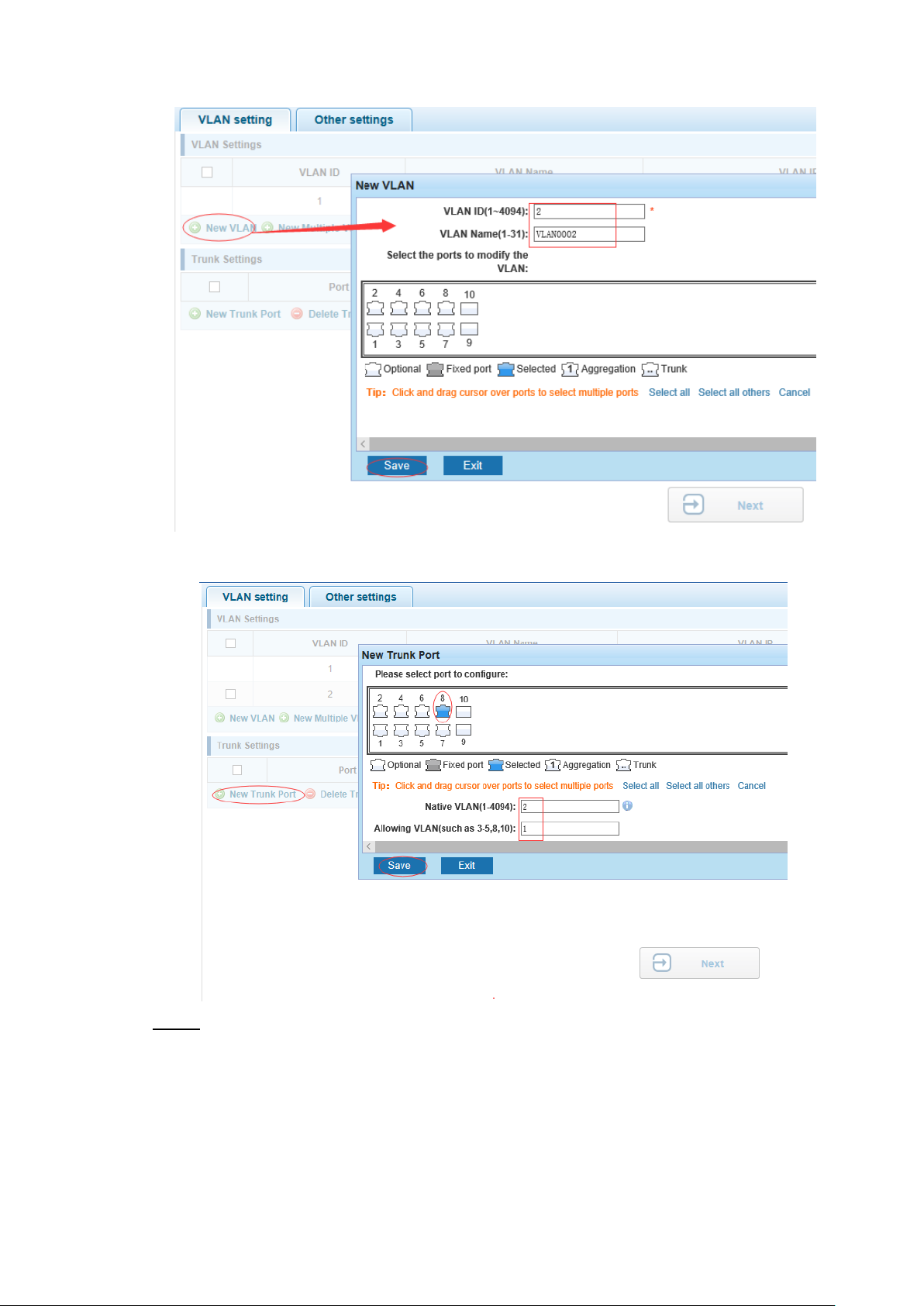
VLAN setting I Figure 4-3
VLAN setting II Figure 4-4
Click "next step" button, into other settings, such as: manage ip address set as Step 2
192.168.1.11, device name set as switch-123, default gateway with the dns server set
as 172.16.1.241.
Switch Configuration 12
Page 23
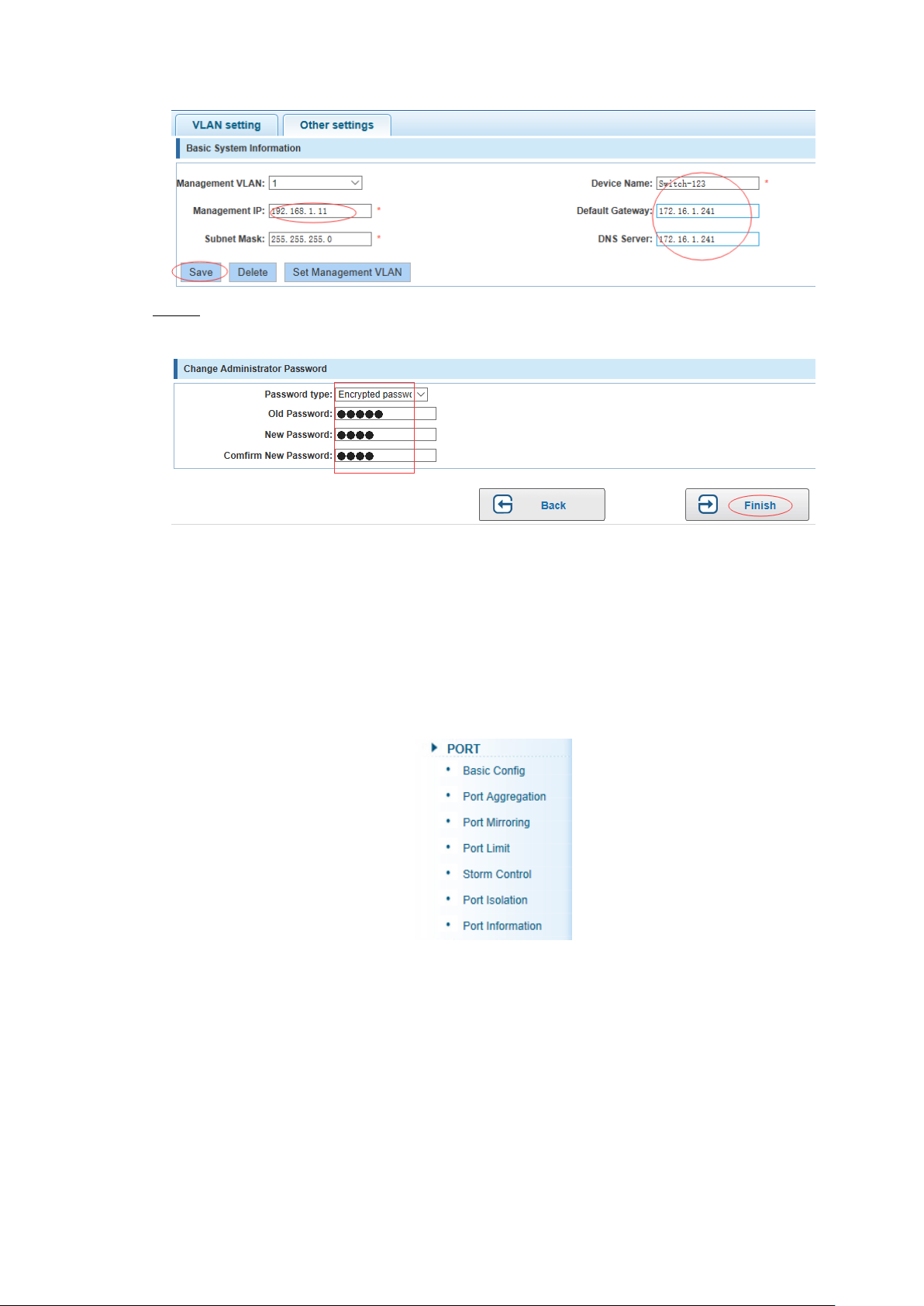
Save Figure 4-5
Use 192.168.1.11 to log in, set a new password for admin1234. Step 3
Finish Figure 4-6
4.2 Port
In the navigation bar to select "PORT", you may conduct Basic config, Port aggregation, Port
mirroring, Port limit and port isolation.
4.2.1 Basic config
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>Basic config", For panel port to port described , port
speed, port status, working mode, flow control, cross line order configuration, the following
picture:
Port Figure 4-7
Switch Configuration 13
Page 24
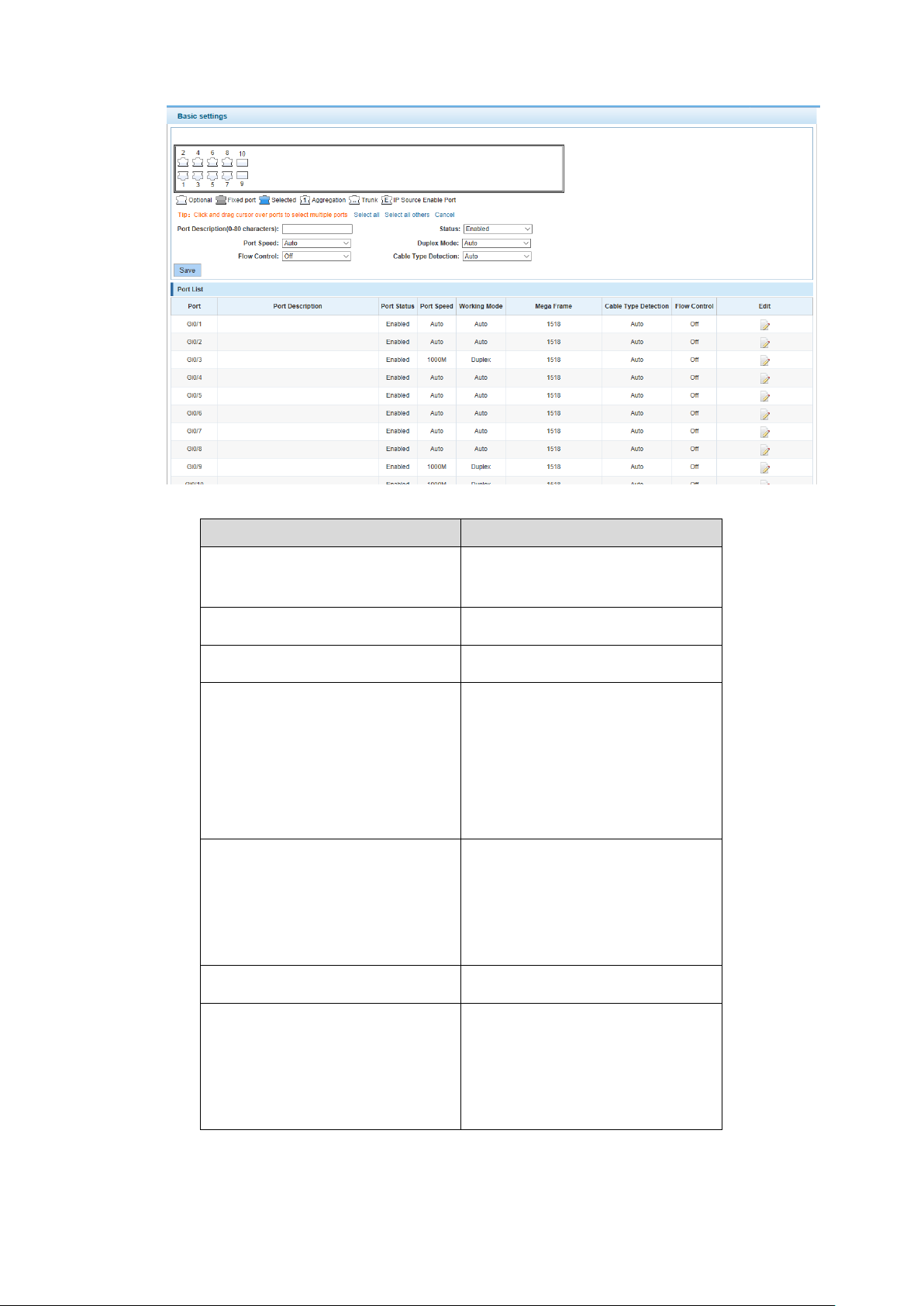
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Port
Select the current configuration
port number
Status
Choose whether to close link port
Flow Control
Whether open flow control
Port Speed
Can choose the following kinds:
Auto
10 M
100 M
1000 M
Duplex Mode
Can choose the following kinds:
Auto
Duplex
Half duplex
Port Description
The port is described
Cable Type Detection
Can choose the following kinds:
Auto
MDI
MDIX
Basic settings I Figure 4-8
【Instructions】
Open flow control should be negotiated will close, negotiated close is to set port speed rate and
working mode. Set the port rate more than actual rate of port, the port will be up.
Switch Configuration 14
Page 25
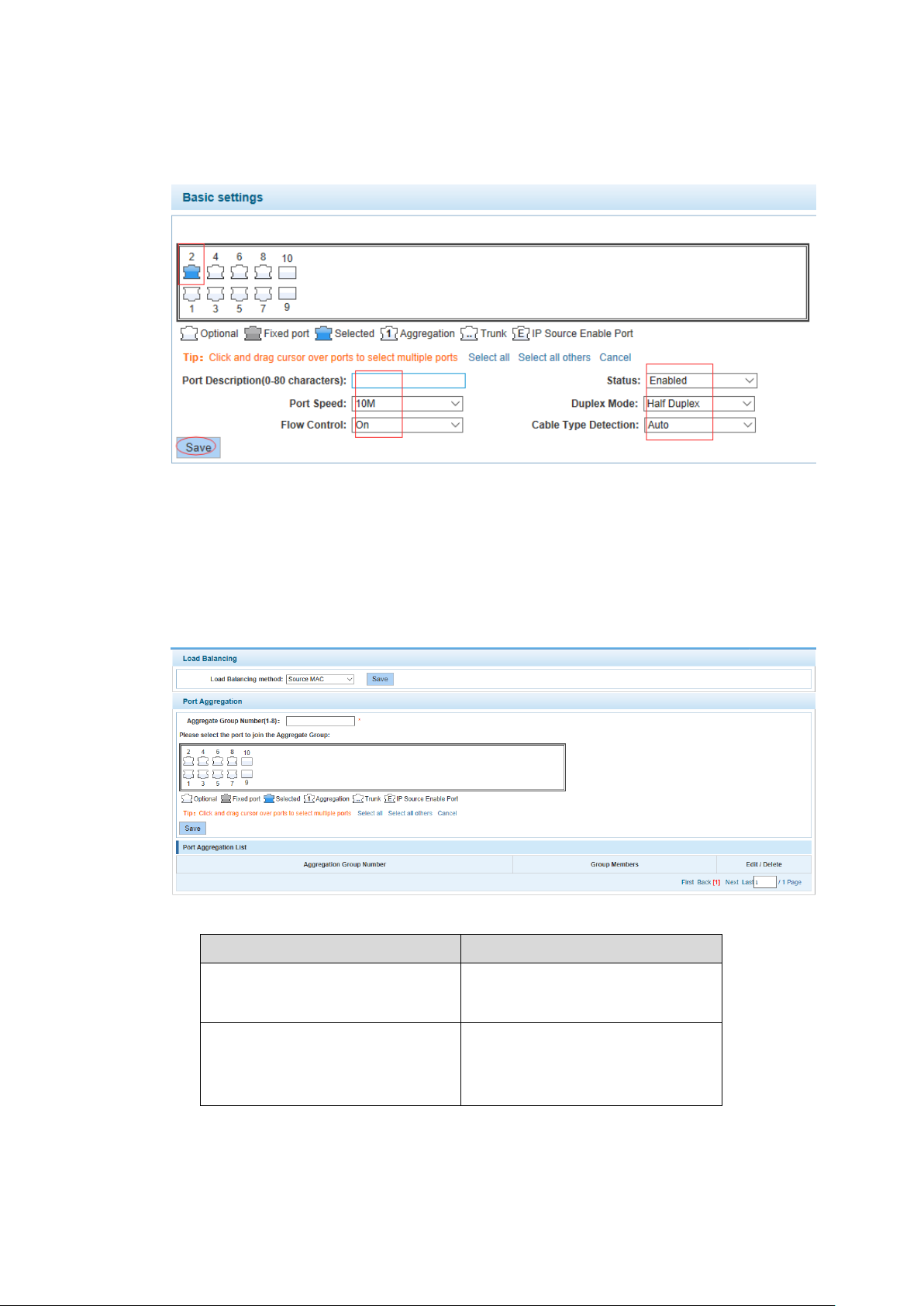
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
Aggregation Group Number
Switch can be set up 8 link trunk
group, group_1 to group_8
Member port
For each of the members of the
group and add your own port, and
with members of other groups
Such as: The port is set to 10 M, half duplex, open flow control and cross line sequence and
port state.
4.2.2 Port aggregation
Basic settings II Figure 4-9
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>port aggregation", In order to expand the port
bandwidth or achieve the bandwidth of the redundancy backup, the following picture:
Port aggregation Figure 4-10
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Open the port of the ARP check function, the port of the important device ARP, the port of the
VLAN MAC function, and the monitor port in the port image cannot be added!
【Configuration Example】
Switch Configuration 15
Page 26
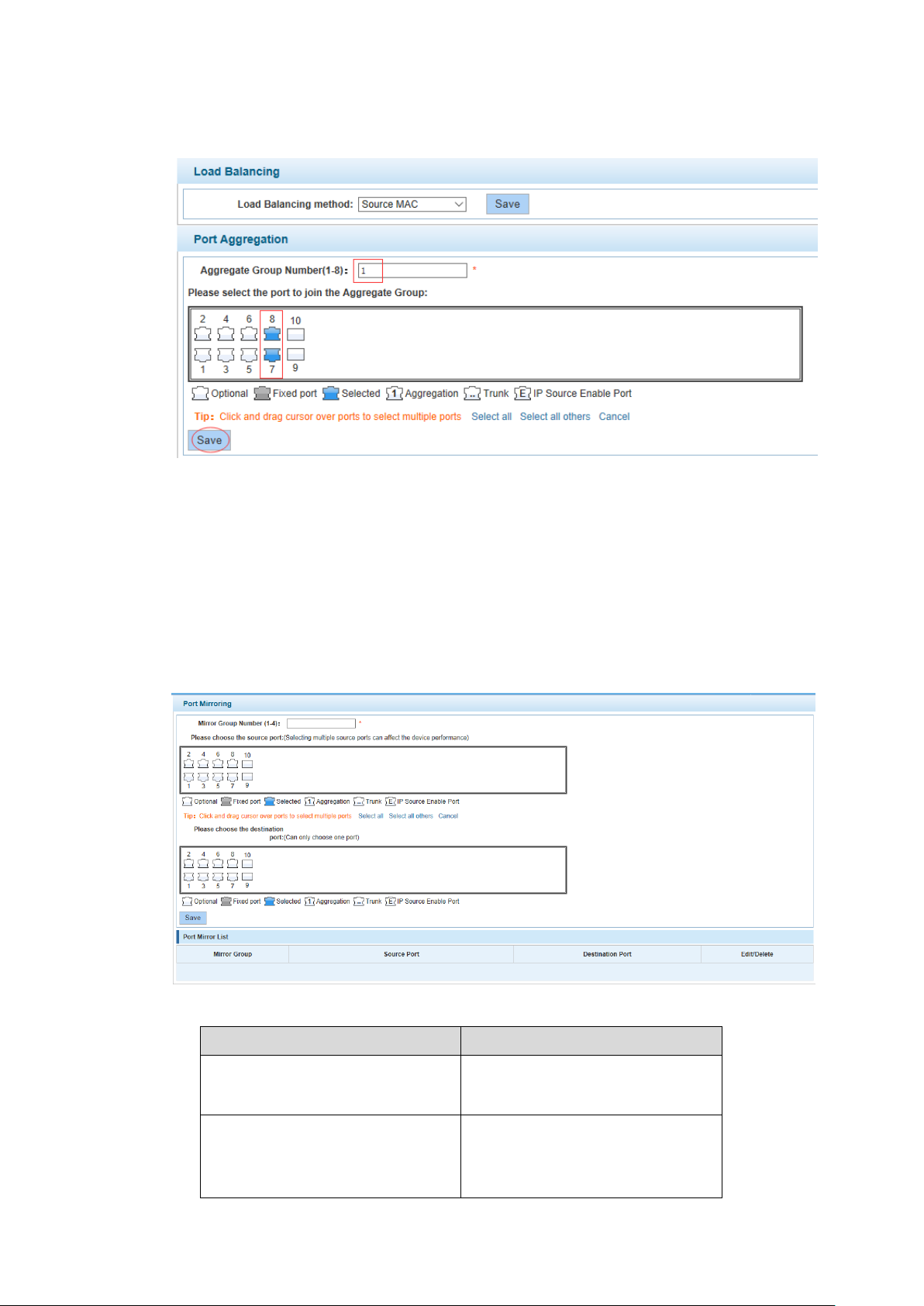
Such as: set the port 7, 8, for aggregation port 1, lets this aggregation port 1 connected to other
Parameter
Description
Source port
To monitor the port in and out of
flow
Destination port
Set destination port, All packets
on the source port are copied and
forwarded to the destination port
switch aggregation port 1 to build switch links.
4.2.3 Port mirroring
Configuration example Figure 4-11
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>port mirroring", Open port mirror feature, All packets on
the source port are copied and forwarded to the destination port, Destination port is usually
connected to a packet analyzer to analyze the source port, Multiple ports can be mirrored to a
destination port, the following picture:
Port mirroring Figure 4-12
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 16
Page 27
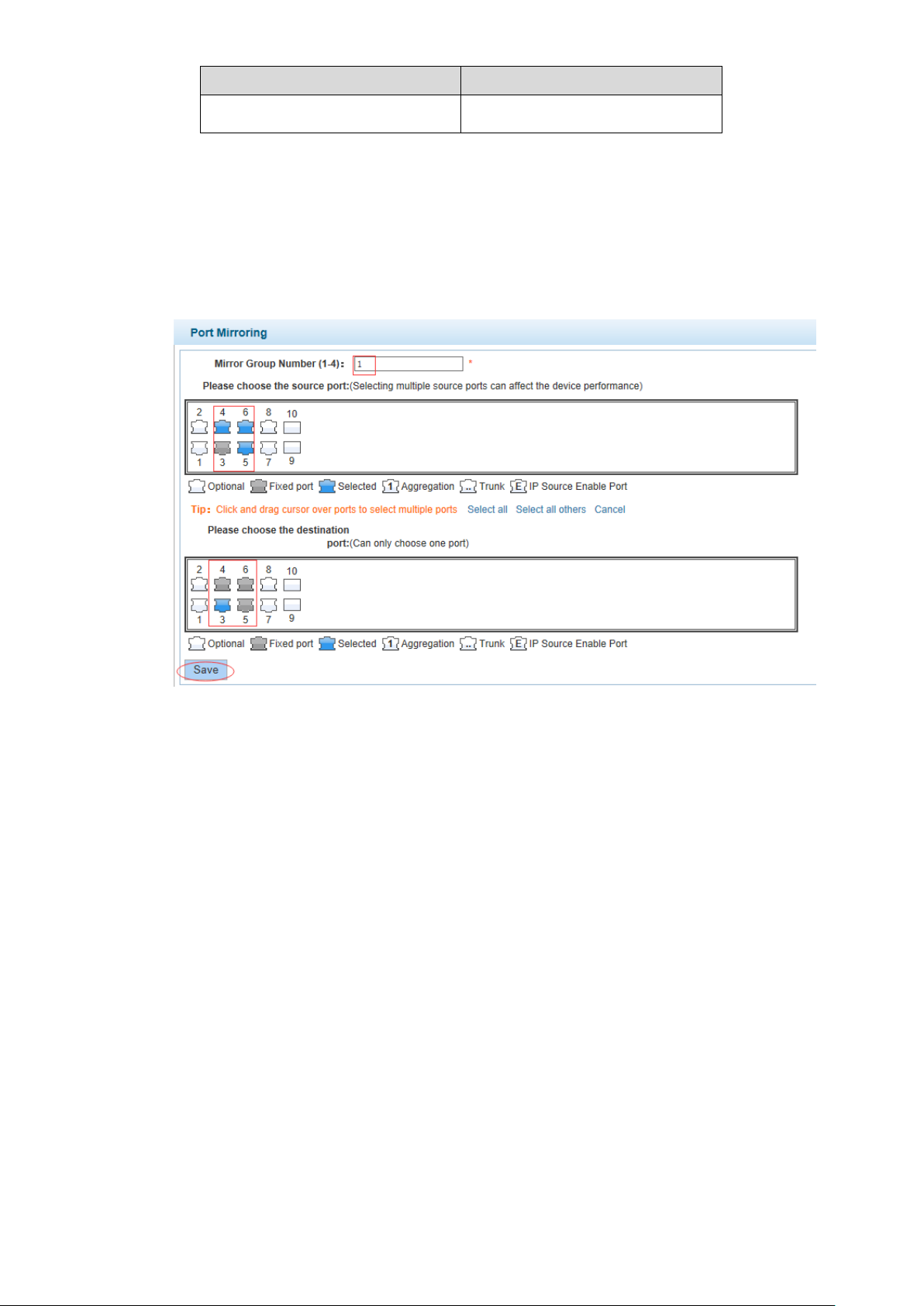
Parameter
Description
Mirror group
Range: 1-4
【Instructions】
The port of the aggregate port cannot be used as a destination port and the source port,
destination port and source port cannot be the same.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: set a mirror group for port 3 regulatory port 4, 5, 6 on and out flow conditions.
Configuration example Figure 4-13
4.2.4 Port rate-limit
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>port rate-limit ", to port output, input speed limit. The
following picture:
Switch Configuration 17
Page 28
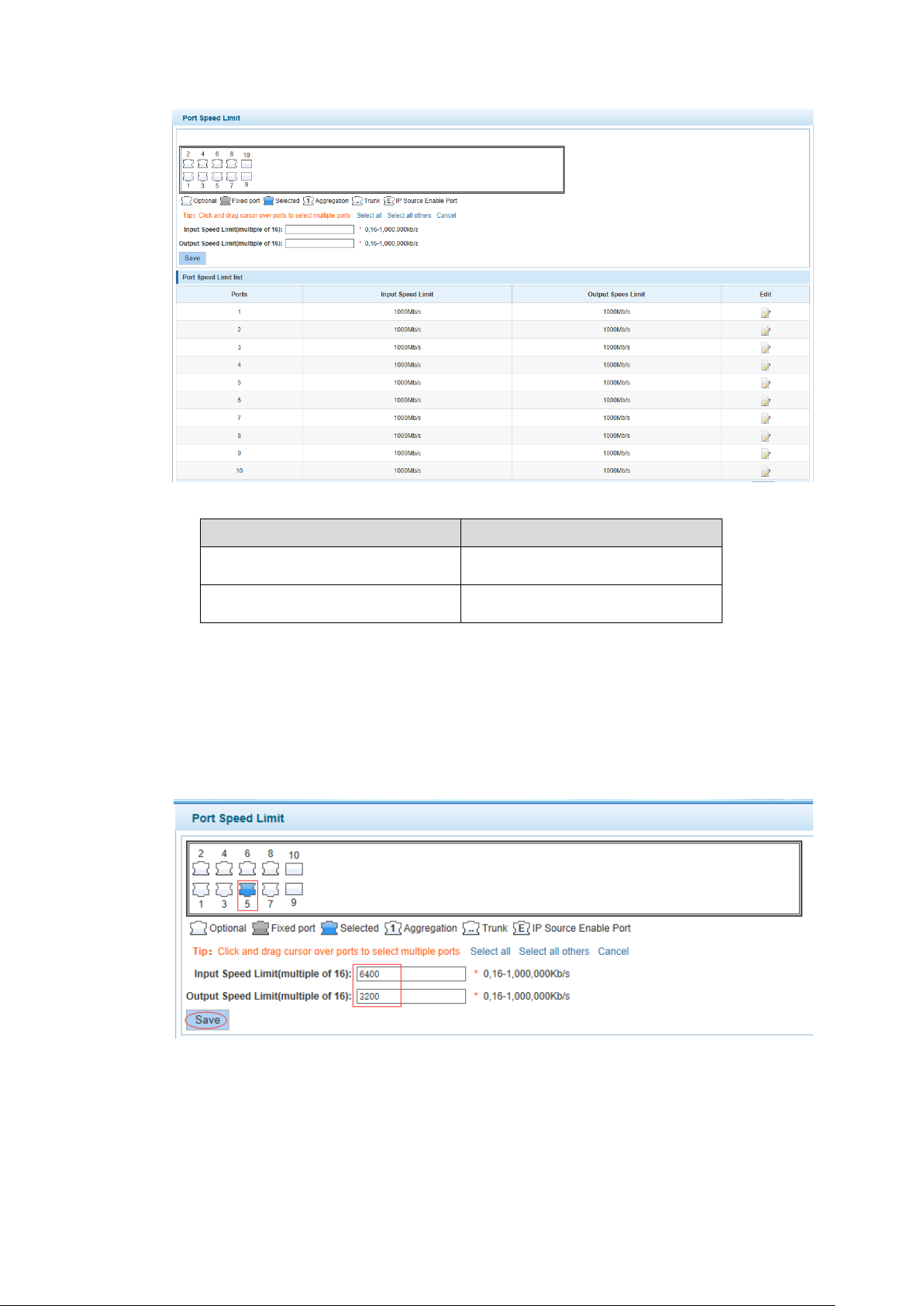
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Input speed limit
Set port input speed
Output speed limit
Set port output speed
Port rate-limit Figure 4-14
【Instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s. That is, the theoretical rate of 1M bandwidth
is125KB/s.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: the port 5 input rate is set to 6400 KB/s, the output rate is set to 3200 KB/s.
Configuration example Figure 4-15
4.2.5 Storm control
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>Storm control", to port storm control config. The
following picture:
Switch Configuration 18
Page 29

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Broadcast Limit
Storm suppression value of the
broadcast packets
Multicast Limit
Storm suppression value of the
multicast packets
Unicast Limit
Storm suppression value of the
unicast packets
Storm control Figure 4-16
【Instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s. That is, the theoretical rate of 1M bandwidth
is 125KB/s.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: should be forwarded to the port 1-8 of all kinds of packet forwarding rate is 5000 KB/s.
Switch Configuration 19
Page 30

4.2.6 Port isolation
Parameter
Description
Source port
Choose a port, to configure the
isolated port
Isolated port
Port will be isolated
In the navigation bar to select "PORT>port isolation ", ports are isolated. The following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-17
Port isolation Figure 4-18
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Open port isolation function, all packets on the source port are not forwarded from the isolated
port, the selected ports are isolated.
Ports that have been added to the aggregate port aren't also capable of being a destination port
and source port, destination port and source port cannot be the same.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: the port 3, 4, 5, and 6 ports isolated.
Switch Configuration 20
Page 31

Configuration example I Figure 4-19
Parameter
Description
Input Flow
Port input flow statistics
Output Flow
Port output flow statistics
Configuration example II Figure 4-20
4.2.7 Port information
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>Port Information”, the following picture:
Port information Figure 4-21
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Show port input and output streams information port connection status, belongs to VLAN.
【Configuration Example】
Switch Configuration 21
Page 32

Enter port number 8 for the query.
Parameter
Description
VLAN ID
VLAN number
VLAN name
VLAN mark
VLAN IP address
Manage switch IP address
4.3 VLAN
In the navigation bar to select "VLAN", you can manage the VLAN config, Trunk Settings and
Hybrid Settings, the following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-22
VLAN settings Figure 4-23
4.3.1 VLAN Settings
In the navigation bar to select "VLAN config>VLAN Settings", Vlans can be created and set
the port to the VLAN (port default state for the access mode), the following picture:
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Management VLAN, the default VLAN cannot be deleted. Add ports to access port, port access
mode can only be a member of the VLAN.
【Configuration Example】
VLAN settings Figure 4-24
Such as: connect switches pc1, pc2 couldn't ping each other, will be one of the PC connection
port belongs to a VLAN 2.
Switch Configuration 22
Page 33

4.3.2 Access Port Settings
Parameter
Description
Native VLAN
Only set one
Configuration example Figure 4-25
In the navigation bar to select "VLAN config>Access-port setting", can set port to Access
port, the following picture:
Access port settings Figure 4-26
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Switch Configuration 23
Native VLAN: Refers to the default Access VLAN, must be the same as the end of the VLAN
Native port, otherwise it can’t work.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Port 8, Access VLAN2.
Page 34

Configuration example I Figure 4-27
Parameter
Description
Native VLAN
Only set one
Allowing VLAN
Can set up multiple
Configuration example II Figure 4-28
4.3.3 Trunk-port setting
In the navigation bar to select "VLAN config>trunk-port setting", can set port to Trunk port,
the following picture:
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Native VLAN: as a Trunk, the mouth will belong to a Native VLAN. The so-called Native VLAN,
is refers to UNTAG send or receive a message on the interface, is considered belongs to the
VLAN. Obviously, the interface of the default VLAN ID (PVID) in the IEEE 802.1 Q VLAN ID is
the Native VLAN. At the same time, send belong to Native VLAN frame on the Trunk, must
adopt UNTAG way.
Trunk port Figure 4-29
Allowed VLAN list: a Trunk can transport the equipment support by default all the VLAN traffic
(1-4094). But, also can by setting the permission VLAN Trunk at the mouth of the list to limit the
flow of some VLAN can't through the Trunk.
Switch Configuration 24
Page 35

【Configuration Example】
Such as: PVID=VLAN2
PC1:192.168.1.122, port 8, access VLAN2
PC2:192.168.1.123, port 7, Trunk allowed VLAN 1-2
PC3:192.168.1.124, port 6, access VLAN1 (The default port belongs to VLAN1)
Can let the PC2 PING PC1, cannot PING PC3
Configuration example I Figure 4-30
Configuration example II Figure 4-31
4.3.4 Hybrid-port setting
In the navigation bar to select "VLAN config>hybrid-port setting", Can set the port to take the
tag and without the tag, the following picture:
【Instructions】
Hybrid port to packet:
Receives a packet, judge whether there is a VLAN information: if there is no play in port PVID,
exchanged and forwarding, if have, whether the Hybrid port allows the VLAN data into: if can be
forwarded, or discarded (untag on port configuration is not considered, untag configuration only
work when to send it a message)
Hybrid port settings Figure 4-32
Hybrid port to send packet:
Switch Configuration 25
Page 36

Determine the VLAN in this port attributes (disp interface can see the port to which Step 1
VLAN untag, which VLAN tag).
If it is untag stripping VLAN information, send again, if the tag is sent directly. Step 2
【Configuration Example】
Such as: create vlans 10, 20, VLAN sets the Native VLAN port 1 to 10, to tag VLAN for 10, 20,
sets the Native VLAN port 2 to 20, to tag VLAN for 10, 20.
Switch Configuration 26
Page 37

Configuration example I Figure 4-33
Configuration example II Figure 4-34
Configuration example III Figure 4-35
Configuration example IV Figure 4-36
Switch Configuration 27
Page 38

This system e0/1 and the receive system e0/2 PC can be exchanged, but when each data
taken from a VLAN is different
Data from the pc1, by inter0/1 pvid VLAN10 encapsulation VLAN10 labeled into switches,
switch found system e0/2 allows 10 data through the VLAN, so the data is forwarded to the
system e0/2, because the system e0/2 VLAN is untagged 10, then switches at this time to
remove packet VLAN10 tag, in the form of ordinary package sent to pc2, pc1 - > pc2 is VLAN10
walking at this time.
Again to analyze pc2 gave pc1 package process, data from the pc2, by inter0/2 pvid VLAN20
encapsulation VLAN20 labeled into switch, switch found system e0/1 allows VLAN by 20 data,
so the data is forwarded to the system e0/1, because the system e0/1 on the VLAN is untagged
20, then switches remove packets on VLAN20 tag at this time, in the form of ordinary package
sent to pc1, pc2 at this time - > pc1 is VLAN 20.
4.4 Fault/Safety
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety", you can set Anti attack, Channel detection and
ACL configuration.
Fault/safety Figure 4-37
4.4.1 Anti attack
4.4.1.1 DHCP
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety>anti attack>DHCP", Open the DHCP anti-attack
function, intercepting counterfeit DHCP server and address depletion attack packets ban
kangaroo DHCP server, the following picture:
【Instructions】
DHCP Figure 4-38
DHCP trusted port configuration, select the port as a trusted port. Prohibit DHCP for address,
select the port and save, you can disable this feature for the port.
Switch Configuration 28
Page 39

Open DHCP attack prevention function, need to set the DHCP protective vlan simultaneously,
other functions to take effect.
【Configuration Example】
DHCP snooping open Step 1
Snooping open Figure 4-39
Setting DHCP snooping vlan Step 2
Set DHCP snooping vlan Figure 4-40
Set the connection router 8 ports for trust, then 6 port is set to the prohibit. Step 3
Set trusted router Figure 4-41
Set restricted ports Figure 4-42
Verify source mac F0:DE:F1:12:98:D2, set server ip address to 192.168.1.110. Step 4
Verify MAC address Figure 4-43
Set option82 information Step 5
Switch Configuration 29
Page 40

Set option82 information Figure 4-44
IP address Figure 4-45
The port 7 for binding. Step 6
Binding table Figure 4-46
4.4.1.2 OS
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety>anti attack>DOS", Open the anti DOS attack
function, intercept Land attack packets, illegal TCP packets, to ensure that the device or server
to provide normal service to legitimate users, the following picture:
【Instructions】
Open the anti DOS attack function, intercept Land attack packets, illegal TCP packets, to
ensure that the device or server to provide normal service to legitimate users.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Open the anti DOS attack function
DOS Figure 4-47
Switch Configuration 30
Page 41

4.4.1.3 IP source guard
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety>anti attack>ip source guard", Through the source
port security is enabled, on port forwarding the packet filter control, prevent illegal message
through the port, thereby limiting the illegal use of network resources, improve the safety of the
port, the following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-48
IP source guard Figure 4-49
【Instructions】
Add the port that is currently being used as a IP source protection enable port, the port will not
be able to use.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: to open source IP protection enabled port first, then to binding.
Switch Configuration 31
Page 42

Configuration example I Figure 4-50
Configuration example II Figure 4-51
4.4.1.4 IP/Mac/Port
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety>anti attack>IP/Mac/Port", automatically detect the
port based IP address, MAC address of the mapping relationship, and then realize the function
of a key binding, the following picture:
【Instructions】
IP/Mac/Port Figure 4-52
Switch Configuration 32
Page 43

A bond must be bound before the binding to enable the switch to open, And if you want to
access shall be binding and switch the IP address of the same network segment .
【Configuration Example】
Such as: the binding to make first can open, must be a key bindings port 7
Configuration example I Figure 4-53
Configuration example II Figure 4-54
Can check the delete option.
4.4.2 Channel detection
4.4.2.1 Ping
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety> channel detection>ping", Use ping function to
test internet connect and host whether to arrive. The following picture:
Configuration example IV Figure 4-55
Switch Configuration 33
Page 44

Ping Figure 4-56
Parameter
Description
Destination IP address
Fill in the IP address of the need
to detect
Timeout in Seconds
Range of 1 to 10
Ping Count
Testing number
Parameter
Description
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
Use ping function to test internet connect and host whether to arrive.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: PING connects the IP address of the PC.
4.4.2.2 tracert
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety> channel detection>tracert". Tracert detection
can detect to the destination through the .The following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-57
Tracert Figure 4-58
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 34
Page 45

Parameter
Description
Destination IP address
Fill in the IP address of the need
to detect
Timeout period
Range of 1 to 10
【instruction】
The function is used to detect more is up to and reach the destination path. If a destination
unreachable, diagnose problems.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Tracert connect the IP address of the PC.
Configuration example Figure 4-59
4.4.2.3 Cable test
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety> channel detection>cable test", Can detect
connection device status, the following picture:
【Configuration Example】
Cable test Figure 4-60
Switch Configuration 35
Page 46

4.4.3 ACL
In the navigation bar to select "fault/safety>ACL", can be applied to port ACL rules and
Settings to take effect in time.
Configuration example Figure 4-61
ACL Figure 4-62
【Instruction】
The ACL rules are sequenced, row in front of the match will be priority rule. Many, if the strategy
items operating time is relatively longer.
Basic principles:
According to the order, as long as there is a meet, will not continue to find. Step 1
Implied refused, if don't match, so must match the final implied refused entry, cisco Step 2
default.
Any only under the condition of the minimum permissions to the user can satisfy their Step 3
demand.
Don't forget to apply the ACL to the port. Step 4
【Configuration Example】
such as: test time is every Monday to Friday 9 to 18 points, set port 1-6 cannot access the
network .
steps: building ACL time - building ACL rules - is applied to the port.
Switch Configuration 36
Page 47

Configuration example I Figure 4-63
Configuration example II Figure 4-64
Configuration example III Figure 4-65
Configuration example IV Figure 4-66
Switch Configuration 37
Page 48

4.5 PoE
Parameter
Description
In the navigation bar to select "PoE", you can set the PoE Port Config configuration.
Configuration example V Figure 4-67
PoE Figure 4-68
4.5.1 PoE Port Config
4.5.1.1 Poe Port Config
In the navigation bar to select "POE>POE Port Config>Poe Port Config", you can set Poe
Port, As follows.
Poe port Config Figure 4-69
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 38
Page 49

Parameter
Description
port enabled
You can enable or disable PoE
function
Power supply priority
Configure port priority, when the
load exceeds the maximum
power POE, low priority port
equipment will be dropped
threshold
You can specify threshold
Port power
You can configure max power of
port
【Configuration Example】
Such as: The PoE function of port 8 can be enabled, the maximum Port power is 23 W,
threshold is 15mA, and the Power supply priority is high.
4.5.1.2 Temperature distribution
Configuration example Figure 4-70
In the navigation bar to select "POE>POE port Config>Temperature distribution", you can view
temperature distribution, As follows.
4.6 STP
In the navigation bar to select "STP", you can set to the MSTP region and STP bridge
configuration.
Switch Configuration 39
Temperature distribution Figure 4-71
Page 50

4.6.1 MSTP region
Parameter
Description
Region Name
Configure the region name
Revision Level
Parameter configuration revision
level
Instance ID
Select configuration instance ID
VLAN ID
Mapping of the VLAN
configuration instance
In the navigation bar to select "STP>MSTP region", Can modify the domain and domain name,
add instance is mapped to a VLAN. The following picture.
STP Figure 4-72
MSTP region Figure 4-73
【Parameter Description】
【instruction】
An instance can only be mapped to a VLAN, instance and VLAN is a one-to-one relationship.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: change the region to DEADBEEF0102, region name is 123, instance 4 is mapped to a
VLAN 2, in the first need to create a VLAN 2.
Switch Configuration 40
Page 51

4.6.2 STP bridge
Parameter
Description
Instance Priority
Whether open instance priority
Configuration example I Figure 4-74
Configuration example II Figure 4-75
In the navigation bar to select "STP>STP bridge", Can be related to bridge, port configuration,
the following picture:
STP bridge Figure 4-76
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 41
Page 52

Parameter
Description
setting
Instance ID
Select the created instance id is
configured
Bridge Priority
Priority setting bridge example,
the default instance bridge priority
for 32768
Enable
Whether to open the STP bridge
function
Mode
The model is divided into: the
STP, RSTP, MSTP
Hello Time
Switches sends bpdu in packet
interval
Max Age
Ports are not yet received a
message in the time, will initiate
topology changes
Forward Delay
The state of the port switch time
Port Priority
Set port instance priority, defaults
to 128, you must enter multiple of
16, the range of 0-240
Path Cost
Configure port costs
Port Fast
Select configuration state
Auto Edge
Select configuration state
Point to Point
Select configuration state
BPDU Guard
Select configuration state
BPDU Filter
Select configuration state
Compatible
Select configuration state
Root Guard
Select configuration state
TC Guard
Select configuration state
TC Ignore
Select configuration state
【Instruction】
(hello_time+1)×2<=max_age<=(f_delay-1)×2 , enable the switch to set instance Step 1
priority.
Enable STP or switch mode would spend 2 times of the forward delay time. Step 2
【Configuration Example】
Open the STP, configuration has to create an instance of the priority, configuration time Step 1
parameters, set the pattern to MSTP.
Switch Configuration 42
Page 53

Configuration example I Figure 4-77
Configuration example II Figure 4-78
Set MSTP has launched port configuration, select the created instance, set priority Step 2
(port configuration is not online, on-line configuration will only take effect, can click on
the "view the current configuration" button to view the configured completed)
4.7 DHCP relay
In the navigation bar to select "DHCP relay", you can set to the DHCP relay and option82.
Switch Configuration 43
Page 54

4.7.1 DHCP relay
Parameter
Description
IP address
DHCP server address
status
Invalid and valid
In the navigation bar to select "DHCP relay>DHCP relay", Open the DHCP relay function, set
up and view the relay server IP address and its status. The following picture.
【Parameter Description】
DHCP relay Figure 4-79
Enable Figure 4-80
【Instruction】
If open the function of relay agent, then receives the broadcast DHCP message, to be delivered
in the form of unicast to configure on the server. The DHCP server to IP and switches in the
same network segment will only take effect.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: setting DHCP server ip for 192.168.1.22
4.7.2 0ption82
In the navigation bar to select "DHCP relay>option82", can set to OPTION82 circuit control,
proxy remote, ip address. The following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-81
Switch Configuration 44
Page 55

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
VLAN ID
the DHCP request message in the
VLAN, value range is 1 ~ 4094
Circuit Control
Circuit ID to populate the user
custom content, scope of string
length is 3 ~ 63
Proxy Remote
Configuration ASCII remote id
string value, the length of the
range of 1 ~ 63
IP Address
Decimal IP address
Option82 Figure 4-82
【Instruction】
Switches, relay information to the DHCP server will take option82, VLAN ID must be configured
to DHCP message taken VLAN can bring option82 information.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: add circuit control, proxy remote, ip address information.
Switch Configuration 45
Page 56

Configuration example I Figure 4-83
Configuration example II Figure 4-84
Configuration example III Figure 4-85
4.8 QoS
In the navigation bar to select "QoS", you can set to the Remark, queue config and mapping
the queue.
4.8.1 Queue config
In the navigation bar to select" QoS>queue config", Can be set up queue scheduling
policy .the following picture:
QoS Figure 4-86
Switch Configuration 46
Page 57

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Scheduling strategy
Can choose four kinds of modes:
RR round-robin scheduling
SP absolute priority scheduling
WRR weighted round-robin
scheduling
WFQ weighted fair scheduling
WRR-weights
Set the weights of each queue,
they will be in proportion to
occupy the bandwidth to send
data
Queue config Figure 4-87
【Instruction】
Queue 7 cannot for 0.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: set the scheduling strategy for WRR, weight value respectively, 10, 11, 12, 12, 14, 15,
16, 17.
4.8.2 Mapping the queue
4.8.2.1 COS Queue Map
Configuration example Figure 4-88
In the navigation bar to select "QoS>mapping the queue>COS Queue Map", Service
Switch Configuration 47
category can be mapped to the corresponding queue. The following picture.
Page 58

COS queue map Figure 4-89
Parameter
Description
Server ID
COS the VLAN priority fields (0 to
7)
Queue ID
Set each cosine value mapping
queue number (0 to 7)
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Such as: cos 3 mapping to the queue 7, set the queue weight 7 to 10.
Configuration example I Figure 4-90
4.8.2.2 DSCP COS Map
In the navigation bar to select "QoS>mapping the queue>DSCP COS Map", Differential
service can be mapped to the corresponding service categories. the following picture:
Configuration example II Figure 4-91
Switch Configuration 48
Page 59

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Server list
DSCP field has seven (0-63) is
divided into four tables
Server ID
Map the DSCP to COS fields (0 to
7), based on the cosine is
mapped to a queue
DSCP COS map Figure 4-92
【Instruction】
Cos priority is greater than the DSCP, DSCP priority is greater than the port.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: the DSCP value of 3, 12, 23 mapping to cos 5.
Configuration example Figure 4-93
4.8.2.3 Port COS Map
In the navigation bar to select "QoS>mapping the queue>Port COS Map", Port can be
mapped to the corresponding service categories. the following picture:
Switch Configuration 49
Page 60

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Port
Select the port number (1-10)
Service ID
Mapped to the service ID, and
then according to the service ID
into the queue
Port COS map Figure 4-94
【Instruction】
Cos priority is greater than the DSCP, DSCP priority is greater than the port.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: port 4, 5, 6 respectively cos4, cos5, cos6.
Switch Configuration 50
Page 61

Configuration example I Figure 4-95
Configuration example II Figure 4-96
Configuration example III Figure 4-97
Configuration example IV Figure 4-98
4.9 Addr table
In the navigation bar to select “Address table", you can set to MAC Management, MAC
learning and Aging and MAC Filter.
Switch Configuration 51
Page 62

4.9.1 MAC Management
Parameter
Description
Clear Mac
Can choose to clear the multicast
Mac address, clear dynamic
unicast Mac address, clear static
unicast Mac address, clear the
specified Mac address, Mac
address table
VLAN
Fill in the need to add or delete
VLAN id, not create VLAN to
create can only take effect
In the navigation bar to select “Address table>MAC Management", you can add static Mac
and delete Mac and view to the current of the Mac address table. The following picture:
MAC management Figure 4-99
MAC management Figure 4-100
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 52
Page 63

【Instruction】
According to different conditions to clear Mac address, view/add/learn the Mac address, Mac
address filtering.
【Configuration Example】
The port 6 Mac set to static Mac. Step 1
Configuration example I Figure 4-101
Clear port 6 static Mac addresses. Step 2
Configuration example II Figure 4-102
4.9.2 MAC Learning and Aging
In the navigation bar to select “address table>MAC Learning and Aging", Can be set up port
Mac address study limit and Mac address aging time. The following picture:
Switch Configuration 53
Page 64

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Mac address
Range 0-8191,default 8191
Mac address study limit
Default 300
MAC learning and aging Figure 4-103
【Configuration Example】
Setting port 2, 3, 4, 5 address study limit for 2000. Step 1
Will be dropped or learn the Mac address of the port equipment after 2 minutes Step 2
disappear automatically from the Mac address table.
Configuration example I Figure 4-104
Switch Configuration 54
Page 65

4.9.3 MAC Filter
Parameter
Description
Mac address
Can’t add multicast Mac address
VLAN
VLAN number
In the navigation bar to select "address table>MAC Filter", Can be filtered according to the
condition does not need the Mac address. The following picture:
【Parameter Description】
Configuration example II Figure 4-105
MAC filter Figure 4-106
【Configuration Example】
Such as: the Mac address for 00:20:15:09:12:12 added to the filter in the table.
4.10 SNMP
In the navigation bar to select “SNMP", you can set to the Snmp config and Rmon config.
Configuration example I Figure 4-107
Switch Configuration 55
Page 66

4.10.2 Snmp config
Parameter
Description
group
Community string, is equal to the
NMS and Snmp agent
4.10.2.1 Snmp config
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp >Snmp config", you can Snmp function enable. The
following picture:
SNMP Figure 4-108
SNMP Config Figure 4-109
【Instruction】
The SNMP function must be turned on in the configuration RMON, otherwise it will be
configured to fail.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: open Snmp.
4.10.2.2 Community config
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp >Snmp config>community config", Can specify group
access. The following picture.
Configuration example Figure 4-110
Community Config Figure 4-111
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 56
Page 67

Parameter
Description
communication between the
password
Access authority
Read-only: specify the NMS
(Snmp host) of MIB variables can
only be read, cannot be modified
Read-only can write: specify the
NMS (Snmp host) of MIB
variables can only read, can also
be modified
【Instruction】
Parameter
Description
View name
View name
include
Indicate the MIB object number
contained within the view
exclude
Indicate the MIB object son
number was left out of view
The upper limit of the number of groups is 8.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: add a read-write group called public.
4.10.2.3 View config
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp >Snmp config>view config", Set the view the rules to
allow or disable access to some of the MIB object. The following picture.
Configuration example Figure 4-112
View Config Figure 4-113
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 57
Page 68

Parameter
Description
MIB Subtree OID
View the associated MIB object, is
a number of MIB
Subtree mask
MIB OID mask
【Instruction】
Parameter
Description
Group name
Group name
Security level
Attestation not only encryption:
this group of users transmission
of the message need to verify the
data don't need to confidential
Each view is best to configure a view rule; otherwise it will affect the SNMP function.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: establish a view 123 , MIB subtree oid .1.3.6.1 contain among them.
Configuration example I Figure 4-114
Configuration example II Figure 4-115
4.10.2.4 Group config
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp>Snmp config>group config", setting Snmp group. The
following picture.
【Parameter Description】
group Config Figure 4-116
Switch Configuration 58
Page 69

Parameter
Description
No authentication encryption: this
group of users' messages don't
need to verify data transmission
also does not need to be kept
secret
Both authentication and
encryption: this group of users
need to verify the news of
transmission and transmission of
data need to be kept secret
Read view, read and write
view ,study view
The associated view name
【Instruction】
Before the cap on the number set of configuration of 8, the new group needs a new view to
create a group.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: firstly, new view 123, then new group of goup1.
Configuration example I Figure 4-117
Configuration example II Figure 4-118
4.10.2.5 User config
Switch Configuration 59
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp>Snmp config>user config", setting Snmp user. The
following picture:
Page 70

【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
User Name
User name, range 1-16
Security Level
Attestation not only encryption:
this group of users transmission
of the message need to verify the
data don't need to confidential
No authentication encryption: this
group of users' messages don't
need to verify data transmission
also does not need to be kept
secret
Both authentication and
encryption: this group of users
need to verify the news of
transmission and transmission of
data need to be kept secret
Authentication Mode
Specified use MD5 authentication
protocol or SHA authentication
protocol
Authentication Password
Range 8-10
Encrypt Mode
Specified using AES encryption
protocol or DES encryption
protocol
Group Name
A user group name
Encrypt Password
Range 8-60
User Config Figure 4-119
【Instruction】
Cap on the number configuration of 8, users need a new view and group to use, the user's
security level must be consistent with the group level of security. Add a user authentication and
encryption, and configure belong to groups of users; the user will be used for Snmpv3
connection.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: new view 123, the newly built group group1, new user1.
Switch Configuration 60
Page 71

4.10.2.6 Trap Config
Parameter
Description
Destination IP address
Snmp host ipv4 address
Security name
Snmp user name
version
V1,V2,V3
Security mode
Specified using AES encryption
protocol or DES encryption
protocol
Group name
User group name
Configuration example Figure 4-120
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp>Snmp config>Trap Config", Can specify sent the trap
messages to Snmp host (NMS). The following picture:
Trap Config Figure 4-121
【Parameter Description】
【Instruction】
The Trap cap on the number configuration of 8, you can configure a number of different Snmp
Trap host used to receive messages. Trigger the trap message time: port Linkup/LinkDown,
equipment of cold - start (restart when power supply drop)/warm - start (a warm restart), and
Rmon set port statistical fluctuation threshold.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: setting hoset 192.168.1.30 receives trap information.
Switch Configuration 61
Page 72

4.10.3 Rmon config
Parameter
Description
Index
The index number, the value
range of statistical information
table is 1 ~ 65535
Interface Name
To monitor the source port
owner
Set the table creator, range: 1 ~
30 characters of a string
4.10.3.1 Statistics group
Configuration example Figure 4-122
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp>Rmon config>statistics group", Set an Ethernet
interface statistics .the following picture:
Statistics group Figure 4-123
【Parameter Description】
【Instruction】
At the time of configuration Rmon Snmp functions must be open; otherwise the prompt dialog
box will appear.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: set up monitoring Ethernet port after 4 to check the data.
Switch Configuration 62
Page 73

Configuration example I Figure 4-124
Parameter
Description
Index
Historical control table item index
number, value range is 1 ~ 65535
Interface Name
To record the Ethernet interface
Maximum Number of Samples
Set the history control table item
of the corresponding table
capacity, namely the Max for
number of records the history
Configuration example II Figure 4-125
4.10.3.2 History group
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp>Rmon config>history group", Record the history of an
Ethernet interface information. The following picture.
【Parameter Description】
History group Figure 4-126
Switch Configuration 63
Page 74

Parameter
Description
table, value range is 1 ~ 65535
Sample Period
Set up the statistical period,
scope for 5 ~ 3600, the unit is in
seconds
Owner
Set the table creator, range: 1 ~
30 characters of a string
【Instruction】
Parameter
Description
Index
The index number, the value
range of the event table is 1 ~
65535
Description
The Trap events, when the event
is triggered, the system will send
the Trap message, Log events,
At the time of configuration Rmon Snmp functions must be open, otherwise the prompt dialog
box will appear.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: monitor Ethernet port 4 historical information.
4.10.3.3 Event group
Configuration example Figure 4-127
In the navigation bar to select “Snmp >Rmon config>event group", The way in which define
events trigger and record them. The following picture.
Event group Figure 4-128
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 64
Page 75

Parameter
Description
when the event is triggered, the
system will log
Owner
Set the table creator, ownername
for 1 ~ 30 characters of a string
【Instruction】
Parameter
Description
Index
The alarm list items index
number, value range is 1 ~ 65535
Static Event
Statistical type
values :3:DropEvents. 4:Octets.
5:Pkts. 6:BroadcastPkts.
7:MulticastPkts.
8:CRCAlignErrors.
9:UndersizePkts.
10:OversizePkts. 11:Fragments.
12:Jabbers. 12:Collisions.
14:Pkts64Octets.
At the time of configuration Rmon Snmp functions must be open; otherwise the prompt dialog
box will appear.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: create an event to trigger 345, the system sends the trap message and log.
4.10.3.4 Alarm group
Configuration example Figure 4-129
In the navigation bar to select" Snmp>Rmon config>alarm group", define alarm group. The
following picture.
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 65
Alarm group Figure 4-130
Page 76

Parameter
Description
15:Pkts65to127Octets.
16:Pkts128to255Octets.
17:Pkts256to511Octets.
18:Pkts512to1023Octets.
19:Pkts1024to1518Octets
Statistical Group Index
Set up the corresponding
statistics statistical index number,
decided to statistics to monitor the
port number
Sampling Time Interval
Sampling time interval, the scope
for 5 ~ 65535, the unit for seconds
Sampling Type
Sample types for the absolute
value of sampling, the sampling
time arrived directly extracting the
value of a variable
Last Sample Count
Sampling type for change value
sampling, extraction of the arrival
of the sampling time is variable in
the change of the sampling
interval value
Upper Alarm threshold Limit
Set the upper limit the Parameter
values
Lower Alarm threshold Limit
Set the lower limit Parameter
values
Upper Alarm/Lower Alarm
threshold Limit Events
Upper/lower limit reached, for
each event
Owner
Set the table creator, ownername
for 1 ~ 30 characters of a string
【Instruction】
At the time of configuration Rmon Snmp functions must be open, otherwise the prompt dialog
box will appear. This configuration needs to configure statistics groups and events.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: new statistics group of 77 and the event group 345, set up more than 12 and below
the lower limit 3 , Beyond the scope of alarm.
Switch Configuration 66
Page 77

4.11 LACP
In the navigation bar to select "LACP”, you can set to the lacp config.
Configuration example Figure 4-131
LACP Figure 4-132
4.11.2 Lacp config
In the navigation bar to select "LACP>Lacp config" the following picture:
Switch Configuration 67
Page 78

LACP settings Figure 4-133
4.11.2.2 LACP Setting
In the navigation bar to select "LACP>Lacp config>LACP settings” the following picture:
LACP settings Figure 4-134
LACP status
Switch Configuration 68
Page 79

LACP status Figure 4-135
Open or close LACP.
LACP public parameter settings
LACP public parameter settings Figure 4-136
You can set to System settings, range 1-65535.
LACP activation port parameter settings
Port priority: You can set to Port priority. Rang 1-65535
Aggregate port number: You can select the Aggregate port number.
Aggregate model: You can select the Aggregate port number. Include active and passive.
4.11.2.3 LACP Display
LACP activation port parameter settings Figure 4-137
In the navigation bar to select “LACP>Lacp config>LACP Display”,You can see the table of
lacp. The following picture:
Switch Configuration 69
Page 80

4.12 SYSTEM
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM", you can set to the system config, system update,
config management, config save, administor privileges and info collect.
LACP display Figure 4-138
System Figure 4-139
4.12.2 System config
4.12.2.1 System settings
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>system config>System settings", Basic information
set switch. The following picture:
System settings Figure 4-140
【Parameter Description】
Switch Configuration 70
Page 81

Parameter
Description
Device Name
Switch name
Management VLAN
Switches use VLAN management
Management IP
Switch IP address management
Timeout
Don't use more than login timeout
after login to log in again
【Configuration Example】
Set up the VLAN 2 is management VLAN, should first created VLAN 2 the VLAN Step 1
Settings, and set a free port in the VLAN 2.
Configuration example I Figure 4-141
Configuration example II Figure 4-142
Insert the PC interface 9 or 10 ports, set up the management IP for 192.168.2.12, Step 2
device name is yoyo, timeout for 20 minutes, Jumbo frame for 5000.
Switch Configuration 71
Configuration example III Figure 4-143
Page 82

Configuration example IV Figure 4-144
Use 192.168.2.12 logging in, sets the system time. Step 3
Configuration example V Figure 4-145
4.12.2.2 System restart
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>system config>system restart", equipment can be
restarted. The following picture:
【Instruction】
System restart Figure 4-146
Switch Configuration 72
Page 83

Click the button to restart the switch. The restart process may take 1 minute. Please wait
patiently. The page will be refreshed automatically after device
restart.http://192.168.2.1/system/sysreload.htm?1448508984027
【Configuration Example】
Such as: click "restart" button.
4.12.2.3 EEE Enable
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>system config>EEE Enable", The password change
to equipment. The following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-147
EEE enable Figure 4-148
【Instruction】
Energy Efficient Ethernet, Open the EEE features by default.
4.12.2.4 Password
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>system config>password", The password change
to equipment. The following picture:
【Instruction】
If you set a new Web login password, then log in again after seting the new password. Step 4
Password cannot contain Chinese, full-width characters, question marks and spaces. Step 5
If forget the password reset, can be reset in the console. Step 6
Password Figure 4-149
switch(config)# password admin
New Password:3456
Confirm Password:3456
【Configuration Example】
Switch Configuration 73
Page 84

Such as: amend the password to 1234.
4.12.2.5 SSH login
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>system config>ssh login", SSH open. The following
picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-150
SSH login Figure 4-151
【Instruction】
Configure the user to be able to switch through the SSH login device.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: SSH open, you can CRT to log in.
4.12.2.6 Telnet login
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>system config>Telnet login", Telnet open. The
following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-152
Telnet login Figure 4-153
【Instruction】
Configure the user to be able to switch through the Telnet login device.
Switch Configuration 74
Page 85

【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
Log switch
Open and close
Server IP
Appoint to server address
Send Log Level
0-7
Keyword
Enter the required query of
characters
Such as: Telnet open, PC Telnet function open, you can log in.
4.12.2.7 System log
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>password change>system log", to view the log and
set up the log server. the following picture:
Configuration example Figure 4-154
System log Figure 4-155
【Parameter Description】
【Instruction】
Open log switch, set up the syslog server, system log will automatically be pushed to the server.
【Configuration Example】
The error log information in 192.168.1.110 pushed to the server Step 1
Switch Configuration 75
Page 86

Input the Mac keywords, click "query “button, click on the "clear log" button and can Step 2
clear the log.
Figure 4-156
Figure 4-157
4.12.3 System upgrade
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>system upgrade", Optional upgrade file to upgrade.
The following picture.
【Instruction】
Please confirm that the upgraded version of the same model and the same model. Step 1
In the upgrade process, you may encounter flash to make the page is temporarily Step 2
unable to respond to the page, this time cannot power off or restart the device, until
prompted to upgrade successfully!
Figure 4-158
Switch Configuration 76
Page 87

4.12.4 Config management
4.12.4.1 Import/Export Config
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>config management>Import/Export Config", can
import and export configuration files, the backup file. The following picture:
【Instruction】
Import process cannot be closed or refresh the page, or import will fail!
After the introduction of configuration, to enable the new configuration, please in this page
Restart device Otherwise configuration does not take effect.
Figure 4-159
【Configuration Example】
In the configuration first save the page, click save configuration to save the current Step 1
configuration, then export the configuration.
Configuration example I Figure 4-160
Import configuration. Step 2
Switch Configuration 77
Page 88

Configuration example II Figure 4-161
Configuration example III Figure 4-162
Backup. Step 3
4.12.4.2 Restore Config
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>config management>Restore Config", you can
configure backup file. The following picture:
Configuration example IV Figure 4-163
Switch Configuration 78
Page 89

Restore Config Figure 4-164
【Instruction】
Operating this page should be in the current configuration page first, the backup file.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: restore backup.
Configuration example Figure 4-165
4.12.4.3 Factory Reset
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>config management> Factory configura", Can
export the current configuration and restore factory configuration .the following picture:
【Instruction】
Restore the factory configuration, will delete all the current configuration. If you have any useful
configuration, the current system can lead the factory configuration again after the current
configuration.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: restore configuration can be the guide before they leave the current configuration.
Factory reset Figure 4-166
Switch Configuration 79
Page 90

4.12.5 Config save
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>config save", you can save current configuration.
The following picture.
【Instruction】
Save settings will delete all default configurations. If there are useful configurations,
clickbackup Configurations before save the settings.
Configuration example Figure 4-167
Config save Figure 4-168
【Configuration Example】
Such as: click "save settings" button.
4.12.6 Administrator privileges
In the navigation bar to select "SYSTEM>administrator privileges", Configurable ordinary
users. The following picture.
Configuration example Figure 4-169
Administrator settings Figure 4-170
【Instruction】
Only the admin of the super administrator can access this page is used to manage users and
visitors. The user can log in the Web management system of equipment for routine
maintenance. In addition to the admin and user, can add up to five users. Ordinary users can
only access information system home page.
【Configuration Example】
Switch Configuration 80
Page 91

Such as:
4.12.7 Info collect
In the navigation bar to select “SYSTEM>info collect", you can collect to the system debug
information. The following picture.
Configuration example Figure 4-171
Info collect Figure 4-172
【Instruction】
Collect useful infomation, it may take a few moment.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: click on "collect" button.
Switch Configuration 81
Page 92

Technical Specifications Appendix 1
Hardware Specifications
Standards and
Protocols
IEEE 802.3i, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3x, IEEE
802.3z, IEEE802.1Q , IEEE802.1p, IEEE802.3af, IEEE802.3at
Interface
8 x 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-Negotiation ports
2 x 100/1000Mbps SFP port
1 x Console port
1 x AC Power Connector
Network Media
10BASE-T: UTP category 3,4 cable (maximum 100m)
100BASE-TX: UTP category 5,5e cable (maximum 100m)
1000Base-T: UTP category 5, 5e,6 cable (maximum 100m)
1000Base-X:MMF,SMF
Transfer Method
Store-and-Forward
MAC Address Table
8K
Switching Capacity
20Gbps
Packet Forwarding
Rate
14.88Mbps
Packet Buffer
4.1Mbit
Jumbo Frame
10kBytes
PoE Ports(RJ45)
8* PoE ports compliant with 802.3at/af
Power Pin
Assignment
1/2(+),3/6(-)
PoE Budget
140W
Indicator
s
Per
Device
Power(Green),System(Green)
Per Port
Link/Act/Speed:
Green(1000Mbps)/Amber(100/10Mbps) ,PoE(Orange)
Dimensions
(L×W×H)
340*200*44mm
Environment
Operating Temperature: -0℃ - 45℃
Storage Temperature: -40℃ - 70℃
Operating Humidity: 5%~95% non-condensing
Storage humidity: 5%~95% non-condensing
Software Specification
Basic function
Ethernet Setup
Three layers of functional
The ARP deception,
the network cheating
The security policy
ACE capacity
The abbreviations in this glossary are related to the Manual.
Technical Specifications 82
Page 93

Software Specification
STP/RSTP/MSTP
Storm-control
Port Monitor
Port rate-limit
MAC filtering
Filtering the IP port
Static binding IP and
MAC
Arp trust port
Static routing capacity
Ping and Traceroute
ACL
QoS
DAI
VLAN
Port based VLAN
802.1Q VLAN
Safety features
Radius
Tacacs+
Preventing DOS
attacks
dot1x
The gateway ARP
deception
Application protocol
DHCP Relay
DHCP snooping
DHCP Client
FTP/TFTP
Management
HTTP WEB
Telnet
SSH
Console
Other function
LLDP
IGMP Snooping
SNMPV1,V2c,V3
RMON(1,2,3,9)
POE Management
POE Status
Power supply
management
mode(auto/energy/stati
c)
The port priority
Technical Specifications 83
 Loading...
Loading...