
DVD PLAYER
DVG-6000D

CONTENTS
1. PRECAUTIONS------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
AFETY PRECAUTIONS
1-1 S
ERVICING PRECAUTIONS
1-2 S
1-2-1 General Serving Precautions------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2
1-2-2 Insulation Checking Procedure---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
1-3 ESD P
RECAUTIONS
2. REFERENCE INFORMATION ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
OMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
2-1 C
2-1-1 DVD ATAPI Loader ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
2-1-2 NTSC/PAL Digital Video Encoder (AV3168)----------------------------------------------------------------------------6
2-1-3 DVD Processor Chip (Swan-2
2-1-4 8-Pin, 24-Bit, 96kHz Stereo D/A CONVERTER (CS4338)---------------------------------------------------------- 14
2-1-5 Serial EEPROM, 2K (256 x 8) (AT24C02/01) ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
2-1-6 4-Megabit (512 x 8) FLASH RAM (MX29F040) --------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
2-1-7 512K X 16 Bit X 2 Banks Synchronous DRAM (A43L0616) ------------------------------------------------------- 17
3. PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
4. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22
4-1 BASIC
4-2 S
4-3 S
4-4 S
4-5 S
4-6 S
4-7 R
4-10 S
4-11 S
ONNECTIONS
C
ELECTING VIDEO
ELECTING THE DESIRED
ELECTING THE DESIRED
ELECTING THE DESIRED
EARCHING
ESUME PLAY
ELECTING SUBTITLE LANGUAGE
ELECTING ANGLE
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 23
5. DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 25
6. TROUBLESHOOTING ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 26
7. ELECTRICAL PART LIST --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 27
8. BLOCK DIAGRAM ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 34
9. CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 35
10. WIRING DIAGRAM--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 47
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
TM
ES4318)------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 10
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 22
MODE ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 22
MENU ITEM
DVD
MP3
MP3
FOLDER
TITLE
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 23
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 23
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 23
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 23
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
1. Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
1) Before returning an instrument to the customer, always
make a safety check of the entire instrument, including, but
not limited to, the following items:
(1) Be sure that no built-in protective devices are defective
or have been defeated during servicing.
(1) Protective shields are provided to protect both the
technician and the customer. Correctly replace all
missing protective shields, including any remove for
servicing convenience.
(2) When reinstalling the chassis and/or other
assembly in the cabinet, be sure to put back in place
all protective devices, including, but not limited to,
nonmetallic control knobs, insulating fish papers,
adjustment and compartment covers/shields, and
isolation resistor/capacitor networks. Do not operate
this instrument or permit it to be operated without all
protective devices correctly installed and functioning.
(2) Be sure that there are no cabinet opening through which
adults or children might be able to insert their fingers
and contact a hazardous voltage. Such openings
include, but are not limited to, excessively wide
cabinet ventilation slots, and an improperly fitted
and/or incorrectly secured cabinet back cover.
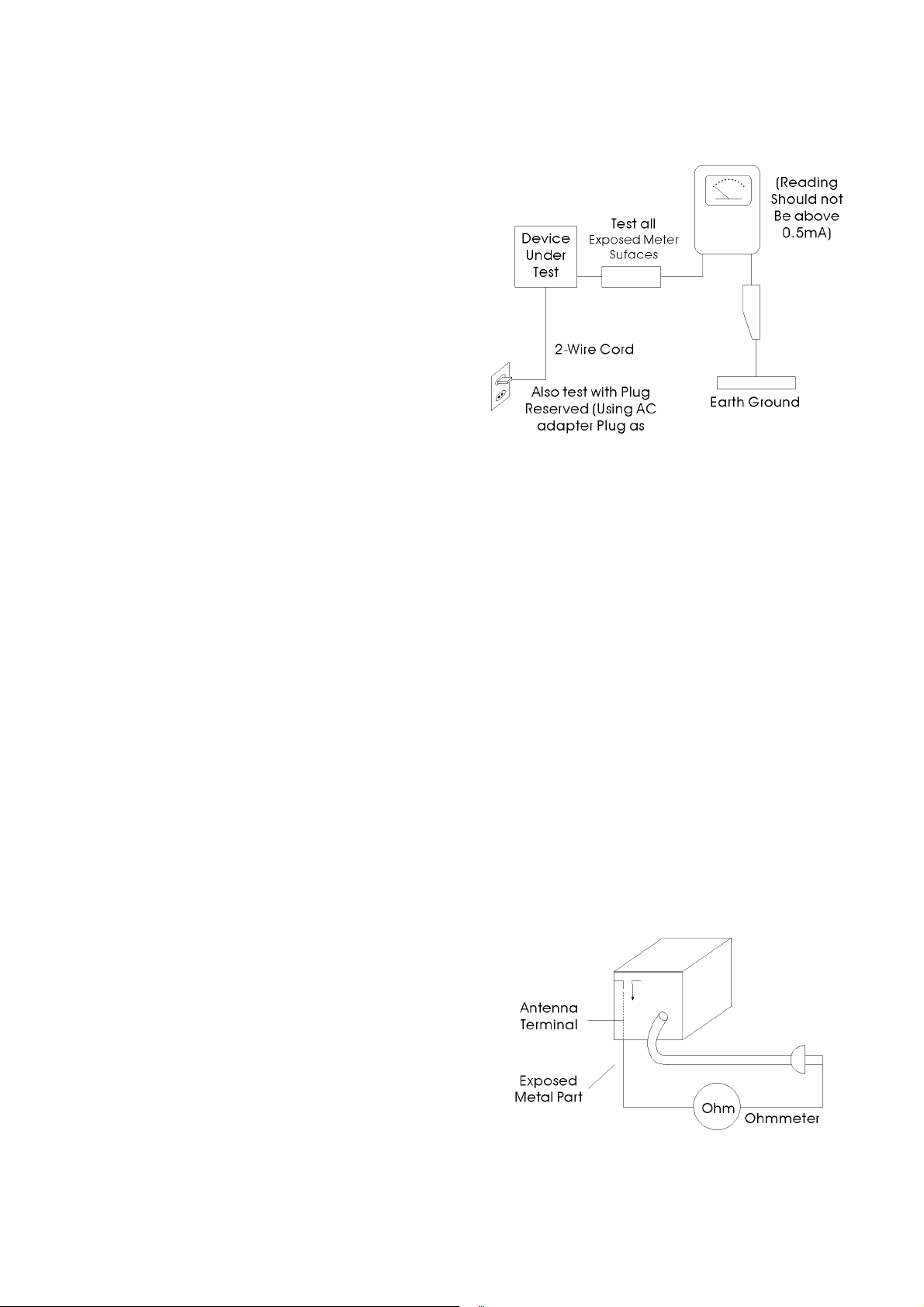
(3) Leakage Current Hot Check-With the instrument
completely reassembled, plug the AC line cord
directly into a 240V AC outlet. (Do not use an
isolation transformer during this test.) Use a leakage
current tester or a metering system that complies with
American National Standards institute (ANSI) C101.1
Leakage.
Current for Appliances and underwriters Laboratories
(UL) 1270 (40.7). With the instrument’s AC switch
first in the ON position and then in the OFF position,
measure from a known earth ground (metal water pipe,
conduit, etc.) to all exposed metal parts of the
instrument (antennas, handle brackets, metal cabinets,
screwheads, metallic overlays, control shafts, etc.),
especially and exposed metal parts that offer an
electrical return path to the chassis.
Any current measured must not exceed 0.5mA.
Reverse the instrument power cord plug in the outlet
and repeat the test.
AC Leakage Test
Any measurements not within the limits specified
herein indicate a potential shock hazard that must be
eliminated before returning the instrument to the
customer.
(4) Insulation Resistance Test Cold Check-(1) Unplug the
power supply cord and connect a jumper wore
between the two prongs of the plug. (2) Turn on the
power switch of the instrument. (3) Measure the
resistance with an ohmmeter between the jumpered
AC plug and all exposed metallic cabinet parts on the
instrument, such as screwheads, antenna, control
shafts, handle brackets, etc. When an exposed
metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the
reading should be between 1 and 5.2 megohm. When
there is no return path to the chassis, the reading must
be infinite. If the reading is not within the limits
specified, there is the possibility of a shock hazard,
and the instrument must be re-pared and rechecked
before it is returned to the customer.
Insulation Resistance Test
2) Read and comply with all caution and safety related
1

notes non or inside the cabinet, or on the chassis.
3) Design Alteration Warning-Do not alter of add to the
mechanical or electrical design of this instrument.
Design alterations and additions, including but not
limited to, circuit modifications and the addition of
items such as auxiliary audio output connections,
might alter the safety characteristics of this instrument
and create a hazard to the user. Any design alterations
or additions will make you, the service, responsible
for personal injury or property damage resulting there
from.
4) Observe original lead dress. Take extra care to assure
correct lead dress in the following areas:
(1) near sharp edges, (2) near thermally hot parts (be
sure that leads and components do not touch
thermally hot parts), (3) the AC supply, (4) high
voltage, and (5) antenna wiring. Always inspect in all
areas for pinched, out-of-place, or frayed wiring. Do
not change spacing between a component and the
printed-circuit board, Check the AC power cord for
damage.
5) Components, parts, and/or wiring that appear to have
overheated or that are otherwise damaged should be
replaced with components, parts and/or wiring that
meet original specifications. Additionally determine
the cause of overheating and/or damage and, if
necessary, take corrective action to remove and
potential safety hazard.
6) Product Safety Notice-Some electrical and mechanical
parts have special safety-related characteristics which
are often not evident from visual inspection, nor can
the protection they give necessarily be obtained by
replacing them with components rated for higher
voltage, wattage, etc. Parts that have special safety
characteristics are identified by shading, an (
(
) on schematics and parts lists. Use of a substitute
replacement that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the recommended replacement part
might created shock, fire and/or other hazards.
Product safety is under review continuously and new
instructions are issued whenever appropriate.
) or a
1-2 Servicing Precautions
CAUTION: Before servicing Instruments covered by this
service manual and its supplements, read and follow the
Safety Precautions section of this manual.
Note: If unforeseen circument create conflict between the
following servicing precautions and any of the safety
precautions, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember; Safety First
1-2-1 General Serving Precautions
(1) a. Always unplug the instrument’s AC power cord from
the AC power source before (1) removing or
reinstalling any component, circuit board, module or
any other instrument assembly. (2) disconnecting
any instrument electrical plug or other electrical
connection. (3) connecting a test substitute in
parallel with an electrolytic capacitor in the
instrument.
b. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks
with which instruments covered by this service
manual might be equipped.
c. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any
of its electrical assemblies unless all solid-state
device heat sinks are correctly installed.
d. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead to
the instrument chassis ground before connecting the
test instrument positive lead. Always remove the test
instrument ground lead last.
Note: Refer to the Safety Precautions section ground
lead last.
(2) The service precautions are indicated or printed on the
cabinet, chassis or components. When servicing,
follow the printed or indicated service precautions
and service materials.
(3) The components used in the unit have a specified flame
resistance and dielectric strength.
When replacing components, use components which
have the same ratings, by (
circuit diagram are important for safety or for the
characteristics of the unit. Always replace them with
the exact replacement components.
(4) An insulation tube or tape is sometimes used and some
components are raised above the printed wiring board
for safety. The internal wiring is sometimes clamped
to prevent contact with heating components. Install
such elements as they were.
(5) After servicing, always check that the removed screws,
) or by ( ) in the
2

components, and wiring have been installed correctly
and that the portion around the serviced part has not
been damaged and so on. Further, check the insulation
between the blades of the attachment plus and
accessible conductive parts.
1-2-2 Insulation Checking Procedure
Disconnect the attachment plug from the AC outlet and
1-3 ESD Precautions
turn the power ON. Connect the insulation resistance meter
(500V) to the blades of the attachment plug. The insulation
resistance between each blade of the attachment plug and
accessible conductive parts (see note) should be more than
1 Megohm.
Note: Accessible conductive parts include metal panels,
input terminals, earphone jacks, etc.
Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD)
Some semiconductor (solid static electricity) devices can
be damaged easily by static electricity.
Such compo9nents commonly are called Electrostatically
Sensitive Devices (ESD). Examples of typical ESD devices
are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor chip components. The following techniques
of component damage caused by static electricity.
(1) immediately before handling any semiconductor
components or semiconductor-equipped assembly,
drain off any electrostatic charge on your body by
touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain
and wear a commercially available discharging wrist
strap device, which should be removed for potential
shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit
under test.
(2) after removing an electrical assembly equipped with
ESD devices, place the assembly on a conductive
surface such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic
charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
(3) Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or
unsolder ESD device.
(4) Use only an anti-static solder removal devices. Some
solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static”
can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESD devices.
(5) Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESD
devices.
(6) Do not remove a replacement ESD device from its
protective package until immediately before you are
ready to install it. (Most replacement ES devices are
packaged with leads electrically shorted together by
conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable
conductive materials).
(7) Immediately before removing the protective materials
from the leads of a replacement ES device touch the
protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly
into which the device will be installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or
circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
(8) Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged
replacement ESD devices. (Otherwise harmless
motion such as the brushing together of your clothes
fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor
can generate static electricity sufficient to damage an
ESD device).
3

2. Reference Information
2-1 Component Descriptions
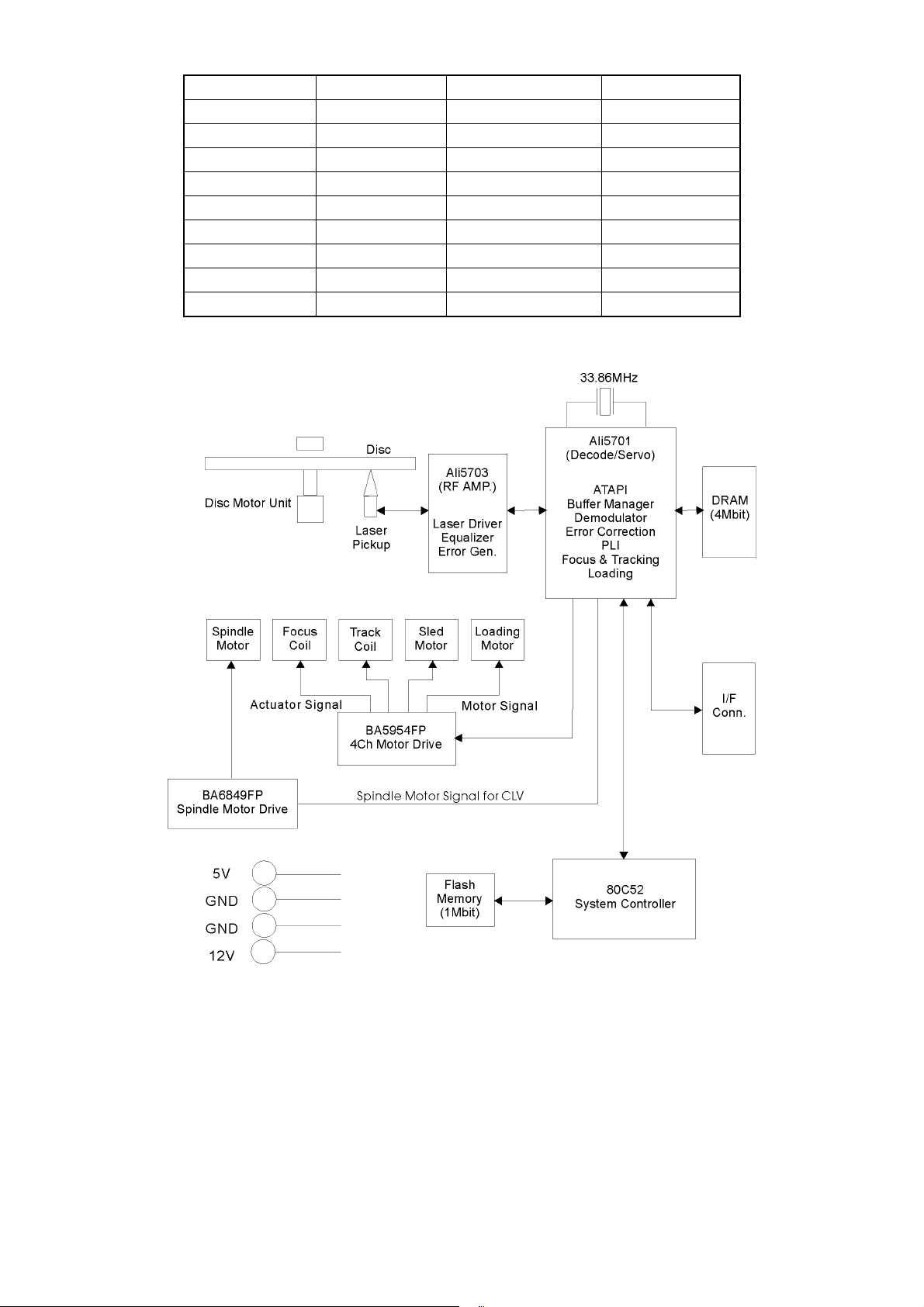
2-1-1 DVD ATAPI Loader
D.C. Power Supply
A 4-pin shrouded, keyed male connector is used to provide the D.C.Power.
The pin assignment is described below.
PIN DC VOLTS
1 +12V
2 GND
3 GND
4 +5V
Interface Connector
A 39-pin male, unshielded, shrouded, keyed connector are applied.
Please refer to Section 7-2-3 regarding its pin definition.
Electrical Characteristics
1. Power
1-1. Voltage
+5V DC with ± 5% tolerance. Less than 100mVp-p Ripple Voltage
+12V DC with ± 10% tolerance, less than 150mVp-p Ripple Voltage
1-2. Current
Continuous Reading
+5V DC 500mA (Average)
+12V DC 300mA (Average)
Seeking & Spin up
+5V DC 0.8A (Maximum)
+12V DC 1.5A (Maximum)
2. Signal Summary
The physical interface consists of single ended TTL compatible receivers.
3. Connector Pin Definition
I/F Signals I/O Pin # I/F Signals I/O Pin #
Reset 1 DMARQ 21
GND 2 GND 22
DD7 3 DIOW 23
DD8 4 GND 24
DD6 5 DIOR 25
DD9 6 GND 26
DD5 7 IORDY 27
DD10 8 CSEL 28
DD4 9 DMACK 29
DD11 10 GND 30
DD3 11 INTRQ 31
4
4. Block Diagram
I/F Signals I/O Pin # I/F Signals I/O Pin #
DD12 12 IOCS16 32
DD2 13 DA1 33
DD13 14 PDIAG 34
DD1 15 DA0 35
DD14 16 DA1 36
DD0 17 CS1FS 37
DD15 18 CS3FS 38
GND 19 DASP 39
NC 20 GND 40
5
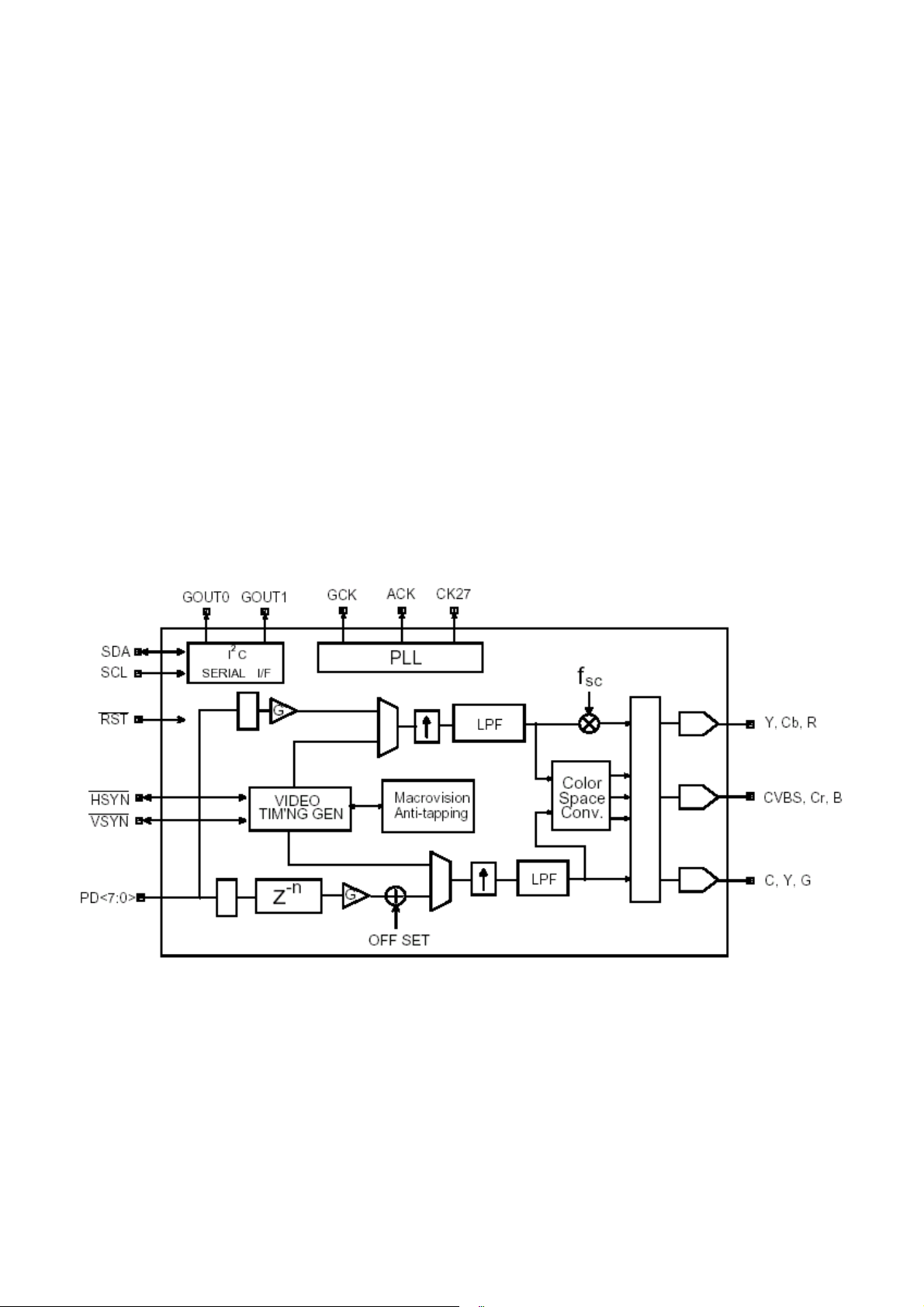
2-1-2 NTSC/PAL Digital Video Encoder (AV3168)
FEATURES
• Fully CCIR 624 performance compliance NTSC and
PAL (B,D,G,H,I,M and N) video encoder.
• Composite, S-video, Component Y/Cb/Cr (Sony,
Matsushita, and SMPTE) or RGB output.
• Triple 10-bit digital to analog converter.
• Accepts 27 Mhz multiplexed 8-bit digital video inputs.
• Master or Slave 4-Field NTSC or 8-Field PAL video
timing generation.
• CCIR 656 EAV SYNC extraction.
• Automatic NTSC or PAL timing detection in slave
mode operation.
• Automatic or User Programmable Chroma Filter
Selection.
• Macrovision Anti-Tapping Rev 7.01 support in
AV3168 Only.
• Closed Caption Support.
• Contrast and Brightness control.
Clock Generation
• 3 outputs for 27 MHz video clock, 16.934, 18.432 and
36.864 Mhz audio clock, and 40.5, 54.0, 67.5 and
81.0 MHz general purpose clocks.
• Requires a single 27 Mhz crystal.
General
• CVBS and S-video DAC power down controls.
2
• I
C compatible serial control bus.
• Single +5 volt power supply.
Application
• Digital Video Disk (DVD)
• Digital Set-Top Box
• PC Video, Multimedia
Ordering Information
AV3168/69-CL 44-pin PLCC
AV3168/69-CQ 44-pin TQFP
DESCRIPTION
The AV3168 is a mixed signal CMOS monolithic device. It comprise with a PAL and NTSC Video Encoder, Color
Space Converter and Clock Generator, The Clock Generator outputs a video, an audio and a programmable
general purpose clock. This IC implemented Macrovision Anti-tapping 7.01, intended for DVD and Settop Box
applications.
The video encoder converts CCIR 601 8-bit multiplexed digital video into RGB, component YCbCr, encoded NTSC
or PAL (BDGHIMN) signals. It contains three 10-bit DACs to support simultaneous S-video and composite video;
or component video display. Brightness and Contrast control are also provided.
6
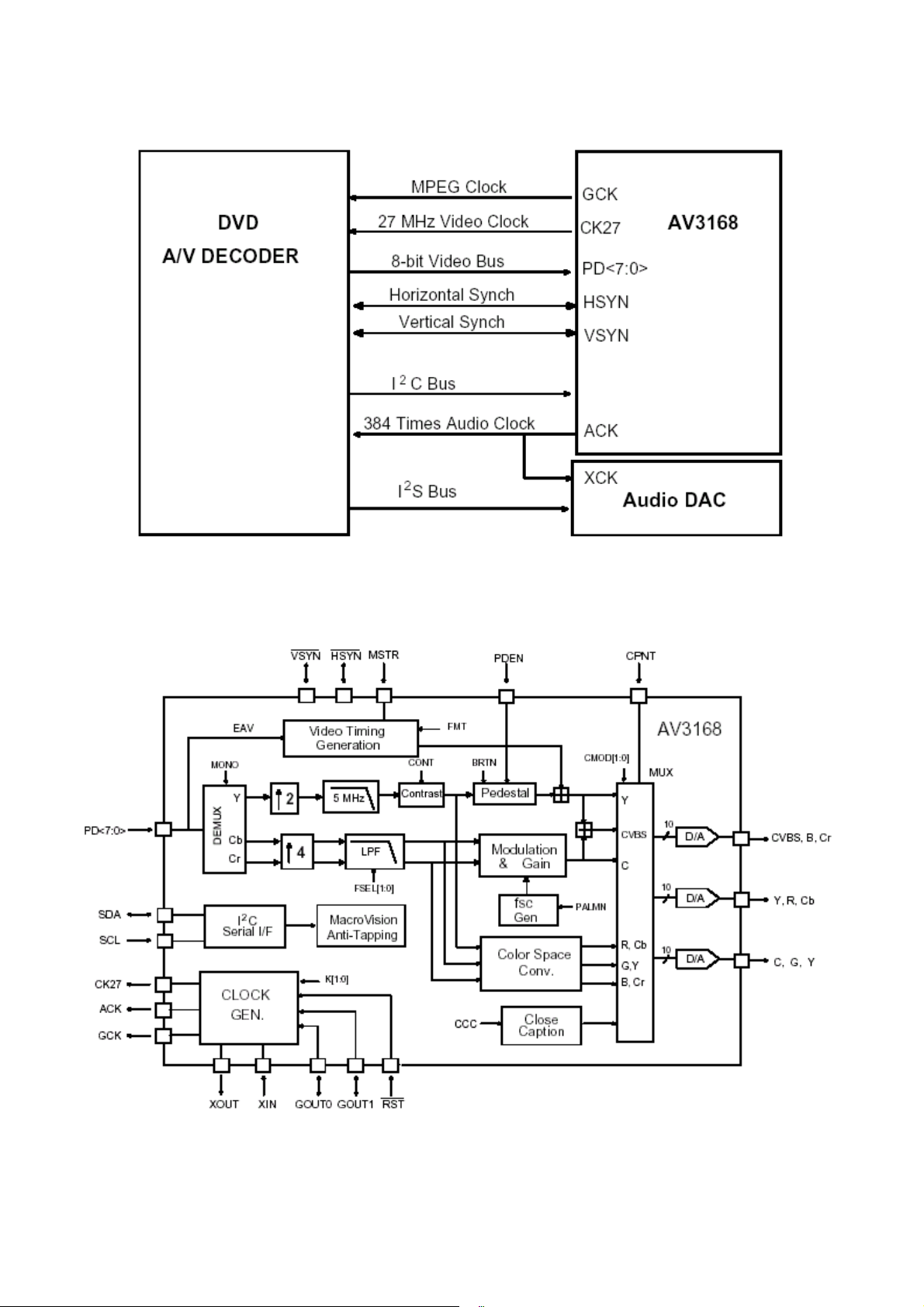
The Clock Generator outputs three clocks for video, audio and system to simplify the system configuration and
maintain A/V synchronization.
Typical Application Connection
AV3168 Detailed Block Diagram
7
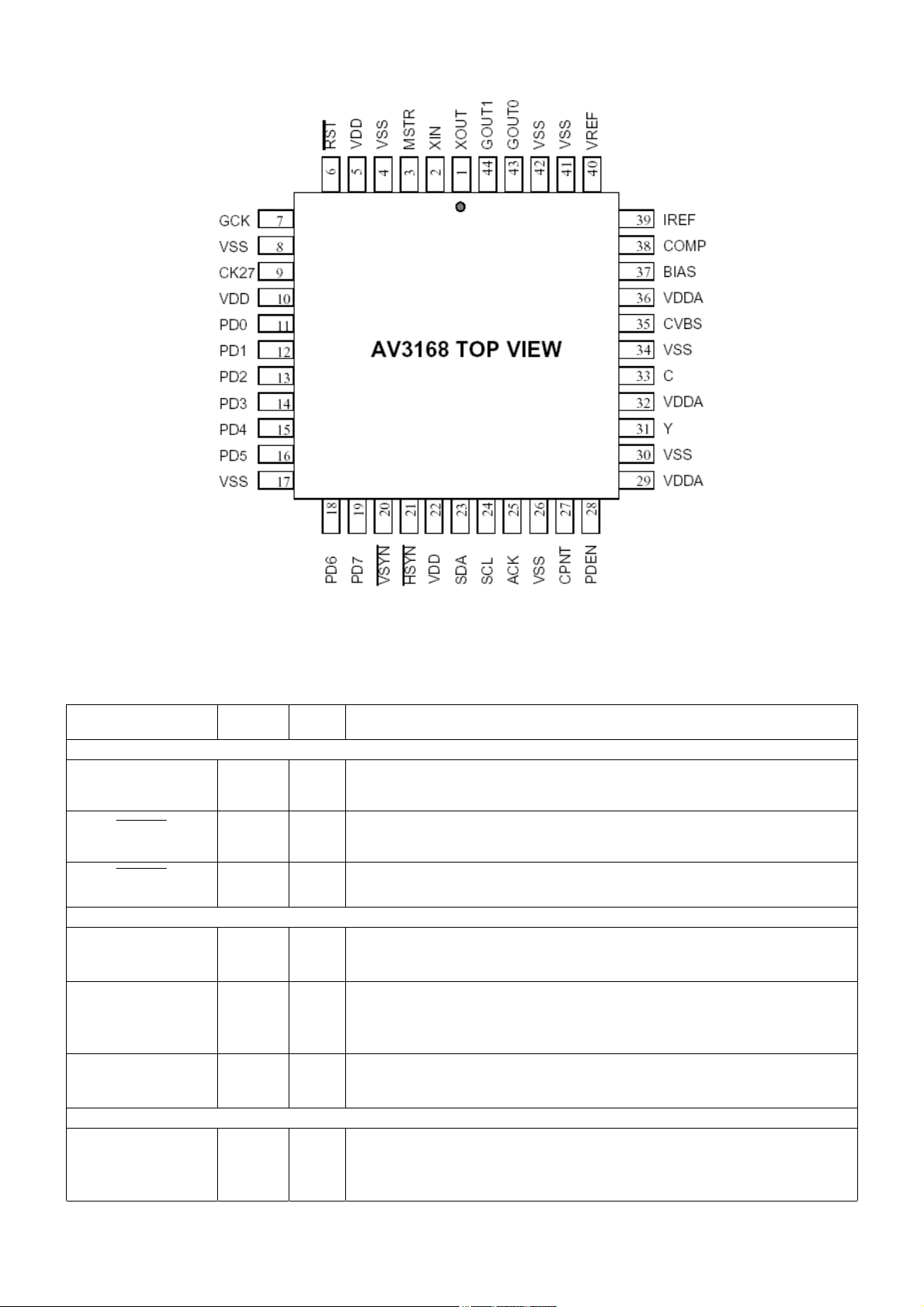
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name Pin # Type
DIGITAL VIDEO INPUT
PD<7 -0>
11-16
18-19
Description
I Multiplexed Cb, Y, and Cr digital video input bus.
HSYN
VSYN
VIDEO CONTROL SIGNALS
MSTR 3 I
CPNT 27 I
PDEN 28 1
20 I/O
21
I/O In slave mode (MSTR pin is low) Vertical Sync input. In master mode
In Slave Mode (MSTR pin is low) Horizontal Synch input. In Master
Mode (MSTR pin is high) Horizontal Synch output.
Vertical Sync output.
Master Mode;
If this pin is high, the chip outputs horizontal and vertical sync signals.
Otherwise it receives both horizontal and vertical sync signals.
Select either component or composite video output.
0: Simultaneous Composite and S-Video output.
1: Component video output either RGB or YCbCr determined by the
register CR0[5:4].
Pedestal enable pins.
When this pin is high 7.5 IRE is added for the NTSC composite analog
output.
VIDEO ANALOG OUTPUT, REFERENCE AND COMPENSATION
Analog video output
CVBS 35 O
8
Determined by the state of CPNT pin and CR0[5:4]
CPNT CR0[5] CR0 [4]
0 X X: Composite video output
Pin Name Pin # Type
1 X 0: Cr output in CbCr component mode
1 0 X: :
1 1 1: Blue color output in RGB mode
Analog video output
Determined by the state of CPNT pin and CR0[5:4]
CPNT CR0[5] CR0 [4]
Y 31 O
C 33 O
VREF 40 I/O
IREF 39 I
COMP 38 I
BIAS 37 I/O
SERIALCONTRL BUS
SCL 24 I Serial bus clock
SDA 23 I/0
CLOCK SIGNALS
GCK 7 O
GCK 7 O
CK27 9 O 27 MHz clock output pin.
ACK 25 I/O
XIN 2 I 27 Mhz oscillator input
XOUT 1 O 27 Mhz oscillator output
MISCELLANEOUS SIGNALS
RST
6 I
0 X X: S-Video Y output.
1 X 0: Cb output in CbCr component mode
1 0 X: :
1 1 1: R color output in RGB mode
Analog video output
Determined by the state of CPNT pin and CR0[5:4]
CPNT CR0[5] CR0 [4]
0 X X: S-Video C output.
1 1 0: Cb output in CbCr component mode
1 0 X: :
1 1 X: Green color output in RGB mode
Voltage reference. It has an internal voltage reference circuit, but may
be overridden by an external voltage reference input. A 0.1 uF ceramic
capacitor is required between this pin and GND.
A resistor should be connected between this pin and GND to control the
DAC output current. The recommended value is 198 (382) ohm 1%
metal film resistor for double (single) end 75 ohm termination.
Compensation capacitor for the DAC internal reference amplifier. A 0.1
uF ceramic capacitor is required between this pin and VDDA.
DAC bias voltage. A 0.1 uf ceramic capacitor must be used to
de-couple this pin to VDDA.
Serial bus address and data input and output pin.
Open drain output.
General Purpose Clock. Clock frequency is determined by the state of
GOUT[1:0] when
0 0 : 40.5 MHz clock output.
0 1: 54.0 MHz clock output.
1 0: 67.5 Mhz clock output.
1 1: 81.0 MHz
General Purpose Clock. Clock frequency is determined by the state of
GOUT[1:0] when
0 0 : 40.5 MHz clock output.
0 1: 54.0 MHz clock output.
1 0: 67.5 Mhz clock output.
1 1: 81.0 MHz
384*fs Audio clock output pin.
Controlled by CR2[1:0]
0 0: 384 * 44.1 KHz (16.934MHz) clock output.
0 1: 384 * 48.0 KHz (18.432MHz) clock output.
1 0: 384 * 88.2 KHz (33.868MHz) clock output.
1 1. 384 * 96.0 KHz (36.864MHz) clock output.
Active low chip reset input. Chip is in the power down mode when the
RST is low.
Description
RST pin is low.
RST pin is low.
GOUT1 44 O
Dual function pin.
9
Pin Name Pin # Type
Description
GCK frequency select pin when RST is low.
General purpose output pin when
Dual function pin.
GOUT0 43 I
POWER AND GROUND
VDD
VSS
VDDA
10, 22,
5
8, 17,
26, 30,
34, 41,
42, 4
29,
32,36
GND Digital ground
+5V Digital power supply
+5V Analog video power supply
GCK frequency select pin when
pin when
RST
2-1-3 DVD Processor Chip (Swan-2TM ES4318)
* Features
Single-chip DVD video decoder in a 208-pin PQFP package
Supports MPEG-1 system and MPEG-2 program streams
Programmable multimedia processor architecture
Compatible with Audio CD, Video CD, VCD 3.0, and Super Video CD (SVCD)
DVD Navigation 1
Built-in content Scrambling System (CSS)
- Audio
Built-in Karaoke key-shift function
DolbyTM Digital 2-channel down mix audio output for DolbyTM
Dolby Pro Logic
Linear PCM streams for24 bit / 96KHz
Concurrent S/PDIF out and 2-channel audio output
Sensaura Dolby Digital Virtual Surround
DTS Digital Surround 2-channel down mix stereo output
S/PDIF output for encoded AC-3, DTS Digital output or Linear PCM
- Peripheral
Glueless interface to DVD loaders (ATAPI or A/V bus I/F)
Bi-directional 12C audio interface
8 general-purpose auxiliary ports
Single 27MHz clock input
- Smart Technology
SmartZoomTM for motion zoom & pan
SmartZoomTM for NTSC to PAL conversion and vice versa
SmartZoomTM for video error concealment
10
is high
is high
RST
RST is low. General purpose output
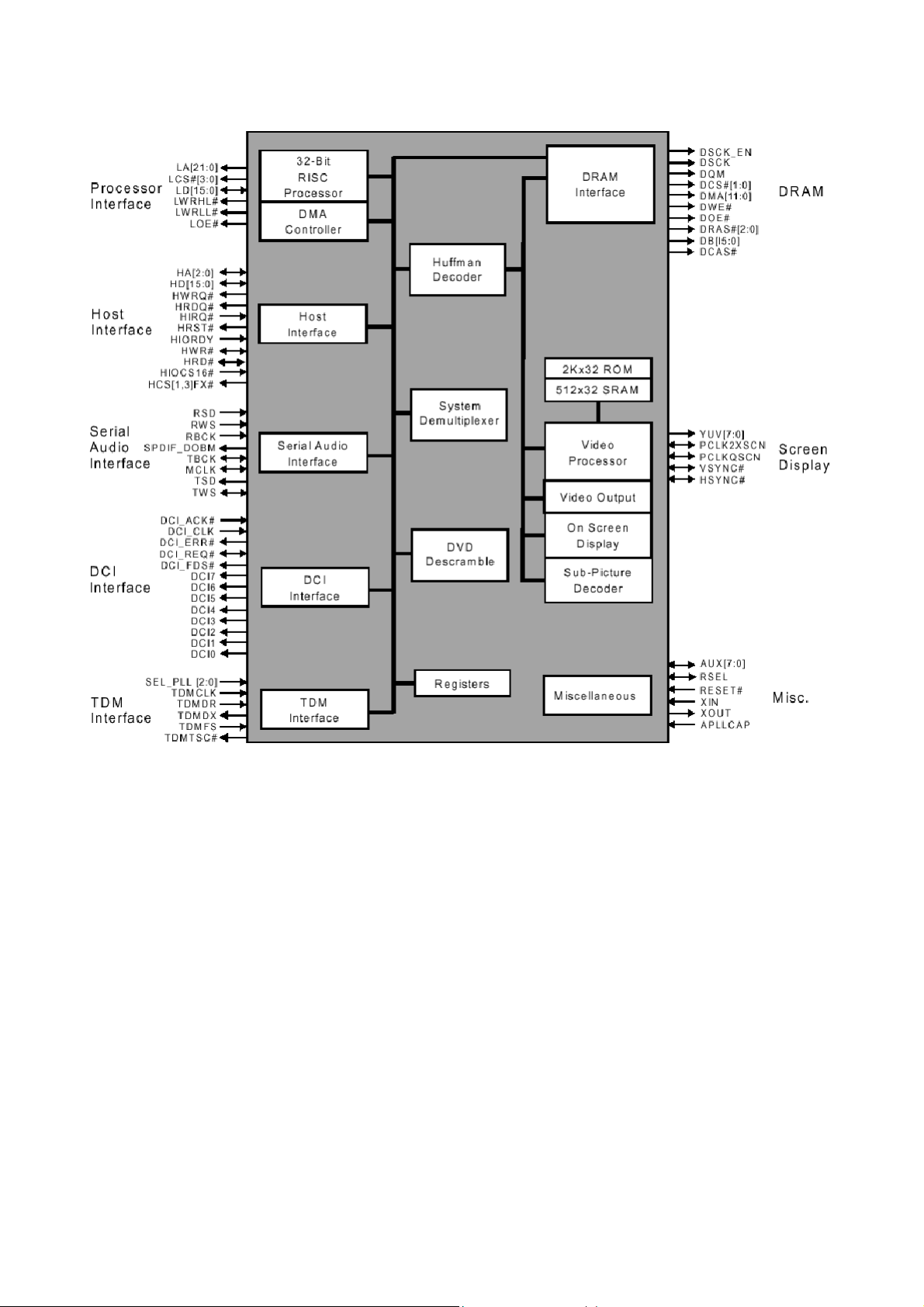
* Functional Description
11
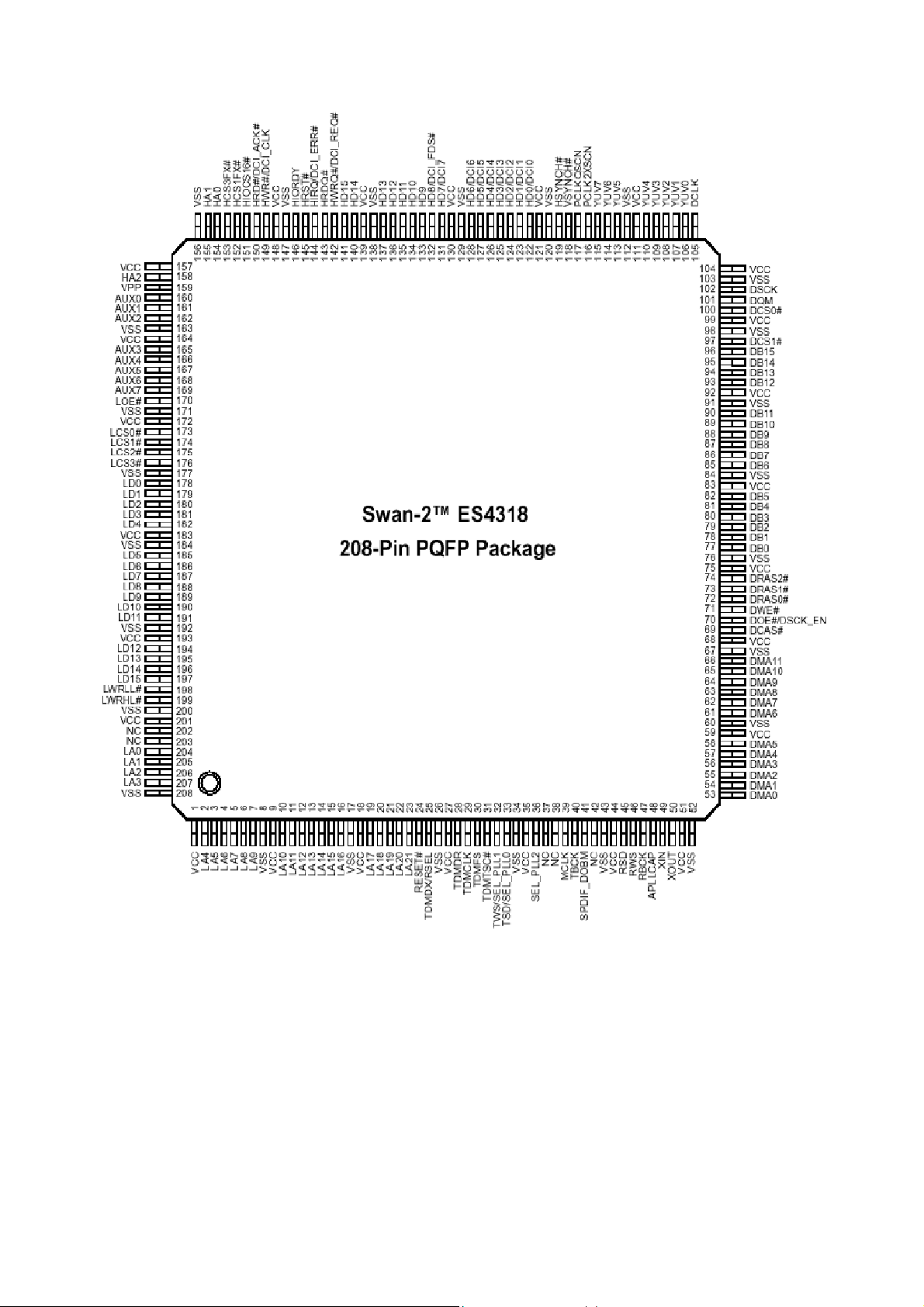
* Pinout Diagram
12
* PIN DESCRIPTON
prog
Name Number I/O Definition
1, 9, 18, 27, 35, 44, 51, 59, 68, 75, 83,
VCC
121, 130, 139, 148, 157, 164, 172, 183,
92, 99, 104, 111,
193, 201
LA[21:0] 23:19, 16:10, 7:2, 207:204 O Device address output
8, 17, 26, 34, 43, 52, 60, 67, 76, 84, 91, 98, 103,
VSS
112, 120, 129, 138,
147,156,163,171,177,184, 192, 200, 208
RESET# 24 I Reset input active low.
TDMDX O TDM transmit data
RSEL 25 I
TDMDR 28 I TDM receive data.
TDMCLK 29 I TDM clock input.
TDMFS 30 I TDM frame synch.
TDMTSC# 31 O TDM output enable, active low.
TWS
SEL_PLL1
TSD
SEL_PLL0
32
33
SEL_PLL2 36
MCLK 39 I/O Audio master clock for audio DAC.
TBCK 40 I/O Audio transmit bit clock.
SDIF_DOBM 41 O S/PDIF (IEC958) Format Output.
RSD 45 I Audio receive serial data.
RWS 46 I Audio receive frame synch.
RBCK 47 I Audio receive bit clock.
APLLCAP 48 I Analog PLL Capacitor.
XIN 49 I Crystal input.
XOUT 50 O Crystal output.
DMA[11:0] 66:61, 58:53 O DRAM address bus.
DCAS# 69 O Column address strobe, active low.
DOE#
DSCK-EN
70
DWE# 71 O DRAM write enable, active low.
DRAS[2.0]# 74:72 O Row address strobe, active low.
DB[15:0] 96:93, 90:85, 82:77 I/O DRAM data bus.
DCS[1:0]# 97,100 O SDRAM chip select [1:0], active low.
DQM 101 O Data input/ output mask.
DSCK 102 O Clock to SDRAM.
DCLK 105 I Clock input (27MHz).
YUV[7.0] 115:113, 110:106 O 8-bit YUV output.
PCLK2XSC
N
116 I/O 2X pixel clock.
PCLKQSCN 117 I/O Pixel clock.
VSYNCH# 118 I/O
HSYNCH# 119 I/O
I 3.65 V ± 150 mv.
I Ground
ROM Select
RSEL Selection
0 16-bit ROM
1 8-bit ROM
O
I
Audio transmit frame sync.
Select PLL1.
Audio transmit serial data port.
Select PLL0.
O
SEL_PLL2 SEL_PLL0 Clock Output
I
0 0 2.5 x DCLK
0 1 3 x DCLK
1 0 3.5 x DCLK
1 1 4 x DCLK
Select PLL2. See the table for pin number
33.
O
I
Output enable, active low.
Clock enable, active low.
Vertical synch for screen video interface,
programmable for rising or falling edge,
active low.
Horizontal synch for screen video interface,
rammable for rising or falling edge,
13
 Loading...
Loading...