Cypress Semiconductor CY37256P208-125NI, CY37256P208-125NC, CY37256P160-83AI, CY37256P160-83AC, CY37256P160-154AC Datasheet
...
5V, 3.3V, ISR™ High-Performance CPLD
s
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose, CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Revised May 7, 2 003
Features
• In-System Reprogrammable™ (ISR™) CMOS CPLDs
—JT AG interface for reconfigu rabili ty
—Design changes do not cause pinout changes
—Design changes do not cause timing changes
• High density
—32 to 512 macrocells
—32 to 264 I/O pins
—Five dedicated inputs including four clock pins
• Simple timing model
—No fanout delays
—No expande r delays
—No dedicated vs. I/O pin delays
—No additional delay through PIM
—No penalty for using full 16 product terms
—No delay for steering or sharing product terms
• 3.3V and 5V versions
• PCI-compatible
[1]
• Programmable bus-hold capabilities on all I/Os
• Intelligent product term allocator provides:
—0 to 16 product terms to any macrocell
—Product term steering on an individual basis
—Product term sharing among local macrocells
• Flexible clocking
—Four synchronous clocks per device
—Product term clocking
—Clock polarity control per logic block
• Consistent packa ge/pinout offering across al l densities
—Simplifies design migration
—Same pinout for 3.3V and 5.0V devices
• Packages
—44 to 400 leads in PLCC, CLCC, PQFP, TQFP, CQFP,
BGA, and Fine-Pitch BGA packages
General Description
The Ultra37000™ fam ily of CMOS CPLDs pr ovides a range of
high-density programmable logic solutions with unparalleled
system performance. The Ultra37000 family is designed to
bring the flexibil ity , ease of use, and performance of th e 22V10
to high-density CP LDs. The arch itecture is based on a number
of logic bloc ks that are co nnected by a P rogrammab le Interconnect Matrix (PIM). Each logic block features its own
product term array, product term allocator, and 16 mac rocell s.
The PIM distributes signals from the logic block ou tputs and all
input pins to the logic block inputs.
All of the Ul t ra3 7 00 0 de vi ce s a re el ec t rically eras ab le a n d I n System Reprogrammable (ISR), which simplifies both design
and manufacturing flows, thereby reducing costs. The ISR
feature provides the ability to reconfigure the devices without
having design changes cause pinout or timing changes. The
Cypress ISR function is implemented through a JTAGcompliant serial interface. Data is shifted in and out through
the TDI and TDO pins, respectively. Because of the superior
routability an d simp le t iming model of the Ul tra370 00 devi ces,
ISR allows users to ch ange exis ting logic designs whi le simultaneously fixing pinout assignments and maintaining system
performance.
The entire family features JTAG for ISR and boundary scan,
and is compatible with the PCI Local Bus specification,
meeting the electrical and timing requirements. The
Ultra37000 family features user programmable bus-hold
capabilities on all I/Os.
Ultra37000 5.0V Devices
The Ultra37000 devices operate with a 5V supply and can
support 5V or 3.3V I/O levels. V
CCO
connections pr ovide th e
capability of interfacing to either a 5V or 3.3V bus. By
connecting the V
CCO
pins to 5V the user insures 5V TT L levels
on the outputs. If V
CCO
is connected to 3.3V the output levels
meet 3.3V JEDEC standard CMOS levels and are 5V tolerant.
These devices require 5V ISR programming.
Ultra37000V 3.3V Devices
Devices operating with a 3.3V suppl y require 3.3V o n all V
CCO
pins, reducing the device’s power consumption. These
devices support 3.3V JEDEC standard CMOS output levels,
and are 5V-tolerant. These devices allow 3.3V ISR
programming.
Note:
1. Due to the 5V-tolerant nature of 3.3V device I/Os, the I/Os are not clamped to V
CC
, PCI V
IH
= 2V.
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 2 of 63
Selection Guide
5.0V Selection Guide
3.3V Selection Guide
General Information
Device Macrocells
Dedicated
Inputs I/O Pins Speed (t
PD
) Speed (f
MAX
)
CY37032 32 5 32 6 200
CY37064 64 5 32/64 6 200
CY37128 128 5 64/128 6.5 167
CY37192 192 5 120 7.5 154
CY37256 256 5 128/160/192 7.5 154
CY37384 384 5 160/192 10 118
CY37512 512 5 160/192/264 10 118
Speed Bins
Device 200 167 154 143 125 100 83 66
CY37032 X X X
CY37064 X X X
CY37128 X X X
CY37192 X X X
CY37256 X X X
CY37384 X X
CY37512 X X X
Device-Package Offering and I/O Count
Device
44-
Lead
TQFP
44-
Lead
PLCC
44-
Lead
CLCC
84-
Lead
PLCC
84-
Lead
CLCC
100-
Lead
TQFP
160-
Lead
TQFP
160-
Lead
CQFP
208-
Lead
PQFP
208-
Lead
CQFP
256Lead
BGA
352Lead
BGA
CY37032 37 37
CY37064 37 37 37 69 69
CY37128 69 69 69 133
CY37192 125
CY37256 133 133 165 197
CY37384 165 197
CY37512 165 165 197 269
General Information
Device Macrocells
Dedicated
Inputs I/O Pins Speed (t
PD
) Speed (f
MAX
)
CY37032V 32 5 32 8.5 143
CY37064V 64 5 32/64 8.5 143
CY37128V 128 5 64/80/128 10 125
CY37192V 192 5 120 12 100
CY37256V 256 5 128/160/192 12 100
CY37384V 384 5 160/192 15 83
CY37512V 512 5 160/192/264 15 83
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 3 of 63
Architecture Overview of Ultra37000 Family
Programmable Interconnect Matrix
The Programmable Interconnect Matrix (PIM) consists of a
completely global routing matrix for signals from I/O pins and
feedbacks from the logic blocks. The PIM provides extremely
robust interconnection to avoid fitting and density limitations.
The inputs to the PIM consist of all I/O and dedicated input pins
and all mac r oc el l fe ed ba c ks fr om w i thi n t h e lo g ic b lo ck s. Th e
number of PIM input s increases with pin co unt and the number
of logic blocks. The outputs from the PIM are signals ro uted to
the appropriate logic blocks. Each logic block receives 36
inputs from the PIM and their compl ements, allow ing for 32-bit
operations to be implemented in a single pass through the
device. The wide number of inputs to the logic block also
improves the routing capacity of the Ultra37000 family.
An important feature of the PIM is its simple timing. The propagation delay through the PIM is accounted for in the timing
specifications fo r each devi ce. Th ere is no ad dition al del ay for
traveling through the PIM. In fact, all inputs travel through the
PIM. As a result, there are no route-dependent timing parameters on the Ultra37000 devices. The worst-case PIM delays
are incorporated in all appropriate Ultra37000 specifications.
Routing signals through the PIM is completely invisible to the
user . All routing is accomplished by software—no hand routing
is necessary. Warp™ and third- party dev elopm ent packag es
automatically route designs for the Ultra37000 family in a
matter of minutes. Finally, the rich routing resources of the
Ultra37000 family accommodate last minute logic changes
while maintaining fixed pin assignments.
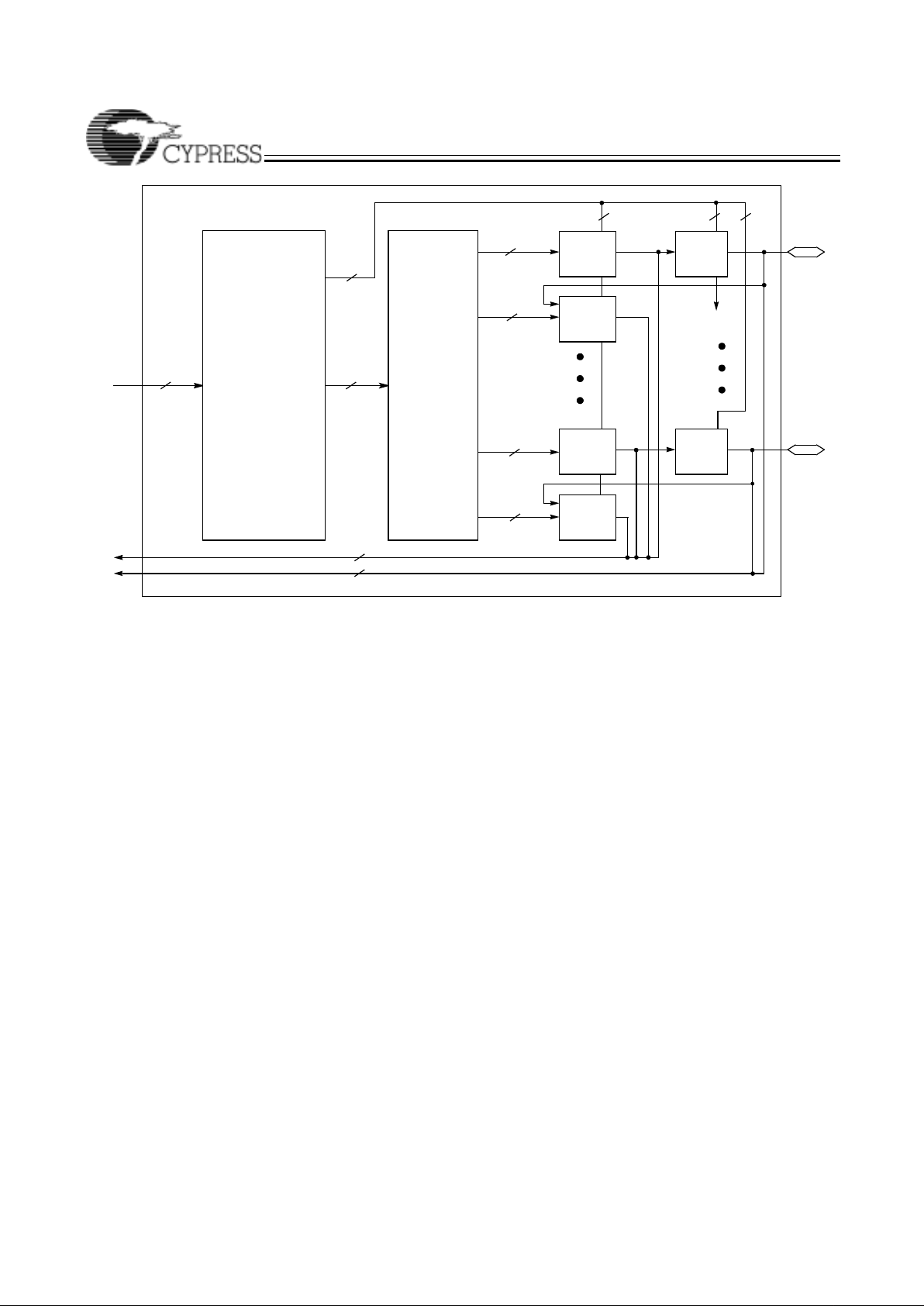
Logic Block
The logic block is the basic building block of the Ultra37000
architect ure. It consis ts of a prod uct te rm arra y, an intelligen t
product-term allocator, 16 macrocells, and a number of I/O
cells. The number of I/O cells varies depending on the device
used. Refe r to Figure 1 for the block diagram.
Product Term Array
Each logic block features a 72 x 87 programmable product
term array. This array accepts 36 inputs from the PIM, which
originate from macrocell feedbacks and device pins. Active
LOW and active HIGH versions of each of these inputs are
generated to create the full 72-input field. The 87 product
terms in the array can be created from any of the 72 inputs.
Of the 87 product terms, 80 are for general-purpose use for
the 16 macrocells in the logic block. Four of the remaining
seven product terms i n the logic block are ou tpu t en abl e (O E)
product terms. Each of the OE product terms controls up to
eight of the 16 macrocells and is selectable on an individual
macrocell basis. In other words, each I/O cell can select
between one of two OE product terms to control the output
buffer. The first two of these four OE product terms are
available to the upper half of the I/ O macrocells in a logic block.
The other two OE product te rms are a vailabl e to the lower half
of the I/O macrocells in a logic block.
The next two product terms in each logic block are dedicated
asynchronous set and asynchronous reset product terms. The
final product te rm is th e produ ct term clo ck. The set, r eset, OE
and product term clock have polarity control to realize OR
functions in a single pass through the array.
Speed Bins
Device 200 167 154 143 125 100 83 66
CY37032V X X
CY37064V X X
CY37128V
XX X
CY37192V XX
CY37256V XXX
CY37384V XX
CY37512V
XXX
Shaded areas indicate preliminary speed bins.
Device-Package Offering & I/O Count
Device
44-
Lead
TQFP
44-
Lead
PLCC
44-
Lead
CLCC
48-
Lead
FBGA
84-
Lead
PLCC
84-
Lead
CLCC
100-
Lead
TQFP
100-
Lead
FBGA
160-
Lead
TQFP
160-
Lead
CQFP
208-
Lead
PQFP
208-
Lead
CQFP
256-
Lead
BGA
256-
Lead
FBGA
352-
Lead
BGA
400-
Lead
FBGA
CY37032V 37 37 37
CY37064V 37 37 37 37 69 69 69
CY37128V 69 69 69 85 133
CY37192V 125
CY37256V 133 133 165 197 197
CY37384V 165 197
CY37512V 165 165 197 269 269
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 4 of 63
Low-Power Option
Each logic block can operate in high-speed mode for critical
path performance, or in low-power mode for power conservation. The logic bloc k mode is se t by the user on a l ogic block
by logic block basis.
Product Term Allocator
Through the product term allocator, software automatically
distributes product terms among the 16 macrocells in the logic
block as needed. A total of 80 p roduct terms are available from
the local product term array. The product term allocator
provides two important capabilities without affecting performance: product term steering and product term sharing.
Product Term Steering
Product term steering is the process of assigning product
terms to macrocell s as neede d. For e xamp le, if o ne ma croce ll
requires ten produc t terms whi le anot her need s just th ree, the
product term allocator will “steer” ten product terms to one
macrocell and three to the other. On Ultra37000 devices,
product terms are steere d on an ind ividu al bas is. Any n umber
between 0 and 16 product terms can be steered to any
macrocell. Note that 0 product terms is useful in cases where
a particular macrocell is unused or used as an input register.
Product Term Sharing
Product term sharing i s the process of using the same p roduct
term among multiple macrocells. For example, if more than
one output has one or more product terms in its equation that
are common to other outputs, those product terms are only
programmed once. The Ultra37000 product term allocator
allows sharing across groups of four output macrocells in a
variable fashion. The software automatically takes advantage
of this capability—the user does not have to intervene.
Note that neither product term sharing nor product term
steering have any effect on the speed of the product. All worstcase steering and sharing configurations have been incorporated in the timing specifications for the Ultra37000 devices.
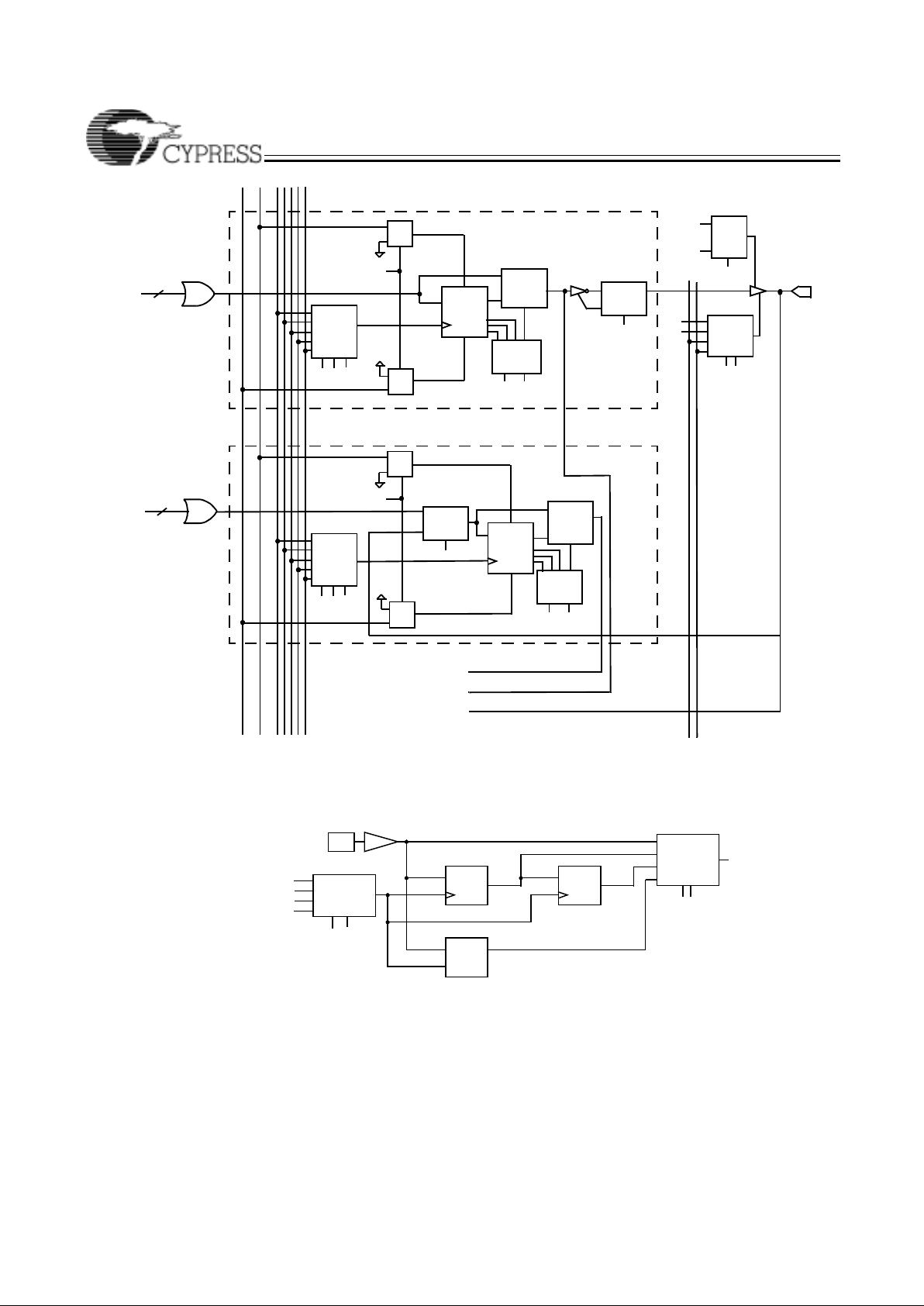
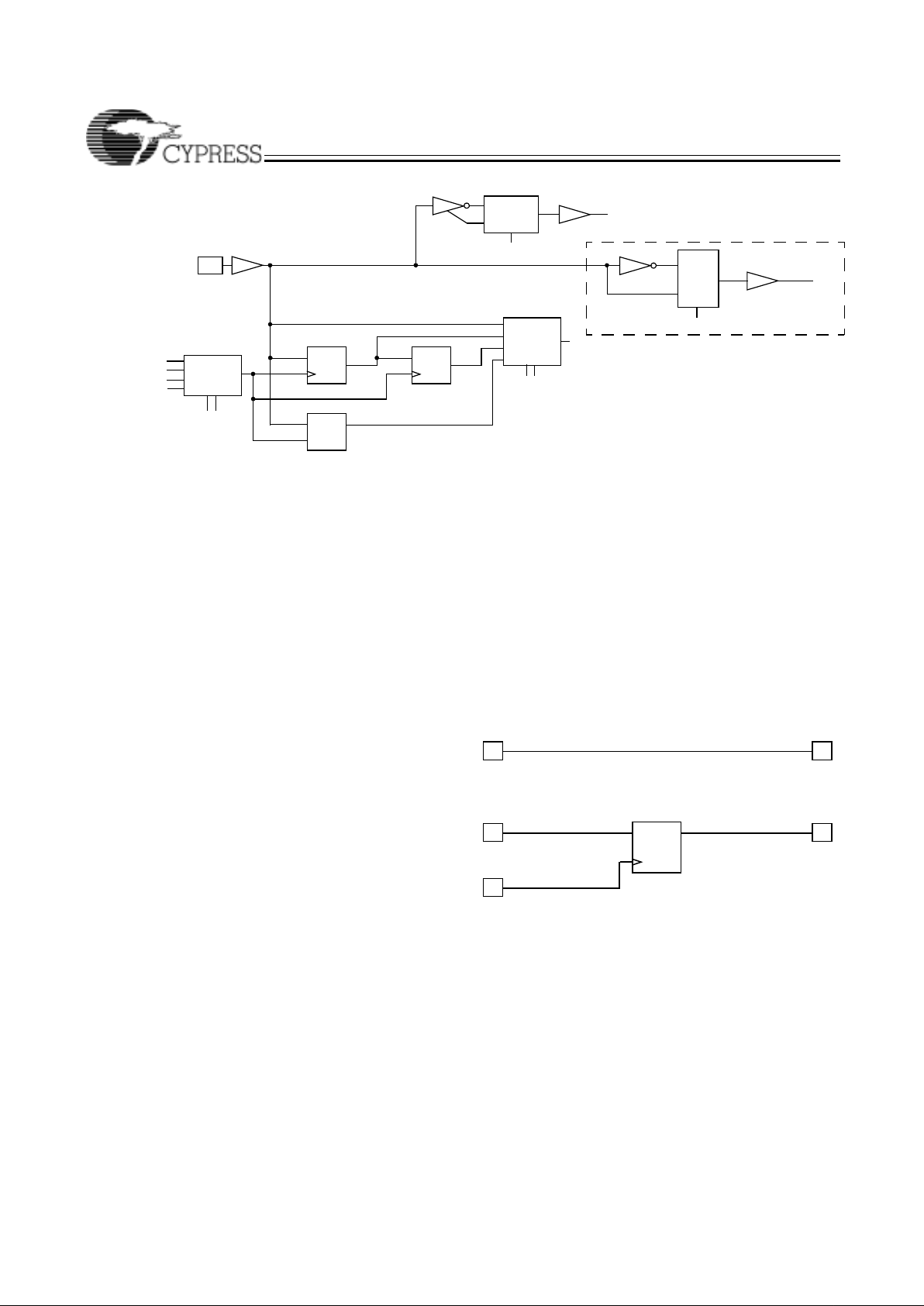
Ultra37000 Macrocell
Within each logic block there are 16 macrocells. Macrocells
can either be I/O Macrocells, which include an I/O Cell which
is associated with an I/O pin, or buried Macrocells, which do
not connect to an I/O. The combination of I/O Macrocells and
buried Macrocells varies from device to device.
Buried Macrocell
Figure 2 displays the architecture of buried macrocells. The
buried macrocell features a register tha t can be confi gured as
combinatorial, a D flip-flop, a T flip-flop, or a level-triggered
latch.
The register can be asynchronously set or asynchronously
reset at the logic block level with the separate set and reset
product terms. Each of these pro duct terms features programmable polarity. This allows the registers to be set or reset
based on an AND expression or an OR expression.
Clocking of the register is very flexible. Four global
synchronous clocks and a product term clock are available to
clock the register. Furthermore, each clock features programmable polarity so that registers can be triggered on falling as
well as rising edges (see the Clo cking sec tio n). Cloc k pol ari t y
is chosen at the logic block level.
The buried macrocell also supports input register capability.
The buried macrocell can be configured to act as an input
Figure 1. Logic Block with 50% Buried Macrocells
I/O
CELL
0
PRODUCT
TERM
ALLOCATOR
I/O
CELL
14
MACRO-
CELL
0
MACRO-
CELL
1
MACRO-
CELL
14
0−16
PRODUCT
TERMS
72 x 87
PRODUCT TERM
ARRAY
8036
8
16
TO
PIM
FROM
PIM
7
3
2
MACRO-
CELL
15
2
to cells
2, 4, 6 8, 10, 12
0−16
PRODUCT
TERMS
0−16
PRODUCT
TERMS
0−16
PRODUCT
TERMS

Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 5 of 63
register (D-type or latch) whose input comes from the I/O pin
associated with the neighboring macrocell. The output of all
buried macrocells is sent directly to the PIM regardless of its
configuration.
I/O Macrocell
Figure 2 illustrates the architecture of the I/O macrocell. The
I/O macrocell supports the same functions as the buried
macrocell with the addi tion of I/O capabi lity . At the output of the
macrocell, a polarity control mux is available to select active
LOW or active HIGH signals. This has the added advantage
of allowing significant logic reduction to occur in many applications.
The Ultra37000 m acrocell featu res a feedba ck path to the PIM
separate from the I/O pin input path. This means that if the
macrocell is buried (fed back internally only), the associated
I/O pin can still be used as an input.
Bus Hold Capabilities on all I/Os
Bus-hold, which is an i mprov ed ver sion o f the p opula r intern al
pull-up resistor, is a weak latch connected to the pin that does
not degrade the device’s performance. As a latch, bus-hold
maintains the last state of a pin when the pin is placed in a
high-impedance state, thus reducing system noise in businterface applications. Bus-hold additionally allows unused
device pins to remain unconnected on the board, which is
particularly useful during prototyping as designers can route
new signals to the device without cutting trace connections to
V
CC
or GND. For more informati on, see th e applicati on note
“Understanding Bus-Hold - A Feature of Cypress CPLDs.”
Programmable Slew Rate Control
Each output has a pro grammable c onfiguratio n bit, which sets
the output slew rate t o fast or slow . For design s concerned with
meeting FCC emissi ons st and ards the slo w edge pro vides for
lower system noise. For designs requiring very high performance the fast edge rate provides maximum system performance.
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 6 of 63
f
Figure 2. I/O and Buried Macrocells
Figure 3. Input Macrocell
C2 C3
DECODE
C2 C3
DECODE
0
1
2
3
O
C6
C5
“0”
“1”
0
1
O
D/T/L
Q
R
P
0
1
2
3
O
C0
0
1
O
C4
FEEDBACK TO PIM
FEEDBACK TO PIM
BLOCK RESET
0−16
TERMS
I/O MACROCELL
I/O CELL
FROM PTM
0
1
O
D/T/L Q
R
P
FROM PTM
1
O
C7
FEEDBACK TO PIM
BURIED MACROCELL
0
ASYNCHRONOUS
PRODUCT
0−16
TERMS
PRODUCT
C1
4
0
1
2
3
Q
4
C24
C0C1
C24
C25
C25
4 SYNCHRONOUS CLOCKS (CLK0,CLK1,CLK2,CLK3)
1 ASYNCHRONOUS CLOCK(PTCLK)
BLOCK PRESET
ASYNCHRONOUS
FAST
SLOW
C26
SLEW
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
OE0
OE1
0
1
2
3
O
C12 C13
TO PIM
D
Q
D
Q
D
Q
LE
INPUT PIN
0
1
2
O
C10
FROM CLOCK
POLARITY MUXES
3
C11
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 7 of 63
Clocking
Each I/O and buried macroc ell has access to four synchronou s
clocks (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3) as well as an
asynchronous product term clock PTCLK. Each input
macrocell has access to all four synchronous clocks.
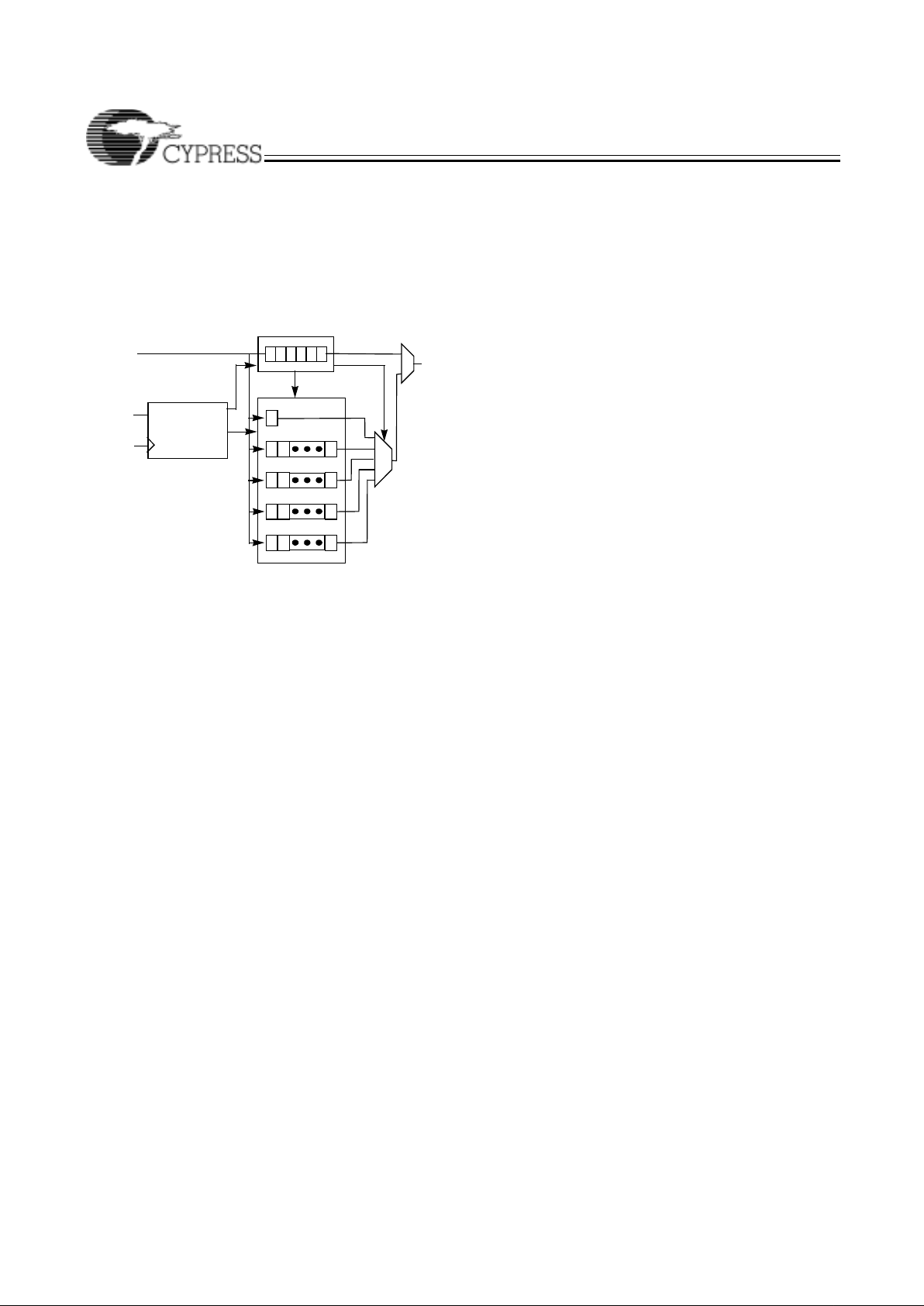
Dedicated Inputs/Clocks
Five pins on each member of the Ultra37000 family ar e designated as input-only. There are two types of dedicated inputs
on Ultra37000 devices: input pins and input/clock pins.
Figure 3 illustrates the architecture for input pins. Four input
options are available for the user: combinatorial, registered,
double-registered, or latched. If a registered or latched option
is selected, any one of the input clocks can be selected for
control.
Figure 4 illustrates the architecture for the input/clock pins.
Like the input pins, input/clock pins can be combinatorial,
registered, double-registered, or latched. In addition, these
pins feed the clocking structures throughout the device. The
clock path at the input has user-configurable polarity.
Product Term Clocking
In addition to the four synchronous clocks, the Ultra37000
family also has a product term clock for asynchronous
clocking. Each logic block has an independent product term
clock which is available to a ll 16 macrocells . Each product te rm
clock also supports user configurable polarity selection.
Timing Model
One of the most impo rtan t feature s of the U ltra3 7000 fa mily is
the simplicity of its timing. All delays are worst case and
system performance is unaf fected by the features use d. Figure
5 illustrates the true timing model for the 167-MHz devices in
high speed mode. For combinatorial paths, any input to any
output incurs a 6.5-ns worst-case delay regardless of the
amount of logic used. For synch ronous syst ems, the inp ut setup time to the outpu t macroc ells for a ny input is 3.5 ns a nd the
clock to output time is also 4.0 ns. These measurements are
for any output and synchronous clock, regardless of the logic
used.
The Ultra37000 features:
• No fanout delays
• No expander delays
• No dedicated vs. I/O pin delays
• No additional delay through PIM
• No penalty for using 0–16 product terms
• No added delay for steering product terms
• No added delay for sharing product terms
• No routing delays
• No output bypass delays
The simple timing model of the Ultra37000 family eliminates
unexpected performance penalties.
JTAG and PCI Standards
PCI Compliance
5V operation of the Ultra37000 is fully compliant with the PCI
Local Bus Specification published by the PCI Special Interest
Group. The 3.3V products meet all PCI requirements except
for the output 3.3V clamp, which is in direct conflict with 5V
tolerance. The Ultra37000 family’s simple and predictable
timing model ensures compliance with the PCI AC specifications independent of the design.
Figure 4. Input/Clock Macrocell
0
1
2
3
O
C10C11
TO PIM
D
Q
D
Q
D
Q
LE
INPUT/CLOCK PIN
0
1
2
O
FROM CLOCK
CLOCK PINS
0
1
O
C12
TO CLOCK MUX ON
ALL INPUT MACROCELLS
TO CLOCK MUX
IN EACH
3
0
1
CLOCK POLARITY MUX
ONE PER LOGIC BLOCK
FOR EACH CLOCK INPUT
POLARITY INPUT
LOGIC BLOCK
C8
C9
C13, C14, C15 OR C16
O
Figure 5. Timing Model for CY37128
COMBINATORIAL SIGNAL
REGISTERED SIGNAL
D,T,L O
CLOCK
INPUT
INPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
tS = 3.5 ns
t
CO
= 4.5 ns
t
PD
= 6.5 ns
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 8 of 63
IEEE 1149.1-compliant JTAG
The Ultra37000 family has an IEEE 1149.1 JTAG interface for
both Boundary Scan and ISR.
Boundary Scan
The Ultra37000 family supports Bypass, Sample/Preload,
Extest, Idcode, and Usercode boundary sc an instructions. The
JTAG interface is shown in Figure 6.
In-System Reprogramming (ISR)
In-System Reprogram ming is the comb ination of the capability
to program or reprogram a device on-board, and the ability to
support design changes without changing the system timing
or device pinout. This combination means design changes
during debug or field upgrades do not cause board respins.
The Ultra37000 family implements ISR by providing a JTAG
compliant interface for on-board programming, robust routing
resources for pinout flexibility, and a simple timing model for
consistent system performance.
Development Software Support
Warp
Warp is a st ate-of-the-art compil er and complete CPLD de sign
tool. For design entry , Warp provides an IEEE-STD-1076/1164
VHDL text editor , an IEEE-STD-1364 V erilo g text editor, and a
graphical finite state machine editor. It provides optimized
synthesis and fitting by replacing basic circuits with ones preoptimized for the target device, by implementing logic in
unused memory an d by perfect comm unication betwee n fitting
and synthesis. To facilitate design and debugging, Warp
provides graphical timing simulation and analysis.
Warp Professional
™
Warp Professional contains several additional features. It
provides an extra method of design entry with its graphical
block diagram ed itor. It allows up to 5 ms timin g simulation
instead of only 2 ms. It allows comp arison of waveforms before
and after design changes.
Warp Enterprise
™
Warp Enterprise provides even more features. It provides
unlimited timing simulation and source-level behavioral
simulation as well as a debug ger. It has the ability to generate
graphical HDL blocks from HDL text. It can even generate
testbenches.
Warp is available for PC and UNIX platforms. Some features
are not avai lable i n the U NIX ve rsion. For fur ther infor matio n
see the Warp for PC, W arp for UNIX, Warp Profession al and
Warp Enterprise data sheets on Cypress’s web site
(www.cypress.com).
Third-Party Software
Although Warp is a complete CP LD developm ent tool o n its
own, it interfaces with nearly every third party EDA tool. All
major third-party software vendors provide support for the
Ultra37000 family o f de vi ce s. Refe r to the th ird-party software
data sheet or contact your local sales office for a list of
currently supported third-p a rty vendors.
Programming
There are four programming options available for Ultra37000
devices. The first method is to use a PC with the 37000
UltraISR programming cable and software. With this method,
the ISR pins of the Ultra37000 devices are routed to a
connector at the edge of the printed circuit board. The 37000
UltraISR programming cable is then connected between the
parallel port of the PC and this connector. A simple configuration file instructs the ISR software of the programming
operations to be perform ed on each of the Ultra 37000 device s
in the system. The ISR s oftware then automatic ally co mpletes
all of the necessary dat a manipulatio ns required to accomplis h
the programming, reading, verifying, and other ISR functions.
For more information on the Cypress ISR Interface, see the
ISR Programming Kit data sheet (CY3700i).
The second meth od for programming U ltra37000 device s is on
automatic test equip ment (A TE). This i s accomplished throu gh
a file created by the ISR sof tware. Check th e Cypress web site
for the latest ISR software download information.
The third programming option for Ultra37000 devices is to
utilize the embedded controller or processor that already
exists in the s ystem. T he Ultr a37000 ISR softw are assi sts in
this method by converting the device JEDEC maps into the
ISR serial stream that c ont ains the ISR ins tructi on inf ormati on
and the addresses and data of locations to be programmed.
The embedded controller then simply directs this ISR stream
to the chain of Ultra37000 devices to complete the desired
reconfiguring or diagnostic operations. Contact your local
sales office for information on availability of this option.
The fourth method for programming Ultra37000 devices is to
use the same programmer that is currently being used to
program F
LASH370i devices.
For all pinout, electrical, and timing requirements, refer to
device data shee ts. For ISR cable an d software speci fications,
refer to the UltraISR kit data sheet (CY3700i).
Third-Party Programmers
As with development software, Cypress support is available
on a wide va riety of thi rd-par ty prog rammer s. All majo r thir dparty programmers (including BP Micro, Data I/O, and SMS)
support the Ultra37000 family.
Figure 6. JTAG Interface
Instruction Register
Boundary Scan
idcode
Usercode
ISR Prog .
Bypass Reg.
Data Registers
JTAG
TAP
CONTROLLER
TDO
TDI
TMS
TCK
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 9 of 63
Logic Block Diagrams
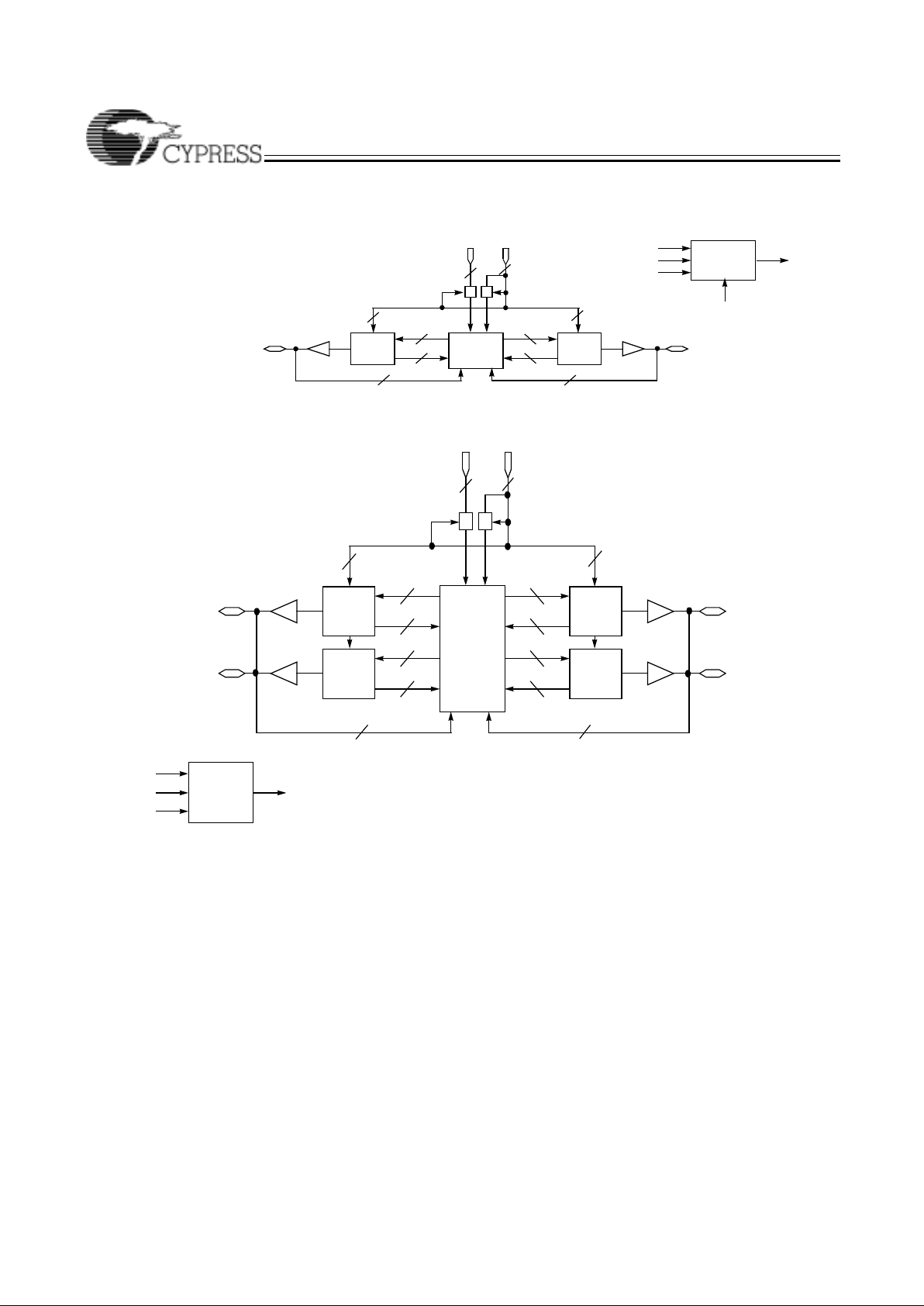
CY37032/CY37032V
LOGIC
BLOCK
B
LOGIC
BLOCK
A
36
16
36
16
Input
Clock/
Input
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
I/O
0
−I/O
15
I/O16−I/O
31
4
4
4
16
16
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
PIM
JTAG
EN
LOGIC
BLOCK
D
LOGIC
BLOCK
C
LOGIC
BLOCK
A
LOGIC
BLOCK
B
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
Input
Clock/
Input
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
I/O
0
-I/O
15
I/O16-I/O
31
I/O48-I/O
63
I/O32-I/O
47
4
4
4
32
32
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
PIM
CY37064/CY37064V (100-Lead TQFP)
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 10 of 63
Logic Block Diagrams (continued)
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
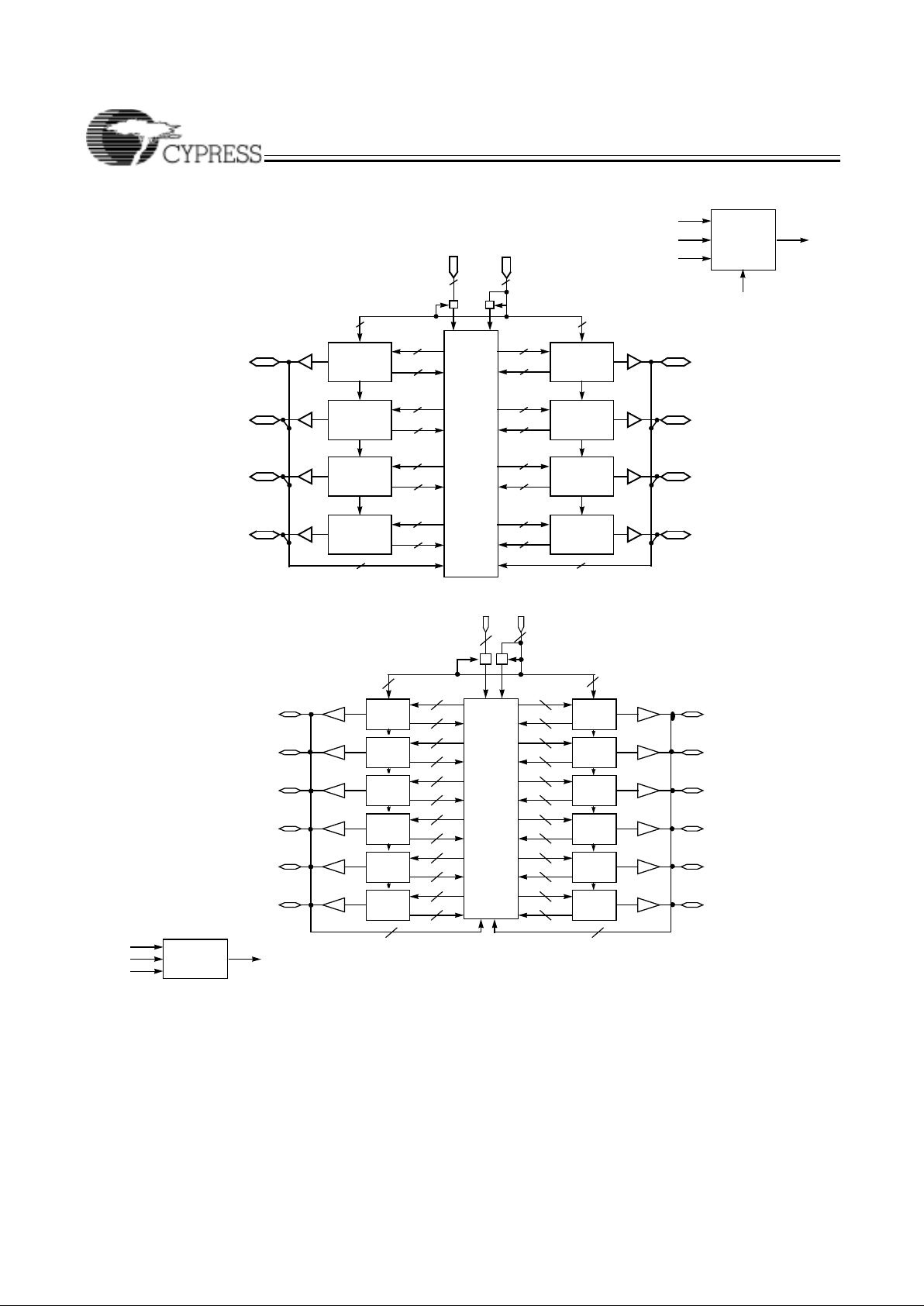
CY37128/CY37128V (160-lead TQFP)
PIM
INPUT
MACROCELL
CLOCK
INPUTS
4 4
36
16
16
36
LOGIC
BLOCK
36
16
16
36
16 I/Os
36 36
36
16
16
36
16
16
64
64
41
INPUT/CLOCK
MACROCELLS
I/O
0
–I/O
15
A
INPUTS
LOGIC
BLOCK
C
LOGIC
BLOCK
B
LOGIC
BLOCK
D
LOGIC
BLOCK
H
LOGIC
BLOCK
G
LOGIC
BLOCK
F
LOGIC
BLOCK
E
I/O16–I/O
31
I/O32–I/O
47
I/O28–I/O
63
I/O
112
–I/O
127
I/O96–I/O
111
I/O80–I/O
95
I/O64–I/O
79
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
16 I/Os
JTAG
EN
LOGIC
BLOCK
H
LOGIC
BLOCK
L
LOGIC
BLOCK
I
LOGIC
BLOCK
J
LOGIC
BLOCK
K
LOGIC
BLOCK
A
LOGIC
BLOCK
B
LOGIC
BLOCK
C
LOGIC
BLOCK
D
LOGIC
BLOCK
E
LOGIC
BLOCK
G
LOGIC
BLOCK
F
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
PIM
Input
Clock/
Input
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
10 I/Os
I/O
0
–I/O
9
I/O10–I/O
19
I/O20–I/O
29
I/O30–I/O
39
I/O40–I/O
49
I/O50–I/O
59
I/O
110
–I/O
119
I/O
100
–I/O
109
I/O90–I/O
99
I/O80–I/O
89
I/O70–I/O
79
I/O60–I/O
69
4
4
4
6060
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
CY37192/CY37192V (160-lead TQFP)
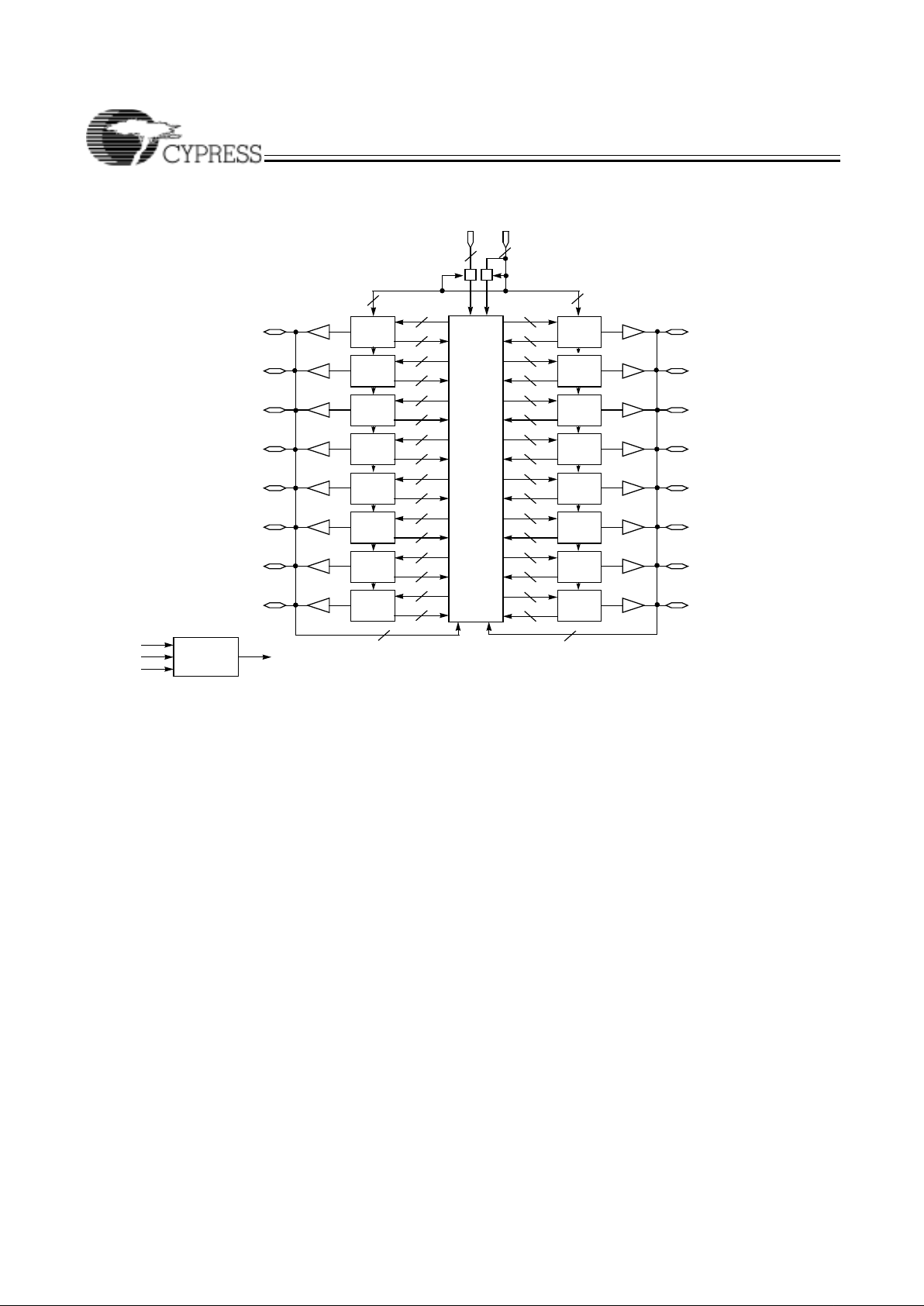
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 11 of 63
Logic Block Diagrams (continued)
CY37256/CY37256V (256-lead BGA)
LOGIC
BLOCK
G
LOGIC
BLOCK
H
LOGIC
BLOCK
I
LOGIC
BLOCK
J
LOGIC
BLOCK
L
LOGIC
BLOCK
P
LOGIC
BLOCK
M
LOGIC
BLOCK
N
LOGIC
BLOCK
O
LOGIC
BLOCK
A
LOGIC
BLOCK
B
LOGIC
BLOCK
C
LOGIC
BLOCK
D
LOGIC
BLOCK
E
LOGIC
BLOCK
K
LOGIC
BLOCK
F
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
PIM
Input
Clock/
Input
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
I/O
0
−I/O
11
I/O12−I/O
23
I/O24−I/O
35
I/O36−I/O
47
I/O48−I/O
59
I/O60−I/O
71
I/O72−I/O
83
I/O84−I/O
95
I/O
180
−I/O
191
I/O
168
−I/O
179
I/O
156
−I/O
167
I/O
144
−I/O
155
I/O
132
−I/O
143
I/O
120
−I/O
131
I/O
108
−I/O
119
I/O96−I/O
107
4
4
4
96
96
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
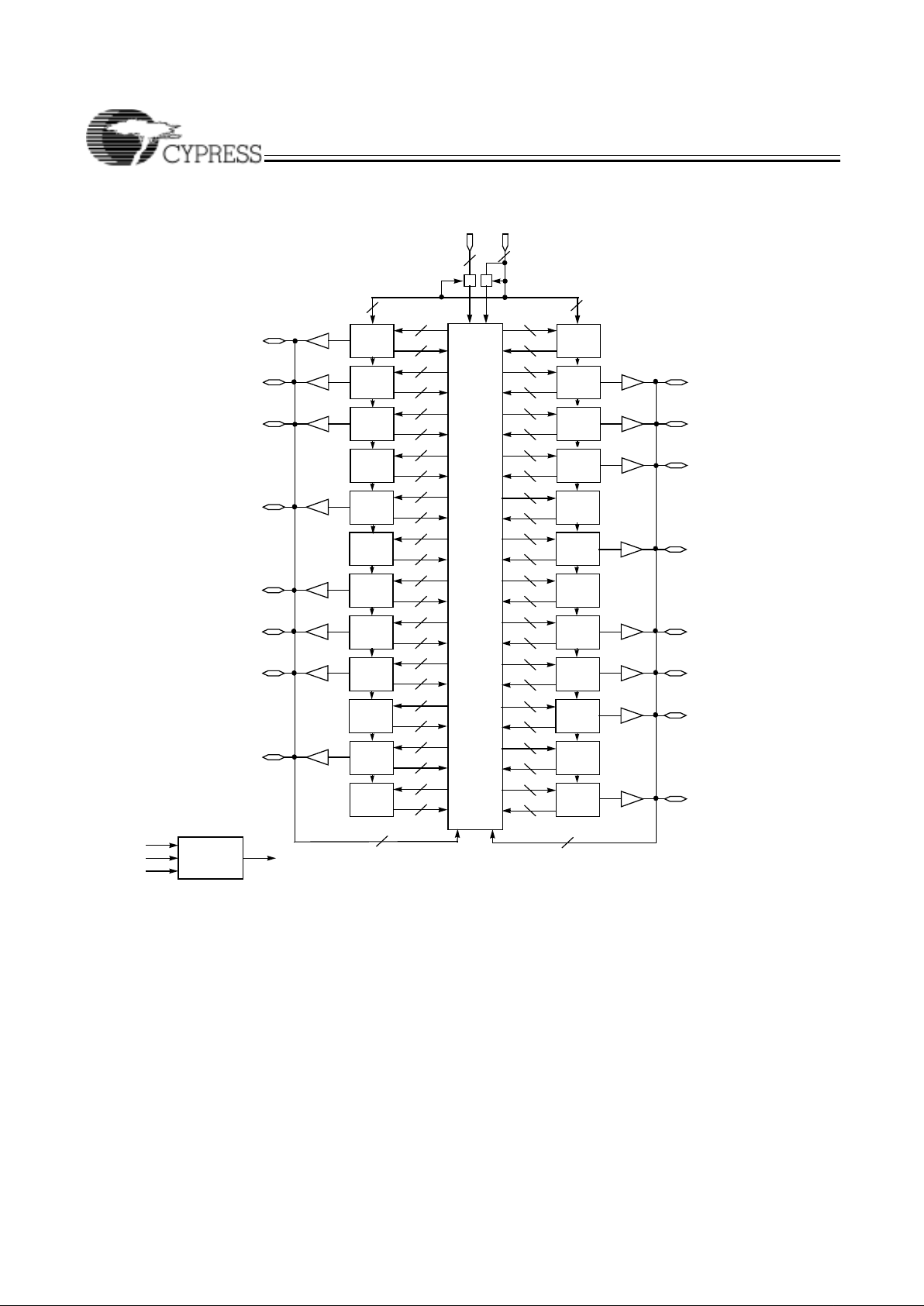
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 12 of 63
Logic Block Diagrams (continued)
CY37384/CY37384V (256-Lead BGA)
LOGIC
BLOCK
AH
LOGIC
BLOCK
AI
LOGIC
BLOCK
BD
LOGIC
BLOCK
BE
LOGIC
BLOCK
BG
LOGIC
BLOCK
BL
LOGIC
BLOCK
BI
LOGIC
BLOCK
BJ
LOGIC
BLOCK
BK
LOGIC
BLOCK
AA
LOGIC
BLOCK
AB
LOGIC
BLOCK
AC
LOGIC
BLOCK
AD
LOGIC
BLOCK
AF
LOGIC
BLOCK
BF
LOGIC
BLOCK
AG
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
PIM
Input
Clock/
Input
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
I/O
0
−I/O
11
I/O12−I/O
23
I/O24−I/O
35
I/O48−I/O
59
I/O60−I/O
71
I/O72−I/O
83
I/O
168
−I/O
191
I/O
156
−I/O
179
I/O
144
−I/O
167
I/O
120
−I/O
143
I/O
108
−I/O
131
4
4
4
96
96
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
LOGIC
BLOCK
AJ
LOGIC
BLOCK
BC
16
16
12 I/Os
I/O
96
−I/O
119
LOGIC
BLOCK
AK
LOGIC
BLOCK
BB
16
16
12 I/Os
I/O
84
−I/O
95
LOGIC
BLOCK
AL
LOGIC
BLOCK
BA
16
16
12 I/Os
I/O
96
−I/O
107
LOGIC
BLOCK
AE
LOGIC
BLOCK
BH
16
16
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
I/O
36
−I/O
47
I/O
132
−I/O
155
36
36
36
36
36
36
36
36
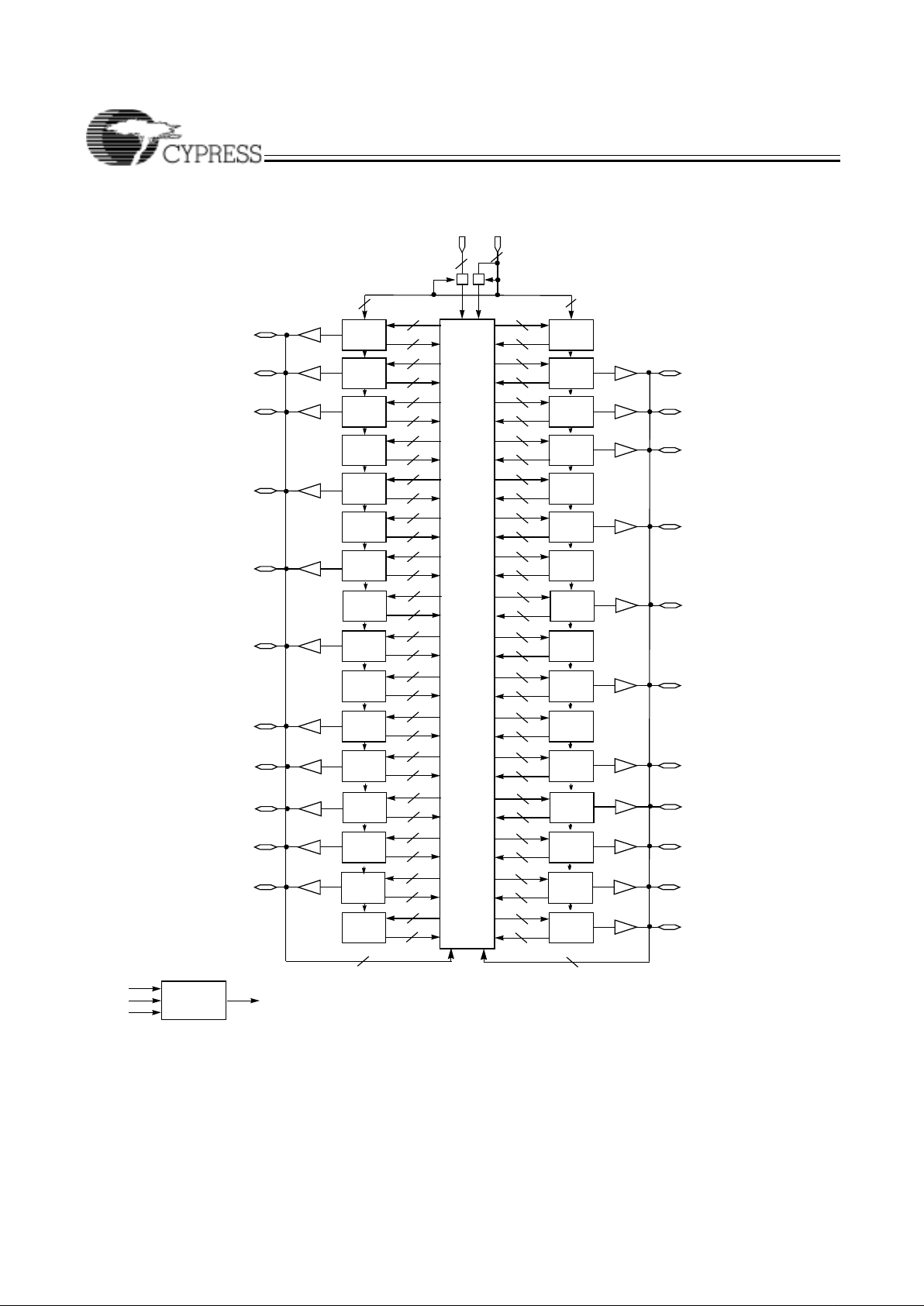
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 13 of 63
Logic Block Diagrams (continued)
CY37512/CY37512V (352-Lead BGA)
LOGIC
BLOCK
AG
LOGIC
BLOCK
AH
LOGIC
BLOCK
BI
LOGIC
BLOCK
BJ
LOGIC
BLOCK
BL
LOGIC
BLOCK
BP
LOGIC
BLOCK
BM
LOGIC
BLOCK
BN
LOGIC
BLOCK
BO
LOGIC
BLOCK
AA
LOGIC
BLOCK
AB
LOGIC
BLOCK
AC
LOGIC
BLOCK
AD
LOGIC
BLOCK
AE
LOGIC
BLOCK
BK
LOGIC
BLOCK
AF
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
36
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
36
16
Input
Clock/
Input
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
I/O
0
−
I/O
11
I/O12−
I/O
23
I/O24−
I/O
35
I/O36−
I/O
47
I/O48−
I/O
59
I/O60−
I/O
71
I/O72−
I/O
83
I/O84−
I/O
95
I/O
252
−
I/O
263
I/O
240
−
I/O
251
I/O
228
−
I/O
239
I/O
216
−
I/O
227
I/O
204
−
I/O
215
4
4
4
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
JTAG Tap
Controller
1
PIM
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AI
LOGIC
BLOCK
BH
12 I/Os
I/O
96
−
I/O
107
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AJ
LOGIC
BLOCK
BG
12 I/Os
12 I/Os
I/O
108
−
I/O
119
I/O
192
−
I/O
203
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AK
LOGIC
BLOCK
BF
12 I/Os
I/O
120
−
I/O
131
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AL
LOGIC
BLOCK
BE
12 I/Os
I/O
180
−
I/O
191
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AM
LOGIC
BLOCK
BD
12 I/Os
I/O
168
−
I/O
179
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AN
LOGIC
BLOCK
BC
12 I/Os
I/O
156
−
I/O
167
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AO
LOGIC
BLOCK
BB
12 I/Os
I/O
144
−
I/O
155
16
36
36
16
LOGIC
BLOCK
AP
LOGIC
BLOCK
BA
12 I/Os
I/O
132
−
I/O
143
16
132132
16
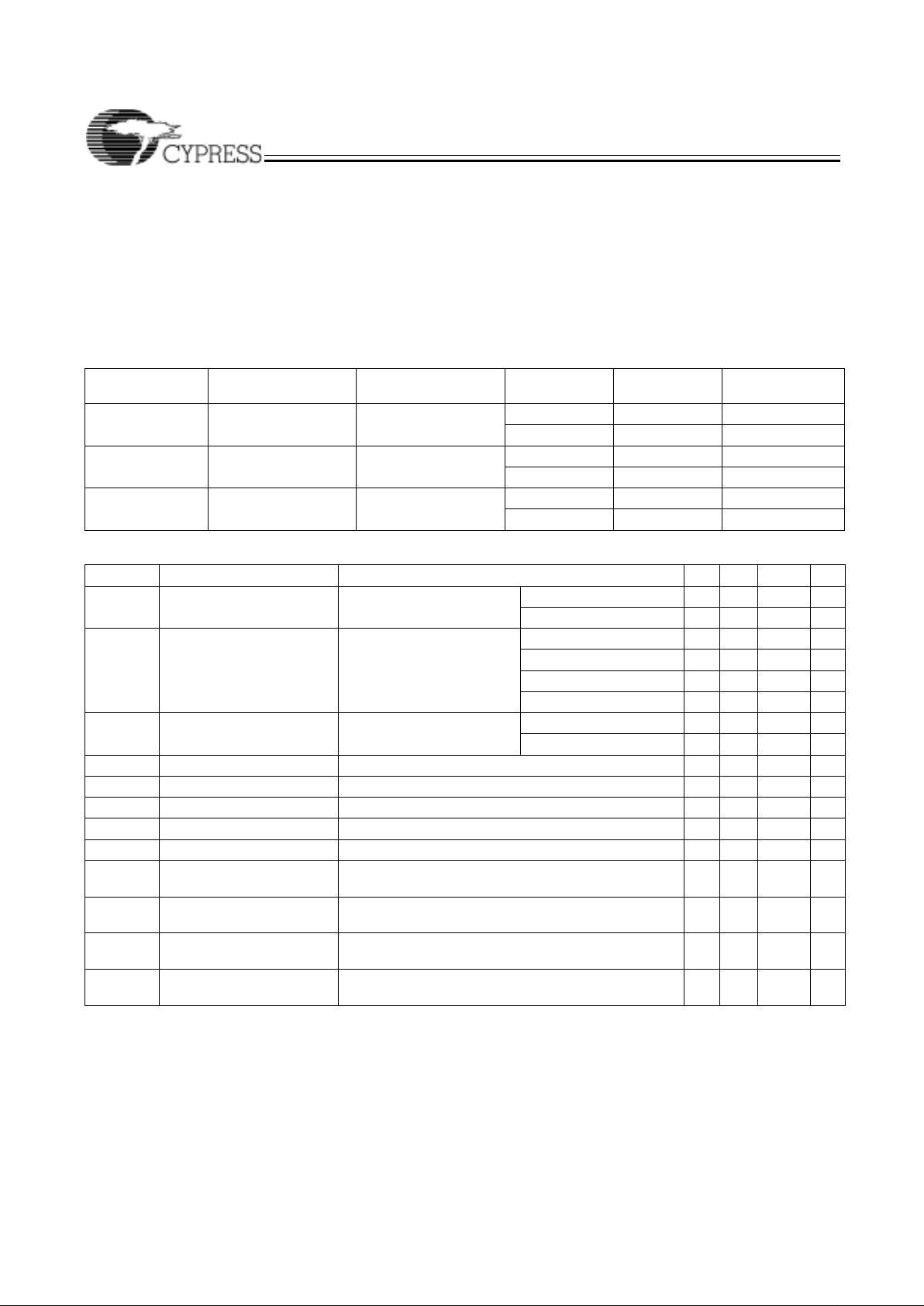
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 14 of 63
5.0V Device Characteristics
Maximum Ratings
(Above which the us efu l l ife ma y be impaired. For us er gui delines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature .................................–65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied.............................................–55°C to +125°C
Supply Voltage to Ground Potential...............–0.5V to +7.0V
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in High-Z State................................................–0.5V to +7.0V
DC Input Voltage............................................–0.5V to +7.0V
DC Program Voltage.............................................4.5 to 5.5V
Current into Outputs....................................................16 mA
Static Discharge Voltage...........................................> 2001V
(per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch-up Current.....................................................> 200 mA
Operating Range
[2]
Range
Ambient
Temperature
[2]
Junction
Temperature
Output
Condition V
CC
V
CCO
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 0°C to +90°C 5V 5V ± 0.25V 5V ± 0.25V
3.3V 5V ± 0.25V 3.3V ± 0.3V
Industrial –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +105°C 5V 5V ± 0.5V 5V ± 0.5V
3.3V 5V ± 0.5V 3.3V ± 0.3V
Military
[3]
–55°C to +125°C –55°C to +130°C 5V 5V ± 0.5V 5V ± 0.5V
3.3V 5V ± 0.5V 3.3V ± 0.3V
5.0V Device Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description T est Conditi ons Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage VCC = Min. IOH = –3.2 mA (Com’l/Ind)
[4]
2.4 V
IOH = –2.0 mA (Mil)
[4]
2.4 V
V
OHZ
Output HIGH Voltage with
Output Disabled
[5]
VCC = Max. IOH = 0 µA (Com’l)
[6]
4.2 V
IOH = 0 µA (Ind/Mil)
[6]
4.5 V
IOH = –100 µA (Com’l)
[6]
3.6 V
IOH = –150 µA (Ind/Mil)
[6]
3.6 V
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage VCC = Min. IOL = 16 mA (Com’l/Ind)
[4]
0.5 V
IOL = 12 mA (Mil)
[4]
0.5 V
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage Guaranteed Input Logical HIGH Voltage for all Inputs
[7]
2.0 V
CCmax
V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage Guaranteed Input Logical LOW Voltage for all Inputs
[7]
–0.5 0.8 V
I
IX
Input Load Current VI = GND OR VCC, Bus-Hold Disabled –10 10 µA
I
OZ
Output Leakage Current VO = GND or VCC, Output Disabled, Bus-Hold Disabled –50 50 µA
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current
[8, 5]
VCC = Max., V
OUT
= 0.5V –30 –160 mA
I
BHL
Input Bus-Hold LOW
Sustaining Current
VCC = Min., VIL = 0.8V +75 µA
I
BHH
Input Bus-Hold HIGH
Sustaining Current
VCC = Min., VIH = 2.0V –75 µA
I
BHLO
Input Bus-Hold LOW
Overdrive Current
VCC = Max. +500 µA
I
BHHO
Input Bus-Hold HIGH
Overdrive Current
VCC = Max. –500 µA
Notes:
2. Normal Programming Conditions apply across Ambient Temperature Range for specified programming methods. For more information on programming the
Ultra37000 Family devices, please refer to the Application Note titled “An Introduction to In System Reprogramming with the Ultra37000.”
3. T
A
is the “Instant On” case temperature.
4. IOH = –2 mA, IOL = 2 mA for TDO.
5. Tested initially and after any design or process changes that may affect these parameters.
6. When the I/O is output disabled, the bus-hold circuit can weakly pull the I/O to above 3.6V if no leakage current is allowed. Note that all I/Os are output disabled
during ISR programming. Refer to the application note “Understanding Bus-Hold” for additional information.
7. These are absolute values with respect to device ground. All overshoots due to system or tester noise are included.
8. Not more than one output should be tested at a time. Duration of the short circuit should not exceed 1 second. V
OUT
= 0.5V has been chosen to avoid test
problems caused by tester ground degradation.
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 15 of 63
3.3V Device Characteristics
Maximum Ratings
(Above which the us efu l l ife ma y be impaired. For us er gui delines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature .................................–65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied.............................................–55°C to +125°C
Supply Voltage to Ground Potential...............–0.5V to +4.6V
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in High-Z State................................................–0.5V to +7.0V
DC Input Voltage............................................–0.5V to +7.0V
DC Program Voltage.............................................3.0 to 3.6V
Current into Outputs......................................................8 mA
Static Discharge Voltage............................................>2001V
(per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch-up Current......................................................>200 mA
Inductance
[5]
Parameter Description
Test
Conditions
44-
Lead
TQFP
44-
Lead
PLCC
44-
Lead
CLCC
84-
Lead
PLCC
84-
Lead
CLCC
100-
Lead
TQFP
160-
Lead
TQFP
208-
Lead
PQFP Unit
L Maximum Pin
Inductance
VIN = 5.0V
at f = 1 MHz
2 5 2 8 5 8 9 11 nH
Capacitance
[5]
Parameter Description Test Conditions Max. Unit
C
I/O
Input/Output Capacitance VIN = 5.0V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 10 pF
C
CLK
Clock Signal Capacitance VIN = 5.0V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 12 pF
C
DP
Dual Function Pins
[9]
VIN = 5.0V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 16 pF
Endurance Characteristics
[5]
Parameter Description T est Condit ions Min. Typ. Unit
N Minimum Reprogramming Cycles Normal Programming Conditions
[2]
1,000 10,000 Cycles
Operating Range
[2]
Range Ambient Temperature
[2]
Junction Te mperature V
CC
[10]
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 0°C to +90°C 3.3V ± 0.3V
Industrial –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +105°C
3.3V ± 0.3V
Military
[3]
–55°C to +125°C –55°C to +130°C 3.3V ± 0.3V
3.3V Device Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage VCC = Min. IOH = –4 mA (Com’l)
[4]
2.4 V
IOH = –3 mA (Mil)
[4]
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage VCC = Min. IOL = 8 mA (Com’l)
[4]
0.5 V
IOL = 6 mA (Mil)
[4]
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage Guaranteed In put Logical HIGH V oltage for
all Inputs
[7]
2.0 5.5 V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage Guaranteed Inpu t Lo gic al LO W Voltage for
all Inputs
[7]
–0.5 0.8 V
I
IX
Input Load Current VI = GND OR VCC, Bus-Hold Disabled –10 10 µA
I
OZ
Output Leakage Current VO = GND or VCC, Output Disabled, Bus-
Hold Disabled
–50 50 µA
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current
[8, 5]
VCC = Max., V
OUT
= 0.5V –30 –160 mA
I
BHL
Input Bus-Hold LOW Sustaining
Current
VCC = Min., VIL = 0.8V +75 µA
Notes:
9. Dual pins are I/O with JTAG pins.
10. For CY37064VP100-143AC, CY37064VP100-143BBC, CY37064VP44-143AC, CY37064VP48-143BAC; Operating Range: V
CC
is 3.3V± 0.16V.
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 16 of 63
I
BHH
Input Bus-Hold HIGH Sustaining
Current
VCC = Min., VIH = 2.0V –75 µA
I
BHLO
Input Bus-Hold LOW Overdrive
Current
VCC = Max. +500 µA
I
BHHO
Input Bus-Hold HIGH Overdrive
Current
VCC = Max. –500 µA
Inductance
[5]
Parameter Description
Test
Conditions
44-
Lead
TQFP
44-
Lead
PLCC
44-
Lead
CLCC
84-
Lead
PLCC
84-
Lead
CLCC
100-
Lead
TQFP
160-
Lead
TQFP
208-
Lead
PQFP Unit
L Maximum Pin
Inductance
VIN = 3.3V
at f = 1 MHz
2 5 2 8 5 8 9 11 nH
Capacitance
[5]
Parameter Description Test Conditions Max. Unit
C
I/O
Input/Output Capacitance VIN = 3.3V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 8 pF
C
CLK
Clock Signal Capacitance VIN = 3.3V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 12 pF
C
DP
Dual Functional Pins
[9]
VIN = 3.3V at f = 1 MHz at TA = 25°C 16 pF
Endurance Characteristics
[5]
Parameter Description T est Condit ions Min. Typ. Unit
N Minimum Reprogramming Cycles Normal Programming Conditions
[2]
1,000 10,000 Cycles
3.3V Device Electrical Characteristics Over the Operating Range (continued)
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min. Max. Unit
AC Characteristics
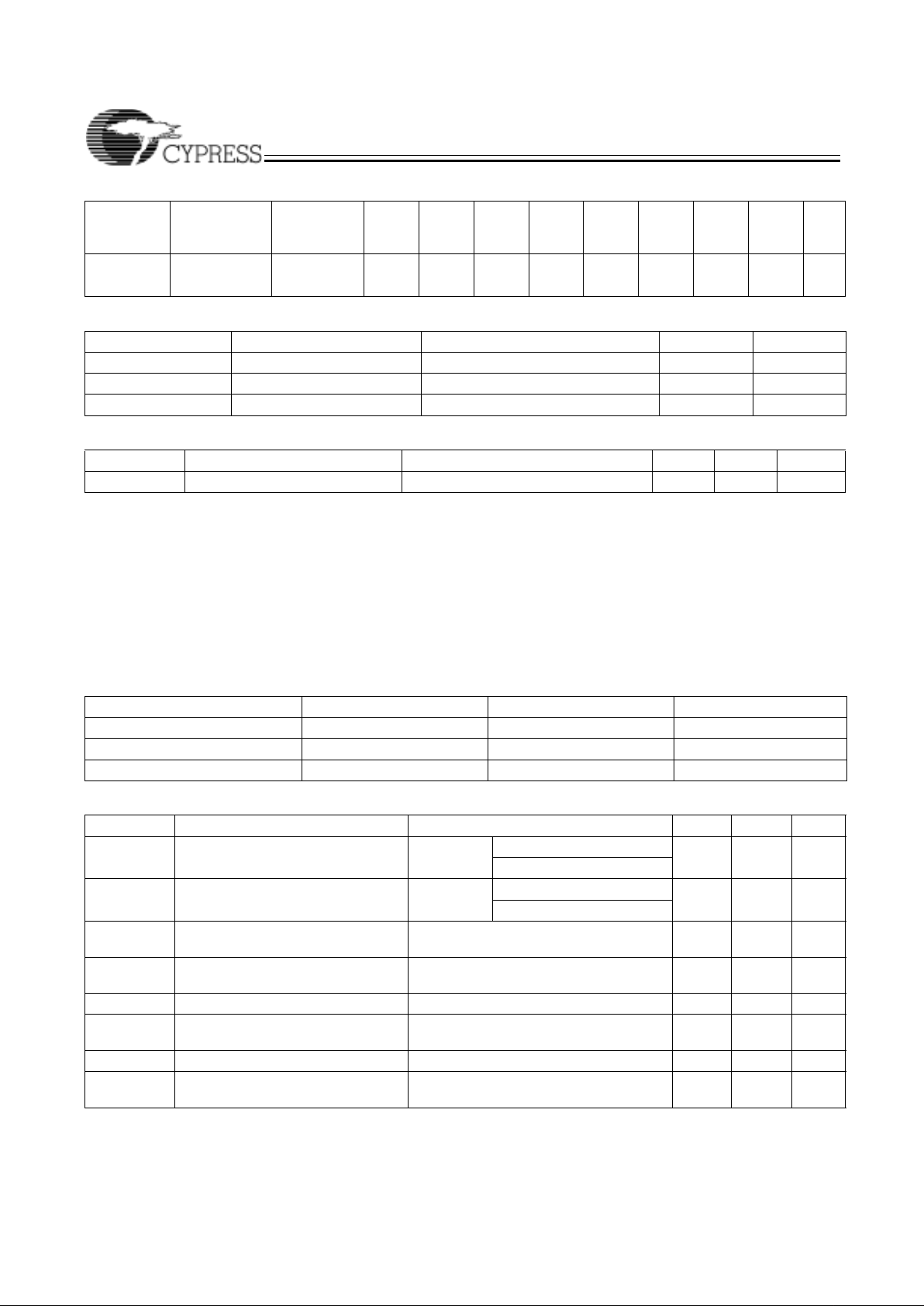
5.0V AC Test Loads and Waveforms
90%
10%
3.0V
GND
90%
10%
ALL INPUT PULSES
5V
OUTPUT
35 pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
5V
OUTPUT
5 pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
(a) (b)
<2 ns
OUTPUT
238Ω (COM’L)
319Ω(MIL)
170Ω (COM’L)
236Ω(MIL)
99Ω (COM’L)
136Ω (MIL)
Equivalent to: THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT
2.08V (COM'L)
2.13V (MIL)
238Ω (COM'L)
319Ω(MIL)
170Ω (COM'L)
236Ω(MIL)
<2 ns
(c)
5 OR 35 pF
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 17 of 63
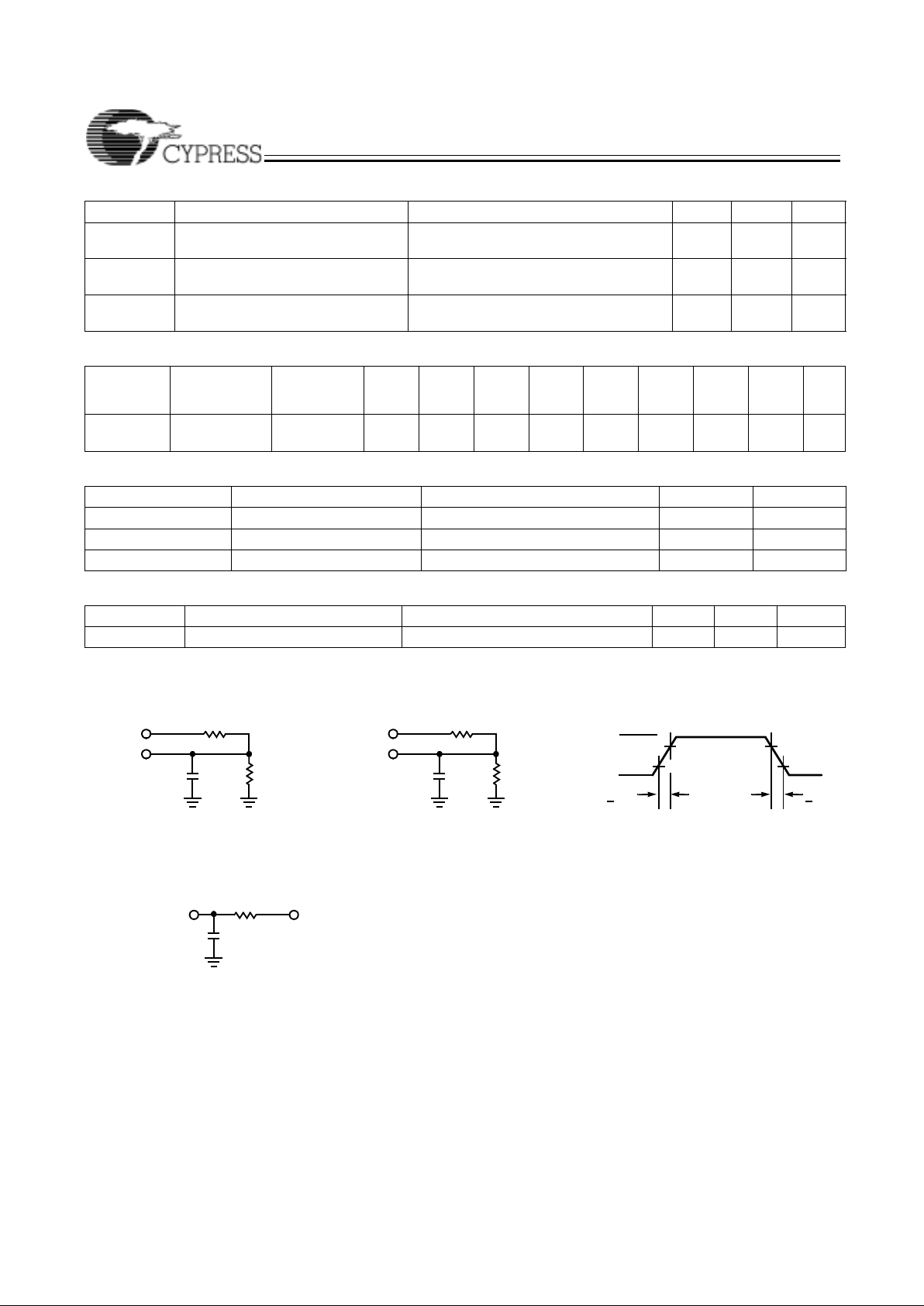
3.3V AC Test Loads and Waveforms
AC Characteristics
90%
10%
3.0V
GND
90%
10%
ALL INPUT PULSES
3.3V
OUTPUT
35 pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
3.3V
OUTPUT
5 pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
(a) (b)
<2 ns
OUTPUT
295Ω (COM’L)
393Ω(MIL)
340Ω (COM’L)
453Ω(MIL)
Equivalent to: THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT
1.77V (COM'L)
1.77V (MIL)
295Ω (COM'L)
393Ω(MIL)
340Ω (COM'L)
453Ω(MIL)
<2 ns
(c)
270Ω (MIL)
158Ω(COM’L)
5 OR 35 pF
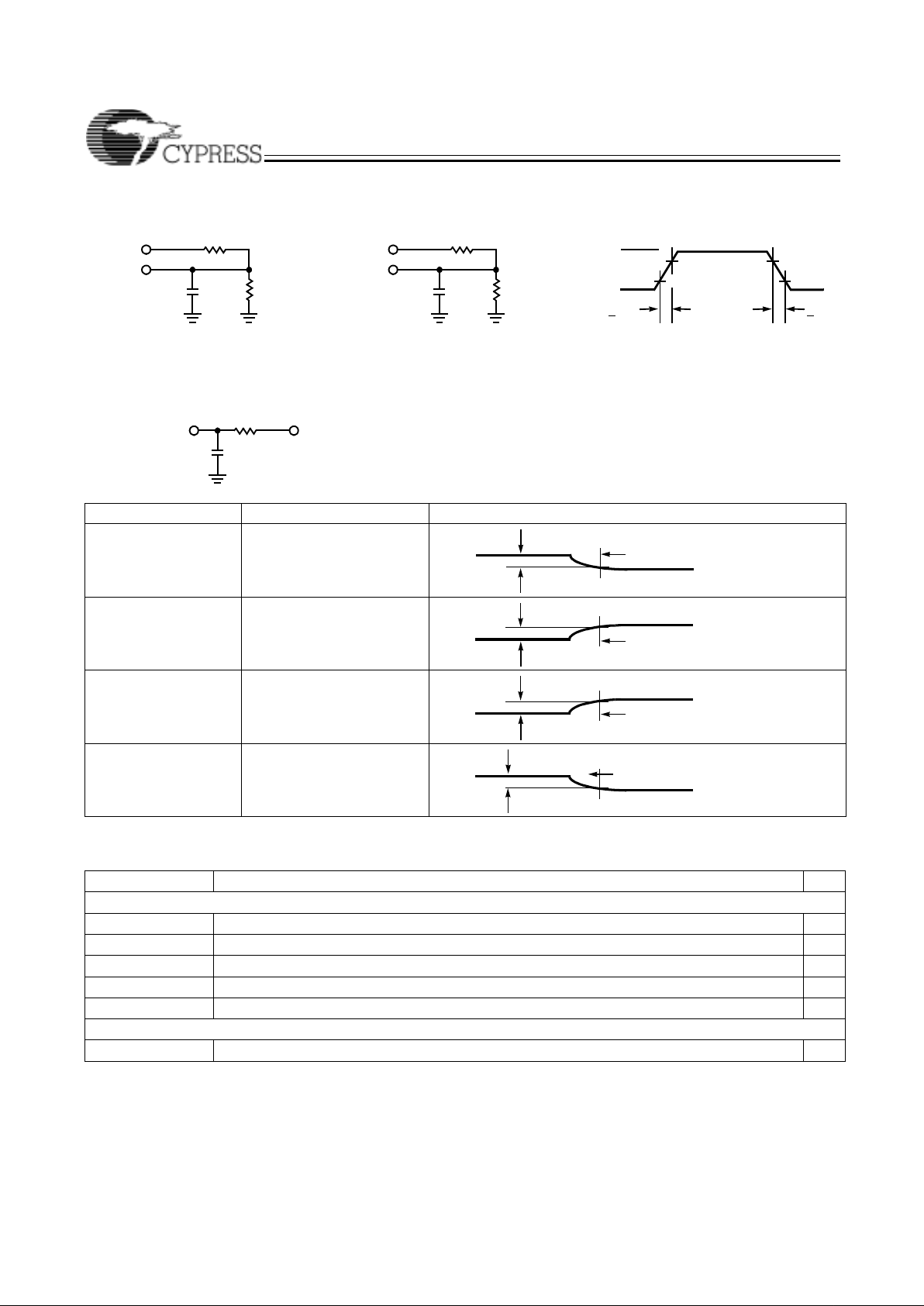
Parameter
[11]
V
X
Output Waveform—Measurement Level
t
ER(–)
1.5V
t
ER(+)
2.6V
t
EA(+)
1.5V
t
EA(–)
V
the
(d) Test Waveforms
V
OH
V
X
0.5V
V
OL
V
X
0.5V
V
X
V
O
H
0.5V
V
X
V
OL
0.5V
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
[12]
Parameter Description Unit
Combinatorial Mode Parameters
t
PD
[13, 14, 15]
Input to Combinatorial Output ns
t
PDL
[13, 14, 15]
Input to Output Through Transparent Input or Output Latch ns
t
PDLL
[13, 14, 15]
Input to Output Through Transparent Input and Output Latches ns
t
EA
[13, 14, 15]
Input to Output Enable ns
t
ER
[11, 13 ]
Input to Output Disable ns
Input Register Parameters
t
WL
Clock or Latch Enable Input LOW Time
[8]
ns
Notes:
11. t
ER
measured with 5-pF AC Test Load and tEA measured with 35-pF AC Test Load.
12. All AC parameters are measured with two outputs switching and 35-pF AC Test Load.
13. Logic Blocks operating in Low-Power Mode, add t
LP
to this spec.
14. Outputs using Slow Output Slew Rate, add t
SLEW
to this spec.
15. When V
CCO
= 3.3V, add t
3.3IO
to this spec.
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 18 of 63
t
WH
Clock or Latch Enable Input HIGH Time
[8]
ns
t
IS
Input Register or Latch Set-up Time ns
t
IH
Input Register or Latch Hold Time ns
t
ICO
[13, 14, 15]
Input Register Clock or Latch Enable to Combinatorial Output ns
t
ICOL
[13, 14, 15]
Input Register Clock or Latch Enable to Output Through Transparent Output Latch ns
Synchronous Clocking Parameters
t
CO
[14, 15]
Synchronous Clock (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable to Output ns
t
S
[13]
Set-Up Time from Input to Sync. Clk (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable ns
t
H
Register or Latch Data Ho ld Time ns
t
CO2
[13, 14, 15]
Output Synchronous Clock (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable to Com binatoria l Output
Delay (Through Logic Array)
ns
t
SCS
[13]
Output Synchronous Clock (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable to Outpu t Sy nc hro nou s
Clock (CLK
0
, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable (Through Logic Array)
ns
t
SL
[13]
Set-Up Time from Inp ut T hrou gh Transparent Latch to Output Regist er Sy nc hron ou s C l ock (CL K0
CLK
1
, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable
ns
t
HL
Hold Time for Input Through Transparent Latch from Output Register Synchronous Clock (CLK0,
CLK
1
, CLK2, or CLK3) or Latch Enable
ns
Product Term Clock ing Param eters
t
COPT
[13, 14, 15]
Product Term Clock or Latch Enable (PTCLK) to Output ns
t
SPT
Set-Up Time from Input to Product Term Clock or Latch Enable (PTCLK) ns
t
HPT
Register or Latch Data Ho ld Time ns
t
ISPT
[13]
Set-Up Time for Buried Register used as an Input Register from Input to Product Term Clock or
Latch Enable (PTCLK)
ns
t
IHPT
Buried Reg ister Used as an Input Register or Lat ch Data Hold Time ns
t
CO2PT
[13, 14, 15]
Product Term Clock or Latch Enable (PTCLK) to Output Delay (Through Logic Array) ns
Pipelined Mode Parameters
t
ICS
[13]
Input Register Synchronous Clock (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3) to Output Register S ync hro nou s
Clock (CLK0, CLK1, CLK2, or CLK3)
ns
Operating Frequency Parameters
f
MAX1
Maximum Frequency with Internal Feedback (Lesser of 1/t
SCS
, 1/(tS + tH), or 1/tCO)
[5]
MHz
f
MAX2
Maximum Frequency Data Path in Output Registered/Latched Mode (Lesser of 1/(tWL + tWH),
1/(t
S+tH
), or 1/tCO)
[5]
MHz
f
MAX3
Maximum Frequency with External Feedback (Lesser of 1/(tCO + tS) or 1/(tWL + tWH)
[5]
MHz
f
MAX4
Maximum Frequency in Pipelined Mode (Lesser of 1/(tCO + tIS), 1/t
ICS
, 1/(tWL + tWH), 1/(tIS + tIH),
or 1/t
SCS
)
[5]
MHz
Reset/Preset Parameters
t
RW
Asynchronous Re se t Width
[5]
ns
t
RR
[13]
Asynchronous Reset Recovery Time
[5]
ns
t
RO
[13, 14, 15]
Asynchronous Reset to Output ns
t
PW
Asynchronous Preset Widt h
[5]
ns
t
PR
[13]
Asynchronous Preset Recovery Time
[5]
ns
t
PO
[13, 14, 15]
Asynchronous Preset to Output ns
User Option Parameters
t
LP
Low Power Adder ns
t
SLEW
Slow Output Slew Rate Adder ns
t
3.3IO
3.3V I/O Mode Timing Adder
[5]
ns
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
[12]
(continued)
Parameter Description Unit
Ultra37000 CPLD Fami
ly
Document #: 38-03007 Rev. *B Page 19 of 63
JTAG Timing Parameters
t
S JTAG
Set-up Time from TDI and TMS to TCK
[5]
ns
t
H JTAG
Hold Time on TDI and TMS
[5]
ns
t
CO JTAG
Falling Edge of TCK to TDO
[5]
ns
f
JTAG
Maximum JTAG Tap Controller Frequency
[5]
ns
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
[12]
(continued)
Parameter Description Unit
Switching Characteristics Over the Operating Range
[12]
Parameter
200 MHz 167 MHz
154 MHz 143 MHz 125 MHz 100 MHz 83 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
Combinatorial Mode Parameters
t
PD
[13, 14, 15]
6 6.5 7.5 8.5 10 12 15 20 ns
t
PDL
[13, 14, 15]
11 12.5 14.5 16 16.5 17 19 22 ns
t
PDLL
[13, 14, 15]
12 13.5 15.5 17 17.5 18 20 24 ns
t
EA
[13, 14, 15]
8 8.5 11 13 14 16 19 24 ns
t
ER
[11, 13 ]
8 8.5 11 13 14 16 19 24 ns
Input Register Parameters
t
WL
2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 3 3 4 5 ns
t
WH
2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 3 3 4 5 ns
t
IS
2 222 2 2.5 3 4ns
t
IH
2 222 2 2.5 3 4ns
t
ICO
[13, 14, 15]
11 11 11 12.5 12.5 16 19 24 ns
t
ICOL
[13, 14, 15]
12 12 12 14 16 18 21 26 ns
Synchronous Clocking Parameters
t
CO
[14, 15]
444.56 6.5
[16]
6.5
[17]
8
[18]
10 ns
t
S
[13]
44555.5
[16]
6
[17]
8
[18]
10 ns
t
H
0000 0 0 0 0ns
t
CO2
[13, 14, 15]
9.5 10 11 12 14 16 19 24 ns
t
SCS
[13]
5 66.57 8
[16]
10 12 15 ns
t
SL
[13]
7.5 7.5 8.5 9 10 12 15 15 ns
t
HL
0 000 0 0 0 0ns
Product Term Clock ing Param eters
t
COPT
[13, 14, 15]
7101013 13 13 1520ns
t
SPT
2.5 2.5 2.5 3 5 5.5 6 7 ns
t
HPT
2.5 2.5 2.5 3 5 5.5 6 7 ns
t
ISPT
[13]
0000 0000ns
t
IHPT
6 6.5 6.5 7.5 9 11 14 19 ns
t
CO2PT
[13, 14,
15]
12 14 15 19 19 21 24 30 ns
Pipelined Mode Parameters
t
ICS
[13]
56678
[16]
10 12 15 ns
Notes:
16. The following values correspond to the CY37512 and CY37384 devices: t
CO
= 5 ns, tS = 6.5 ns, t
SCS
= 8.5 ns, t
ICS
= 8.5 ns, f
MAX1
= 118 MHz.
17. The following values correspond to the CY37192V and CY37256V devices: t
CO
= 6 ns, tS = 7 ns, f
MAX2
= 143 MHz, f
MAX3
= 77 MHz, and f
MAX4
= 100 MHz;
and for the CY37512 devices: t
S
= 7 ns.
18. The following values correspond to the CY37512V and CY37384V devices: t
CO
= 6.5 ns, tS = 9.5 ns, and f
MAX2
= 105 MHz.
 Loading...
Loading...