
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
EZ-BT™ WICED Module
General Description
Note
1. Connection range tested module-to-module in full line-of-sight environment, free of obstacles or interference sources with output power of +9.0 dBm. Actual range will
vary based on end product design, environment, receive sensitity and transmit output power of the central deivce.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 is a fully integrated Bluetooth Smart
Ready wireless module. The CYBT-3330xx-02 includes an
onboard crystal oscillator, passive components, flash memory,
and the Cypress CYW20706 silicon device. Refer to the
CYW20706 datasheet for additional details on the capabilities of
the silicon device used in this module.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 supports peripheral functions (ADC and
PWM), UART, I2C, and SPI communication, and a PCM/I2S
audio interface. The CYBT-3330xx-02 includes a royalty-free
Bluetooth stack compatible with Bluetooth 5.0 in a 12.0 × 13.5 ×
1.95 mm package.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 includes 512 KB of onboard serial flash
memory and is designed for standalone operation. The
CYBT-3330xx-02 uses an integrated power amplifier to achieve
Class I or Class II output power capability.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 is offered in two certified versions. The
CYBT-333032-02 supports an external antenna through an RF
solder pad output. The CYBT-333047-02 supports an external
antenna via a u-FL connector.
Module Description
n Module size: 12.00 mm × 13.50 mm × 1.95 mm
n Bluetooth 5.0 Qualified Smart Ready module
p QDID: TBD
p Declaration ID: TBD
n Certified to FCC, ISED, MIC, and CE regulations
n Castelated solder pad connections for ease-of-use
n 512-KB on-module serial flash memory
n Up to 11 GPIOs
n Temperature range: –30 °C to +85 °C
n Cortex-M3 32-bit processor
n Maximum TX output power
p +12 dbm for Bluetooth Classic
p +9 dBm for Bluetooth Low Energy
• BLE connection range of up to 250 meters at 9 dBm
n RX Receive Sensitivity:
p Bluetooth Classic:
• –93.5 dBm at 1 Mbps, GFSK
• –95.5 dBm at 2 Mbps,
π/4-DQPSK
• –89.5 dBm at 3 Mbps, 8-DPSK
p –96.5 dBm for Bluetooth Low Energy
[1]
Power Consumption
n Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) at 8 dBm
p Peak TX current: 52.5 mA
p Peak RX current consumption: 26.4 mA
n Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) at 0 dBm
p 1-second interval BLE ADV average current consumption:
315 uA
n Low power mode support
p Deep Sleep: 2.69 uA
Functional Capabilities
n Σ-Δ ADC for audio (12 bits) and DC measurement (10 bits)
n Serial Communications interface compatible with I
n Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) support for both master and
2
C slaves
slave modes
n HCI interface through UART
n PCM/I2S Audio interface
n Two-wire Global Coexistence Interface (GCI)
n Integrated peripherals such as PWM, ADC
n Programmable output power control
n Supports extended synchronous connections (eSCO), for
enhanced voice quality by allowing for retransmission of
dropped packets
n Bluetooth wideband speech support
Benefits
CYBT-3330xx-02 provides all necessary components required to
operate BLE and/or BR/EDR communication standards.
n Proven hardware design ready to use
n Dual-mode operation eliminates the need for multiple modules
n Cost optimized for applications without space constraints
n Nonvolatile memory for self-sufficient operation and
Over-the-air updates
n Bluetooth SIG Listed with QDID and Declaration ID
n Fully certified module eliminates the time needed for design,
development and certification processes
n WICED™ STUDIO provides an easy-to-use integrated design
environment (IDE) to configure, develop, and program a
Bluetooth application
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Revised September 18, 2018
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
More Information
Cypress provides a wealth of data at www.cypress.com to help you to select the right module for your design, and to help you to
quickly and effectively integrate the module into your design.
References
n Overview: EZ-BLE/BT Module Portfolio, Module Roadmap
n CYW20706 BT Silicon Datasheet
n Development Kits:
p CYBT-333047-EVAL, CYBT-333047-02 Evaluation Board
n Test and Debug Tools:
p CYSmart, Bluetooth
p CYSmart Mobile, Bluetooth
®
LE Test and Debug Tool (Windows)
®
LE Test and Debug Tool
(Android/iOS Mobile App)
n Knowledge Base Article
p KBA97095 - EZ-BLE™ Module Placement
p KBA213260- RF Regulatory Certifications for
CYBT-343026-01 EZ-BT™ WICED Modules
p KBA213976 - FAQ for BLE and Regulatory Certifications with
EZ-BLE modules
p KBA210802 - Queries on BLE Qualification and Declaration
Processes
p KBA218122 - 3D Model Files for EZ-BLE/EZ-BT Modules
p KBA221025 - Platform Files for CYBT-343026-EVAL
p KBA223428 - Programming an EZ-BT WICED Module
Development Environments
Wireless Connectivity for Embedded Devices (WICED) Studio Software Development Kit (SDK)
Cypress' WICED® (Wireless Connectivity for Embedded Devices) is a full-featured platform with proven Software Development Kits
(SDKs) and turnkey hardware solutions from partners to readily enable Wi-Fi and Bluetooth® connectivity in system design.
WICED Studio is the only SDK for the Internet of Things (IoT) that combines Wi-Fi and Bluetooth into a single integrated development
environment. In addition to providing WICED APIs and an application framework designed to abstract complexity, WICED Studio also
leverages many common industry standards.
Technical Support
n Cypress Community: Whether you’re a customer, partner or a developer interested in the latest Cypress innovations, the Cypress
Developer Community offers you a place to learn, share and engage with both Cypress experts and other embedded engineers
around the world.
n Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Learn more about our Bluetooth ECO System.
n Visit our support page and create a technical support case or contact a local sales representatives. If you are in the United States,
you can talk to our technical support team by calling our toll-free number: +1-800-541-4736. Select option 2 at the prompt.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 2 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Contents
Overview............................................................................ 4
Functional Block Diagram ........................................... 4
Module Description...................................................... 4
Pad Connection Interface ................................................ 6
Recommended Host PCB Layout ................................... 7
Module Connections ........................................................ 9
Connections and Optional External Components....... 10
Power Connections (VDDIN)..................................... 10
External Reset (XRES).............................................. 10
Multiple-Bonded GPIO Connections ......................... 11
Critical Components List ........................................... 13
Qualified Antenna for CYBT-3330xx-02 .................... 13
Functional Description................................................... 14
Bluetooth Baseband Core ......................................... 14
Microcontroller Unit ................................................... 16
External Reset (XRES).............................................. 17
Integrated Radio Transceiver........................................ 18
Transmitter Path........................................................ 18
Receiver Path............................................................ 18
Local Oscillator Generation....................................... 18
Calibration ................................................................. 18
Internal LDO.............................................................. 19
Collaborative Coexistence............................................. 19
Global Coexistence Interface ........................................ 19
SECI I/O .................................................................... 19
Peripheral and Communication Interfaces .................. 20
I2C Communication Interface.................................... 20
HCI UART Interface .................................................. 20
Peripheral UART Interface ........................................ 21
Serial Peripheral Interface......................................... 21
PCM Interface ........................................................... 21
Clock Frequencies.......................................................... 21
GPIO Port ........................................................................ 22
PWM................................................................................. 22
Power Management Unit................................................ 24
RF Power Management ............................................ 24
Host Controller Power Management ......................... 24
BBC Power Management.......................................... 24
Electrical Characteristics............................................... 25
Chipset RF Specifications ............................................. 27
Timing and AC Characteristics ..................................... 30
UART Timing............................................................. 30
SPI Timing.....................................................
I2C Interface Timing.................................................. 33
PCM Interface Timing................................................ 34
I2S Interface Timing .................................................. 38
Environmental Specifications ....................................... 41
Environmental Compliance ....................................... 41
RF Certification.......................................................... 41
Safety Certification .................................................... 41
Environmental Conditions ......................................... 41
ESD and EMI Protection ........................................... 41
Regulatory Information.................................................. 42
FCC........................................................................... 42
ISED.......................................................................... 43
European Declaration of Conformity ......................... 44
MIC Japan................................................................. 44
Packaging........................................................................ 45
Ordering Information...................................................... 47
Acronyms........................................................................ 48
Document Conventions ................................................. 50
Units of Measure ....................................................... 50
Document History Page................................................. 51
Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information...................... 52
Worldwide Sales and Design Support....................... 52
Products .................................................................... 52
PSoC® Solutions ...................................................... 52
Cypress Developer Community................................. 52
Technical Support ..................................................... 52
............ 31
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 3 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
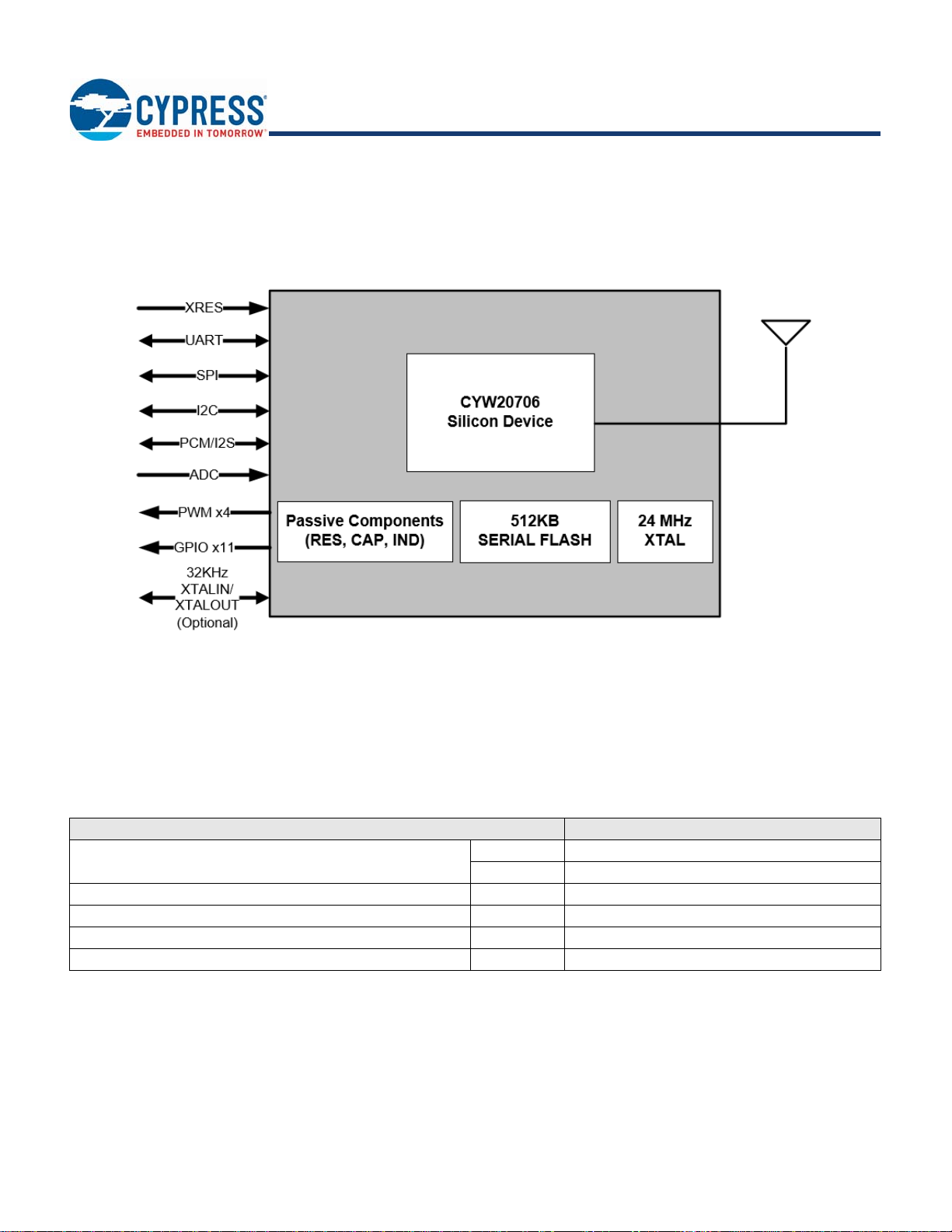
Overview
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1 illustrates the CYBT-3330xx-02 functional block diagram.
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram
Module Description
The CYBT-3330xx-02 module is a complete module designed to be soldered to the application’s main board.
Module Dimensions and Drawing
Cypress reserves the right to select components from various vendors to achieve the Bluetooth module functionality. Such selections
will still guarantee that all mechanical specifications and module certifications are maintained. Designs should be held within the
physical dimensions shown in the mechanical drawings in Figure 2 on page 5. All dimensions are in millimeters (mm).
Table 1. Module Design Dimensions
Dimension Item Specification
Module dimensions
PCB thickness Height (H) 0.50 ± 0.05 mm
Shield height Height (H) 1.45 mm typical
Maximum component height Height (H) 1.45 mm typical
Total module thickness (bottom of module to highest component) Height (H) 1.95 mm typical
See Figure 2 for the mechanical reference drawing for CYBT-3330xx-02.
Length (X) 12.00 ± 0.15 mm
Width (Y) 13.50 ± 0.15 mm
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 4 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
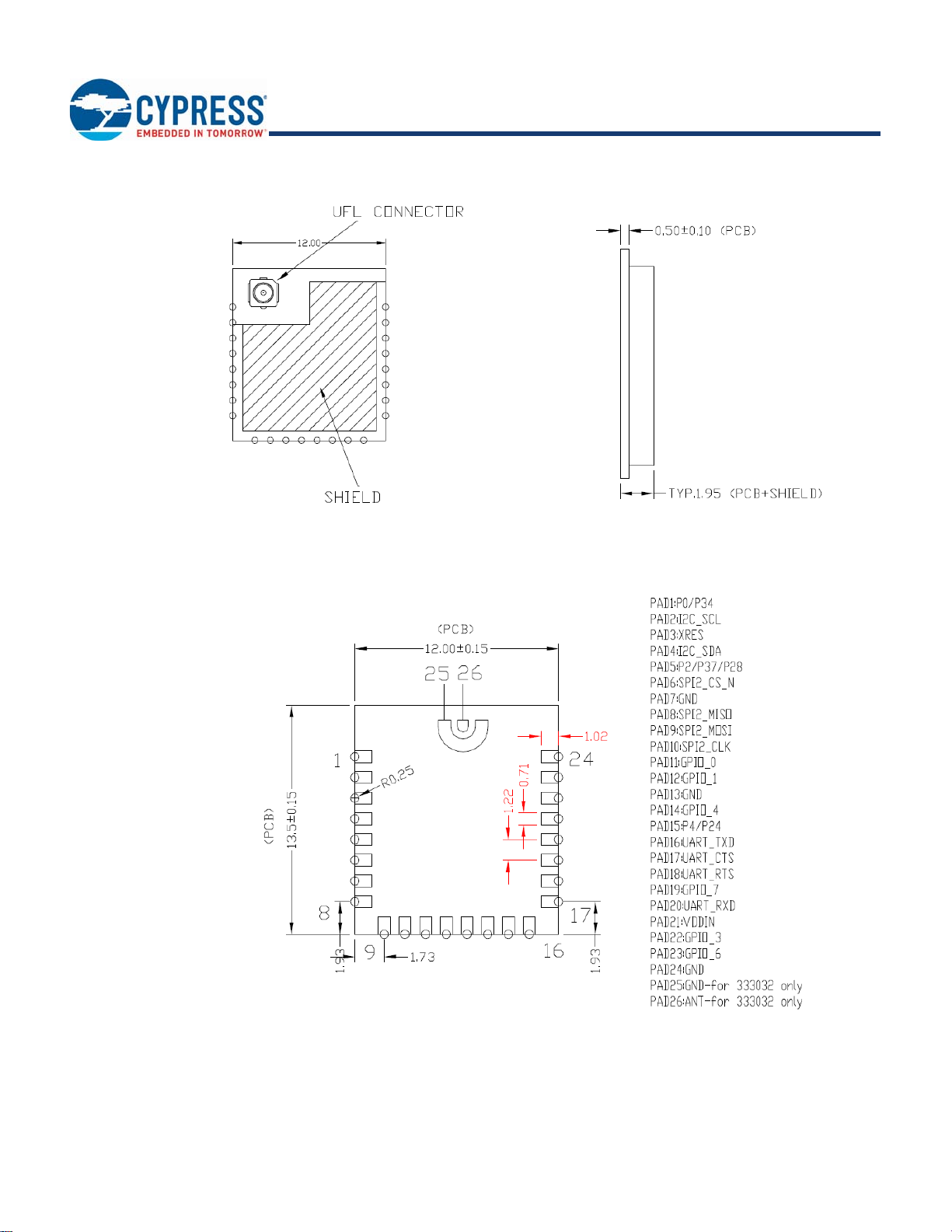
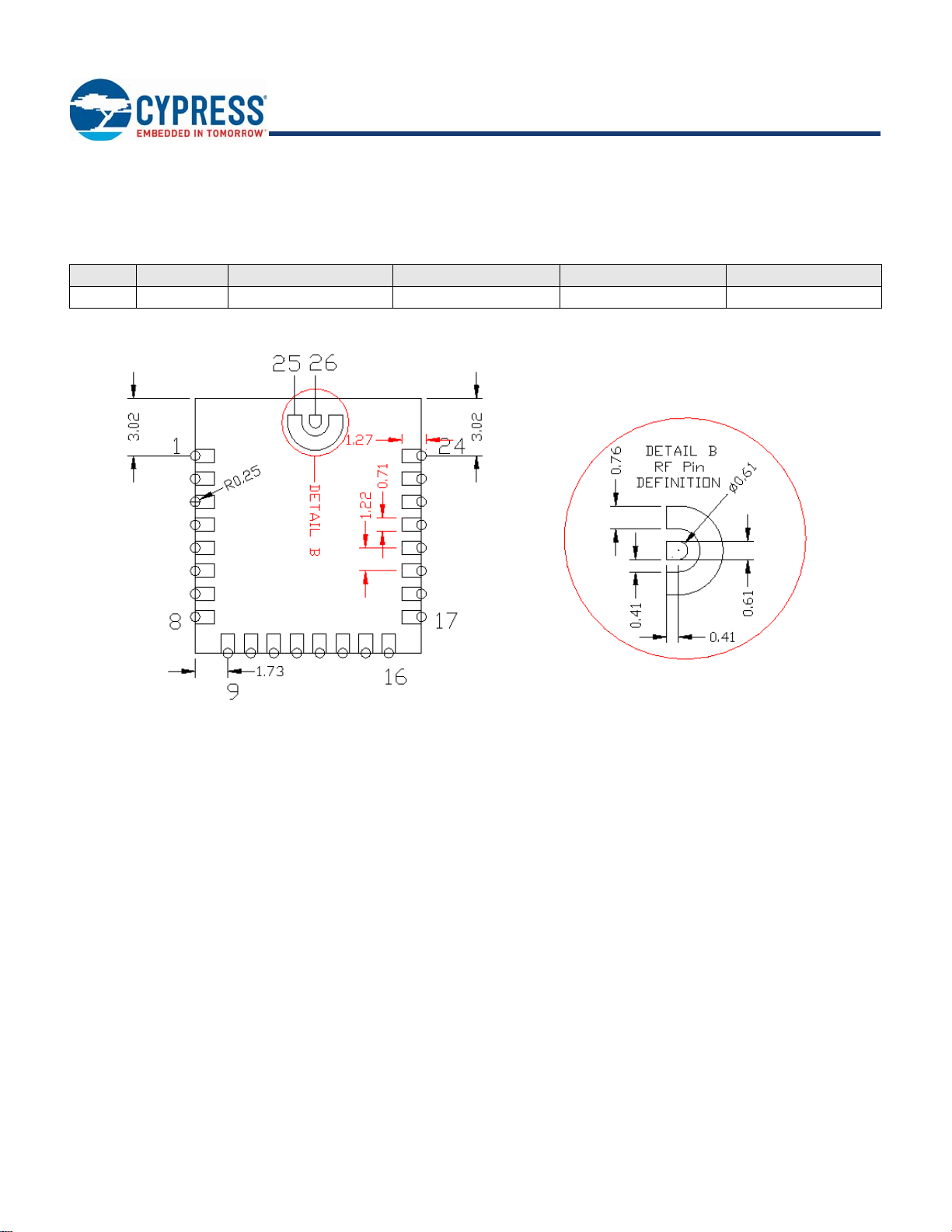
Figure 2. Module Mechanical Drawing
Bottom View
Side View
Top View (Seen from Top)
Notes
2. No metal should be located beneath or above the antenna area. Only bare PCB material should be located beneath the antenna area. For more information on
recommended host PCB layout, see “Recommended Host PCB Layout” on page 7.
3. The CYBT-3330xx-02 includes castellated pad connections, denoted as the circular openings at the pad location above.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 5 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Pad Connection Interface
As shown in the bottom view of Figure 2 on page 5, the CYBT-3330xx-02 connects to the host board via solder pads on the backside
of the module. Tab l e 2 and Figure 3 detail the solder pad length, width, and pitch dimensions of the CYBT-3330xx-02 module.
Table 2. Connection Description
Name Connections Connection Type Pad Length Dimension Pad Width Dimension Pad Pitch
SP 26 Solder Pads 1.02 mm 0.71 mm 1.22 mm
Figure 3. Solder Pad Dimensions (Seen from Bottom
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 6 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Recommended Host PCB Layout
Top View (Seen on Host PCB)
Top View (Seen on Host PCB)
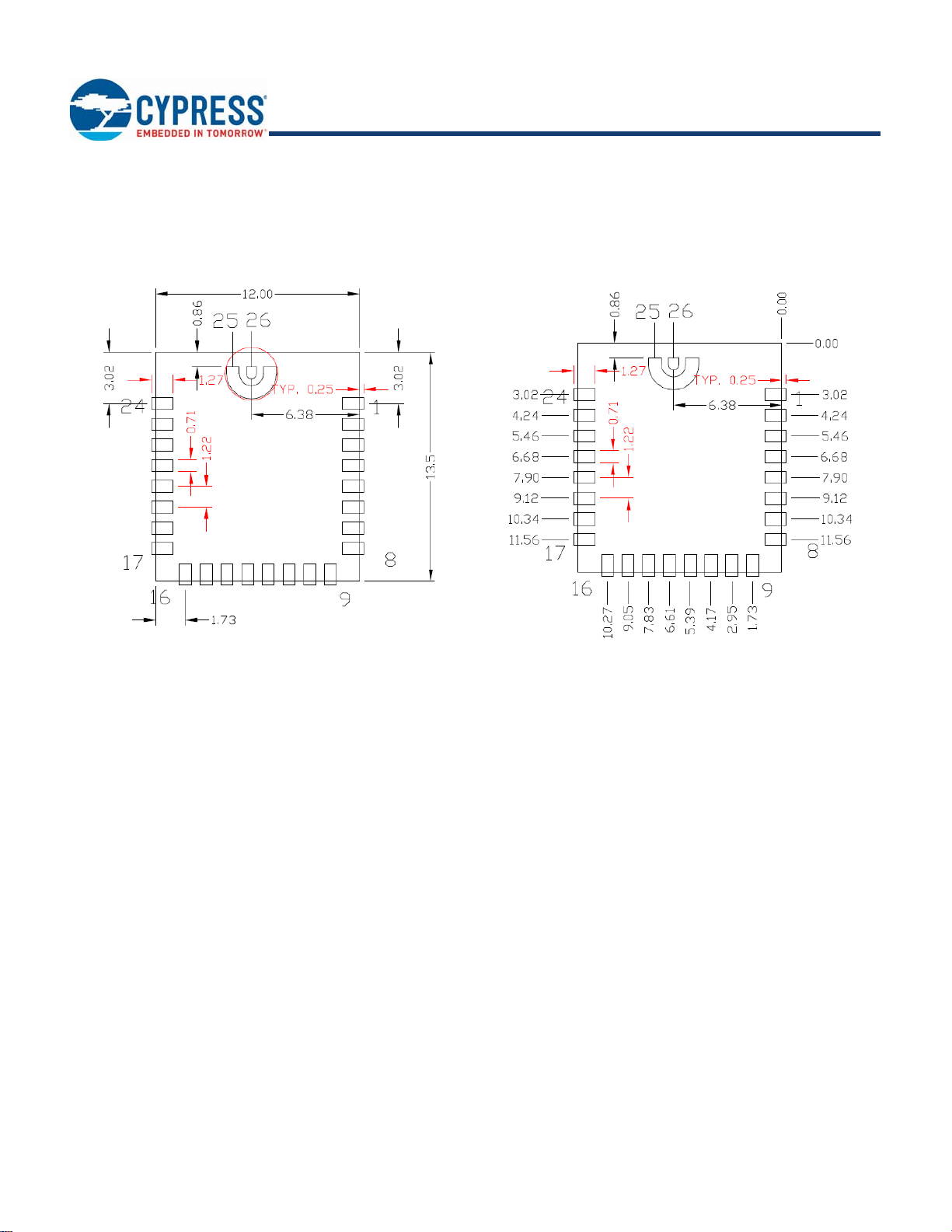
Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, and Tabl e 3 provide details that can be used for the recommended host PCB layout pattern for the
CYBT-3330xx-02. Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise noted. Pad length of 1.27 mm (0.635 mm from center of the pad
on either side) shown in Figure 6 is the minimum recommended host pad length. The host PCB layout pattern can be completed using
either Figure 4, Figure 5, or Figure 6. It is not necessary to use all figures to complete the host PCB layout pattern.
Figure 4. CYBT-3330xx-02 Host Layout (Dimensioned) Figure 5. CYBT-3330xx-02 Host Layout (Relative to Origin)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 7 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
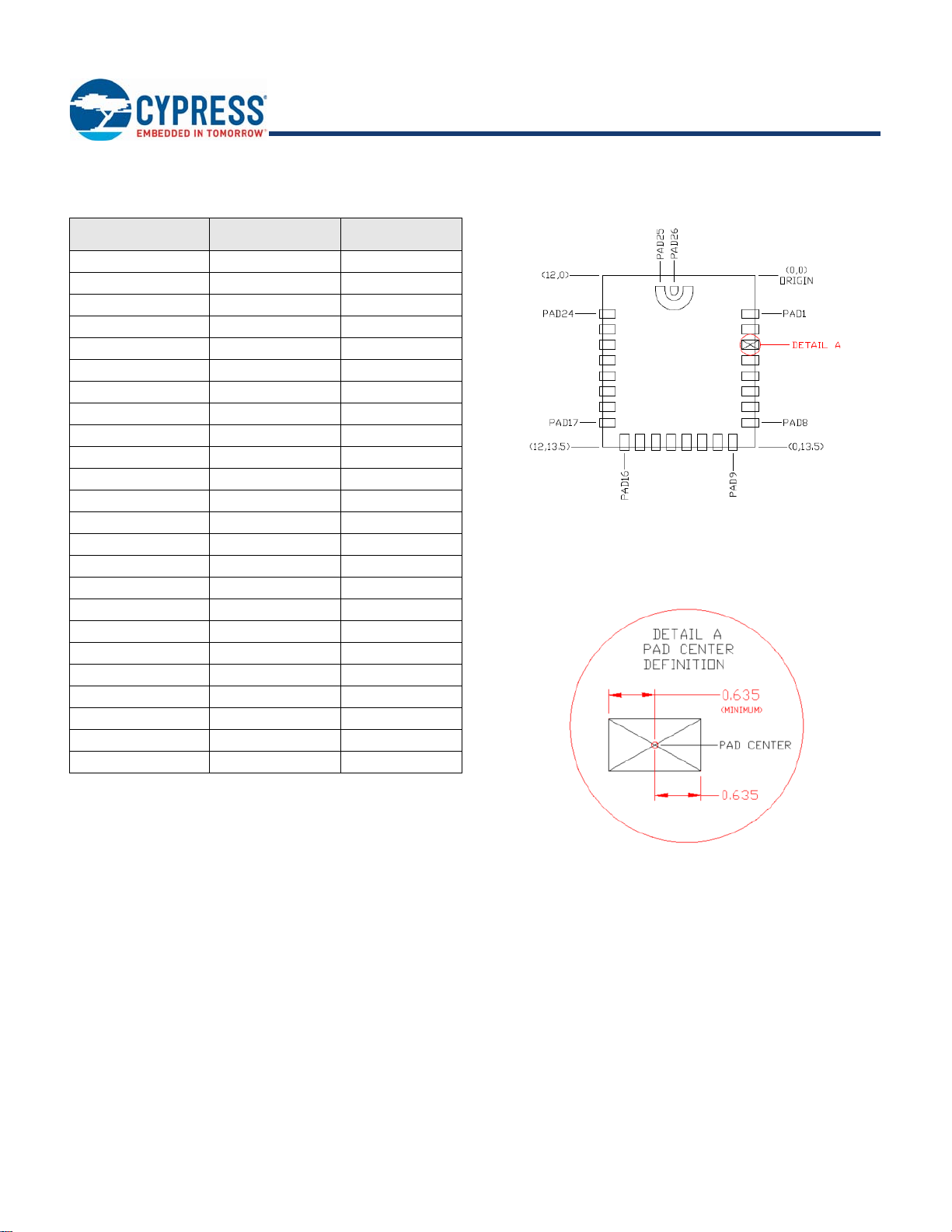
Ta bl e 3 provides the center location for each solder pad on the CYBT-3330xx-02. All dimensions are referenced to the center of the
Top View (Seen on Host PCB)
solder pad. Refer to Figure 6 for the location of each module solder pad.
Table 3. Module Solder Pad Location Figure 6. Solder Pad Reference Location
Solder Pad
(Center of Pad)
1 (0.38, 3.02) (14.96, 118.90)
2 (0.38, 4.24) (14.96, 166.93)
3 (0.38, 5.46) (14.96, 214.96)
4 (0.38, 6.68) (14.96, 262.99)
5 (0.38, 7.90) (14.96, 311.02)
6 (0.38, 9.12) (14.96, 359.05)
7 (0.38, 10.34) (14.96, 407.09)
8 (0.38, 11.56) (14.96, 455.12)
9 (1.73, 13.09) (68.11, 515.35)
10 (2.95, 13.09) (116.14, 515.35)
11 (4.17, 13.09) (164.17, 515.35)
12 (5.39, 13.09) (212.20, 515.35)
13 (6.61, 13.09) (260.24, 515.35)
14 (7.83, 13.09) (308.27, 515.35)
15 (9.05, 13.09) (356.30, 515.35)
16 (10.27, 13.09) (404.33, 515.35)
17 (11.62, 11.56) (457.48, 455.12)
18 (11.62, 10.34) (457.48, 407.09)
19 (11.62, 9.12) (457.48, 359.05)
20 (11.62, 7.90) (457.48, 311.02)
21 (11.62, 6.68) (457.48, 262.99)
22 (11.62, 5.46) (457.48, 214.96)
23 (11.62, 4.24) (457.48, 166.93)
24 (11.62, 3.02) (457.48, 118.90)
Location (X,Y) from
Orign (mm)
Dimension from
Orign (mils)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 8 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Module Connections
Note
4. The CYBT-3330xx-02 contains a single SPI (SPI1) peripheral supporting both master or slave configurations. SPI2 is used for on-module serial memory interface.
5. In Master mode, any available GPIO can be configured as SPI1_CS. This function is not explicitly shown in the table above.
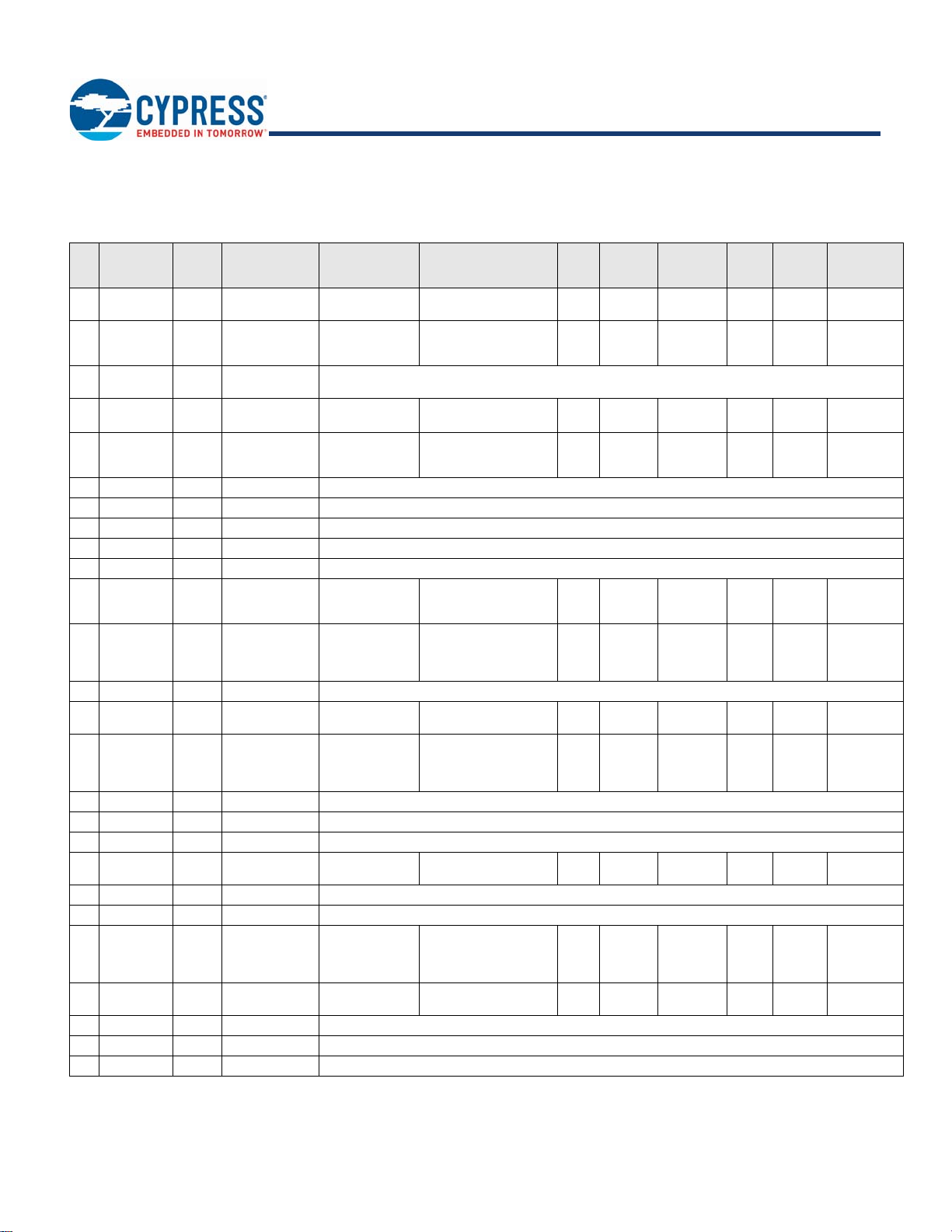
Ta bl e 4 details the solder pad connection definitions and available functions for the pad connections for the CYBT-3330xx-02 module.
Ta bl e 4 lists the CYBT-3330xx-02 solder pads, the silicon device pin, and denotes what functions are available for each solder pad.
Table 4. CYBT-3330xx-02 Solder Pad Connection Definitions
Pad Name
Pad
1P0/P34 C8
2 I2C_SCL A8
3XRES
4 I2C_SDA C7
5 P2/P37/P28 B7
6 SPI2_CS_N D7 N/A No Connect (Used for on-module memory SPI interface for CYBT-3330xx-02)
7 GND GND GND Ground
8 SPI2_MISO D8 N/A No Connect (Used for on-module memory SPI interface for CYBT-3330xx-02)
9 SPI2_MOSI E8 N/A No Connect (Used for on-module memory SPI interface for CYBT-3330xx-02)
10 SPI2_CLK E7 N/A No Connect (Used for on-module memory SPI interface for CYBT-3330xx-02)
11 GPI O_0 F8
12 GPIO_1 F7
13 GND GND GND Ground
14 GPIO_4 D6
15 P4/P24 G8
16 UART_TXD F4 BT_UART_TXD HCI UART Transmit Data
17 UART_CTS G4 BT_UART_CTS HCI UART Clear To Send Input
18 UART_RTS F3 BT_UART_RTS HCI UART Request To Send Output
19 GPIO_7 C6
20 UART_RXD F5 BT_UART_RXD HCI UART Receive Data
21 VDDIN G1 VDDIN VDDIN (2.3V ~ 3.6V)
22 GPIO_3 C5
23 GPIO_6 B6
24 GND GND GND Ground
25 GND GND GND Ground - Only functional for CYBT-333032-02; No Connect for CYBT-333047-02
26 ANT A2 RFOP RF Antenna Port Input/Output - Only functional for CYBT-333032-02; No Connect for CYBT-333047-02
Silicon
Pin
Name
RESET
_N
Silicon
Port-Pin Name
PCM_Sync/
I2S_WS/P0/P34
I2S_DO/
PCM_Out/P3/
P29/P35
RESET_N External Reset (Active Low)
PCM_IN/
I2S_DI/P12
PCM_CLK/
I2S_CLK/P2/
P28/P37
BT_GPIO_0/
P36/P38
BT_GPIO_1/
P25/P32
BT_GPIO_4/P6/
P31/LPO_IN
BT_CLK_REQ/
P4/P24
BT_GPIO_7/
P30
BT_GPIO_3/
P27/P33
BT_GPIO_6/
P11/P26
UART SPI
PUART_TX/P0
PUART_RX/P34
PUART_CTS/
P3 or P35
PUART_RX/P2
PUART_RX/P25
PUART_TX/P32
PUART_RTS/P6
PUART_TX/P31
PUART_RX/P4
PUART_TX/P24
PUART_RTS/
P30
PUART_RX/P33
SPI1_CS(slave)/P2
SPI1_MOSI(master)/P2
SPI1_MISO(slave)/P37
[4,5]
SPI1_MOSI/P0
(master/slave)
SPI1_CLK/P3
(master/slave)
SPI1_CLK/P36
SPI1_MOSI/P38
(master/slave)
SPI1_MISO/P25
(master/slave)
SPI1_CS/P32
(slave)
SPI1_CS/P6
(slave)
SPI1_MOSI/P4
(master/slave)
SPI1_CLK/P24
(master/slave)
SPI1_MOSI/P27
(master/slave)
SPI1_MOSI/P33
(slave)
SPI1_CS/P26
(slave)
I2C ADC COEX
IN29/P0
IN5/P34
SCL
IN4/P35
SDA/
IN10/29
P35
SDA IN23/P12
SCL/
IN11/P28
P37
IN2/P37
IN3/P36
IN1/P38
IN7/P32
IN8/P31 3
IN9/P30
IN6/P33
IN24/P11
3(GCI_SE
CI_OUT)
3(GCI_SE
CI_IN)
CLK/
XTAL
ACLK1
/P37
ACLK0
/P36
ACLK0
/P32
ACLK1
/P33
GPIO
3 PCM_Sync
3
(P3/P29
/P35)
3
(P12)
3
3
(DevWa
ke)
3
(HostWa
ke)
3
(CLK_R
EQ)
3
3
3
I2S_WS
I2S_DO
PCM_Out
PWM3 (P29)
PCM_IN
PWM2 (P28)
I2S_CLK
PCM_CLK
Ext LPO In
PWM1 (P27)
PWM0 (P26)
Other
I2S_DI
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 9 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Connections and Optional External Components
Power Connections (VDDIN)
The CYBT-3330xx-02 contains one power supply connection, VDDIN. VDDIN accepts a supply input range of 2.3 V to 3.6 V for
CYBT-3330xx-02. Ta b le 11 provides this specification. The maximum power supply ripple for this power connection is 100 mV, as
shown in Table 11.
It is not required to place any power supply decoupling or noise reduction circuitry on the host PCB. If desired, an external ferrite bead
between the supply and the module connection can be included, but is not necessary. If used, the ferrite bead should be positioned
as close as possible to the module pin connection and the recommended ferrite bead value is 330 Ω, 100 MHz.
Considerations and Optional Components for Brown Out (BO) Conditions
Power supply design must be completed to ensure that the CYBT-3330xx-02 module does not encounter a Brown Out condition,
which can lead to unexpected functionality, or module lock up. A Brown Out condition may be met if power supply provided to the
module during power up or reset is in the following range:
V
≤ VDDIN ≤ V
IL
Refer to Table 12 for the VIL and V
System design should ensure that the condition above is not encountered when power is removed from the system. In the event that
this cannot be guaranteed (that is, battery installation, high-value power capacitors with slow discharge), it is recommended that an
external voltage detection device be used to prevent the Brown Out voltage range from occurring during power removal. Refer to
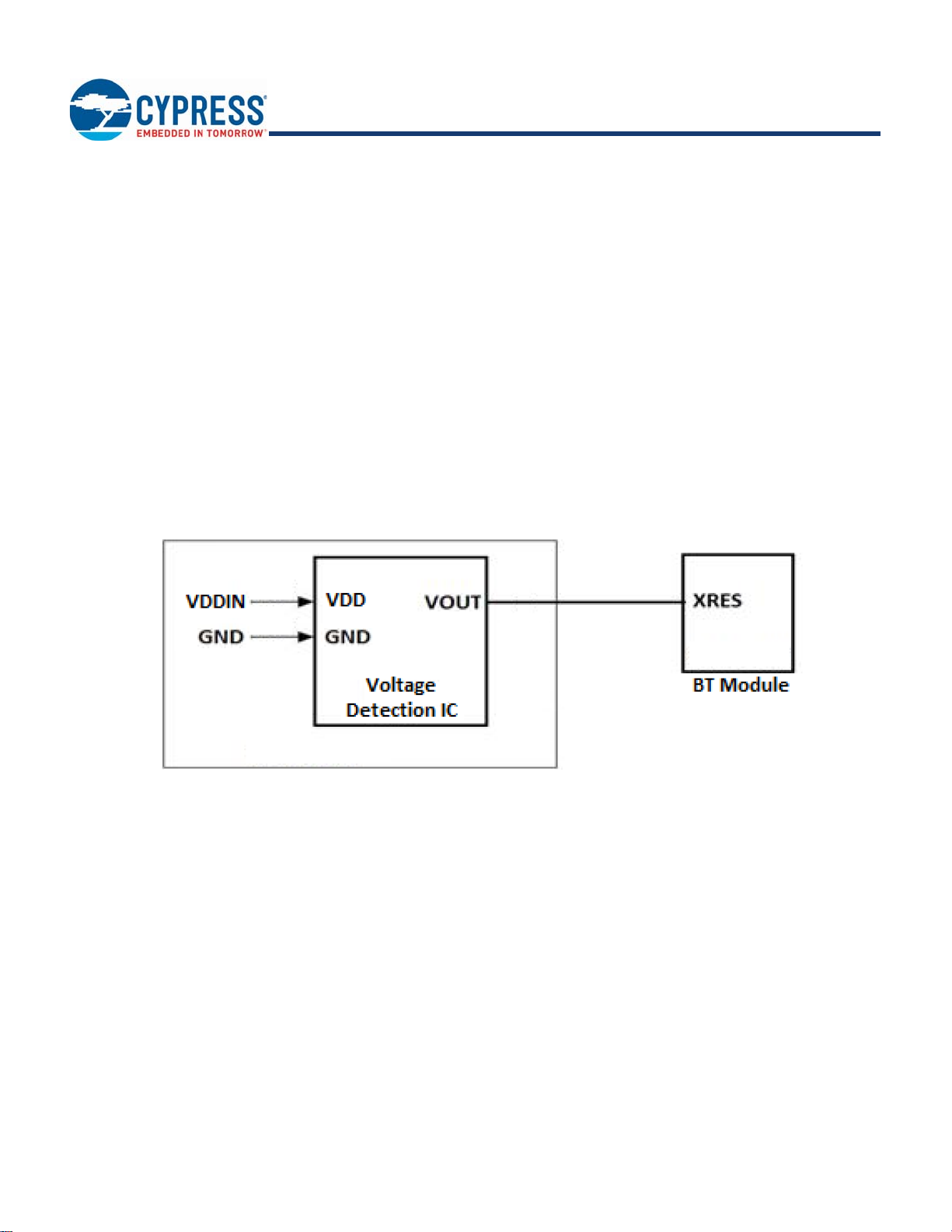
Figure 7 for the recommended circuit design when using an external voltage detection IC.
Figure 7. Reference Circuit Block Diagram for External Voltage Detection IC
specifications.
IH
IH
In the event that the module does encounter a Brown Out condition, and is operating erratically or not responsive, power cycling the
module will correct this issue and once reset, the module should operate correctly. Brown Out conditions can potentially cause issues
that cannot be corrected, but in general, a power-on-reset operation will correct a Brown Out condition.
External Reset (XRES)
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has an integrated power-on reset circuit, which completely resets all circuits to a known power-on state. This
action can also be evoked by an external reset signal, forcing it into a power-on reset state. The XRES signal is an active-low signal,
which is an input to the CYBT-3330xx-02 module (solder pad 3). The CYBT-3330xx-02 module
resistor on the XRES input
During power-on operation, the XRES connection to the CYBT-3330xx-02 is required to be held low 50 ms after the VDD power supply
input to the module is stable. This can be accomplished in the following ways:
n The host device should connect a GPIO to the XRES of the Cypress CYBT-3330xx-02 module and pull XRES low until VDD is
stable. XRES is recommended to be released 50 ms after VDDIN is stable.
n If the XRES connection of the CYBT-3330xx-02 module is not used in the application, a 10-µF capacitor may be connected to the
XRES solder pad of the CYBT-3330xx-02 in order to delay the XRES release. The capacitor value for this recommended implementation is approximate, and the exact value may differ depending on the VDDIN power supply ramp time of the system. The capacitor
value should result in an XRES release timing of 50 ms after VDDIN stability.
n The XRES release timing may be controlled by a external voltage detection IC. XRES should be released 50 ms after VDD is stable.
Refer to Figure 10 on page 17 for XRES operating and timing requirements during power-on events.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 10 of 52
does not require an external pull-up
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Multiple-Bonded GPIO Connections
The CYBT-3330xx-02 contains GPIOs, which are multiple-bonded at the silicon level. If any of these dual-bonded GPIOs are used,
only the functionality and features for one of these port pins may be used. The desired port pin should be configured in the WICED
Studio SDK. For details on the features and functions that each of these multiple-bonded GPIOs provide, refer to Table 4.
The list below details the multiple-bonded GPIOs available on the CYBT-3330xx-02 module:
n PAD 1 P0/34: I2S_WS_PCM_SYNC/P0/P34 (triple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 2 I2C_SCL: I2S_PCM_OUT/P3/P29/P35 (quadruple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 4 I2C_SDA: I2S_PCM_IN/P12 (dual bonded; only one of two is available)
n PAD 5 P2/P37/P28: I2S_PCM_CLK/P2/P28/P37 (quadruple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 11 GPIO_0: GPIO_0/P36/P38 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 12 GPIO_1: GPIO_1/P25/P32 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 14 GPIO_4: GPIO_4/LPO_IN/P6/P31 (quadruple bonded; only of four is available)
n PAD 15 P4/P24: BT_CLK_REQ/P4/P24 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 19 GPIO_7: GPIO_7/P30 (Dual bonded; only one of two is available)
n PAD 22 GPIO_3: GPIO_3/P27/P33 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 23 GPIO_6: GPIO_6/P11/P26 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 11 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
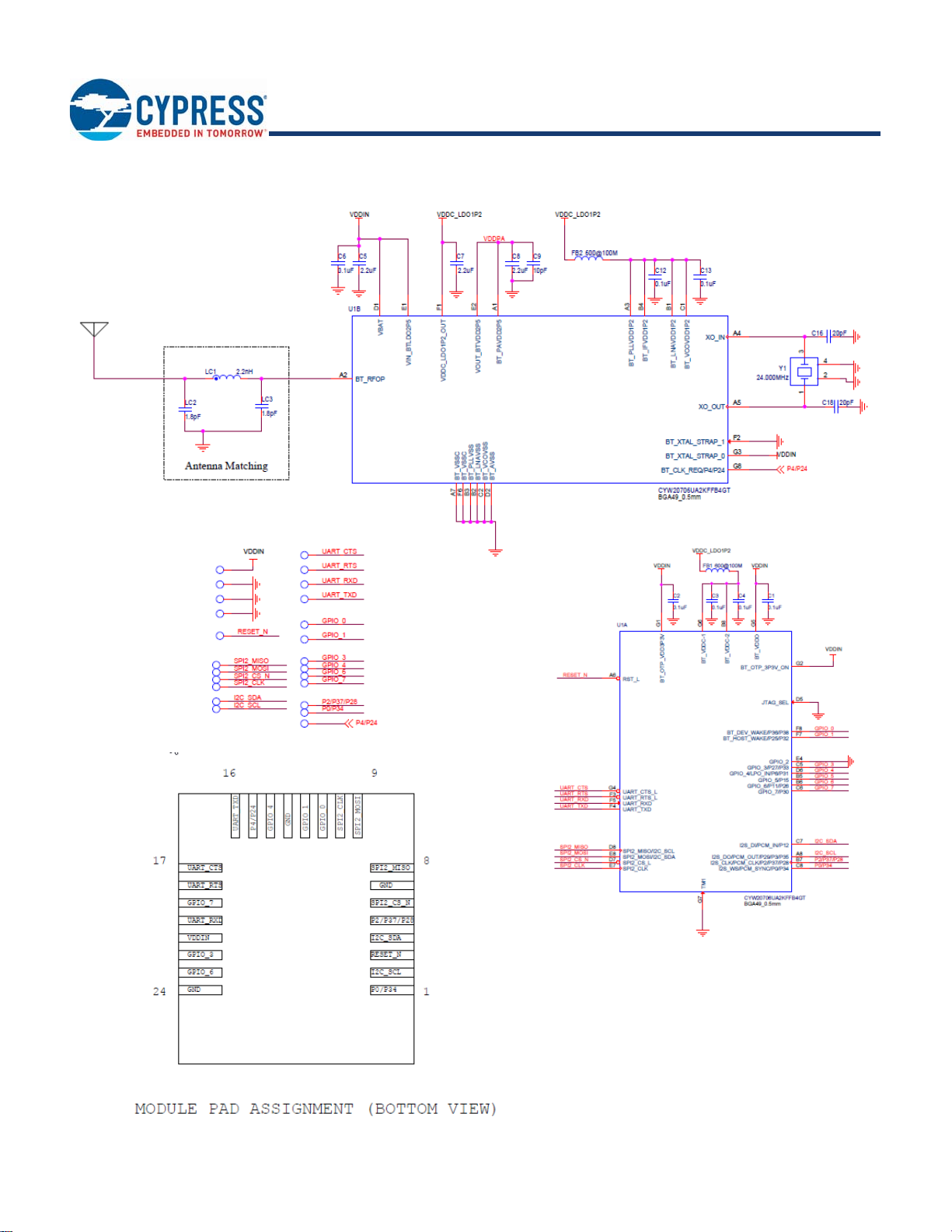
Figure 8 illustrates the CYBT-3330xx-02 schematic.
Figure 8. CYBT-3330xx-02 Schematic Diagram
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 12 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Critical Components List
Ta bl e 5 details the critical components used in the CYBT-3330xx-02 module.
Table 5. Critical Component List
Component Reference Designator Description
Silicon U1 49-pin FBGA BT/BLE Silicon Device - CYW20706
Silicon U2 8-pin TDF8N, 512K Serial Flash
Crystal Y1 24.000 MHz, 12PF
Qualified Antenna for
The CYBT-3330xx-02 module has been designed to work with a standard 2.2 dBi dipole antenna. Any antenna of equivalent or less
gain can be used without additional application and testing for FCC regulations. Ta b le 6 details the approved antennas for the
CYBT-3330xx-02 module for Bluetooth operation.
Table 6. Qualified Antennas
Manufacturer Part Number Gain
Antenova B4844-01 2.2 dBi
Pulse W1030 2.0 dBi
* Cable loss (between antenna and module) is 1 dB
CYBT-3330xx-02
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 13 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Functional Description
Bluetooth Baseband Core
The Bluetooth Baseband Core (BBC) implements all of the time-critical functions required for high-performance Bluetooth operation.
The BBC manages the buffering, segmentation, and routing of data for all connections. It also buffers data that passes through it,
handles data flow control, schedules SCO/ACL and TX/RX transactions, monitors Bluetooth slot usage, optimally segments and
packages data into baseband packets, manages connection status indicators, and composes and decodes HCI packets. In addition
to these functions, it independently handles HCI event types, and HCI command types. The following transmit and receive functions
are also implemented in the BBC hardware to increase reliability and security of the TX/RX data before sending over the air:
n Symbol timing recovery, data deframing, forward error correction (FEC), header error control (HEC), cyclic redundancy check (CRC),
data decryption, and data dewhitening in the receiver.
n Data framing, FEC generation, HEC generation, CRC generation, key generation, data encryption, and data whitening in the
transmitter.
Table 7. Bluetooth Features
Bluetooth 1.0 Bluetooth 1.2 Bluetooth 2.0
Basic Rate Interlaced Scans EDR 2 Mbps and 3 Mbp
SCO Adaptive Frequency Hopping –
Paging and Inquiry eSCO –
Page and Inquiry Scan – –
Sniff – –
Bluetooth 2.1 Bluetooth 3.0 Bluetooth 4.0
Secure Simple Pairing Unicast Connectionless Data Bluetooth Low Energy
Enhanced Inquiry Response Enhanced Power Control –
Sniff Subrating eSCO –
Bluetooth 4.1 Bluetooth 4.2
Low Duty Cycle Advertising Data Packet Length Extension
Dual Mode LE Secure Connection
LE Link Layer Topology Link Layer Privacy
Link Control Layer
The link control layer is part of the Bluetooth link control functions that are implemented in dedicated logic in the link control unit (LCU).
This layer consists of the command controller that takes commands from the software, and other controllers that are activated or
configured by the command controller, to perform the link control tasks. Each task is performed in a different state in the Bluetooth
Link Controller.
n States:
p Standby
p Connection
p Page
p Page Scan
p Inquiry
p Inquiry Scan
p Sniff
p Advertising
p Scanning
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 14 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Test Mode Support
The CYBT-3330xx-02 fully supports Bluetooth Test mode as described in
Part I:1 of the Specification of the Bluetooth System Version
3.0. This includes the transmitter tests, normal and delayed loopback tests, and reduced hopping sequence.
In addition to the standard Bluetooth Test Mode, the CYBT-3330xx-02 also supports enhanced testing features to simplify RF
debugging and qualification and type-approval testing. These features include:
n Fixed frequency carrier wave (unmodulated) transmission
p Simplifies some type-approval measurements (Japan)
p Aids in transmitter performance analysis
n Fixed frequency constant receiver mode
p Receiver output directed to I/O pin
p Allows for direct BER measurements using standard RF test equipment
p Facilitates spurious emissions testing for receive mode
n Fixed frequency constant transmission
p 8-bit fixed pattern or PRBS-9
p Enables modulated signal measurements with standard RF test equipment.
Frequency Hopping Generator
The frequency hopping sequence generator selects the correct hopping channel number based on the link controller state, Bluetooth
clock, and device address.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 15 of 52
PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Microcontroller Unit
The microprocessor unit in CYBT-3330xx-02 runs software from the link control (LC) layer up to the host controller interface (HCI).
The microprocessor is based on the Cortex-M3 32-bit RISC processor with embedded ICE-RT debug and JTAG interface units. The
microprocessor also includes 848 KB of ROM memory for program storage and boot ROM, 352 KB of RAM for data scratch-pad, and
patch RAM code.
The internal boot ROM provides flexibility during power-on reset to enable the same device to be used in various configurations. At
power-up, the lower layer protocol stack is executed from the internal ROM.
External patches can be applied to the ROM-based firmware to provide flexibility for bug fixes and features additions. These patches
can be downloaded using external NVRAM. The device can also support the integration of user applications and profiles using an
external serial flash memory.
NVRAM Configuration Data and Storage
NVRAM contains configuration information about the customer application, including the following:
n Fractional-N information
n BD_ADDR
n UART baud rate
n SDP service record
n File system information used for code, code patches, or data. The CYBT-3330xx-02 uses SPI Serial Flash for NVRAM storage.
One-Time Programmable Memory
The microprocessor unit in CYBT-3330xx-02 includes 2 KB of one-time programmable (OTP) memory allow manufacturing customization and to avoid the need for an on-board NVRAM. If customization is not required, then the OTP does not need to be programmed.
Whether the OTP is programmed or not, to save power it is disabled when the boot process is complete. The OTP is designed to
store a minimal amount of information. Aside from OTP data, most user configuration information will be downloaded to RAM after
the CYBT-3330xx-02 boots and is ready for host transport communication.
The OTP contents are limited to:
n Parameters required prior to downloading the user configuration to RAM.
n Parameters unique to each part and each customer (for example, the Bluetooth device address and/or the software license key).
n VDDIN for the module must be kept to 3.0 V to 3.6 V power supply range if OTP is used in the application.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 16 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
External Reset (XRES)
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has an integrated power-on reset circuit that completely resets all circuits to a known power-on state. An external
active low reset signal, XRES, can be used to put the CYBT-3330xx-02 in the reset state. The XRES pin has an internal pull-up resistor
and, in most applications, it does not require anything to be connected to it.
Figure 9. External Reset Internal Timing
External Reset (XRES) Recommended External Components and Proper Operation
During a power-on event, the XRES line of the CYBT-3330xx-02 is required to be held low 50 ms after the VDD power supply input
to the module is stable. Refer to Figure 10 for the Power-On XRES timing operation. This power-on operation can be accomplished
in the following ways:
n A host device should connect a GPIO to the XRES of the Cypress CYBT-3330xx-02 module and pull XRES low until VDD is stable.
XRES can be released after VDD is stable.
n If the XRES connection of the CYBT-3330xx-02 module is not used in the application, a 10-µF capacitor may be connected to the
XRES solder pad of the CYBT-3330xx-02.
n The XRES release timing can also be controlled via an external voltage detection circuit.
Figure 10. Power-On External Reset (XRES) Operation
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 17 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Integrated Radio Transceiver
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has an integrated radio transceiver that has been optimized for use in 2.4-GHz Bluetooth wireless systems. It
has been designed to provide low-power, low-cost, robust communications for applications operating in the globally available 2.4-GHz
unlicensed ISM band. The CYBT-3330xx-02 is fully compliant with the Bluetooth Radio Specification and enhanced data rate (EDR)
specification and meets or exceeds the requirements to provide the highest communication link quality of service.
Transmitter Path
The CYBT-3330xx-02 a fully integrated zero-IF transmitter. The baseband transmit data is GFSK-modulated in the modem block and
upconverted to the 2.4-GHz ISM band in the transmitter path. The transmitter path consists of signal filtering, I/Q upconversion, output
power amplifier, and RF filtering. The transmitter path also incorporates π/4-DQPSK for 2 Mbps and 8-DPSK for 3 Mbps to support
EDR. The transmitter section is compatible with the BLE specification. The transmitter PA bias can also be adjusted to provide
Bluetooth class 1 or class 2 operation.
Digital Modulator
The digital modulator performs the data modulation and filtering required for the GFSK,
digital modulator minimizes any frequency drift or anomalies in the modulation characteristics of the transmitted signal and is much
more stable than direct VCO modulation schemes.
Digital Demodulator and Bit Synchronizer
The digital demodulator and bit synchronizer take the low-IF received signal and perform an optimal frequency tracking and bit
synchronization algorithm.
Power Amplifier
The fully integrated PA supports Class 1 or Class 2 output using a highly linearized, temperature-compensated design. This provides
greater flexibility in front-end matching and filtering. Due to the linear nature of the PA combined with some integrated filtering, external
filtering is required to meet the Bluetooth and regulatory harmonic and spurious requirements. For integrated mobile handset applications in which Bluetooth is integrated next to the cellular radio, external filtering can be applied to achieve near thermal noise levels
for spurious and radiated noise emissions. The transmitter features a sophisticated on-chip transmit signal strength indicator (TSSI)
block to keep the absolute output power variation within a tight range across process, voltage, and temperature.
π4-DQPSK, and 8-DPSK signal. The fully
Receiver Path
The receiver path uses a low-IF scheme to downconvert the received signal for demodulation in the digital demodulator and bit
synchronizer. The receiver path provides a high degree of linearity, an extended dynamic range, and high-order on-chip channel
filtering to ensure reliable operation in the noisy 2.4 GHz ISM band. The front-end topology, with built-in out-of-band attenuation,
enables the CYBT-3330xx-02 to be used in most applications with minimal off-chip filtering. For integrated handset operation, in which
the Bluetooth function is integrated close to the cellular transmitter, external filtering is required to eliminate the desensitization of the
receiver by the cellular transmit signal.
Digital Demodulator and Bit Synchronizer
The digital demodulator and bit synchronizer take the low-IF received signal and perform an optimal frequency tracking and bit
synchronization algorithm.
Receiver Signal Strength Indicator
The radio portion of the CYBT-3330xx-02 provides a receiver signal strength indicator (RSSI) to the baseband. This enables the
controller to take part in a Bluetooth power-controlled link by providing a metric of its own receiver signal strength to determine whether
the transmitter should increase or decrease its output power.
Local Oscillator Generation
The local oscillator (LO) provides fast frequency hopping (1600 hops/second) across the 79 maximum available channels. The LO
generation sub-block employs an architecture for high immunity to LO pulling during PA operation. The CYBT-3330xx-02 uses an
internal loop filter.
Calibration
The CYBT-3330xx-02 radio transceiver features an automated calibration scheme that is fully self-contained in the radio. No user
interaction is required during normal operation or during manufacturing to provide optimal performance. Calibration tunes the performance of all the major blocks within the radio to within 2% of optimal conditions, including gain and phase characteristics of filters,
matching between key components, and key gain blocks. This takes into account process variation and temperature variation.
Calibration occurs transparently during normal operation during the settling time of the hops, and calibrates for temperature variations
as the device cools and heats during normal operation in its environment.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 18 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Internal LDO
The microprocessor in CYBT-3330xx-02 uses two LDOs – one for 1.2 V and the other for 2.5 V. The 1.2-V LDO provides power to
the baseband and radio and the 2.5-V LDO powers the PA.
Collaborative Coexistence
The CYBT-3330xx-02 provides extensions and collaborative coexistence to the standard Bluetooth AFH for direct communication with
WLAN devices. Collaborative coexistence enables WLAN and Bluetooth to operate simultaneously in a single device. The device
supports industry-standard coexistence signaling, including 802.15.2, and supports Cypress and third-party WLAN solutions.
Global Coexistence Interface
The CYBT-3330xx-02 supports the proprietary Cypress Global Coexistence Interface (GCI) which is a 2-wire interface.
The following key features are associated with the interface:
n Enhanced coexistence data can be exchanged over GCI_SECI_IN and GCI_SECI_OUT a two-wire interface, one serial input
(GCI_SECI_IN), and one serial output (GCI_SECI_OUT). The pad configuration registers must be programmed to choose the digital
I/O pins that serve the GCI_SECI_IN and GCI_SECI_OUT function.
n It supports generic UART communication between WLAN and Bluetooth devices.
n To conserve power, it is disabled when inactive.
n It supports automatic resynchronization upon waking from sleep mode.
n It supports a baud rate of up to 4 Mbps.
SECI I/O
The microprocessor in CYBT-3330xx-02 has dedicated GCI_SECI_IN (PAD 23/GPIO_6) and GCI_SECI_OUT (PAD19/GPIO_7) pins.
Refer to Table 4, which detail the module solder pad number used for SECI I/O.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 19 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Peripheral and Communication Interfaces
I2C Communication Interface
The CYBT-3330xx-02 provides a 2-pin master I2C interface, which can be used to retrieve configuration information from an external
EEPROM or to communicate with peripherals such as track-ball or touch-pad modules, and motion tracking ICs used in mouse
devices. This interface is compatible with I2C slave devices. I2C does not support multimaster capability or flexible wait-state insertion
by either master or slave devices.
The following transfer clock rates are supported by the I
n 100 kHz
n 400 kHz
n 800 kHz (not a standard I
n 1 MHz (Compatibility with high-speed I
2
C-compatible speed.)
2
C-compatible devices is not guaranteed.)
2
C:
The following transfer types are supported by the I
n Read (Up to 127 bytes can be read)
n Write (Up to 127 bytes can be written)
n Read-then-Write (Up to 127 bytes can be read and up to 127 bytes can be written)
n Write-then-Read (Up to127 bytes can be written and up to 127 bytes can be read)
2
C:
Hardware controls the transfers, requiring minimal firmware setup and supervision.
The clock pad (I2C_SCL) and data pad 2 (I2C_SDA) are both open-drain I/O pins. Pull-up resistors, external to the CYBT-3330xx-02,
are required on both the SCL and SDA pad for proper operation.
HCI UART Interface
The UART physical interface is a standard, 4-wire interface (RX, TX, RTS, and CTS) with adjustable baud rates from 38400 bps to
4 Mbps. During initial boot, UART speeds may be limited to 750 kbps. The baud rate may be selected via a vendor-specific UART
HCI command. The CYBT-3330xx-02 has a 1040-byte receive FIFO and a 1040-byte transmit FIFO to support enhanced data rates.
The interface supports the Bluetooth UART HCI (H4) specification. The default baud rate for H4 is 115.2 kbaud.
The UART clock default setting is 24 MHz, and can be configured to run as high as 48 MHz to support up to 4 Mbps. The baud rate
of the CYBT-3330xx-02UART is controlled by two values. The first is a UART clock divisor (set in the DLBR register) that divides the
UART clock by an integer multiple of 16. The second is a baud rate adjustment (set in the DHBR register) that is used to specify a
number of UART clock cycles to stuff in the first or second half of each bit time. Up to eight UART cycles can be inserted into the first
half of each bit time, and up to eight UART clock cycles can be inserted into the end of each bit time.
Ta bl e 8 contains example values to generate common baud rates with a 24 MHz UART clock.
Table 8. Common Baud Rate Examples, 24 MHz Clock
Baud Rate (bps)
4M 0xFF 0xF4 High rate 0.00
3M 0xFF 0xF8 High rate 0.00
2M 0XFF 0XF4 High rate 0.00
1M 0X44 0XFF Normal 0.00
921600 0x05 0x05 Normal 0.16
460800 0x02 0x02 Normal 0.16
230400 0x04 0x04 Normal 0.16
115200 0x00 0x00 Normal 0.16
57600 0x00 0x00 Normal 0.16
38400 0x01 0x00 Normal 0.00
Baud Rate Adjustment
High Nibble Low Nibble
Mode Error (%)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 20 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Normally, the UART baud rate is set by a configuration record downloaded after reset. Support for changing the baud rate during
normal HCI UART operation is included through a vendor-specific command that allows the host to adjust the contents of the baud
rate registers.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 UART operates correctly with the host UART as long as the combined baud rate error of the two devices is
within ±2%.
Peripheral UART Interface
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has a second UART that may be used to interface to other peripherals. This peripheral UART is accessed
through the optional I/O ports, which can be configured individually and separately for each signal as shown in Ta b le 9
Table 9. CYBT-3330xx-02 Peripheral UART
Signal Name PUART_TX PUART_RX PUART_CTS_N PUART_RTS_N
PUART Port Configuration #1 P0 P2 P3 P6
PUART Port Configuration #2 P31 P33 P35 P30
Serial Peripheral Interface
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has two independent SPI interfaces. One is a master-only interface (SPI2) and the other (SPI1) can be either
a master or a slave. Each interface has a 64-byte transmit buffer and a 64-byte receive buffer. To support more flexibility for user
applications, the CYBT-3330xx-02 has optional I/O ports that can be configured individually and separately for each functional pin.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 acts as an SPI master device that supports 3.3 V SPI slaves. In master mode, refer to Tabl e 4 to identify the
solder pads avialable for SPI1_MISO, SPI1_MOSI, and SPI1_CLK connections. NOTE: In master mode, any available GPIO can be
assigned as SPI1_CS.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 can also act as an SPI slave device that supports a 3.3 V SPI master. For SPI1 slave mode, refer to Table 4 to
identify the solder pads available for SPI1 slave mode connections.
SPI voltage depends on V
; therefore, V
DDIN
should be set to 3.3 V for SPI communication.
DDIN
PCM Interface
The CYBT-3330xx-02 includes a PCM interface that shares pins with the I2S interface. The PCM Interface on the CYBT-3330xx-02
can connect to linear PCM codec devices in master or slave mode. In master mode, the CYBT-3330xx-02 generates the PCM_CLK
and PCM_SYNC signals. In slave mode, these signals are provided by another master on the PCM interface and are inputs to the
CYBT-3330xx-02.
Slot Mapping
The CYBT-3330xx-02 supports up to three simultaneous full-duplex SCO or eSCO channels through the PCM interface. These three
channels are time-multiplexed onto the single PCM interface by using a time-slotting scheme where the 8 kHz or 16 kHz audio sample
interval is divided into as many as 16 slots. The number of slots is dependent on the selected interface rate (128 kHz, 512 kHz, or
1024 kHz). The corresponding number of slots for these interface rate is 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16, respectively. Transmit and receive PCM
data from an SCO channel is always mapped to the same slot. The PCM data output driver tristates its output on unused slots to allow
other devices to share the same PCM interface signals. The data output driver tristates its output after the falling edge of the PCM
clock during the last bit of the slot.
Frame Synchronization
The CYBT-3330xx-02 supports both short- and long-frame synchronization in both master and slave modes. In short-frame synchronization mode, the frame synchronization signal is an active-high pulse at the audio frame rate that is a single-bit period in width and
is synchronized to the rising edge of the bit clock. The PCM slave looks for a high on the falling edge of the bit clock and expects the
first bit of the first slot to start at the next rising edge of the clock. In long-frame synchronization mode, the frame synchronization
signal is again an active-high pulse at the audio frame rate; however, the duration is three bit periods and the pulse starts coincident
with the first bit of the first slot.
Data Formatting
The CYBT-3330xx-02 may be configured to generate and accept several different data formats. For conventional narrowband speech
mode, the CYBT-3330xx-02 uses 13 of the 16 bits in each PCM frame. The location and order of these 13 bits can be configured to
support various data formats on the PCM interface. The remaining three bits are ignored on the input and may be filled with 0s, 1s, a
sign bit, or a programmed value on the output. The default format is 13-bit 2’s complement data, left justified, and clocked MSB first.
Clock Frequencies
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has an integrated 24 MHz crystal on the module. There is no need to add an additional crystal oscillator.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 21 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
GPIO Port
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has a maximum of 11 GPIOs. All GPIOs support programmable pull-ups and are capable of driving up to 8 mA
at 3.3 V or 4 mA at 1.8 V, except chips P26, P27, P28, and P29, which are capable of driving up to 16 mA at 3.3 V.
The following GPIOs are available on the module pads:
n PAD 1 P0/34: I2S_WS_PCM_SYNC/P0/P34 (triple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 2 I2C_SCL: I2S_PCM_OUT/P3/P29/P35 (quadruple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 4 I2C_SDA: I2S_PCM_IN/P12 (dual bonded; only one of two is available)
n PAD 5 P2/P37/P28: I2S_PCM_CLK/P2/P28/P37 (quadruple bonded; only one of four is available)
n PAD 11 GPIO_0: GPIO_0/P36/P38 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 12 GPIO_1: GPIO_1/P25/P32 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 14 GPIO_4: GPIO_4/LPO_IN/P6/P31 (quadruple bonded; only of four is available)
n PAD 15 P4/P24: BT_CLK_REQ/P4/P24 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 19 GPIO_7: GPIO_7/P30 (Dual bonded; only one of two is available)
n PAD 22 GPIO_3: GPIO_3/P27/P33 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
n PAD 23 GPIO_6: GPIO_6/P11/P26 (triple bonded; only one of three is available)
Refer to Table 4 to determine what GPIOs can be configured as ADC Inputs.
NOTE: Any available GPIO can be used for SPI1_CS when in master mode.
Port 26–Port 29 in PAD 23/PAD 22/PAD 5/PAD 2
P[26:29] in PAD 23/PAD 22/PAD 5/PAD 2 consists of four pins. All pins are capable of sinking up to 16 mA for LEDs. These pins also
have PWM functionality, which can be used for LED dimming.
For a description of the capabilities of all GPIOs, see Ta b le 4.
PWM
The CYBT-3330xx-02 has four PWMs (PWM0-3). The PWM module consists of the following:
n The following GPIOs can be mapped as PWMs, module pad shown in [ ]:
p PWM0: P26 on P11/P26 [Pad 23]
p PWM1: P27 on P33/P27 [Pad 22]
p PWM2: P28 on P2/P37/P28 [Pad 5]
p PWM3: P29 on P3/P35/P29/I2C_SCL [Pad 2]
n PWM1-4: Each of the four PWM channels contains the following registers:
p 10-bit initial value register (read/write)
p 10-bit toggle register (read/write)
p 10-bit PWM counter value register (read)
n PWM configuration register shared among PWM1-4 (read/write). This 12-bit register is used:
p To configure each PWM channel
p To select the clock of each PWM channel
p To change the phase of each PWM channel
Figure 11 shows the structure of one PWM.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 22 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Figure 11. PWM Block Diagram
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 23 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Power Management Unit
The Power Management Unit (PMU) provides power management features that can be invoked by software through power
management registers or packet-handling in the baseband core.
RF Power Management
The BBC generates power-down control signals for the transmit path, receive path, PLL, and power amplifier to the 2.4-GHz transceiver, which then processes the power-down functions accordingly.
Host Controller Power Management
Power is automatically managed by the firmware based on input device activity. As a power-saving task, the firmware controls the
disabling of the on-chip regulator when in deep sleep (HIDOFF) mode.
BBC Power Management
There are several low-power operations for the BBC:
n Physical layer packet handling turns RF on and off dynamically within packet TX and RX.
n Bluetooth-specified low-power connection mode. While in these low-power connection modes, the CYBT-3330xx-02 runs on the
Low Power Oscillator and wakes up after a predefined time period.
The CYBT-3330xx-02 automatically adjusts its power dissipation based on user activity. The following power modes are supported:
n Active mode
n Idle mode
n Sleep mode
n HIDOFF (Deep Sleep) mode
The CYBT-3330xx-02 transitions to the next lower state after a programmable period of user inactivity. Busy mode is immediately
entered when user activity resumes.
In HIDOFF (Deep Sleep) mode, the CYBT-3330xx-02 baseband and core are powered off by disabling power to LDOOUT. The VDDO
domain remains powered up and will turn the remainder of the chip on when it detects user events. This mode minimizes chip power
consumption and is intended for long periods of inactivity.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 24 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Electrical Characteristics
Note
6. Overall performance degrades beyond minimum and maximum supply voltages.The voltage range specified is determined by the minimum and maximum operating
voltage of the SPI Serial Flash included on the module.
Ta bl e 1 0 shows the maximum electrical rating for voltages referenced to VDDIN pad.
Table 10. Maximum Electrical Rating
Rating Symbol Val ue Unit
V
DDIN
Voltage on input or output pin – V
Operating ambient temperature range T
Storage temperature range T
– 3.795 V
opr
stg
SS – 0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
–30 to +85 °C
–40 to +85 °C
Ta bl e 11 shows the power supply characteristics for the range T
= 0 to 125 °C.
J
Table 11. Power Supply
Parameter Description Minimum
V
DDIN
V
DDIN_RIPPLE
Power Supply Input (CYBT-3330xx-02) 2.3 – 3.6 V
Maximum Power Supply Ripple for V
input voltage – – 100 mV
DDIN
[6]
Typical Maximum
[6]
Ta bl e 1 2 shows the specifications for the digital voltage levels.
Table 12. Digital Voltage Levels
Characteristics Symbol Min Ty p Max Unit
Input low voltage V
Input high voltage V
Output low voltage V
Output high voltage V
Input capacitance (V
domain) C
DDMEM
IL
IH
OL
OH
IN
––0.8V
2.0 – – V
––0.4V
V
– 0.4 – – V
DDIN
––0.4pF
Ta bl e 1 3 shows the current consumption measurements
Table 13. Bluetooth, BLE, BR and EDR Current Consumption
Parameter Description
Silicon or
Module
Parameter
Output
Power
Level/Class Typ
Unit
Bluetooth Classic (BR, EDR)
3DM5/3DH5 HCI control mode Silicon Class 1 37.1 mA
DM1/DH1 HCI control mode Silicon Class 1 32.2 mA
DM3/DH3 HCI control mode Silicon Class 1 38.2 mA
DM5/DH5 HCI control mode Silicon Class 1 38.5 mA
RX
1M_BR
TX
1M_BR
RX
23M_EDR
TX
23M_EDR
Peak receive (1 Mbps) current level when receiving
a basic rate packet (radio only)
Peak transmit (1 Mbps) current level when transmitting a basic rate packet (radio only)
Peak receive (EDR) current level when receiving a
2 or 3 Mbps rate packet (radio only)
Peak transmit (EDR) current level when transmitting a 2 or 3 Mbps rate packet (radio only)
Silicon Class 1 26.4 mA
Silicon 10 dBm 60.3 mA
Silicon Class 1 26.4 mA
Silicon 8 dBm 52.5 mA
Deep Sleep Deep Sleep (HIDOFF) current Module All 2.69 uA
Unit
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 25 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Table 13. Bluetooth, BLE, BR and EDR Current Consumption
Parameter Description
Silicon or
Module
Parameter
Output
Power
Level/Class
Typ
Unit
Bluetooth Classic (BR, EDR)
IDLE Module is idle, non-discoverable and
non-connectable
I
Scan
P
Scan
I
Scan+PScan
Inquiry Scan (1.28 seconds) Module Class 1 0.65 mA
Page scan (1.28 seconds) Module Class 1 0.65 mA
Inquiry scan + Page Scan (1.28 seconds) Module Class 1 1.2 mA
Module Class 1 0.11 mA
Connected Connected with no data transfer Module Class 1 2.6 mA
Connected + P
Connected + I
Scan
Scan
+ P
Connected with no data transfer + Page Scan (1.28
seconds)
Connected with no data transfer + Inquiry
Scan
Scan(1.28 seconds) + Page Scan (1.28 seconds)
Module Class 1 3.3 mA
Module Class 1 3.6 mA
Connected + SNIFF Connected with no data transfer + SNIFF (500 ms) Module Class 1 0.95 mA
Connected + SNIFF+ I
+ P
Scan
Connected with no data transfer + SNIFF (500 ms)
Scan
+ Inquiry Scan and Page Scan 1.28 seconds
Module Class 1 1.9 mA
TX_BR Data transfer @ 115200 baud rate Module Class 1 22 mA
TX+SNIFF_BR Data transfer @ 115200 baud rate + Sniff (500 ms) Module Class 1 5.5 mA
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
RX
TX
Peak
Peak RX current Module
Peak
Peak TX Current Module
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
42
54
56
28
28
28
mA
mA
Deep Sleep Deep Sleep (HIDOFF) current Module All 2.69 uA
Connection_1s
Connection_4s
Adv_640
Adv_30
Adv_1s
Connection - 1-second interval Module
Connection - 4-second interval Module
Advertisement (low duty cycle) - 640 ms Module
Advertisement (high duty cycle) - 30 ms Module
1-second non-connectable advertisement
(Beacon)
Module
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
-2.5dBm
+6.5 dBm
+9.0 dBm
970
980
1000
900
945
950
0.4
0.5
0.5
3.8
4.2
4.3
315
350
350
uA
uA
mA
mA
uA
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 26 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Chipset RF Specifications
Notes
7. Typical operating conditions are 1.22-V operating voltage and 25°C ambient temperature.
8. The receiver sensitivity is measured at BER of 0.1% on the device interface.
9. Meets this specification using front-end band pass filter.
All specifications in Ta bl e 1 4 are for industrial temperatures and are single-ended. Unused inputs are left open.
Table 14. Chipset Receiver RF Specifications
Parameter Conditions Minimum Typica l
General
Frequency range – 2402 – 2480 MHz
GFSK, 0.1% BER, 1 Mbps – –93.5 – dBm
RX sensitivity
Maximum input GFSK, 1 Mbps – – –20 dBm
Maximum input
C/I cochannel GFSK, 0.1% BER – 9.5 11 dB
C/I 1 MHz adjacent channel GFSK, 0.1% BER – –5 0 dB
C/I 2 MHz adjacent channel GFSK, 0.1% BER – –40 –30.0 dB
3 MHz adjacent channel GFSK, 0.1% BER – –49 –40.0 dB
C/I >
C/I image channel GFSK, 0.1% BER – –27 –9.0 dB
C/I 1 MHz adjacent to image
channel
C/I cochannel
C/I 1 MHz adjacent channel
C/I 2 MHz adjacent channel
3 MHz adjacent channel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –50 –40.0 dB
C/I >
C/I image channel
C/I 1 MHz adjacent to image
channel
C/I cochannel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – 17 21 dB
C/I 1 MHz adjacent channel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –5 5 dB
C/I 2 MHz adjacent channel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –40 –25.0 dB
3 MHz adjacent channel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –47 –33.0 dB
C/I >
C/I Image channel 8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –20 0 dB
C/I 1 MHz adjacent to image
channel
30 MHz–2000 MHz 0.1% BER – –10.0 – dBm
2000–2399 MHz 0.1% BER – –27 – dBm
[8]
LE GFSK, 0.1% BER, 1 Mbps – –96.5 – dBm
π/4-DQPSK, 0.01% BER, 2 Mbps – –95.5 – dBm
8-DPSK, 0.01% BER, 3 Mbps – –89.5 – dBm
π/4-DQPSK, 8-DPSK, 2/3 Mbps – – –20 dBm
Interference Performance
GFSK, 0.1% BER – –37 –20.0 dB
π/4-DQPSK, 0.1% BER – 11 13 dB
π/4-DQPSK, 0.1% BER – –8 0 dB
π/4-DQPSK, 0.1% BER – –40 –30.0 dB
π/4-DQPSK, 0.1% BER – –27 –7.0 dB
π/4-DQPSK, 0.1% BER – –40 –20.0 dB
8-DPSK, 0.1% BER – –35 –13.0 dB
Out-of-Band Blocking Performance (CW)
[9]
[7]
Maximum Unit
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 27 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Table 14. Chipset Receiver RF Specifications (continued)
Notes
10. Numbers are referred to the pin output with an external BPF filter.
11. f0 = -64 dBm Bluetooth-modulated signal, f1 = –39 dBm sine wave, f2 = –39 dBm Bluetooth-modulated signal, f0 = 2f1 – f2, and |f2 – f1| = n*1 MHz, where n is 3, 4,
or 5. For the typical case, n = 4.
12. Includes baseband radiated emissions.
Parameter Conditions Minimum Typica l
[7]
Maximum Unit
2498–3000 MHz 0.1% BER – –27 – dBm
3000 MHz–12.75 GHz 0.1% BER – –10.0 – dBm
Out-of-Band Blocking Performance, Modulated Interferer
776–764 MHz CDMA – –10
824–849 MHz CDMA – –10
1850–1910 MHz CDMA – –23
824–849 MHz EDGE/GSM – –10
880–915 MHz EDGE/GSM – –10
1710–1785 MHz EDGE/GSM – –23
1850–1910 MHz EDGE/GSM – –23
1850–1910 MHz WCDMA – –23
1920–1980 MHz WCDMA – –23
Intermodulation Performance
[11]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
[10]
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
–dBm
BT, Df = 5 MHz – –39.0 – – dBm
Spurious Emissions
[12]
30 MHz to 1 GHz – – – –62 dBm
1 GHz to 12.75 GHz – – – –47 dBm
65 MHz to 108 MHz FM Rx – –147 – dBm/Hz
746 MHz to 764 MHz CDMA – –147 – dBm/Hz
851–894 MHz CDMA – –147 – dBm/Hz
925–960 MHz EDGE/GSM – –147 – dBm/Hz
1805–1880 MHz EDGE/GSM – –147 – dBm/Hz
1930–1990 MHz PCS – –147 – dBm/Hz
2110–2170 MHz WCDMA – –147 – dBm/Hz
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 28 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Table 15. Chipset Transmitter RF Specifications
13. TBD dBm output for GFSK measured with PAVDD = 2.5 V.
14. TBD dBm output for EDR measured with PAVDD = 2.5 V.
15. Maximum value is the value required for Bluetooth qualification.
16. Meets this spec using a front-end band-pass filter.
17. Dirty Tx is Off.
18. The BLE Tx power can be increased to compensate for front-end losses such as BPF, diplexer, switch, etc. The output is capped at 12 dBm out. The BLE Tx power
at the antenna port cannot exceed the 10 dBm EIRP specification limit.
19. At least 99.9% of all delta F2 max frequency values recorded over 10 packets must be greater than 185 kHz.
Parameter Conditions Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
General
Frequency range – 2402 – 2480 MHz
Class1: GFSK Tx power
Class1: EDR Tx power
[13]
[14]
––12–dBm
––9–dBm
Class 2: GFSK Tx power – – 2 – dBm
Power control step – 2 4 8 dB
Modulation Accuracy
π/4-DQPSK Frequency Stability – –10 – 10 kHz
π/4-DQPSK RMS DEVM – – – 20 %
π/4-QPSK Peak DEVM – – – 35 %
π/4-DQPSK 99% DEVM – – – 30 %
8-DPSK frequency stability – –10 – 10 kHz
8-DPSK RMS DEVM – – – 13 %
8-DPSK Peak DEVM – – – 25 %
8-DPSK 99% DEVM – – – 20 %
In-Band Spurious Emissions
1.0 MHz < |M – N| < 1.5 MHz – – – –26 dBc
1.5 MHz < |M – N| < 2.5 MHz – – – –20 dBm
|M – N| >
30 MHz to 1 GHz – – – –36.0
1 GHz to 12.75 GHz – – – –30.0
1.8 GHz to 1.9 GHz – – – –47.0 dBm
5.15 GHz to 5.3 GHz – – – –47.0 dBm
2.5 MHz – – – –40 dBm
Out-of-Band Spurious Emissions
[15]
[15, 16]
dBm
dBm
Table 16. Chipset BLE RF Specifications
Parameter Conditions Minimum Ty pic al Maximum Unit
Frequency range N/A 2402 – 2480 MHz
Rx sense
Tx power
[17]
[18]
GFSK, 0.1% BER, 1 Mbps – –96.5 – dBm
N/A ––9dBm
Mod Char: Delta F1 average N/A 225 255 275 kHz
Mod Char: Delta F2 max
[19]
N/A 99.9 – – %
Mod Char: Ratio N/A 0.8 0.95 – %
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 29 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Timing and AC Characteristics
In this section, use the numbers listed in the Reference column of each table to interpret the following timing diagrams.
UART Timing
Table 17. UART Timing Specifications
Reference Characteristics Min Max Unit
1 Delay time, UART_CTS_N low to UART_TXD valid – 24 Baud out cycles
2 Setup time, UART_CTS_N high before midpoint of stop bit – 10 ns
3 Delay time, midpoint of stop bit to UART_RTS_N high – 2 Baud out cycles
Figure 12. UART Timing
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 30 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
SPI Timing
The SPI interface supports clock speeds up to 12 MHz
Ta bl e 1 8 and Figure 13 show the timing requirements when operating in SPI Mode 0 and 2, and SPI Mode 1 and 3, respectively.
Table 18. SPI Mode 0 and 2
Reference Characteristics Minimum Maximum Unit
1
2
3 Time from master assert SPI_CSN to first clock edge 20
4 Setup time for MOSI data lines 8
5 Hold time for MOSI data lines 8
6 Time from last sample on MOSI/MISO to slave deassert SPI_INT 0 100 ns
7 Time from slave deassert SPI_INT to master deassert SPI_CSN 0
8 Idle time between subsequent SPI transactions 1 SCK
Time from slave assert SPI_INT to master assert SPI_CSN (DirectRead)
Time from master assert SPI_CSN to slave assert SPI_INT (DirectWrite)
Figure 13. SPI Timing – Mode 0 and 2
0
0
∞ ns
∞ ns
∞ ns
½ SCK ns
½ SCK ns
∞ ns
∞ ns
Ta bl e 1 9 and Figure 14 show the timing requirements when operating in SPI Mode 1 and 3.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 31 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Table 19. SPI Mode 1 and 3
Reference Characteristics Minimum Maximum Unit
1
2
3 Time from master assert SPI_CSN to first clock edge 20 ∞ ns
4 Setup time for MOSI data lines 8
5 Hold time for MOSI data lines 8
6
7
8 Idle time between subsequent SPI transactions 1 SCK ∞ ns
Time from slave assert SPI_INT to master assert
SPI_CSN (DirectRead)
Time from master assert SPI_CSN to slave assert
SPI_INT (DirectWrite)
Time from last sample on MOSI/MISO to slave
deassert SPI_INT
Time from slave deassert SPI_INT to master
deassert SPI_CSN
Figure 14. SPI Timing – Mode 1 and 3
0
0 ∞ ns
0 100 ns
0
∞ ns
½ SCK ns
½ SCK ns
∞ ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 32 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
I2C Interface Timing
Notes
20. As a transmitter, 125 ns of delay is provided to bridge the undefined region of the falling edge of SCL to avoid unintended generation of START or STOP conditions.
21. Time that the cbus must be free before a new transaction can start.
Table 20. I2C Interface Timing Specifications
Reference Characteristics Min Max Unit
1 Clock frequency – 100 kHz
400
800
1000
2 START condition setup time 650 – ns
3 START condition hold time 280 – ns
4 Clock low time 650 – ns
5 Clock high time 280 – ns
6 Data input hold time
7 Data input setup time 100 – ns
8 STOP condition setup time 280 – ns
9 Output valid from clock – 400 ns
10 Bus free time
[20]
[21]
Figure 15. I2C Interface Timing Diagram
0 – ns
650 – ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 33 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
PCM Interface Timing
Short Frame Sync, Master Mode
Figure 16. PCM Timing Diagram (Short Frame Sync, Master Mode)
Table 21. PCM Interface Timing Specifications (Short Frame Sync, Master Mode)
Reference Characteristics Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
1 PCM bit clock frequency – – 12 MHz
2 PCM bit clock LOW 41.0 – – ns
3 PCM bit clock HIGH 41.0 – – ns
4 PCM_SYNC delay 0 – 25.0 ns
5 PCM_OUT delay 0 – 25.0 ns
6 PCM_IN setup 8.0 – – ns
7 PCM_IN hold 8.0 – – ns
8 Delay from rising edge of PCM_BCLK during last bit period
to PCM_OUT becoming high impedance
0
–25.0 ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 34 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Short Frame Sync, Slave Mode
Figure 17. PCM Timing Diagram (Short Frame Sync, Slave Mode)
Table 22. PCM Interface Timing Specifications (Short Frame Sync, Slave Mode)
Reference Characteristics Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
1 PCM bit clock frequency – – 12.0 MHz
2 PCM bit clock LOW 41.0 – – ns
3 PCM bit clock HIGH 41.0 – – ns
4 PCM_SYNC setup 8.0 – – ns
5 PCM_SYNC hold 8.0 – – ns
6 PCM_OUT delay 0 – 25.0 ns
7 PCM_IN setup 8.0 – – ns
8 PCM_IN hold 8.0 – – ns
9 Delay from rising edge of PCM_BCLK during last bit
period to PCM_OUT becoming high impedance
0
– 25.0 ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 35 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Long Frame Sync, Master Mode
Figure 18. PCM Timing Diagram (Long Frame Sync, Master Mode)
Table 23. PCM Interface Timing Specifications (Long Frame Sync, Master Mode)
Reference Characteristics Minimum Typ ical Maximum Unit
1 PCM bit clock frequency – – 12 MHz
2 PCM bit clock LOW 41.0 – – ns
3 PCM bit clock HIGH 41.0 – – ns
4 PCM_SYNC delay 0 – 25.0 ns
5 PCM_OUT delay 0 – 25.0 ns
6 PCM_IN setup 8.0 – – ns
7 PCM_IN hold 8.0 – – ns
8
Delay from rising edge of PCM_BCLK during last bit period
to PCM_OUT becoming high impedance
0
–25.0ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 36 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Long Frame Sync, Slave Mode
Figure 19. PCM Timing Diagram (Long Frame Sync, Slave Mode)
Table 24. PCM Interface Timing Specifications (Long Frame Sync, Slave Mode)
Reference Characteristics Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
1 PCM bit clock frequency – – 12 MHz
2 PCM bit clock LOW 41.0 – – ns
3 PCM bit clock HIGH 41.0 – – ns
4 PCM_SYNC setup 8.0 – – ns
5 PCM_SYNC hold 8.0 – – ns
6 PCM_OUT delay 0 – 25.0 ns
7 PCM_IN setup 8.0 – – ns
8 PCM_IN hold 8.0 – – ns
9
Delay from rising edge of PCM_BCLK during last bit period
to PCM_OUT becoming high impedance
0 – 25.0 ns
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 37 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
I2S Interface Timing
The I2S interface supports both master and slave modes. The I2S signals are:
2
n I
S clock: I2S SCK
2
n I
S Word Select: I2S WS
2
n I
S Data Out: I2S SDO
2
n I
S Data In: I2S SDI
2
I
S SCK and I2S WS become outputs in master mode and inputs in slave mode, while I2S SDO always stays as an output. The channel
word length is 16 bits and the data is justified so that the MSB of the left-channel data is aligned with the MSB of the I
2
S specification. The MSB of each data word is transmitted one bit clock cycle after the I2S WS transition, synchronous with the falling
I
edge of bit clock. Left-channel data is transmitted when I
2
S WS is low, and right-channel data is transmitted when I2S WS is high.
Data bits sent by the CYBT-3330xx-02 are synchronized with the falling edge of I2S_SCK and should be sampled by the receiver on
the rising edge of I2S_SSCK.
The clock rate in master mode is either of the following:
n 48 kHz x 32 bits per frame = 1.536 MHz
n 48 kHz x 50 bits per frame = 2.400 MHz
2
S bus, per the
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 38 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
The master clock is generated from the input reference clock using a N/M clock divider. In the slave mode, any clock rate is supported
Notes
22. The system clock period T must be greater than Ttr and Tr because both the transmitter and receiver have to be able to handle the data transfer rate.
23. At all data rates in master mode, the transmitter or receiver generates a clock signal with a fixed mark/space ratio. For this reason, tHC and tLC are specified with
respect to T.
24. In slave mode, the transmitter and receiver need a clock signal with minimum HIGH and LOW periods so that they can detect the signal. So long as the minimum
periods are greater than 0.35Tr, any clock that meets the requirements can be used.
25. Because the delay (tdtr) and the maximum transmitter speed (defined by Ttr) are related, a fast transmitter driven by a slow clock edge can result in tdtr not exceeding
tRC which means thtr becomes zero or negative. Therefore, the transmitter has to guarantee that thtr is greater than or equal to zero, so long as the clock rise-time
tRC is not more than tRCmax, where tRCmax is not less than 0.15Ttr.
26. To allow data to be clocked out on a falling edge, the delay is specified with respect to the rising edge of the clock signal and T, always giving the receiver sufficient
setup time.
27. The data setup and hold time must not be less than the specified receiver setup and hold time.
to a maximum of 3.072 MHz. Timing values specified in Ta bl e 2 5 are relative to high and low threshold levels.
Table 25. Timing for I
2
S Transmitters and Receivers
Transmitter Receiver
Lower LImit Upper Limit Lower Limit Upper Limit
Notes
Clock Period T
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
T
tr
–––
T
r
– – – Note 22
Master Mode: Clock generated by transmitter or receiver
HIGH t
LOWt
LC
HC
0.35T
0.35T
tr
tr
–––
–––
0.35T
0.35T
tr
tr
– – – Note 23
– – – Note 23
Slave Mode: Clock accepted by transmitter or receiver
HIGH t
HC
LOW t
LC
Rise time t
RC
–
–
––
0.35T
0.35T
tr
tr
0.15T
–––
–––
tr
– – – – Note 25
0.35T
0.35T
tr
tr
– – Note 24
– – Note 24
Transmitter
Delay t
dtr
Hold time t
htr
–––0.8T––––Note 26
0–––––––Note 26
Receiver
Setup time t
Hold time t
sr
hr
–––––
–––––0––Note 27
0.2T
r
– – Note 27
Note: The time periods specified in Figure 20 and Figure 21 are defined by the transmitter speed. The receiver specifications must
match transmitter performance.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 39 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Figure 20. I2S Transmitter Timing
Figure 21. I
2
S Receiver Timing
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 40 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Environmental Specifications
Note
28. This does not apply to the RF pins (ANT).
Environmental Compliance
This CYBT-3330xx-02 BLE module is produced in compliance with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and
Halogen-Free (HF) directives. The Cypress module and components used to produce this module are RoHS and HF compliant.
RF Certification
The CYBT-3330xx-02 module will be certified under the following RF certification standards at production release.
n FCC: TBD
n CE
n IC: TBD
n MIC: TBD
Safety Certification
The CYBT-3330xx-02 module complies with the following safety regulations:
n Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. (UL): Filing E331901
n CSA
n TUV
Environmental Conditions
Ta bl e 2 6 describes the operating and storage conditions for the Cypress BLE module.
Table 26. Environmental Conditions for CYBT-3330xx-02
Description Minimum Specification Maximum Specification
Operating temperature −30 °C 85 °C
Operating humidity (relative, non-condensation) 5% 85%
Thermal ramp rate
Storage temperature
Storage temperature and humidity
ESD: Module integrated into end system
Components
[28]
– 3 °C/minute
–40 °C 85 °C
– 85 °C at 85%
–
15 kV Air
2.0 kV Contact
ESD and EMI Protection
Exposed components require special attention to ESD and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
A grounded conductive layer inside the device enclosure is suggested for EMI and ESD performance. Any openings in the enclosure
near the module should be surrounded by a grounded conductive layer to provide ESD protection and a low-impedance path to ground.
Device Handling: Proper ESD protocol must be followed in manufacturing to ensure component reliability.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 41 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Regulatory Information
FCC
FCC NOTICE:
The device CYBT-3330xx-02 complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. The device meets the requirements for modular transmitter
approval as detailed in FCC public Notice DA00-1407.transmitter Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
CAUTION:
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly approved by
Cypress Semiconductor may void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
n
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
n
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
n
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
n
LABELING REQUIREMENTS:
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) must ensure that FCC labelling requirements are met. This includes a clearly visible
label on the outside of the OEM enclosure specifying the appropriate Cypress Semiconductor FCC identifier for this product as well
as the FCC Notice above. The FCC identifier is FCC ID: WAP3047
In any case the end product must be labeled exterior with "Contains FCC ID: WAP3047
ANTENNA WARNING:
The recommended
product, these fixed antennas require installation preventing end-users from replacing them with non-approved antennas. Any antenna
not in the following table must be tested to comply with FCC Section 15.203 for unique antenna connectors and Section 15.247 for
emissions.
RF EXPOSURE:
To comply with FCC RF Exposure requirements, the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) must ensure to install the approved
antenna in the previous.
The preceding statement must be included as a CAUTION statement in manuals, for products operating with the approved antenna
in Ta b le 6 on page 13, to alert users on FCC RF Exposure compliance. Any notification to the end user of installation or removal
instructions about the integrated radio module is not allowed.
The radiated output power of CYBT-3330xx-02 with the dipole antenna (Antenova_B4844 and Pulse_W1030)
radio frequency exposure limits.
Never theless, use CYBT-3330xx-02 in s
End users may not be provided with the module installation instructions. OEM integrators and end users must be provided with
transmitter operating conditions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
antennas are listed in
Table 6 on page 13. When integrated in the OEMs
uch a manner that minimizes the potential for human contact during normal operation.
.
"
is far below the FCC
SAR is not required for this module as long as the distance is higher than 9mm away from user since the maximum
maximum output power is below FCC threshold.
-
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 42 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
ISED
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED) Certification
CYBT-3330xx-02 is licensed to meet the regulatory requirements of Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED),
License: IC: 7922A-3047
Manufacturers of mobile, fixed or portable devices incorporating this module are advised to clarify any regulatory questions and ensure
compliance for SAR and/or RF exposure limits. Users can obtain Canadian information on RF exposure and compliance from
www.ic.gc.ca.
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed in Ta b le 6 on page 13, having a maximum gain of 2.2 dBi. Antennas
not included in this list or having a gain greater than 2.2 dBi are strictly prohibited for use with this device. The required antenna
impedance is 50 ohms. The antenna used for this transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
ISED NOTICE:
The device CYBT-3330xx-02 including the specified antennas comply with Canada RSS-GEN Rules. The device meets the require-
ments for modular transmitter approval as detailed in RSS-GEN. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
L'appareil CYBT-3330xx-02, y compris les antennes spÈcifiÈes, sont conformes aux RËgles RSS-GEN de Canada. L'appareil rÈpond
aux exigences d'approbation de l'Èmetteur modulaire tel que dÈcrit dans RSS-GEN. L'opÈration est soumise aux deux conditions
suivantes: (1) Cet appareil ne doit pas causer d'interfÈrences nuisibles, et (2) Cet appareil doit accepter toute interfÈrence reÁue, y
compris les interfÈrences pouvant entraÓner un fonctionnement indÈsirable.
ISED INTERFERENCE STATEMENT FOR CANADA
This device complies with Innovation, Science and Economic Development (ISED) Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s).
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Cet appareil est conforme à la norme sur l'innovation, la science et le développement économique (ISED) norme RSS exempte de
licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur
de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
ISED RADIATION EXPOSURE STATEMENT FOR CANADA
This equipment complies with ISED radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be
installed and operated with a minimum distance of 15 mm between the radiator and your body.
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux radiations ISED prévues pour un environnement incontrôlé. Cet équipement
doit être installé et utilisé avec un minimum de 15 mm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
LABELING REQUIREMENTS:
The Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) must ensure that ISED labelling requirements are met. This includes a clearly visible
label on the outside of the OEM enclosure specifying the appropriate Cypress Semiconductor IC identifier for this product as well as
the ISED Notices above. The IC identifier is TBD. In any case, the end product must be labeled in its exterior with "Contains IC:
7922A-3047
"
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 43 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
European Declaration of Conformity
Hereby, Cypress Semiconductor declares that the Bluetooth module CYBT-3330xx-02 complies with the essential requirements and
other relevant provisions of Directive 2014. As a result of the conformity assessment procedure described in Annex III of the Directive
2014, the end-customer equipment should be labeled as follows:
All versions of the CYBT-3330xx-02 in the specified reference design can be used in the following countries: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus,
Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta,
Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, The Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and Norway.
MIC Japan
CYBT-3330xx-02 is certified as a module with certification number TBD. End products that integrate CYBT-3330xx-02 do not need
additional MIC Japan certification for the end product.
End product can display the certification label of the embedded module.
Figure 22. MIC Label
TBD
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 44 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Packaging
Table 27. Solder Reflow Peak Temperature
Module Part Number Package Maximum Peak Temperature Maximum Time at Peak Temperature No. of Cycles
CYBT-3330xx-02 24-pad SMT 260 °C 30 seconds 2
Table 28. Package Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL), IPC/JEDEC J-STD-2
Module Part Number Package MSL
CYBT-3330xx-02 26-pad SMT MSL 3
The CYBT-3330xx-02 is offered in tape and reel packaging. Figure 23 details the tape dimensions used for the CYBT-3330xx-02.TBD
Figure 23. CYBT-3330xx-02 Tape Dimensions (TBD)
Figure 24 details the orientation of the CYBT-3330xx-02 in the tape as well as the direction for unreeling.TBD
Figure 24. Component Orientation in Tape and Unreeling Direction (TBD)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 45 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Figure 25 details reel dimensions used for the CYBT-3330xx-02.TBD
Figure 25. Reel Dimensions
The CYBT-3330xx-02 is designed to be used with pick-and-place equipment in an SMT manufacturing environment. The
center-of-mass for the CYBT-3330xx-02 is detailed in Figure 26.
Figure 26. CYBT-3330xx-02 Center of Mass (TBD)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 46 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Ordering Information
Ta bl e 2 9 lists the CYBT-3330xx-02 part number and features. Table 30 lists the reel shipment quantities for the CYBT-3330xx-02.
Table 29. Ordering Information
Part Number
CYBT-3330
Table 30. Tape and Reel Package Quantity and Minimum Order Amount
Description Minimum Reel Quantity Maximum Reel Quantity Comments
Reel Quantity
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Order Increment (OI)
The CYBT-3330xx-02 is offered in tape and reel packaging. The CYBT-3330xx-02 ships in a reel size of 500.
For additional information and a complete list of Cypress Semiconductor Wireless products, contact your local Cypress sales
representative. To locate the nearest Cypress office, visit our website.
U.S. Cypress Headquarters Address 198 Champion Court, San Jose, CA 95134
U.S. Cypress Headquarter Contact Info (408) 943-2600
Cypress website address http://www.cypress.com
XX-02 24 512 352 Yes Yes 4 26-SMT Tape and Reel
CPU
Speed
(MHz)
Flash
Size (KB)
RAM
Size (KB)
500 500 Ships in 500 unit reel quantities.
500 – –
500 – –
UART
I2C
(BSC)
PWM Package Packaging
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 47 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Acronyms
Table 31. Acronyms Used in this Document
Acronym Description Acronym Description
ADC analog-to-digital converter IDE integrated development environment
ALU arithmetic logic unit I2C, or IIC Inter-Integrated Circuit, a communications
AMUXBUS analog multiplexer bus IC Industry Canada
API application programming interface IIR infinite impulse response, see also FIR
®
ARM
BLE Bluetooth Low Energy IMO internal main oscillator, see also ILO
Bluetooth
SIG
BW bandwidth I/O input/output, see also GPIO, DIO, SIO, USBIO
CAN Controller Area Network, a communications
CE European Conformity IPSR interrupt program status register
CSA Canadian Standards Association IRQ interrupt request
CMRR common-mode rejection ratio ITM instrumentation trace macrocell
CPU central processing unit KC Korea Certification
CRC cyclic redundancy check, an error-checking
ECC error correcting code LIN Local Interconnect Network, a communica-
ECO external crystal oscillator LNA low noise amplifier
EEPROM electrically erasable programmable read-only
EMI electromagnetic interference LUT lookup table
EMIF external memory interface LVD low-voltage detect, see also LVI
EOC end of conversion LVI low-voltage interrupt, see also HVI
EOF end of frame LVTTL low-voltage transistor-transistor logic
ESD electrostatic discharge MAC multiply-accumulate
FCC Federal Communications Commission MCU microcontroller unit
FET field-effect transistor MIC Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communica-
FIR finite impulse response, see also IIR MISO master-in slave-out
FPB flash patch and breakpoint NC no connect
FS full-speed NMI nonmaskable interrupt
GPIO general-purpose input/output, applies to a PSoC
HCI host controller interface NVIC nested vectored interrupt controller
HVI high-voltage interrupt, see also LVI, LVD NVL nonvolatile latch, see also WOL
IC integrated circuit Opamp operational amplifier
IDAC current DAC, see also DAC, VDAC PA power amplifier
advanced RISC machine, a CPU architecture ILO internal low-speed oscillator, see also IMO
Bluetooth Special Interest Group INL integral nonlinearity, see also DNL
IPOR initial power-on reset
protocol
LCD liquid crystal display
protocol
LR link register
memory
NRZ non-return-to-zero
pin
protocol
tions protocol.
tions (Japan)
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 48 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Table 31. Acronyms Used in this Document (continued)
Acronym Description Acronym Description
PAL programmable array logic, see also PLD SOF start of frame
PC program counter S/H sample and hold
PCB printed circuit board SINAD signal to noise and distortion ratio
PGA programmable gain amplifier SIO special input/output, GPIO with advanced
features. See GPIO.
PHUB peripheral hub SMT surface-mount technology; a method for
producing electronic circuitry in which the
components are placed directly onto the
surface of PCBs
PHY physical layer SPI Serial Peripheral Interface, a communications
protocol
PICU port interrupt control unit SR slew rate
PLA programmable logic array SRAM static random access memory
PLD programmable logic device, see also PAL SRES software reset
PLL phase-locked loop STN super twisted nematic
PMDD package material declaration data sheet SWD serial wire debug, a test protocol
POR power-on reset SWV single-wire viewer
PRES precise power-on reset TD transaction descriptor, see also DMA
PRS pseudo random sequence THD total harmonic distortion
PS port read data register TIA transimpedance amplifier
®
PSoC
PSRR power supply rejection ratio TRM technical reference manual
PWM pulse-width modulator TTL transistor-transistor logic
QDID qualification design ID TUV Germany: Technischer Überwachungs-Verein
RAM random-access memory TX transmit
RISC reduced-instruction-set computing UART Universal Asynchronous Transmitter Receiver,
RMS root-mean-square UDB universal digital block
RTC real-time clock USB Universal Serial Bus
RTL register transfer language USBIO USB input/output, PSoC pins used to connect
RTR remote transmission request VDAC voltage DAC, see also DAC, IDAC
RX receive WDT watchdog timer
SAR successive approximation register WOL write once latch, see also NVL
SC/CT switched capacitor/continuous time WRES watchdog timer reset
SCL I
SDA I
SOC start of conversion
Programmable System-on-Chip™ TN twisted nematic
(Technical Inspection Association)
a communications protocol
to a USB port
2
C serial clock XRES external reset I/O pin
2
C serial data XTAL crystal
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 49 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Document Conventions
Units of Measure
Table 32. Units of Measure
Symbol Unit of Measure
°C degrees Celsius
dB decibel
dBm decibel-milliwatts
fF femtofarads
Hz hertz
KB 1024 bytes
kbps kilobits per second
Khr kilohour
kHz kilohertz
kΩ kilo ohm
ksps kilosamples per second
LSB least significant bit
Mbps megabits per second
MHz megahertz
MΩ mega-ohm
Msps megasamples per second
µA microampere
µF microfarad
µH microhenry
µs microsecond
µV microvolt
µW microwatt
mA milliampere
ms millisecond
mV millivolt
nA nanoampere
ns nanosecond
nV nanovolt
Ω ohm
pF picofarad
ppm parts per million
ps picosecond
s second
sps samples per second
sqrtHz square root of hertz
Vvolt
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 50 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Document History Page
Document Title: CYBT-3330xx-02 EZ-BTTM WICED Module
Document Number: 002-25196
Revision ECN
** SHNG 07/03/2017 Preliminary datasheet for CYBT-3330xx-02 module.
Orig. of
Change
Submission
Date
Description of Change
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Page 51 of 52

PRELIMINARY
CYBT-3330xx-02
Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information
Worldwide Sales and Design Support
Cypress maintains a worldwide network of offices, solution centers, manufacturer’s representatives, and distributors. To find the office
closest to you, visit us at Cypress Locations.
Products
ARM® Cortex® Microcontrollers cypress.com/arm
Automotive cypress.com/automotive
Clocks & Buffers cypress.com/clocks
Interface cypress.com/interface
Internet of Things cypress.com/iot
Memory cypress.com/memory
Microcontrollers cypress.com/mcu
PSoC cypress.com/psoc
Power Management ICs cypress.com/pmic
Touch Sensing cypress.com/touch
USB Controllers cypress.com/usb
Wireless Connectivity cypress.com/wireless
PSoC® Solutions
PSoC 1 | PSoC 3 | PSoC 4 | PSoC 5LP | PSoC 6
Cypress Developer Community
Forums | WICED IOT Forums | Projects | Video | Blogs |
Training | Components
Technical Support
cypress.com/support
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2017-2018. This document is the property of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation and its subsidiaries, including Spansion LLC ("Cypress"). This document,
including any software or firmware included or referenced in this document ("Software"), is owned by Cypress under the intellectual property laws and treaties of the United States and other countries
worldwide. Cypress reserves all rights under such laws and treaties and does not, except as specifically stated in this paragraph, grant any license under its patents, copyrights, trademarks, or other
intellectual property rights. If the Software is not accompanied by a license agreement and you do not otherwise have a written agreement with Cypress governing the use of the Software, then Cypress
hereby grants you a personal, non-exclusive, nontransferable license (without the right to sublicense) (1) under its copyright rights in the Software (a) for Software provided in source code form, to
modify and reproduce the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products, only internally within your organization, and (b) to distribute the Software in binary code form externally to end users
(either directly or indirectly through resellers and distributors), solely for use on Cypress hardware product units, and (2) under those claims of Cypress's patents that are infringed by the Software (as
provided by Cypress, unmodified) to make, use, distribute, and import the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products. Any other use, reproduction, modification, translation, or compilation
of the Software is prohibited.
TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY SOFTWARE
OR ACCOMPANYING HARDWARE, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. To the extent
permitted by applicable law, Cypress reserves the right to make changes to this document without further notice. Cypress does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit described in this document. Any information provided in this document, including any sample design information or programming code, is provided only for reference purposes. It is
the responsibility of the user of this document to properly design, program, and test the functionality and safety of any application made of this information and any resulting product. Cypress products
are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as critical components in systems designed or intended for the operation of weapons, weapons systems, nuclear installations, life-support devices or
systems, other medical devices or systems (including resuscitation equipment and surgical implants), pollution control or hazardous substances management, or other uses where the failure of the
device or system could cause personal injury, death, or property damage ("Unintended Uses"). A critical component is any component of a device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably
expected to cause the failure of the device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. Cypress is not liable, in whole or in part, and you shall and hereby do release Cypress from any claim,
damage, or other liability arising from or related to all Unintended Uses of Cypress products. You shall indemnify and hold Cypress harmless from and against all claims, costs, damages, and other
liabilities, including claims for personal injury or death, arising from or related to any Unintended Uses of Cypress products.
Cypress, the Cypress logo, Spansion, the Spansion logo, and combinations thereof, WICED, PSoC, CapSense, EZ-USB, F-RAM, and Traveo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cypress in
the United States and other countries. For a more complete list of Cypress trademarks, visit cypress.com. Other names and brands may be claimed as property of their respective owners.
Document Number: 002-25196 Rev. ** Revised September 18, 2018 Page 52 of 52
 Loading...
Loading...