CYPRESS W230-03 User Manual
3
PRELIMINARY
Spread Spectrum FTG for VIA K7 Chipset
Features
• Maximized EMI Suppression using Cypress’s Spread
Spectrum technology
• Single-chip system frequency synthesizer for VIA K7
chipset
• Two copies of CPU output
• Six copies of PCI output
• One 48-MHz output for USB
• One 24-MHz or 48-MHz output for SIO
• Two buffered reference outputs
• Thirteen SDRAM outputs provide support for 3 DIMMs
• Supports frequencies up to 200 MHz
2
•I
C™ interface for programming
• Power management control inputs
• Available in 48-pin SSOP
Key Specifications
CPU to CPU Output Skew:.........................................175 ps
PCI to PCI Output Skew:............................................ 500 ps
: .................................................................... 3.3V±5%
V
DDQ3
SDRAMIN to SDRAM0:12 Delay:..........................3.7 ns typ.
Table 1. Mode Input Table
Mode Pin 2
0CPU_STOP#
1REF0
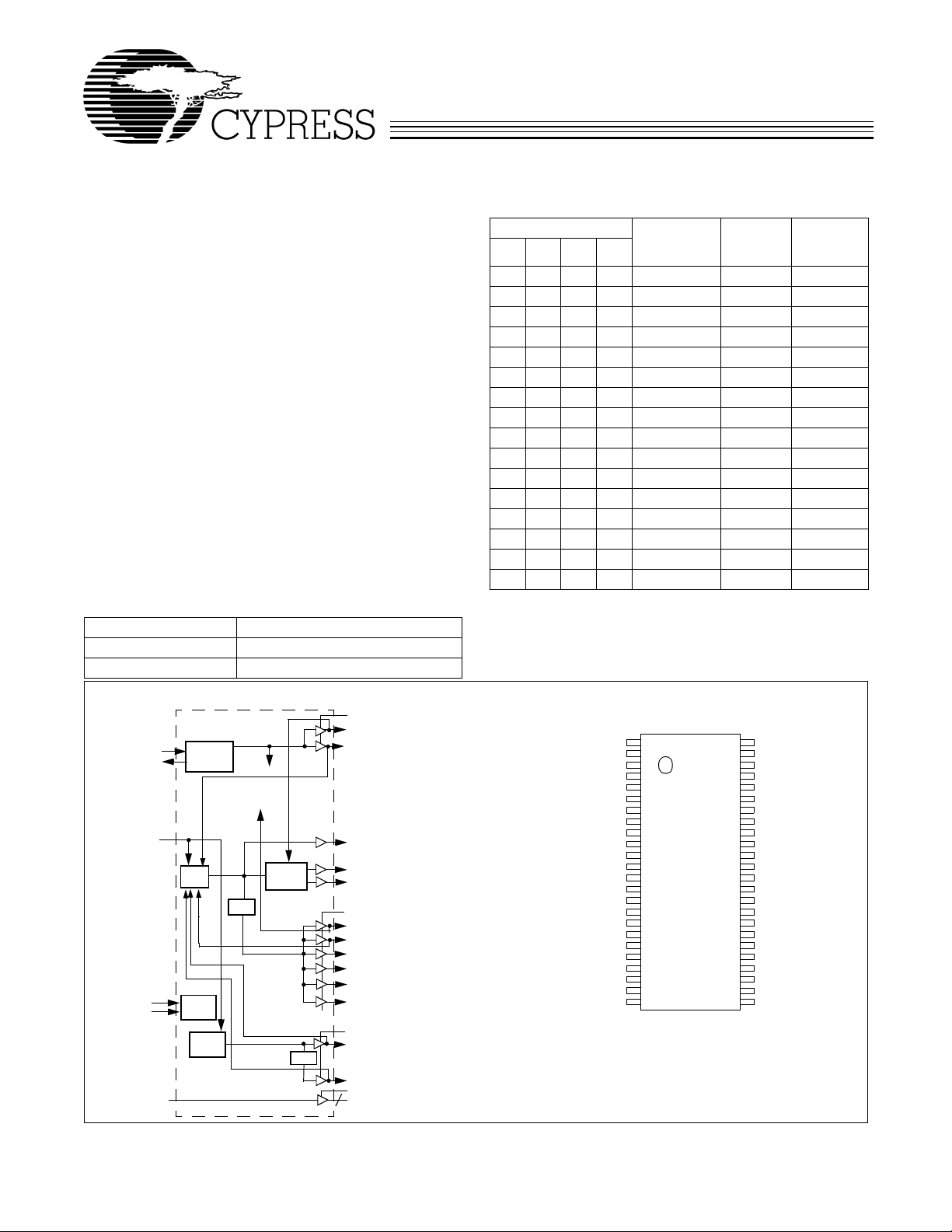
Block Diagram
VDDQ3
REF0/(CPU_STOP#)
X1
X2
PWRDWN#
SDATA
SCLK
SDRAMIN
I2C is a trademark of Phillips Corporation.
PLL 1
I2C
Logic
PLL2
XTAL
OSC
÷2,3,4
PLL Ref Freq
I/O Pin
Control
Control
Stop
Clock
÷2
REF1/FS0
CPU_CS
CPUT0
CPUC0
VDDQ3
PCI0/MODE
PCI1/FS1
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
VDDQ3
48MHz/FS2
24_48MHz/FS3
VDDQ3
SDRAM0:12
13
W230-03
Table 2. Pin Selectable Frequency
Input Address CPU_CS
1111 100.0 33.3 –0.5%
1110 100.0 33.3 OFF
1 1 0 1 100.0 33.3 ±0.5%
1100 95.0 31.7 OFF
1011 133.3 33.3 –0.5%
1010 133.3 33.3 OFF
1 0 0 1 133.3 33.3 ±0.5%
1000 102.0 34.0 OFF
0111 104.0 34.6 OFF
0110 106.0 35.3 OFF
0101 107.0 35.6 OFF
0100 108.0 36.0 OFF
0011 109.0 36.3 OFF
0 0 1 0 110.0 36.6 OFF
0 0 0 1 111.0 37.0 OFF
0 0 0 0 112.0 37.3 OFF
Pin Configuration
REF0/(CPU_STOP#)
Note:
1. Internal pull-up resistors should not be relied upon for setting I/O
VDDQ3
GND
VDDQ3
PCI0/MODE
PCI1/FS1*
GND
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
VDDQ3
SDRAMIN
GND
SDRAM11
SDRAM10
VDDQ3
SDRAM9
SDRAM8
GND
SDATA
I2C
{
SCLK
pins HIGH. Pin function with parentheses determined by MODE pin
resistor strapping. Unlike other I/O pins, input FS3 has an internal
pull-down resistor.
X1
X2
CPUT0
(MHz)
[1]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
PCI 0:5
(MHz)
48
REF1/FS0*
47
GND
46
CPU_CS
45
GND
44
CPUC0
43
CPUT0
42
VDDQ3
41
PWRDWN#*
40
W230-03
SDRAM12
39
GND
38
SDRAM0
37
SDRAM1
36
VDDQ3
35
SDRAM2
34
SDRAM3
33
GND
32
SDRAM4
31
SDRAM5
30
VDDQ3
29
SDRAM6
28
SDRAM7
27
VDDQ3
26
48MHz/FS2*
25
24_48MHz/FS3^
Spread
SpectrumFS3 FS2 FS1 FS0
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose • CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-07357 Rev. *A Revised December 26, 2002
PRELIMINARY
W230-03
Pin Definitions
Pin Name Pin No. Pin Type Pin Description
CPUT0,
CPUC0,
CPU_CS 46 O CPU Clock Output for Chipset: CPU_CS is the push-pull clock output for the
PCI2:5 10, 11, 12, 13 O PCI Clock Outputs 2 through 5: These four PCI clo ck output s ar e contro lled by
PCI1/FS1 8 I/O Fixed PCI Clock Outpu t/Frequ ency Select 1: As an outp ut, frequ ency is set by
PCI0/MODE 7 I/O Fixed PCI Clock Output/Mode: As an outpu t, frequency is se t by the FS0:3 inpu ts
PWRDWN# 41 I PWRDWN# Input: LVTTL-comp atible inpu t that plac es the de vice in p ower-down
48MHz/FS2 2 6 I/O 48-MHz Output/Frequency Se lect 2: 4 8 MHz i s provided in norm al opera tion. In
24_48MHz/
FS3
REF1/FS0 48 I/O Reference Clock Output 1/Freque ncy Select 2: 3.3V 14.318-M Hz output clock.
REF0/
CPU_STOP
#
SDRAMIN 15 I Buffered Input Pin: Th e signal provide d to this input pin is buffered to 13 ou tputs
SDRAM0:12 38, 37, 35,
SCLK 24 I Clock pin for I
SDATA 23 I/O Data pin for I
X1 4 I Crystal Connection or External Reference Frequency I nput: This pin has d ual
X2 5 I Crystal Connection: An input connection for an external 14.318-MHz crystal. If
VDDQ3 1, 6, 14, 19,
GND 3, 9, 16, 22,
43, 44 O
(open-drain)
25 I/O 24_48-MHz Output/Frequency Select 3: In standard PC systems, this output can
2 I/O Reference Clock Output 0 or CPU_STOP# Input Pin: Function is determined
O Buffered Outputs: These thirteen dedicated outputs provide copies of the signal
34, 32, 31,
29, 28, 21,
20, 18, 17, 40
P Power Connection: Power supply for core logi c, PLL ci rcu itry, SDRAM outputs,
27, 30, 36, 42
G Ground Connections: Connect all ground pins to the common system ground
33, 39, 45, 47
CPU Clock Output 0: CPUT0 and CPUC0 are the dif ferential CPU clo ck outputs
for the K7 processor.
chipset. It has the same phase relationship as CPUT0.
the PWRDWN# control pin. Frequency is set by FS0:3 inputs or through serial
input interface, see Tables 2 and 6 for details. Output voltage swing is controlled
by voltage applied to VDDQ3.
FS0:3 inputs or through serial input interface. This output is controlled by the
PWRDWN# input. This pin also serves as a power-on strap option to determine
device operating frequency as described in Table 2.
or through serial input interface, see Tables 2 and 6. This output is controlled by
the PWRDWN# input. This pin also serves as a power-on strap option to determine
the function of pin 2, see Table 1 for details.
mode when held LOW. In power-down mode, CPUC0 will be three-sta ted and al l
the other output clocks will be driven LOW.
standard PC systems, this output can be used as the reference fo r the Uni ver sal
Serial Bus host controller. This pin also serves as a power on strap option to
determine device operating frequency as described in Table 2.
be used as the cloc k input for a Sup er I/O chip. T he output frequ ency is control led
by Configuration Byte 3 bit[6]. The default output frequency is 48 MHz. This pin
also serves as a power-on strap option to determine device operating frequency
as describe d in Table 2.
This pin also serves as a power-on strap option to determine device operating
frequency as describ ed in T able 2. Upon power-u p, FS0 input will be latched whic h
will set clock frequencies as described in Table 2.
by the MODE pin. When CPU_STOP# input is asserted LOW, it will drive CPUT0
and CPU_CS to logic 0, an d it will three-sta te CPUC0. When thi s pin is configured
as an output , this pin becomes a 3.3V 14 .318-MHz output clock.
(SDRAM0:12).
provided at the SDRAMIN in put . The sw in g is set by VDDQ 3, and they are deactivated when PWRDWN# input is set LOW.
2
C circuitry.
2
C circuitry.
functions. It can be used as an external 14.318-MHz crystal connection or as an
external reference frequency input.
using an external reference, thi s pin must be left unconnected.
PCI outputs, reference ou tputs, 48-M Hz output, a nd 24_48-MH z output. Connect
to 3.3V supply
plane.
Document #: 38-07357 Rev. *A Page 2 of 15
PRELIMINARY
Overview
The W230-03 was developed as a single-chip device to meet
the clocking needs of VIA K7 core logic chip sets. In addition
to the typical output s provided by a standa rd FTG, the W23003 adds a thirteenth output buffer, supporting SDRAM DIMM
modules in conjunction with the chipset.
Cypress’s proprietary spread spectrum frequency synthesis
technique is a feature of the CPU and PCI outputs. When enabled, this feature reduces the peak EM I measurements of n ot
only the output signals and their harmonics, but also of any
other clock signals that are properly synchronized to them.
Functional Description
I/O Pin Operation
Pins 7, 8, 25, 26, and 48 are dual-purpose l/O pins. Upon
power-up these pins act as logic inputs, allowing the determination of assigned device functions. A short time after powerup, the logic state of each pin is latched and the pins become
clock outputs. This feature reduces device pin count by combining clock outputs with inp ut sel ec t pins .
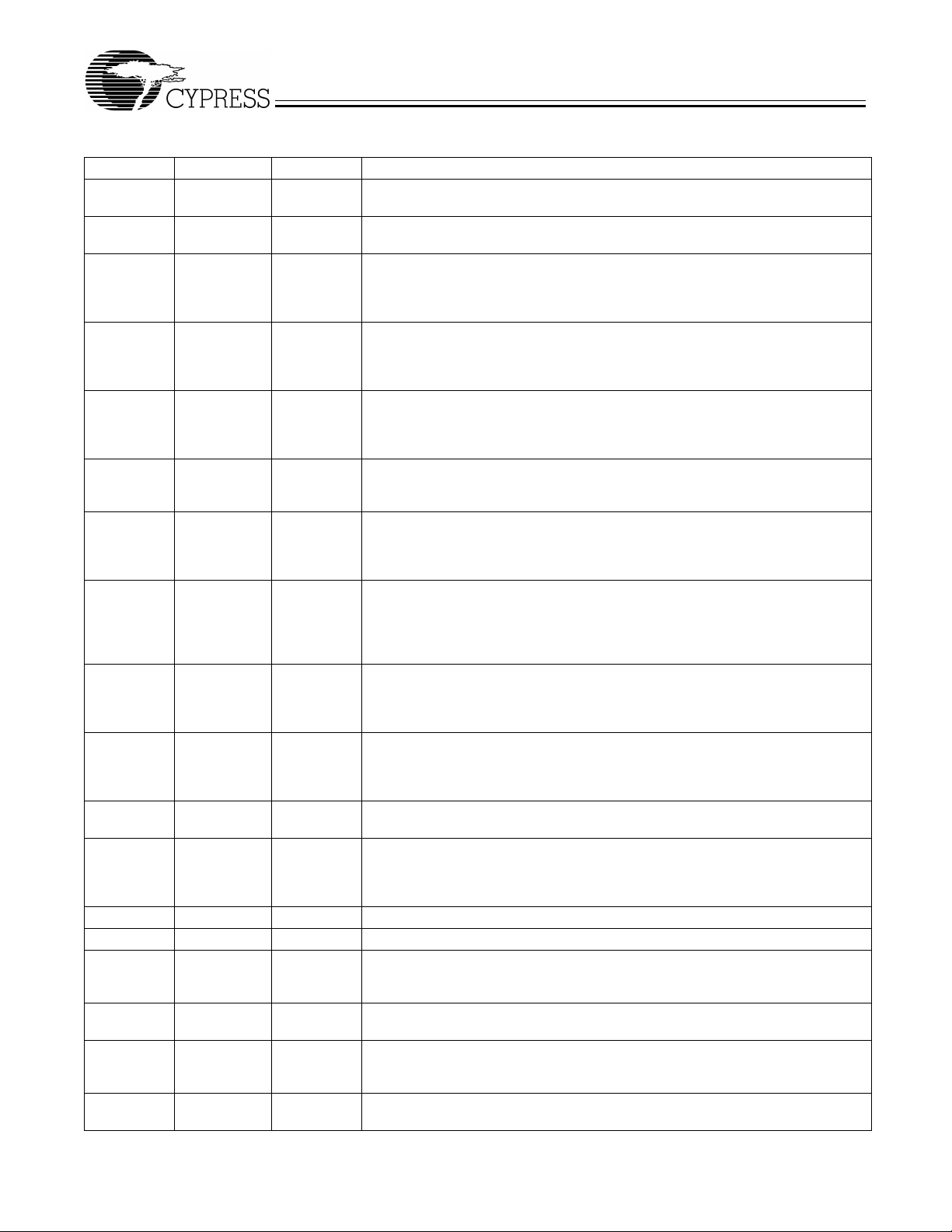
An external 10 -kΩ “strapping” resistor is connected between
the l/O pin and ground or V
latch to “0,” connect ion to V
Figure 2 show two suggested methods for strapping resistor
connections.
. Connection to ground sets a
DD
sets a latch to “1.” Figure 1 and
DD
W230-03
Upon W230-03 power-up, the first 2 ms of operation is used
for input logic selection. During this period, the five I/O pin s (7,
8, 25, 26, 48) are three-stated, allowing the output strapping
resistor on the l/O pins to pull the pins and their associated
capacitive clock load to either a logic HIGH or LOW state. At
the end of the 2- ms period, the establ ished logic “0” or “1”
condition of the l/O pin is latched. Next the output buffer is
enabled converting the l/O pins into operating clock outputs.
The 2-ms timer starts when V
can only be reset by turning V
It should be noted that the strapping resistors have no significant effect on clock output signal integrity. The drive impedance of clock outputs is <40Ω (nominal), which is minimally
affected by th e 1 0-k Ω str a p t o gro u nd or V
ries termination resistor, the output strapping resistor should
be placed as close to the l/O pin as possible in order to keep
the interc onne cti ng t race sh ort . Th e trac e fr om the res isto r to
ground or V
to prevent system noise coupling during input logic sampling.
should be kept less than two inches in length
DD
When the clock outputs are enabled following the 2-ms input
period, the specified output frequency is delivered on the pin,
assuming that V
full value, outpu t frequency initial ly may be below ta rget but will
has stabilized . If VDD has not yet reached
DD
increase to target once V
case, a short output clock cycle may be produced from the
CPU clock outputs when the outputs are enabled.
V
DD
reaches 2.0V. The input bits
DD
off and then back on again.
DD
. As with the se-
DD
voltage has stabilized. In either
DD
Output Strapping Resistor
W230-03
Power-on
Reset
Timer
W230-03
Power-on
Reset
Timer
10 k
Output Three-state
Output
Buffer
Hold
Output
Low
QD
Data
Latch
(Load Option 1)
(Load Option 0)
10 k
Ω
Ω
Figure 1. Input Logic Selection Through Resistor Load Option
Jumper Options
V
DD
Ω
10 k
Output
Buffer
Output Three-state
Hold
Output
Low
QD
Data
Latch
Resistor Value R
Series Termination Resistor
R
Output Strapping Resistor
Series Termination Resistor
R
Clock Load
Clock Load
Figure 2. Input Logic Selection Through Jumper Option
Document #: 38-07357 Rev. *A Page 3 of 15
PRELIMINARY
Spread Spectrum Frequency Timing Generator
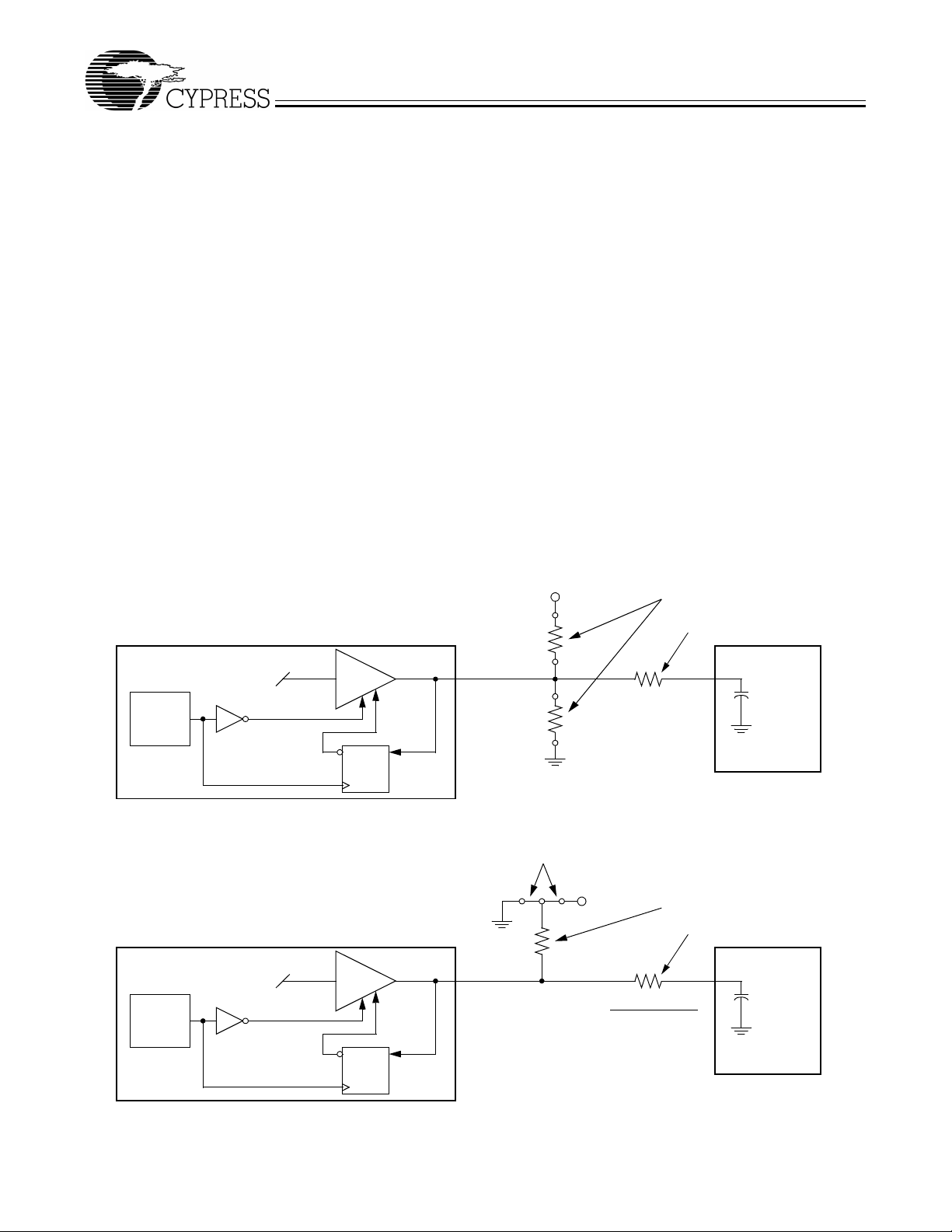
The device generates a clock that is frequency modulated in
order to increase th e bandwidt h that it occu pies. By inc reasing
the bandwidth of the fundamental and its harmonics, the amplitudes of the radiated electromagnetic emissions are reduced. This effect is depicted in Figure 3.
As shown in Figure 3, a harmonic of a modulated clock has a
much lower amplit ude than that of an unmodulated si gnal. The
reduction in amplitude is dependent on the harmonic number
and the frequency deviation or spread. The equation for the
reduction is:
dB = 6.5 + 9*log
Amplitude (dB)
(P) + 9*log10(F)
10
SSFTG Typical Clock
W230-03
Where P is the pe rcentage of deviation and F is the frequenc y
in MHz where the reduction is measured.
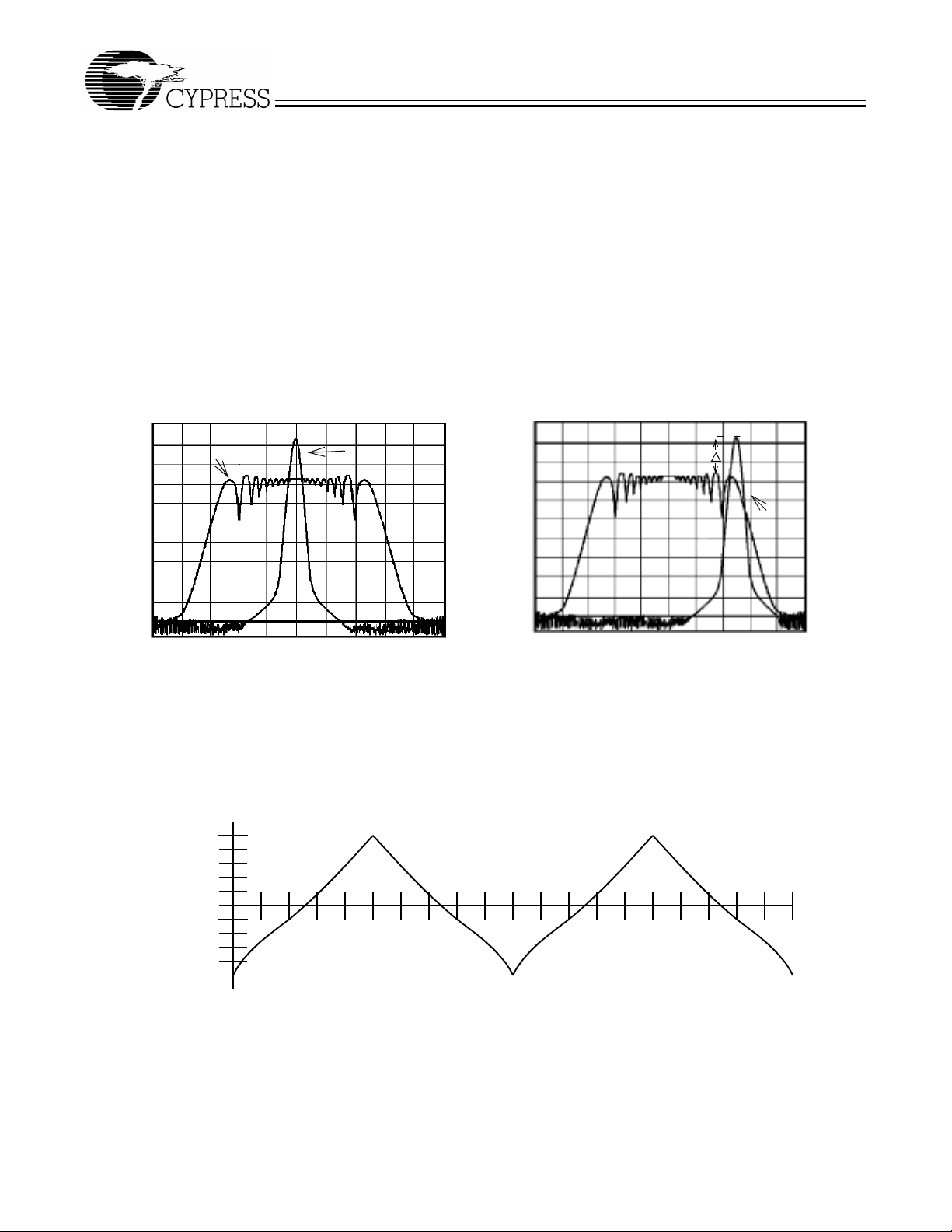
The output clock is modulated with a waveform depicted in
Figure 4. This waveform, as discusse d in “Spread Spectrum
Clock Generation for the Reduction of Radiated Emi ssions” by
Bush, Fessler, and Hardin produces the maximum reduction
in the amplitude of radiated electromagnetic emissions. The
deviation select ed for this ch ip is spec ified in Table 6. Fi gure 4
details the Cypress spread ing patt ern. Cypre ss does of fer o ptions with more spread and greater EMI reduction. Contact
your local Sales representative for details on these devices.
Spread Spectrum clocking is activated or deactivated by selecting the approp riate v alues for bits 1 –0 in da ta byt e 0 of th e
2
C data stream. Refer to Table 6 for more details.
I
EMI Reduction
Spread
Spectrum
Enabled
Amplitude (dB)
Non-
Spread
Speactrum
Frequency Span (MHz)
Center Spread
Frequency Span (MHz)
Down Spread
Figure 3. Clock Harmonic with and without SSCG Modulation Frequency Domain Representation
MAX (0%)
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
FREQUENCY
MIN (–0.5%)
90%
100%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
Figure 4. Ty pical Modulation Profile
100%
Document #: 38-07357 Rev. *A Page 4 of 15
PRELIMINARY
Serial Data In te rface
The W230-03 features a two-pin, serial data interface that can
be used to configure inte rnal regi ster settin gs that con trol particular device functions. Upon power-up, the W230-03 initializes with default reg ist er s ett ing s, ther efore the use of this serial data interface is optional. The serial interface is write-only
(to the clock chip) and is the dedica ted func tion of dev ice pin s
SDATA and SCLOCK. In motherboard applications, SDATA
and SCLOCK are typically driven by two logic outputs of the
Table 3. Serial Data Interface Control Functions Summary
Control Function Description Common Application
Clock Output Disable Any individual cloc k output(s) ca n be disabled . Dis-
abled outputs are actively held LOW.
CPU Clock Frequency
Selection
Spread Spectrum
Enabling
Output Three-state Puts clock output into a high impedance state. Production PCB testing.
(Reserved) Reserved function for future devic e revisi on or pro-
Provides CPU/PCI frequency selections through
software. Frequency is changed in a smooth and
controlled fashion.
Enables or disables spread spectrum clocking. For EMI reduction.
duction device testing .
chipset. Clock device register changes are normally made
upon system initialization, if any are required. The interface
can also be used during system opera tio n for power manag ement functions. Ta b l e 3 summa rizes the contro l functions of
the serial data interface.
Operation
Data is written to the W230-03 in eleven bytes of eight bits
each. Bytes are written in the order shown in Table 4.
Unused outputs are disabled to reduce EMI
and system power. Examples are clock outputs to unused PCI slots.
For alternate microprocessors and power
management options. Sm ooth frequency transition allows CPU frequency change under
normal system operation.
No user application. Regi ster bit mus t be written as 0.
W230-03
Table 4. Byte Writing Sequence
Byte Sequence Byte Name Bit Sequence Byte Description
1 Sla ve Address 1 1010010 Commands the W230-03 to ac cept the bits in D ata Bytes 0–6 for internal
2 Command
Code
3 Byte Count Don’t Care Unused by the W230-0 3, therefore bit values are i gnored (“don’t care”).
4 Data Byte 0 Refer to Table 5 The data bits in Data Bytes 0–7 set internal W230-03 registers that
5Data Byte 1
6Data Byte 2
7Data Byte 3
8Data Byte 4
9Data Byte 5
10 Data Byte 6
11 Data Byte 7
Don’t Care Unused by the W230-0 3, therefore bi t values are i gnored (“don’t care”).
register configurati on. Since o ther dev ices may e xist o n the sa me co mmon serial data bus, it is necessary to have a specific slave address for
each potential rec eiver. The slave receiver addres s f or the W230-03 is
1 10100 10. Re giste r settin g wi ll not be mad e if th e Slave Addres s is n ot
correct (or is for an alternate slave receiver).
This byte must be include d in the data write sequence to mainta in proper
byte allocation. The Com mand Co de Byte is par t of the standar d serial
communication protocol and may be used when writing to another addressed slave receiver on the serial data bus.
This byte must be include d in the data write sequence to mainta in proper
byte allocation. Th e Byte C o unt Byte is part of the standard serial communication protocol and may be used when writing to another addressed slave receiver on the serial data bus.
control device op erat ion . The data bits are only accepted when the Address Byte bit sequence is 11010010, as noted above. For description
of bit control functions, re fer to Table 5, Data Byte Serial Configuration
Map.
Document #: 38-07357 Rev. *A Page 5 of 15
 Loading...
Loading...