Page 1
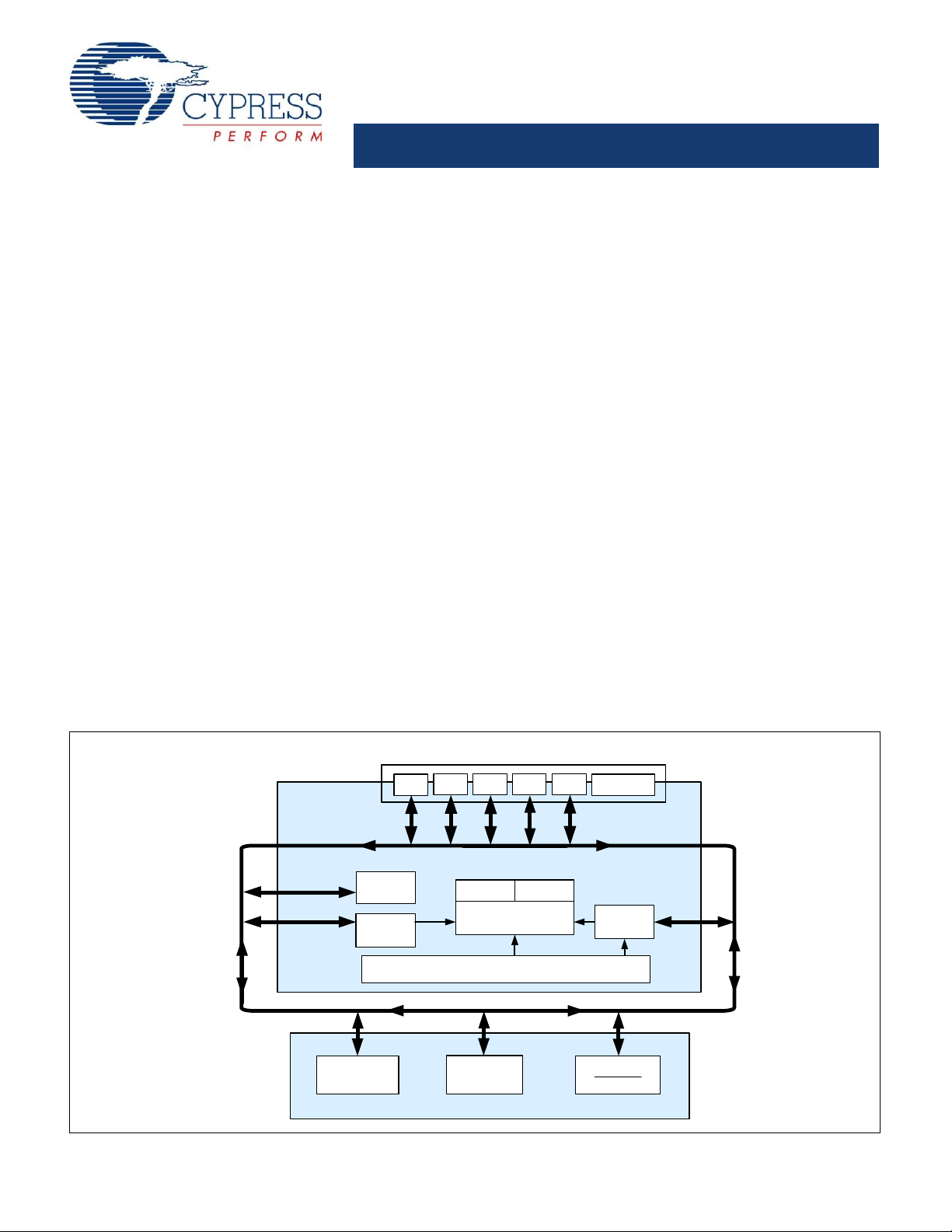
enCoRe™ V Low Voltage Microcontroller
CY7C604XX
Features
System Bus
6/12/24 MHz Internal Main Oscillator
CPU Core
(M8C)
SROM Flash 32K
SYSTEM RESOURCES
I2C Slave/SPI
Master-Slave
POR and LVD
System Resets
Port 1 Port 0
Sleep and
Watchdog
Port 3 Por t 2
Prog. LDO
SRAM
2048 Bytes
Interrupt
Controller
enCoRe V
Low Voltage
CORE
3 16-Bit
Timers
Port 4
enCoRe V LV Block Diagram
■ Powerful Harvard Architecture Processor
❐ M8C processor speeds running up to 24 MHz
❐ Low power at high processing speeds
❐ Interrupt controller
❐ 1.71V to 3.6V operating voltage
❐ Temperature range: 0°C to 70°C
■ Flexible On-Chip Memory
❐ Up to 32K Flash program storage
• 50,000 Erase and write cycles
• Flexible protection modes
❐ Up to 2048 bytes SRAM data storage
❐ In-System Serial Programming (ISSP)
■ Complete Development Tools
❐ Free development tool (PSoC Designer™)
❐ Full featured, in-circuit emulator and programmer
❐ Full speed emulation
❐ Complex breakpoint structure
❐ 128K trace memory
■ Precision, Programmable Clocking
❐ Crystal-less oscillator with support for an external crystal or
resonator
❐ Internal ±5.0% 6, 12, or 24 MHz main oscillator
❐ Internal low speed oscillator at 32 kHz for watchdog and
sleep.The frequency range is 19 to 50 kHz with a 32 kHz
typical value
■ Programmable Pin Configurations
❐ 25 mA sink current on all GPIO
❐ Pull Up, High Z, Open Drain, CMOS drive modes on all GPIO
❐ Configurable inputs on all GPIO
❐ Low dropout voltage regulator for Port 1 pins. Programmable
to output 3.0, 2.5, or 1.8V at the I/O pins
❐ Selectable, regulated digital I/O on Port 1
• Configurable input threshol d for Port 1
• 3.0V, 20 mA total Port 1 source current
• Hot-swappable
❐ 5 mA strong drive mode on Ports 0 and 1
■ Additional System Resources
❐ Configurable communication speeds
2
❐ I
C Slave
• Selectable to 50 kHz, 100 kHz, or 400 kHz
• Implementation requires no clock stretching
• Implementation during sleep modes with less than 100 mA
• Hardware address detection
❐ SPI master and SPI slave
• Configurable between 93.75 kHz and 12 MHz
❐ Three 16-bit timers
❐ 8-bit ADC used to monitor battery voltage or other signals -
with external components
❐ Watchdog and sleep timers
❐ Integrated supervisory circuit
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Revised January 30, 2009
[+] Feedback
Page 2

CY7C604XX
Functional Overview
The enCoRe V LV family of devices are designed to replace
multiple traditional low voltage microcontroller system components with one, low cost single chip programmable component.
Communication peripherals (I2C/SPI), a fast CPU, Flash
program memory, SRAM dat a memory, and configurable I/O are
included in a range of convenient pinouts.
The architecture for this device family, as illustrated in enCoRe
V LV Block Diagram, is comprised of two main areas: the CPU
core and the system resources. Depending on the enCoRe V LV
package, up to 36 general purpose IO (GPIO) are also included.
Enhancements over the Cypress’s legacy low voltage microcontrollers include faster CPU at lower voltage operation, lower
current consumption, twice the RAM and Flash, hot-swapable
I/Os, I2C hardware address recognition, new very low current
sleep mode, and new package options.
The enCoRe V LV Core
The enCoRe V LV Core is a powerful engine that supports a rich
instruction set. It encompasses SRAM for data storage, an
interrupt controller, sleep and watchdog timers, and IMO
(internal main oscillator) and ILO (internal low speed oscillator).
The CPU core, called the M8C, is a powerful processor with
speeds up to 24 MHz. The M8C is a four-MIPS, 8-bit Harvard
architecture microprocessor.
System Resources provide additional capability, such as a
configurable I
interface and various system resets supported by the M8C.
Additional System Resources
System Resources, some of which have been previously listed,
provide additional capability useful to complete systems.
Additional resources include low voltage detection and power on
reset. The following statements describe the merits of each
system resource:
■ 8-bit on-chip ADC shared betwe en System Performance
manager (used to calculate parameters based on temperature
for flash write operations) and the user.
■ The I
or 400 kHz communication over two wires. SPI communication
over three or four wires runs at speeds of 46.9 kHz to 3 MHz
(lower for a slower system clock).
2
■ In I
C slave mode, the hardware address recognition feature
reduces the already low power consumption by eliminating the
need for CPU intervention until a packet addressed to the target
device has been received.
■ Low Voltage Detection (LVD) interrupts can signal the appli-
cation of falling voltage levels, while the advanced POR (Power
On Reset) circuit eliminates the need for a system supervisor.
■ The 5V maximum input, 1.8, 2.5, or 3V selectable output, low
dropout regulator (LDO) provides regulation for I/Os. A register
controlled bypass mode enables the user to disable the LDO.
■ Standard Cypress PSoC IDE tools are available for debugging
the enCoRe V LV family of parts.
2
C slave and SPI master-slave communication
2
C slave and SPI master-slave module provides 50, 100,
Getting Started
The quickest way to understanding the enCoRe V silicon is by
reading this data sheet and using the PSoC Designer Integrated
Development Environment (IDE). This data sheet is an overview
of the enCoRe V integrated circuit and presents specific pin,
register, and electrical specifications. For in-depth information,
along with detailed programming information, reference the
PSoC Programmable System-on-Chip Technical Reference
Manual, for CY8C28xxx PSoC devices.
For up-to-date Ordering, Packaging, and Electrical Specification
information, reference the latest enCoRe V device data sheets
on the web at http://www.cypress.com.
Development Kits
Development Kits are available online from Cypress at
www.cypress.com/shop and through a growing number of
regional and global distributors, which include Arrow, Avnet,
Digi-Key, Farnell, Future Electronics, and Newark.
Training
Free technical training (on demand, webinars, and workshops)
is available online at www.cypress.com/training. The training
covers a wide variety of topics and skill levels to assist you in
your designs.
CyPros Consultants
Certified PSoC Consultants offer everything from technical
assistance to completed PSoC designs. To contact or become a
PSoC Consultant go to www.cypress.com/cypros.
Solutions Library
Visit our growing library of solution focused designs at
www.cypress.com/solutions. Here you can find various appli-
cation designs that include firmware and hardware design files
that enable you to complete your designs quickly.
Technical Support
For assistance with technical issues, search KnowledgeBase
articles and forums at www.cypress.com/support. If you cannot
find an answer to your question, call technical support at
1-800-541-4736.
Application Notes
Application notes are an excellent introduction to the wide variety
of possible PSoC designs. They are located here:
www.cypress.com/psoc. Select Application Notes under the
Documentation tab.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 2 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 3

CY7C604XX
Development Tools
PSoC Designer is a Microsoft® Windows-based, integrated
development environment for the Programmable
System-on-Chip (PSoC) devices. The PSoC Designer IDE runs
on Windows XP or Windows Vista.
This system provides design database management by project,
an integrated debugger with In-Circuit Emulator, in-system
programming support, and built-in support for third-party assemblers and C compilers.
PSoC Designer also supports C language compilers developed
specifically for the devices in the enCoRe and PSoC families.
PSoC Designer Software Subsystems
Chip-Level View
The chip-level view is a traditional integrated development
environment (IDE) based on PSoC Designer 4.4. Choose a base
device to work with and then select different onboard analog and
digital components called user modules that use the PSoC
blocks. Examples of user modules are ADCs, DACs, Amplifiers,
and Filters. Configure the user modules for the chosen application and connect them to each other and to the proper pins.
Then generate your project. This prepopulates your project with
APIs and libraries that you can use to program your application.
The tool also supports easy development of multiple configurations and dynamic reconfiguration. Dynamic reconfiguration
enables changing configurations at run time.
System-Level View
The system-level view is a drag-and-drop visual embedded
system design environment based on PSoC Designer.
Hybrid Designs
You can begin in the system-level view, allow it to choose and
configure your user modules, routing, and generate code, then
switch to the chip-level view to gain complete control over
on-chip resources. All views of the project share common code
editor, builder , and common debug, emulation, and programming
tools.
Code Generation Tools
PSoC Designer supports multiple third-party C compilers and
assemblers. The code generation tools work seamlessly within
the PSoC Designer interface and have been tested with a full
range of debugging tools. The choice is yours.
Assemblers. The assemblers allow assembly code to be
merged seamlessly with C code. Link libraries automatically use
absolute addressing or are compiled in relative mode, and linked
with other software modules to get absolute addressing.
C Language Compilers. C language compilers are available
that support the enCoRe and PSoC families of devices. The
products allow you to create complete C programs for the PSoC
family devices.
The optimizing C compilers provide all the features of C tailored
to the PSoC architecture. They come complete with embedded
libraries providing port and bus operations, standard keypad and
display support, and extended math functionality.
Debugger
PSoC Designer has a debug environment that provides
hardware in-circuit emulation, allowing you to test the program in
a physical system while providing an internal view of the PSoC
device. Debugger commands allow the designer to read and
program flash, read and write data memory, read and write I/O
registers, read and write CPU registers, set and clear breakpoints, and provide program run, halt, and step control. The
debugger also allows the designer to create a trace buffer of
registers and memory locations of interest.
Online Help System
The online help system displays online, context-sensitive help
for the user. Designed for procedural help and quick reference,
each functional subsystem has its own context-sensitive help.
This system also provides tutorials and links to FAQs and an
Online Support Forum to aid the designer in getting started.
In-Circuit Emulator
A low cost, high functionality ICE (In-Circuit Emulator) is
available for development support. This hardware has the
capability to program single devices.
The emulator consists of a base unit that connects to the PC by
way of a USB port. The base unit is universal and operates with
all enCoRe and PSoC devices. Emulation pods for each device
family are available separately. The emulation pod takes the
place of the PSoC device in the target board and performs full
speed (24 MHz) operation.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 3 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 4

CY7C604XX
Designing with PSoC Designer
The development process for the enCoRe V device differs from
that of a traditional fixed function microprocessor. Powerful
PSoC Designer tools get the core of your design up and running
in minutes instead of hours.
The development process can be summarized in the following
four steps:
1. Select Components
2. Configure Components
3. Organize and Connect
4. Generate, Verify, and Debug
Select Components
The chip-level views provide a library of pre-built, pre-tested
hardware peripheral components. These components are called
“user modules.” User modules make selecting and implementing
peripheral devices simple, and come in analog, digital, and
mixed-signal varieties.
Configure Components
Each of the components you select establishes the basic register
settings that implement the selected function. They also provide
parameters and properties that allow you to tailor their precise
configuration to your particular application.
The chip-level user modules are documented in data sheets that
are viewed directly in PSoC Designer. These data sheets explain
the internal operation of the component and provide performance specifications. Each data sheet describes the use of each
user module parameter and contains other information you may
need to successfully implement your design.
Organize and Connect
You build signal chains at the chip level by interconnecting user
modules to each other and the I/O pins, or connect system-level
inputs, outputs, and communication interfaces to each other with
valuator functions. In the chip-level view, you perform the
selection, configuration, and routing so that you have complete
control over the use of all on-chip resources.
Generate, Verify, and Debug
When you are ready to test the hardware configuration or move
on to developing code for the project, you perform the “Generate
Configuration Files” step. This causes PSoC Designer to
generate source code that automatically configures the device to
your specification and provides the software for the system.
Both system-level and chip-level designs generate software
based on your design. The chip-level design provides application
programming interfaces (APIs) with high-level functions to
control and respond to hardware events at run time and interrupt
service routines that you can adapt as needed. The system-level
design also generates a C main() program that completely
controls the chosen application and contains placeholders for
custom code at strategic positions allowing you to further refine
the software without disrupting the generated code.
A complete code development environment allows you to
develop and customize your applications in C, assembly
language, or both.
The last step in the development process takes place inside
PSoC Designer’s Debugger (access by clicking the Connect
icon). PSoC Designer downloads the HEX image to the In-Circuit
Emulator (ICE) where it runs at full speed. PSoC Designer
debugging capabilities rival those of systems costing many times
more. In addition to traditional single-step, run-to-breakpoint and
watch-variable features, the debug interface provides a large
trace buffer and allows you to define complex breakpoint events
that include monitoring address and data bus values, memory
locations and external signals.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 4 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 5

CY7C604XX
Document Conventions
Acronyms Used
The following table lists the acronyms that are used in this
document.
Acronym Description
API application programming interface
CPU central processing unit
GPIO general purpose IO
ICE in-circuit emulator
ILO internal low speed oscillator
IMO internal main oscillator
IO input/output
LSb least significant bit
LVD low voltage detect
MSb most significant bit
POR pow er on rese t
PPOR precision power on reset
PSoC® Programmable System-on-Chip™
SLIMO slow IMO
SRAM static random access memory
Units of Measure
A units of measure table is located in the Electrical Specifications
section. Table 7 on page 14 lists all the abbreviations used to
measure the enCoRe V LV devices.
Numeric Naming
Hexadecimal numbers are represented with all letters in
uppercase with an appended lowercase ‘h’ (for example, ‘14h’ or
‘3Ah’). Hexadecimal numbers may also be represented by a ‘0x’
prefix, the C coding convention. Binary numbers have an
appended lowercase ‘b’ (for example, 01010100b’ or
‘01000011b’). Numbers not indicated by an ‘h’, ‘b’, or 0x are
decimal.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 5 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 6
CY7C604XX
Pin Configuration
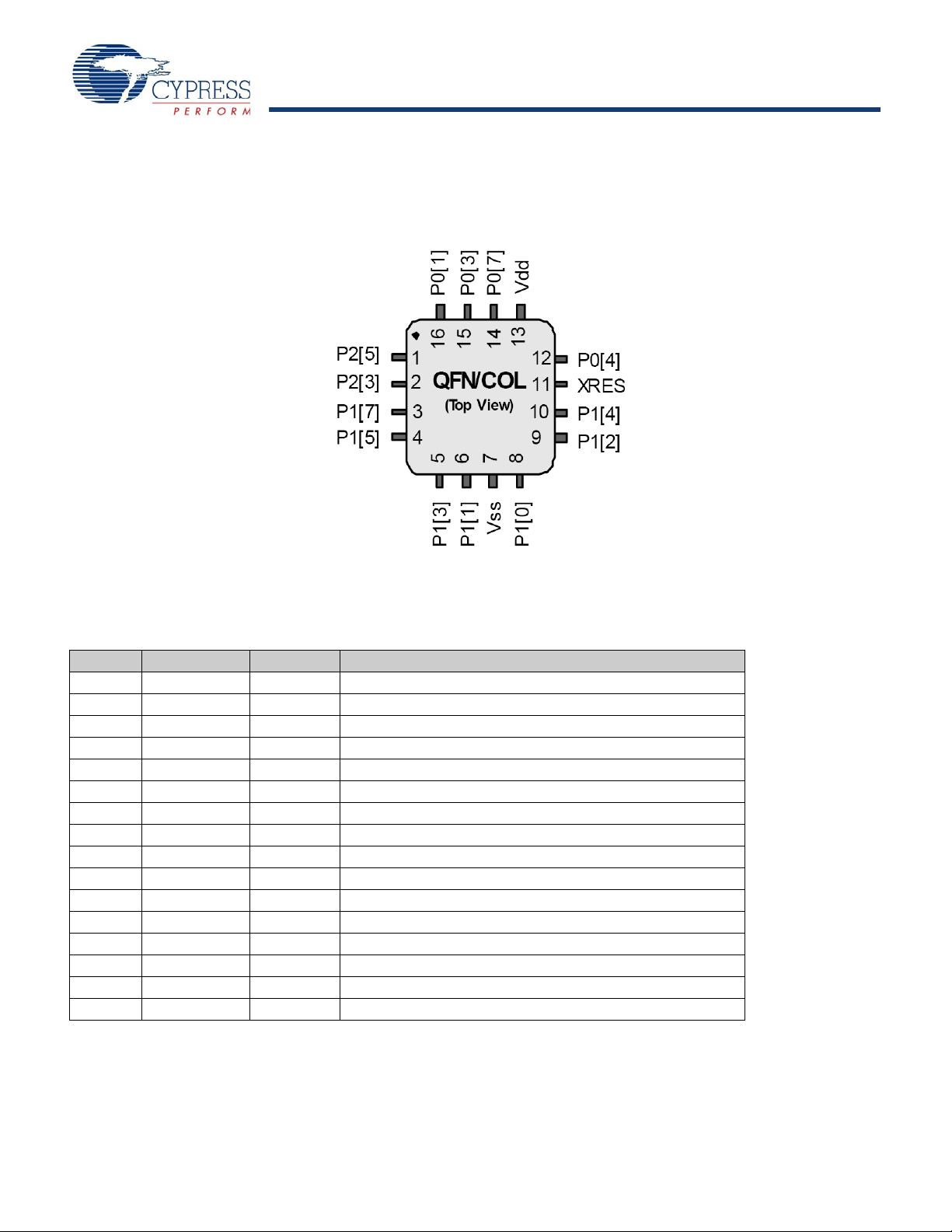
16-Pin Part Pinout
Figure 1. CY7C60413 16-Pin enCoRe V LV Device
Table 1. 16-Pin Part Pinout (QFN)
Pin No. Type Name Description
1 I/O P2[5] Digital I/O, Crystal Out (Xout)
2 I/O P2[3] Digital I/O, Crystal In (Xin)
3 IOHR P1[7] Digital I/O, I2C SCL, SPI SS
4 IOHR P1[5] Digital I/O, I2C SDA, SPI MISO
5 IOHR P1[3] Digital I/O, SPI CLK
6 IOHR P1[1] Digital I/O, ISSP CLK, I2C SCL, SPI MOSI
7 Power Vss Ground Pin
8 IOHR P1[0] Digital I/O, ISSP DATA, I2C SDA, SPI CLK
9 IOHR P1[2] Digital I/O
10 IOHR P1[4] Digital I/O, optional external clock input (EXTCLK)
11 Input XRES Active high external reset with internal pull down
12 IOHR P0[4] Digital I/O
13 Power Vdd Power Pin
14 IOHR P0[7] Digital I/O
15 IOHR P0[3] Digital I/O
16 IOHR P0[1] Digital I/O
LEGEND I = Input, O = Output, OH = 5 mA High Output Drive, R = Regulated Output.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 6 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 7
CY7C604XX
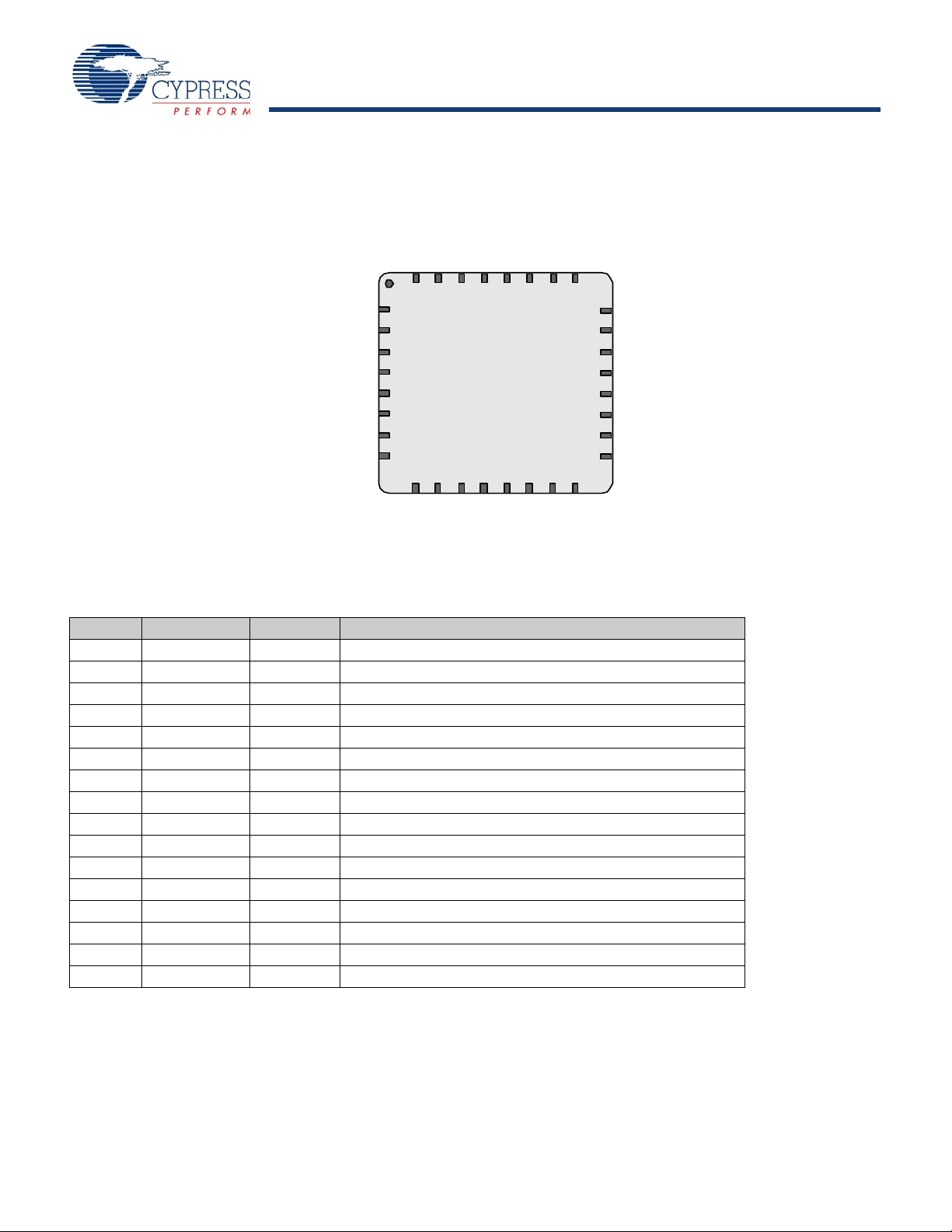
32-Pin Part Pinout
Notes
1. During power up or reset event, device P1[0] and P1[1] may disturb the I2C bus. Use alternate pins if issues are encountered.
2. These are the in-system serial programming (ISSP) pins, that are not High Z at power on reset (POR)
P0 [1 ]
P2[7]
P2[5]
P2[3]
P2[1]
P3[3]
QFN
(Top View)
9
10111213141516
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
32313029282726
25
Vss
P0[3]
P0[7]
Vdd
P0[6]
P0[4]
P0[2]
P3[1]
P1[7 ]
P0[0]
P2[6]
P3[0]
XRES
P1[5]
P1[3]
P1[1]
Vss
P1[0]
P1[2]
P1[4]
P1[6]
P2[4]
P2[2]
P2[0]
P3[2]
P0[5]
Figure 2. CY7C60445 32-Pin enCoRe V LV Device
Table 2. 32-Pin Part Pinout (QFN)
Pin No. Type Name Description
1 IOH P0[1] Digital I/O
2 I/O P2[7] Digital I/O
3 I/O P2[5] Digital I/O, Crystal Out (Xout)
4 I/O P2[3] Digital I/O, Crystal In (Xin)
5 I/O P2[1] Digital I/O
6 I/O P3[3] Digital I/O
7 I/O P3[1] Digital I/O
8 IOHR P1[7] Digital I/O, I2C SCL, SPI SS
9 IOHR P1[5] Digital I/O, I2C SDA, SPI MISO
10 IOHR P1[3] Digital I/O, SPI CLK
11 IOHR P1[1]
12 Power Vss Ground connection
13 IOHR P1[0]
14 IOHR P1[2] Digital I/O
15 IOHR P1[4] Digital I/O, optional external clock input (EXTCLK)
16 IOHR P1[6] Digital I/O
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
Digital I/O, ISSP CLK, I2C SCL, SPI MOSI
Digital I/O, ISSP DATA, I2C SDA, SPI CLK
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 7 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 8
CY7C604XX
Table 2. 32-Pin Part Pinout (QFN) (continued)
Notes
3. During power up or reset event, device P1[0] and P1[1] may disturb the I2C bus. Use alternate pins if issues are encountered.
4. These are the in-system serial programming (ISSP) pins, that are not High Z at power on reset (POR)
Pin No. Type Name Description
17 Reset Input XRES Active high external reset with internal pull down
18 I/O P3[0] Digital I/O
19 I/O P3[2] Digital I/O
20 I/O P2[0] Digital I/O
21 I/O P2[2] Digital I/O
22 I/O P2[4] Digital I/O
23 I/O P2[6] Digital I/O
24 IOH P0[0] Digital I/O
25 IOH P0[2] Digital I/O
26 IOH P0[4] Digital I/O
27 IOH P0[6] Digital I/O
28 Power Vdd Supply voltage
29 IOH P0[7] Digital I/O
30 IOH P0[5] Digital I/O
31 IOH P0[3] Digital I/O
32 Power Vss Ground connection
CP Power Vss Center pad must be connected to ground
LEGEND I = Input, O = Output, OH = 5 mA High Output Drive, R = Regulated Output.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 8 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 9
CY7C604XX
48-Pin Part Pinout
QFN
(Top V ie w )
P0[1]
Vss
P0[3]
P0[5]
P0[7]
Vdd
P0[6]
10
11
12
P2[7]
P2[5]
P2[3]
P2[1]
P4[3]
P4[1]
P3[7]
P3[5]
P3[3]
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
36
4847464544
43424140393837
P0[2]
P0[0]
P2[6]
P2[4]
P2[2]
P2[0]
P3[2]
P3[0]
XRES
P1[6]
P0[4]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
131415161718192021
22
23
24
NC
NC
P1[3]
P1[1]
Vss
NC
NC
Vdd
P1[0]
P1[2]
P1[4]
NC
P3[1]
P1[7]
P1[5]
P3[4]
P3[6]
P4[0]
P4[2]
NC
NC
Figure 3. CY7C60455/CY7C60456 48-Pin enCoRe V LV Device
Table 3. 48-Pin Part Pinout (QFN)
Pin No. Type Name Description
1NCNC No connection
2 I/O P2[7] Digital I/O
3 I/O P2[5] Digital I/O, Crystal Out (Xout)
4 I/O P2[3] Digital I/O, Crystal In (Xin)
5 I/O P2[1] Digital I/O
6 I/O P4[3] Digital I/O
7 I/O P4[1] Digital I/O
8 I/O P3[7] Digital I/O
9 I/O P3[5] Digital I/O
10 I/O P3[3] Digital I/O
11 I/O P3[1] Digital I/O
12 IOHR P1[7] Digital I/O, I2C SCL, SPI SS
13 IOHR P1[5] Digital I/O, I2C SDA, SPI MISO
14 NC NC No connection
15 NC NC No connection
16 IOHR P1[3] Digital I/O, SPI CLK
17 IOHR P1[1]
(3, 4)
Digital I/O, ISSP CLK, I2C SCL, SPI MOSI
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 9 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 10

CY7C604XX
Table 3. 48-Pin Part Pinout (QFN) (continued)
Pin No. Type Name Description
18 Power Vss Supply ground
19 NC NC No connection
20 NC NC No connection
21 Power Vdd Supply voltage
22 IOHR P1[0]
(3, 4)
Digital I/O, ISSP DATA, I2C SDA, SPI CLK
23 IOHR P1[2] Digital I/O
24 IOHR P1[4] Digital I/O, optional external clock inpu t (EXTCLK)
25 IOHR P1[6] Digital I/O
26 XRES Ext Reset Active high external reset with internal pull down
27 I/O P3[0] Digital I/O
28 I/O P3[2] Digital I/O
29 I/O P3[4] Digital I/O
30 I/O P3[6] Digital I/O
31 I/O P4[0] Digital I/O
32 I/O P4[2] Digital I/O
33 I/O P2[0] Digital I/O
34 I/O P2[2] Digital I/O
35 I/O P2[4] Digital I/O
36 I/O P2[6] Digital I/O
37 IOH P0[0] Digital I/O
38 IOH P0[2] Digital I/O
39 IOH P0[4] Digital I/O
40 IOH P0[6] Digital I/O
41 Power Vdd Supply voltage
42 NC NC No connection
43 NC NC No connection
44 IOH P0[7] Digital I/O
45 IOH P0[5] Digital I/O
46 IOH P0[3] Digital I/O
47 Power Vss Supply ground
48 IOH P0[1] Digital I/O
CP Power Vss Center pad must be connected to ground
LEGEND I = Input, O = Output, OH = 5 mA High Output Drive, R = Regulated Output
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 10 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 11

CY7C604XX
Register Reference
The section discusses the registers of the enCoRe V LV device. It lists all the registers in mapping tables, in address order.
Register Conventions
The register conventions specific to this section are listed in the
following table.
Table 4. Register Conventions
Convention Description
R Read register or bits
W Write register or bits
L Logical register or bits
C Clearable register or bits
# Access is bit specific
Register Mapping Tables
The enCoRe V LV device has a total register address space of
512 bytes. The register space is also referred to as IO space and
is broken into two parts: Bank 0 (user space) and Bank 1 (configuration space). The XIO bit in the Flag register (CPU_F) determines which bank the user is currently in. When the XIO bit is
set, the user is said to be in the “extended” address space or the
“configuration” registers.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 11 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 12

CY7C604XX
Table 5. Register Map Bank 0 Table: User Space
Name Addr (0,Hex) Access Name Addr (0,Hex) Access Name Addr (0,Hex) Access Name Addr (0,Hex) Access
PRT0DR 00 RW 40 80 C0
PRT0IE 01 RW 41 81 C1
PRT1DR 04 RW 44 84 C4
PRT1IE 05 RW 45 85 C5
PRT2DR 08 RW 48 88 I2C_XCFG C8 RW
PRT2IE 09 RW 49 89 I2C_XSTAT C9 R
PRT3DR 0C RW 4C 8C I2C_CP CC R
PRT3IE 0D RW 4D 8D CPU_BP CD RW
PRT4DR 10 RW 50 90 CUR_PP D0 RW
PRT4IE 11 RW 51 91 STK_PP D1 RW
SPI_TXR 29 W 69 A9 E9
SPI_RXR 2A R 6A AA EA
SPI_CR 2B # 6B AB EB
Gray fields are reserved and should not be accessed. # Access is bit specific.
02 42 82 C2
03 43 83 C3
06 46 86 C6
07 47 87 C7
0A 4A 8A I2C_ADDR CA RW
0B 4B 8B I2C_BP CB R
0E 4E 8E CPU_CP CE R
0F 4F 8F I2C_BUF CF RW
12 52 92 D2
13 53 93 IDX_PP D3 RW
14 54 94 MVR_PP D4 RW
15 55 95 MVW_PP D5 RW
16 56 96 I2C_CFG D6 RW
17 57 97 I2C_SCR D7 #
18 58 98 I2C_DR D8 RW
19 59 99 D9
1A 5A 9A INT_CLR0 DA RW
1B 5B 9B INT_CLR1 DB RW
1C 5C 9C INT_CLR2 DC RW
1D 5D 9D INT_CLR3 DD RW
1E 5E 9E INT_MSK2 DE RW
1F 5F 9F INT_MSK1 DF RW
20 60 A0 INT_MSK0 E0 RW
21 61 A1 INT_SW_EN E1 RW
22 62 A2 INT_VC E2 RC
23 63 A3 RES_WDT E3 W
24 64 A4 INT_MSK3 E4 RW
25 65 A5 E5
26 66 A6 E6
27 67 A7 E7
28 68 A8 E8
2C 6C AC EC
2D 6D AD ED
2E 6E AE EE
2F 6F AF EF
30 70 PT0_CFG B0 RW F0
31 71 PT0_DAT A1 B1 RW F1
32 72 PT0_DAT A0 B2 RW F2
33 73 PT1_CFG B3 RW F3
34 74 PT1_DAT A1 B4 RW F4
35 75 PT1_DAT A0 B5 RW F5
36 76 PT2_CFG B6 RW F6
37 77 PT2_DAT A1 B7 RW CPU_F F7 RL
38 78 PT2_DAT A0 B8 RW F8
39 79 B9 F9
3A 7A BA FA
3B 7B BB FB
3C 7C BC FC
3D 7D BD FD
3E 7E BE CPU_SCR1 FE #
3F 7F BF CPU_SCR0 FF #
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 12 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 13

CY7C604XX
Table 6. Register Map Bank 1 Table: Configuration Space
Name Addr (1,Hex) Access Name Addr (1,Hex) Access Name Addr (1,Hex) Access Name Addr (1,Hex) Access
PRT0DM0 00 RW 40 80 C0
PRT0DM1 01 RW 41 81 C1
PRT1DM0 04 RW 44 84 C4
PRT1DM1 05 RW 45 85 C5
PRT2DM0 08 RW 48 88 C8
PRT2DM1 09 RW 49 89 C9
PRT3DM0 0C RW 4C 8C CC
PRT3DM1 0D RW 4D 8D CD
PRT4DM0 10 RW 50 90 D0
PRT4DM1 11 RW 51 91 D1
SPI_CFG 29 RW 69 A9 ILO_TR E9 W
Gray fields are reserved and should not be accessed. # Access is bit specific.
02 42 82 C2
03 43 83 C3
06 46 86 C6
07 47 87 C7
0A 4A 8A CA
0B 4B 8B CB
0E 4E 8E CE
0F 4F 8F CF
12 52 92 D2
13 53 93 D3
14 54 94 D4
15 55 95 D5
16 56 96 D6
17 57 97 D7
18 58 98 D8
19 59 99 D9
1A 5A 9A DA
1B 5B 9B DB
1C 5C 9C IO_CFG DC RW
1D 5D 9D OUT_P1 DD RW
1E 5E 9E DE
1F 5F 9F DF
20 60 A0 OSC_CR0 E0 RW
21 61 A1 ECO_CFG E1 #
22 62 A2 OSC_CR2 E2 RW
23 63 A3 VL T_CR E3 RW
24 64 A4 VL T_CMP E4 R
25 65 A5 E5
26 66 A6 E6
27 67 A7 E7
28 68 A8 IMO_TR E8 W
2A 6A AA EA
2B 6B AB SLP_CFG EB RW
2C TMP_DR0 6C RW AC SLP_CFG2 EC RW
2D TMP_DR1 6D RW AD SLP_CFG3 ED RW
2E TMP_DR2 6E RW AE EE
2F TMP_DR3 6F RW AF EF
30 70 B0 F0
31 71 B1 F1
32 72 B2 F2
33 73 B3 F3
34 74 B4 F4
35 75 B5 F5
36 76 B6 F6
37 77 B7 CPU_F F7 RL
38 78 B8 F8
39 79 B9 F9
3A 7A BA FA
3B 7B BB FB
3C 7C BC FC
3D 7D BD FD
3E 7E BE FE
3F 7F BF FF
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 13 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 14

CY7C604XX
Electrical Specifications
3.6V
750 kHz
24 MHz
CPU Frequency
Vdd Voltage
1.71V
3 MHz
V
a
l
i
d
O
p
e
r
a
t
i
n
g
R
e
g
i
o
n
3.6V
750 kHz 6 MHz 24 MHz
IMO Frequency
Vdd Voltage
3 MHz
1.71V
SLIMO
Mode
= 01
12 MHz
SLIMO
Mode
= 00
SLIMO
Mode
= 10
This section presents the DC and AC electrical specifications of the enCoRe V LV devices. For the most up to date electrical
specifications, verify that you have the most recent data sheet available by visiting the company web site at http://www.cypress.com.
Figure 4. Voltage versus CPU Frequency Figure 5. IMO Frequency Trim Options
The following table lists the units of measure that are used in this chapter.
Table 7. Units of Measure
Symbol Unit of Measure Symbol Unit of Measure
o
C degree Celsius μW microwatts
dB decibels mA milli-ampere
fF femto farad ms milli-second
Hz hertz mV milli-volts
KB 1024 bytes nA nanoampere
Kbit 1024 bi ts ns nanosecond
kHz kilohertz nV nanovolts
kΩ kilohm Ω ohm
MHz megahertz pA picoampere
MΩ megaohm pF picofarad
μA microampere pp peak-to-peak
μF microfarad ppm parts per million
μH microhenry ps picosecond
μs microsecond sps samples per second
μV microvolts s sigma: one standard deviation
μVrms microvolts root-mean-square V volts
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 14 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 15

CY7C604XX
ADC Electrical Specifications
Table 8. ADC Electrical Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Input
Input Voltage Range Vss 1.3 V This gives 72% of maximum code
Input Capacitance 5 pF
Resolution 8 Bits
8-Bit Sample Rate 23.4375 ksps Data Clock set to 6 MHz. Sample Rate
= 0.001/(2^Resolution/Data clock)
DC Accuracy
DNL -1 +2 LSb For any configuration
INL -2 +2 LSb For any configuration
Offset Error 0 15 90 mV
Operating Current 275 350 μA
Data Clock 2.25 12 MHz Source is chip’s internal main oscillator.
Monotonicity Not guaranteed. See DNL
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSRR (Vdd>3.0V) 24 dB
PSRR (2.2 < Vdd < 3.0) 30 dB
PSRR (2.0 < Vdd < 2.2) 12 dB
PSRR (Vdd < 2.0) 0 dB
Gain Error 1 5 %FSR For any resolution
Input Resistance 1/(500fF*D
ata-Clock)
1/(400fF*D
ata-Clock)
1/(300fF*D
ata-Clock)
See AC Chip Level Specifications for
accuracy.
Ω Equivalent switched cap input resis-
tance for 8-, 9-, or 10-bit resolution.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 15 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY7C604XX
(6)
Notes
5. Higher storage temperatures reduce data retention ti me. Reco mmended storage tempe rature is +25°C ± 25°C. Extende d duration sto rage temperat ures above 85°C
degrade reliability.
6. Human Body Model ESD.
7. According to JESD78 standard.
8. The temperature rise from ambient to junction is package specific. See on page 27. The user must limit the power consumption to comply with this requirement.
Maximum Ratings
Storage Temperature (T
Supply Voltage Relative to Vss (Vdd)............. -0.5V to +4.0V
DC Input Voltage (V
IO
DC Voltage Applied to Tri-state (V
Maximum Current into any Port Pin (I
(5)
)
-55oC to 125oC (Typical +25oC)
STG
)....................Vss - 0.5V to Vdd + 0.5V
)Vss - 0.5V to Vdd + 0.5V
IOZ
). -25mA to +50 mA
MIO
Electro Static Discharge Voltage (ESD)
Latch-up Current (LU)
(7)
...........................................200 mA
Operating Conditions
Ambient Temperature (TA)..................................0oC to 70oC
Operational Die Temperature (TJ)
(8)
..................2000V
...................0oC to 85oC
DC Electrical Characteristics
DC Chip Level Specifications
Table 9 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 9. DC Chip Level Specifications
Parameter Description Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Vdd Supply Voltage See table titled DC POR and LVD
Specifications on page 20.
I
DD24
Supply Current, IMO = 24 MHz Conditions are Vdd = 3.0V, TA = 25oC,
CPU = 24 MHz
No I2C/SPI
I
DD12
Supply Current, IMO = 12 MHz Conditions are Vdd = 3.0V, TA = 25oC,
CPU = 12 MHz
No I2C/SPI
I
DD6
Supply Current, IMO = 6 MHz Conditions are Vdd = 3.0V, TA = 25oC,
CPU = 6 MHz
No I2C/SPI
I
SB0
I
SB1
Deep Sleep Current Vdd = 3.0V, TA = 25oC, IO regulator
turned off
Standby Current with POR, LVD, and
Sleep Timer
Vdd = 3.0V, TA = 25oC, IO regulator
turned off
1.71 – 3.6 V
– – 3.1 mA
– – 2.0 mA
– – 1.5 mA
– 0.1 – μA
– – 1.5 μA
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 16 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 17

CY7C604XX
DC General Purpose I/O Specifications
The following tables list guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the voltage and temperature ranges: 1.71V to 3.6V and
0°C ≤ T
Table 10. 3.0V to 3.6V DC GPIO Specifications
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ Max Units
R
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
I
C
≤ 70°C. Typical parameters apply to 3.3V at 25°C. These are for design guidance only.
A
PU
OH1
OH2
OH3
Pull Up Resistor 4 5.6 8 kΩ
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH < 10 μA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
IOH = 1 mA, maximum of 20 mA source
current in all I/Os
IOH < 10 μA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
Disabled for Port 1
OH4
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH = 5 mA, maximum of 20 mA source
current in all I/Os
Disabled for Port 1
OH5
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH < 10 μA, Vdd > 3.1V, maximum of 4
I/Os all sourcing 5 mA
Enabled for 3V Out
OH6
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH = 5 mA, Vdd > 3.1V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
Enabled for 3V Out
OH7
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 2.5V
IOH < 10 μA, Vdd > 2.7V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
Out
OH8
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 2.5V
IOH = 2 mA, Vdd > 2.7V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
Out
OH9
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 1.8V
IOH < 10 μA, Vdd > 2.7V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
Out
OH10
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 1.8V
IOH = 1 mA, Vdd > 2.7V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
Out
OL
Low Output Voltage IOL = 25 mA, Vdd > 3.3V , maximum of 60
mA sink current on even port pins (for
example, P0[2] and P1[4]) and 60 mA sink
current on odd port pins (for example,
P0[3] and P1[5])
IL
IH
H
IL
PIN
Input Low Voltage – – 0.80 V
Input High Voltage 2.00 – V
Input Hysteresis Voltage – 80 – mV
Input Leakage (Absolute Value) – 0.001 1 µA
Pin Capacitance Package and pin dependent
Temp = 25
o
C
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Vdd - 0.9 – – V
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Vdd - 0.9 – – V
2.85 3.00 3.3 V
2.20 – – V
2.35 2.50 2.75 V
1.90 – – V
1.60 1.80 2.1 V
1.20 – – V
––0.75V
0.5
1.7 5 pF
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 17 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 18

CY7C604XX
Table 11. 2.4V to 3.0V DC GPIO Specifications
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ Max Units
R
V
V
V
PU
OH1
OH2
OH3
Pull Up Resistor 4 5.6 8 kΩ
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH < 10 μA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
IOH = 0.2 mA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
IOH < 10 μA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Vdd - 0.4 – – V
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Disabled for Port 1
V
OH4
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH = 2 mA, maximum of 10 mA source
current in all I/Os
Vdd - 0.5 – – V
Disabled for Port 1
V
OH5A
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 1.8V
IOH < 10 μA, Vdd > 2.4V , maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os.
1.50 1.80 2.10 V
Out
V
OH6A
High Output Voltage
Port 1 Pins with LDO Enabled for 1.8V
IOH = 1 mA, Vdd > 2.4V, maximum of 20
mA source current in all I/Os
1.20 – – V
Out
V
OL
Low Output Voltage IOL = 10 mA, maximum of 30 mA sink
current on even port pins (for example,
––0.75V
P0[2] and P1[4]) and 30 mA sink current
on odd port pins (for example, P0[3] and
P1[5])
V
IL
V
IH
V
H
I
IL
C
PIN
Input Low Voltage – – 0.72 V
Input High Voltage 1.6 – V
Input Hysteresis Voltage – 80 – mV
Input Leakage (Absolute Value) – 0.001 1 µA
Capacitive Load on Pins Package and pin dependent
Temp = 25
o
C
0.5
1.7 5 pF
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 18 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 19

CY7C604XX
Table 12. 1.71V to 2.4V DC GPIO Specifications
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ Max Units
R
V
V
V
PU
OH1
OH2
OH3
Pull Up Resistor 4 5.6 8 kΩ
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 2 or 3 Pins
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH = 10 μA, maximum of 10 mA
source current in all I/Os
IOH = 0.5 mA, maximum of 10 mA
source current in all I/Os
IOH = 100 μA, maximum of 10 mA
source current in all I/Os
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Vdd - 0.5 – – V
Vdd - 0.2 – – V
Disabled for Port 1
V
OH4
High Output Voltage
Port 0 or 1 Pins with LDO Regulator
IOH = 2 mA, maximum of 10 mA
source current in all I/Os
Vdd - 0.5 – – V
Disabled for Port 1
V
OL
Low Output Voltage IOL = 5 mA, maximum of 20 mA sink
current on even port pins (for
––0.4V
example, P0[2] and P1[4]) and 30 mA
sink current on odd port pins (for
example, P0[3] and P1[5])
V
IL
V
IH
V
H
I
IL
C
PIN
Input Low Voltage – – 0.3 x Vdd V
Input High Voltage 0.65 x Vdd – V
Input Hysteresis Voltage – 80 – mV
Input Leakage (Absolute Value) – 0.001 1 µA
Capacitive Load on Pins Package and pin dependent.
Temp = 25
o
C
0.5
1.7 5 pF
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 19 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 20

CY7C604XX
DC POR and LVD Specifications
Notes
9. Vdd must be greater than or equal to 1.71V during startup, reset from the XR ES pin, or reset from watchdog.
10.Always greater than 50 mV above V
PPOR1
for falling supply.
11.Always greater than 50 mV above V
PPOR2
for falling supply.
12.Always greater than 50 mV above V
PPOR3
for falling supply.
13.Always greater than 50 mV above V
PPOR0
voltage for falling supply.
14.Driving internal pull down resistor.
15.See appropriate DC General Purpose I/O Specifications table. Fo r Vdd > 3V use V
OH4
in Table 10 on page 17
16.Erase/write cycles per block.
17.Following maximum Flash write cycles at Tamb = 55C and Tj = 70C.
Table 13 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 13. DC POR and LVD Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
(9)
1.61 1.66
2.36
2.60
2.82
2.40
2.64
2.85
2.95
3.06
1.84
1.75
2.45
2.71
2.92
3.02
3.13
1.9
1.8
1.71
2.41
2.66
2.95
2.51
2.78
2.99
3.09
3.20
2.32
1.84
V
PPOR0
V
PPOR1
V
PPOR2
V
PPOR3
V
LVD0
V
LVD1
V
LVD2
V
LVD3
V
LVD4
V
LVD5
V
LVD6
Vdd Va lue for PPOR Trip
PORLEV[1:0] = 00b, HPOR = 0
PORLEV[1:0] = 00b, HPOR = 1
PORLEV[1:0] = 01b, HPOR = 1
PORLEV[1:0] = 10b, HPOR = 1
Vdd Value for LVD Trip
VM[2:0] = 000b
VM[2:0] = 001b
VM[2:0] = 010b
(10)
(11)
(12)
VM[2:0] = 011b
VM[2:0] = 100b
VM[2:0] = 101b
VM[2:0] = 110b
(13)
DC Programming Specifications
Table 14 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 14. DC Programming Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
Vdd
I
DDP
V
ILP
V
IHP
I
ILP
I
IHP
V
OLV
V
OHV
Flash
Flash
IWRITE
ENPB
DR
Supply Voltage for Flash Write Operations 1.71 – – V
Supply Current During Programming or Verify – 5 25 mA
Input Low Voltage During Programming or Verify – – V
Input High Voltage During Programming or Verify V
Input Current when Applying Vilp to P1[0] or P1[1] During
Programming or Verify
Input Current when Applying Vihp to P1[0] or P1[1]
During Programming or Verify
(14)
(14)
IH
– – 0.2 mA
– – 1.5 mA
– – V
IL
Output Low Voltage During Programming or Verify – – Vss + 0.75 V
Output High Voltage During Programming or Verify V
Flash Write Endurance
Flash Data Retention
(16)
(17)
OH
(13)
– Vdd V
50,000 – – Cycles
10 20 – Years
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 20 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 21

CY7C604XX
AC Electrical Characteristics
Notes
18.Digital clocking functions.
19.CPU speed.
20.Trimmed using factory trim values.
AC Chip Level Specifications
Table 15 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 15. AC Chip Level Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
F
MAX
F
CPU
F
32K1
F
IMO24
F
IMO12
F
IMO6
DC
T
RAMP
IMO
Maximum Operating Frequency
Maximum Processing Frequency
Internal Low Speed Oscillator Frequency 19 32 50 kHz
Internal Main Oscillator Stability for 24 MHz ± 5%
Internal Main Oscillator Stability for 12 MHz
Internal Main Oscillator Stability for 6 MHz
Duty Cycle of IMO 40 50 60 %
Supply Ramp Time 0 – – μs
(18)
(19)
(20)
(20)
(20)
24 – – MHz
24 – – MHz
22.8 24 25.2 MHz
11.4 12 12.6 MHz
5.7 6.0 6.3 MHz
AC General Purpose IO Specifications
Table 16 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 16. AC GPIO Specifications
Symbol Description Conditions Min Typ Max Units
F
GPIO
TRise23 Rise Time, Strong Mode, Cload
TRise23L Rise Time, Strong Mode Low
TRise01 Rise Time, Strong Mode, Cload
TRise01L Rise Time, Strong Mode Low
TFall Fall Time, S trong Mode, Cload =
GPIO Operating Frequency Normal Strong Mode, Port 0, 1 0
Normal Strong Mode, Port 2, 3 0 - 3 MHz for
Vdd = 3.0 to 3.6V, 10% – 90%
= 50 pF
Ports 2 or 3
Vdd = 2.4 to 3.0V, 10% – 90%
Vdd = 1.71 to 3.0V, 10% – 90% 15 – 100 ns
Supply, Cload = 50 pF
Ports 2 or 3
Vdd = 3.0 to 3.6V, 10% – 90%
= 50 pF
LDO enabled or disabled
Ports 0 or 1
Vdd = 2.4 to 3.0V, 10% – 90%
LDO enabled or disabled
Vdd = 1.71 to 3.0V, 10% – 90%
Supply, Cload = 50 pF
LDO enabled or disabled
Ports 0 or 1
Vdd = 3.0 to 3.6V, 10% – 90%
50 pF
All Ports
Vdd = 1.71 to 3.0V, 10% - 90%
–
6 MHz for
1.71V<Vdd<2.4V
0
–
12 MHz for
2.4V<Vdd<3.6V
1.71V<Vdd<2.4V
6 MHz for
3.0V<Vdd<3.6V
15
15
10
10
–
–
–
–
80
100
50
70
15 – 100 ns
10
10
–
–
80
80
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 21 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 22

CY7C604XX
Figure 6. GPIO Timing Diagram
TFall
TRise23
TRise01
90%
10%
GPIO Pin
Output
Voltage
AC External Clock Specifications
Table 17 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 17. AC External Clock Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
F
OSCEXT
– High Period 20.6
– Low Period 20.6
– Power Up IMO to Switch 150 – – μs
Frequency 0.750 – 25.2 MHz
– 5300 ns
– –ns
AC Programming Specifications
Table 18 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 18. AC Programming Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
T
RSCLK
T
FSCLK
T
SSCLK
T
HSCLK
F
SCLK
T
ERASEB
T
WRITE
T
DSCLK1
T
DSCLK2
Rise Time of SCLK 1 – 20 ns
Fall Time of SCLK 1 – 20 ns
Data Set up Time to Falling Edge of SCLK 40 – – ns
Data Hold Time from Falling Edge of SCLK 40 – – ns
Frequency of SCLK 0 – 8 MHz
Flash Erase Time (Block) – – 18 ms
Flash Block Write Time – – 25 ms
Data Out Delay from Falling Edge of SCLK,
– – 85 ns
3.0V<Vdd<3.6V
Data Out Delay from Falling Edge of SCLK,
– – 130 ns
1.71V<Vdd<3.0V
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 22 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 23

CY7C604XX
Figure 7. Timing Diagram - AC Programming Cycle
Notes
21.Output clock frequency is half of input clock rate.
AC SPI Specifications
Table 19 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
Table 19. AC SPI Specifications
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
F
F
T
SPIM
SPIS
SS
Maximum Input Clock Frequency Selection, Master
2.4V<Vdd<3.6V
Maximum Input Clock Frequency Selection, Master
1.71V<Vdd<2.4V
Maximum Input Clock Frequency Selection, Slave
2.4V<Vdd<3.6V
Maximum Input Clock Frequency Selection, Slave
1.71V<Vdd<2.4V
Width of SS_ Negated Between Transmissions 50 – – ns
(21)
(21)
– – 12
- - 6
– – 12
– – 6
MHz
MHz
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 23 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 24

CY7C604XX
AC I2C Specifications
SDA
SCL
S
Sr SP
T
BUFI2C
T
SPI2C
T
HDSTAI2C
T
SUSTOI2C
T
SUSTAI2C
T
LOWI2C
T
HIGHI2C
T
HDDATI2C
T
HDSTAI2C
T
SUDATI2C
Notes
22.A fast mode I2C bus device can be used in a standard mode I2C bus system, but the requirement t
SU;DAT
Š 250 ns must then be met. This is automatically the case
if the device does not stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal. If su ch device does stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal, it must output the next data bit to the
SDA line t
rmax
+ t
SU;DAT
= 1000 + 250 = 1250 ns (according to the standard mode I2C bus specification) before the SCL line is released.
Table 20 lists guaranteed maximum and minimum specifications for the entire voltage and temperature ranges.
2
Table 20. AC Characteristics of the I
Symbol Description
F
SCLI2C
T
HDSTAI2C
T
LOWI2C
T
HIGHI2C
T
SUSTAI2C
T
HDDATI2C
T
SUDATI2C
T
SUSTOI2C
T
BUFI2C
T
SPI2C
SCL Clock Frequency 0 100 0 400 kHz
Hold Time (repeated) ST ART Condition. After this period,
the first clock pulse is generated.
LOW Period of the SCL Clock 4.7 –1.3– μs
HIGH Period of the SCL Clock 4.0 –0.6– μs
Setup Time for a Repeated START Condition 4.7 –0.6– μs
Data Hold Time 0 –0– μs
Data Setup Time 250 –100
Setup Time for STOP Condition 4.0 –0.6– μs
Bus Free Time Between a STOP and START Condition 4.7 –1.3– μs
Pulse Width of Spikes are Suppressed by the Input Filter – – 0 50 ns
Figure 8. Definition of Timing for Fast/Standard Mode on the I
C SDA and SCL Pins
Standard Mode Fast Mode
Min Max Min Max
4.0 –0.6– μs
(22)
2
C Bus
Units
–ns
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 24 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 25

CY7C604XX
Package Diagram
001-09116 *D
This section illustrates the packaging specifications for the enCoRe V LV device, along with the thermal impedances for each package.
Important Note Emulation tools may require a larger area on the target PCB than the chip’s footprint. For a detailed description of
the enCoRe V LV emulation tools and their dimensions, refer to the development kit.
Packaging Dimensions
Figure 9. 16-Pin (3 x 3 mm) QFN (001-09116)
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 25 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 26

CY7C604XX
Figure 10. 32-Pin (5 x 5 x 0.55 mm) QFN (001-42168)
001-42168 *C
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 26 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 27

CY7C604XX
Figure 11. 48-Pin (7 x 7 x 0.9 mm) QFN (001-13191)
001-13191 *C
Package Handling
Some IC packages require baking before they are soldered onto a PCB to remove moisture that may have been absorbed after leaving
the factory. A label on the package has details about the actual bake temperature and the minimum bake time to remove this moisture.
The maximum bake time is the aggregate time that the parts exposed to the bake temperature. Exceeding this exposure may degrade
device reliability.
Table 21.Package Handling
Parameter Description Minimum Typical Maximum Unit
TBAKETEMP Bake Temperature 125 See package label
TBAKETIME Bake Time See package label 72 hours
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 27 of 30
o
C
[+] Feedback
Page 28

CY7C604XX
Thermal Impedances
Notes
23.T
J
= TA + Power x θ
JA.
24.To achieve the thermal impedance specified for the package, solder the center thermal pad to the PCB ground plane.
25.Higher temperatures may be required based on the solder melting point. T ypical tempe ratures for solder are 220 ± 5°C with Sn-Pb or 245 ± 5° C with Sn- Ag-Cu p aste.
Refer to the solder manufacturer specifications.
Package Typical θJA
(23)
16 QFN 32.69 oC/W
32 QFN
48 QFN
(24)
(24)
19.51 oC/W
17.68 oC/W
Solder Reflow Peak Temperature
Following is the minimum solder reflow peak temperature to achieve good solderability.
Package Minimum Peak Temperature
(25)
Maximum Peak Temperature
16 QFN 240oC 260oC
32 QFN 240oC 260oC
48 QFN 240oC 260oC
Ordering Information
Ordering Code Package Information Flash SRAM No. of GPIOs Target Applications
CY7C60413-16LKXC 16-Pin QFN (3x3 mm) 8K 1K 13 Feature-rich Wireless Mouse
CY7C64013-16LKXCT 16-Pin QFN (3X3 mm) 8K 1K 13 Feature-rich Wireless Mouse
CY7C60445-32LQXC 32-Pin QFN
(5x5x0.55 mm)
CY7C60445-32LQXCT 32-Pin QFN - (Tape and Reel)
(5x5x0.55 mm)
CY7C60455-48LTXC 48-Pin QFN
(7x7x0.9 mm)
CY7C60455-48LTXCT 48-Pin QFN - (Tape and Reel)
(7x7x0.9 mm)
CY7C60456-48LTXC 48-Pin QFN
(7x7x0.9 mm)
CY7C60456-48LTXCT 48-Pin QFN - (Tape and Reel)
(7x7x0.9 mm)
16K 1K 28 Feature-Rich Wireless Mouse
16K 1K 28 Feature-Rich Wireless Mouse
16K 1K 36 Mid-Tier Wireless Keyboard
16K 1K 36 Mid-Tier Wireless Keyboard
32K 2K 36 Feature-Rich Wireless
Keyboard
32K 2K 36 Feature-Rich Wireless
Keyboard
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 28 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 29

CY7C604XX
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C604XX, enCoRe™ V Low Voltage Microcontroller
Document Number: 001-12395
Rev. ECN No.
Orig. of
Change
** 626516 TYJ See ECN New data sheet
*A 735721 TYJ/ARI See ECN Added new block diagram, replaced TBDs, corrected values, updated pinout infor-
*B 1120504 ARI See ECN Corrected the description to pin 29 on T able 1, the Typ/Max values for I
*C 1225864 AESA/ARI See ECN Corrected the description to pin 13, 29 on Table 1 and 22,44 on Table 2.
*D 1446763 AESA See ECN Changed T
*E 1639963 AESA See ECN P ost to www.cypress.com
*F 2138889 TYJ/PYRS See ECN Updated Ordering Code table:
*G 2583853 TYJ/PYRS/
HMT
Submission
Date
Description of Change
mation, changed part number to reflect new specifications.
DC chip-level specifications, and the Min voltage value for Vdd
Programming Specifications table.
Corrected Flash Write Endurance minimum value in the DC Programming Specifications table.
Corrected the Flash Erase Time max value and the Flash Block Write Time max
value in the AC Programming Specifications table.
Implemented new latest template.
Added sections Register Reference, Register Conventions and Register Mapping
Tables. Corrected Max values on the DC Chip-Level Specifications table.
parameter, max value to 18ms in Table 13, AC Programming
Specification.
ERASEB
- Ordering code changed for 32-QFN package: From -32LKXC to -32LTXC
- Added a new package type – “LTXC” for 48-QFN
- Included Tape and Reel ordering code for 32-QFN and 48-QFN packages
Changed active current values at 24, 12 and 6MHz in table “DC Chip-Level Specifications”
- IDD24: 2.15 to 3.1mA
- IDD12: 1.45 to 2.0mA
- IDD6: 1.1 to 1.5mA
Added information on using P1[0] and P1[1] as the I2C interface during POR or
reset events
10/10/08 Converted from Preliminary to Final
ADC resolution changed from 10-bit to 8-bit
On Page1, SPI Master and Slave – speeds changed
Rephrased battery monitoring clause in page 1 to include “with external components”
Included ADC specifications table
Voh5, Voh7, Voh9 specs changed
Flash data retention – condition added to Note [15]
Input leakage spec changed to 25 nA max
Under AC Char, Frequency accuracy of ILO corrected
GPIO rise time for ports 0,1 and ports 2,3 made common
AC Programming specifications updated
Included AC Programming cycle timing diagram
AC SPI specification updated
Spec change for 32-QFN package
Input Leakage Current maximum value changed to 1 uA
Maximum specification for V
Minimum voltages for F
(Table 18)
Updated V
Updated Thermal impedance values for the packages - Table 20.
parameter in Table 13
OHV
SPIM
OH5A
and F
Update Development T ools, add Designing with PSoC Designer. Edit, fix links and
table format. Update TMs. Update maximum data in Table 12. DC POR and LVD
Specifications.
in the DC
IWRITE
parameter changed from 2.0 to 2.1V
specifications changed from 1.8V to 1.71V
SPIS
SB0
on the
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Page 29 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 30

CY7C604XX
Document Title: CY7C604XX, enCoRe™ V Low Voltage Microcontroller
Document Number: 001-12395
*H 2653717 DVJA/PYRS 02/04/09 Changed master page from CY7C60445, CY7C6045X to CY7C604XX.
Updated Features, Functional Overview, Development Tools, and Designing with
PSoC Designer sections.
Removed ‘GUI - graphical user interface’ from Document Conventions acronym
table.
Added Figure 1 and T able 1 (16-pin part information) to Pin Configurations section.
Removed ‘O - Only a read/write register or bits’ in Table 4
Edited T able 8: removed 10-bit resolution information and corrected units column.
Added Figure 9 (16-pin part information) to Package Dimensions section.
Added ‘Package Handling’ section.
Added 8K part ‘CY7C60413-16LKXC’ to Ordering Information.
Sales, Solutions, and Legal Information
Worldwide Sales and Design Support
Cypress maintains a worldwide network of offices, solution centers, manufacturer’s representatives, and distributors. T o find the office
closest to you, visit us at cypress.com/sales.
Products
PSoC psoc.cypress.com
Clocks & Buffers clocks.cypress.com
Wireless wireless.cypress.com
Memories memory.cypress.com
Image Sensors image.cypress.com
PSoC Solutions
General psoc.cypress.com/solutions
Low Power/Low Voltage psoc.cypress.com/low-power
Precision Analog psoc.cypress.com/precision-analog
LCD Drive psoc.cypress.com/lcd-drive
CAN 2.0b psoc.cypress.com/can
USB psoc.cypress.com/usb
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2006- 2009. The infor mation cont ain ed herein is subj ect to change wi thout notice. C ypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of
any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be us ed fo r
medical, life support, life saving, critica l contr o l or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreem en t w it h Cypr ess. Fu rth er mor e, Cypre ss does not author iz e it s pr o ducts for use as
critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or fa ilure may reasonably be expe cted to result in significa nt injury to the us er . The inclu sion of Cypress p roducts in life -support systems
application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign),
United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Cypress hereby gr ant s to l icense e a pers onal, no n-exclu sive , non-tr ansfer able license to copy, use, modify, crea te der ivative works of ,
and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for the sole purpose of creating custom software and or firmware in support of licensee product to be used only in conjunctio n with a Cypress
integrated circuit as specified in the ap plicable agreem ent. Any reprod uction, modificatio n, translation, co mpilation, or repr esentation of this Source Code except as specifi ed above is prohib ited without
the express written permission of Cypress.
Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to make changes without further notice to the materials descr ibed herein. Cypress does n ot
assume any liability arising out of the app licati on or use o f any pr oduct or circ uit de scribed herein . Cypr ess does n ot auth orize its p roducts fo r use as critical compon ents in life-su pport systems whe re
a malfunction or failure may reason ably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress’ product in a life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer
assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement.
Document Number: 001-12395 Rev *H Revised January 30, 2009 Page 30 of 30
enCoRe™, PSoC Designer™ and Programmable System - on - Ch i p™ are tr ad em ar ks an d PS oC ® is a re gistered trademark of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. All other tr ade m ar ks or re gi ster e d
trademarks referenced herein are property of the respective corporations. Purchase of I2C components from Cypress or one of its sublicensed Associated Companies conveys a license under the
Philips I2C Patent Rights to use these components in an I2C system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips. All products and company names
mentioned in this document may be the trademarks of their respective holders.
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...