Page 1
72-Mbit (2M x 36/4M x 18/1M x 72)
Flow-Through SRAM with NoBL™ Architecture
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Features
Functional Description
■ No Bus Latency™ (NoBL™) architecture eliminates dead
cycles between write and read cycles
■ Supports up to 133 MHz bus operations with zero wait states
■ Data transfers on every clock
■ Pin compatible and functionally equivalent to ZBT™ devices
■ Internally self timed output buffer control to eliminate the need
to use OE
■ Registered inputs for flow through operation
■ Byte Write capability
■ 2.5V IO supply (V
■ Fast clock-to-output times
❐ 6.5 ns (for 133-MHz device)
■ Clock Enable (CEN) pin to enable clock and suspend operation
■ Synchronous self timed writes
■ Asynchronous Output Enable (OE)
■ CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25 available in
DDQ
)
JEDEC-standard Pb-free 100-pin TQFP, Pb-free and
non-Pb-free 165-ball FBGA package. CY7C1475BV25
available in Pb-free and non-Pb-free 209-ball FBGA package.
■ Three Chip Enables (CE
expansion.
■ Automatic power down feature available using ZZ mode or CE
, CE2, CE3) for simple depth
1
deselect.
■ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan compatible
■ Burst Capability - linear or interleaved burst order
■ Low standby power
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
are 2.5V, 2M x 36/4M x 18/1M x 72 synchronous flow through
burst SRAMs designed specifically to support unlimited true
back-to-back read or write operations without the insertion of
wait states. The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and
CY7C1475BV25 are equipped with the advanced No Bus
Latency (NoBL) logic required to enable consecutive read or
write operations with data transferred on every clock cycle. This
feature dramatically improves the throughput of data through the
SRAM, especially in systems that require frequent write-read
transitions.
All synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled by
the rising edge of the clock. The clock inpu t is qualified by the
Clock Enable (CEN
) signal, which when deasserted suspends
operation and extends the previous clock cycle. Maximum
access delay from the clock rise is 6.5 ns (133-MHz device).
Write operations are controlled by two or four Byte Write Select
(BW
) and a Write Enable (WE) input. All writes are conducted
X
with on-chip synchronous self timed write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
) provide easy bank selection
, CE2, CE3) and an
1
and output tri-state control. To avoid bus contention, the output
drivers are synchronously tri-stated during the data portion of a
write sequence.
For best practice recommendations, refer to the Cypress application note AN1064, SRAM System Guidelines.
Selection Guide
Description 133 MHz 100 MHz Unit
Maximum Access Time 6.5 8.5 ns
Maximum Operating Current 305 275 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current 120 120 mA
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 198 Champion Court • San Jose, CA 95134-1709 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Revised February 29, 2008
[+] Feedback
Page 2
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
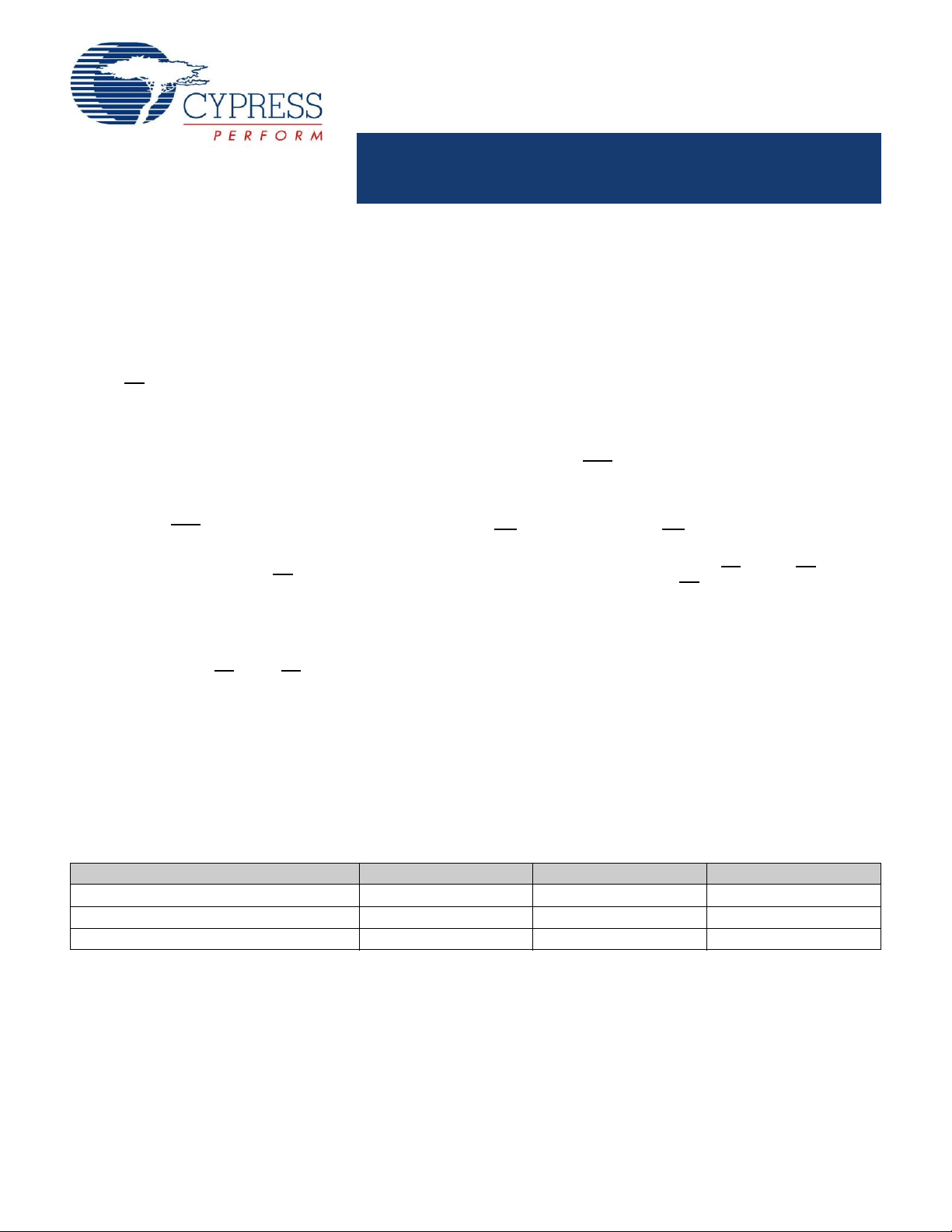
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1471BV25 (2M x 36)
ADDRESS
REGISTER
A1
A0
ADV/LD
C
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER
WRITE REGISTRY
AND DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
READ LOGIC
SLEEP
CONTROL
D1
D0
BURST
LOGIC
CLK
CEN
A0, A1, A
MODE
C
ADV/LD
BW
BW
BW
BW
WE
CE1
CE2
CE3
ZZ
CE
A
B
C
D
OE
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1473BV25 (4M x 18)
A1'
Q1
A0'
Q0
O
U
T
P
D
U
A
T
T
A
B
U
S
F
T
F
E
E
E
R
R
S
I
N
G
E
DQs
DQP
DQP
DQP
DQP
A
B
C
D
WRITE
DRIVERS
MEMORY
ARRAY
INPUT
REGISTER
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
E
CLK
C
EN
A0, A1, A
MODE
C
ADV/LD
BW A
BW B
WE
OE
CE1
CE2
CE3
ZZ
CE
ADDRESS
REGISTER
READ LOGIC
A1
D1
A0
D0
ADV/LD
C
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER
WRITE REGISTRY
AND DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
SLEEP
CONTROL
BURST
LOGIC
Q1
Q0
A1'
A0'
WRITE
DRIVERS
MEMORY
ARRAY
REGISTER
INPUT
O
U
T
P
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
D
U
A
T
T
A
B
U
S
F
T
F
E
E
E
R
R
S
I
N
E
DQs
DQP
DQPB
A
G
E
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 2 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 3
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
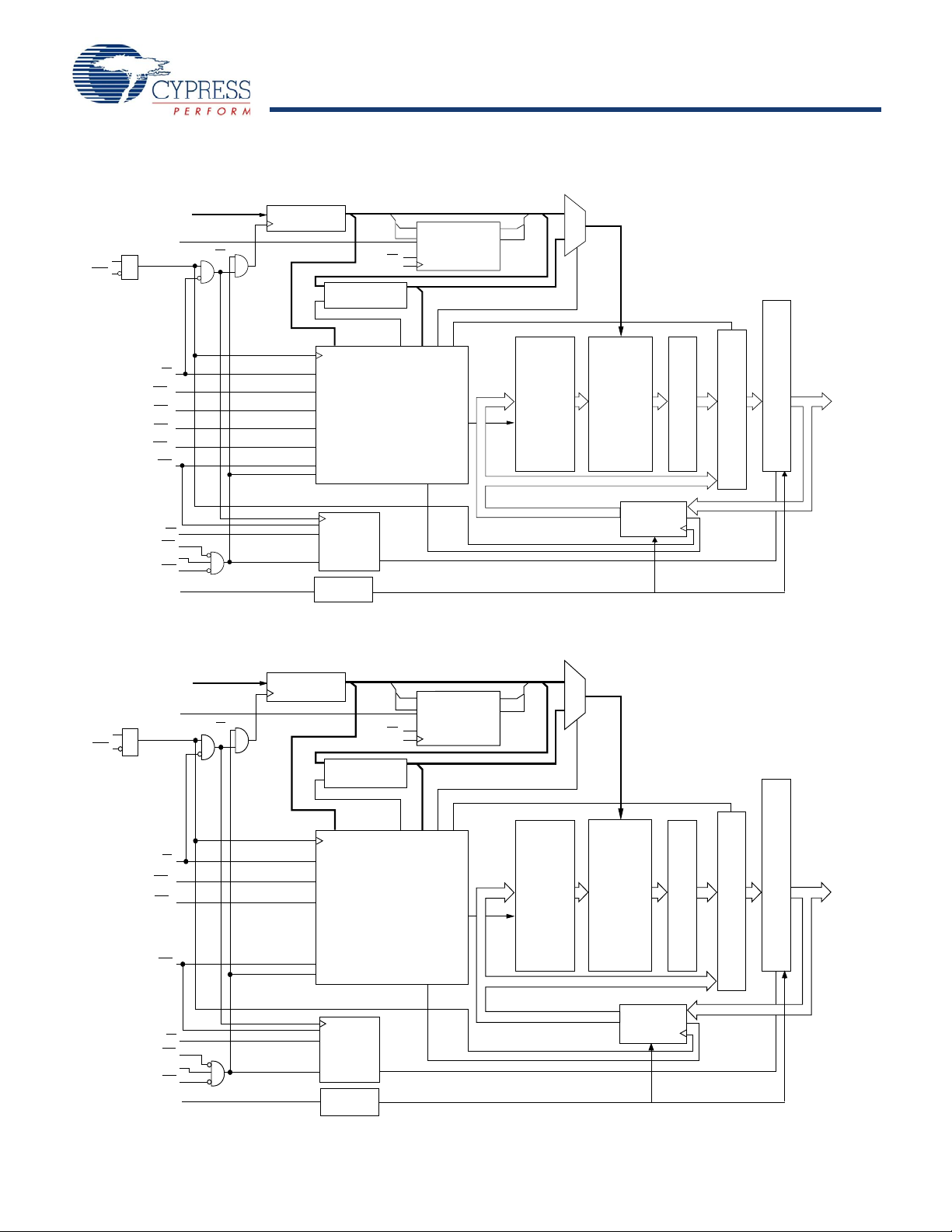
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1475BV25 (1M x 72)
A0, A1, A
C
MODE
CE1
CE2
CE3
OE
READ LOGIC
DQ s
DQ Pa
DQ Pb
DQ Pc
DQ Pd
DQ Pe
DQ Pf
DQ Pg
DQ Ph
D
A
T
A
S
T
E
E
R
I
N
G
O
U
T
P
U
T
B
U
F
F
E
R
S
MEMORY
ARRAY
E
E
INPUT
REGISTER 0
ADDRESS
REGISTER 0
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER 1
BURST
LOGIC
A0'
A1'
D1
D0
Q1
Q0
A0
A1
C
ADV/LD
ADV/LD
E
INPUT
REGISTER 1
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
O
U
T
P
U
T
R
E
G
I
S
T
E
R
S
E
CLK
CEN
WRITE
DRIVERS
BW
a
BW
b
WE
ZZ
BW
c
BW
d
BW
e
BW
f
BW
g
BW
h
Sleep Control
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER 2
WRITE REGISTRY
AND DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 3 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 4
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
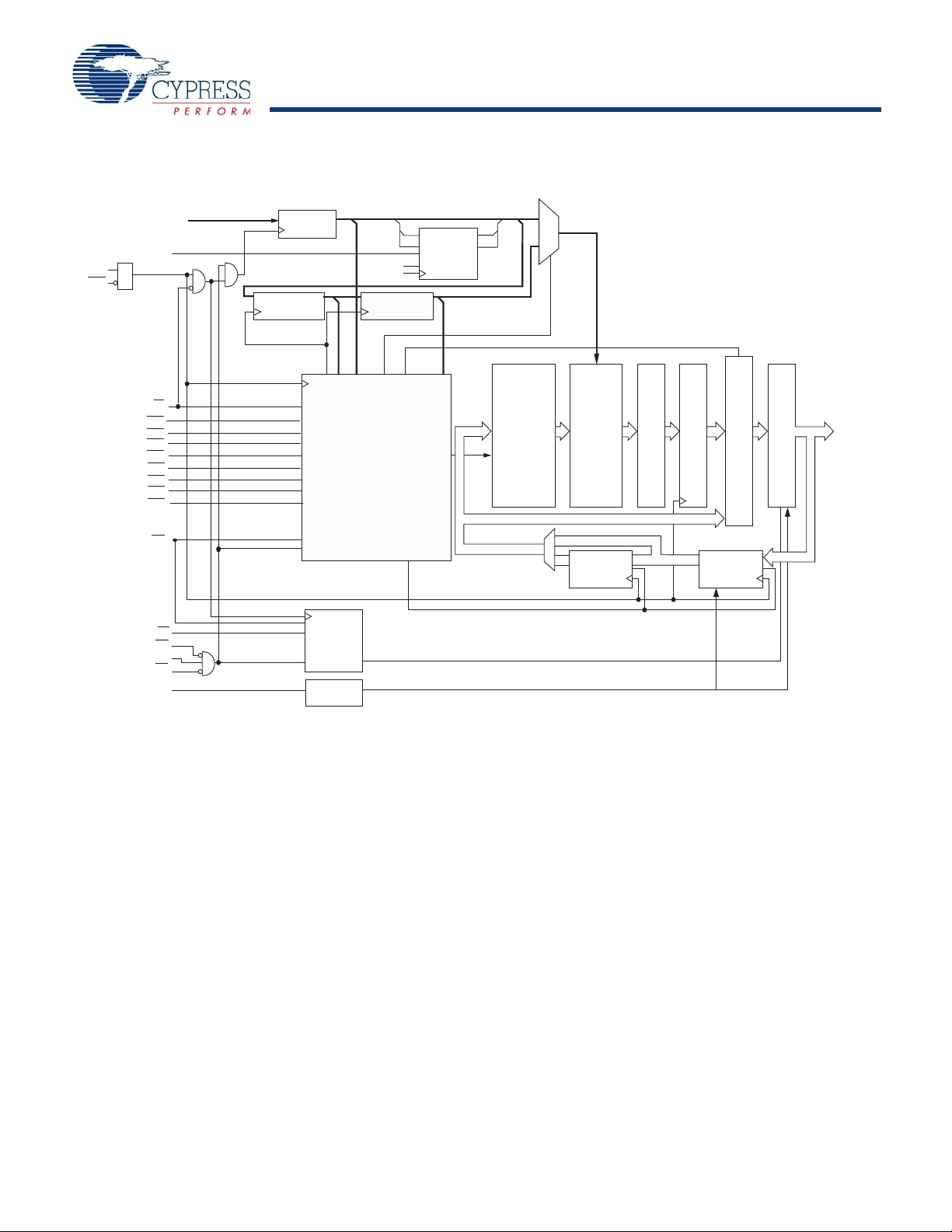
Pin Configurations
A
A
A
A
A1
A0
NC/288M
NC/144M
V
SS
V
DD
A
A
A
A
A
A
DQP
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
SS
NC
V
DD
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQP
A
DQP
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
C
DQ
C
NC
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
D
DQ
D
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQP
D
A
A
CE
1CE2
BWDBW
C
BWBBWACE3VDDV
SS
CLKWECEN
OE
A
A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
3132333435
36
37
38394041424344454647484950
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
100
9998979695949392919089
888786
85
848382
81
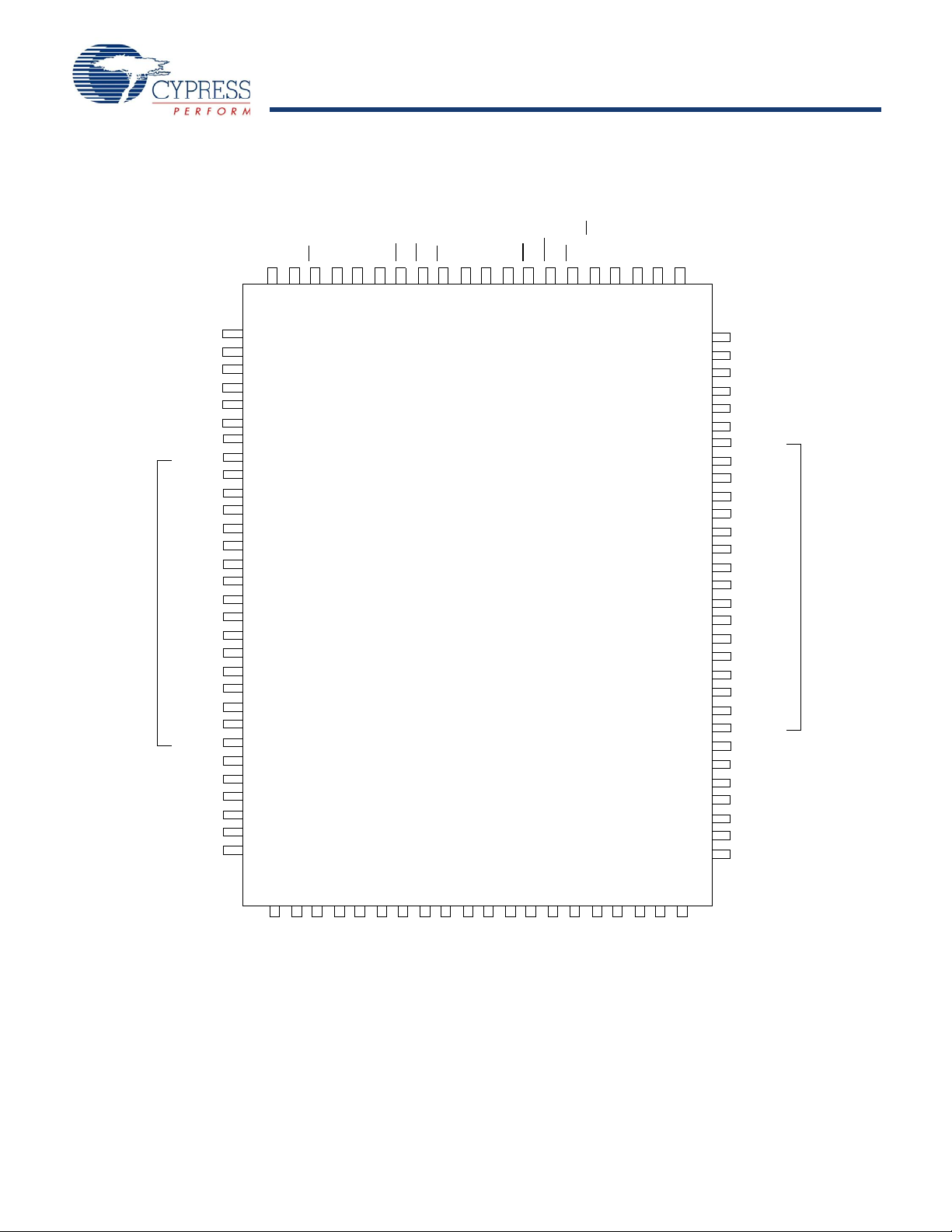
A
A
ADV/LD
ZZ
MODE
A
CY7C1471BV25
BYTE A
BYTE B
BYTE D
BYTE C
A
A
Figure 1. 100- Pin TQFP Pinout
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 4 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 5
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Pin Configurations (continued)
A
A
A
A
A1
A0
NC/288M
NC/144M
V
SS
V
DD
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
DQP
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
SS
NC
V
DD
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
A
DQ
A
NC
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
NC
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQ
B
DQ
B
NC
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQP
B
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A
A
CE
1CE2
NC
NC
BW
BBWA
CE3VDDV
SS
CLK
WE
CEN
OE
A
A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
3132333435
36
37
38394041424344454647484950
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
10099989796959493929190
89
888786
85
848382
81
A
A
ADV/LD
ZZ
MODE
A
CY7C1473BV25
BYTE A
BYTE B
A
A
Figure 2. 100-Pin TQFP Pinout
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 5 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 6
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Pin Configurations (continued)
165-Ball FBGA (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm) Pinout
CY7C1471BV25 (2M x 36)
2345671
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
TDO
NC/576M
NC/1G
DQP
C
DQ
C
DQP
D
NC
DQ
D
CE
1
BW
B
CE
3
BW
C
CEN
A
CE2
DQ
C
DQ
D
DQ
D
MODE
NC
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
A
V
DDQ
BW
D
BW
A
CLK
WE
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TCK
V
SS
TDI
A
A
DQ
C
V
SS
DQ
C
V
SS
DQ
C
DQ
C
NC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
V
SS
A1
DQ
D
DQ
D
NC/144M
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
TMS
891011
NC/288M
A
A
ADV/LD
NC
OE
A
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC DQP
B
V
DDQ
V
DD
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
NC
DQ
B
NC
DQ
A
DQ
A
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DDQ
DQ
B
V
DD
NC
V
DD
DQ
A
V
DD
V
DDQ
DQ
A
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DDQ
DQ
A
V
DDQ
AA
V
SS
A
A
A
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
ZZ
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQP
A
DQ
A
A
V
DDQ
A
A0
A
V
SS
NC
CY7C1473BV25 (4M x 18)
2345671
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
TDO
NC/576M
NC/1G
NC
NC
DQP
B
NC
DQ
B
CE
1
NC CE
3
BW
B
CEN
A
CE2
NC
DQ
B
DQ
B
MODE
NC
DQ
B
DQ
B
NC
NC
NC
A
V
DDQ
NC
BW
A
CLK
WE
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TCK
V
SS
TDI
A
A
DQ
B
V
SS
NC V
SS
DQ
B
NC
NC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
V
SS
A1
DQ
B
NC
NC/144M
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
TMS
891011
NC/288M
A
A
ADV/LD
A
OE
A
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC DQP
A
V
DDQ
V
DD
NC
DQ
A
DQ
A
NC
NC
NC
DQ
A
NC
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DDQ
DQ
A
V
DD
NC
V
DD
NCV
DD
V
DDQ
DQ
A
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
AA
V
SS
A
A
A
DQ
A
NC
NC
ZZ
DQ
A
NC
NC
DQ
A
A
V
DDQ
A
A0
A
V
SS
NC
A
A
A
A
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 6 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 7
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Pin Configurations (continued)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
123456789 1110
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQg
DQc
DQc
DQc
DQc
NC
DQPg
DQh
DQh
DQh
DQh
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQPd
DQPc
DQc
DQc
DQc
DQc
NC
DQh
DQh
DQh
DQh
DQPh
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQf
DQf
DQf
DQf
NC
DQPf
DQa
DQa
DQa
DQa
DQe
DQe
DQe
DQe
DQPa
DQPb
DQf
DQf
DQf
DQf
NC
DQa
DQa
DQa
DQa
DQPe
DQe
DQe
DQe
DQe
AA AA
NC
NC
NC/144M
A A NC/288M
A
AA
AA
A
A1
A0
A
AA
AA
A
NC/576M
NC
NC
NC NC
NC
BWS
b
BWS
f
BWSeBWS
a
BWScBWS
g
BWS
d
BWS
h
TMS
TDI TDO TCK
NC
NC MODE
NC
CEN
V
SS
NC
CLK
NC
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC/1G
V
DD
NC
OE
CE
3
CE
1
CE
2
ADV/LD
WE
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
ZZ
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
SS
NC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
CY7C1475BV25 (1M × 72)
209-Ball FBGA (14 x 22 x 1.76 mm) Pinout
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 7 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 8
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 1. Pin Definitions
Name IO Description
, A1, A Input-
A
0
BW
BW
BW
BW
, BWB,
A
, BWD,
C
, BWF,
E
, BW
G
H
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
WE Input-
Synchronous
ADV/LD Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs Used to Select One of the Address Locations. Sampled at the rising edge
of the CLK. A
are fed to the two-bit burst counter.
[1:0]
Byte Write Inputs, Active LOW. Qualified with WE to conduct writes to the SRAM. Sampled
on the rising edge of CLK.
Write Enable Input, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK if CEN is active LOW.
This signal must be asserted LOW to initiate a write sequence.
Advance/Load Input. Used to advance the on-chip address counter or load a new address.
When HIGH (and CEN
is asserted LOW) the internal burst counter is advanced. When LOW, a
new address can be loaded into the device for an access. After being deselected, ADV/LD
be driven LOW to load a new address.
CLK Input-
Clock
CE
CE
CE
OE
1
2
3
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Synchronous
Input-
Asynchronous
Clock Input. Captures all synchronous inputs to the device. CLK is qualified with CEN. CLK is
only recognized if CEN
is active LOW.
Chip Enable 1 Input, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction
with CE
and CE3 to select or deselect the device.
2
Chip Enable 2 Input, Active HIGH. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction
with CE
and CE3 to select or deselect the device.
1
Chip Enable 3 Input, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in conjunction
with CE
and CE2 to select or deselect the device.
1
Output Enable, Asynchronous Input, Active LOW. Combined with the synchronous logic
block inside the device to control the direction of the IO pins. When LOW, the IO pins are enabled
to behave as outputs. When deasserted HIGH, IO pins are tri-stated, and act as input data pins.
OE
is masked during the data portion of a write sequence, during the first clock when emerging
from a deselected state, when the device has been deselected.
CEN Input-
Synchronous
ZZ Input-
Asynchronous
Clock Enable Input, Active LOW. When asserted LOW the clock signal is recognized by the
SRAM. When deasserted HIGH the clock signal is masked. Because deasserting CEN
not deselect the device, CEN
can be used to extend the previous cycle when required.
ZZ “Sleep” Input. This active HIGH input places the device in a non-time-critical “sleep”
condition with data integrity preserved. For normal operation, this pin must be LOW or left
floating. ZZ pin has an internal pull down.
DQ
s
IO-
Synchronous
Bidirectional Data IO Lines. As inputs, they feed into an on-chip data register that is triggered
by the rising edge of CLK. As outputs, they deliver the data contained in the memory location
specified by the addresses presented during the previous clock rise of the read cycl e. The
direction of the pins is controlled by OE
When HIGH, DQ
tri-stated during the data portion of a write sequence, during the first clock when emerging from
and DQPX are placed in a tri-state condition.The outputs are automatically
s
. When OE is asserted LOW, the pins behave as outputs.
a deselected state, and when the device is deselected, regardless of the state of OE
DQP
X
IO-
Synchronous
Bidirectional Data Parity IO Lines. Functionally, these signals are identical to DQs. During
write sequences, DQP
is controlled by BWX correspondingly.
X
MODE Input Strap Pin Mode Input. Selects the Burst Order of the Device.
When tied to Gnd selects linear burst sequence. When tied to V
leaved burst sequence.
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SS
TDO JTAG serial output
Power Supply Power Supply Inputs to the Core of the Device.
IO Power Supply Power Supply for the IO Circuitry.
Ground Ground for the Device.
Serial Data Out to the JTAG Circuit. Delivers data on the negative edge of TCK. If the JTAG
Synchronous
feature is not used, this pin must be left unconnected. This pin is not available on TQFP
packages.
.
or left floating selects inter-
DD
must
does
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 8 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 9
CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 1. Pin Definitions (continued)
Name IO Description
TDI JTAG serial input
Synchronous
TMS JTAG serial input
Synchronous
Serial Data In to the JTAG Circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature is
not used, leave this pin floating or connected to V
available on TQFP packages.
through a pull up resistor. This pin is not
DD
Serial Data In to the JTAG Circuit. Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature is
not used, this pin can be disconnected or connected to V
packages.
. This pin is not available on TQFP
DD
TCK JTAG-Clock Clock Input to the JTAG Circuitry. If the JTAG feature is not used, connect this pin to VSS.
This pin is not available on TQFP packages.
NC - No Connects. Not internally connected to the die. 144M, 288M, 576M, and 1G are address
expansion pins and are not internally connected to the die.
Functional Overview
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
are synchronous flow through burst SRAMs designed specifically to eliminate wait states during write read transitions. All
synchronous inputs pass through input registers controlled by
the rising edge of the clock. The clock signal is qualified with the
Clock Enable input signal (CEN
is not recognized and all internal states are maintained. All
synchronous operations are qualified with CEN. Maximum
access delay from the clock rise (t
device).
Accesses are initiated by asserting all th ree Chip Enables (CE
CE
, CE3) active at the rising edge of the clock. If CEN is active
2
LOW and ADV/LD
is asserted LOW, the address presented to
the device is latched. The access is either a read or write
operation, depending on the status of the Write Enable (WE
Use Byte Write Select (BW
Write operations are qualified by the WE. All writes are simplified
with on-chip synchronous self- timed write circuitry.
Three synchronous Chip Enables (CE
asynchronous Output Enable (OE
operations (reads, writes, and deselects) are pipelined. ADV/LD
must be driven LOW after the device is deselected to load a new
address for the next operation.
Single Read Accesses
A read access is initiated when the following conditions are
satisfied at clock rise:
■ CEN is asserted LOW
■ CE
, CE2, and CE3 are ALL asserted active
1
■ WE is deasserted HIGH
■ ADV/LD is asserted LOW.
The address presented to the address inputs is latched into the
Address Register and presented to the memory array and control
logic. The control logic determines that a read access is in
progress and allows the requested data to propagate to the
output buffers. The data is available within 6.5 ns (133-MHz
device) provided OE
read access, the output buffers are controlled by OE
internal control logic. OE
requested data. On the subsequent clock, another operation
(read/write/deselect) can be initiated. When the SRAM is
is active LOW. After the first clock of the
). If CEN is HIGH, the clock signal
) is 6.5 ns (133-MHz
CDV
) to conduct Byte Write operations.
X
, CE2, CE3) and an
1
) simplify depth expansion. All
and the
must be driven LOW to drive out the
deselected at clock rise by one of the chip enable signals, the
output is tri-stated immediately.
Burst Read Accesses
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
has an on-chip burst counter that enables the user the ability to
supply a single address and conduct up to four reads without
reasserting the address inputs. ADV/LD
must be driven LOW to
load a new address into the SRAM, as described in the Single
Read Access section. The sequence of the burst counter is
determined by the MODE input signal. A LOW input on MODE
selects a linear burst mode, a HIGH selects an interleaved burst
sequence. Both burst counters use A0 and A1 in the burst
,
1
sequence, and wraps around when incremented sufficiently. A
HIGH input on ADV/LD
regardless of the state of chip enable inputs or WE
at the beginning of a burst cycle. Therefore, the type of access
).
(read or write) is maintained throughout the burst sequence.
increments the internal burst counter
. WE is latched
Single Write Accesses
Write accesses are initiated when these conditions are satisfied
at clock rise:
■ CEN is asserted LOW
■ CE
, CE2, and CE3 are ALL asserted active
1
■ WE is asserted LOW.
The address presented to the address bus is loaded into the
Address Register. The write signals are latched into the Control
Logic block. The data lines are automatically tri-stated
regardless of the state of the OE
external logic to present the data on DQs and DQP
On the next clock rise the data presented to DQs and DQP
a subset for Byte Write operations, see “Truth Table for
Read/Write” on page 12 for details) inputs is latched into the
device and the write is complete. Additional accesses
(read/write/deselect) can be initiated on this cycle.
The data written during the write operation is controlled by BW
signals. The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and
CY7C1475BV25 provide Byte Write capability that is described
in the “Truth Table for Read/Write” on page12. The input WE
with the selected BWx input selectively writes to only the desired
bytes. Bytes not selected during a Byte Write operation remain
unaltered. A synchronous self timed write mechanism is
provided to simplify the write operations. Byte Write capability is
input signal. This allows the
.
X
(or
X
X
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 9 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 10

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
included to greatly simplify read/modify/write sequences, which
can be reduced to simple byte write operations.
Because the CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and
CY7C1475BV25 are common IO devices, data must not be
driven into the device while the outputs are active. The OE
can
be deasserted HIGH before presenting data to the DQs and
DQP
inputs. This tri-states the output drivers. As a safety
X
precaution, DQs and DQP
the data portion of a write cycle, regardless of the state of OE
are automatically tri-stated during
X
.
Burst Write Accesses
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
have an on-chip burst counter that makes it possible to supply a
single address and conduct up to four Write operations without
reasserting the address inputs. Drive ADV/LD
LOW to load the
initial address, as described in the Single Write Access section.
When ADV/LD is driven HIGH on the subsequent clock rise, the
Chip Enables (CE
and the burst counter is incremented. You must drive the correct
, CE2, and CE3) and WE inputs are ignored
1
BWX inputs in each cycle of the Burst Write to write the correct
data bytes.
Sleep Mode
The ZZ input pin is an asynchronous input. Asserting ZZ places
the SRAM in a power conservation “sleep” mode. Two clock
cycles are required to enter into or exit from this “sleep” mode.
While in this mode, data integrity is guaranteed. Accesses
pending when entering the “sleep” mode are not considered valid
nor is the completion of the operation guaranteed. You must
select the device before entering the “sleep” mode. CE
and CE
ZZ input returns LOW.
, must remain inactive for the duration of t
3
ZZREC
, CE2,
1
after the
Table 2. Interleaved Burst Address Table
(MODE = Floating or V
First
Address
A1: A0
DD
Second
Address
A1: A0
)
Third
Address
A1: A0
00 01 10 11
01 00 11 10
10 11 00 01
11 10 01 00
Table 3. Linear Burst Address Table
(MODE = GND)
First
Address
A1: A0
Second
Address
A1: A0
Third
Address
A1: A0
00 01 10 11
01 10 11 00
10 11 00 01
11 00 01 10
Fourth
Address
A1: A0
Fourth
Address
A1: A0
ZZ Mode Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
I
DDZZ
t
ZZS
t
ZZREC
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Sleep mode standby current ZZ > VDD – 0.2V 120 mA
Device operation to ZZ ZZ > VDD – 0.2V 2t
ZZ recovery time ZZ < 0.2V 2t
CYC
ZZ active to sleep current This parameter is sampled 2t
CYC
CYC
ZZ Inactive to exit sleep current This parameter is sampled 0 ns
ns
ns
ns
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 10 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 11

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 4. Truth Table
Notes
1. X = “Don't Care.” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW. BW
X
= L signifies at least one Byte Writ e Select is acti ve , BWX = Valid signifies that the desire d Byte W rite Selects
are asserted, see “Truth Table for Read/Write” on page 12 for details.
2. Write is defined by BW
X
, and WE. See “Truth Table for Read/Write” on page 12.
3. When a write cycle is detected, all IOs are tri-stated, even during byte writes.
4. The DQs and DQP
X
pins are controlled by the current cycle and the OE signal. OE is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock.
5. CEN
= H, inserts wait states.
6. Device powers up deselected with the IOs in a tri-state condition, regardless of OE
.
7. OE
is asynchronous and is not sampled with the clock rise. It is masked internally during write cycles. During a read cycle DQs and DQPX = tri-state when OE is inactive
or when the device is deselected, and DQs and DQP
X
= data when OE is active.
The truth table for CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25 follows.
Operation
Address
Used
CE1CE
ZZ ADV/LD WE BWXOE CEN CLK DQ
CE
2
3
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Deselect Cycle None H X X L L X X X L L->H Tri-S tate
Deselect Cycle None X X H L L X X X L L->H Tri-S tate
Deselect Cycle None X L X L L X X X L L->H Tri-State
Continue Deselect Cycle None X X X L H X X X L L->H Tri-State
Read Cycle
External L H L L L H X L L L->H Data Out (Q)
(Begin Burst)
Read Cycle
Next X X X L H X X L L L->H Data Out (Q)
(Continue Burst)
NOP/Dummy Read
External L H L L L H X H L L->H Tri-State
(Begin Burst)
Dummy Read
Next X X X L H X X H L L->H Tri-State
(Continue Burst)
Write Cycle
External L H L L L L L X L L->H Data In (D)
(Begin Burst)
Write Cycle
Next X X X L H X L X L L->H Data In (D)
(Continue Burst)
NOP/Write Abort
None L H L L L L H X L L->H Tri-State
(Begin Burst)
Write Abort
Next X X X L H X H X L L->H Tri-State
(Continue Burst)
Ignore Clock Edge (Stall) Current X X X L X X X X H L->H Sleep Mode None X X X H X X X X X X Tri-State
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 11 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 12

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 5. Truth Table for Read/Write
Note
8. This table is only a partial listing of the byte write combinations. Any combination of BW
X
is valid. Appropriate write is based on which byte write is active.
The read-write truth table for CY7C1471BV25 follows.
Function
[1, 2, 8]
WE BW
A
BW
B
BW
C
BW
D
Read HXXXX
Write No bytes written L H H H H
Write Byte A – (DQ
Write Byte B – (DQ
Write Byte C – (DQ
Write Byte D – (DQ
and DQPA) LLHHH
A
and DQPB)LHLHH
B
and DQPC)LHHLH
C
and DQPD)LHHHL
D
Write All Bytes LLLLL
Table 6. Truth Table for Read/Write
The read-write truth table for CY7C1473BV25 follows.
[1, 2, 8]
Function
WE BW
b
BW
a
Read HXX
Write – No Bytes Written L H H
Write Byte a – (DQ
Write Byte b – (DQ
and DQPa)LHL
a
and DQPb)LLH
b
Write Both Bytes L L L
Table 7. Truth Table for Read/Write
The read-write truth table for CY7C1475BV25 follows.
Function
[1, 2, 8]
WE BW
x
Read HX
Write – No Bytes Written L H
Write Byte X − (DQ
and DQP
x
x)
Write All Bytes L All BW
LL
= L
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 12 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 13

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
IEEE 1149.1 Serial Boundary Scan (JTAG)
TEST-LOGIC
RESET
RUN-TEST/
IDLE
SELE CT
DR-SCAN
SELE CT
IR-SCAN
CAPTU RE-DR
SHIFT -DR
CAPTU RE-IR
SHIFT -IR
EXIT1-DR
PAU SE-DR
EXIT1-IR
PAU SE-IR
EXIT2-DR
UPDATE-DR
EXIT2-IR
UPDATE-IR
1
1
1
0
1 1
0 0
1 1
1
0
0
0
0 0
0
0
0 0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1 0
Bypass Register
0
Instruction Register
012
Identication Register
012293031 ...
Boundary Scan Register
012..x ...
Sele ction
Circuitry
TCK
TMS
TAP CONTROLLER
TDI TDO
Sele ction
Circuitry
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
incorporate a serial boundary scan T est Access Port (TAP). This
port operates in accordance with IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990
but does not have the set of functions required for full 1149.1
compliance. These functions from the IEEE specification are
excluded because their inclusion places an added delay in the
critical speed path of the SRAM. Note that the TAP controller
functions in a manner that does not conflict with the operation of
other devices using 1149.1 fully compliant TAPs. The TAP
operates using JEDEC-standard 2.5V IO logic levels.
The CY7C1471BV25, CY7C1473BV25, and CY7C1475BV25
contain a TAP controller, instruction register, boundary scan
register, bypass register, and ID register.
Disabling the JTAG Feature
It is possible to operate the SRAM without using the JTAG
feature. To disable the TAP controller, tie TCK LOW (V
prevent clocking of the device. TDI and TMS are internally pulled
up and may be unconnected. They may alternately be connected
to V
through a pull up resistor. TDO must be left unconnected.
DD
During power up, the device comes up in a reset state, which
does not interfere with the operation of the device.
Figure 3. TAP Controller State Diagram
SS
) to
Test Access Port (TAP)
Test Clock (TCK)
The test clock is used only with the TAP controller. All inputs are
captured on the rising edge of TCK. All outputs are driven from
the falling edge of TCK.
Test Mode Select (TMS)
The TMS input gives commands to the TAP controller and is
sampled on the rising edge of TCK. You can leave this ball
unconnected if the TAP is not used. The ball is pulled up internally, resulting in a logic HIGH level.
Test Data In (TDI)
The TDI ball serially inputs information into the registers and is
connected to the input of any of the registers. The register
between TDI and TDO is chosen by the instruction that is loaded
into the TAP instruction register. For information about loading
the instruction register, see the TAP Controller State Diagram.
TDI is internally pulled up and can be unconnected if the TAP is
unused in an application. TDI is connected to the most significant
bit (MSB) of any register. (See TAP Controller Block Diagram.)
Test Data Out (TDO)
The TDO output ball serially clocks data out from the registe rs.
The output is active depending upon the current state of the TAP
state machine. The output changes on the falling edge of TCK.
TDO is connected to the least significant bit (LSB) of any register.
(See Tap Controller State Diagram.)
Figure 4. TAP Controller Block Diagram
The 0/1 next to each state represents the value of TMS at the
rising edge of TCK.
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 13 of 30
Performing a TAP Reset
A RESET is performed by forcing TMS HIGH (VDD) for five rising
edges of TCK. This RESET does not affect the operation of the
SRAM and may be performed while the SRAM is operating.
During power up, the TAP is reset internally to ensure that TDO
comes up in a High-Z state.
[+] Feedback
Page 14

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
TAP Registers
Registers are connected between the TDI and TDO balls and
enable the scanning of data into and out of the SRAM test
circuitry. Only one register is selectable at a time through the
instruction register. Data is serially loaded into the TDI ball on the
rising edge of TCK. Data is output on the TDO ball on the falling
edge of TCK.
Instruction Register
Three-bit instructions can be serially loaded into the instruction
register. This register is loaded when it is placed between the TDI
and TDO balls as shown in the “TAP Controller Block Diagram”
on page 13. During power up, the instruction register is loaded
with the IDCODE instruction. It is also loaded with the IDCODE
instruction if the controller is placed in a reset state as described
in the previous section.
When the TAP controller is in the Capture-IR state, the two least
significant bits are loaded with a binary ‘01’ pattern to enable fault
isolation of the board-level serial test data path.
Bypass Register
To save time when serially shifting data through registers, it is
sometimes advantageous to skip certain chips. The bypass
register is a single-bit register that can be placed between the
TDI and TDO balls. This shifts the data through the SRAM with
minimal delay. The bypass register is set LOW (V
BYPASS instruction is executed.
Boundary Scan Register
The boundary scan register is connected to all the inp ut and
bidirectional balls on the SRAM.
The boundary scan register is loaded with the contents of the
RAM IO ring when the TAP controller is in the Capture-DR state
and is then placed between the TDI and TD O balls when the
controller is moved to the Shift-DR state. The EXTEST,
SAMPLE/PRELOAD and SAMPLE Z instructions can be used to
capture the contents of the IO ring.
The Boundary Scan Order tables show the order in which the bits
are connected. Each bit corresponds to one of the bumps on the
SRAM package. The MSB of the register is connected to TDI and
the LSB is connected to TDO.
Identification (ID) Register
The ID register is loaded with a vendor specific, 32-bit code
during the Capture DR state when the IDCODE command is
loaded in the instruction register. The IDCODE is hardwired into
the SRAM and can be shifted out when the TAP controller is in
the Shift DR state. The ID register has a vendor code and other
information described in “Identification Register Definitions” on
page 17.
) when the
SS
TAP Instruction Set
Overview
Eight different instructions are possible with the three-bit
instruction register. All combinations are listed in “Identification
Codes” on page 17. Three of these instructions are listed as
RESERVED and are not for use. The other five instructions are
described in this section in detail.
The TAP controller used in this SRAM is not fully compliant to the
1149.1 convention because some of the mandatory 1149.1
instructions are not fully implemented.
Y ou cannot use the T AP controller to load address data or control
signals into the SRAM and you cannot preload the IO buffers.
The SRAM does not implement the 1149.1 commands EXTEST
or INTEST or the PRELOAD portion of SAMPLE/PRELOAD;
rather, it performs a capture of the IO ring when these instructions are executed.
Instructions are loaded into the TAP controller during the Shift-IR
state when the instruction register is placed between TDI and
TDO. During this state, instructions are shifted through the
instruction register through the TDI and TDO balls. To execute
the instruction after it is shifted in, the TAP controller must be
moved into the Update-IR state.
EXTEST
EXTEST is a mandatory 1149.1 instruction which is executed
whenever the instruction register is loaded with all 0s. EXTEST
is not implemented in this SRAM TAP controller making this
device not compliant with 1149.1. The TAP controller does
recognize an all-0 instruction.
When an EXTEST instruction is loaded into the instruction
register, the SRAM responds as if a SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction is loaded. There is one difference between the two
instructions. Unlike the SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction,
EXTEST places the SRAM outputs in a High-Z state.
IDCODE
The IDCODE instruction causes a vendor specific, 32-bit code to
load into the instruction register. It also places the instruction
register between the TDI and TDO balls and enables the
IDCODE for shifting out of the device when the TAP controller
enters the Shift-DR state.
The IDCODE instruction is loaded into the instruction register
during power up or whenever the TAP controller is in a test logic
reset state.
SAMPLE Z
The SAMPLE Z instruction connects the boundary scan register
between the TDI and TDO pins when the TAP controller is in a
Shift-DR state. It also places all SRAM outputs into a High-Z
state.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
SAMPLE/PRELOAD is a 1149.1 mandatory instruction. The
PRELOAD portion of this instruction is not implemented, so the
device TAP controller is not fully 1149.1 compliant.
When the SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction is loaded into the
instruction register and the TAP controller is in the Capture-DR
state, a snapshot of data on the inputs and bidirectional balls is
captured in the boundary scan register.
Be aware that the TAP controller clock only operates at a
frequency up to 20 MHz, while the SRAM clock operates more
than an order of magnitude faster. Because there is a large
difference in the clock frequencies, it is possible that, during the
Capture-DR state, an input or output may undergo a transition.
The TAP may then try to capture a signal while in transition
(metastable state). This does not harm the device, but there is
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 14 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 15

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
no guarantee as to the value that is captured. Repeatable results
t
TL
Test Clock
(TCK)
123456
T
est Mode Select
(TMS)
t
TH
Test Data-Out
(TDO)
t
CYC
Test Data-In
(TDI)
t
TMSH
t
TMSS
t
TDIH
t
TDIS
t
TDOX
t
TDOV
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
may not be possible.
To guarantee that the boundary scan register captures the
correct signal value, make certain that the SRAM signal is stabilized long enough to meet the TAP controller’s capture setup plus
hold time (tCS plus tCH).
The SRAM clock input might not be captured correctly if there is
no way in a design to stop (or slow) the clock during a
SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction. If this is an issue, it is still
possible to capture all other signals and simply ignore the value
of the CLK captured in the boundary scan register.
After the data is captured, it is possible to shift out the data by
putting the T AP into the Shift-DR state. This places the boundary
scan register between the TDI and TDO balls.
Figure 5. TAP Timing
Note that since the PRELOAD part of the command is not implemented, putting the TAP to the Update-DR state while performing
a SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction has the same effect as the
Pause-DR command.
BYPASS
When the BYPASS instruction is loaded in the instruction register
and the TAP is placed in a Shift-DR state, the bypass register is
placed between the TDI and TDO balls. The advantage of the
BYPASS instruction is that it shortens the boundary scan path
when multiple devices are connected together on a board.
Reserved
These instructions are not implemented but are reserved for
future use. Do not use these instructions.
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 15 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 16

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
TAP AC Switching Characteristics
TDO
1.25V
20pF
Z = 50Ω
O
50Ω
Notes
9.t
CS
and tCH refer to the setup and hold time requirement s of latch ing d at a from t he boundary scan regist er.
10.Test conditions are specified using the load in T AP AC Test Conditions. t
R/tF
= 1 ns.
11.All voltages refer to V
SS
(GND).
Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description Min Max Unit
Clock
t
TCYC
t
TF
t
TH
t
TL
TCK Clock Cycle Time 50 ns
TCK Clock Frequency 20 MHz
TCK Clock HIGH Time 20 ns
TCK Clock LOW Time 20 ns
Output Times
t
TDOV
t
TDOX
TCK Clock LOW to TDO Valid 10 ns
TCK Clock LOW to TDO Invalid 0 ns
Setup Times
t
TMSS
t
TDIS
t
CS
TMS Setup to TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
TDI Setup to TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
Capture Setup to TCK Rise 5 ns
Hold Times
t
TMSH
t
TDIH
t
CH
TMS Hold after TCK Clock Rise 5 ns
TDI Hold after Clock Rise 5 ns
Capture Hold after Clock Rise 5 ns
[9, 10]
2.5V TAP AC Test Conditions
Figure 6. 2.5V TAP AC Output Load Equivalent
Input pulse levels.................................................VSS to 2.5V
Input rise and fall time .....................................................1 ns
Input timing reference levels.........................................1.25V
Output reference levels ................................................1.25V
Test load termination supply voltage ............................1.25V
TAP DC Electrical Characteristics And Operating Conditions
(0°C < TA < +70°C; VDD = 2.375 to 2.625 unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
V
V
V
V
V
V
I
OH1
OH2
OL1
OL2
IH
IL
X
Output HIGH Voltage IOH = –1.0 mA, V
Output HIGH Voltage IOH = –100 µA, V
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 1.0 mA, V
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 100 µA, V
Input HIGH Voltage V
Input LOW Voltage V
= 2.5V 1.7 VDD + 0.3 V
DDQ
= 2.5V –0.3 0.7 V
DDQ
Input Load Current GND < VIN < V
[11]
= 2.5V 2.0 V
DDQ
= 2.5V 2.1 V
DDQ
= 2.5V 0.4 V
DDQ
= 2.5V 0.2 V
DDQ
DDQ
–5 5 µA
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 16 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 17

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 8. Identification Register Definitions
Instruction Field
Revision Number (31:29) 000 000 000 Describes the version number
Device Depth (28:24) 01011 01011 01011 Reserved for internal use
Architecture/Memory Type(23:18) 001001 001001 001001 Defines memory type and architecture
Bus Width/Density(17:12) 100100 010100 110100 Defines width and density
Cypress JEDEC ID Code (11:1) 00000110100 00000110100 00000110100 Allows unique identification of SRAM
ID Register Presence Indicator (0) 1 1 1 Indicates the presence of an ID register
T able 9. Scan Register Sizes
Register Name Bit Size (x36) Bit Size (x18) Bit Size (x72)
Instruction 3 3 3
Bypass 1 1 1
ID 32 32 32
Boundary Scan Order – 165FBGA 71 52 Boundary Scan Order – 209BGA - - 110
Table 10. Identification Codes
Instruction Code Description
EXTEST 000 Captures IO ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
IDCODE 001 Loads the ID register with the vendor ID code and places the register between TDI
SAMPLE Z 010 Captures IO ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
RESERVED 011 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD 100 Captures IO ring contents. Places the boundary scan register between TDI and TDO.
RESERVED 101 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
RESERVED 110 Do Not Use: This instruction is reserved for future use.
BYPASS 11 1 Places the bypass register between TDI and TDO. This operation does not affect
CY7C1471BV25
(2MX36)
Forces all SRAM outputs to High-Z state. This instruction is not 1149.1 compliant.
and TDO. This operation does not affect SRAM operations.
Forces all SRAM output drivers to a High-Z state.
Does not affect SRAM operation. This instruction does not implement 1149.1 preload
function and is therefore not 1149.1 compliant.
SRAM operation.
CY7C1473BV25
(4MX18)
CY7C1475BV25
(1MX72)
Description
vendor
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 17 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 18

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 11. Boundary Scan Exit Order (2M x 36)
Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID
1C121R341J1161B7
2D1 22P2 42K10 62B6
3E1 23R4 43J10 63A6
4D2 24P6 44H11 64B5
5E2 25R6 45G11 65A5
6F1 26R8 46F11 66A4
7G1 27P3 47E11 67B4
8 F2 28 P4 48 D10 68 B3
9G2 29P8 49D11 69A3
10 J1 30 P9 50 C11 70 A2
11 K1 31 P10 51 G10 71 B2
12 L1 32 R9 52 F10
13 J2 33 R10 53 E10
14 M1 34 R11 54 A9
15 N1 35 N11 55 B9
16 K2 36 M11 56 A10
17 L2 37 L11 57 B10
18 M2 38 M10 58 A8
19 R1 39 L10 59 B8
20 R2 40 K11 60 A7
Table 12. Boundary Scan Exit Order (4M x 18)
Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID Bit # 165-Ball ID
1D214R427L1040B10
2E215P628K1041A8
3F2 16R6 29J10 42B8
4G2 17R8 30H11 43A7
5J1 18P3 31G11 44B7
6K119P432F1145B6
7L1 20P8 33E11 46A6
8M1 21P9 34D11 47B5
9 N1 22 P10 35 C11 48 A4
10 R1 23 R9 36 A11 49 B3
11 R2 24 R10 37 A9 50 A3
12 R3 25 R11 38 B9 51 A2
13 P2 26 M10 39 A10 52 B2
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 18 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 19

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Table 13. Boundary Scan Exit Order (1M x 72)
Bit # 209-Ball ID Bit # 209-Ball ID Bit # 209-Ball ID Bit # 209-Ball ID
1 A1 29 T1 57 U10 85 B11
2A2 30T2 58T11 86B10
3B1 31U1 59T10 87A11
4B2 32U2 60R11 88A10
5 C1 33 V1 61 R10 89 A7
6C2 34V2 62P11 90A5
7D1 35W1 63P10 91A9
8D2 36W2 64N11 92U8
9 E1 37 T6 65 N10 93 A6
10 E2 38 V3 66 M11 94 D6
11 F1 39 V4 67 M10 95 K6
12 F2 40 U4 68 L11 96 B6
13 G1 41 W5 69 L10 97 K3
14 G2 42 V6 70 P6 98 A8
15 H1 43 W6 71 J11 99 B4
16 H2 44 V5 72 J10 100 B3
17 J1 45 U5 73 H11 101 C3
18 J2 46 U6 74 H10 102 C4
19 L1 47 W7 75 G11 103 C8
20 L2 48 V7 76 G10 104 C9
21 M1 49 U7 77 F11 105 B9
22 M2 50 V8 78 F10 106 B8
23 N1 51 V9 79 E10 107 A4
24 N2 52 W11 80 E11 108 C6
25 P1 53 W10 81 D11 109 B7
26 P2 54 V11 82 D10 110 A3
27 R2 55 V10 83 C11
28 R1 56 U11 84 C10
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 19 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 20

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Maximum Ratings
Notes
12.Overshoot: V
IH
(AC) < VDD +1.5V (pulse width less than t
CYC
/2). Undershoot: VIL(AC) > –2V (pulse width less than t
CYC
/2).
13.T
Power-up
: assumes a linear ramp from 0V to VDD(min.) within 200 ms. During this time VIH < VDD and V
DDQ
< VDD.
14.The operation current is calculated with 50% read cycle and 50% write cycle.
Exceeding maximum ratings may impair the useful life of th e
device. These user guidelines are not tested.
Storage Temperature ................................. –65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature with
Power Applied ............................................–55°C to +125°C
Supply Voltage on V
Supply Voltage on V
DC Voltage Applied to Outputs
in Tri-State...........................................–0.5V to V
Relative to GND........–0.5V to +3.6V
DD
Relative to GND.......–0.5V to +V
DDQ
DDQ
DD
+ 0.5V
DC Input Voltage................................... –0.5V to V
Current into Outputs (LOW) ........................................20 mA
Static Discharge Voltage........................................... >2001V
(MIL-STD-883, Method 3015)
Latch Up Current.................................................... >200 mA
Operating Range
Range
Commercial 0°C to +70°C 2.5V –5%/+5% 2.5V–5% to
Industrial –40°C to +85°C
Ambient
Temperature
V
DD
DD
+ 0.5V
V
DDQ
V
DD
Electrical Characteristics
Over the Operating Range
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
V
V
V
V
V
V
I
DD
DDQ
OH
OL
IH
IL
X
Power Supply Voltage 2.375 2.625 V
IO Supply Voltage For 2.5V IO 2.375 V
Output HIGH Voltage For 2.5V IO, I
Output LOW Voltage For 2.5V IO, IOL= 1.0 mA 0.4 V
Input HIGH Voltage
Input LOW Voltage
Input Leakage Current
except ZZ and MODE
Input Current of MODE Input = V
Input Current of ZZ Input = V
I
OZ
I
DD
I
SB1
[14]
Output Leakage Current GND ≤ VI ≤ V
VDD Operating Supply
Current
Automatic CE
Power Down
Current—TTL Inputs
I
SB2
Automatic CE
Power Down
Current—CMOS Inputs
I
SB3
Automatic CE
Power Down
Current—CMOS Inputs
I
SB4
Automatic CE
Power Down
Current—TTL Inputs
[12, 13]
= –1.0 mA 2.0 V
OH
[12]
For 2.5V IO 1.7 VDD + 0.3V V
[12]
For 2.5V IO –0.3 0.7 V
GND ≤ VI ≤ V
Input = V
Input = V
V
= Max, I
DD
f = f
MAX
V
= Max, Device Deselected,
DD
≥ VIH or VIN ≤ V
V
IN
f = f
MAX
V
= Max, Device Deselected,
DD
≤ 0.3V or VIN > VDD – 0.3V,
V
IN
f = 0, inputs static
V
= Max, Device Deselected, or
DD
≤ 0.3V or VIN > V
V
IN
f = f
MAX
V
= Max, Device Deselected,
DD
≥ VDD – 0.3V or VIN ≤ 0.3V,
V
IN
f = 0, inputs static
DDQ
SS
DD
SS
DD
Output Disabled –5 5 μA
DDQ,
= 0 mA,
OUT
= 1/t
CYC
, inputs switching
, inputs switching
IL
DDQ
– 0.3V
6.5 ns cycle, 133 MHz 305 mA
8.5 ns cycle, 100 MHz 275 mA
6.5 ns cycle, 133 MHz 170 mA
8.5 ns cycle, 100 MHz 170 mA
All speeds 120 mA
6.5 ns cycle, 133 MHz 170 mA
8.5 ns cycle, 100 MHz 170 mA
All Speeds 135 mA
–5 5 μA
–30 μA
–5 μA
DD
5 μA
30 μA
V
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 20 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 21

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Capacitance
OUTPUT
R = 1667Ω
R = 1538Ω
5pF
INCLUDING
JIG AND
SCOPE
(a)
(b)
OUTPUT
R
L
= 50Ω
Z
0
= 50Ω
V
L
= 1.25V
2.5V
ALL INPUT PULSES
V
DDQ
GND
90%
10%
90%
10%
≤ 1 ns
≤ 1 ns
(c)
2.5V IO Test Load
Tested initially and after any design or process change that may affect these parameters.
Parameter Description Test Conditions
C
ADDRESS
C
DATA
C
Control Input Capacitance 8 8 8 pF
CTRL
C
CLK
C
IO
Address Input Capacitance TA = 25°C, f = 1 MHz,
V
= 2.5V
Data Input Capacitance 5 5 5 pF
V
DD
DDQ
= 2.5V
Clock Input Capacitance 6 6 6 pF
Input-Output Capacitance 5 5 5 pF
100 TQFP
Max
6 6 6 pF
165 FBGA
Max
209 FBGA
Thermal Resistance
Tested initially and after any design or process change that may affect these parameters.
Parameter Description Test Conditions
Θ
JA
Θ
JC
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
(Junction to Case)
Test conditions follow
standard test methods and
procedures for measuring
thermal impedance,
according to EIA/JESD51.
Figure 7. AC Test Loads and Waveforms
100 TQFP
Package
24.63 16.3 15.2 °C/W
2.28 2.1 1.7 °C/W
165 FBGA
Package
209 FBGA
Package
Max
Unit
Unit
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 21 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 22

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Switching Characteristics
Notes
15.This part has a voltage regulator internally; t
POWER
is the time that the power is supplied above VDD(minimum) initially, before a read or write operation can be initiated.
16.t
CHZ
, t
CLZ,tOELZ
, and t
OEHZ
are specified with AC test conditions shown in part (b) of “AC Test Loads and Waveforms” on page 21. Transition is measured ±200 mV
from steady-state voltage.
17.At any supplied voltage and temperature, t
OEHZ
is less than t
OELZ
and t
CHZ
is less than t
CLZ
to eliminate bus contention between SRAMs when sharing the same dat a
bus. These specifications do not imply a bus contention condition, but refl ect parameters guaranteed over worst case user conditions. Device is designed to achieve
High-Z before Low-Z under the same system conditions.
18.This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
Over the Operating Range. Timing reference level is 1.25V when V
Waveforms” on page 21 unless otherwise noted.
Parameter Description
t
POWER
Clock
t
CYC
t
CH
t
CL
Output Times
t
CDV
t
DOH
t
CLZ
t
CHZ
t
OEV
t
OELZ
t
OEHZ
Setup Times
t
AS
t
ALS
t
WES
t
CENS
t
DS
t
CES
Hold Times
t
AH
t
ALH
t
WEH
t
CENH
t
DH
t
CEH
Clock Cycle Time 7.5 10 ns
Clock HIGH 2.5 3.0 ns
Clock LOW 2.5 3.0 ns
Data Output Valid After CLK Rise 6.5 8.5 ns
Data Output Hold After CLK Rise 2.5 2.5 ns
Clock to Low-Z
Clock to High-Z
[16, 17, 18]
[16, 17, 18]
OE LOW to Output Valid 3.0 3.8 ns
OE LOW to Output Low-Z
OE HIGH to Output High-Z
[16, 17, 18]
[16, 17, 18]
Address Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
ADV/LD Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
WE, BWX Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
CEN Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Data Input Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Chip Enable Setup Before CLK Rise 1.5 1.5 ns
Address Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
ADV/LD Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
WE, BWX Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
CEN Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Data Input Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
Chip Enable Hold After CLK Rise 0.5 0.5 ns
= 2.5V. Test conditions shown in (a) of “AC Test Loads and
DDQ
133 MHz 100 MHz
Min Max Min Max
11ms
3.0 3.0 ns
3.8 4.5 ns
00ns
3.0 4.0 ns
Unit
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 22 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 23

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Switching Waveforms
123456789
10
C
Notes
19.
For this waveform ZZ is tied LOW.
20.When CE
is LOW, CE1 is LOW, CE2 is HIGH, and CE3 is LOW. When CE is HIGH, CE1 is HIGH, CE2 is LOW or CE3 is HIGH.
21.Order of the Burst sequence is determined by the status of the MODE (0 = Linear, 1 = Interleaved). Burst operations are optional.
Figure 8 shows read-write timing waveform.
t
CYC
CLK
t
CENS
t
CENH
t
CH
t
CL
CEN
t
t
CES
CEH
CE
ADV/LD
WE
BWX
[19, 20, 21]
Figure 8. Read/Write Timing
ADDRESS
DQ
A1 A2
t
t
AS
AH
D(A1) D(A2) Q(A4)Q(A3)
t
t
DS
DH
A3
t
t
D(A2+1)
CDV
CLZ
OE
OMMAND
WRITE
D(A1)
WRITE
D(A2)
BURST
WRITE
D(A2+1)
READ
Q(A3)
A4
READ
Q(A4)
t
DOH
t
OEHZ
BURST
READ
Q(A4+1)
A5 A6 A7
t
OEV
t
OELZ
t
Q(A4+1)
WRITE
D(A5)
CHZ
t
DOH
D(A5)
READ
Q(A6)
WRITE
D(A7)
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
D(A7)Q(A6)
DESELECT
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 23 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 24

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Switching Waveforms (continued)
456 78910
123
C
Note
22.The IGNORE CLOCK EDGE or STALL cycle (Clock 3) illustrates CEN
being used to create a pause. A write is not performed during this cycle.
Figure 9 shows NOP, STALL and DESELECT Cycles waveform.
Figure 9. NOP, STALL and DESELECT Cycles
CLK
CEN
CE
ADV/LD
WE
[A:D]
BW
[19, 20, 22]
ADDRESS
A1 A2
DQ
OMMAND
D(A1)
READ
Q(A2)
STALL NOP READ
A3 A4
Q(A2)D(A1) Q(A3)
READ
Q(A3)
WRITE
D(A4)
DON’T CARE UNDEFINED
A5
t
CHZ
D(A4)
STALLWRITE
Q(A5)
Q(A5)
t
DOH
DESELECT CONTINUE
DESELECT
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 24 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 25

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Switching Waveforms (continued)
t
ZZ
I
SUPPLY
CLK
ZZ
t
ZZRE C
A
LL INPUTS
(except ZZ)
DON’T CARE
I
DDZZ
t
ZZI
t
RZZI
Outputs(Q)
High-Z
DESELECT or READ Only
Notes
23.Device must be deselected when entering ZZ mode. See “Truth Table” on page 11 for all possible signal conditions to deselect the device.
24.DQs are in high-Z when exiting ZZ sleep mode.
Figure 10 shows ZZ Mode timing waveform.
[23, 24]
Figure 10. ZZ Mode Timing
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 25 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 26

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Ordering Information
Not all of the speed, package and temperature ranges are ava ilable. Please contact your local sales representative or
visit www.cypress.com for actual products offered.
Speed
(MHz) Ordering Code
133 CY7C1471BV25-133AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free Commercial
CY7C1473BV25-133AXC
CY7C1471BV25-133BZC 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1473BV25-133BZC
CY7C1471BV25-133BZXC 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1473BV25-133BZXC
CY7C1475BV25-133BGC 51-85167 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm)
CY7C1475BV25-133BGXC 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1471BV25-133AXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free lndustrial
CY7C1473BV25-133AXI
CY7C1471BV25-133BZI 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1473BV25-133BZI
CY7C1471BV25-133BZXI 51- 85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1473BV25-133BZXI
CY7C1475BV25-133BGI 51 -85167 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm)
CY7C1475BV25-133BGXI 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm) Pb-Free
100 CY7C1471BV25-100AXC 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free Commercial
CY7C1473BV25-100AXC
CY7C1471BV25-100BZC 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1473BV25-100BZC
CY7C1471BV25-100BZXC 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1473BV25-100BZXC
CY7C1475BV25-100BGC 51-85167 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm)
CY7C1475BV25-100BGXC 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1471BV25-100AXI 51-85050 100-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free lndustrial
CY7C1473BV25-100AXI
CY7C1471BV25-100BZI 51-85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm)
CY7C1473BV25-100BZI
CY7C1471BV25-100BZXI 51- 85165 165-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm) Pb-Free
CY7C1473BV25-100BZXI
CY7C1475BV25-100BGI 51 -85167 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm)
CY7C1475BV25-100BGXI 209-ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (14 × 22 × 1.76 mm) Pb-Free
Package
Diagram
Part and Package Type
Operating
Range
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 26 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 27

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Package Diagrams
51-85050-*B
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.25
GAUGE PLANE
0°-7°
0.60±0.15
1.00 REF.
Figure 11. 100-Pin Thin Plastic Quad Flatpack (14 x 20 x 1.4 mm), 51-85050
16.00±0.20
14.00±0.10
20.00±0.10
22.00±0.20
1
30
0° MIN.
100
R 0.08 MIN.
0.20 MAX.
0.20 MIN.
DETAIL
A
81
0513
80
0.30±0.08
0.65
TYP.
51
STAND-OFF
0.05 MIN.
0.15 MAX.
12°±1°
(8X)
SEATING PLANE
NOTE:
1. JEDEC STD REF MS-026
2. BODY LENGTH DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH
MOLD PROTRUSION/END FLASH SHALL NOT EXCEED 0.0098 in (0.25 mm) PER SIDE
BODY LENGTH DIMENSIONS ARE MAX PLASTIC BODY SIZE INCLUDING MOLD MISMATCH
3. DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS
1.40±0.05
0.20 MAX.
1.60 MAX.
0.10
SEE DETAIL
A
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 27 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 28

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Package Diagrams (continued)
A
1
PIN 1 CORNER
17.00±0.10
15.00±0.10
7.00
1.00
Ø0.45±0.05(165X)
Ø0.25 M C A B
Ø0.05 M C
B
A
0.15(4X)
0.35
1.40 MAX.
SEATING PLANE
0.53±0.05
0.25 C
0.15 C
PIN 1 CORNER
TOP VIEW
BOTTOM VIEW
2345678910
10.00
14.00
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
11
1110986754321
P
R
P
R
K
M
N
L
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
C
1.00
5.00
0.36
+0.05
-0.10
51-85165-*A
Figure 12. 165-Ball FBGA (15 x 17 x 1.4 mm), 51-85165
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 28 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 29

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Package Diagrams (continued)
51-85167-**
Figure 13. 209-Ball FBGA (14 x 22 x 1.76 mm), 51-85167
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Page 29 of 30
[+] Feedback
Page 30

CY7C1471BV25
CY7C1473BV25, CY7C1475BV25
Document History Page
Document Title: CY7C1471BV25/CY7C1473BV25/CY7C1475BV25, 72-Mbit (2M x 36/4M x 18/1M x 72)
Flow-Through SRAM with NoBL™ Architecture
Document Number: 001-15013
REV. ECN NO.
Issue
Date
** 1024500 See ECN VKN/KKVTMP New Data Sheet
*A 1274731 See ECN VKN/AESA Corrected typo in the “NOP, STALL and DESELECT Cycles” waveform
*B 1562503 See ECN VKN/AESA Removed 1.8V IO offering from the data sheet
*C 1897447 See ECN VKN/AESA Added footnote 14 related to IDD
*D 2082487 See ECN VKN Converted from preliminary to final
*E 2159486 See ECN VKN/PYRS Minor Change-Moved to the external web
Orig. of
Change
Description of Change
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2007-2008. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used
for medical, life support, life sa vin g, critical control or safety applications, unl ess p ur sua nt to an express written agreement with Cypress. Fur th ermo r e, Cyp r ess d oe s no t a uth or iz e its products for use
as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress products in life-support
systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign),
United States co pyright la ws and inte rnatio na l tre aty prov isi ons. Cyp ress he reby g rant s to lice nsee a p erson al, no n-ex clusi ve, non-tra nsferable license to copy, use, modify , create derivative works of ,
and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for the sole purpo se of creating custom sof tware and or firm ware in support of licen see product to be use d only in conjunction with a Cypress
integrated circuit as specified in th e applicable agreement. Any reproductio n, modification, translation, co mpilation, o r representati on of this Sour ce Code except as specified above is prohibited without
the express written permission of Cypress.
Disclaimer: CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Cypress reserves the right to make changes without further notice to the materials described herein. Cypress does not
assume any liability arising out of the ap plicati on or u se o f any pr oduct o r circui t descri bed h erein. Cypr ess does not aut horize it s product s for use a s critical compo nent s in life-support systems whe re
a malfunction or failure may reasonab ly be expected to resu lt in significant injury t o the user. The inclusion of Cypress’ prod uct in a life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer
assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress against all charges.
Use may be limited by and subject to the applicable Cypress software license agreement.
Document #: 001-15013 Rev. *E Revised February 29, 2008 Page 30 of 30
NoBL and No Bus Latency are trade marks of Cypress Semic onductor Corporation. Z BT is a trademark of Integra ted Device Technology, Inc. All products and company names mentioned in this
document may be the trademarks of their respective holders.
[+] Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...