
查询CY7C1381C-100AC供应商
18-Mb (512K x 36/1M x 18) Flow-Through SRAM
CY7C1381C
CY7C1383C
Features
• Supports 133-MHz bus operations
• 512K X 36/1M X 18 common I/O
• 3.3V –5% and +10% core power supply (V
• 2.5V or 3.3V I/O supply (V
DDQ
)
• Fast clock-to-output times
— 6.5 ns (133-MHz version)
— 7.5 ns (117-MHz version)
— 8.5 ns (100-MHz version)
• Provide high-performance 2-1-1-1 access rate
• User-selectable burst counter supporting Intel
Pentium interleaved or linear burst sequences
• Separate processor and controller address strobes
• Synchronous self-timed write
• Asynchronous output enable
• Offered in JEDEC-standard 100-pin TQFP ,119-ball BGA
and 165-ball fBGA packages
• JTAG boundary scan for BGA and fBGA packages
• “ZZ” Sleep Mode option
DD
)
Functional Description
[1]
The CY7C1381C/CY7C1383C is a 3.3V, 512K x 36 and 1M x
18 Synchronous Flowthrough SRAMs, respectively designed
to interface with high-speed microprocessors with minimum
glue logic. Maximum access delay from clock rise is 6.5 ns
(133-MHz version). A 2-bit on-chip counter captures the first
address in a burst and increments the address automatically
for the rest of the burst access. All synchronous inputs are
gated by registers controlled by a positive-edge-triggered
Clock Input (CLK). The synchronous inputs include all
addresses, all data inputs, address-pipelining Chip Enable
(
), depth-expansion Chip Enables (CE2 and
CE
1
Control inputs (
), and Global Write (GW). Asynchronous
and
BWE
include the Output Enable
ADSC
,
ADSP
,
and
ADV
(
)
and the ZZ pin
OE
), Write Enables
[2]
), Burst
CE
3
(
BW
inputs
.
The CY7C1381C/CY7C1383C allows either interleaved or
linear burst sequences, selected by the MODE input pin. A
HIGH selects an interleaved burst sequence, while a LOW
selects a linear burst sequence. Burst accesses can be
initiated with the Processor Address Strobe (ADSP
cache Controller Address Strobe (ADSC
) inputs. Address
) or the
advancement is controlled by the Address Advancement
(ADV) input.
Addresses and chip enables are registered at rising edge of
clock when either Address Strobe Processor (
Address Strobe Controller (
) are active. Subsequent
ADSC
ADSP
) or
burst addresses can be internally generated as controlled by
the Advance pin (
ADV
).
The CY7C1381C/CY7C1383C operates from a +3.3V core
power supply while all outputs may operate with either a +2.5
or +3.3V supply. All inputs and outputs are JEDEC-standard
JESD8-5-compatible.
,
x
Selection Guide
133 MHz 117 MHz 100 MHz Unit
Maximum Access Time 6.5 7.5 8.5 ns
Maximum Operating Current 210 190 175 mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current 70 70 70 mA
1
2
3
4
5
6
Notes:
1. For best–practices recommendations, please refer to the Cypress application note System Design Guidelines on www.cypress.com.
2. CE
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose, CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Revised February 26, 2004
are for TQFP and 165 fBGA package only. 119 BGA is offered only in 1 Chip Enable.
3, CE2
C
C
A
B
C
C
7
s
A
B
C
D
A
A
A
B
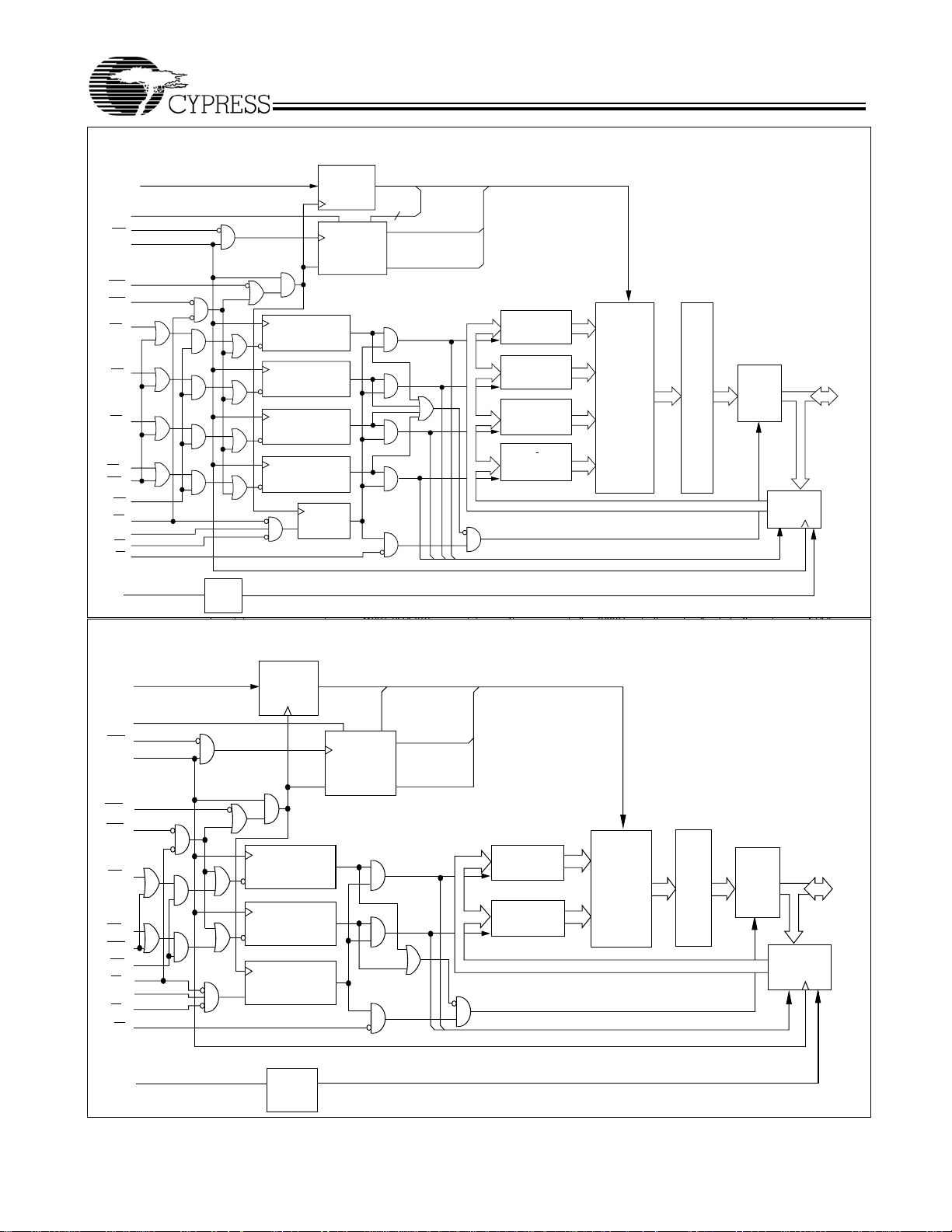
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1381C (512K x 36)
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
D
,
DQP
DQ
BYTE
BYTE
C
,
DQP
DQ
BYTE
ADDRESS
REGISTER
DQ
B
,
DQP
BYTE
DQ
A
,
DQP
BYTE
ENABLE
REGISTER
B
A
,DQP
A
ADDRESS
REGISTER
COUNTER
AND LOGIC
CLR
D
C
B
A
BURST
A
[1:0]
Q1
Q0
ADV/LD
C
A1
A0
WRITE ADDRESS
REGISTER
WRITE REGISTRY
AND DATA COHERENCY
CONTROL LOGIC
A[1:0]
Q1
BURST
COUNTER AND
LOGIC
READ LOGIC
CLR
CONTROL
Q0
SLEEP
D1
D0
BURST
LOGIC
DQ
D
,
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
C
DQ
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
B
,
A1'
Q1
BYTE
A0'
WRITE REGISTER
Q0
DQ
A
,
BYTE
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE
DRIVERS
DQB,DQP
WRITE DRIVER
DQ
A
,DQP
WRITE DRIVER
DQP
,
DQP
DQP
DQP
D
C
MEMORY
B
A
ARRAY
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
O
U
INPUT
REGISTERS
DQ
DQP
DQP
DQP
DQP
T
P
D
MEMORY
ARRAY
S
E
N
S
E
A
M
P
S
U
A
T
T
A
B
U
S
F
T
F
E
E
E
R
R
S
I
N
E
DQs
DQP
DQP
G
INPUT
REGISTER
B
MEMORY
ARRAY
A
E
SENSE
AMPS
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
DQs
DQP
DQP
INPUT
REGISTERS
0, A1, A
MODE
ADV
CLK
ADSC
ADSP
BW
D
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
BW
C
A0, A1, A
BW
B
MODE
A
B
CE
SLEEP
CONTROL
LK
BW
A
EN
BWE
GW
CE1
CE2
CE3
OE
ZZ
8
Logic Block Diagram – CY7C1383C (1M x 18)
0,A1,A
C
ADV/LD
BW
BW
WE
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
WRITE REGISTER
ADDRESS
REGISTER
MODE
ADV
CLK
OE
ADSC
ADSP
BW
BW
B
A
BWE
GW
CE
1
CE
2
CE
3
OE
CE1
CE2
CE3
ZZ
DQB,DQP
WRITE REGISTER
DQ
WRITE REGISTER
ENABLE
REGISTER
ZZ
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 2 of 36
SLEEP
CONTROL
C
C
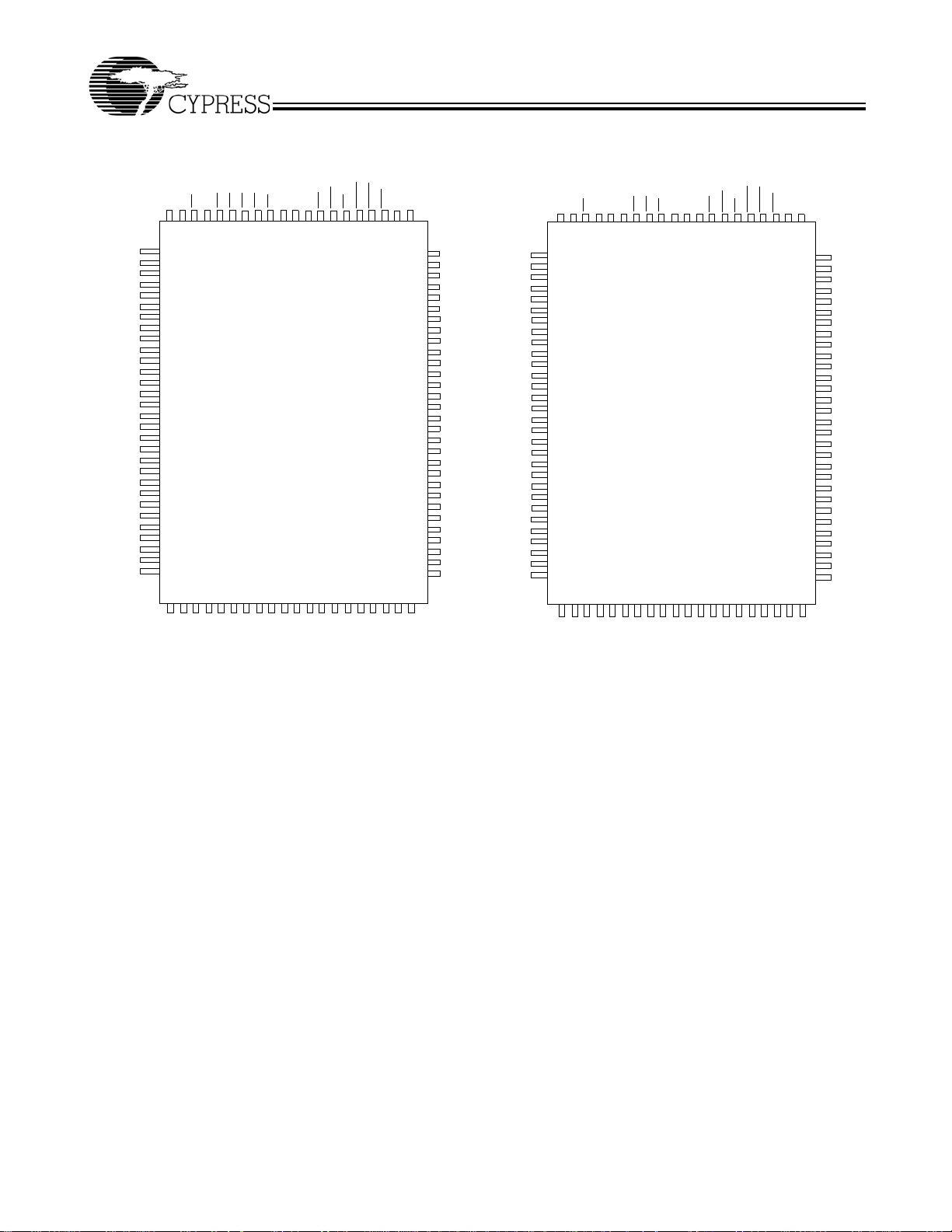
Pin Configurations
1CE2
A
A
BWDBWCBWBBW
CE
A
CE3VDDV
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
100-pin TQFP Pinout
A
A
ADSP
ADV
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
1CE2
A
A
CE
A
NCNCBWBBW
CE3VDDV
SS
CLKGWBWEOEADSC
A
A
ADSP
ADV
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
C
1
C
2
C
3
4
5
C
6
C
7
C
8
C
9
10
11
C
12
C
13
14
15
16
17
D
18
D
19
20
21
D
22
D
23
D
24
D
25
26
27
D
28
D
29
D
30
CY7C1381C
(512K x 36)
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
MODE
AAA
1A0
A
A
NC
NC
SS
DD
V
V
A
A
AAAAA
81
DQP
80
DQ
79
DQ
78
V
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
VSS/DNU
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
50
A
A
100999897969594939291908988878685848382
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
CY7C1383C
(1M x 18)
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
AAA
MODE
1A0
A
A
NC
NC
A
AAAAA
A
SS
DD
V
V
81
A
80
NC
79
NC
78
V
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DDQ
V
SSQ
NC
DQP
DQ
DQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ
DQ
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
DQ
DQ
NC
NC
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
50
A
A
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 3 of 36
C
C
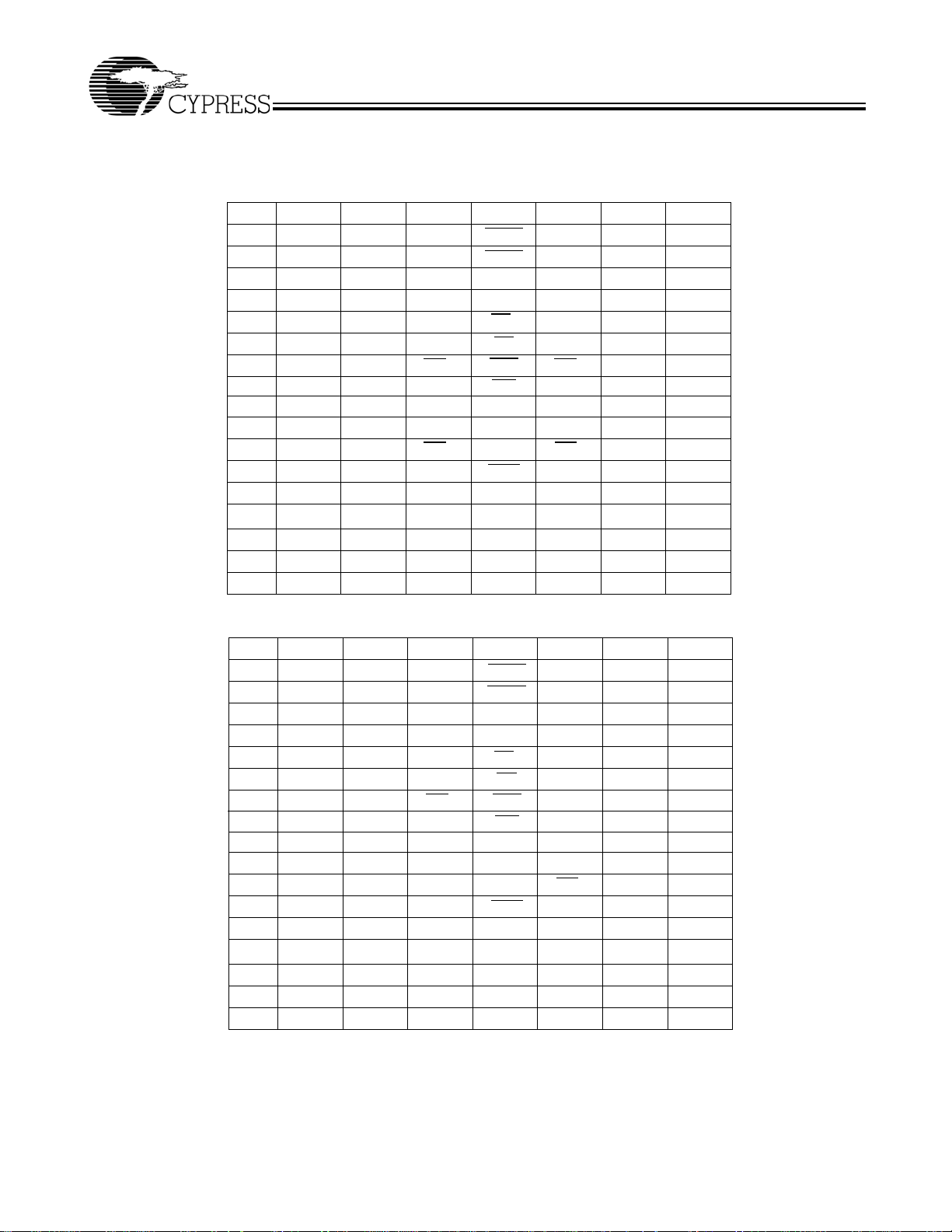
Pin Configurations (continued)
V
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
J
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
119-ball BGA (1 Chip Enable with JTAG)
CY7C1381C (512K x 36)
2345671
DDQ
NC
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
NC
DDQ
AA AA
AA
AA
DQP
C
DQ
C
DQ
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
DD
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
DQ
D
DQP
D
A
V
C
C
C
C
C
V
V
BW
V
SS
SS
SS
SS
NC V
V
BW
V
V
V
SS
SS
SS
SS
D
D
D
D
D
MODE
AAA
ADSP
ADSC
V
DD
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
C
GW
DD
CLK
D
NC
BWE
A1
A0
V
DD
V
V
V
BW
V
NC
V
BW
V
V
V
NC
TDOTCKTDITMS
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
V
DDQ
A
A
AA
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
DQP
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
B
B
DD
A
A
A
A
B
A
DQP
A
NCNC
NC
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
V
DQ
DQ
B
B
DDQ
B
B
DDQ
A
A
DDQ
A
A
B
A
NC
ZZ
V
DDQ
CY7C1383C (1M x 18)
2
V
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
DQ
V
DQ
V
DQ
V
DDQ
NC
NC
B
NC
DDQ
NC
B
DDQ
NC
B
DDQ
B
NC
NC
NC
DDQ
AA AA
AA
NCDQ
DQ
B
NC
DQ
B
NC
V
DD
DQ
B
NC
DQ
B
NC
DQP
B
A
345671
ADSP
V
V
V
V
V
NC
V
BW
V
V
V
NC
A
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
A
SS
SS
SS
AA
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
BW
B
V
SS
NC V
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
MODE
ADSC
V
DD
NC
CE
1
OE
ADV
GW
DD
CLK
NC
BWE
A1
A0
V
DD
ANCA
TDOTCKTDITMS
A
AA
DQP
NC
DQ
NC
DQ
V
DD
NC
DQ
NC
DQ
NC
A
AA
NC
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
A
DQ
A
V
DQ
V
DQ
V
DQ
DDQ
A
NC
DDQ
A
NC
DDQ
NC
A
A
A
A
A
NC
ZZ
V
DDQ
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 4 of 36
C
C
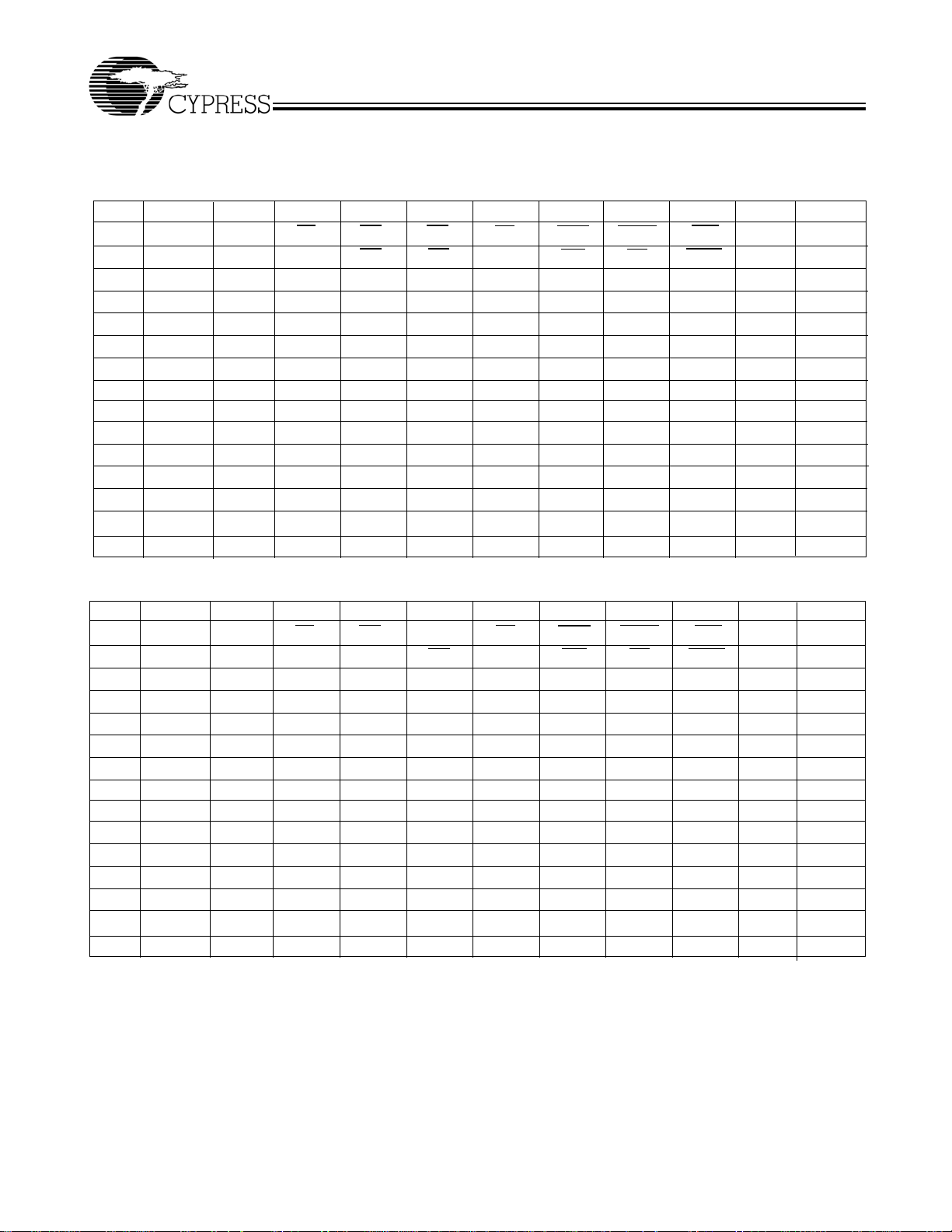
Pin Configurations (continued)
234 5671
NC / 288M
A
B
C
D
G
H
K
M
N
R
NC
DQP
C
DQ
C
E
F
DQ
DQ
DQ
C
C
C
NC
J
L
P
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQP
NC
D
D
D
D
D
MODE
A
A
NC
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
DQ
C
V
SS
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
DQ
D
NC
NC / 72M
NC / 36M
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
CE
CE
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
A
A
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
165-ball fBGA (3 Chip Enable)
CY7C1381C (512K x 36)
891011
BW
1
BW
2
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
BW
C
D
BW
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
NC
TDI
TMS
CE
B
CLK
A
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
A
A1
A0
BWE
3
GW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDO
TCK
ADSC
OE
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
ADV
ADSP
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
A
NC / 144M
A
NC DQP
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQ
A
DQP
A
NC
B
B
B
B
B
ZZ
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
CY7C1383C (1M x 18)
234 5671
NC / 288M
NC
NC
NC
NC V
NC
NC
V
SS
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQP
B
NC
MODE
ACE
A
NC
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
DQ
B
V
SS
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC / 72M
NC / 36M
CE
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
A
A
BW
1
2
B
NC BW
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
NC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDI
TMS
A
CE
CLK
V
SS
V
SS
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
A
A1
891011
BWE
3
GW
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC
TDO
TCKA0
ADSC
OE
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
A
A
ADV
ADSP
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
NC
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
A
A
A
NC / 144M
A
NC DQP
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
NC
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZZ
A
A
A
A
NCV
NC
NC
NC
NC
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 5 of 36
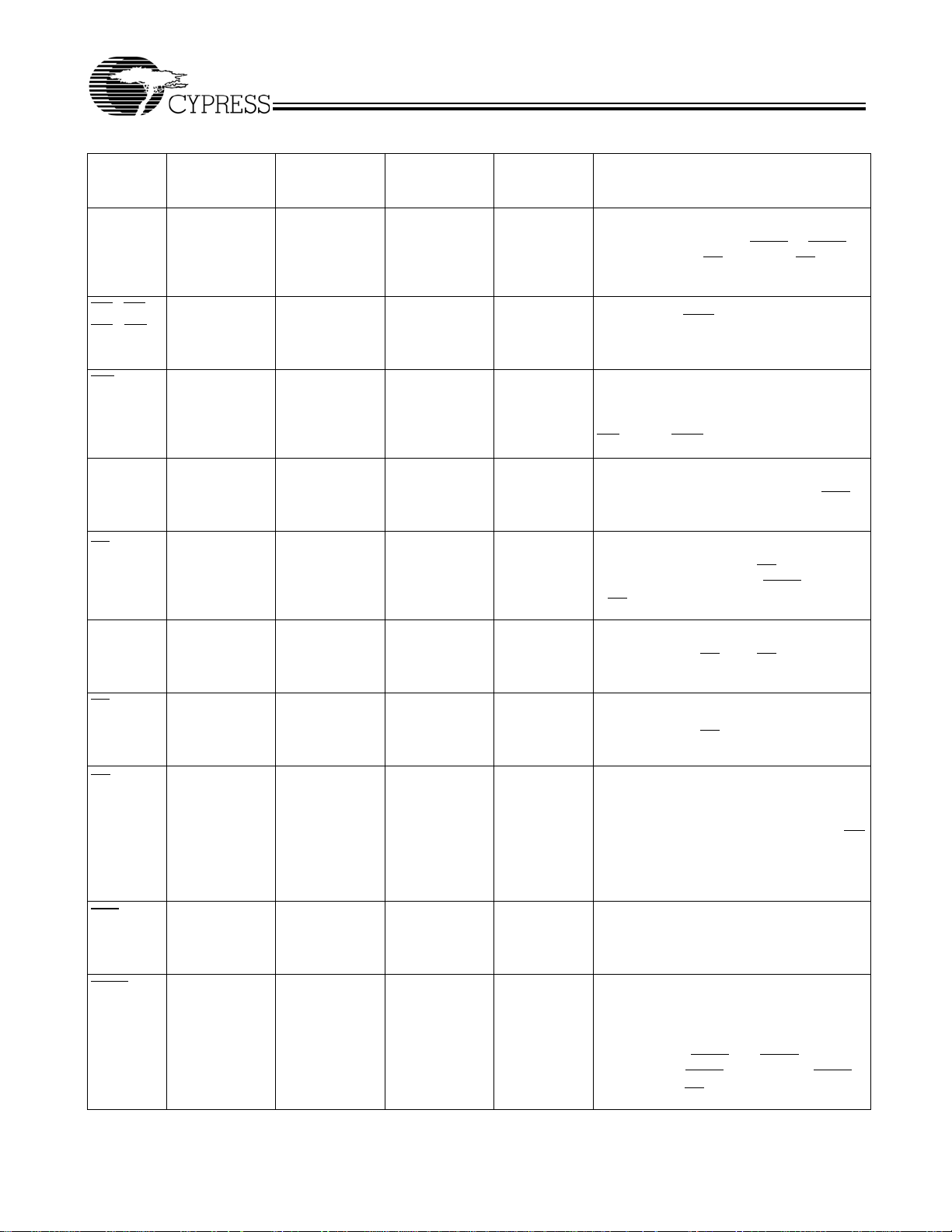
C
C
CY7C1381C–Pin Definitions
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
(3-Chip
Name
, A1 , A 37,36,32,33,34,
A
0
Enable)
35,42,43,44,45,
46,47,48,49,50,
81,82,99,100
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
P4,N4,A2,B2,C2
,R2,A3,B3,C3,T
3,T4,A5,B5,C5,
T5,A6,B6,C6,R6
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
R6,P6,A2,A10,
B2,B10,N6,P3,
Input-
Synchronous
P4,P8,P9,P10,
P11,R3,R4,R8,
R9,R10,R11
BWA,BW
BWC,BW
GW
93,94,95,96 L5,G5,G3,L3 B5,A5,A4,B4 Input-
B
D
88
H4 B7 Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous
CLK 89 K4 B6 Input-
Clock
CE
CE
CE
OE
1
2
[2]
3
98 E4 A3 Input-
Synchronous
97 - B3 Input-
Synchronous
92 - A6 Input-
Synchronous
86 F4 B8 Input-
Asynchronous
Address Inputs used to select one of the
512K address locations. Sampled at the
rising edge of the CLK if ADSP
active LOW, and CE
sampled active. A
1, CE2
feed the 2-bit counter.
[1:0]
or ADSC is
, and CE
[2]
are
3
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW.
Qualified with BWE
to conduct byte writes to
the SRAM. Sampled on the rising edge of
CLK.
Global Write Enable Input, active LOW.
When asserted LOW on the rising edge of
CLK, a global write is conducted (ALL bytes
are written, regardless of the values on
BW
and BWE).
[A:D]
Clock Input. Used to capture all
synchronous inputs to the device. Also used
to increment the burst counter when ADV
is
asserted LOW, during a burst operation.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW. Sampled
on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE2 and CE
select/deselect the device. ADSP
is HIGH.
if CE
1
[2]
to
3
is ignored
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE1 and CE
select/deselect the device.
[2]
to
3
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW. Sampled
on the rising edge of CLK. Used
in
conjunction with CE1 and CE2 to
select/deselect the device.
Output Enable, asynchronous input,
active LOW. Controls the direction of the I/O
pins. When LOW, the I/O pins behave as
outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins
are tri-stated, and act as input data pins. OE
is masked during the first clock of a read
cycle when emerging from a deselected
state.
ADV
83 G4 A9 Input-
Synchronous
Advance Input signal, sampled on the
rising edge of CLK. When asserted, it
automatically increments the address in a
burst cycle.
ADSP
84 A4 B9 Input-
Synchronous
Address Strobe from Processor, sampled
on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW.
When asserted LOW, addresses presented
to the device are captured in the address
registers. A
counter. When ADSP
asserted, only ADSP
ignored when
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 6 of 36
are also loaded into the burst
[1:0]
and ADSC are both
is recognized. ASDP is
CE
is deasserted HIGH
1
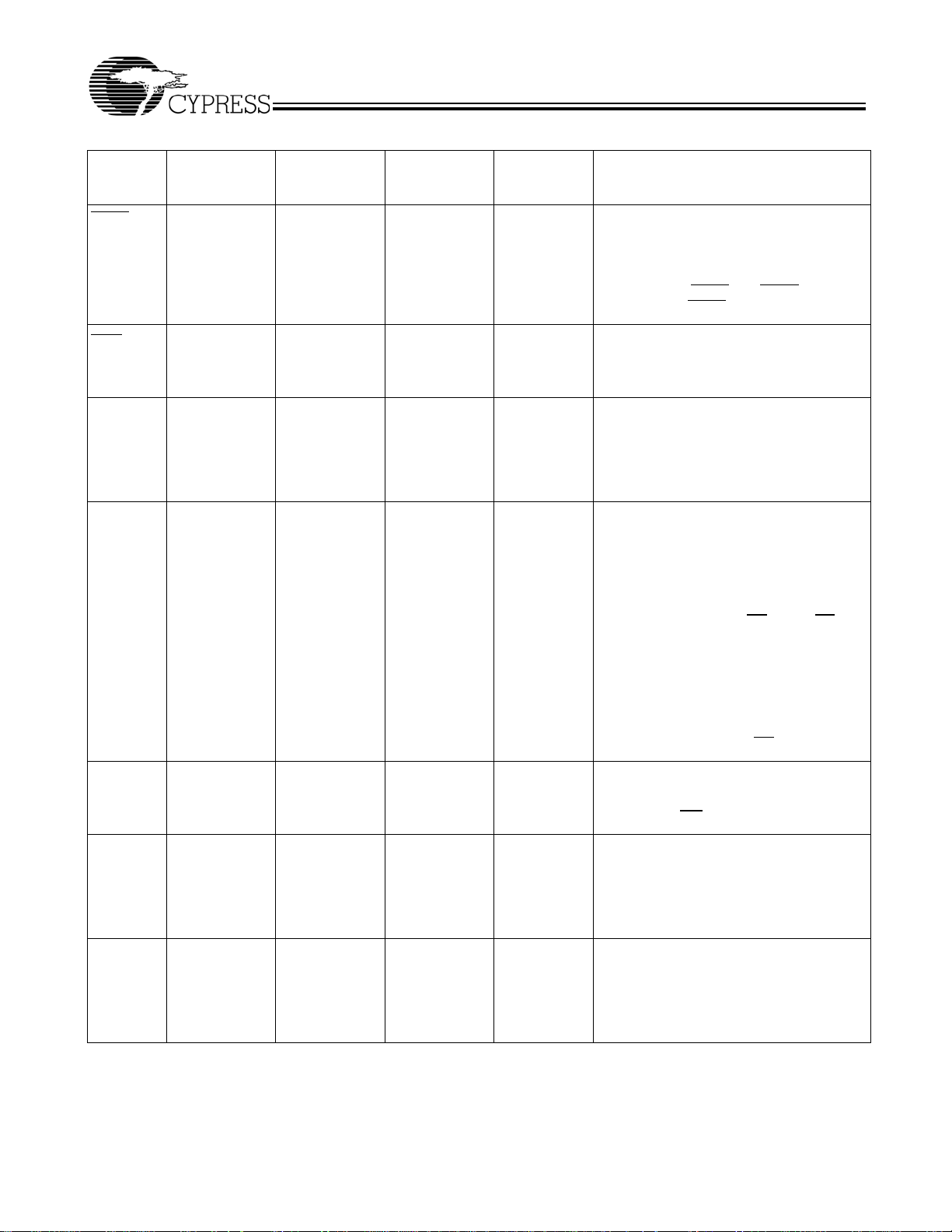
C
C
CY7C1381C–Pin Definitions (continued)
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
Name
ADSC
BWE
ZZ 64 T7 H11 Input-
DQ
s
(3-Chip
Enable)
85 B4 A8 Input-
87 M4 A7 Input-
52,53,56,57,58,
59,62,63,68,69,
72,73,74,75,78,
79,2,3,6,7,8,9,
12,13,18,19,22,
23,24,25,28,29
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
K6,L6,M6,N6,K7
,L7,N7,P7,E6,F
6,G6,H6,D7,E7,
G7,H7,D1,E1,G
1,H1,E2,F2,G2,
H2,K1,L1,N1,P1
,K2,L2,M2,N2
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
Synchronous
Synchronous
Asynchronous
M11,L11,K11,
J11,J10,K10,
L10,M10,D10,
E10,F10,G10,
D11,E11,F11,
G11,D1,E1,
F1,G1,D2,E2,
F2,G2,J1,K1,
L1,M1,J2,
K2,L2,M2,
I/O-
Synchronous
Address Strobe from Controller, sampled
on the rising edge of CLK, active LOW.
When asserted LOW, addresses presented
to the device are captured in the address
registers. A
counter. When ADSP
asserted, only ADSP
Byte Write Enable Input, active LOW.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. This
signal must be asserted LOW to conduct a
byte write.
ZZ “sleep” Input, active HIGH. When
asserted HIGH places the device in a
non-time-critical “sleep” condition with data
integrity preserved. For normal operation,
this pin has to be LOW or left floating. ZZ pin
has an internal pull-down.
Bidirectional Data I/O lines. As inputs, they
feed into an on-chip data register that is
triggered by the rising edge of CLK. As
outputs, they deliver the data contained in
the memory location specified by the
addresses presented during the previous
clock rise of the read cycle. The direction of
the pins is controlled by OE
asserted LOW, the pins behave as outputs.
When HIGH, DQs and DQP
in a tri-state condition.
automatically tri-stated during the data
portion of a write sequence, during the first
clock when emerging from a deselected
state, and when the device is deselected,
regardless of the state of OE
are also loaded into the burst
[1:0]
and ADSC are both
is recognized
. When OE is
are placed
[A:D]
The outputs are
.
.
DQP
[A:D]
MODE 31 R3 R1 Input-Static Selects Burst Order. When tied to GND
V
DD
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 7 of 36
51,80,1,30 P6,D6,D2,P2 N11,C11,C1,N1 I/O-
15,41,65,91 J2,C4,J4,R4,J6 D4,D8,E4,
E8,F4,F8,
G4,G8,H4,
H8,J4,J8,
K4,K8,L4,
L8,M4,M8
Synchronous
Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the
Bidirectional Data Parity I/O Lines.
Functionally, these signals are identical to
DQs. During write sequences, DQP
controlled by BW
selects linear burst sequence. When tied to
or left floating selects interleaved burst
V
DD
sequence. This is a strap pin and should
remain static during device operation. Mode
Pin has an internal pull-up.
device.
correspondingly.
[A:D]
[A:D]
is
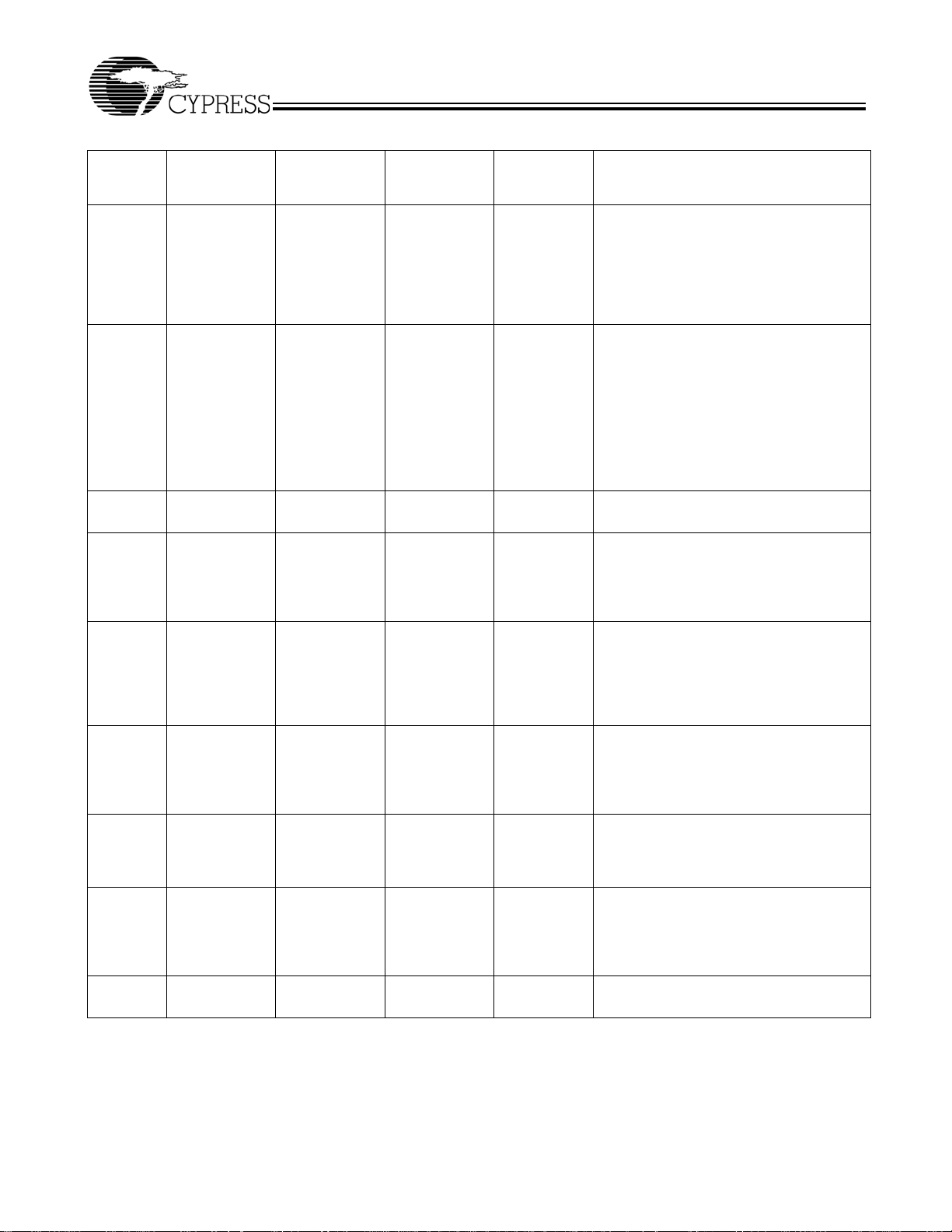
C
C
CY7C1381C–Pin Definitions (continued)
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
Name
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
SSQ
TDO - U5 P7 JTAG serial
(3-Chip
Enable)
4,11,20,27,
54,61,70,77
17,40,67,90 H2,D3,E3,F3,H3
5,10,21,26,
55,60,71,76
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
A1,F1,J1,M1,U1
,
A7,F7,J7,M7,U7
,K3,
M3,N3,
P3,D5,E5,F5,H5
,K5,
M5,N5,P5
- - I/O Ground Ground for the I/O circuitry.
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
C3,C9,D3,
D9,E3,E9,
F3,F9,G3,
G9,J3,J9,
K3,K9,L3,
L9,M3,M9,
N3,N9
C4,C5,C6,
C7,C8,D5,
D6,D7,E5,
E6,E7,F5,
F6,F7,G5,
G6,G7,H5,
H6,H7,J5,
J6,J7,K5,K6,K7,
L5,L6,L7,M5,M6
,M7,N4,N8
I/O Power
Supply
Ground Ground for the core of the device.
output
Synchronous
Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
Serial data-out to the JTAG circuit.
Delivers data on the negative edge of TCK.
If the JTAG feature is not being utilized, this
pin should be left unconnected. This pin is
not available on TQFP packages.
TDI - U3 P5 JTAG serial
TMS - U2 R5 JTAG serial
TCK - U4 R7 JTAG-Clock Clock input to the JTAG circuitry. If the
NC 16,38,39,66 B1,C1,R1,T1,T2
V
/DNU 14 - - Ground/DNU This pin can be connected to Ground or
SS
,J3,D4,L4,J5,R5
,T6,U6,B7,C7,R
7
A1,A11,B1,
B11,C2,C10,H1,
H3,H9,
H10,N2,N5,N7,
N10,P1,P2,R2
input
Synchronous
input
Synchronous
- No Connects. Not internally connected to
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled
on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature
is not being utilized, this pin can be left
floating or connected to V
up resistor. This pin is not available on TQFP
packages.
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit. Sampled
on the rising edge of TCK. If the JTAG feature
is not being utilized, this pin can be disconnected or connected to V
available on TQFP packages.
JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin
must be connected to V
available on TQFP packages.
the die. 18M, 36M, 72M, 144M and 288M are
address expansion pins are not internally
connected to the die.
should be left floating.
through a pull
DD
. This pin is not
DD
. This pin is not
SS
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 8 of 36
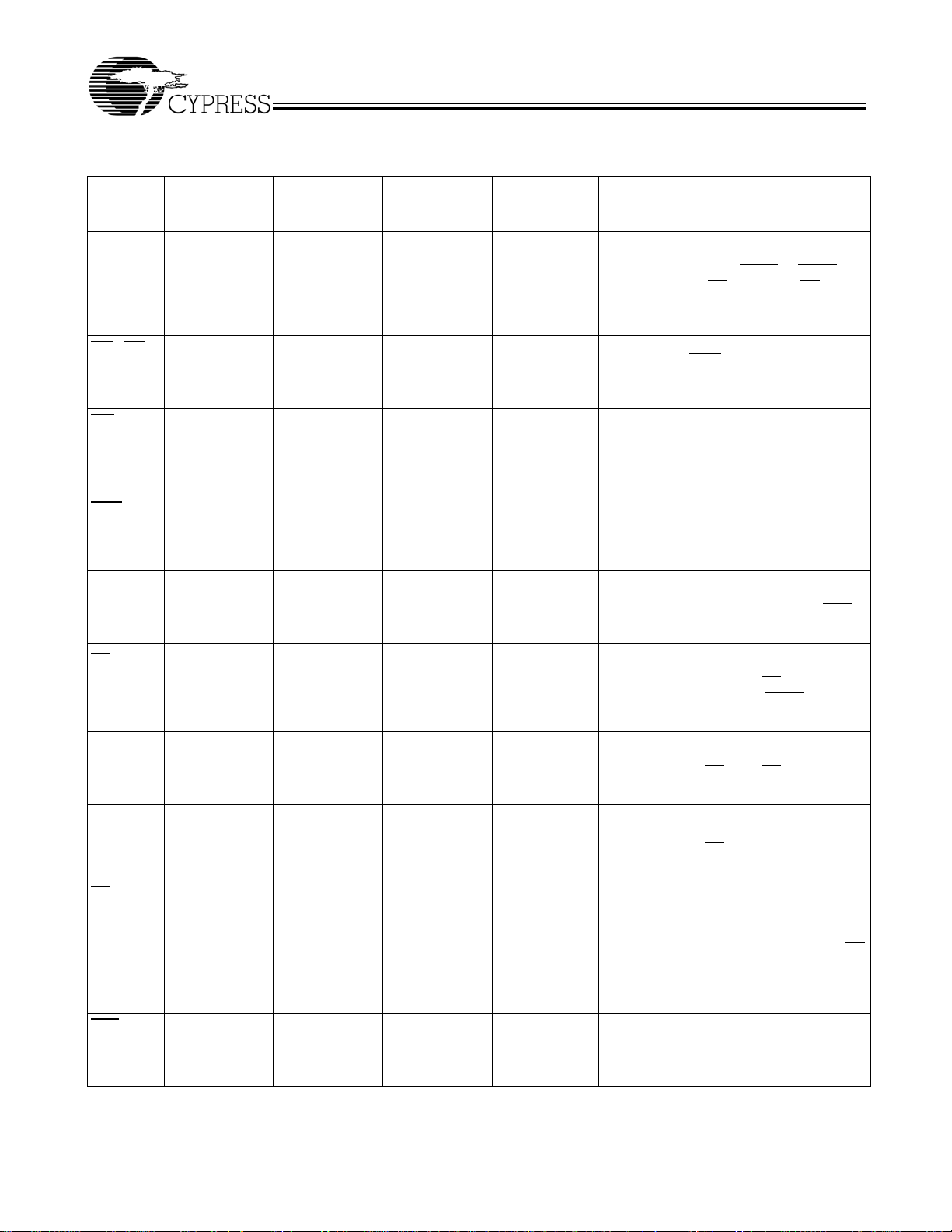
C
C
CY7C1383C:Pin Definitions
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
(3-Chip
Name
, A1 , A 37,36,32,33,34,
A
0
Enable)
35,42,43,44,45,
46,47,48,49,50,
80,81,82,99,100
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
P4,N4,A2,B2,
C2,R2,T2,A3,
B3,C3,T3,A5,
B5,C5,T5,A6,
B6,C6,R6,T6
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
R6,P6,A2,
A10,A11,B2,
Input-
Synchronous
B10,N6,P3,P4,
P8,P9,P10,
P11,R3,R4,
R8,R9,R10,R11
BW
GW
BWE
A,BWB
93,94 L5,G3 B5,A4 Input-
Synchronous
88 H4 B7 Input-
Synchronous
87 M4 A7 Input-
Synchronous
CLK 89 K4 B6 Input-
Clock
CE
CE
CE
OE
ADV
1
2
[2]
3
98 E4 A3 Input-
Synchronous
97 - B3 Input-
Synchronous
92 - A6 Input-
Synchronous
86 F4 B8 Input-
Asynchronous
83 G4 A9 Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs used to select one of the
1M address locations. Sampled at the ris-
ing edge of the CLK if ADSP
active LOW, and CE
sampled active. A
1, CE2
feed the 2-bit counter.
[1:0]
or ADSC is
, and CE
[2]
are
3
Byte Write Select Inputs, active LOW.
Qualified with BWE
to conduct byte writes
to the SRAM. Sampled on the rising edge of
CLK.
Global Write Enable Input, active LOW.
When asserted LOW on the rising edge of
CLK, a global write is conducted (ALL bytes
are written, regardless of the values on
BW
and BWE).
[A:B]
Byte Write Enable Input, active LOW.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. This
signal must be asserted LOW to conduct a
byte write.
Clock Input. Used to capture all
synchronous inputs to the device. Also used
to increment the burst counter when ADV
is
asserted LOW, during a burst operation.
Chip Enable 1 Input, active LOW.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE2 and CE
select/deselect the device. ADSP
if CE
is HIGH.
1
[2]
to
3
is ignored
Chip Enable 2 Input, active HIGH.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK. Used in
conjunction with CE
select/deselect the device.
and CE
1
[2]
to
3
Chip Enable 3 Input, active LOW.
Sampled on the rising edge of CLK.
Used in
conjunction with CE1 and CE2 to
select/deselect the device.
Output Enable, asynchronous input,
active LOW. Controls the direction of the
I/O pins. When LOW, the I/O pins behave as
outputs. When deasserted HIGH, I/O pins
are tri-stated, and act as input data pins. OE
is masked during the first clock of a read
cycle when emerging from a deselected
state.
Advance Input signal, sampled on the
rising edge of CLK. When asserted, it
automatically increments the address in a
burst cycle.
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 9 of 36
C
C
CY7C1383C:Pin Definitions (continued)
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
Name
ADSP
ADSC
ZZ 64 T7 H11 Input-
DQ
s
(3-Chip
Enable)
84 A4 B9 Input-
85 B4 A8 Input-
58,59,62,63,68,
69,72,73,8,9,12,
13,
18,19,22,23
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
P7,K7,G7,E7,F6
,H6,L6,N6,D1,H
1,L1,N1,E2,G2,
K2,M2
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
Synchronous
Synchronous
Asynchronous
J10,K10,
L10,M10,
D11,E11,
F11,G11,J1,K1,
L1,M1,
D2,E2,F2,
G2
I/O-
Synchronous
Address Strobe from Processor,
sampled on the rising edge of CLK,
active LOW. When asserted LOW,
addresses presented to the device are
captured in the address registers. A
also loaded into the burst counter. When
ADSP and ADSC are both asserted, only
ADSP
is recognized. ASDP is ignored when
is deasserted HIGH
CE
1
Address Strobe from Controller,
sampled on the rising edge of CLK,
active LOW. When asserted LOW,
addresses presented to the device are
captured in the address registers. A
also loaded into the burst counter. When
and ADSC
ADSP
is recognized
ADSP
ZZ “sleep” Input, active HIGH. When
asserted HIGH places the device in a
non-time-critical “sleep” condition with data
integrity preserved. For normal operation,
this pin has to be LOW or left floating. ZZ pin
has an internal pull-down.
Bidirectional Data I/O lines. As inputs,
they feed into an on-chip data register that
is triggered by the rising edge of CLK. As
outputs, they deliver the data contained in
the memory location specified by the
addresses presented during the previous
clock rise of the read cycle. The direction of
the pins is controlled by OE
asserted LOW, the pins behave as outputs.
When HIGH, DQs and DQP
in a tri-state condition.
automatically tri-stated during the data
portion of a write sequence, during the first
clock when emerging from a deselected
state, and when the device is deselected,
regardless of the state of OE
are both asserted, only
.
. When OE is
[A:B]
The outputs are
.
are
[1:0]
are
[1:0]
are placed
DQP
[A:B]
MODE 31 R3 R1 Input-Static Selects Burst Order. When tied to GND
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 10 of 36
74,24 D6,P2 C11,N1 I/O-
Synchronous
Bidirectional Data Parity I/O Lines.
Functionally, these signals are identical to
During write sequences, DQP
DQ
s.
controlled by BW
selects linear burst sequence. When tied to
or left floating selects interleaved burst
V
DD
sequence. This is a strap pin and should
remain static during device operation. Mode
Pin has an internal pull-up.
correspondingly.
[A:B]
[A:B]
is
C
C
CY7C1383C:Pin Definitions (continued)
CY7C1381
CY7C1383
TQFP
Name
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
SSQ
TDO - U5 P7 JTAG serial
TDI - U3 P5 JTAG serial
TMS - U2 R5 JTAG serial
TCK - U4 R7 JTAG-Clock Clock input to the JTAG circuitry. If the
(3-Chip
Enable)
15,41,65,91 C4,J2,J4,J6,R4 D4,D8,E4,
4,11,20,27,
54,61,70,77
17,40,67,90 D3,D5,E3,E5,F3
5,10,21,26,
55,60,71,76,
BGA
(1-Chip
Enable)
A1,A7,F1,F7,J1,
J7,M1,M7,U1,U
7
,F5,G5,H3,
H5,K3,K5,L3,M3
,
M5,N3,
N5,P3,P5
- - I/O Ground Ground for the I/O circuitry.
fBGA
(3-Chip
Enable) I/O Description
Power Supply Power supply inputs to the core of the
E8,F4,F8,
G4,G8,
H4,H8,J4,
J8,K4,K8,
L4,L8,M4,
M8
C3,C9,D3,
D9,E3,E9,
F3,F9,G3,
G9,J3,J9,
K3,K9,L3,
L9,M3,M9,
N3,N9
C4,C5,C6,
C7,C8,D5,
D6,D7,E5,
E6,E7,F5,
F6,F7,G5,
G6,G7,H1,
H2,H5,H6,
H7,J5,J6,J7,K5,
K6,K7,L5,L6,L7,
M5,
M6,M7,N4,
N8
I/O Power
Supply
Ground Ground for the core of the device.
output
Synchronous
input
Synchronous
input
Synchronous
device.
Power supply for the I/O circuitry.
Serial data-out to the JTAG circuit.
Delivers data on the negative edge of TCK.
If the JTAG feature is not being utilized, this
pin should be left unconnected. This pin is
not available on TQFP packages.
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit.
Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the
JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin
can be left floating or connected to V
through a pull up resistor. This pin is not
available on TQFP packages.
Serial data-In to the JTAG circuit.
Sampled on the rising edge of TCK. If the
JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin
can be disconnected or connected to V
This pin is not available on TQFP packages.
JTAG feature is not being utilized, this pin
must be connected to V
available on TQFP packages.
. This pin is not
SS
DD
DD
.
Document #: 38-05238 Rev. *B Page 11 of 36
 Loading...
Loading...